NPS Wk9a - Agent-Based Models + Complex Systems
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Mechanistic models
Uses theory to predict what will happen in the real world
Empirical Models
Uses real-world data to help develop a theory
Deterministic Models
Produces the same output for a given set of inputs
Stochastic Models
Incorporates randomness and uncertainty into the model (e.g., k-means is a stochastic model due to random initialization of the mean)
Computational models
• A computational model is a model written in terms
of a computer code that describes a system and the
rules it obeys
• We can run these models to see how the system
changes with time
• Computational models have been referred to as the
third pillar of science, after theory and experiment
What is a simulation?
• The process of running a computational model is called a simulation
• Simulations are used to better understand and predict a real- world process or scenario
When to use simulations?
• When the physical system under study does not exist yet, or the prototype is too expensive to build
§ In a wind tunnel, the effect of turbulence on a new aircraft model
§ Biochemical mechanism of a candidate drug to treat cancer
• When we are trying to predict the future
§ Rates of deforestation after policy interventions
§ Global population growth trends in the next century
§ GDP forecasts for the year 2025
• When the physical system exists but a real experiment is not feasible, due to it being too complicated, too expensive, or too dangerous
§ The dynamics of how a virus spreads during a pandemic
§ The risks of an outbreak of nuclear war
§ How greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere
contribute to a rise in global temperatures
Limitations of simulations
• It might be difficult to verify the results of a simulation if
the actual, real-world system does not exist
• Models may be too simple to properly reflect real-world
phenomena
• The computational cost of running complex simulations
can be high
• It can be a challenge to strike a balance between
simplicity and accuracy
Steps of the modeling/simulation process
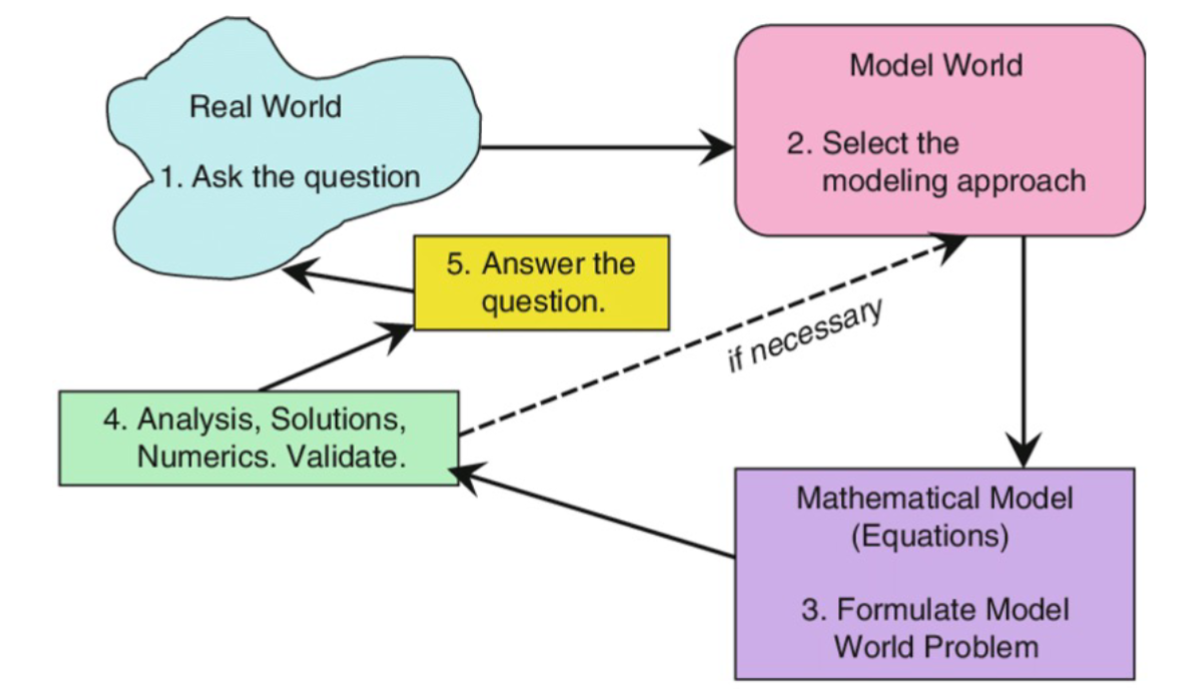
What are complex systems?
Complex systems consist of a large number of locally interacting parts that are evolving in time without any centralized control
Common properties of complex systems:
Non-linearity, emergence, feedback loops
What is Emergence behaviour in complex systems?
In complex systems, emergent global patterns often arise from simple, local interactions and rules
Emergence occurs when a complex entity has properties or behaviours that its constituent parts do not have on their own, and which emerge only when interactions take place as part of a wider whole
What are attractor states in complex systems?
once in an attractor state, the system will never leave it
State the example of the wolf sheep model
What are critical/tipping points in complex systems?
They are thresholds at which small changes to the input parameters have a large impact on the eventual outcome
Use the example of forest fire model