Measurement of Sound (10/6)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
log(1) will ALWAYS equal…
0
how to solve 104 × 105 ?
104+5
how to solve 104 / 105 ?
104-5
antilog10(.3010) = x
x = 2.000
why would people want to use exponents (log scale) in speech and hearing science?
some numbers are too cumbersome to write without them
what is a vibration that typically spread as an audible wave of pressure through a medium?
sound
what makes the tympanic membrane move back and forth?
areas of high pressure and low pressure in a sound wave
sound is detectable by the human ear from ___ Hz to _____ Hz
20-20,000 Hz
what volume range can the ear detect?
0-140 dB
noise is generally described as ____
unwanted/undesirable
what are octave bands?
a range of frequencies where the highest frequency is exactly double the lowest frequency. they are known by their center frequency

what is this an example of? explain
octave bands. they are known by their center frequency. the higher band is double the lower band
what kind of frequency ranges are represented on audiograms? explain
octave bands. each frequency doubles: 250 Hz → 500 Hz → 1000 Hz → 2000 Hz
what are broadband sounds?
sounds that contain a wide and continuous spectrum of frequencies
what is the formula for pressure? explain the relationships between the values. what is the unit?
p = F/A (pressure = Force/Area). pressure is directly proportional to force. pressure is inversely proportional to area. unit: pascals or N/m2
what is the formula for work? explain the relationships between the values. what are the units?
W = Fd (work = Force x distance). work is directly proportional to force. work is directly proportional to distance. units: J
what is the formula for power? explain the relationships between the values. what are the units?
P = W/t (power = work/time). power is directly proportional to work. power is inversely proportional to time. units: watt or Joules/sec
what is the formula for intensity? explain the relationships between the values. what is the unit?
I = P/A (intensity = power/area). intensity is directly proportional to power. intensity is inversely proportional to area. unit: w/m2
what is the relationship between power and pressure?
power = pressure2, pressure = √power
sound power level measures…
the total amount of acoustical energy created by the sound source (independent of listening distance)
sound intensity level measures…
the amount of acoustical energy per unit area (it decreases in proportion to the inverse square of the listening distance)
sound pressure level measures…
the amount of force per unit area (decreases in proportion to the inverse of the listening distance)
what does dB IL measure?
the power per unit area of a sound wave, referenced to a standard power level (typically 10-12 W/m² = the lowest intensity the human ear can hear)
what does dB SPL measure?
the pressure exerted by a sound wave, referenced to the typical threshold of human hearing (20 micropascals aka 20 µPa)
do dB IL and dB SPL measure the same thing? if not, then how can their dB levels be used interchangeably?
no, their measurements represent different physical properties of a sound wave, however, they are related because intensity∝pressure 2
40 dB IL = ____ dB SPL
40
if intensity increases by 10:1 (10 dB), pressure increases by ______
3.16:1 (sq rt of 10)
dB IL uses a _____ ratio and has a log multiplier of ____, while dB SPL uses a ____ ratio and has a log multiplier of ____
intensity/power ratio, log multiplier of 10
pressure ratio, log multiplier of 20
what is absolute acoustic power?
the total rate of sound energy radiated by a sound source, measured in watts (W)
what is relative acoustic power?
a standard, well-defined absolute power level used as a baseline for comparison, such as 10⁻¹² watts
with relative power, we express the level of power in a sound wave by forming a ratio of _____ / ____
absolute power value / reference value
the inverse square law explains how…
intensity decreases as distance from sound source increases
the inverse square law STATES…
the sound energy per unit area at any point is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source
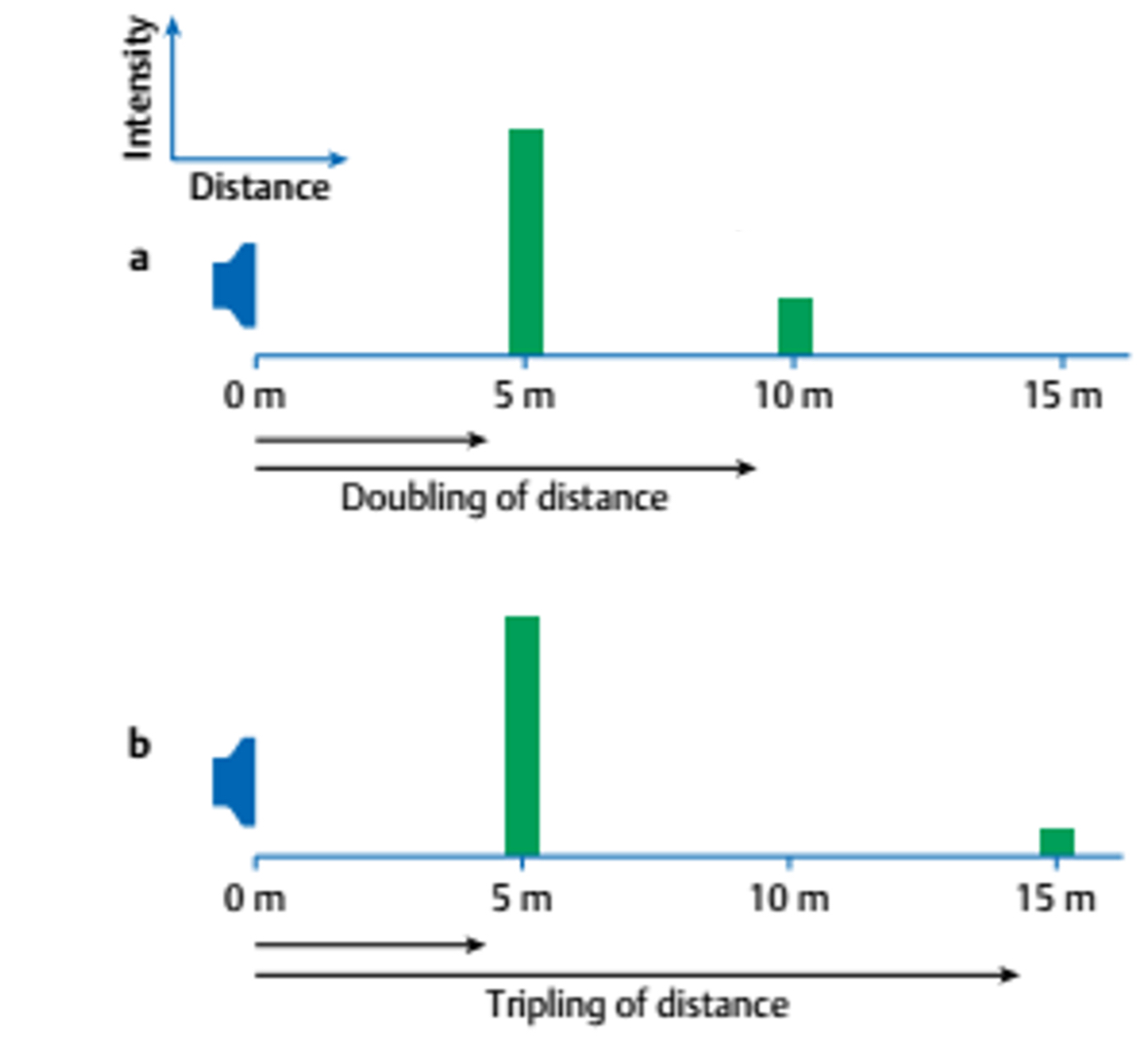
calculate the intensity for 10m and 15m using the inverse square law
10m: ¼ watt/m2, 15: 1/9 watt/m2
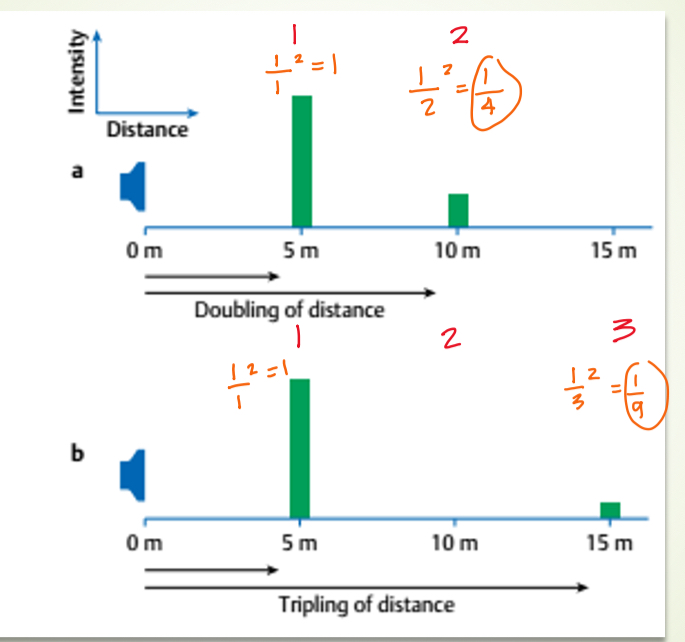
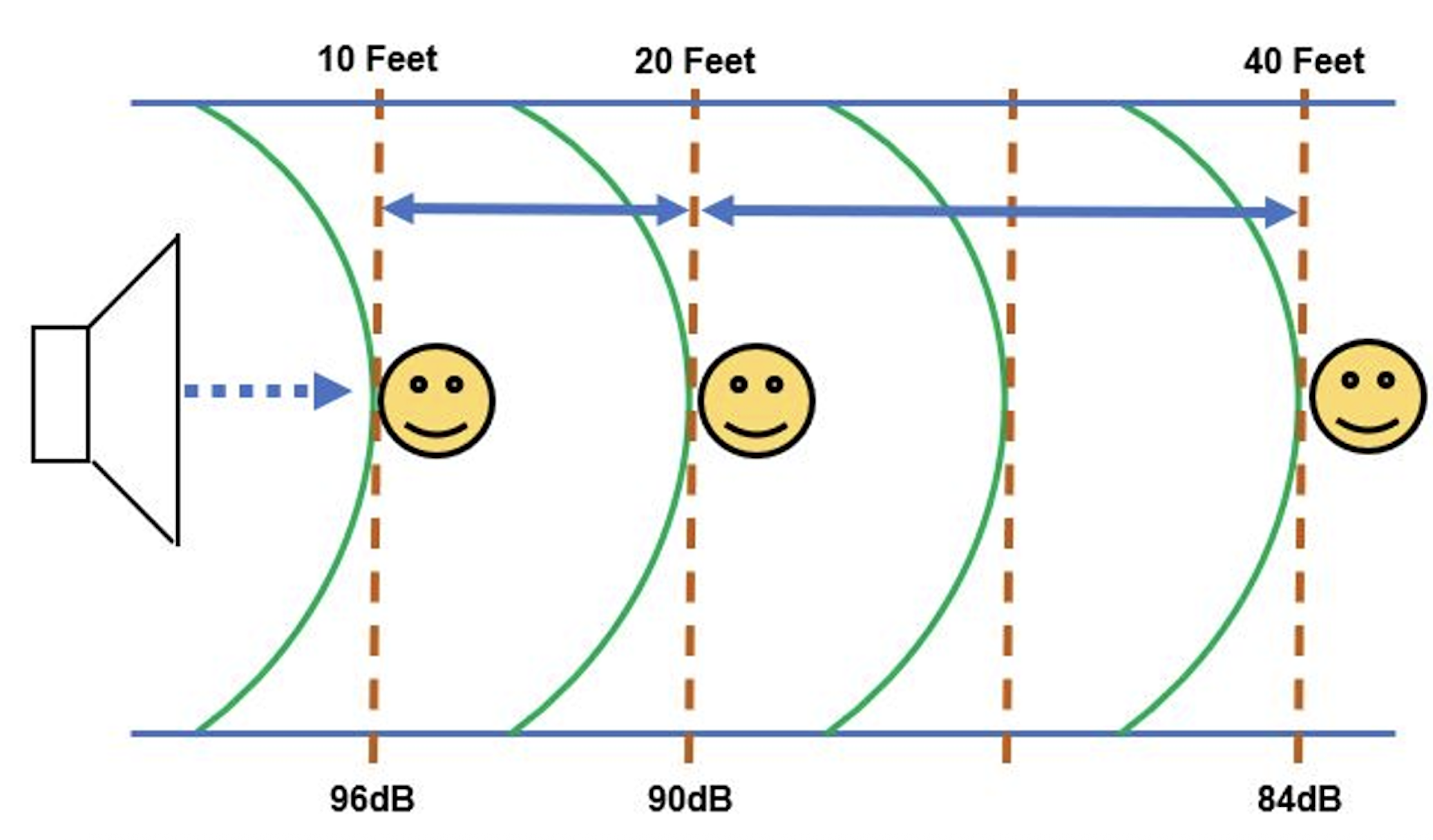
what does this image represent?
inverse square law (intensity decreases as distance increases)
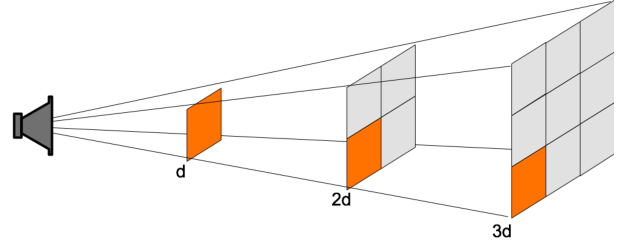
what does this image represent?
inverse square law (sound energy per unit area at any point is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source)
what is absolute intensity (IX)?
the objective measurement of sound energy per unit area, expressed in units like watts per square meter (watt/m²)
what is relative intensity (IR)?
compares an existing sound level to a specific reference level or a perceived baseline
what ratio is used for intensity?
absolute intensity/relative intensity → IX/IR
if the IX (absolute intensity) is 10-8, and the IR (relative intensity) is 10-10, what is the Ix/IR ratio?
102 → 10-8/10-10
if the IX (absolute intensity) is 10-8, and the IR (relative intensity) is 10-12, what is the Ix/IR ratio?
104 → 10-8/10-12
if the IX (absolute intensity) is 10-10, and the IR (relative intensity) is 10-12, what is the Ix/IR ratio?
102 → 10-10/10-12
the log of the ratio IX/IR is called a….
bel
what do positive (+) bels mean?
IX > IR → IX is greater than IR → absolute intensity is greater than relative intensity
what do negative (-) bels mean?
IX < IR → IX is less than IR → absolute intensity is less than relative intensity
if IX = IR, then…
bel = log(IX/IR) = log(1) = 0
if IX = 10-6 watt/m2, and Ir = 10-10 watt/m2, what is the intensity level in bels?
4 bels. Ix/Ir = 10-6/10-10. bel = log(10-6/10-10) = log (10-6 + 10) = log(104) = 4 bels
if Ix = 2 × 10-8 watt/m2, and Ir = 10-12 watt/m2, calculate for bels
4.3 bels N bels = log (2 × 10-8/10-12) = log (2 × 104) = 4.3
to convert bels to decibels, multiply the bel value by ____
10
4.3 bels is equivalent to ____ decibels
43
when looking at log10(Ix/Ir), the unit will be _____. when looking at 10log10(Ix/Ir), the unit will be ____.
bels, decibels
what do 0 decibels mean?
Ix = Ir → 10log(1) = 0
what do positive decibels mean?
Ix > Ir
what do negative decibels mean?
Ix < Ir
what is the equation for dB SPL?
dB SPL = 20log10(px/pr)
a decibel is ___ times the log of an intensity or power ratio
10 → dB IL = 10log10 (Ix/Ir)
a decibel is ___ times the log of a pressure ratio
20 → dB SPL = 20log10 (Ix/Ir)
for every 10-fold change in Ix, dB IL changes by…
10 dB → Log (10) = 1; 1×10 = 10
for every 2-fold change in Ix, dB IL changes by…
3 dB → Log (2) = 0.3; 0.3×10 = 3
if Ix = 10-5 watt/m2, and Ir = 10-12 watt/m2, what is dB IL?
70 dB → dB IL = 10log(10-5/10-12) = 10log(107) = 10×7 = 70
if Ix = 2×10-5 watt/m2, and Ir = 10-12 watt/m2, what is dB IL?
73 dB
if Ix = 4×10-5 watt/m2, and Ir = 10-12 watt/m2, what is dB IL?
76 dB
if intensity is proportional to power, and power is proportional to pressure2, then…
intensity is proportional to pressure2
if pressure increases 2:1, dB SPL increases by…
6 dB → dB SPL = 20log(2/1) = 6
if pressure increases 10:1, dB SPL increases by…
20 dB → dB SPL = 20log(10/1) = 20×1 = 20 dB
if you see Pa (pascals), which dB measurement are you working with?
dB SPL
if you see watt/m2, what kind of dB measurement are you working with?
dB IL
why does dB IL = dB SPL?
because 2×101 Pa is the pressure equivalent to 10-12 watt/m2
if intensity increases by 9x, pressure increases by ___
3x
what is the formula for combining sound intensities with equal source intensities?
dBN = dBi + 10Log (N), where N = # of sources and i = dB IL or dB SPL from one of the equal sources
if 3 girls are shouting at 100 dB each, what is the final dB level?
104.7 dB → dB3 = 100 + 10log3
what are the 5 rules for summations of sound levels?
if 2 sounds of equal intensity are put together, the final dB increases by 3
if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 0-1 dB, the final dB increases by 3
if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 2-3 dB, the final dB increases by 2 dB
if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 4-7 dB, the final dB increases by 1 dB
if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 8+ dB, the intensity difference does not count. the final dB will be the highest of the 2
80 dB + 80 dB =
83 dB (if 2 sounds of equal intensity are put together, they increase by 3dB)
80 dB + 81 dB =
84 dB (if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 0-1 dB, the final dB increases by 3)
90 dB + 92 dB =
94 (if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 2-3 dB, the final dB increases by 2 dB)
94 dB + 97 dB =
98 dB (if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 4-7 dB, the final dB increases by 1 dB)
90 dB + 98 dB =
98 dB (if 2 sounds are added together that differ by 8+ dB, the intensity difference does not count. the final dB will be the highest of the 2)
does it matter if a question about sound summation is stated by reference to dB IL or dB SPL?
no, because it is the intensities/powers that should be added together, not the pressures → dB IL = dB SPL