American Pageant Chapter 21
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
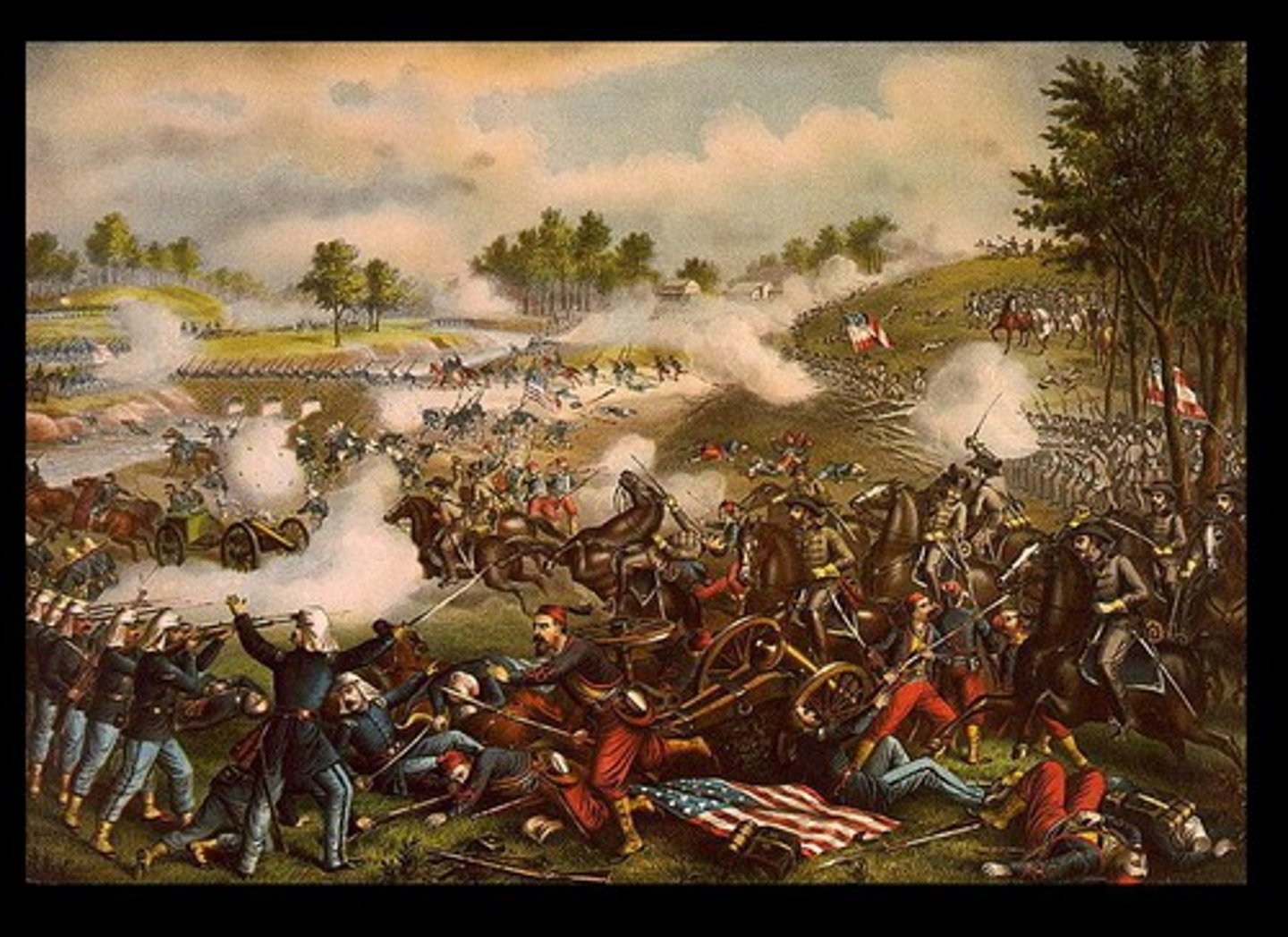
Battle of Bull Run (Manassas Junction)
First major battle of the Civil War and a victory for the South, it dispelled Northern illusions of swift victory.

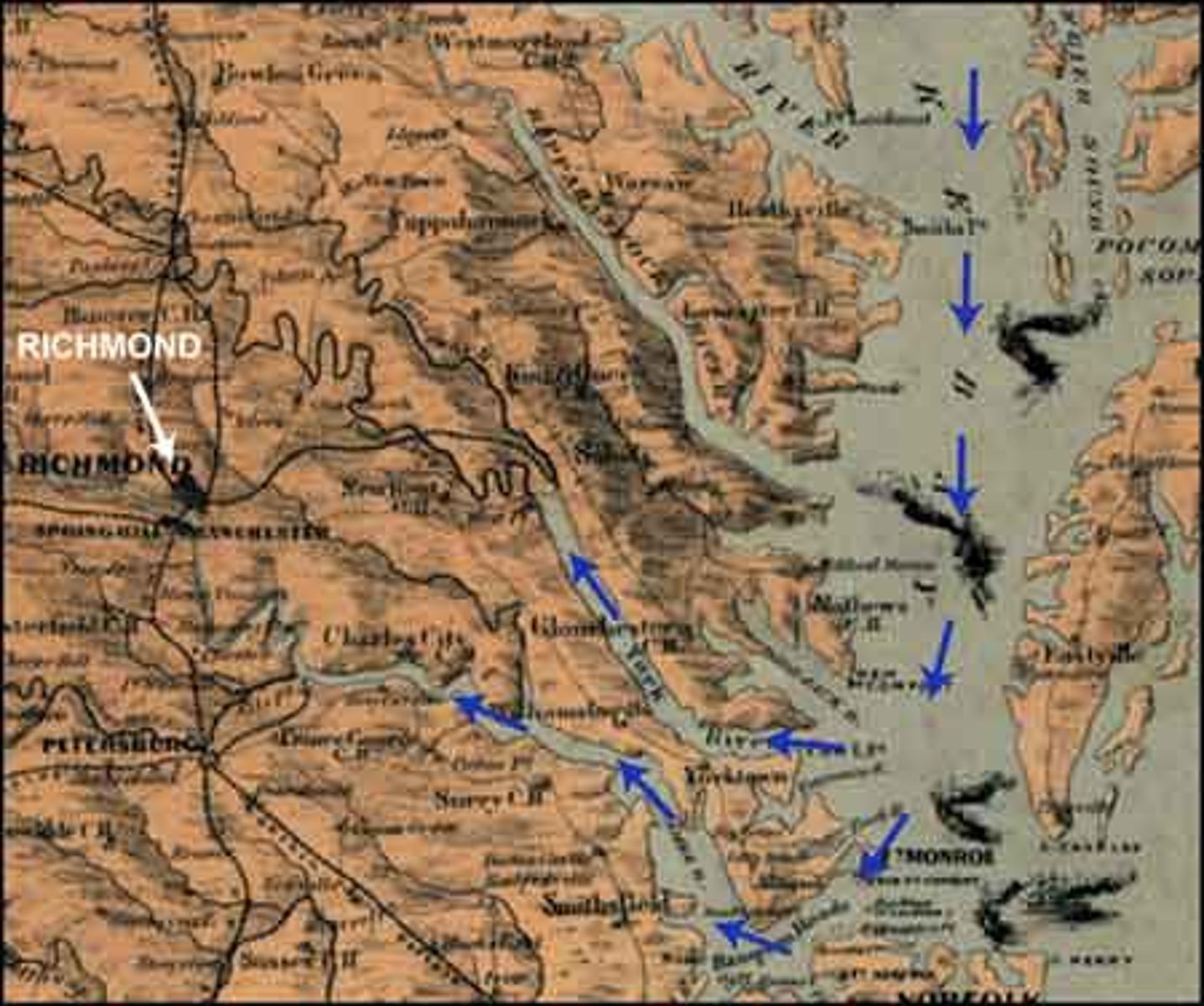
Peninsula Campaign
Union General George B. McClellan's failed effort to seize Richmond, the Confederate Capital. Had McClellan taken Richmond and toppled the Confederacy, slavery would have most likely survived in the South for some time.
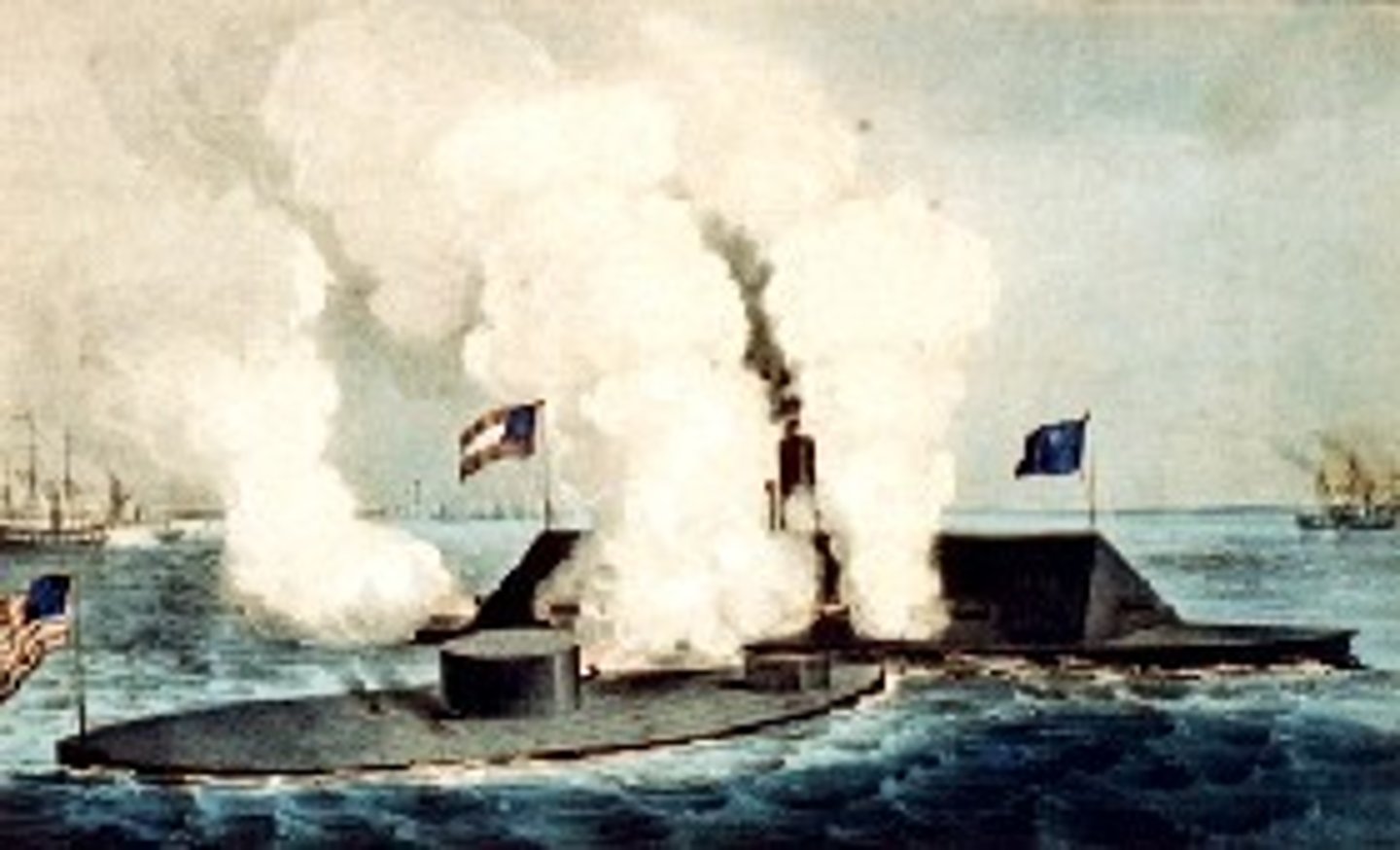
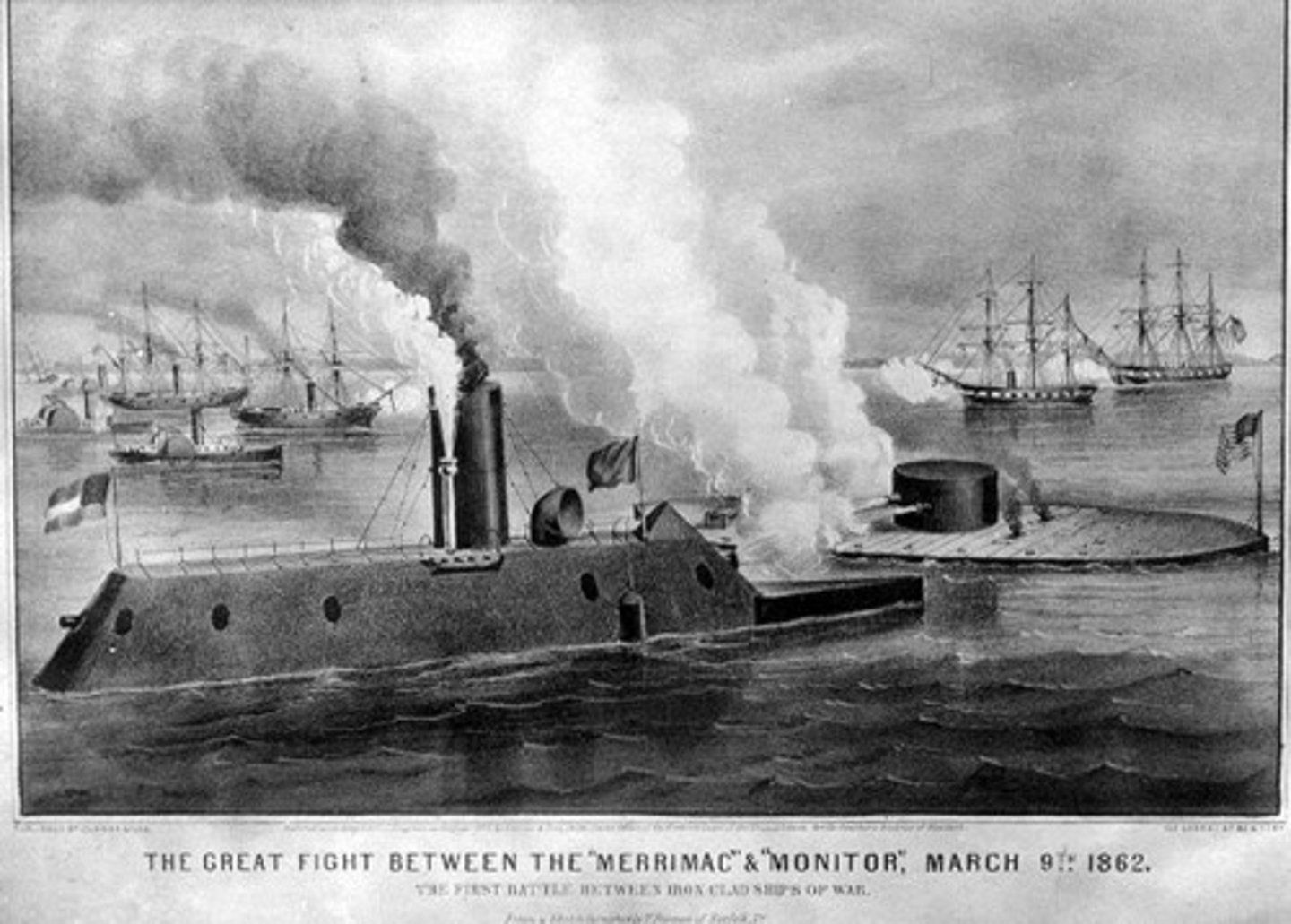
Merrimack
Abandoned Union warship salvaged by the Confederacy. Enforced with iron plates to become an ironclad ship. Renamed "Virginia"

Monitor (ship)
The first Union ironclad held its own battle but was unable to claim a victory.
Second Battle of Bull Run
(1862) a Civil War battle in which the Confederate army forced most of the Union army out of Virginia
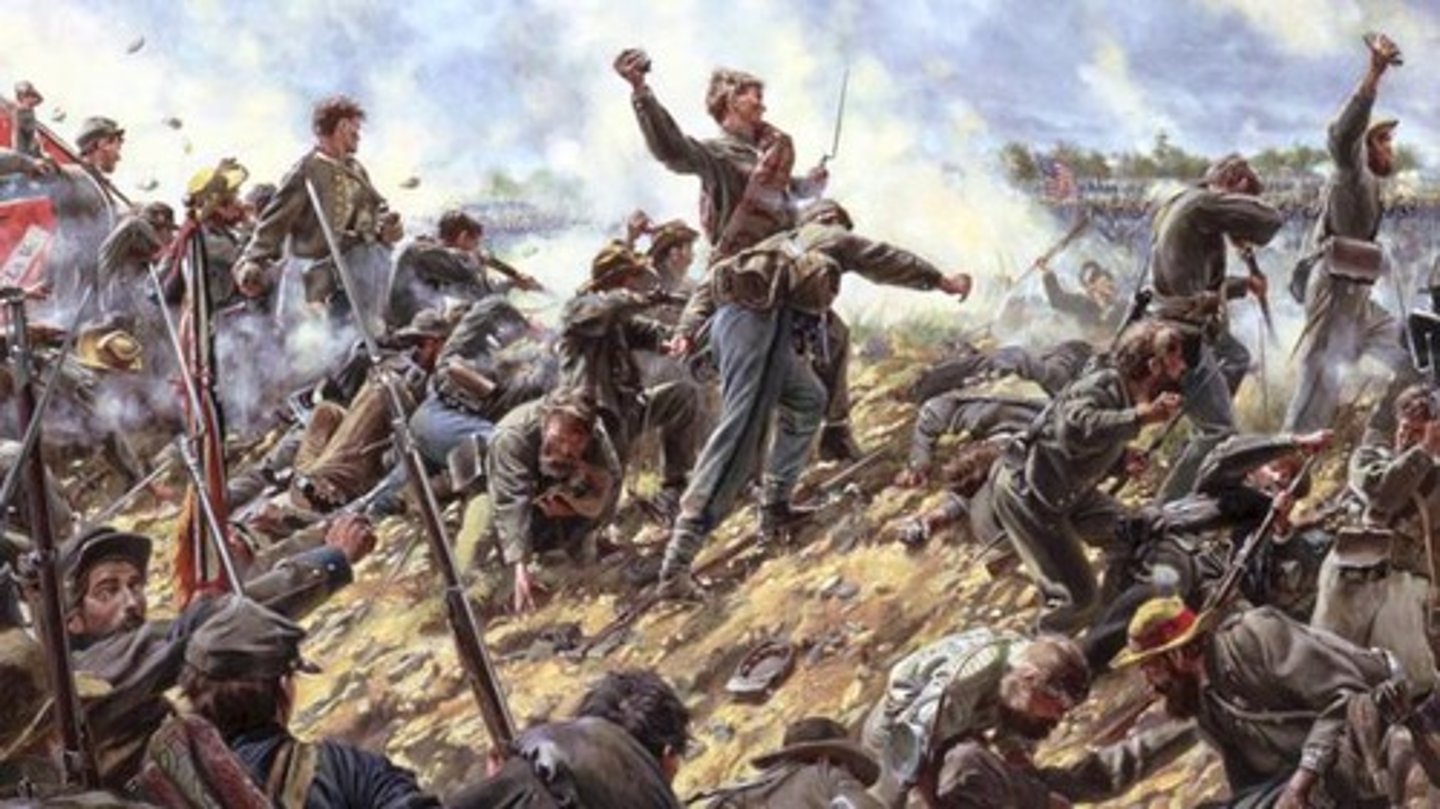

Battle of Antietam
Civil War battle in which the North succeeded in halting Lee's Confederate forces in Maryland. Was the bloodiest battle of the war resulting in 25,000 casualties

Emancipation Proclamation (1863)
Proclamation issued by Lincoln, freeing all slaves in areas still at war with the Union.

Thirteenth Amendment
The constitutional amendment ratified after the Civil War that forbade slavery and involuntary servitude.

Battle of Fredericksburg
The Union, led by Major General Ambrose Burnside, was defeated and lost 12,000 men. General Robert E. Lee, Commander of the Army of Northern Virginia, was the Confederate general who led in the defeat.
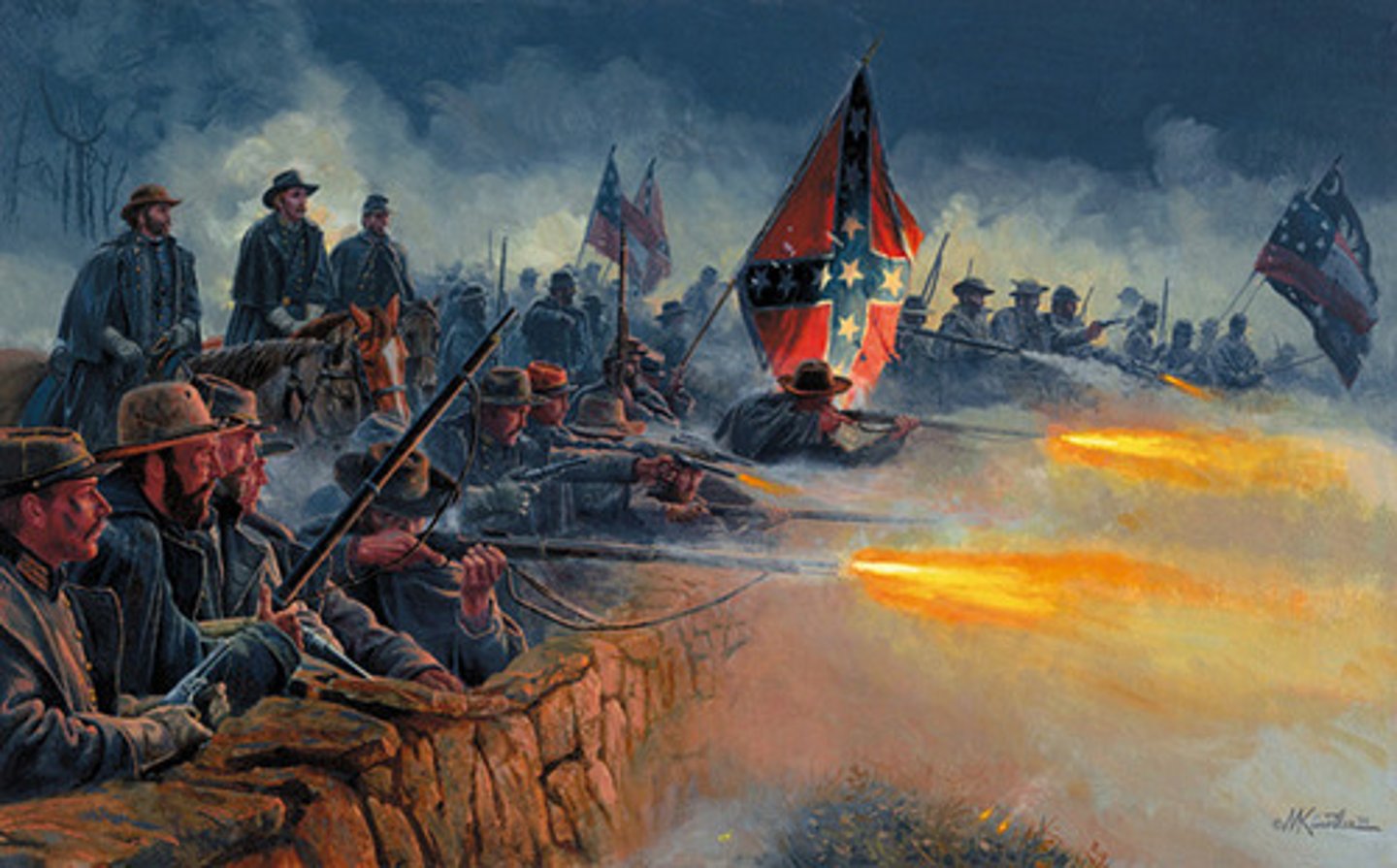

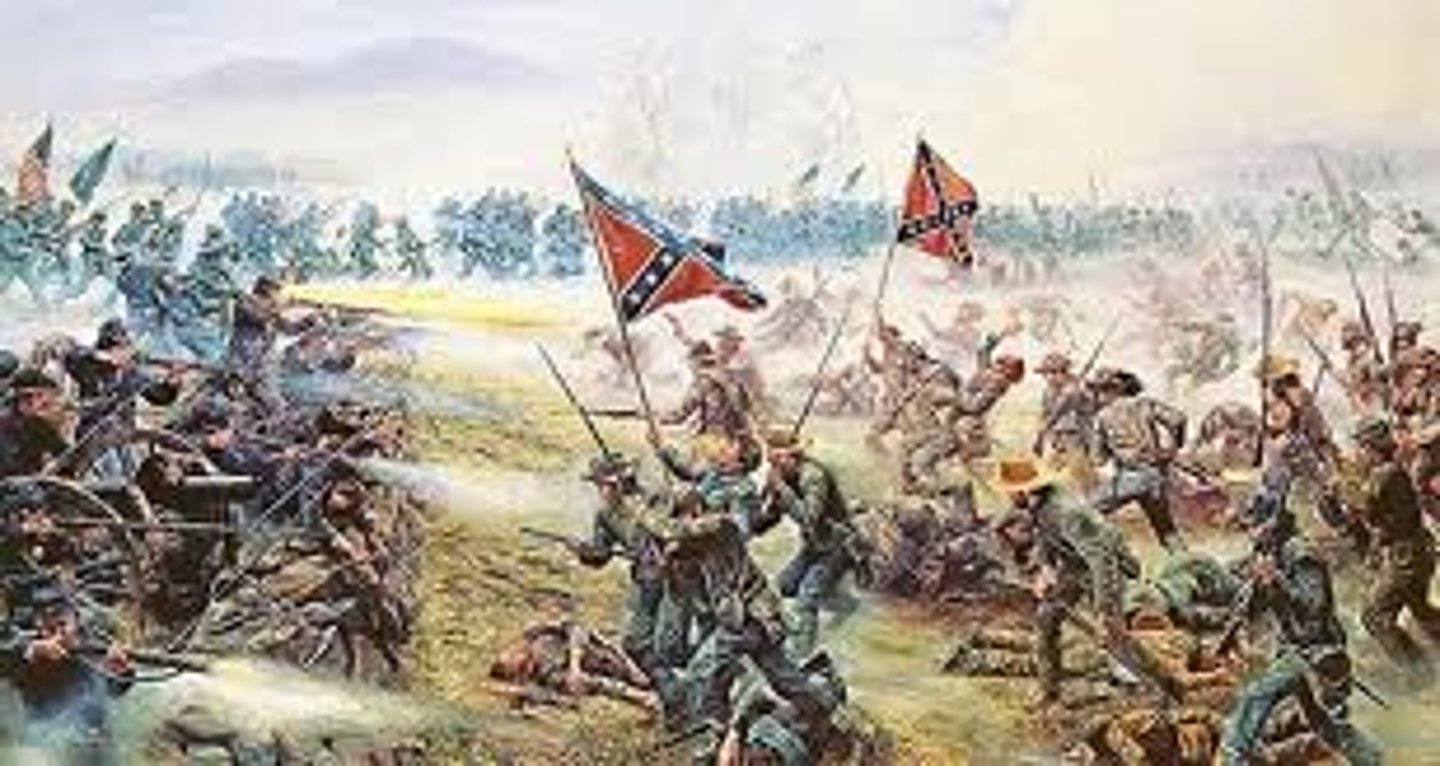
Battle of Gettysburg
Turning point of the War that made it clear the North would win. 50,000 people died, and the South lost its chance to invade the North.

Gettysburg Address
A 3-minute address by Abraham Lincoln during the American Civil War (November 19, 1963) at the dedication of a national cemetery on the site of the Battle of Gettysburg

Battle of Fort Henry and Fort Donelson
(February 1862) Key victory for Union General Ulysses S. Grant, it secured the North's hold on Kentucky and paved the way for Grant's attacks deeper into Tennessee.

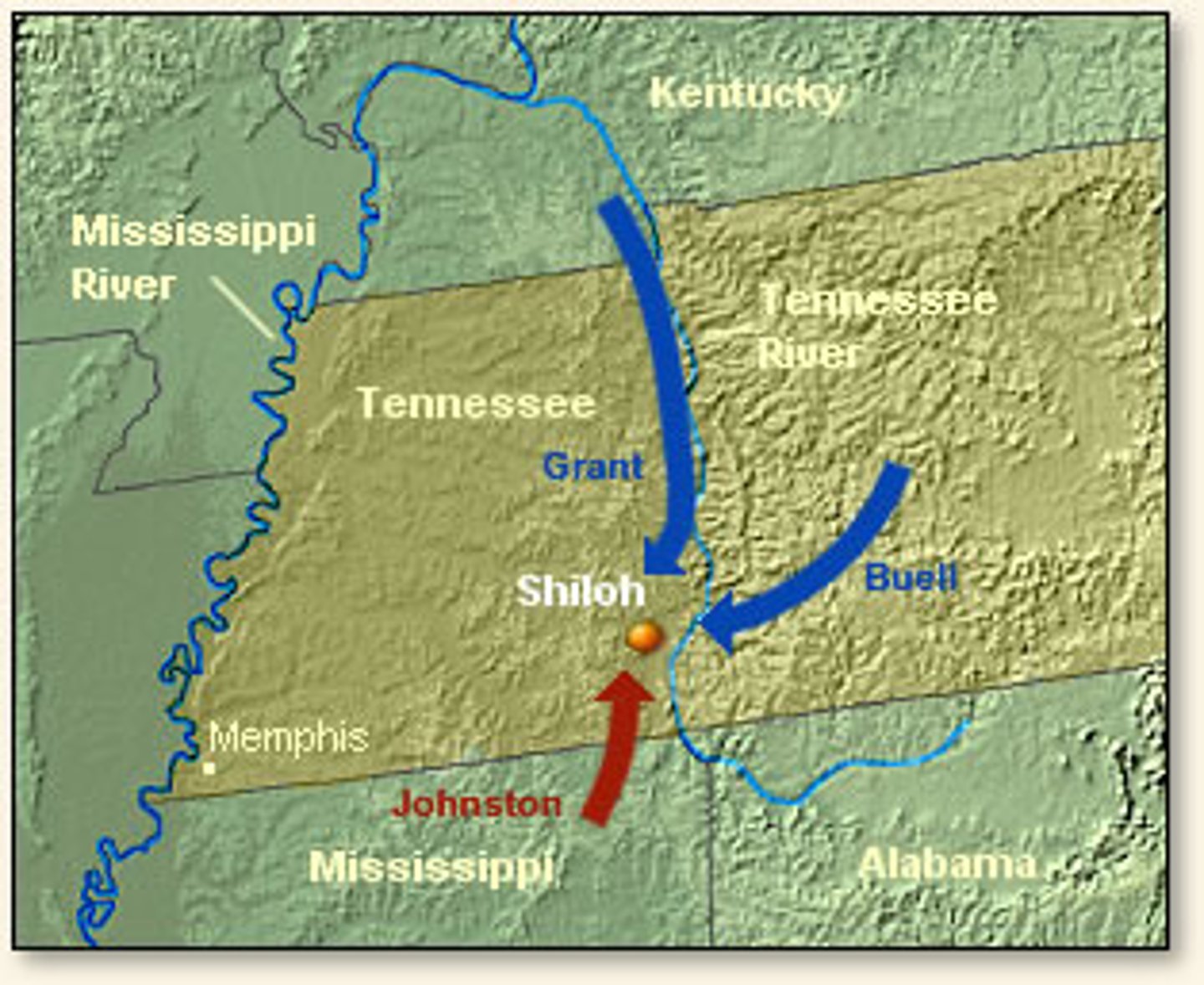
Battle of Shiloh
Confederate forces surprised union troops & drove them across the Tennessee river; union got backup and won the battle but it was one of the most bloody battles in the civil war
Siege of Vicksburg
1863 Union army's blockade of Vicksburg, Mississippi, that led the city to surrender during the Civil War

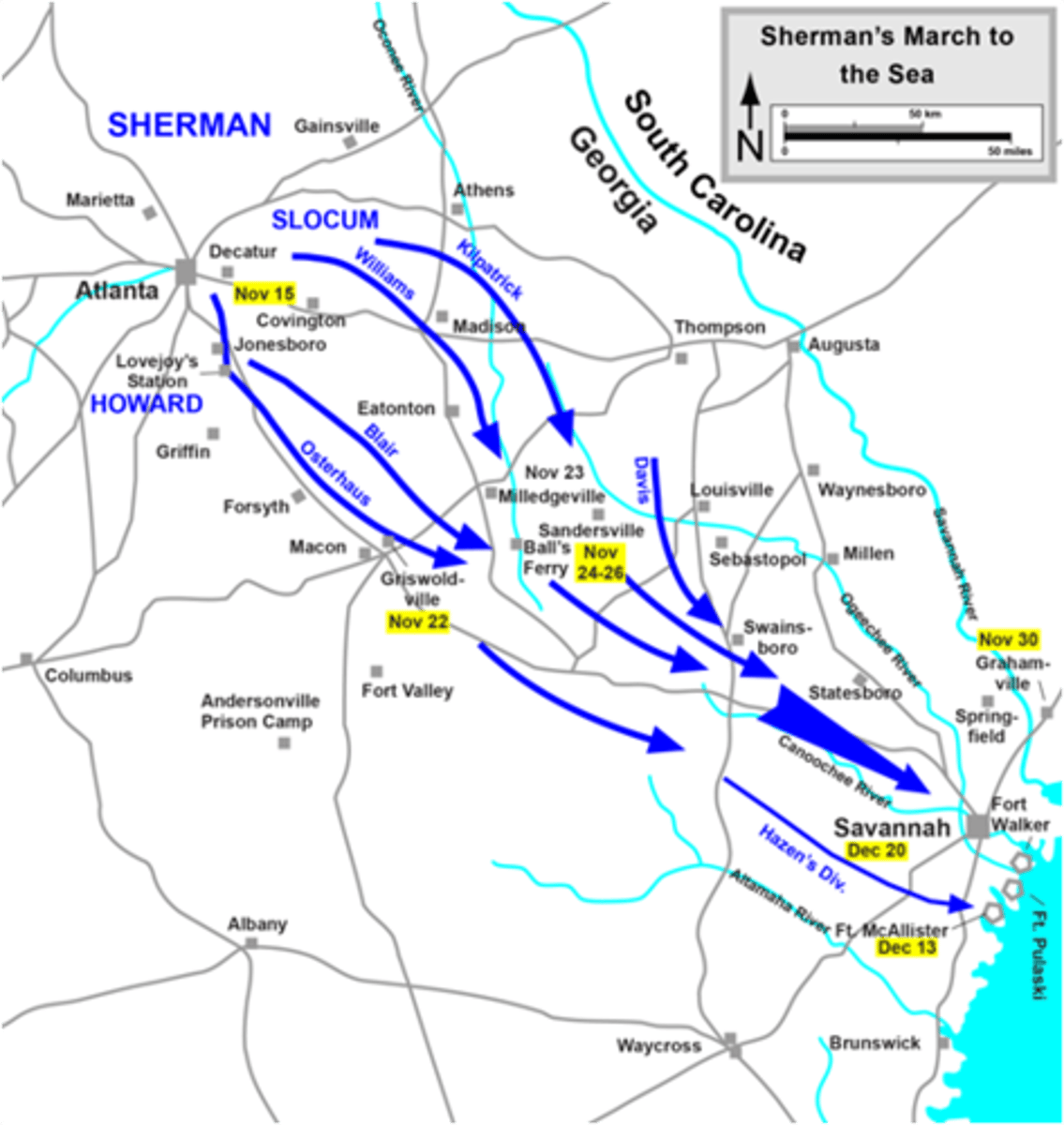
Sherman's march
Union General William Tecumseh Sherman's destructive march through Georgia. An early instance of "total war," purposely targeting infrastructure and civilian property to diminish morale and undercut the Confederate war effort.
Congressional Committee on the Conduct of the War
Established by Congress during the Civil War to oversee military affairs. Largely under the control of Radical Republicans, the committee agitated for a more vigorous war effort and actively pressed Lincoln on the issue of emancipation.

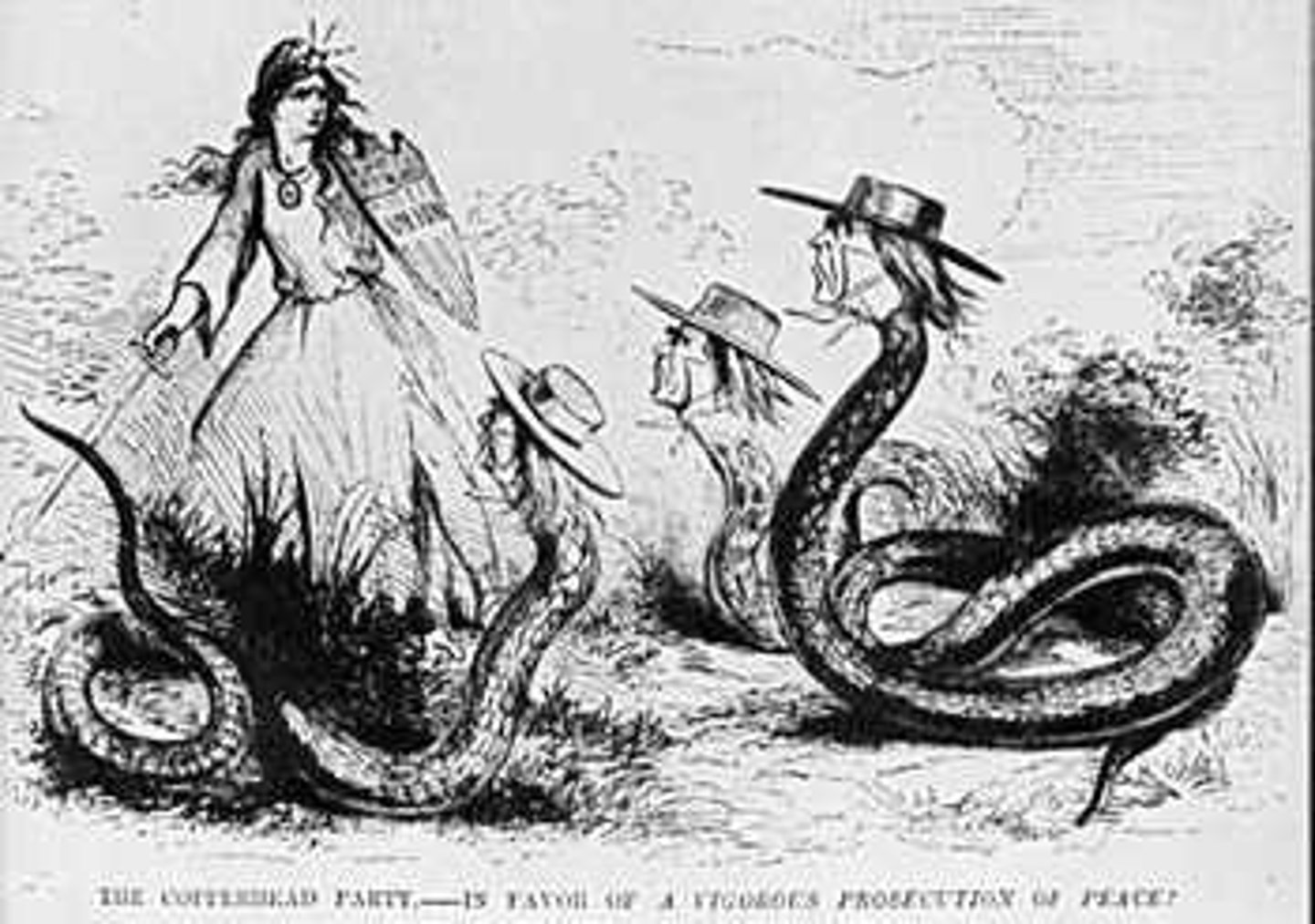
Copperheads
A group of northern Democrats who opposed abolition and sympathized with the South during the Civil War

The Man Without a Country
Edward Everett Hale's fictional account of a treasonous soldier's journeys in exile. The book was widely read in the North, inspiring greater devotion to the Union.

Union party
A coalition party of pro-war Democrats and Republicans formed during the 1864 election to defeat anti-war Northern Democrats.

Wilderness Campaign
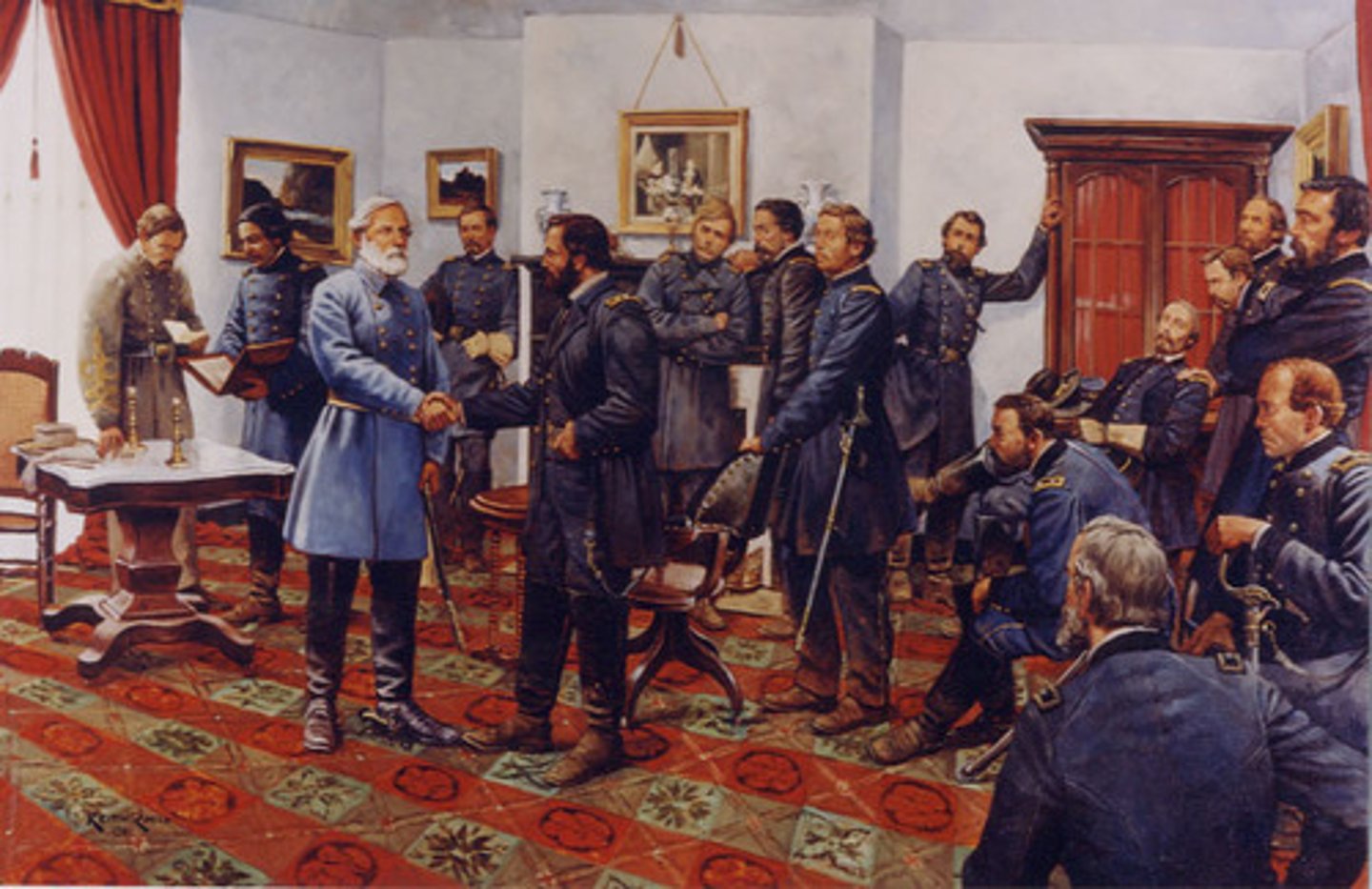
A series of brutal clashes between Ulysses S. Grant's and Robert E. Lee's armies in Virginia, leading up to Grant's capture of Richmond in April of 1865. Having lost Richmond, Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse.
Appomattox Courthouse
Famous as the site of the surrender of the Confederate Army under Robert E. Lee to Union commander Ulysses S. Grant

Reform Bill of 1867
Granted suffrage to all male British citizens, dramatically expanding the electorate. The success of the American democratic experiment, reinforced by the Union victory in the Civil War, was used as one of the arguments in favor of the Bill.

Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson
Confederate general; he commanded troops at both battles of Bull Run and was mortally wounded by his own soldiers at Chancellorsville in 1863.
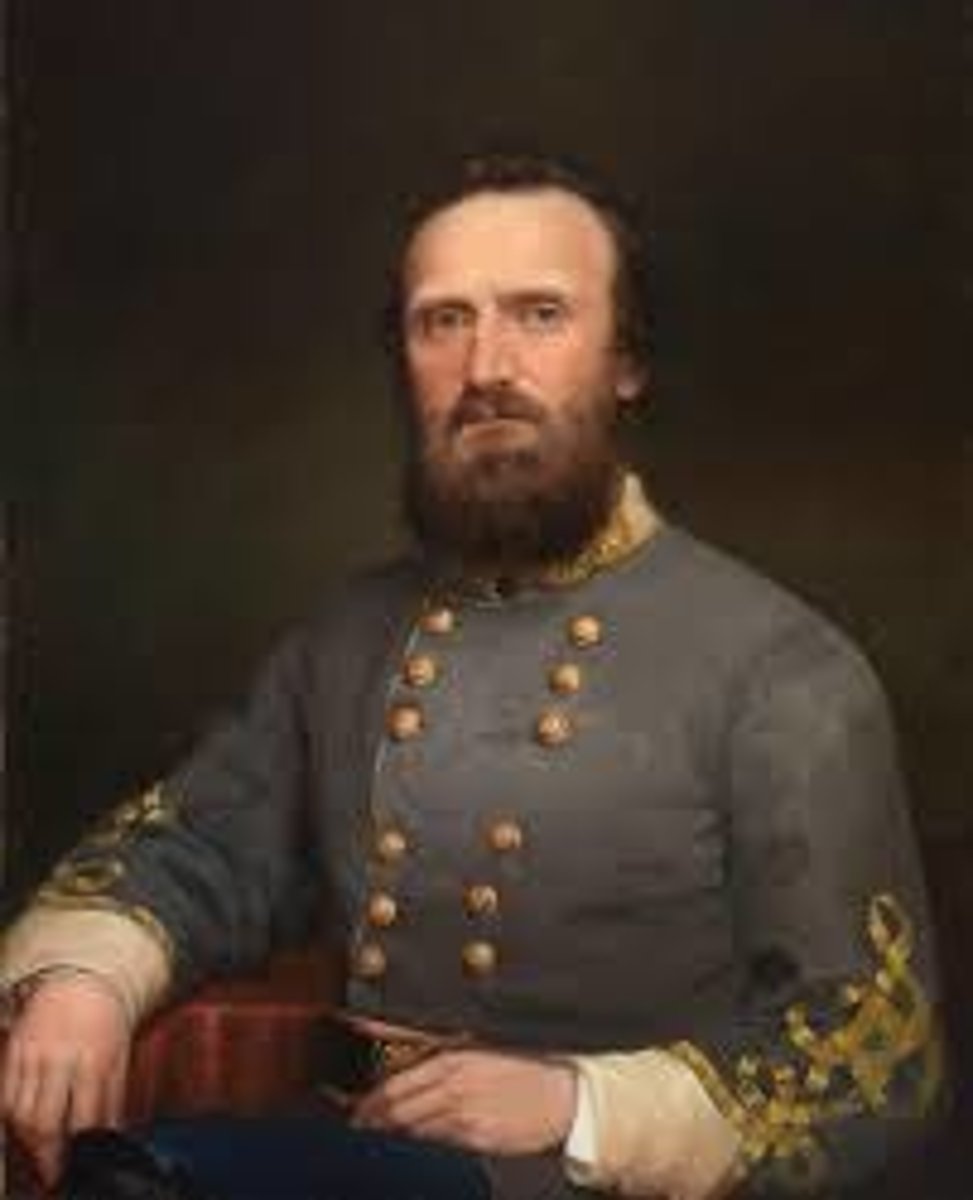

George B. McClellan
A general for northern command of the Army of the Potomac in 1861; nicknamed "Tardy George" because of his failure to move troops to Richmond; lost battle vs. General Lee near the Chesapeake Bay; Lincoln fired him twice.

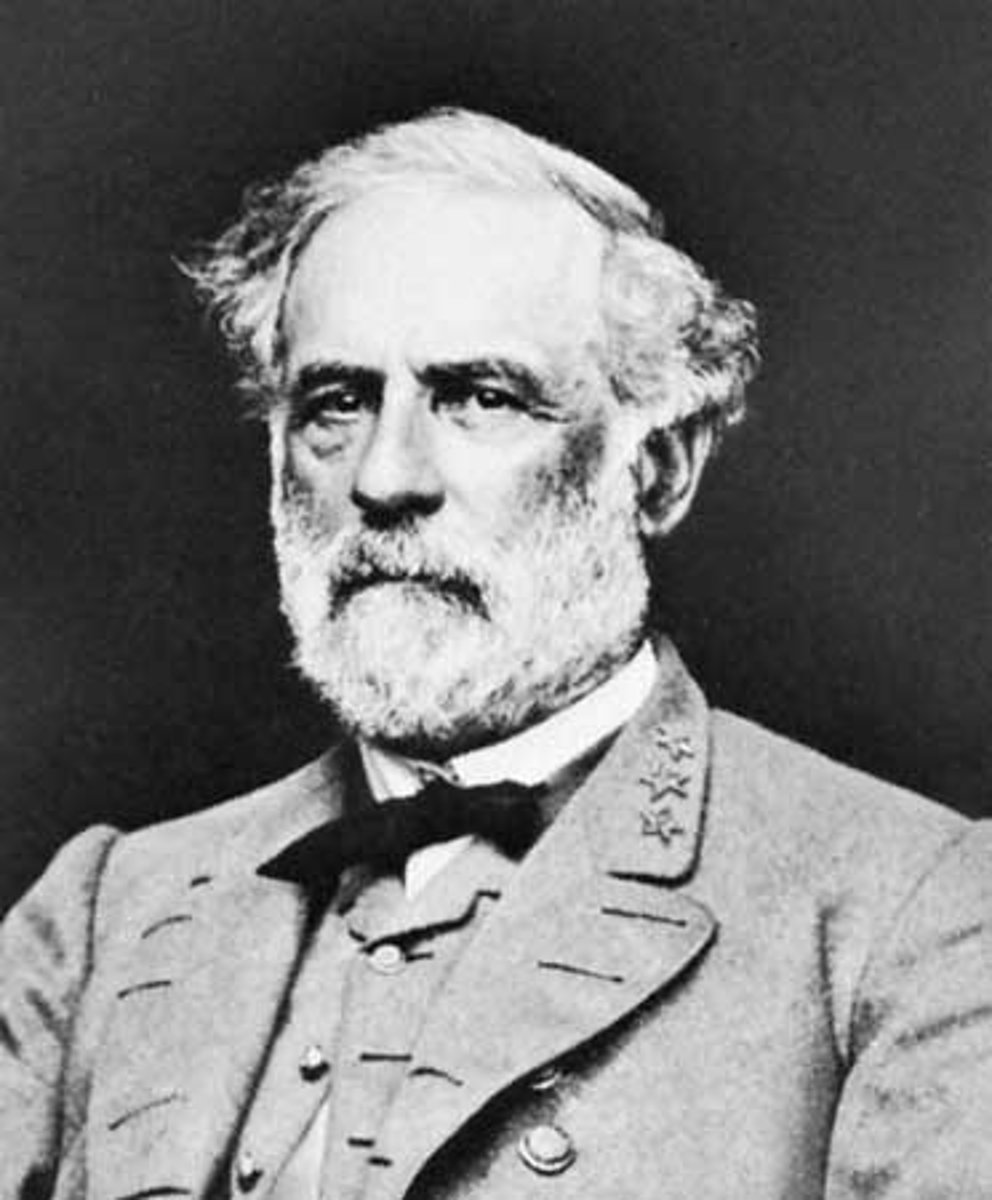
Robert E. Lee
Confederate general who had opposed secession but did not believe the Union should be held together by force

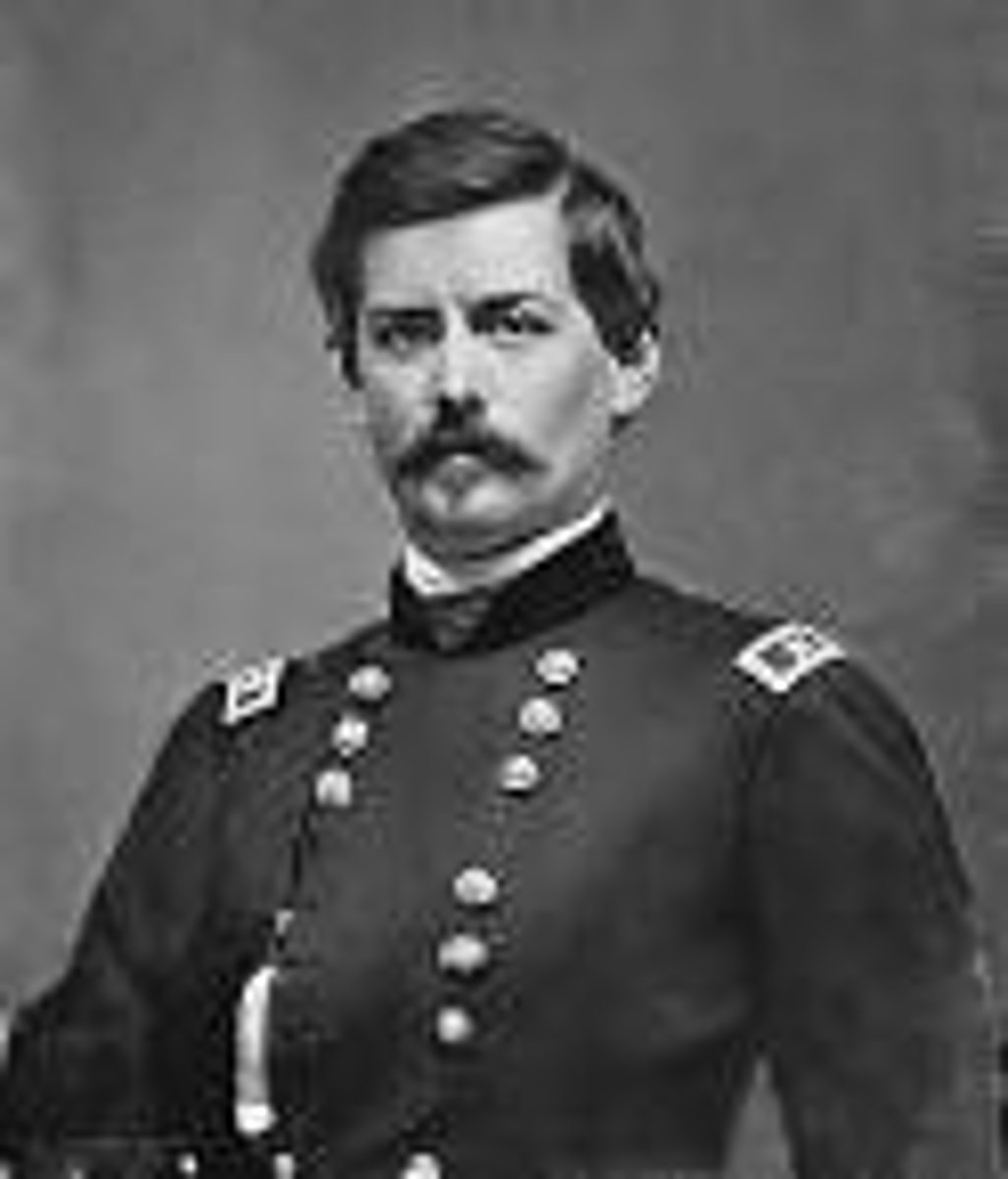
John Pope
Union general with brief but successful career in the Western Theater, but he is best known for his defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run in the East.
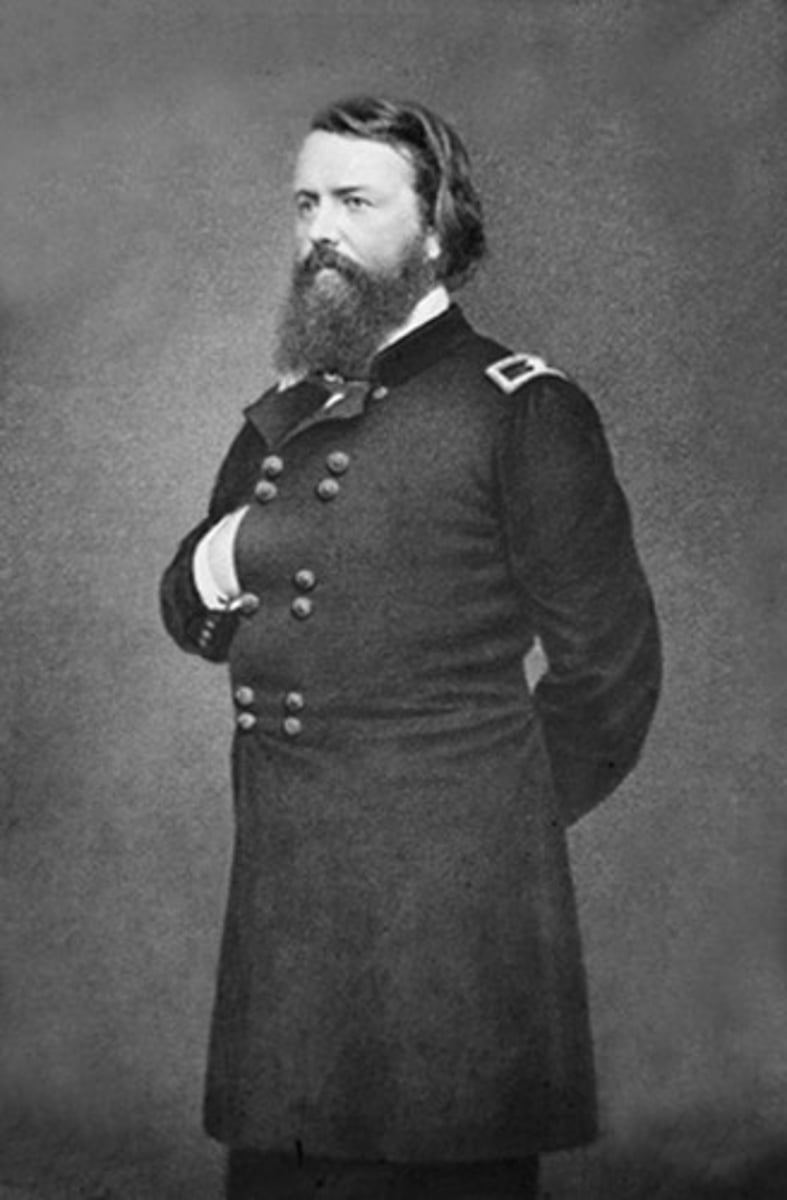

A.E. Burnside
more than 10,000 Northern soldiers were killed when this man, McClellan's successor as commander of the Army of the Potomac, decided on the frontal attack on Lee's Virginia army on December 13, 1862.
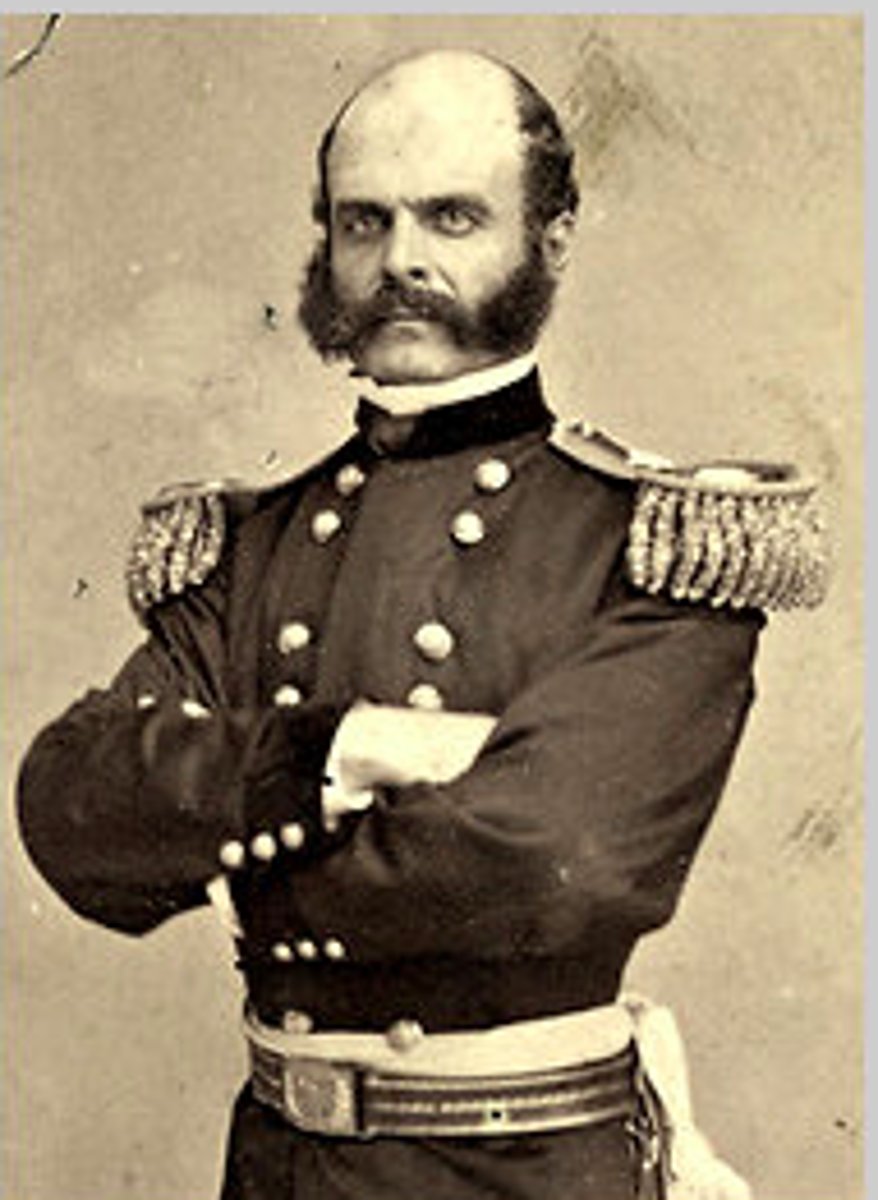

Joseph ("Fighting Joe") Hooker (1814-1879)
Union army general, known as his nickname for his bold attacks on Confederate lines during McClellan's peninsular campaign. He took command of the Army of the Potomac from A.E. Burnside in 1863, a post he lost just six months later after he led a failed attack on Lee's forces at Chancellorsville.
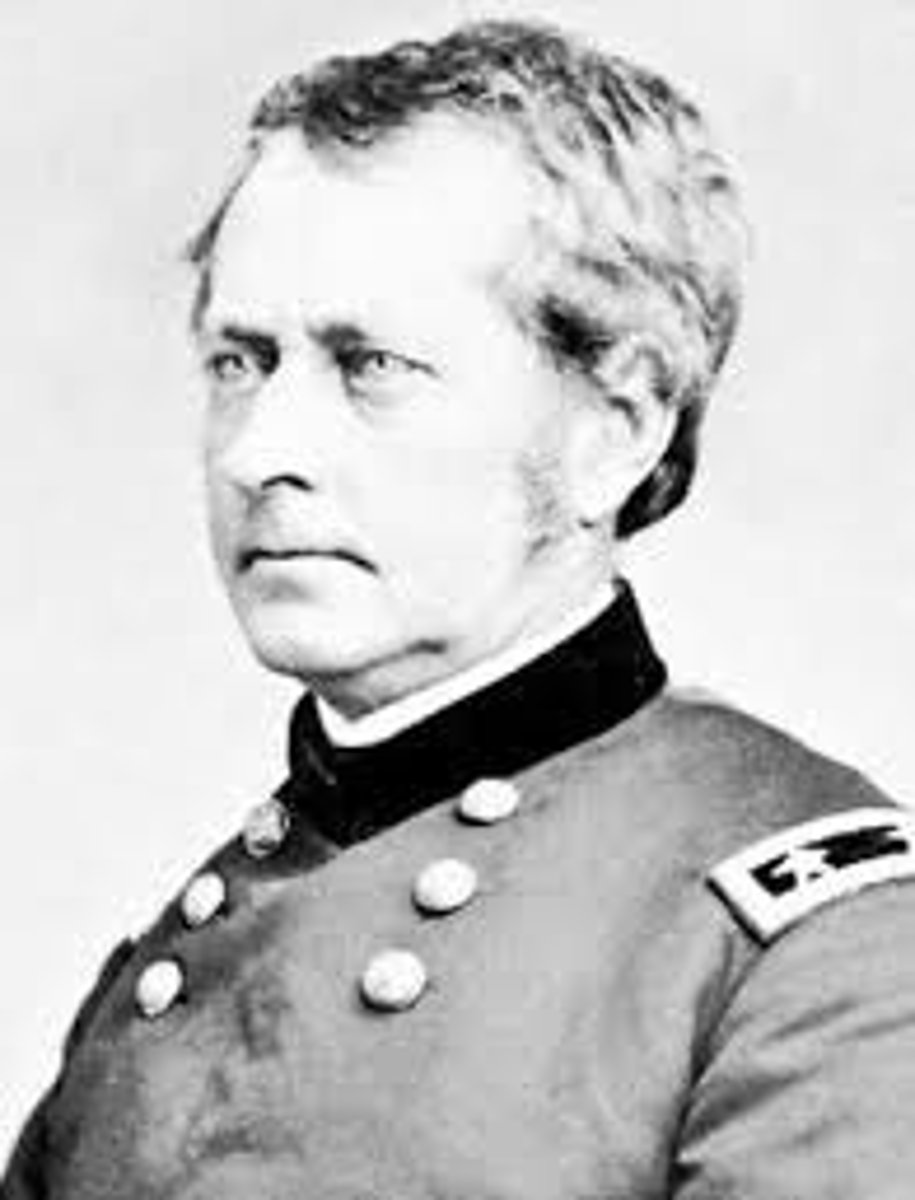

George G. Meade
Union general who replaced Hooker three days before the Battle of Gettysburg, where he finally broke the Confederate attack.
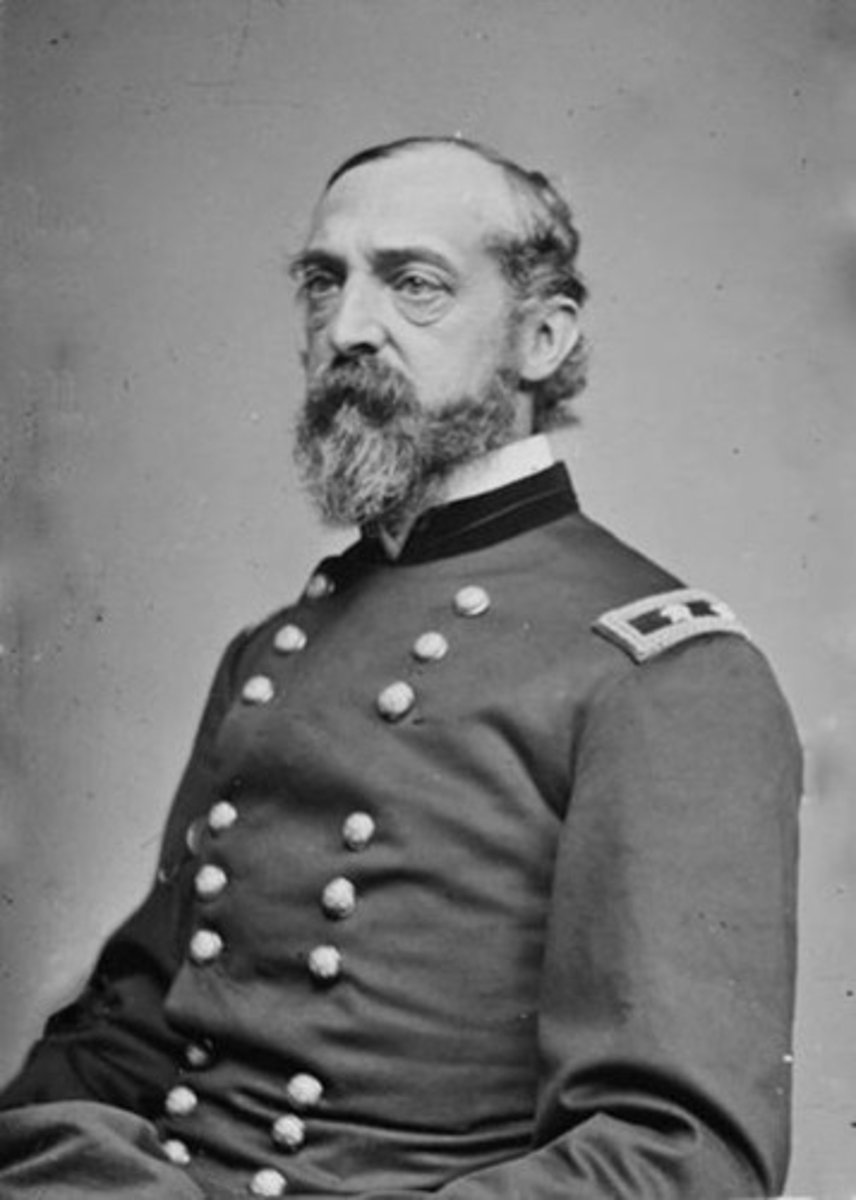

George Pickett
U.S. Army officer who became a general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. He is best remembered for his participation in the futile and bloody assault at the Battle of Gettysburg that bears his name, Pickett's Charge.
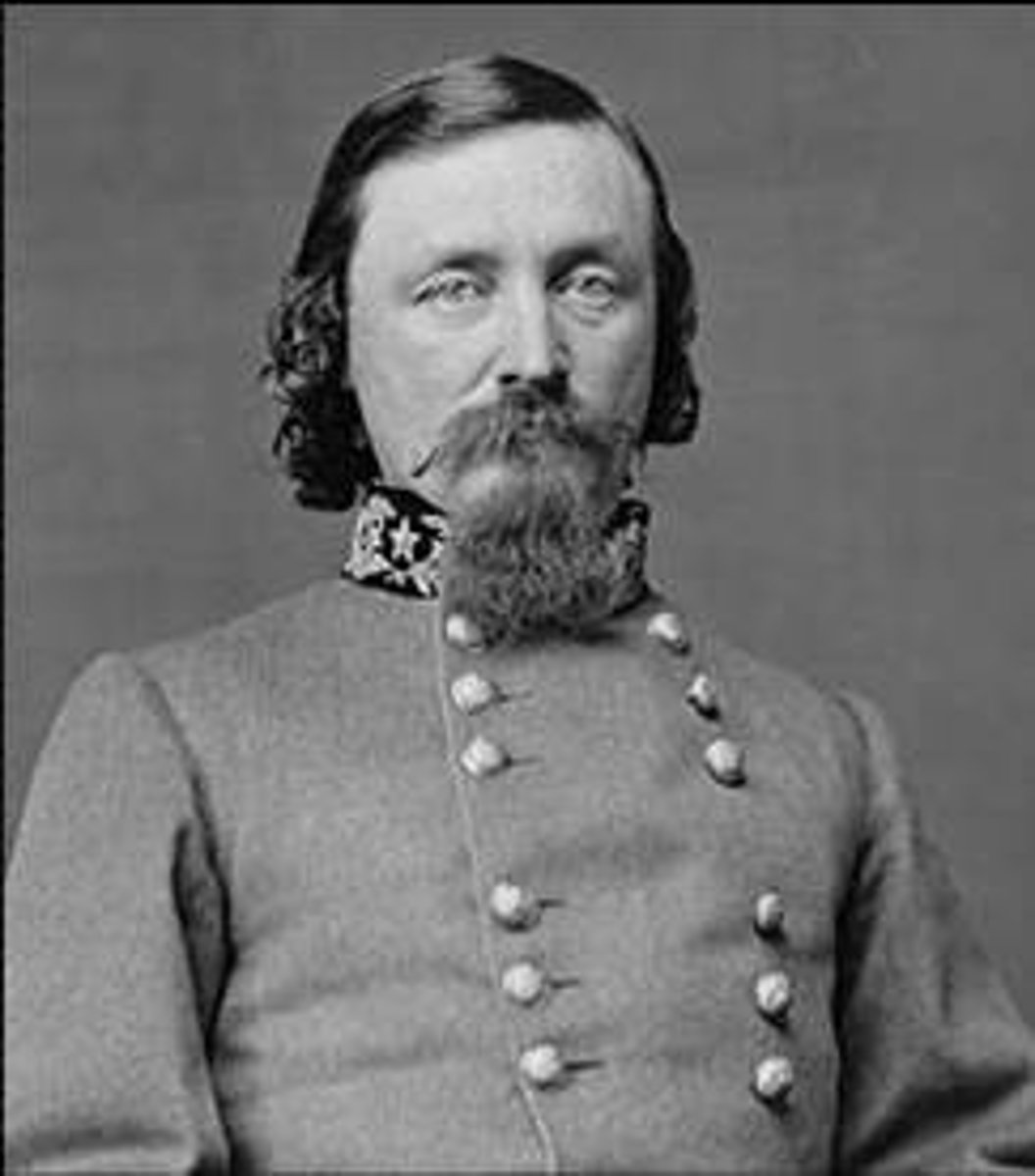

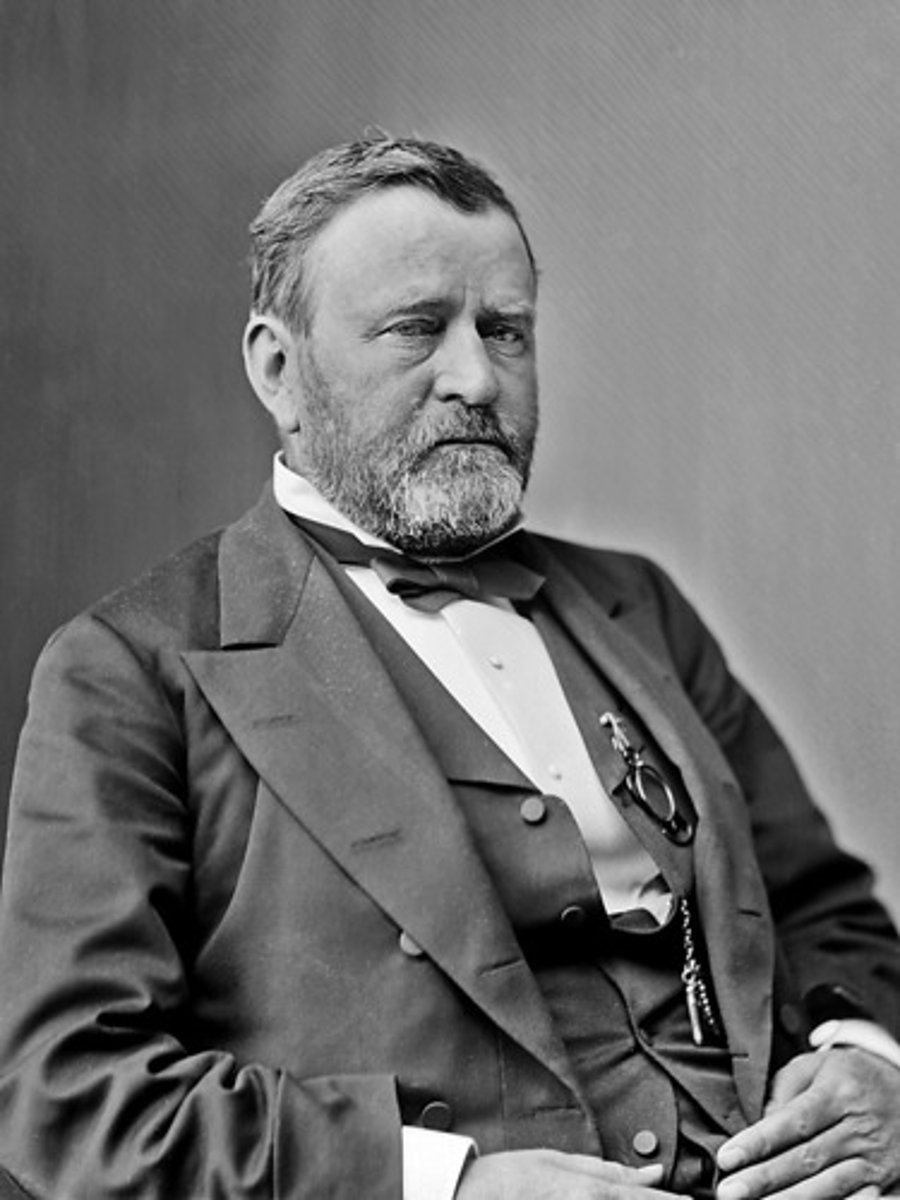
Ulysses S. Grant
an American general and the eighteenth President of the United States (1869-1877). He achieved international fame as the leading Union general in the American Civil War.

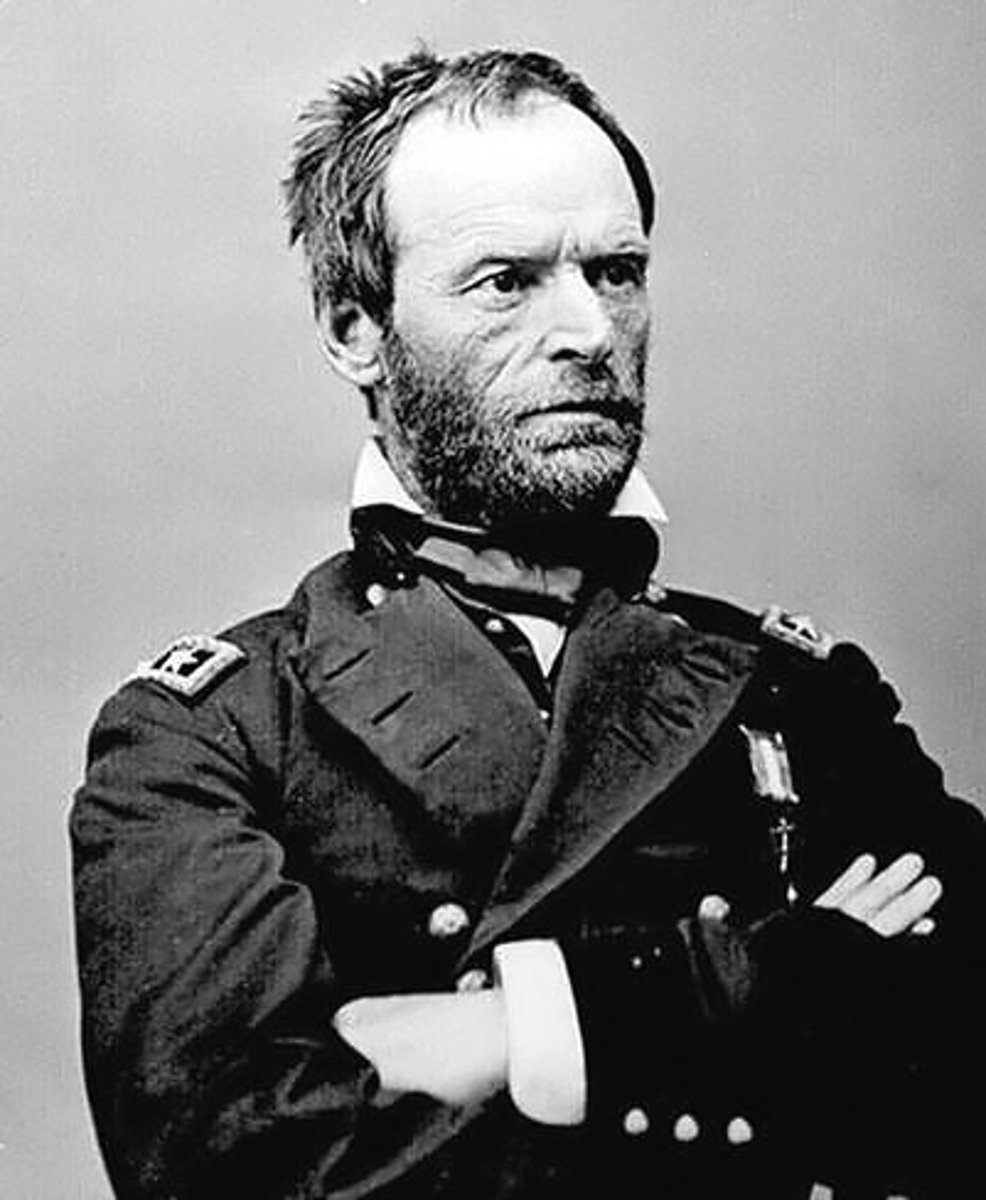
William Tecumseh Sherman
Union General who destroyed South during "march to the sea" from Atlanta to Savannah, example of total war

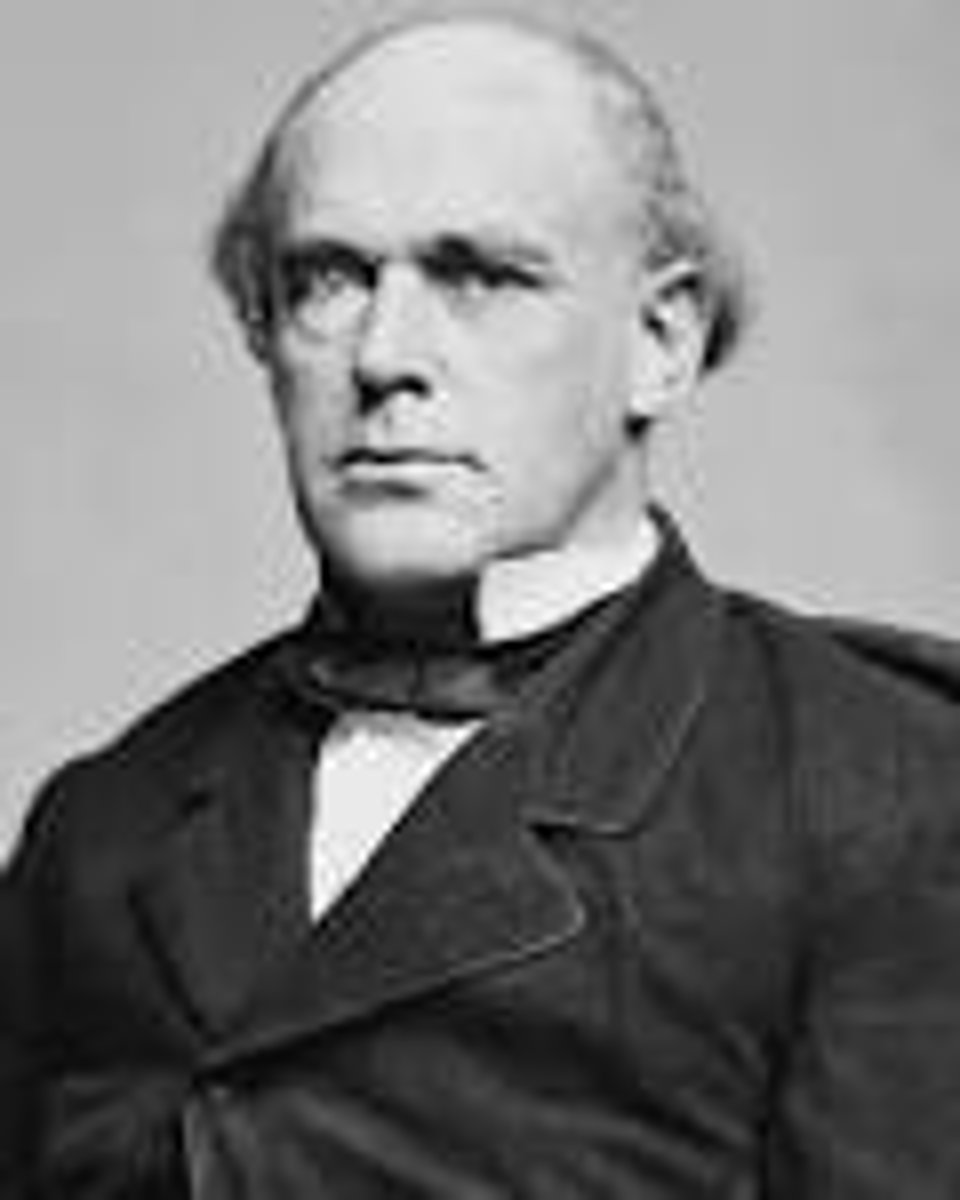
Salmon Chase
Ambitious secretary of the treasury who wanted to replace Lincoln as president in 1864

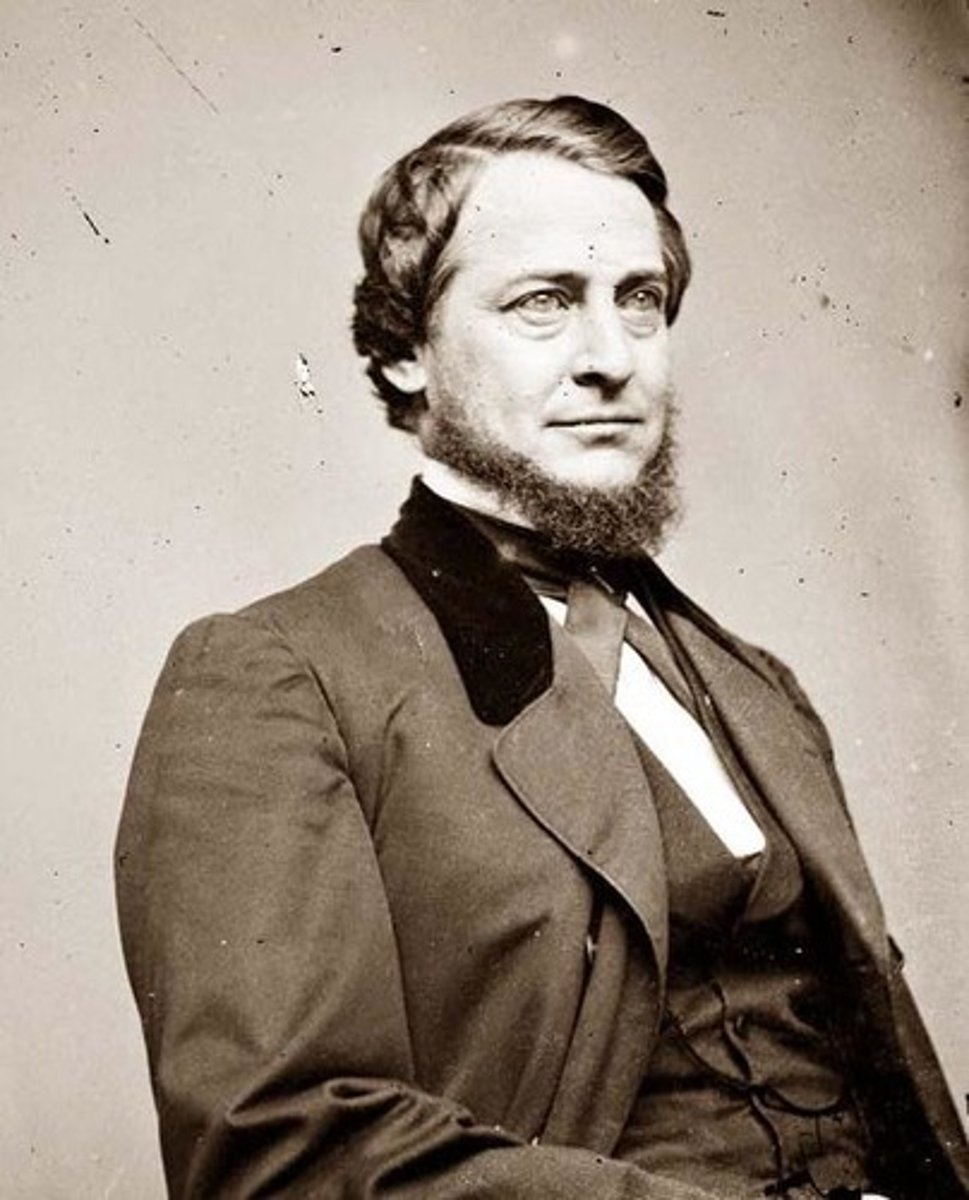
Clement L. Vallandigham
Prominent Copperhead who was an ex-congressman from Ohio, demanded an end to the war, and was banished to the Confederacy

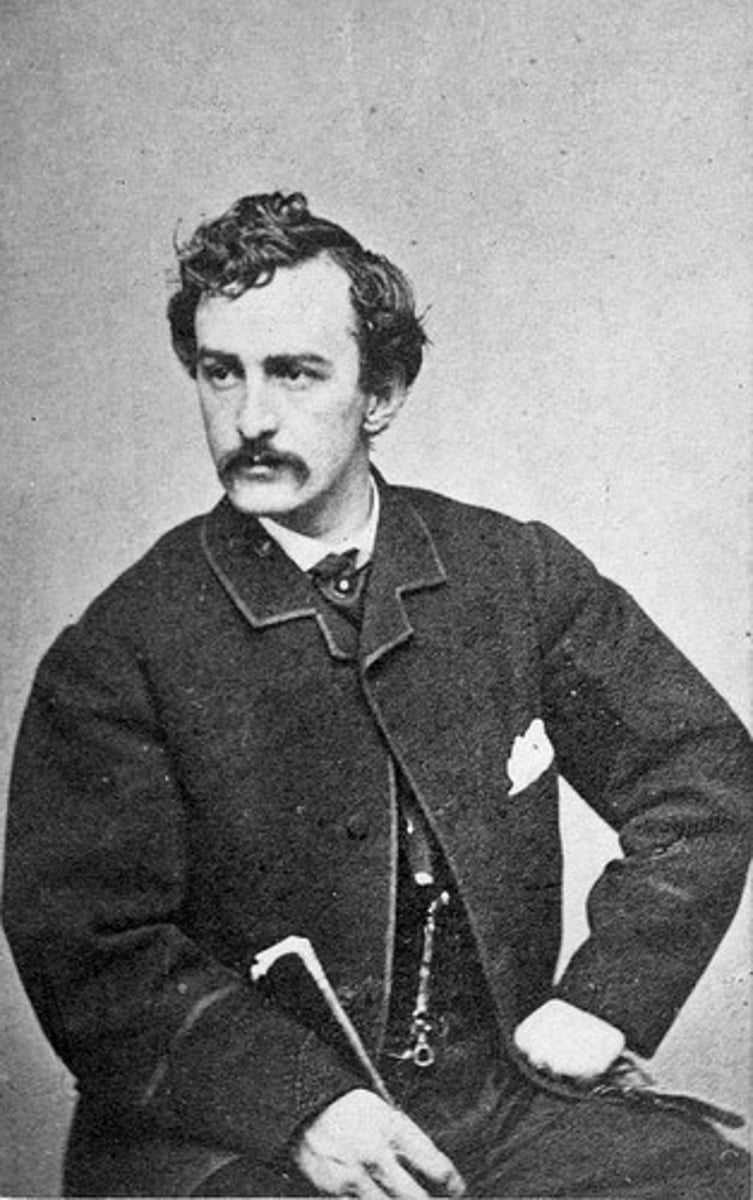
John Wilkes Booth
was an American stage actor who, as part of a conspiracy plot, assassinated Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C. on April 14, 1865.

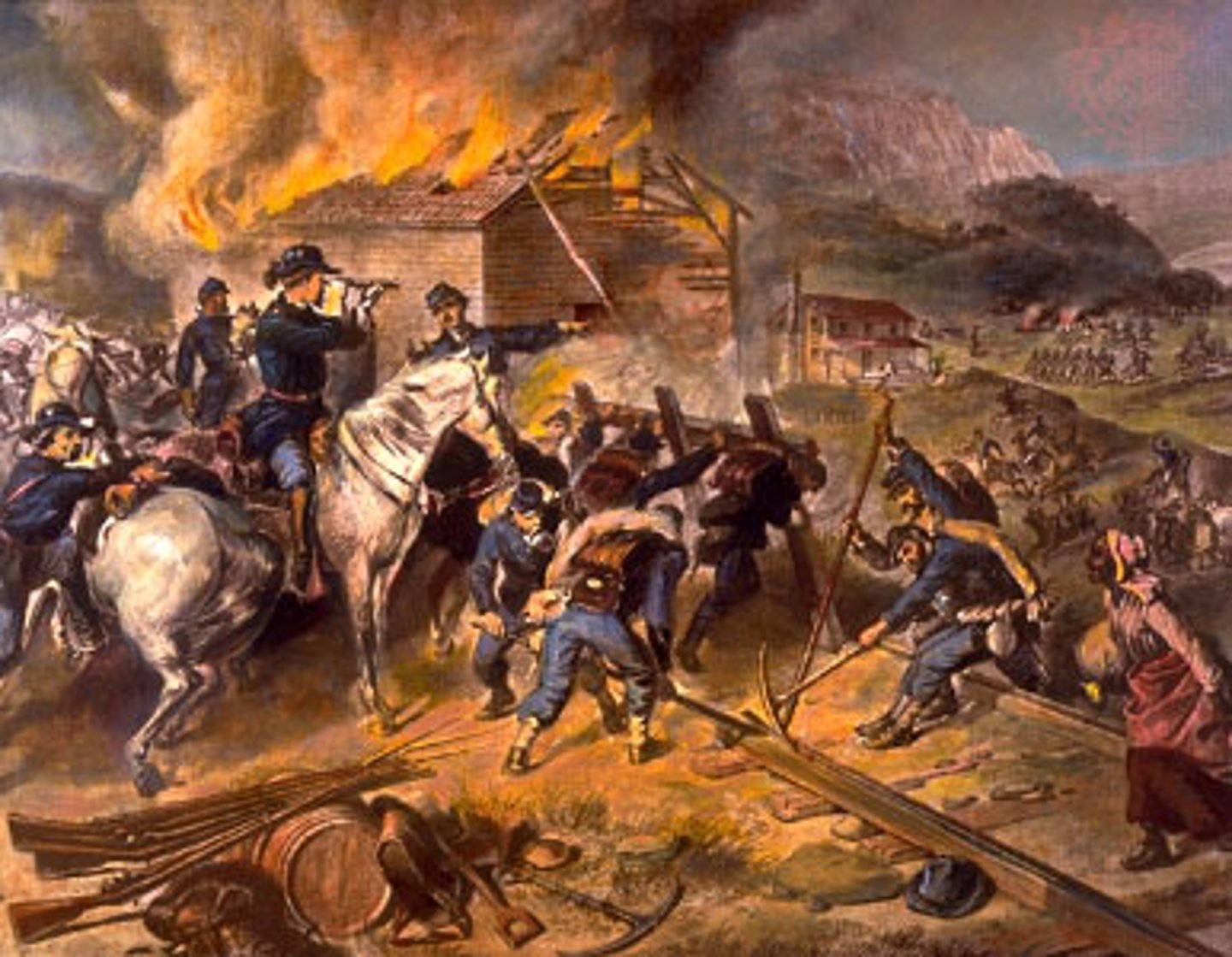
Total War
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort

Ultimate Destination/Continuous Voyage
The Northern Navy enforced the blockade of the seas. London was very unhappy about this leading to a future war.
Remember Fort Pillow
Cry of black units in memory of where several black soldiers surrendered and were executed. The South did not recognize blacks as prisoners of war, and as such, they were slaves in revolt. Once they surrendered, they were executed.

Home Guard
The older men of a county who were charged with defending their neighborhoods during the Civil War

Intelligent contraband
Position for slaves to serve the Union army as spies, guides and scouts
War Democrats/Peace Democrats
President Lincoln had issues with the Democratic Party in the North on how to handle secession. What were the names of the 2 factions of the Democratic Party with vastly differing views and created headaches for Lincoln?

"Lost Cause" Myth
Idealized version of Southern culture; black slaves were happy to be slaves, they were never mistreated. Blacks wanting rights was offensive, outrageous, and a challenge to white supremacy.
