Unit 7: Inference for Quantitative Data (Means) Study Guide Flashcards
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is sampling variability?
the natural variation between a sample mean and the population mean, also called sampling error.
Why is sampling variability important?
It reminds us that a sample mean is only an estimate of the population mean and will not perfectly match the true value.
What are the conditions for constructing a confidence interval for a population mean?
- Random: randomly selected/assigned
- Independent: n < .1N (not necessary for experiments).
- Normality: If the population is normal, any sample size is okay; otherwise, n ≥ 30 (Central Limit Theorem). If population is not stated normal and n is not ≥ 30, create a box plot and check for major outliers and skewness.
What is the formula for a confidence interval for a population mean?
(replace the z with t)
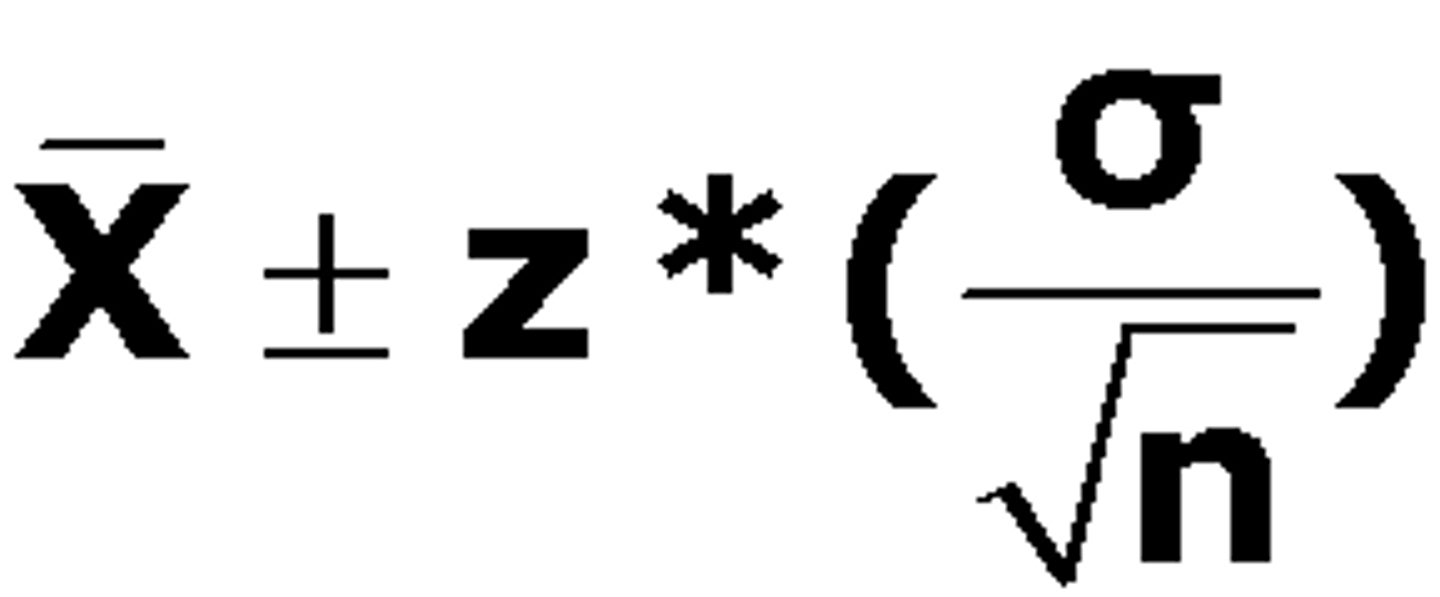
How do you interpret a confidence interval?
"We are ___% confident that the true population mean (context) is between (lower bound) and (upper bound)."
What is the formula for degrees of freedom in a t-interval
df = n - 1
What are the hypothesis in a significance test for a population mean
(H₀): 𝜇 = some value
(Hₐ): 𝜇 >, 𝜇 < or 𝜇 ≠ μ some value
What is the test statistic formula for a one-sample t-test
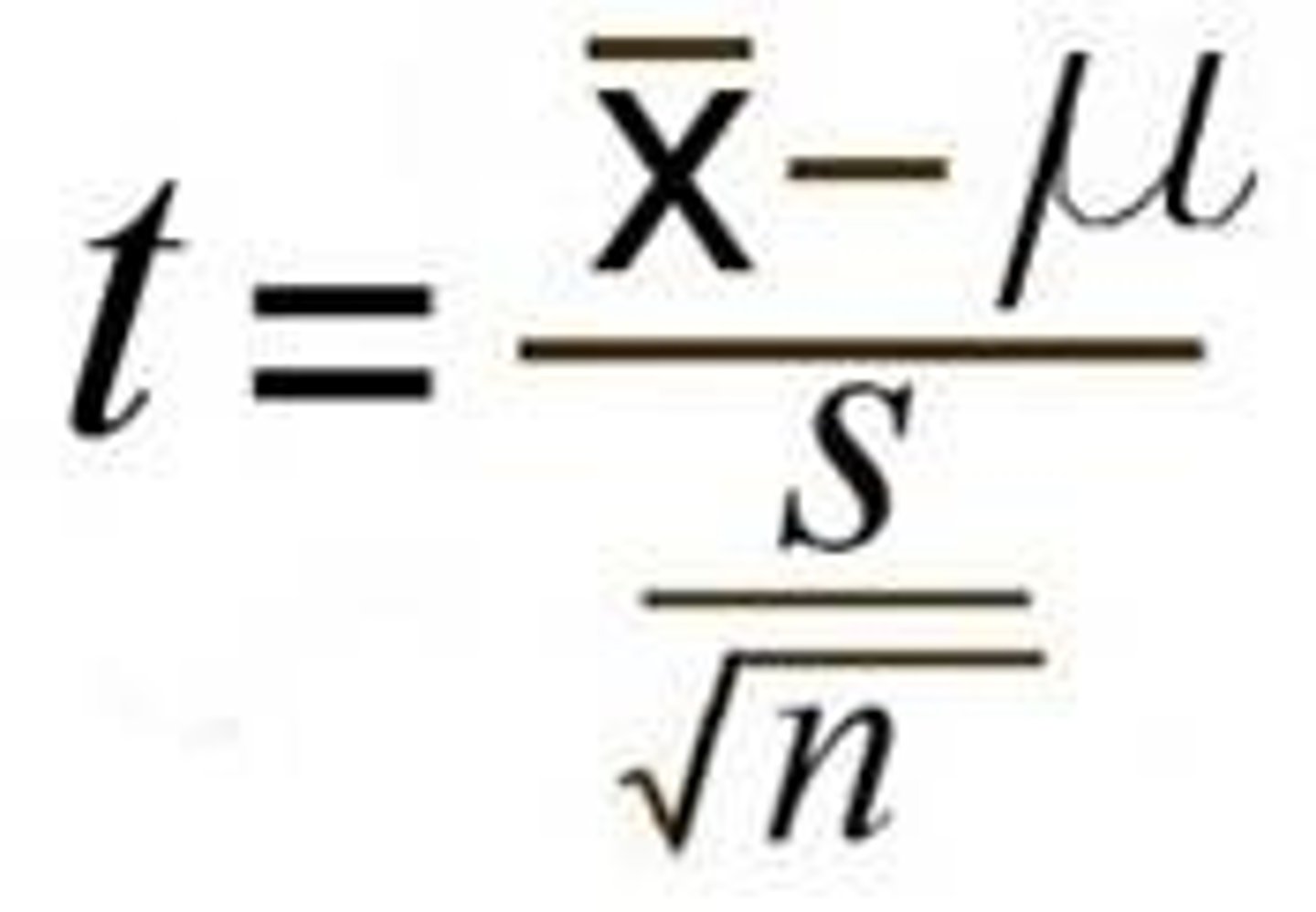
How do you determine the p-value in a t-test?
Use the tcdf function on a calculator to find the probability of obtaining a t-score as extreme or more extreme. or use t-test stat test.
How do you interpret a significance conclusion?
- If p-value < α, reject H₀ → Sufficient evidence for Hₐ
- If p-value ≥ α, fail to reject H₀ → Not enough evidence for Hₐ
What is the formula for a confidence interval for the difference of two means?
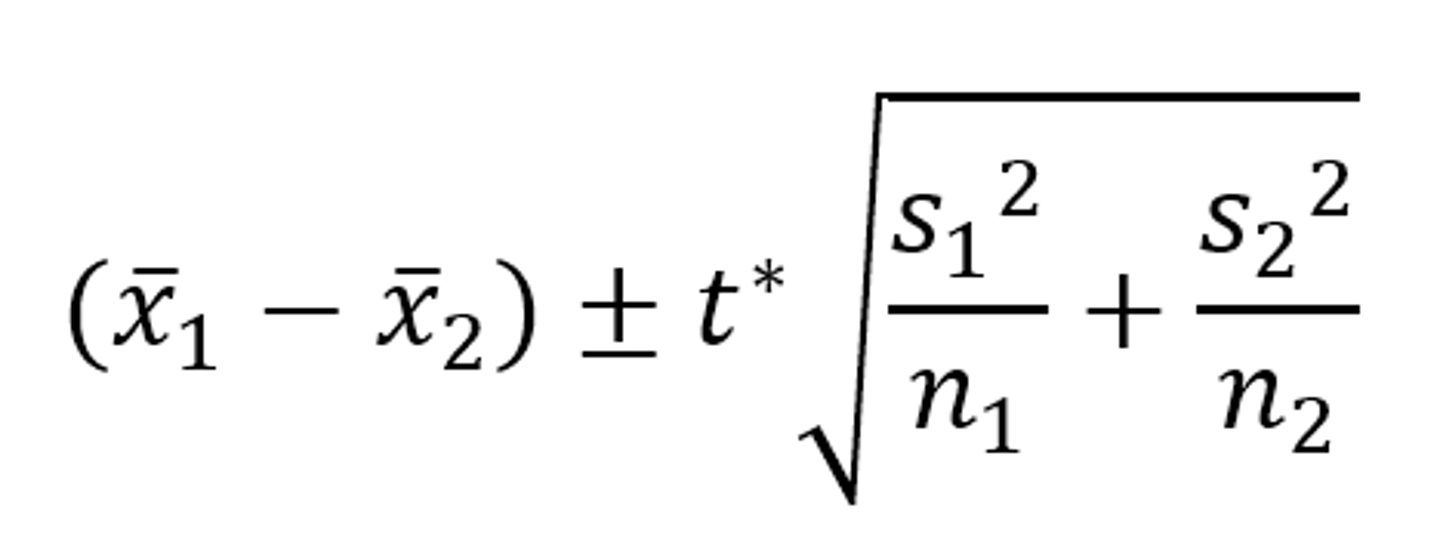
What are the conditions for a two-sample t-interval
- Two random samples
- Independent: n1 < .1N1, n2 < .1N2. not necessary for experiment.
- Normal: n1 ≥ 30, n2 ≥ 30; or check for outliers/skewness
How do you interpret a confidence interval for the difference of two means?
"We are ___% confident that the true difference between the population means is between (lower bound) and (upper bound)."
What are the hypothesis in a two-sample t-test?
- H₀: μ1 - μ2 = 0
- Hₐ: μ1 − μ2 is >, <, or ≠ 0
What is the test statistic for a two-sample t-test?
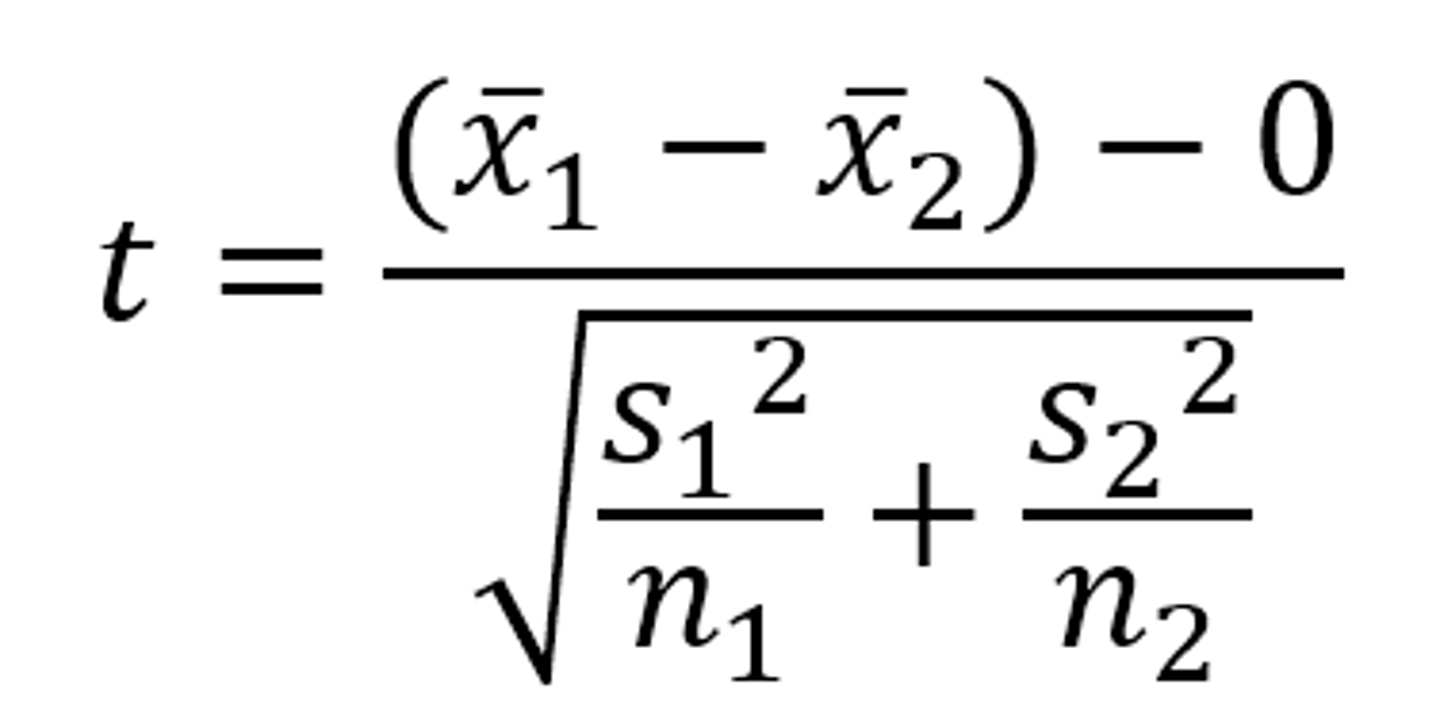
How do you determine the p-value for a two-sample t-test?
Use tcdf with the calculated t-score and degrees of freedom OR use t-test in stat-test.
How do you interpret the results of a two-sample t-test?
- If p-value < α, reject H₀ → Sufficient evidence for Hₐ
- If p-value ≥ α, fail to reject H₀ → Not enough evidence for Hₐ
What is a Type 1 error?
Rejecting Ho when it is actually true.
What is a Type 2 error?
Failing to reject Ho when it is actually false.
What is power?
The probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis (increases with larger sample size).