TAMU BIOL 319 LAB Preface and Lab 1
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Sagittal plane/section
divide the body or organ into right and left portions
Midsagittal plane/section
divides the body or organ into equal right and left sides
Frontal (coronal) plane/section
divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior portions
Transverse (cross section)
divides the body or organ into superior and inferior sides
Oblique
passes through the body or organ at an angle
Anatomical position
To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
Superior (cranial)
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
Inferior (caudal)
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
Anterior (ventral)
Nearer to or at the front of the body
Posterior (dorsal)
Nearer to or at the back of the body
Medial
Nearer to the midline of the body
Lateral
Further from the midline of the body
Intermediate
Between two structures
Ipsilateral
On the same side of the body as another structure
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body as a structure
Proximal
Closer to the trunk or point of attachment
Distal
Farther from the trunk or point of attachment
Superficial
Toward or on surface of the body
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
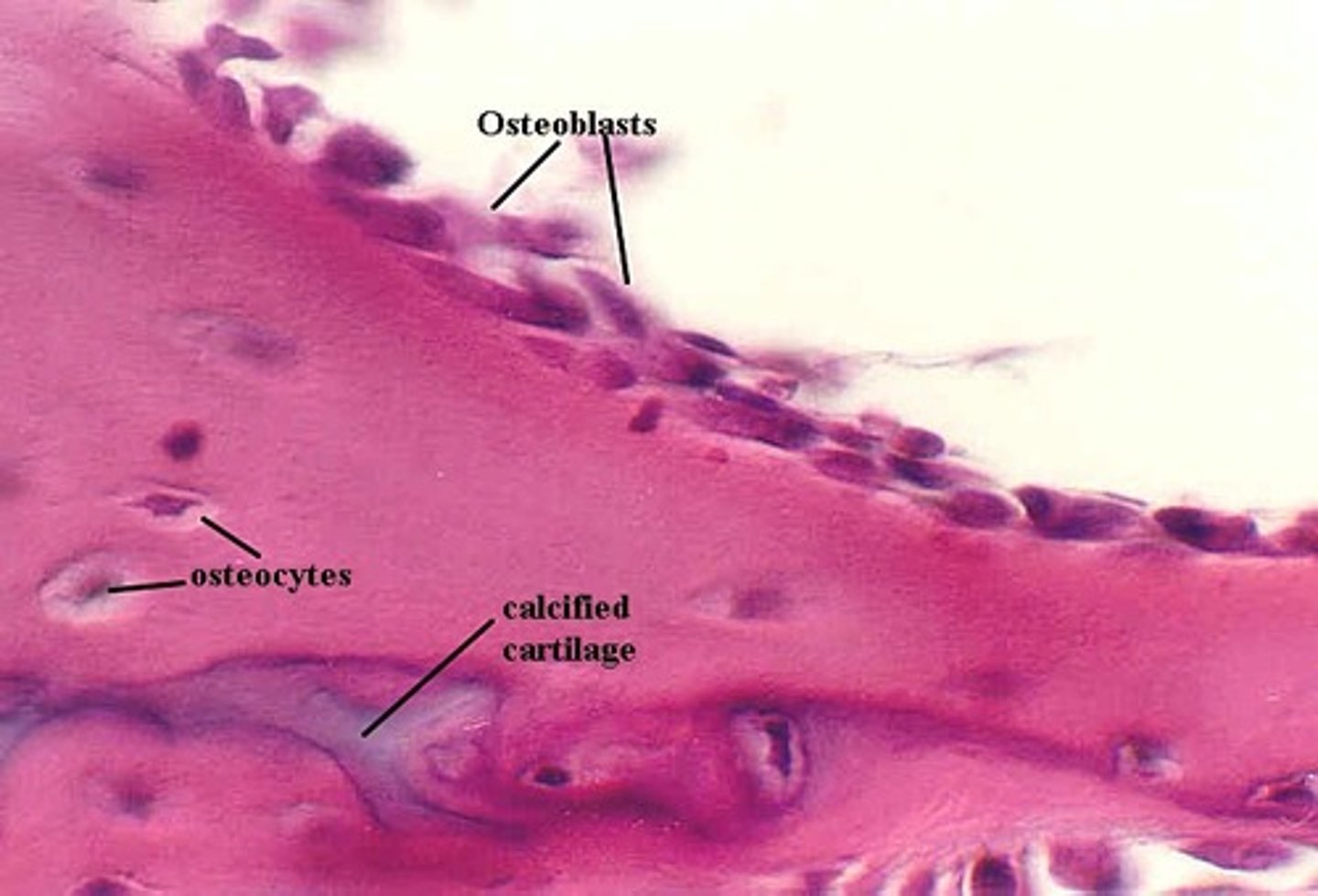
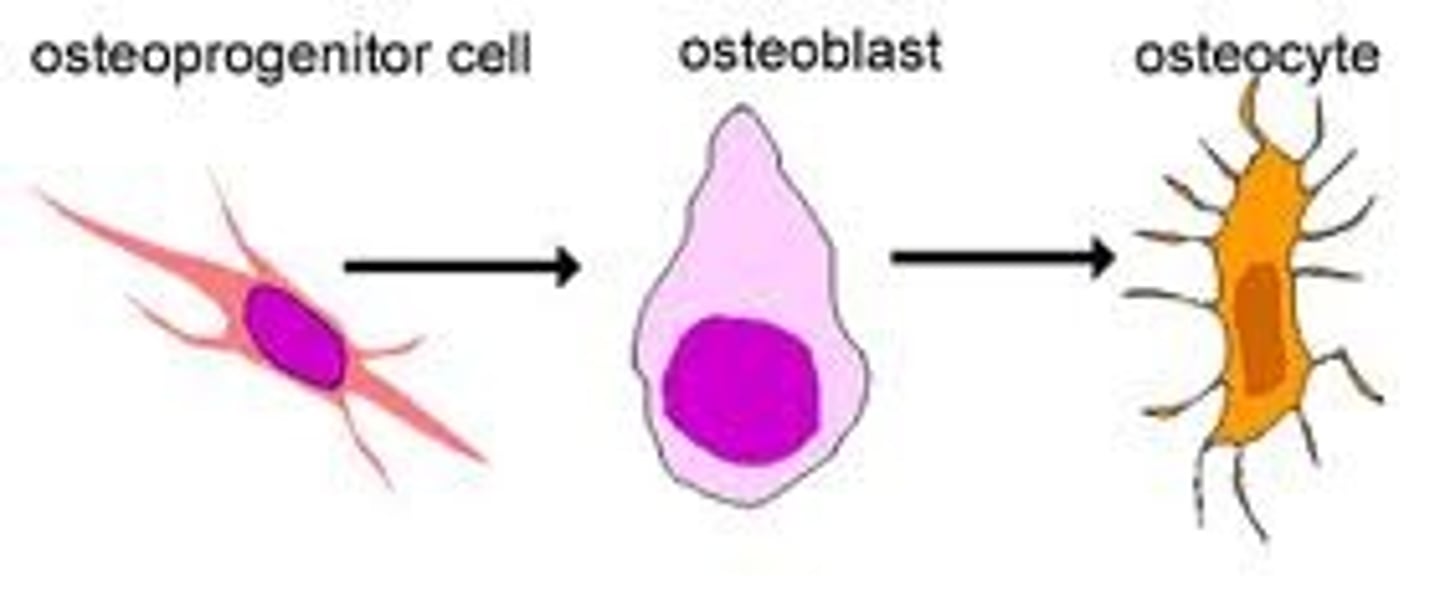
Osteocyte
derived from osteoblasts- involved in bone maintenance
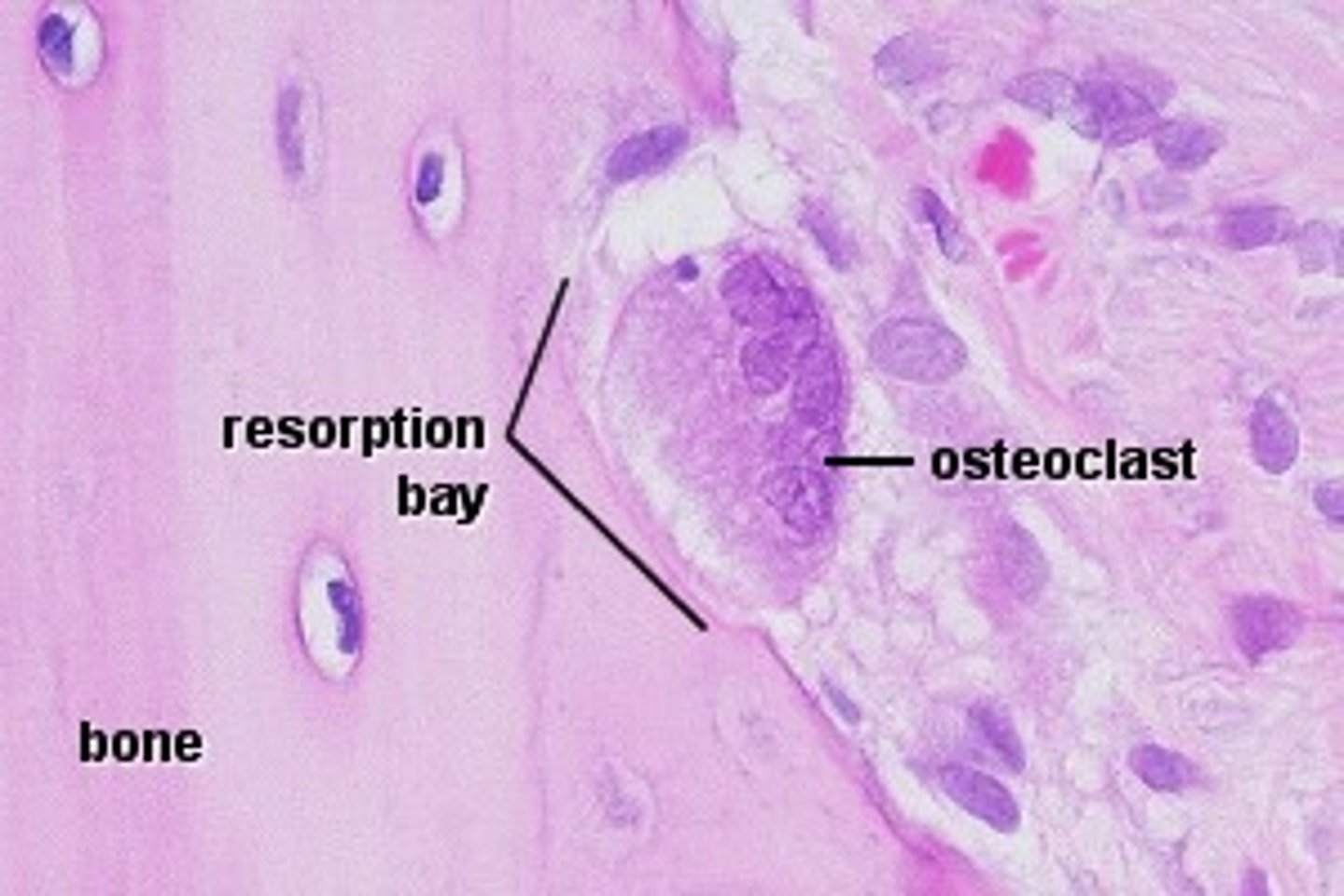
Osteoclast
Multinucleate cell that secretes acids and enzymes to dissolve bone matrix
Osteoblast
Derived from osteoprogenitor cells - secretes organic components of matrix
Osteoprogenitor cells
stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts
Histology
study of tissues
epithelial tissue
tissue that lines and covers organs and internal passageways, creates boundaries between different environments, and forms glands; made up of sheet of cells (joined together via tight junctions and desmosomes)
Apical (free) surface
Surface of the cells that are exposed to the external environment or to an internal passage way or cavity; obtain nutrients by diffusion of substances from connective tissue that are underlying the epithelia
Simple epithelium
Single layer of cells
function: diffusion, absorption, filtration, and secretion
at the free surface, microvilli on the epithelial cell membrane increase surface area for absorption
goblet cells secrete mucus that coats the cell to protect epithelia at free surface
cilia, small motile hair-like projections from the apical surface that sweep substances across the apical surface
Stratified epithelium
Composed of more than one layer of cells
found in areas exposed to abrasions and friction (body surface and upper digestive tract)
mostly for protection
regenerate from basal cells that divide and move out to replace older cells near the apical border
stratified squamous is most common
Regeneration of tissues
How easily the tissues can be regenerated; based on the rate of mitosis and the amount of blood supply
Examples of good to excellent regeneration of tissue
Epithelial tissue, bone, areolar tissue, dense irregular connective tissue, and blood forming tissue
Examples of moderate regeneration of tissue
Smooth muscle and dense regular connective tissue
Examples of weak regeneration of tissue
Skeletal muscle and cartilage
Example of none of almost no regeneration of tissue
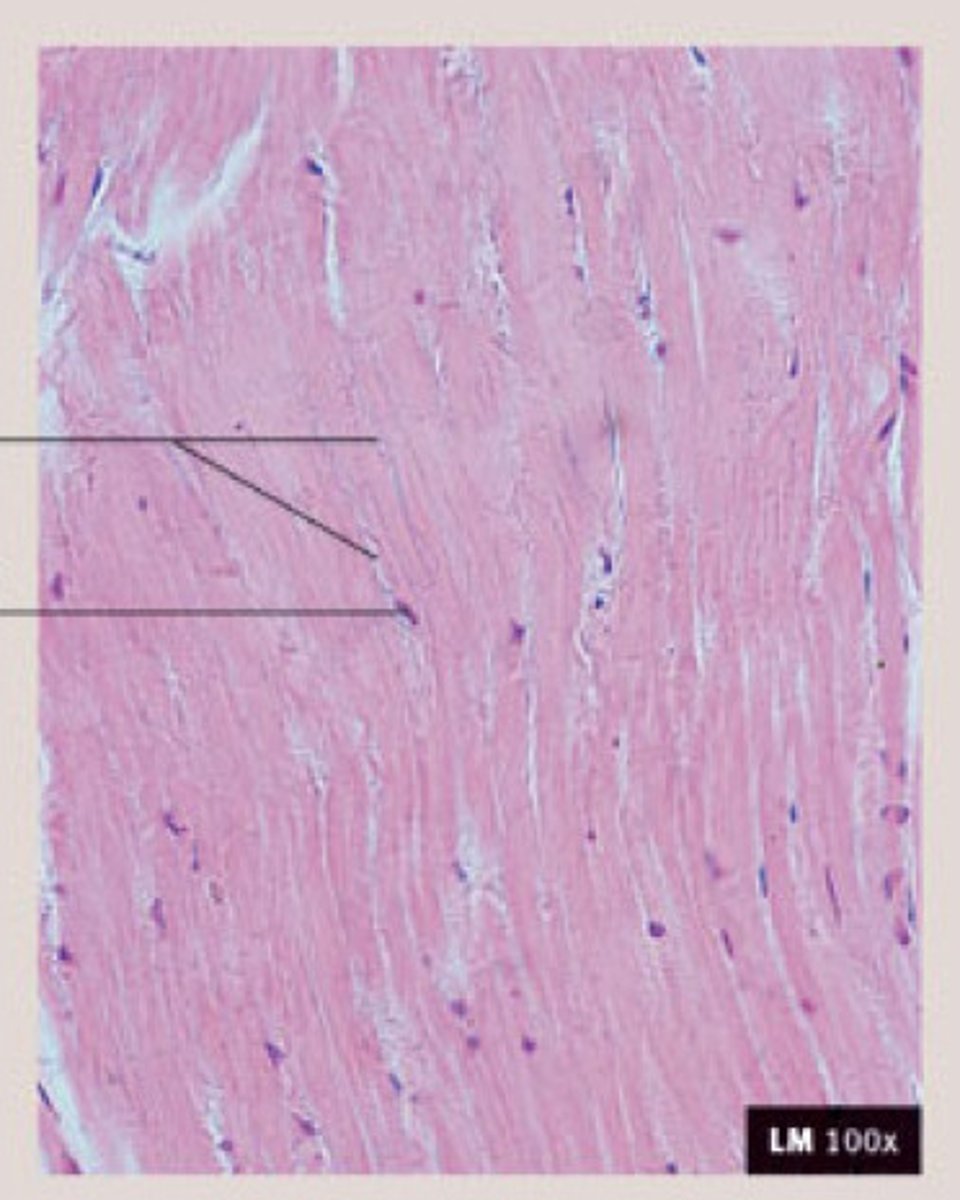
Cardiac muscle tissue and (central nervous system) nervous tissue
Reasons why regeneration of tissue can be high
If the rate of mitosis is high and there is adequate or abundant blood supply
Avascular
No blood vessels or supply
Function: simple squamous epithelium
To allow passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secrets lubricating substances in serosae (tissue lining of a body cavity or outer lining of an organ)
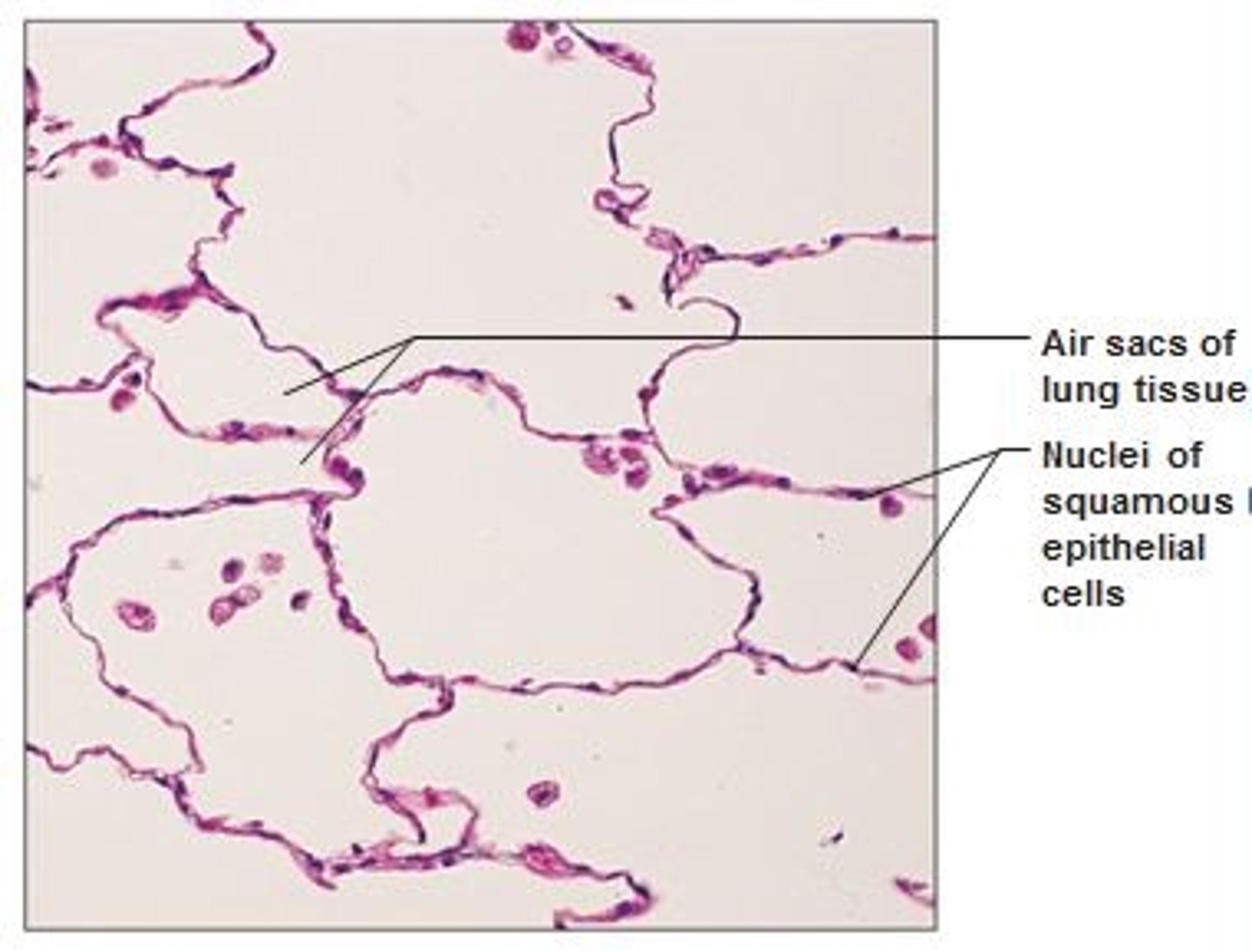
Description: simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm; the simplest of the epithelia
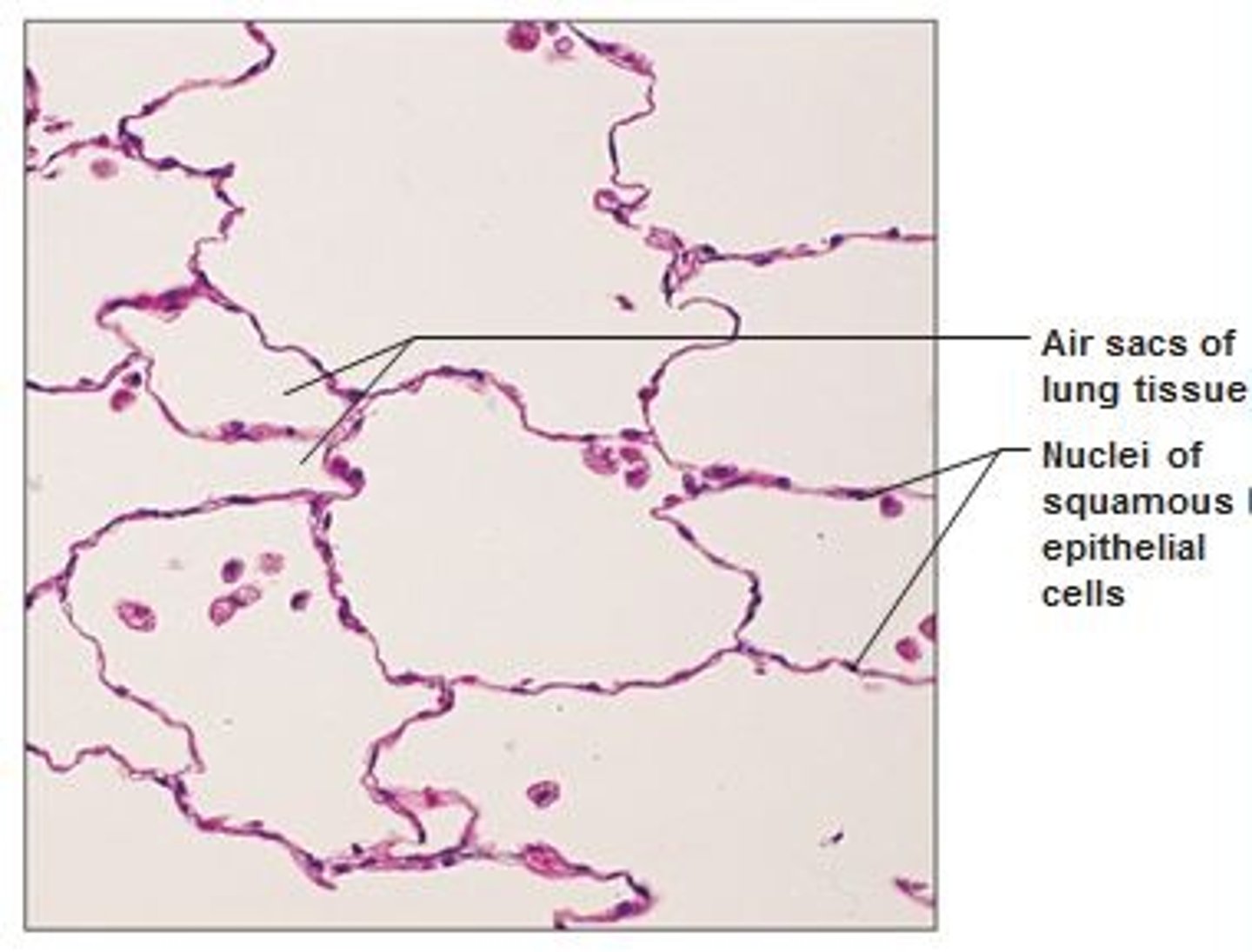
Location: simple squamous epithelium
Kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lining of ventral body cavity
Avelous
Air sack present in between linings of the simple squamous in the lung
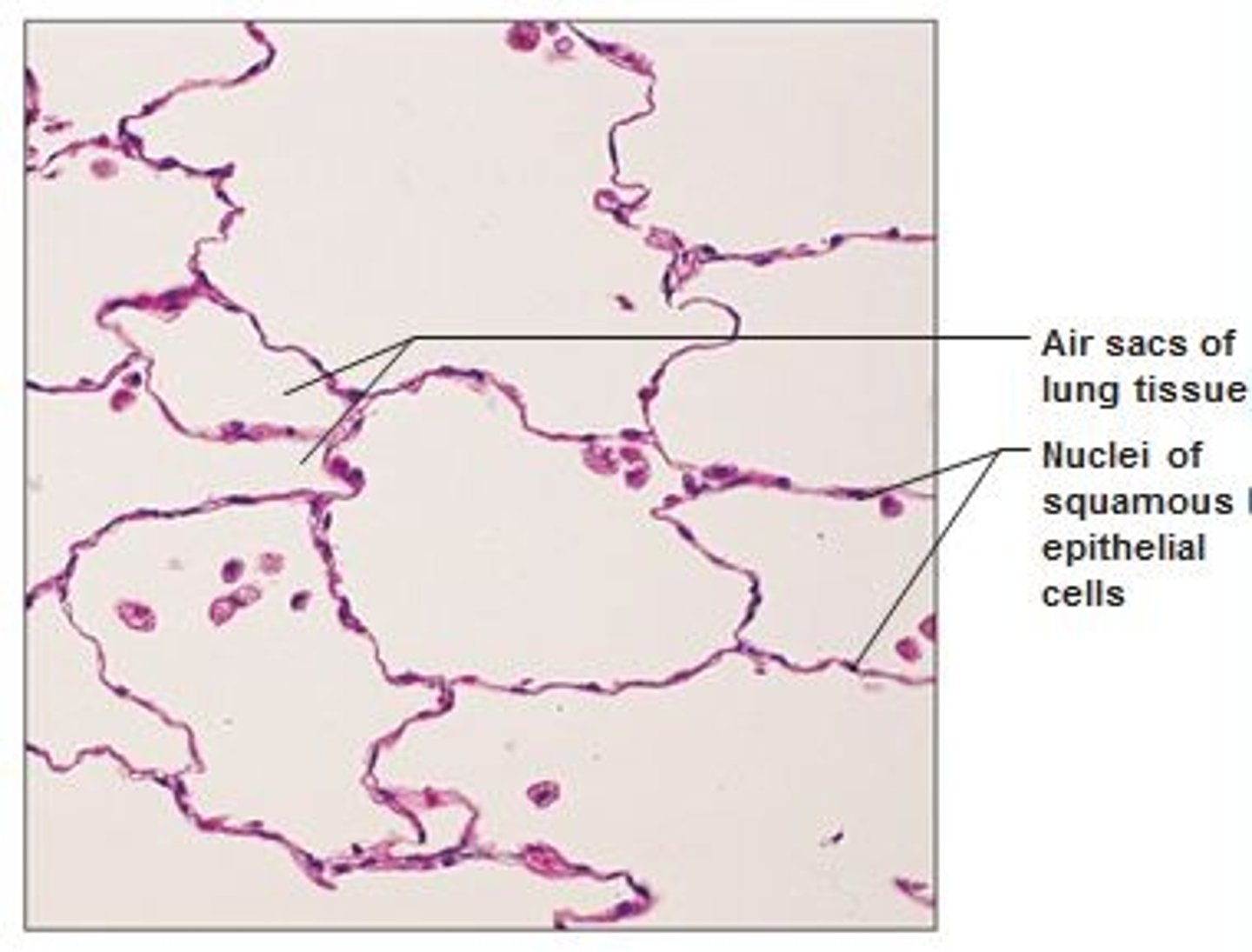
Endothelium
type of simple squamous epithelia that:
provides a slick, friction-reducing lining in lymphatic vessels and in all hollow organs of the cardiovascular system
Mesothelium
type of simple squamous epithelia that:
the epithelium found in serous membranes lining the ventral body cavity and covering its organs
Description: simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube-like cells with large, spherical central nuclei
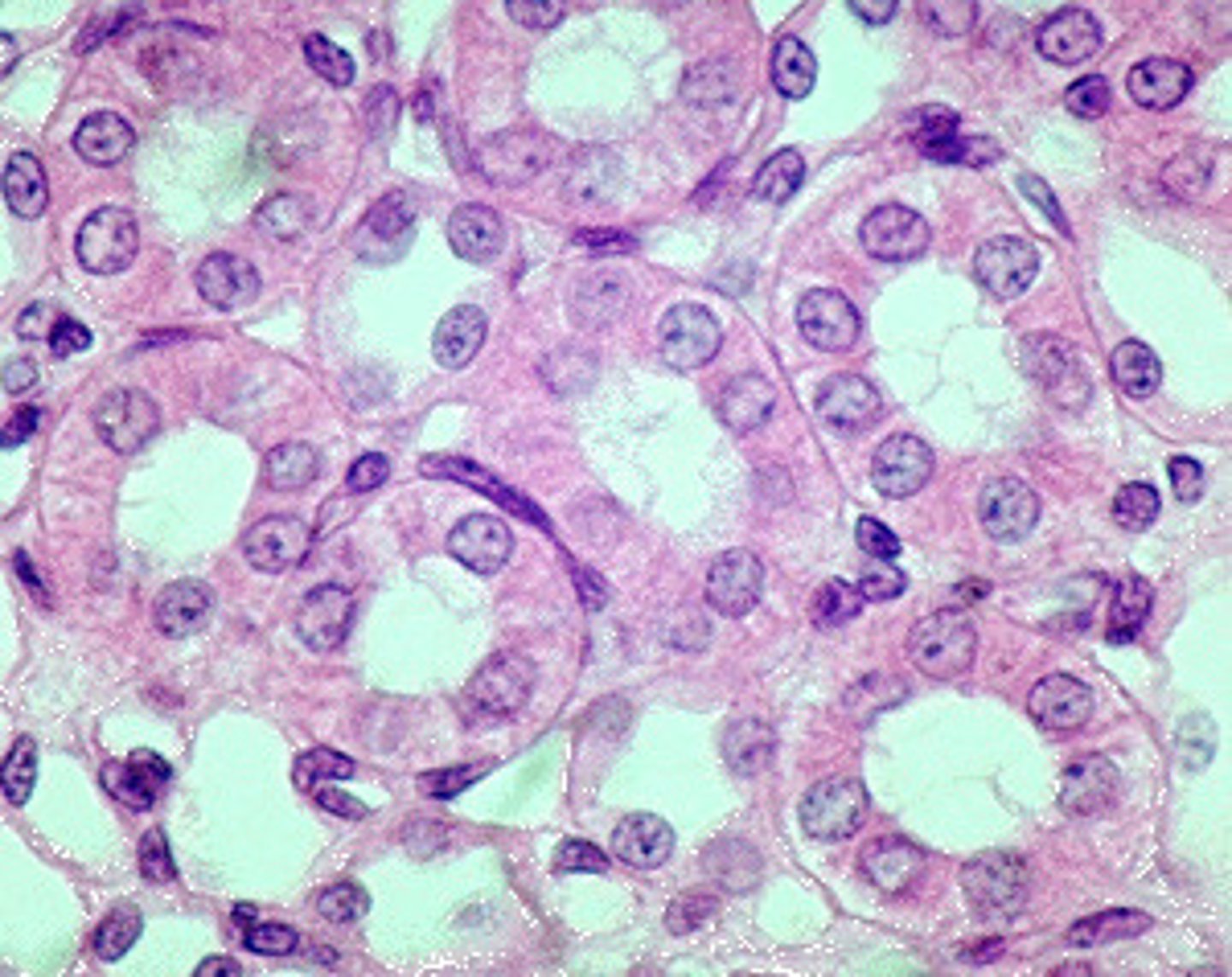
Function: simple cuboidal epithelium
Secretion and absorption
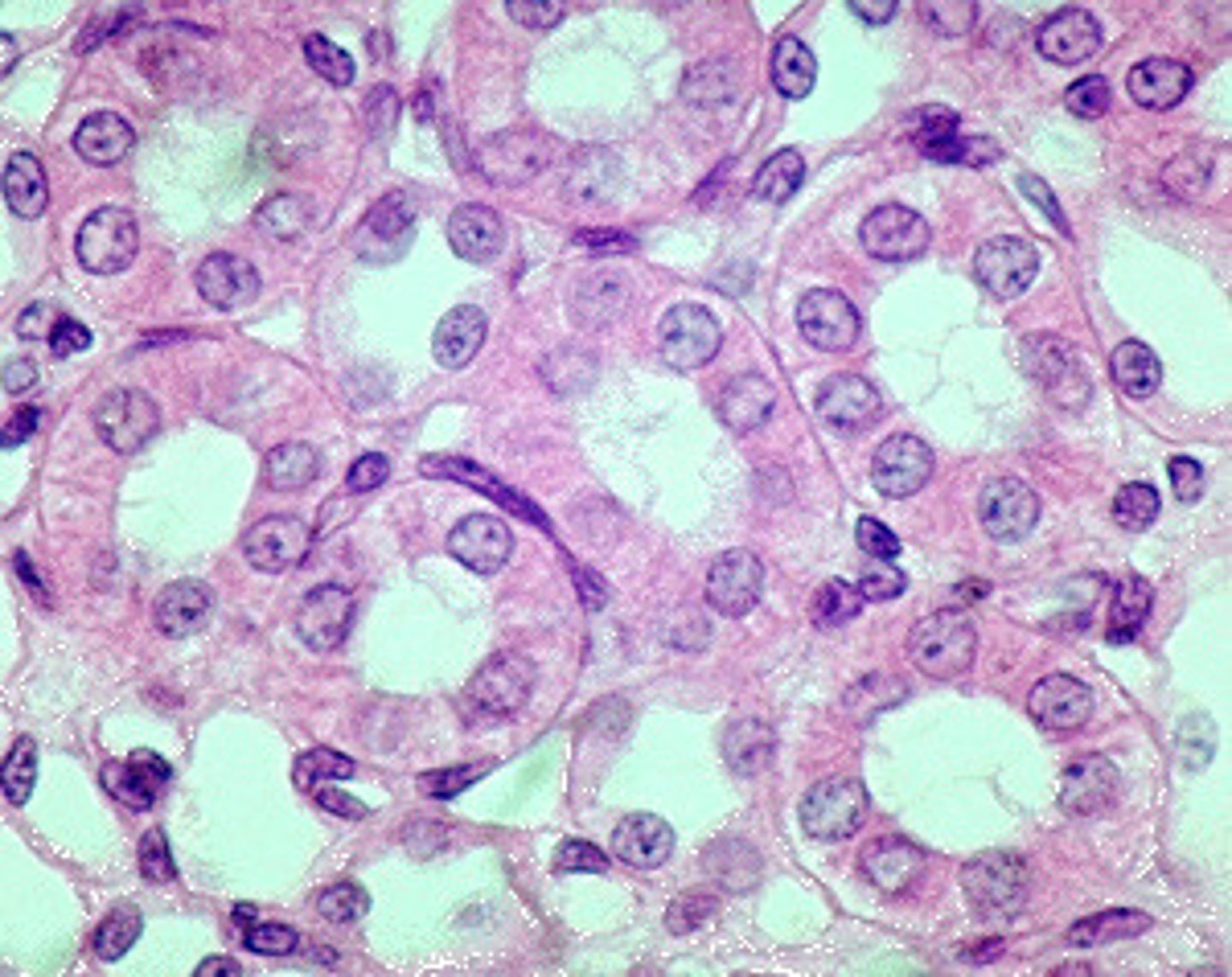
Location: simple cuboidal epithelium
Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface
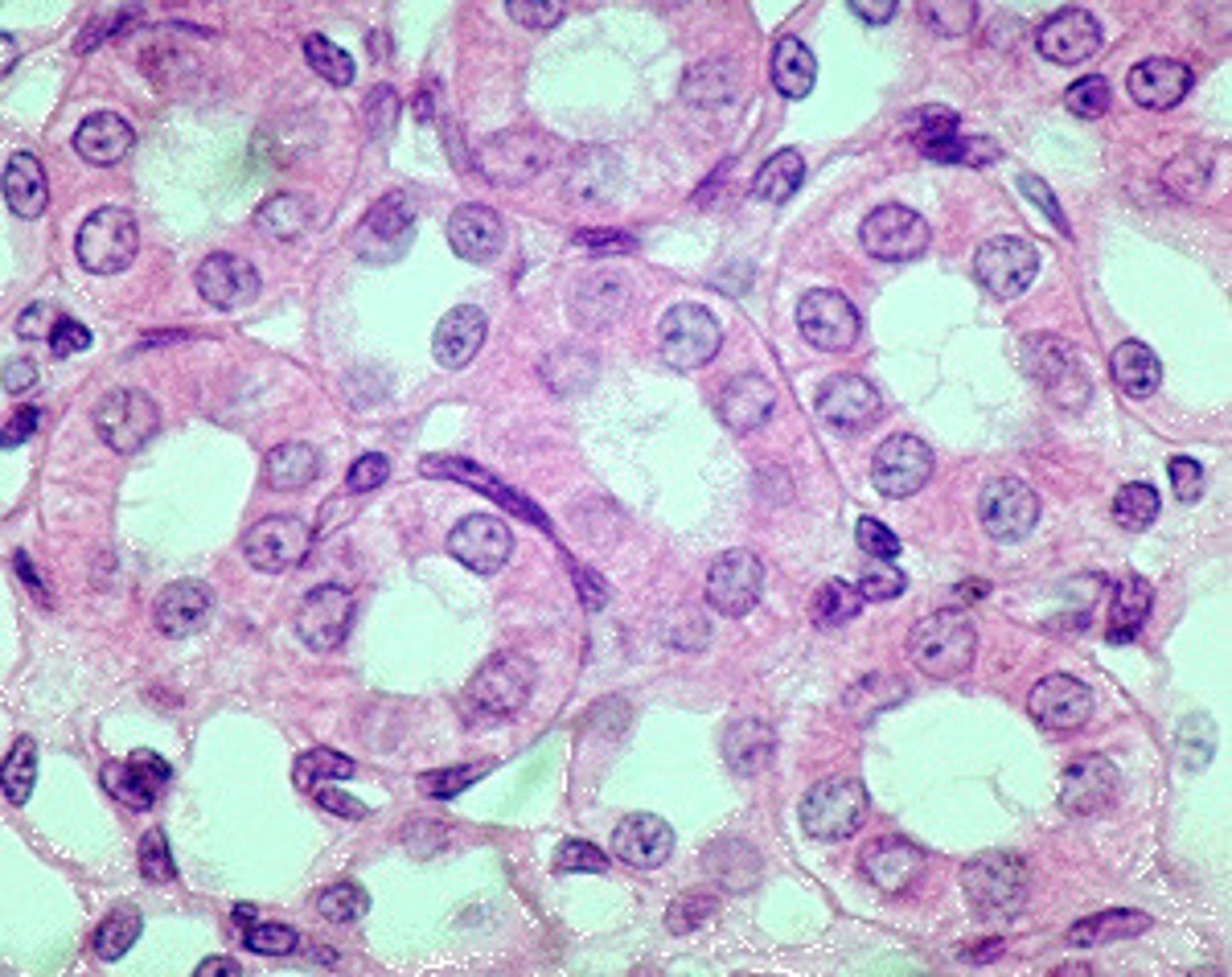
Lumen
pocket that lies in the center of a circle of simple cuboidal epithelium
Description: simple columnar epithelium
single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei; some cells bear microvilli on surface AND cilia; layer may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands (goblet cells)
Function: simple columnar epithelium
absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliary action
Location: simple columnar epithelium
Nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus.
Goblet cells
secrete mucus
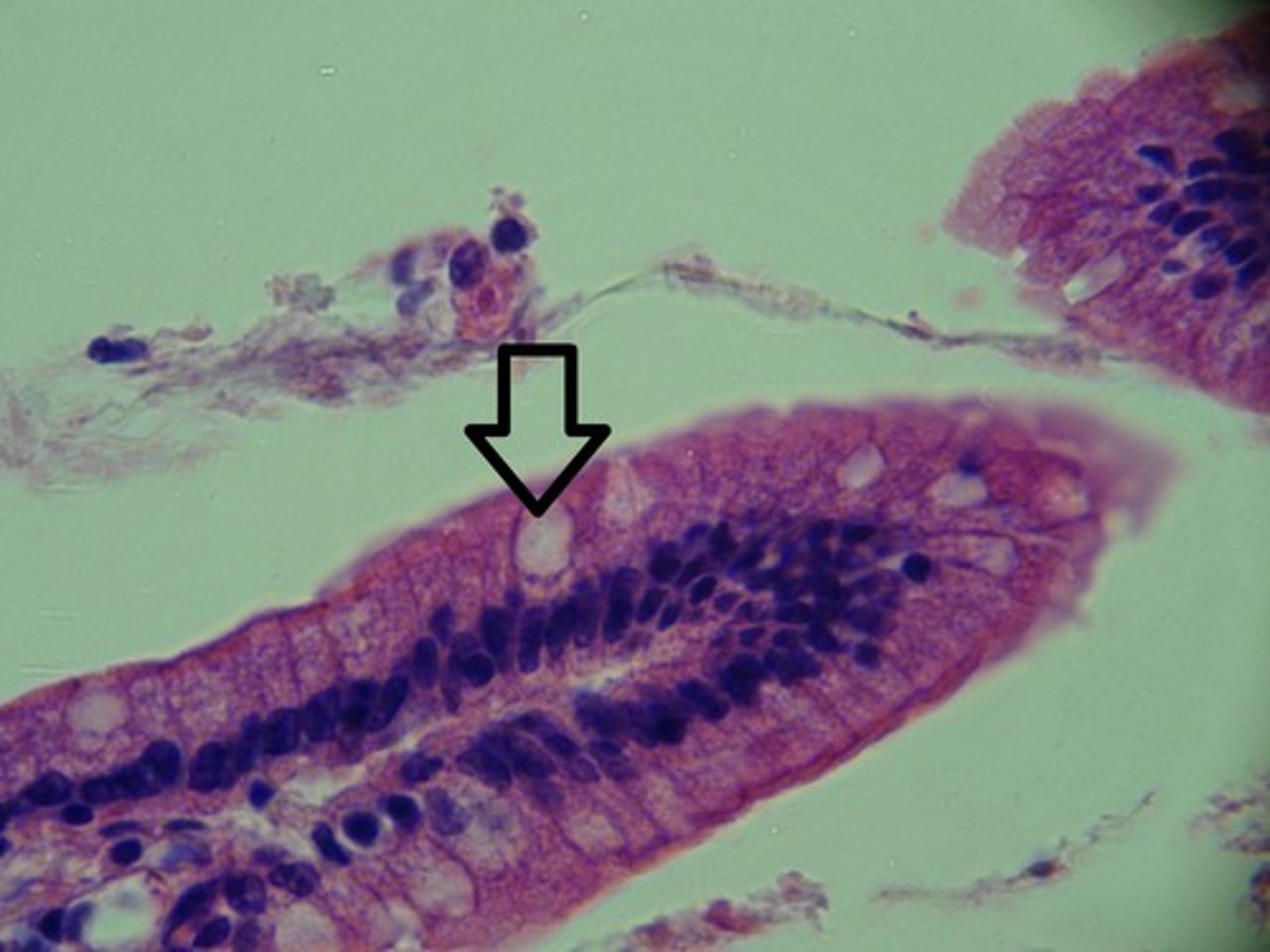
How simple columnar epithelium looks under the microscope
Almost looks like petals with nuclei near the inner rim; the goblet cells look like white pockets
Description: stratified squamous epithelium
thick membrane composed of several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active; surface cells are flattened (squamous); in the keratinized type, the surface cells are full of keratin and dead; basal cells are active in mitosis and produce the cells of the more superficial layers
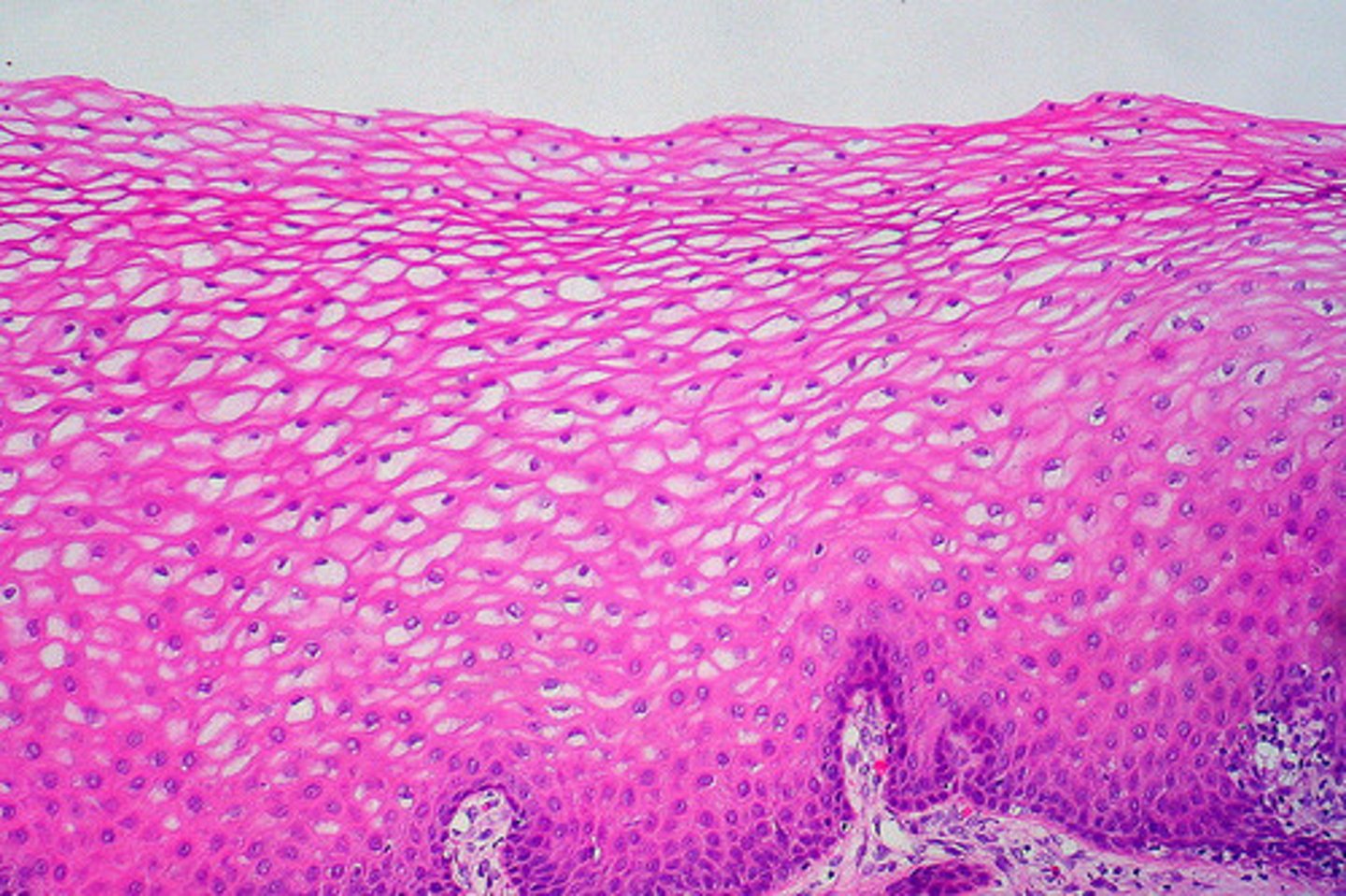
Function: stratified squamous epithelium
protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
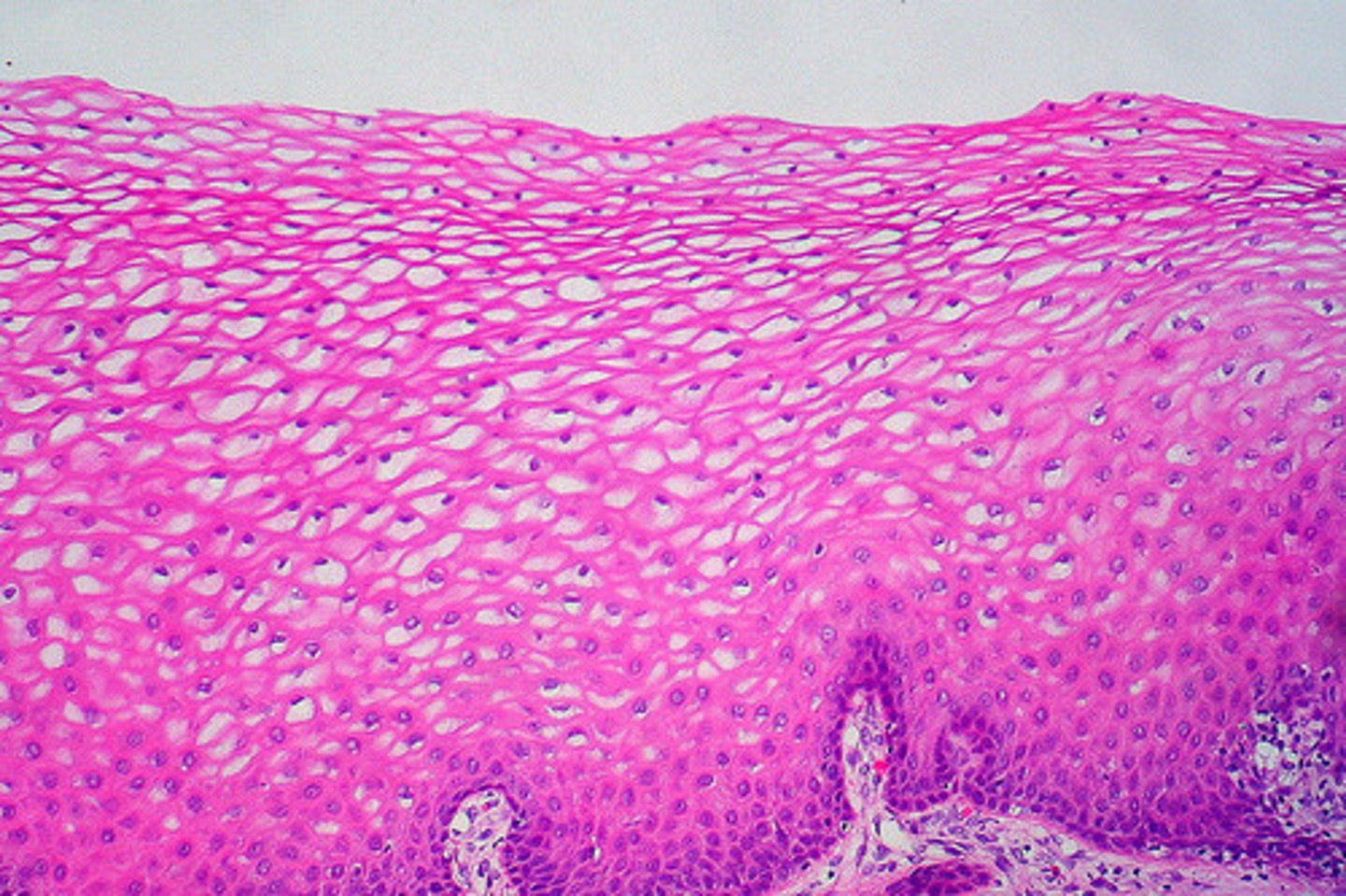
Location: stratified squamous epithelium
nonkeratinized type forms the moist linings of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina; keratinized variety forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane
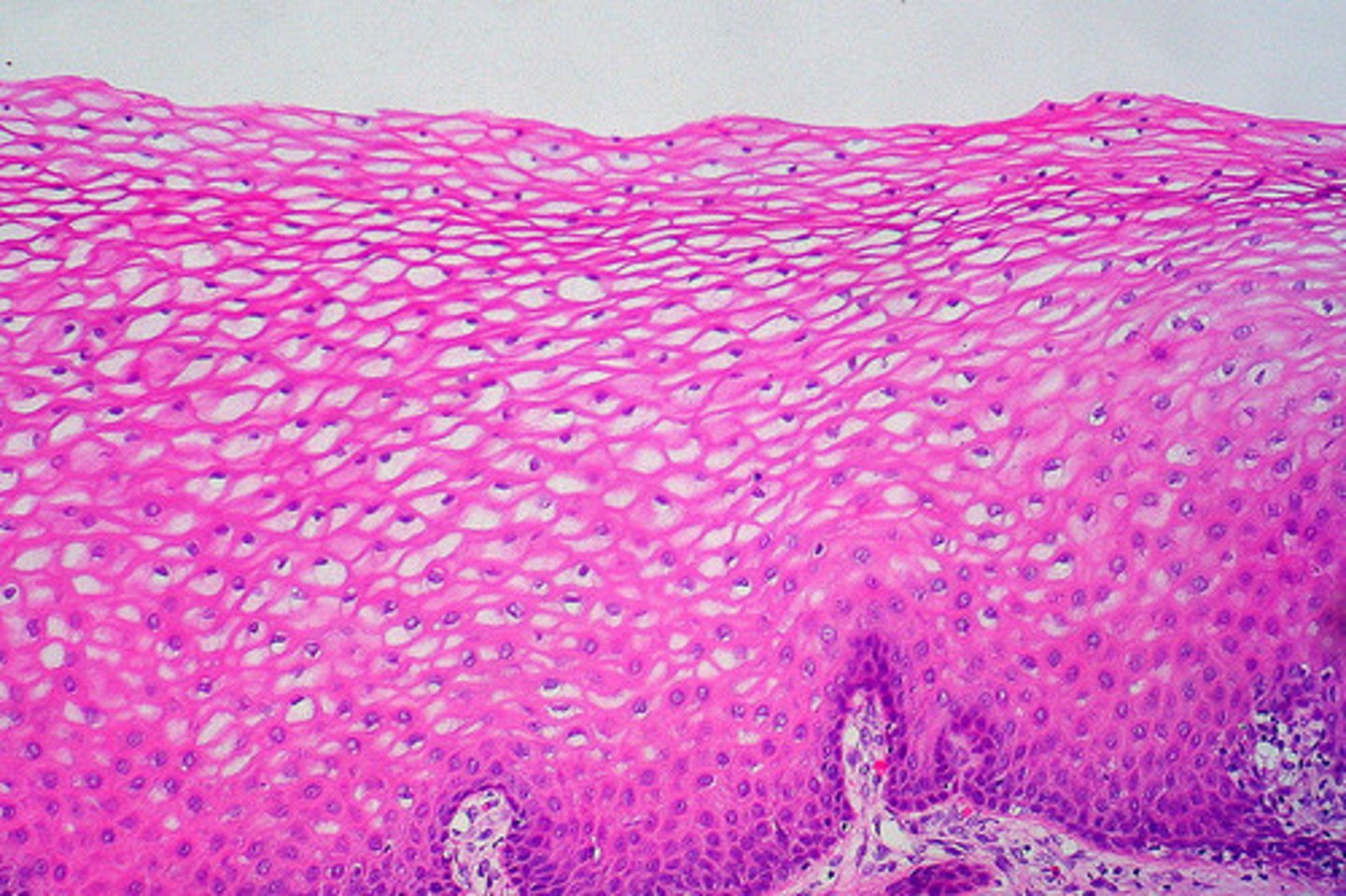
Basement membrane
Cells at the base of an epithelial layer are attached to this
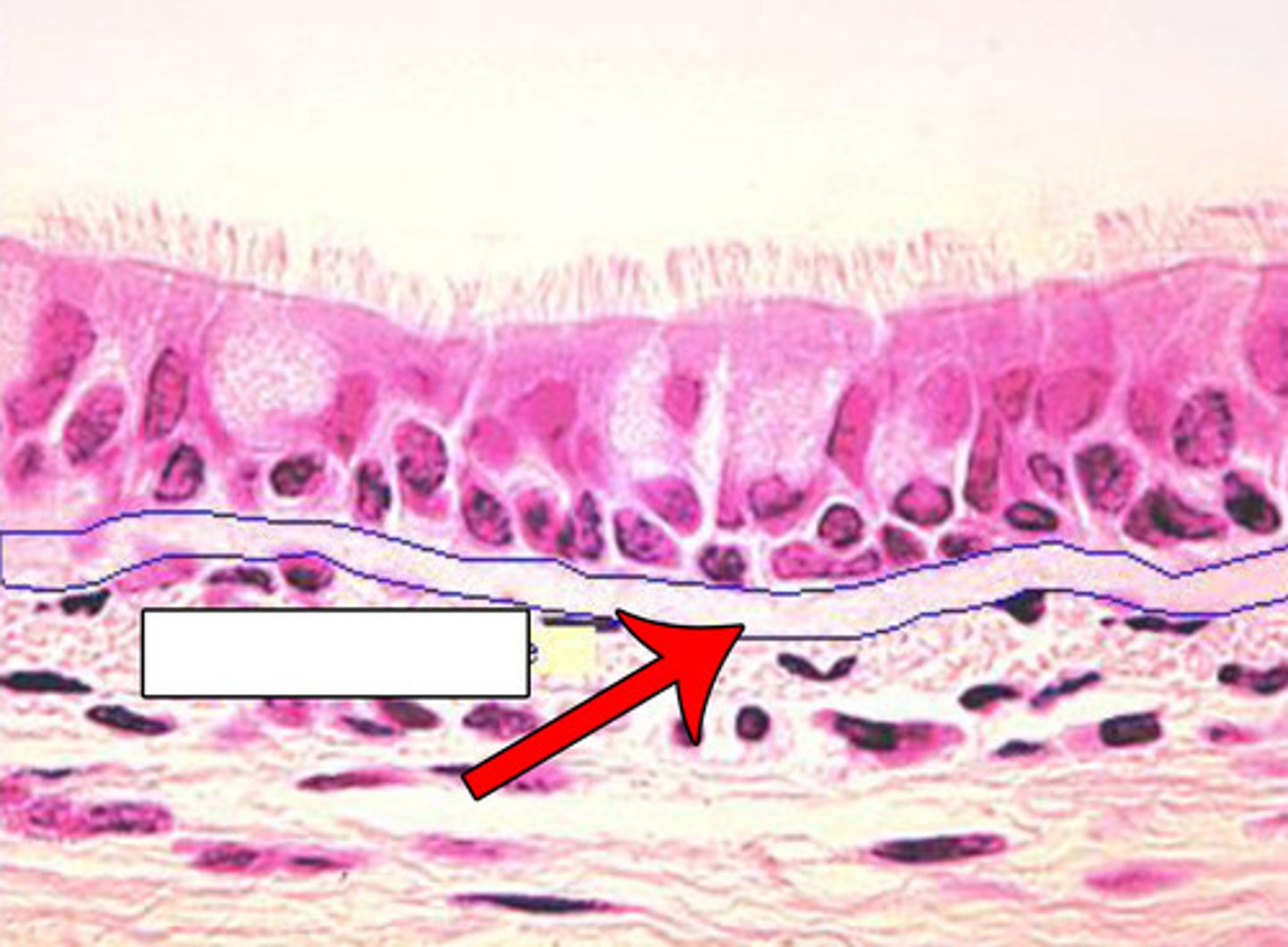
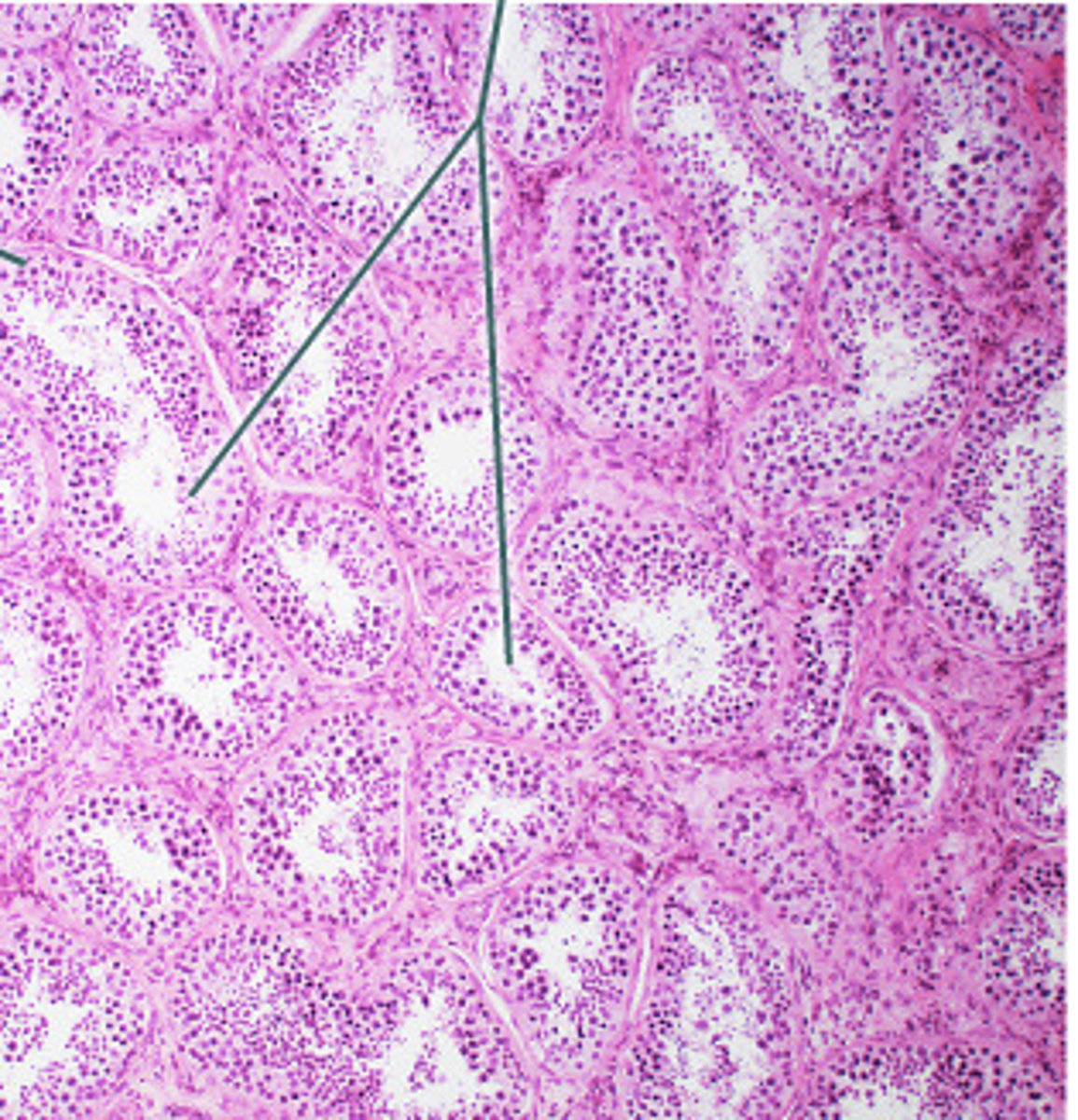
Description: pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface; nuclei seen at different levels; may contain mucus-secreting cells and bear cilia
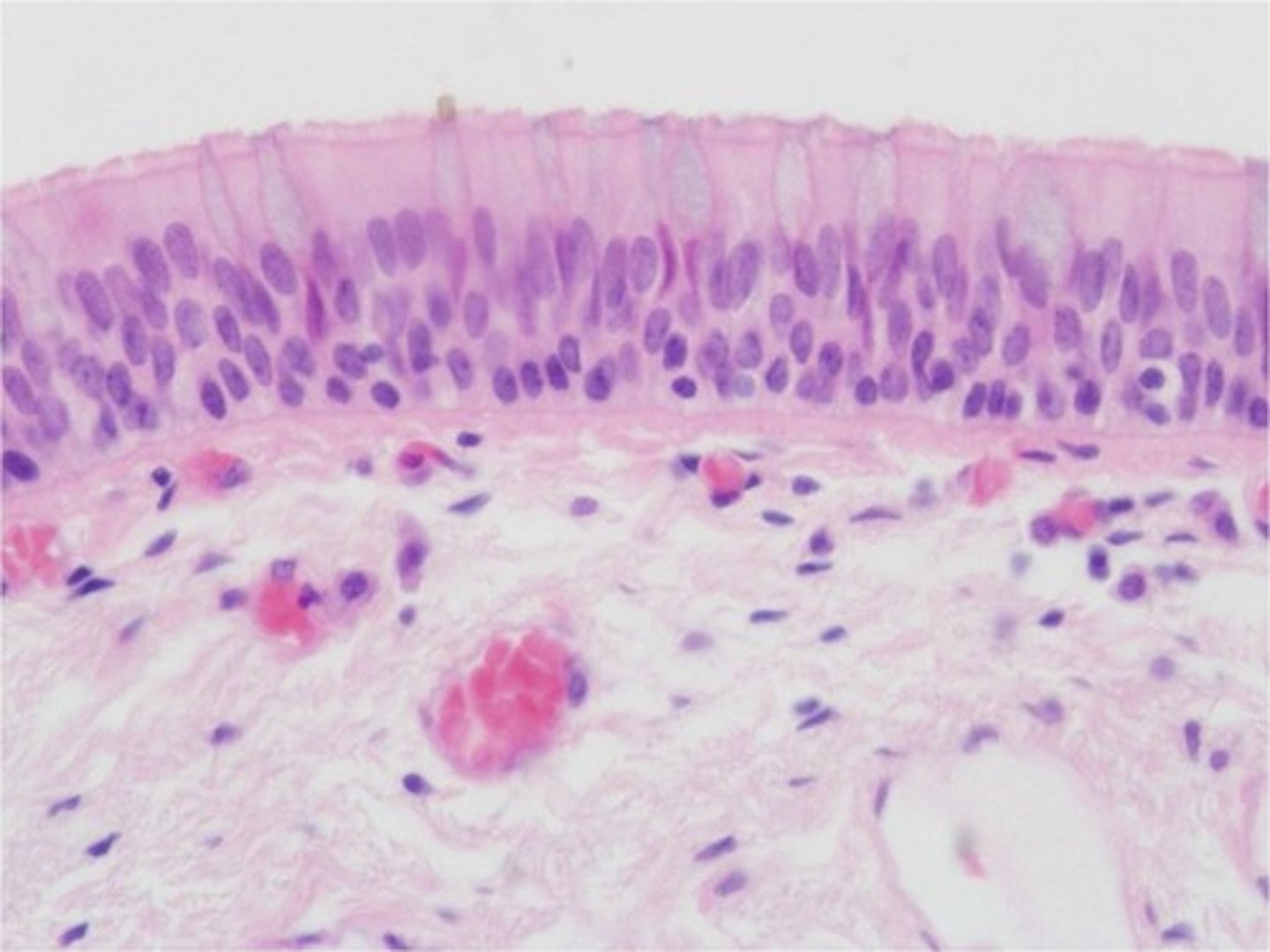
Function: pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Secretion, particularly of mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
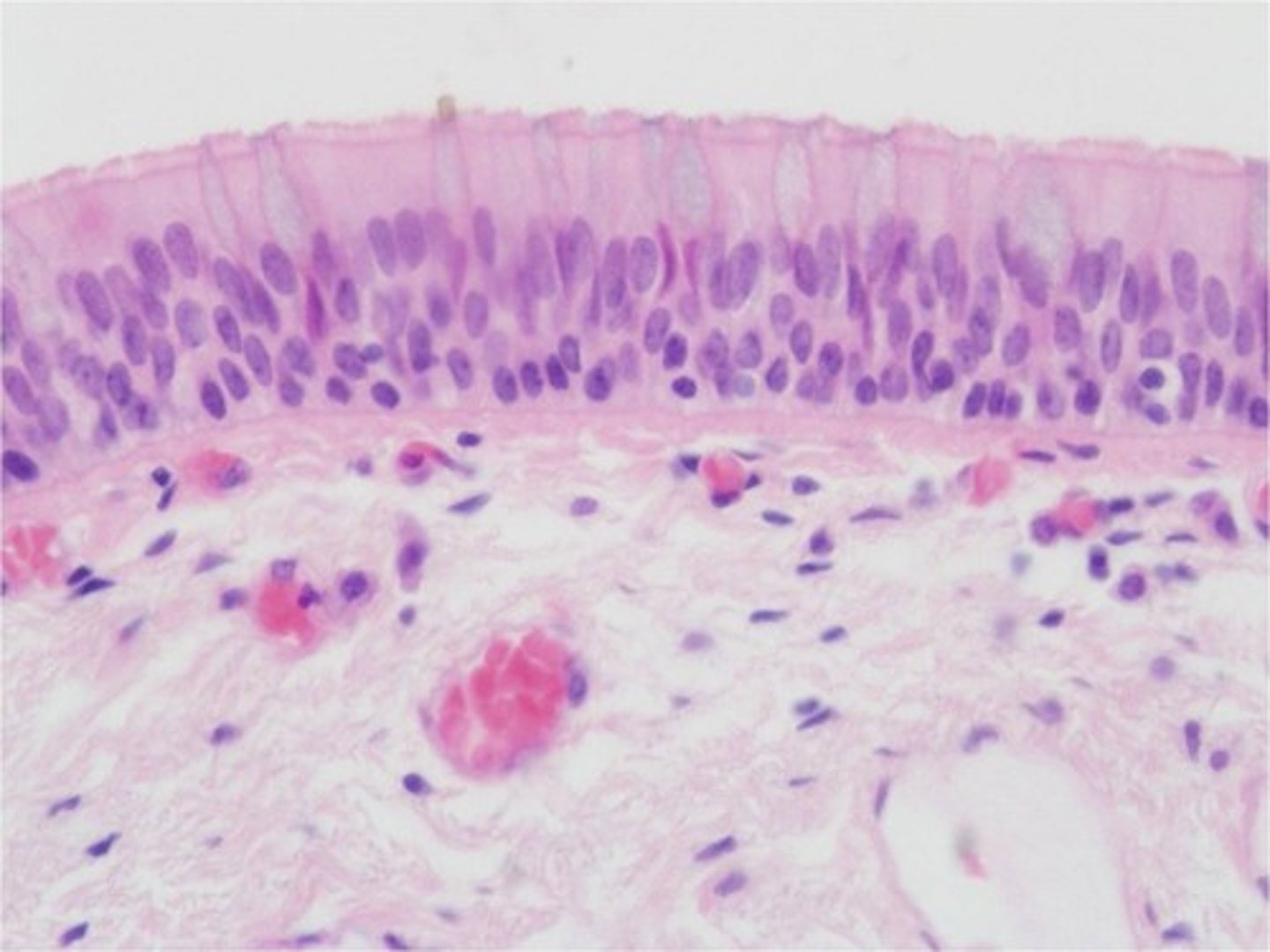
Location: pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Nonciliated type in male's sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands; ciliated variety lines the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract
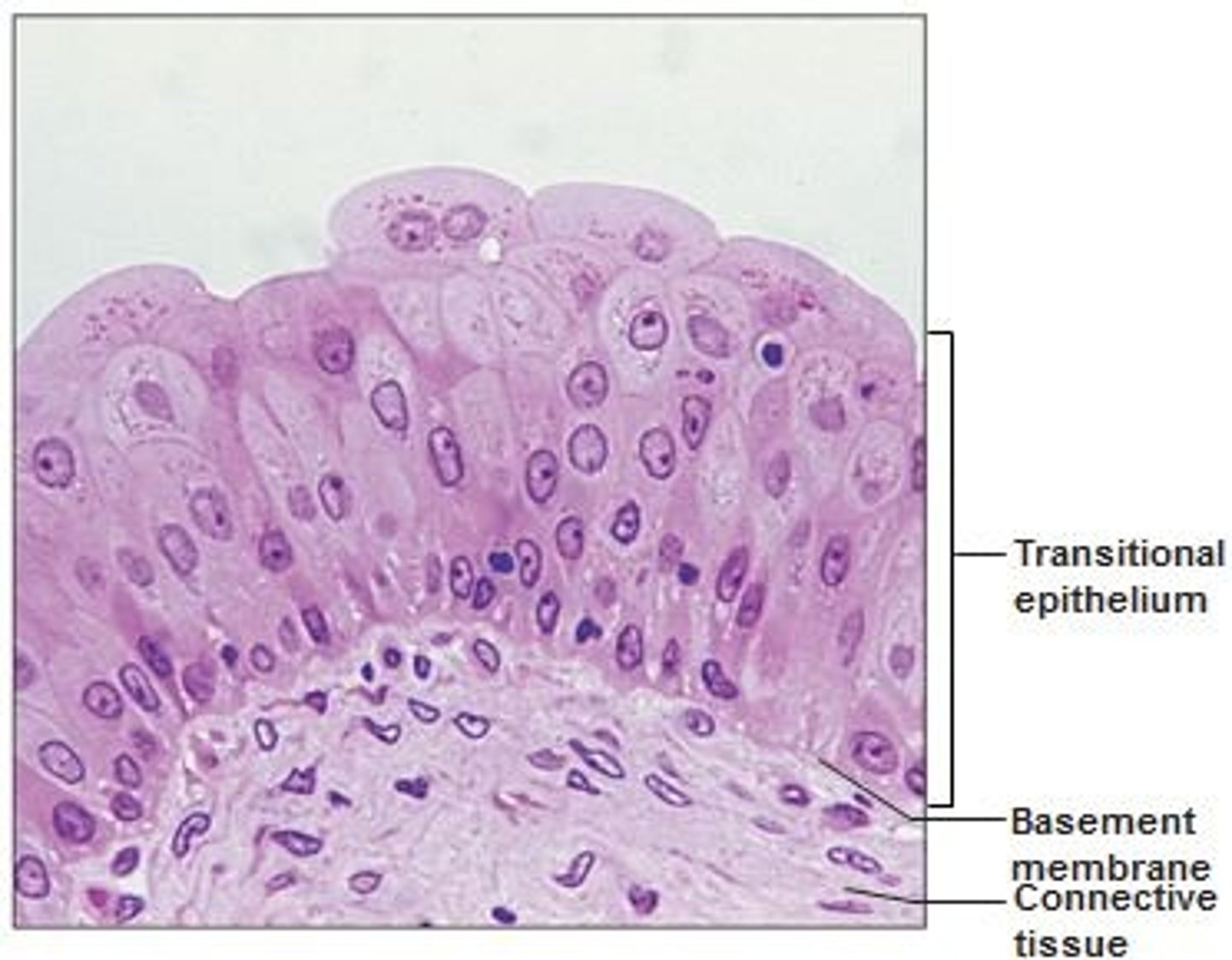
Description: transitional epithelium
resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar; surface cells dome shaped or squamous-like, depending on degree of organ stretch
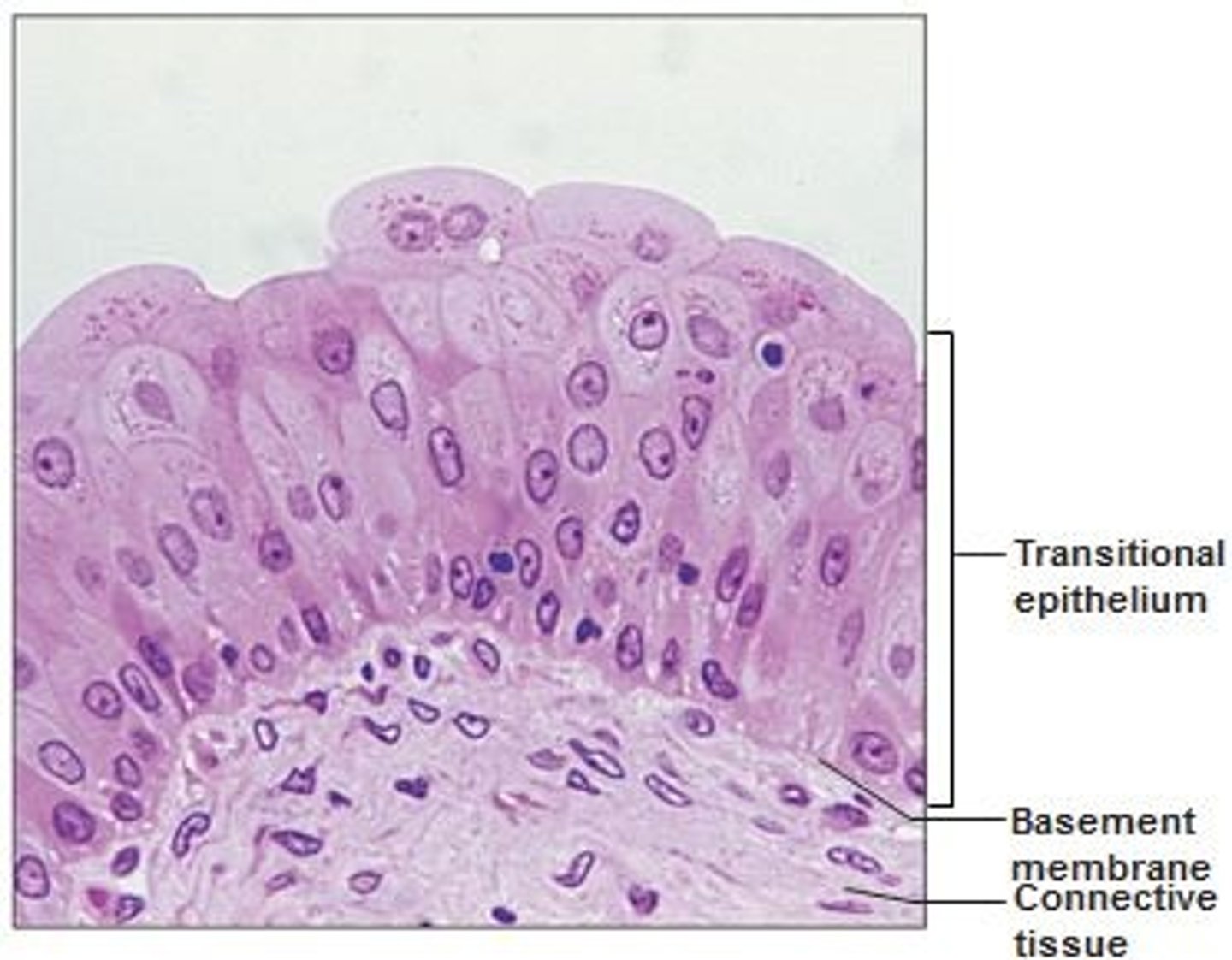
Function: transitional epithelium
stretches readily and permits distension of certain hollow organs (urinary organ by contained urine)
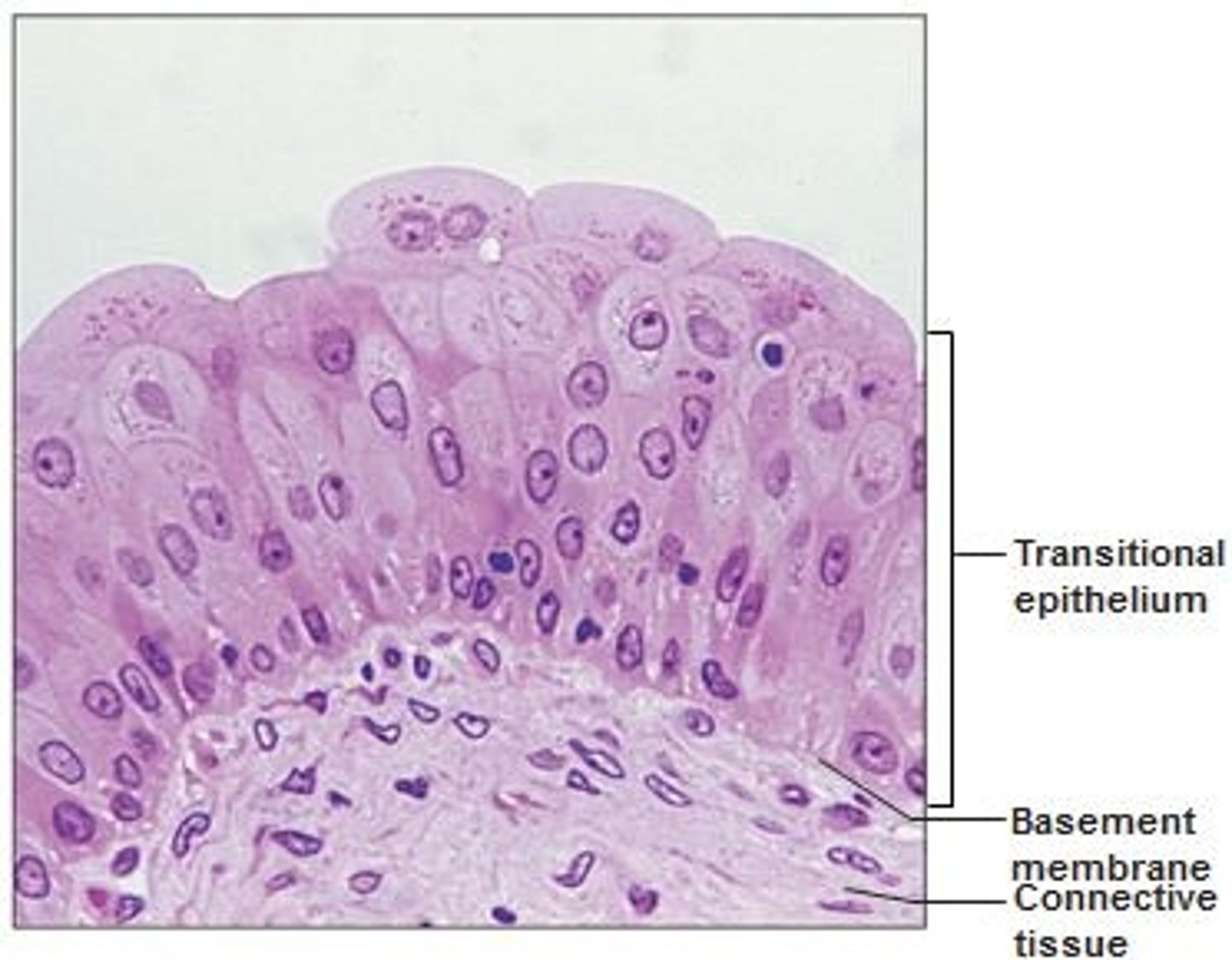
Location: transitional epithelium
lines the ureters, bladder, and part of the urethra
Connective tissue
made from mesenchyme; A body tissue (non-cellular) that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts (also protects, stores reserve energy, insulates the body, and transports substances throughout the body)
Fibroblasts
In connective tissue, stationary cells that secrete the proteins of the fibers.
macrophages patrol these tissues and are mobilized during an infection or injury, migrate to the site of the disturbance, and phagocytize damaged tissue cells and microbes
Mast cells
Detect foreign microorganisms and initiate immune responses against them; release histamine that causes inflammatory response, but also secretes heparin, proteases, and other enzymes
Adipocytes
fat cells; contain vacuoles for storage of lipids, that make up most of the subcutaneous layer
Loose connective tissue
has an open network of protein fibers in a thick, syrupy ground substance and is divided into three groups
Dense connective tissue
Made up of two types of fibers: protein fibers assembled into thick bundles of collagen and elastic fibers with widely scattered cells
Dense regular connective tissue
Protein fibers in the matrix are arranged in parallel bands
Dense irregular connective tissue
fibers are interwoven; has fibers that run in many different directions and is found where tension is exerted from many different directions (capsules of joint and organs, dermis of skin, submucosa of the digestive tract)
What are the two types of fluid connective tissue?
blood and lymph
blood contains red blood cells (erythrocytes) and white blood cells (leukocytes - which mediate immune responses and tissue response to injury)
What are the two types of supporting connective tissue?
bone and cartilage
bone is composed predominantly of calcium phosphate salt (hydroxyapatite); supports and protects the body, provides cavities for synthesis of blood cells and storing fact
bone is more rigid than cartilage because of more collagen fibers and hydroxyapatite
unlike cartilage, bone is highly vascularized and innervated
cartilage can withstand both compression and tension because it is tough and somewhat flexible
Perichondrium
surrounds all supporting connective tissue in cartilage and produces chondroblasts (which secrete fibers and the ground substance of cartilage matrix)
cartilage receives nutrients by diffusion from perichondrium
chondroblasts become trapped in the matrix called lacunae and turn into chondrocytes
What are the three types of cartilage?
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
Which tissue has all 3 fibers present?
Areolar tissue
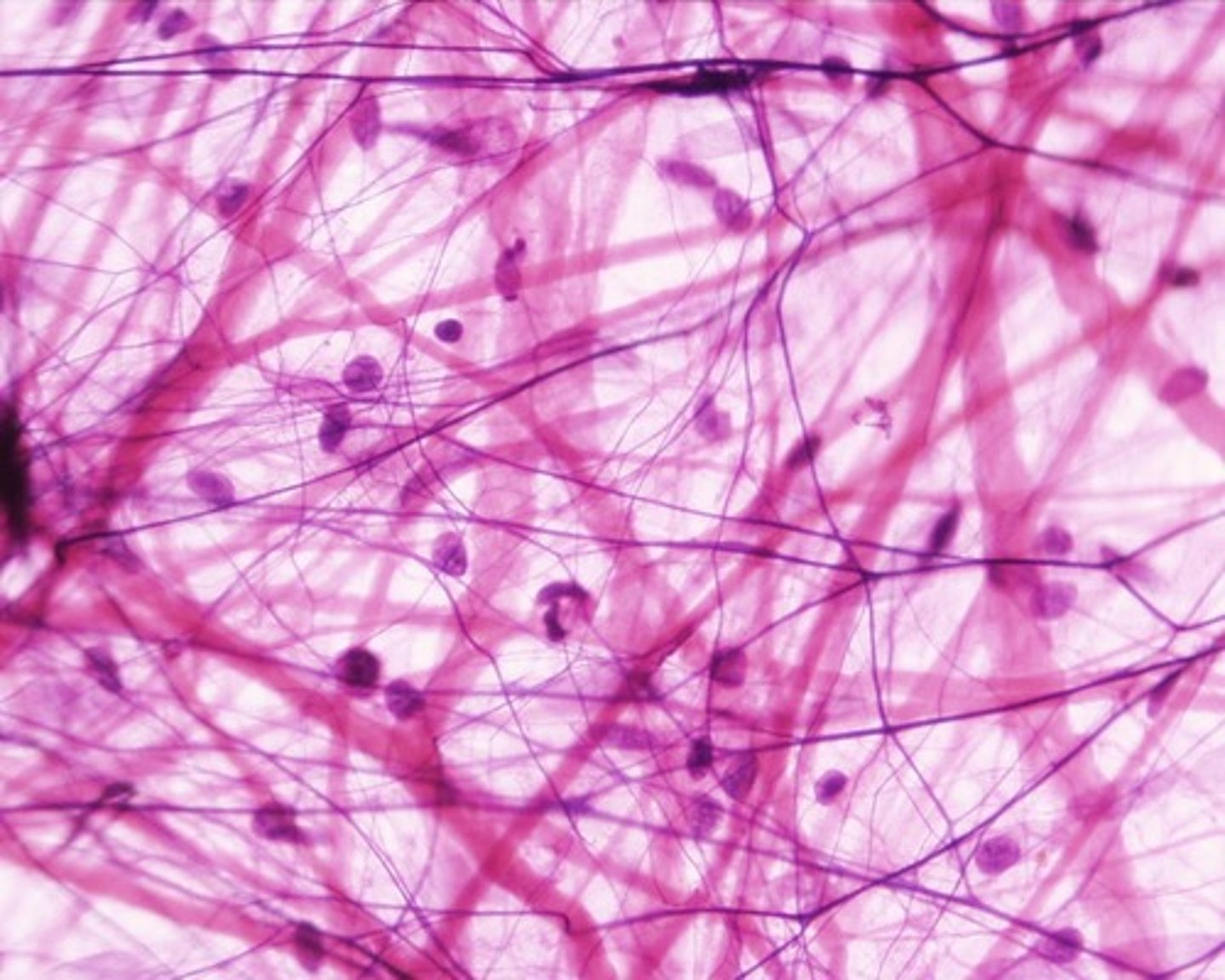
Description: Areolar Connective Tissue
gel-like matrix with all three fiber types; cells: fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and some white blood cells; loose arrangement of fibers creating space for water and salt storage
Function: Areolar Connective Tissue
wraps and cushions organs; its macrophages phagocytize bacteria; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid
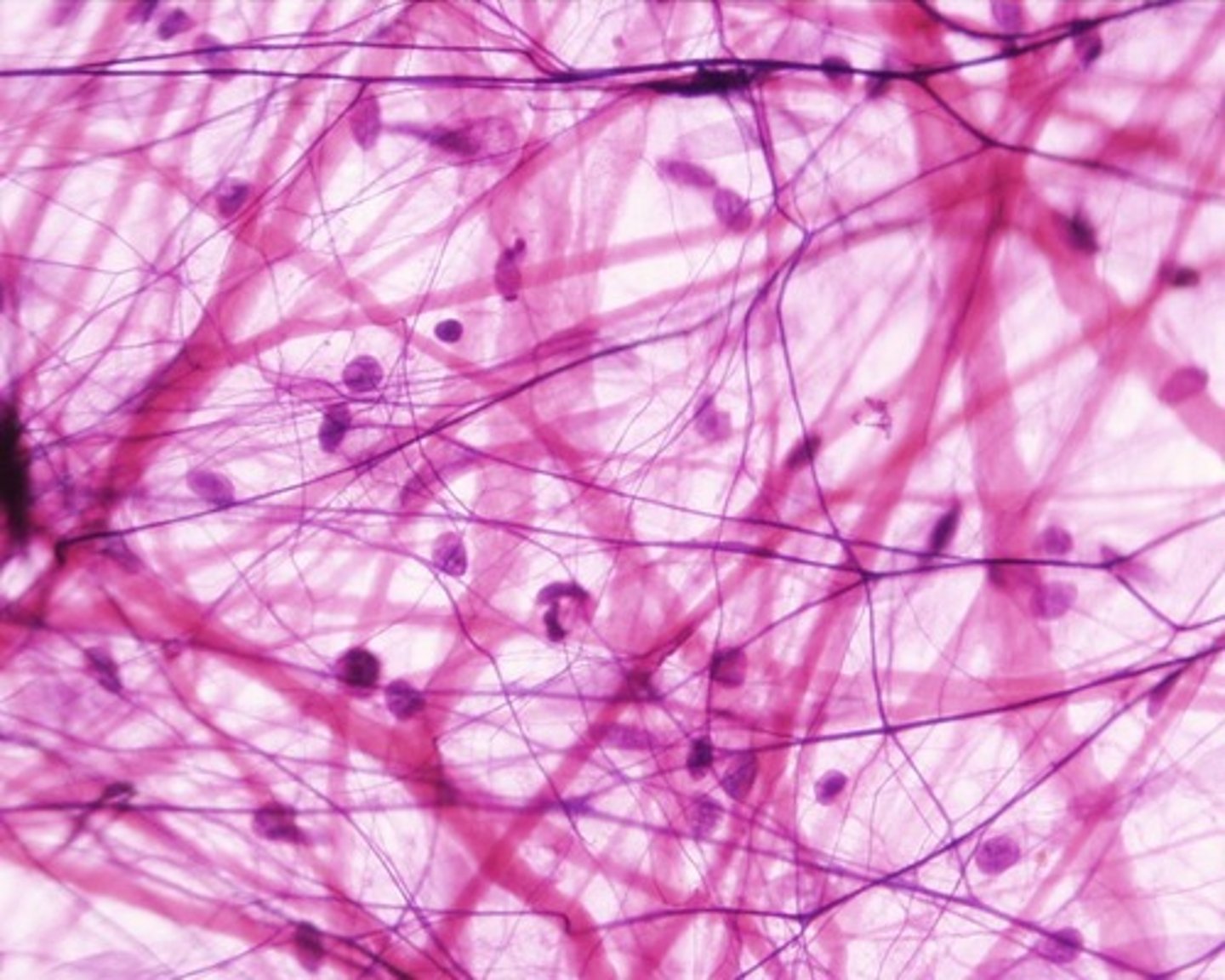
Location: Areolar Connective Tissue
Widely distributed under epithelia (skin) of body, e.g., forms lamina propria of mucous membranes; packages organs; surrounds capillaries.
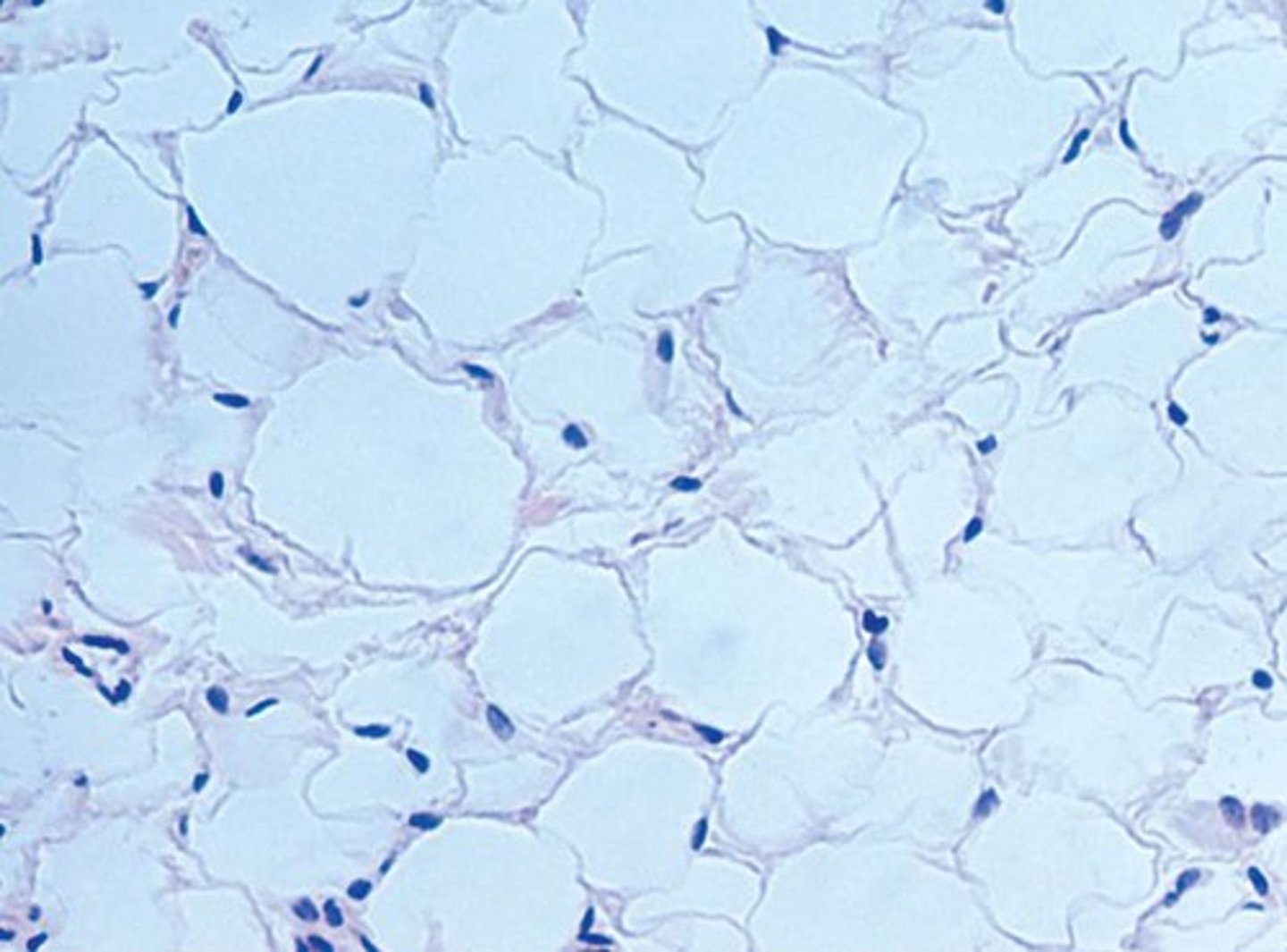
Description: Adipose tissue
matrix as in areolar, but very sparse; closely packed adipocytes, or fat cells, have nucleus pushed to the side by large fat droplet
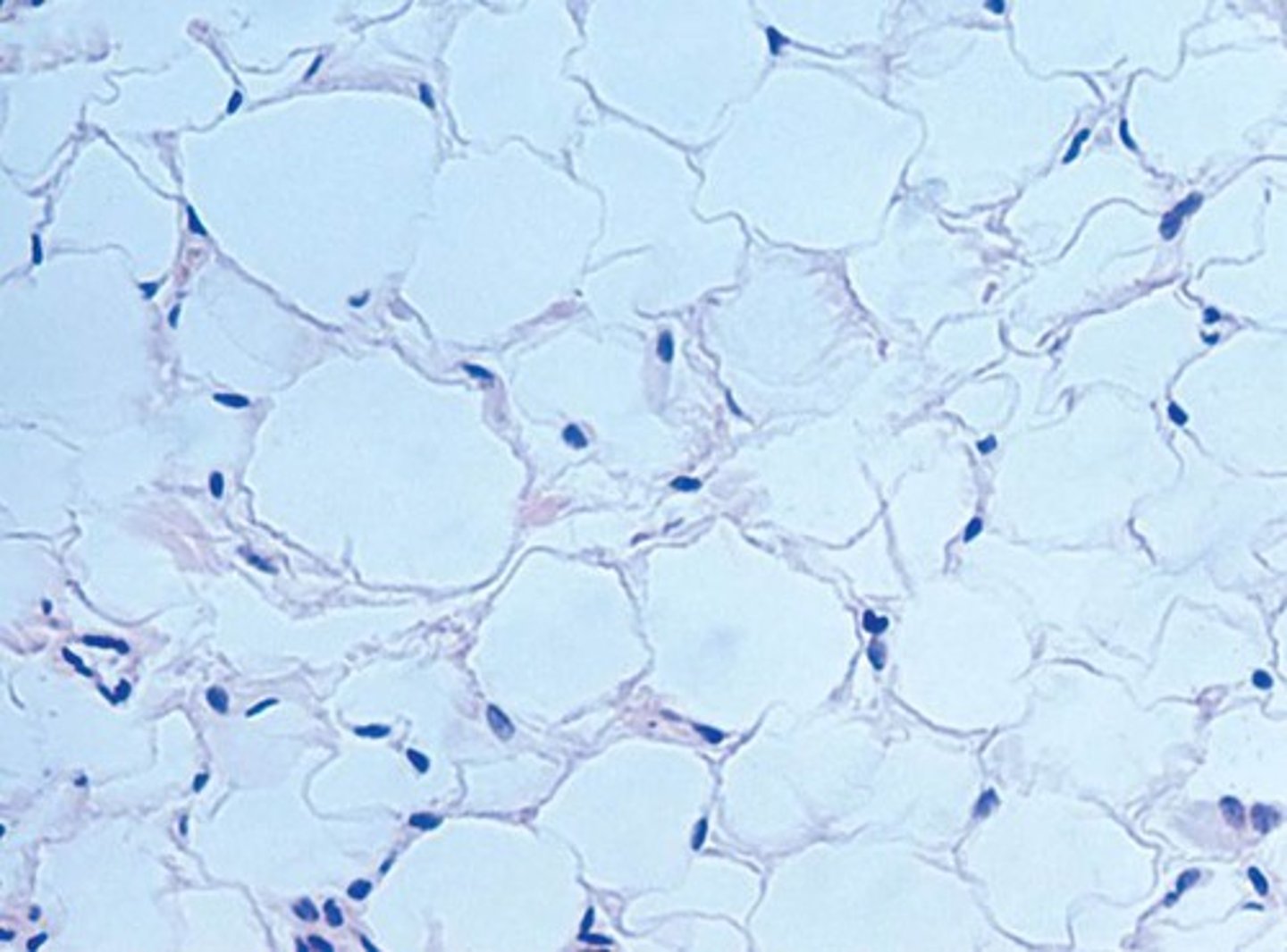
Function: Adipose tissue
provides reserve food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
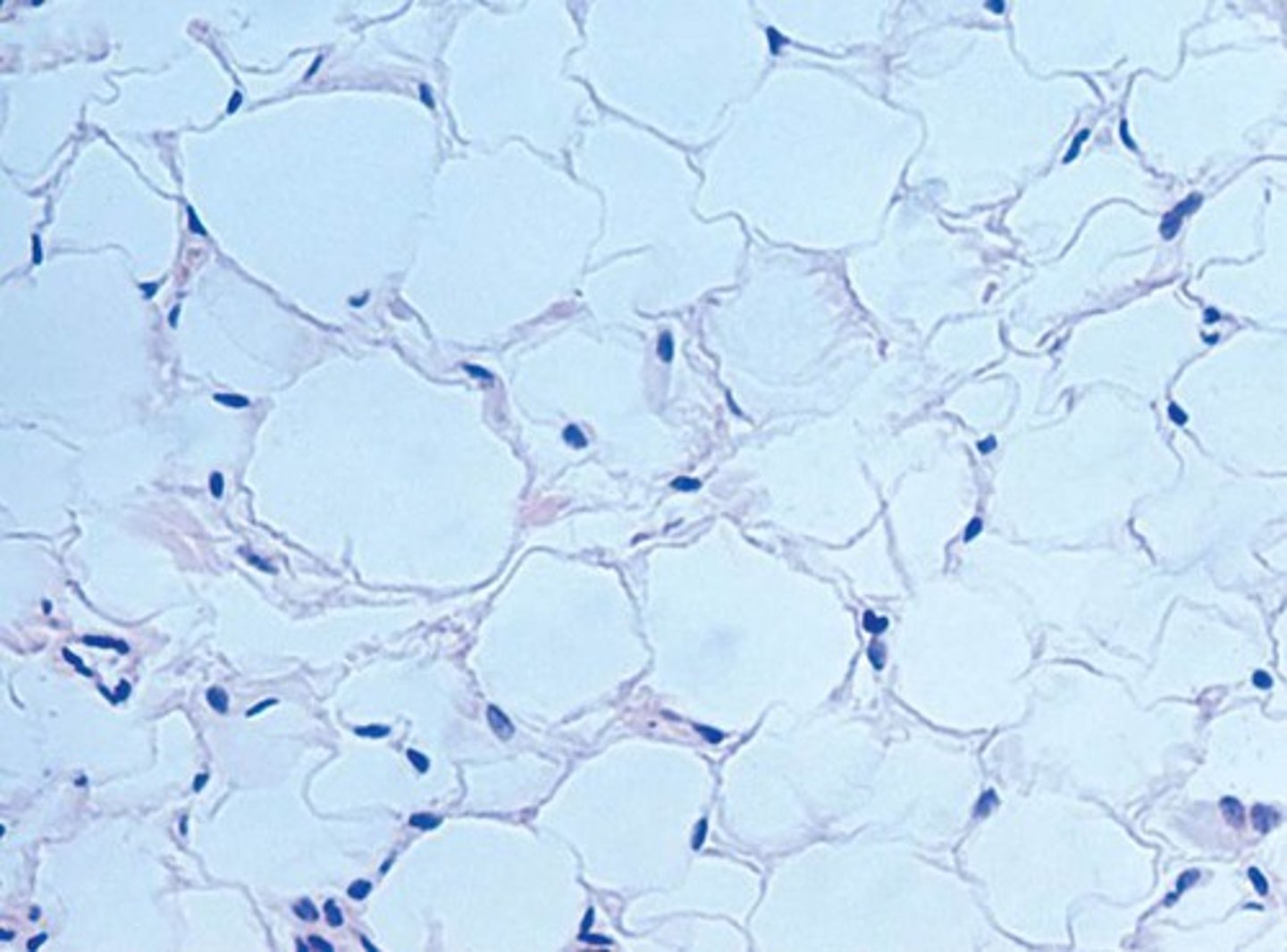
Location: Adipose tissue
under skin in subcutaneous tissue; around kidneys and eyeballs; within abdomen; in breasts; around heart and in bone marrow (serves as fuel for high energy demand organs)
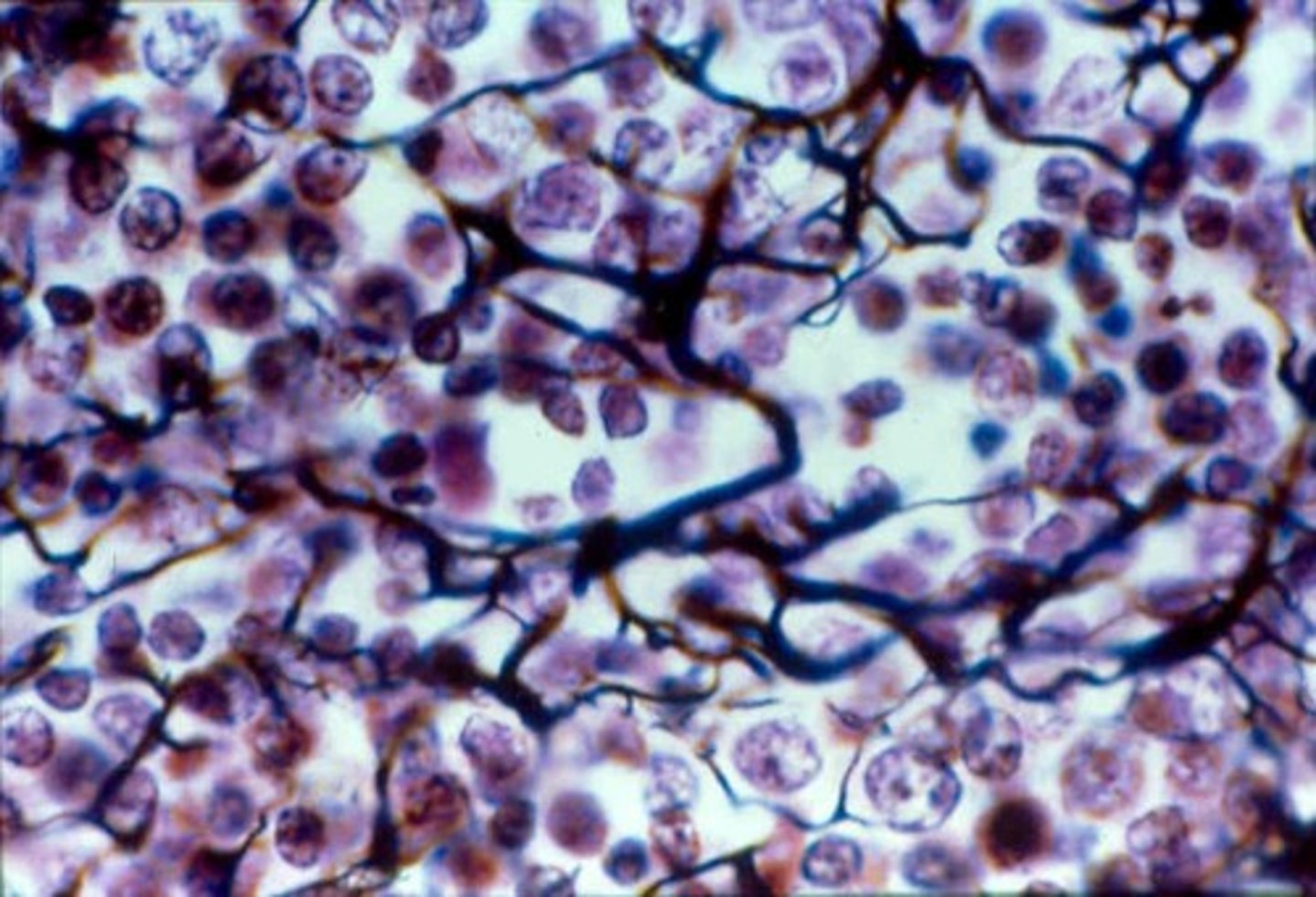
Description: Reticular tissue
network of reticular fibers in a typical loose ground substance; reticular cells lie on the network
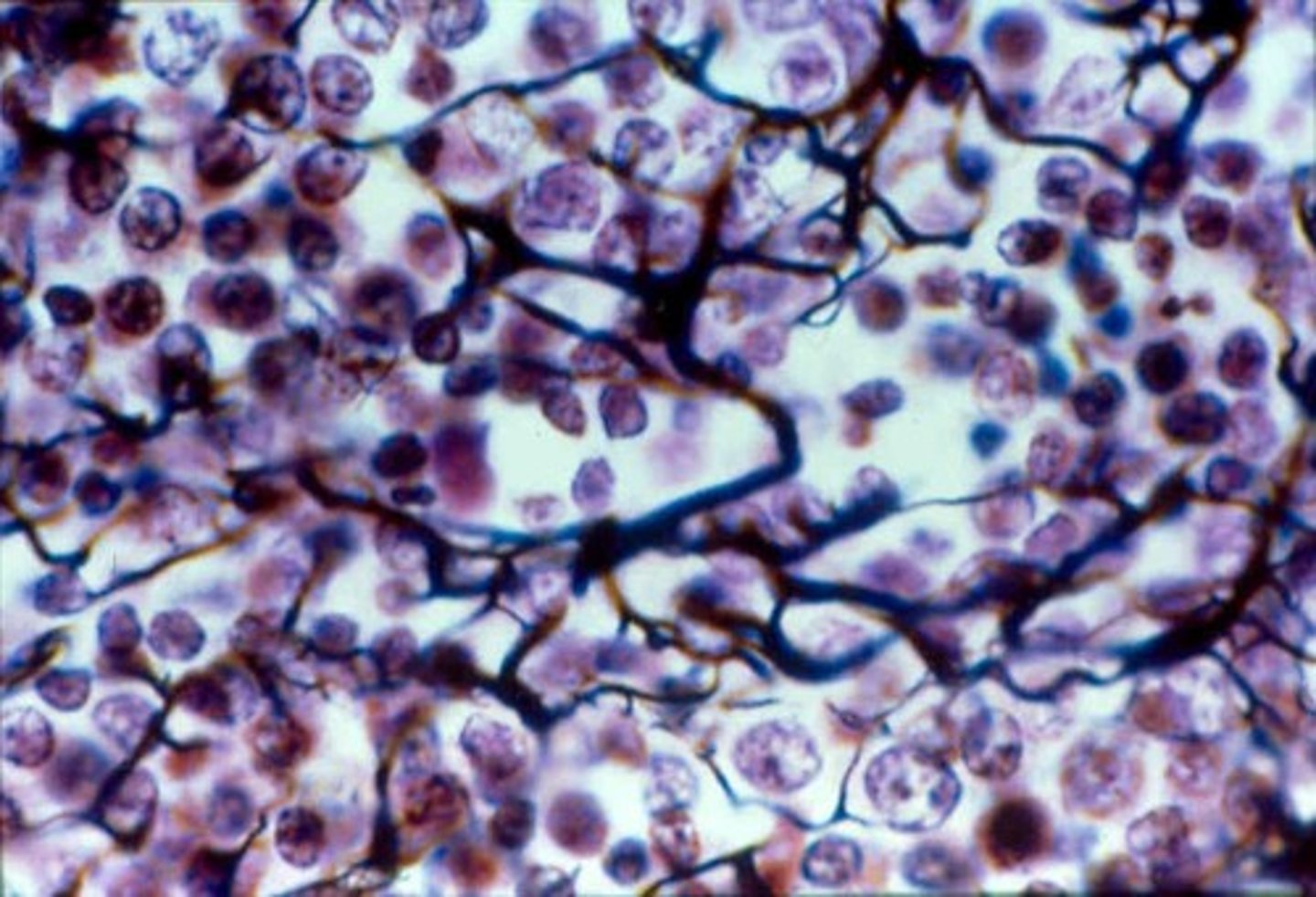
Function: Reticular tissue
fibers form a soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
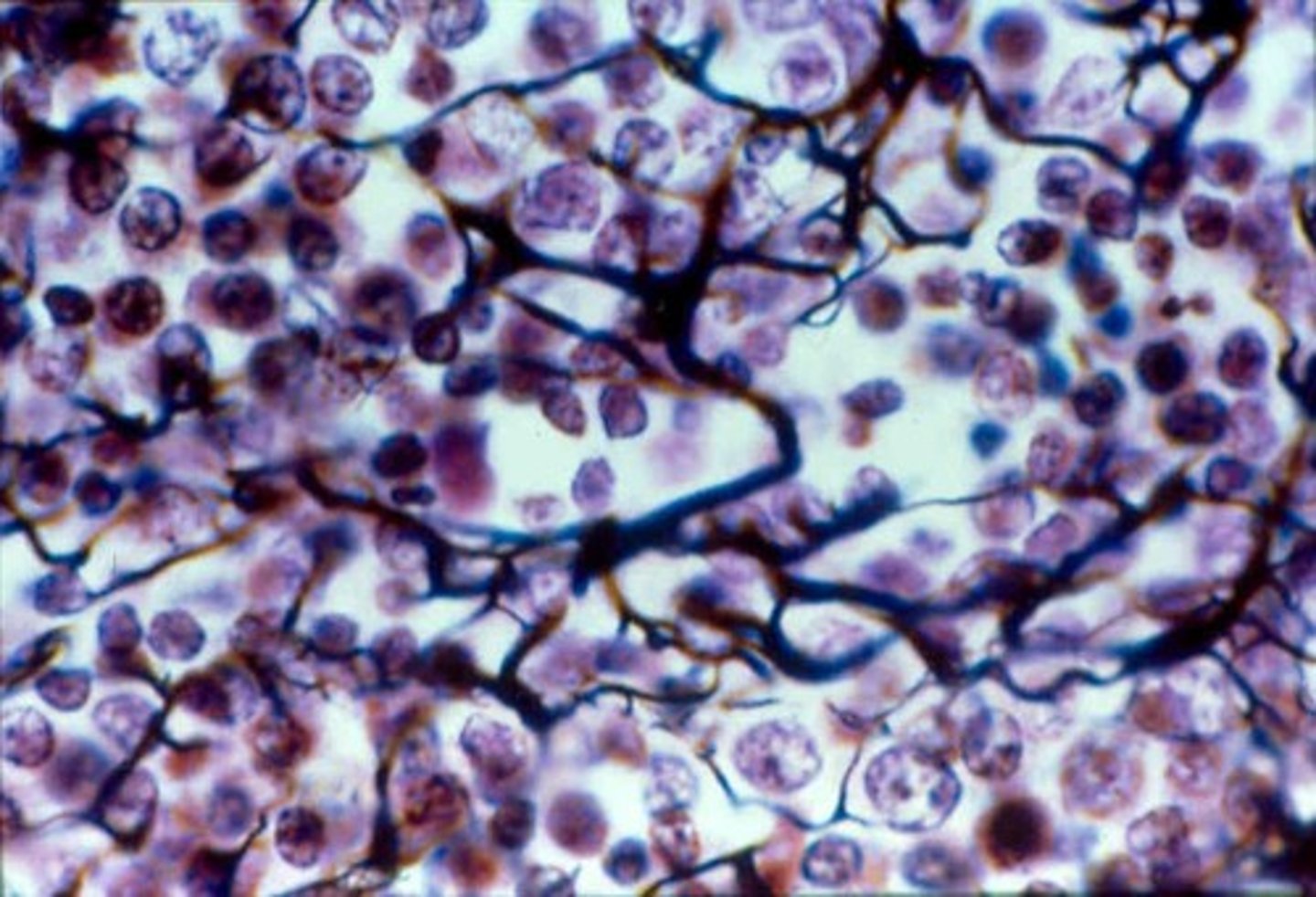
Location: Reticular tissue
lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen)
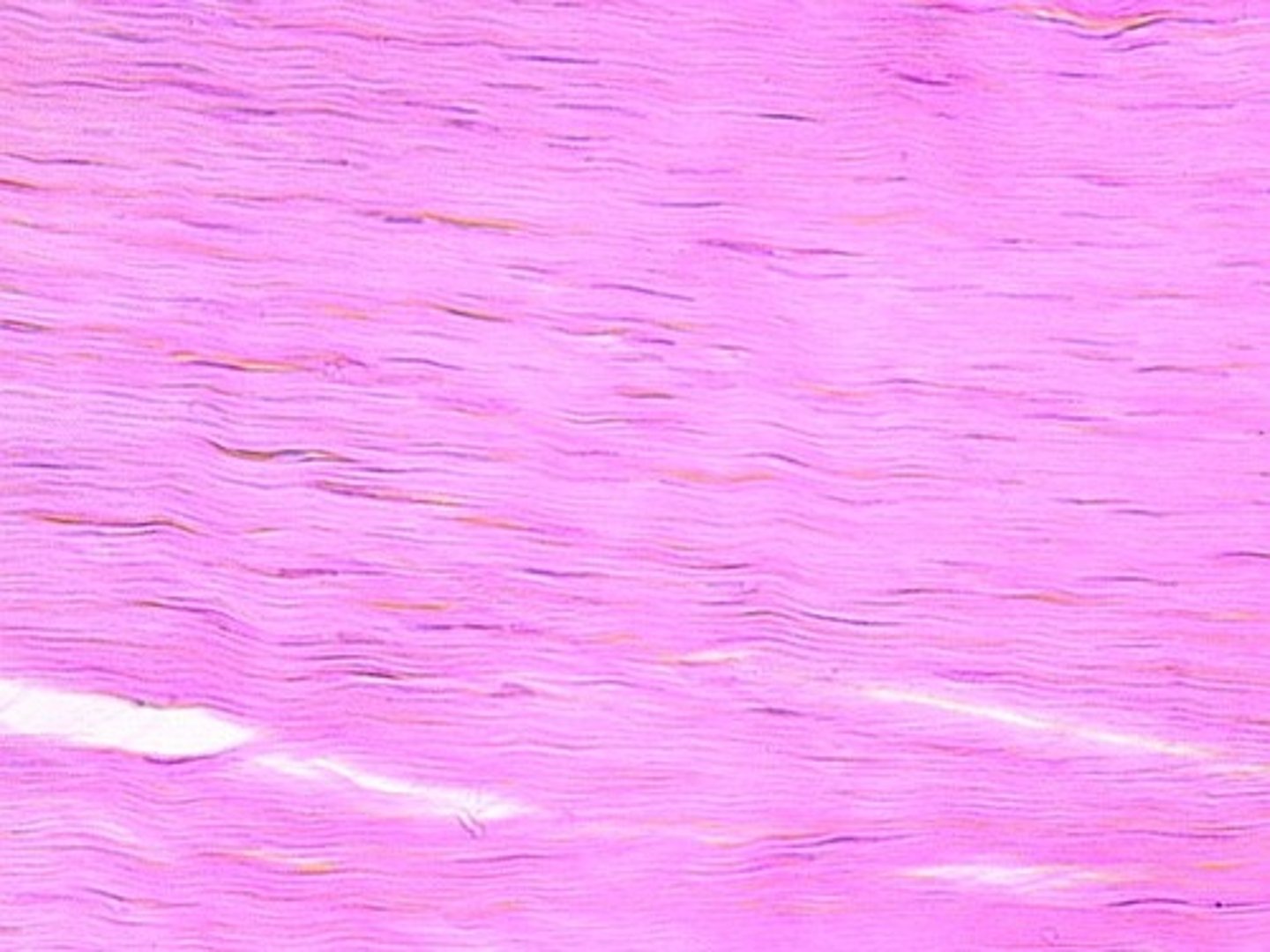
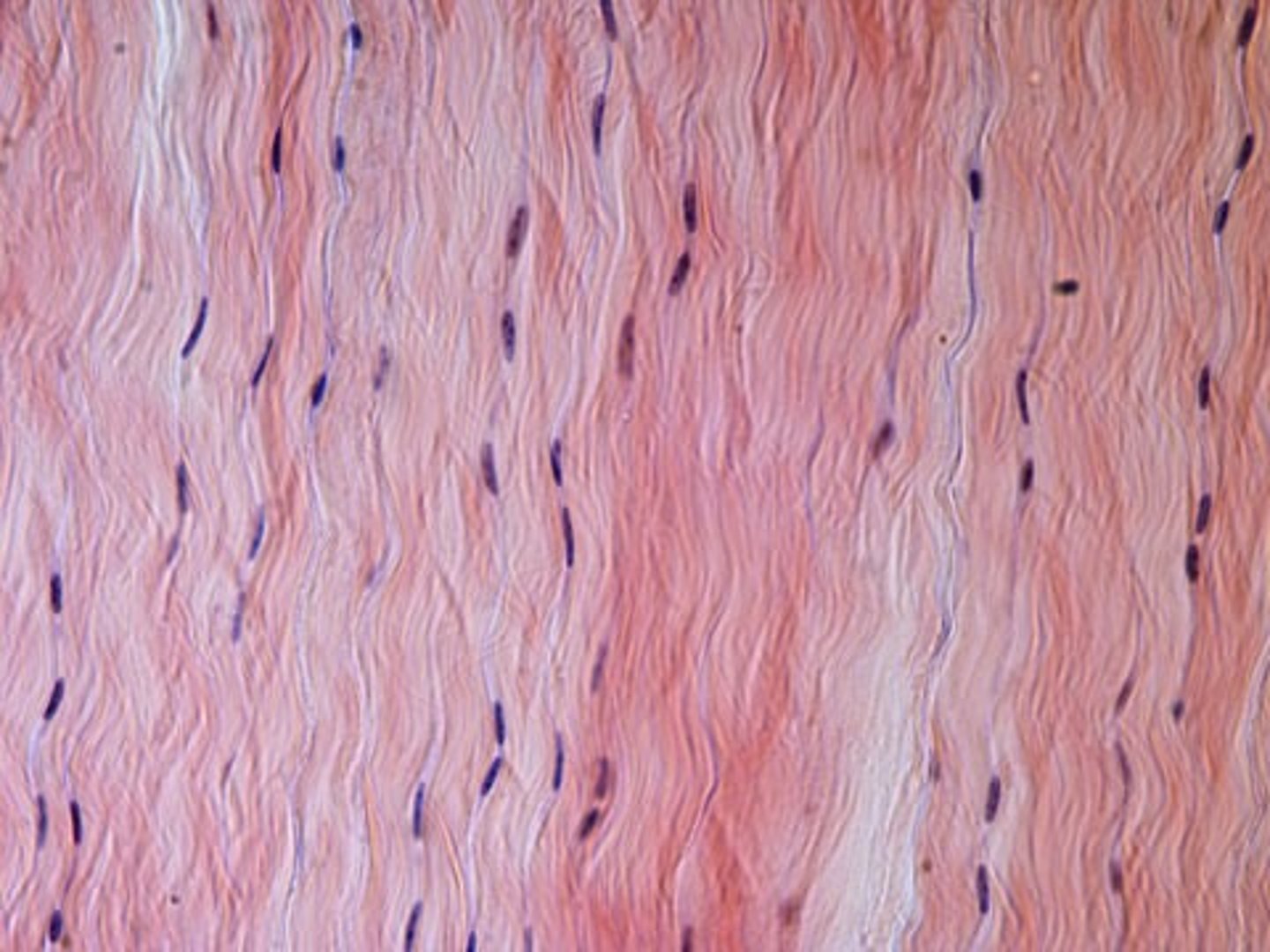
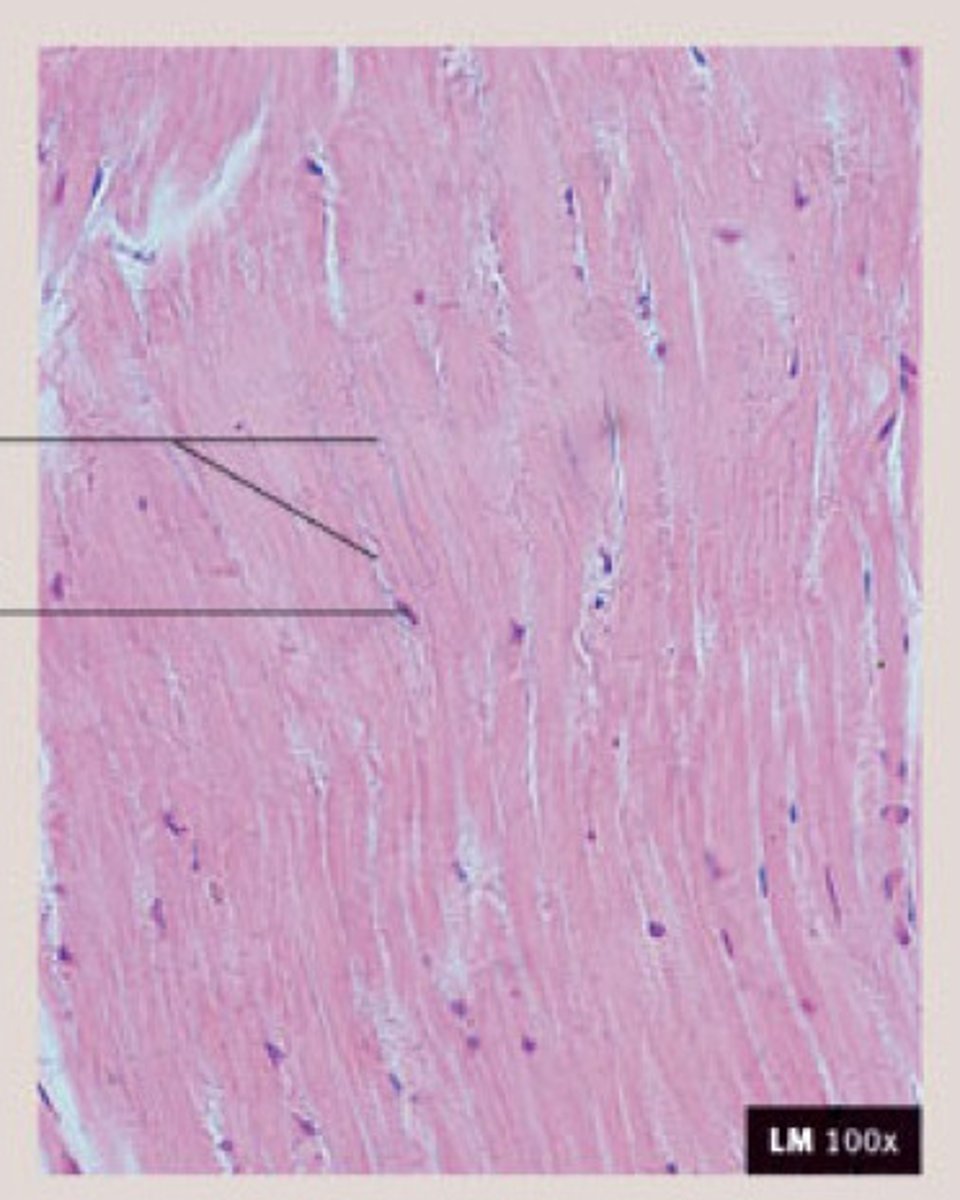
Description: Dense regular connective tissue
Primarily parallel collagen fibers; a few elastic fibers; major cell type is the fibroblast

Function: Dense regular connective tissue
attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
Location: Dense regular connective tissue
Tendons (connect muscle to bone); most ligaments (connect bone to bone); aponeuroses
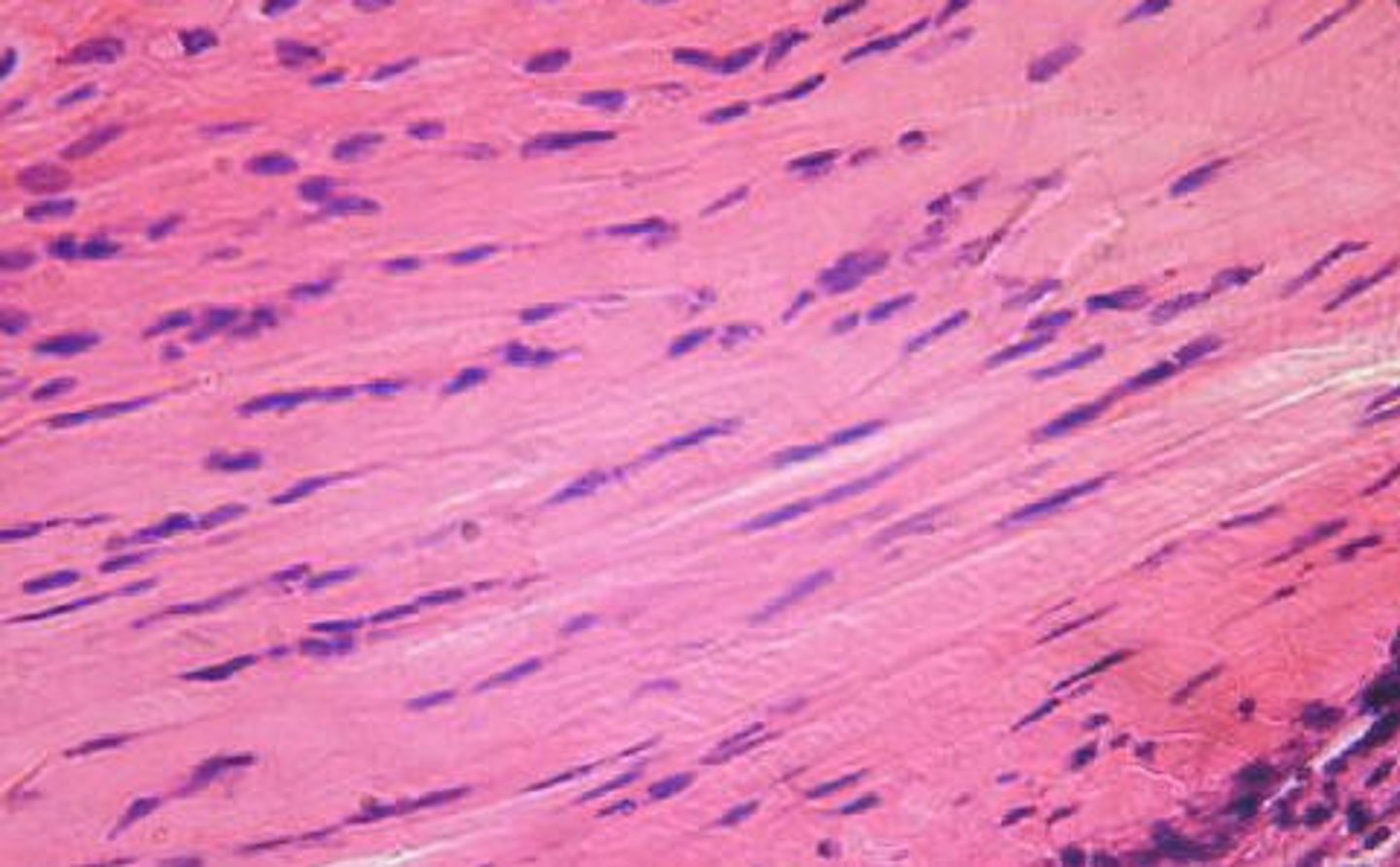
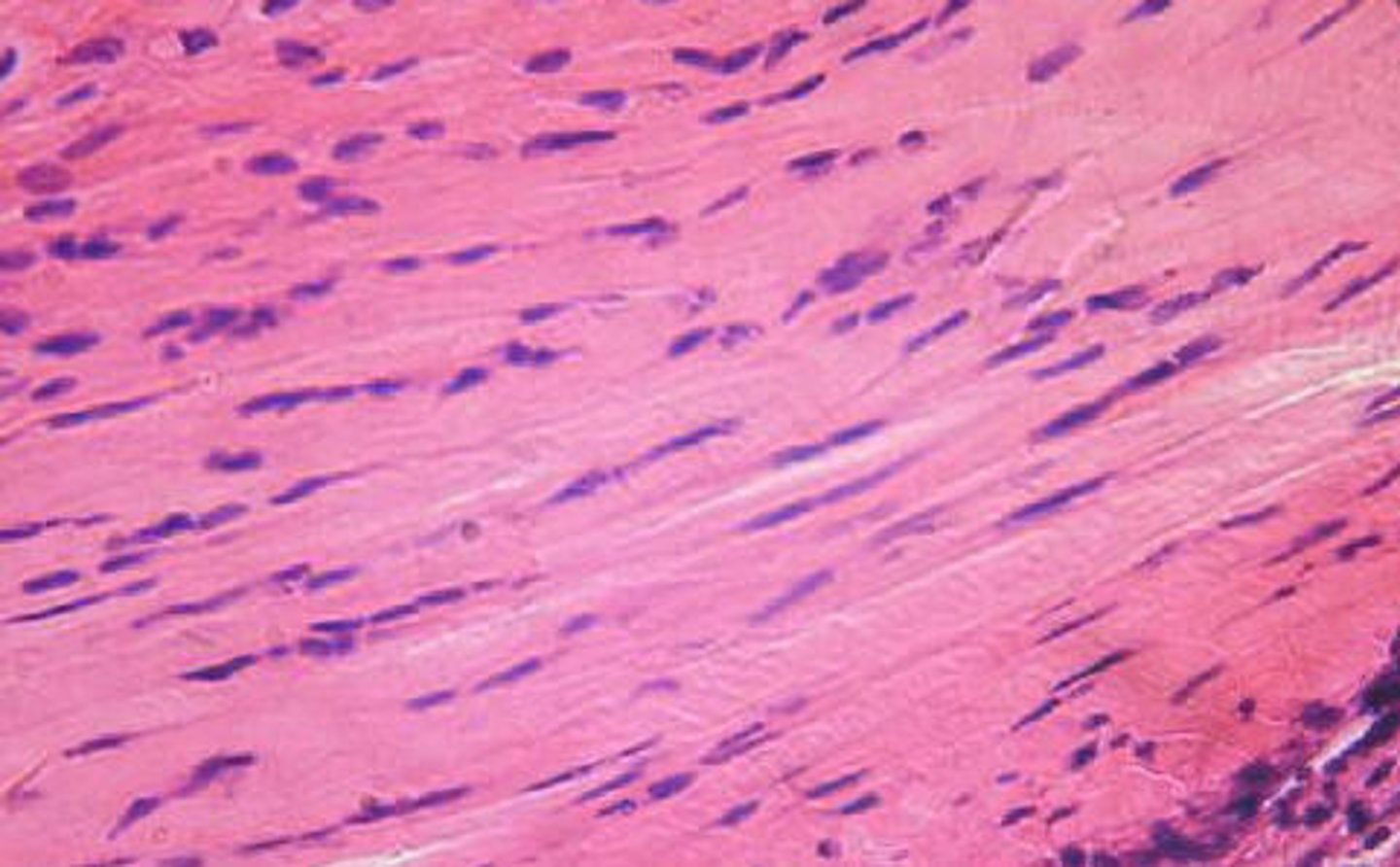
Description: Dense regular elastic tissue
Dense regular elastic tissue containing a high proportion of elastic fibers
Function: Dense regular elastic tissue
Allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs following respiration
Location: Dense regular elastic tissue
walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with the vertebral column; within the walls of the bronchial tubes
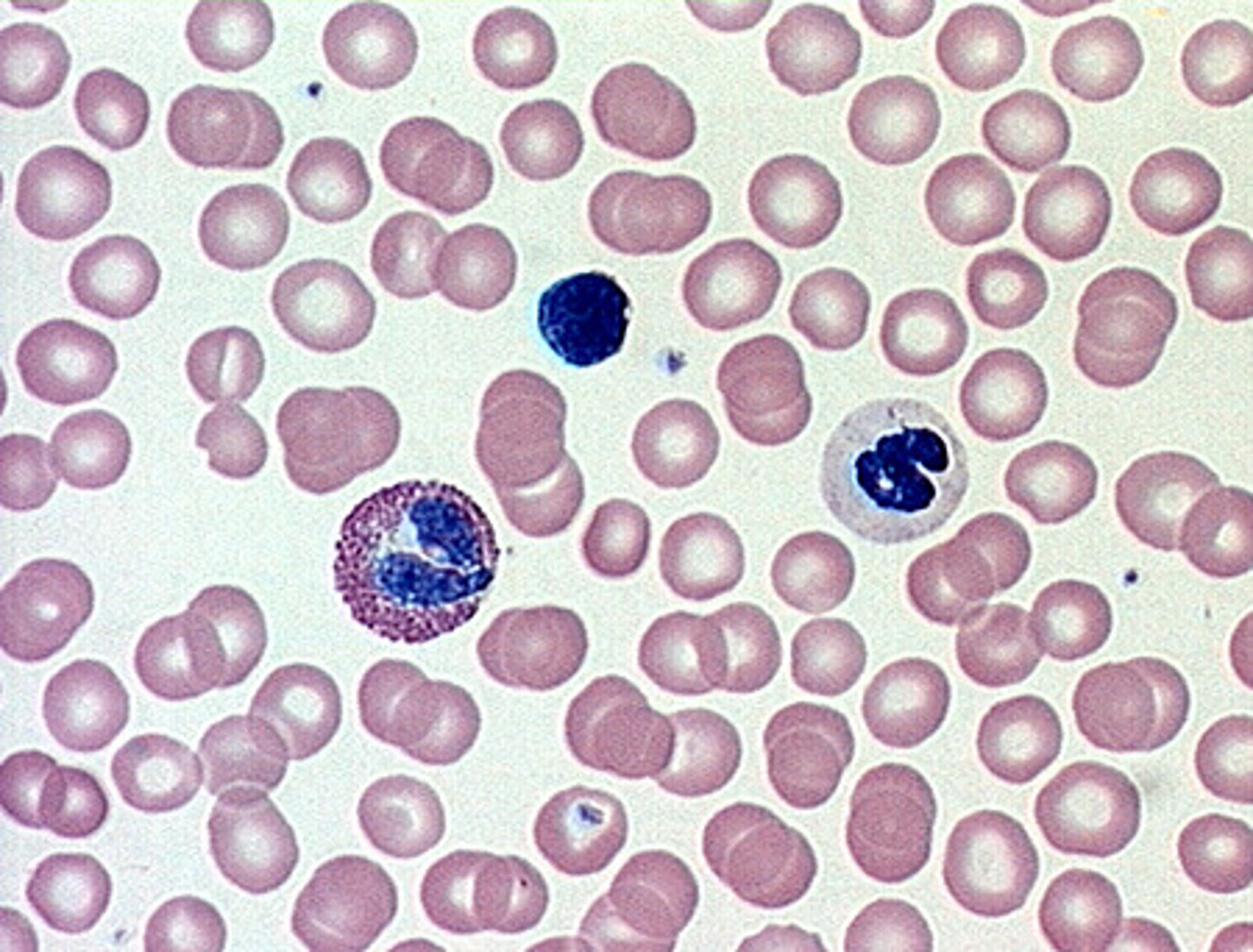
Description: Blood
Red and white blood cells in fluid matrix
erythrocytes: transport blood gases
leukocytes: cells of the immune system and protect the body from infection
thrombocytes: form a plug to reduce bleeding
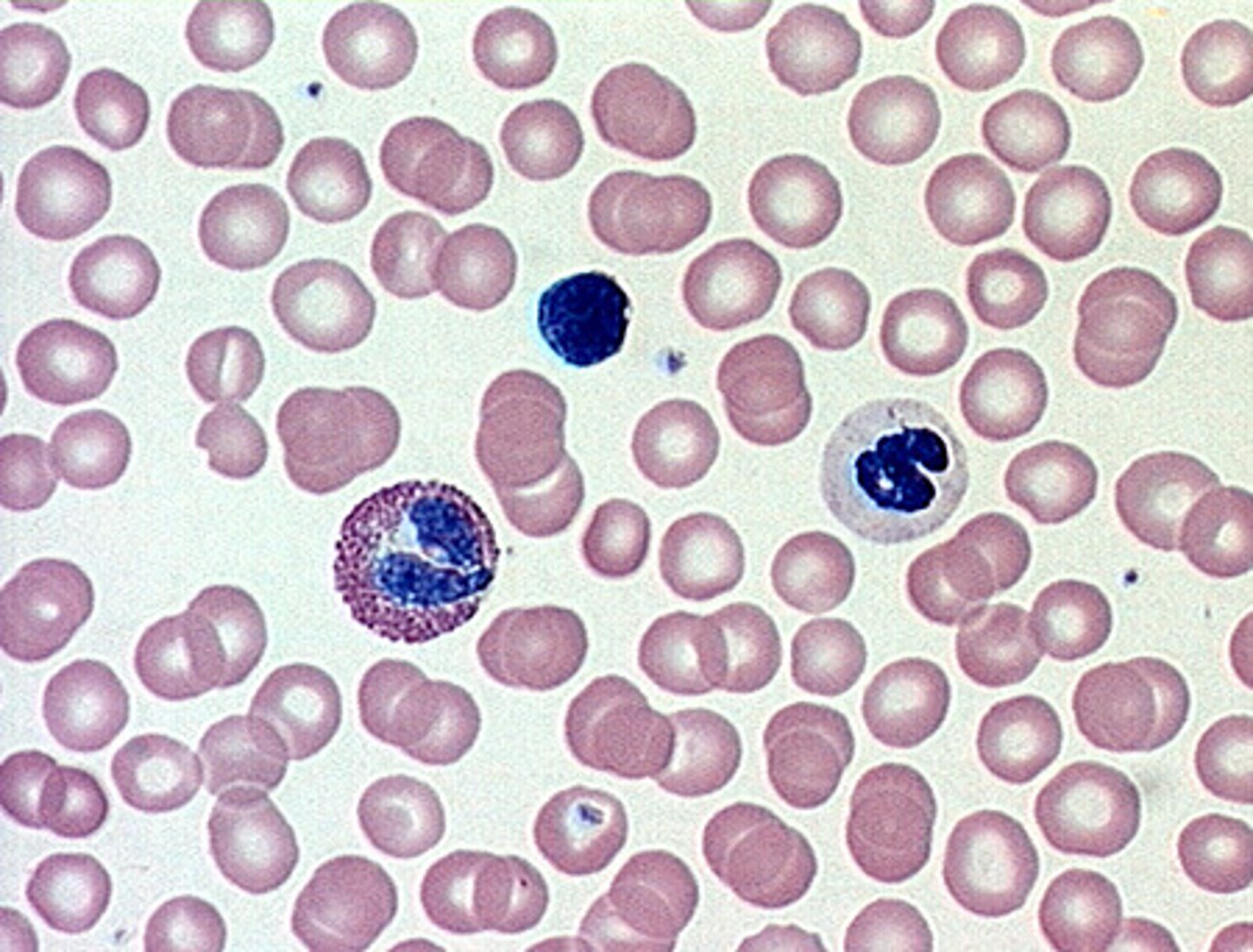
Function: Blood
Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes and other substances
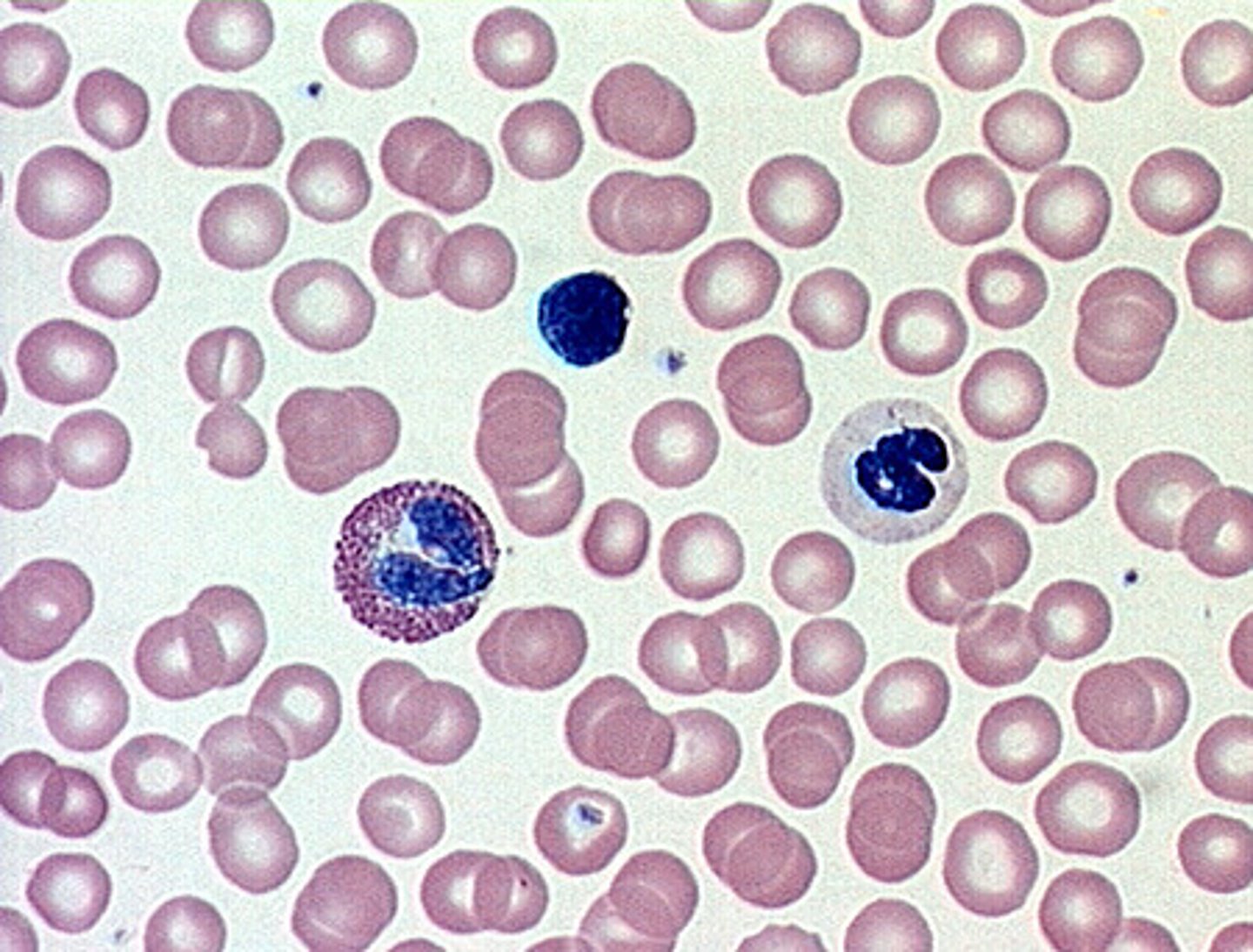
Location: Blood
contained within blood vessels
Description: Bone
hard, calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers; osteocytes lie in lacunae
Function: Bone
bone supports and protects (by enclosing); provides levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
Location: Bone
bones
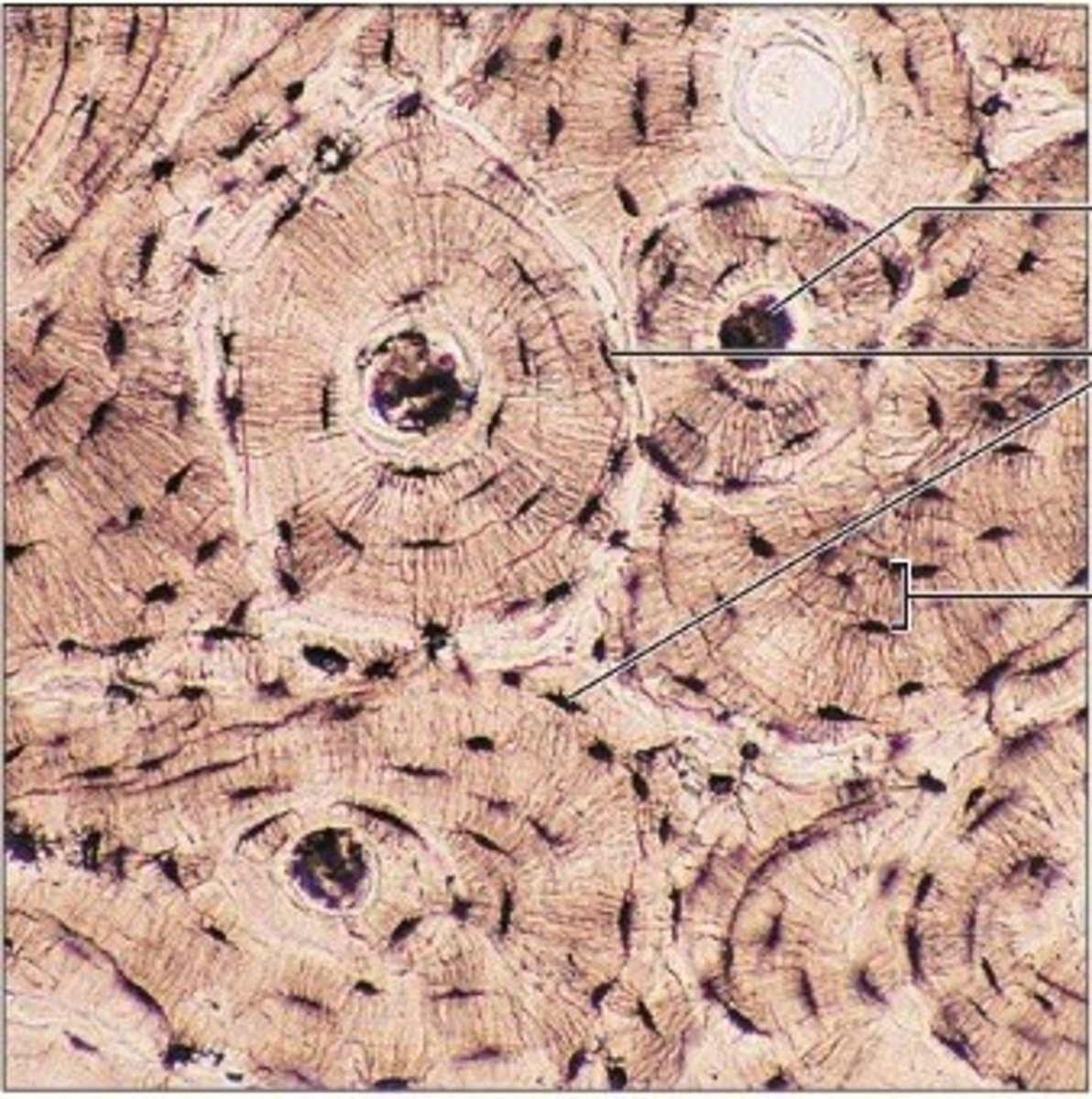
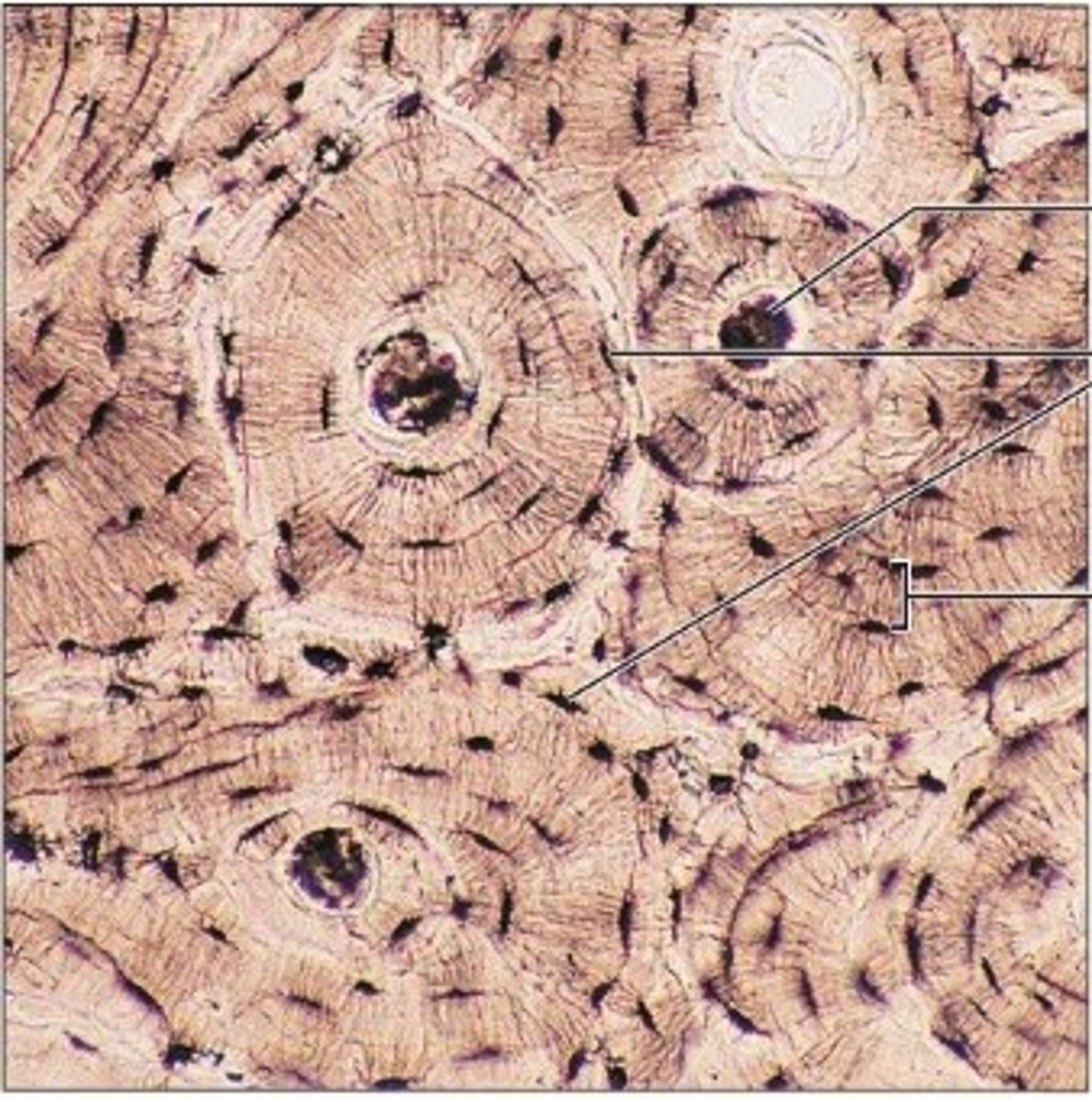
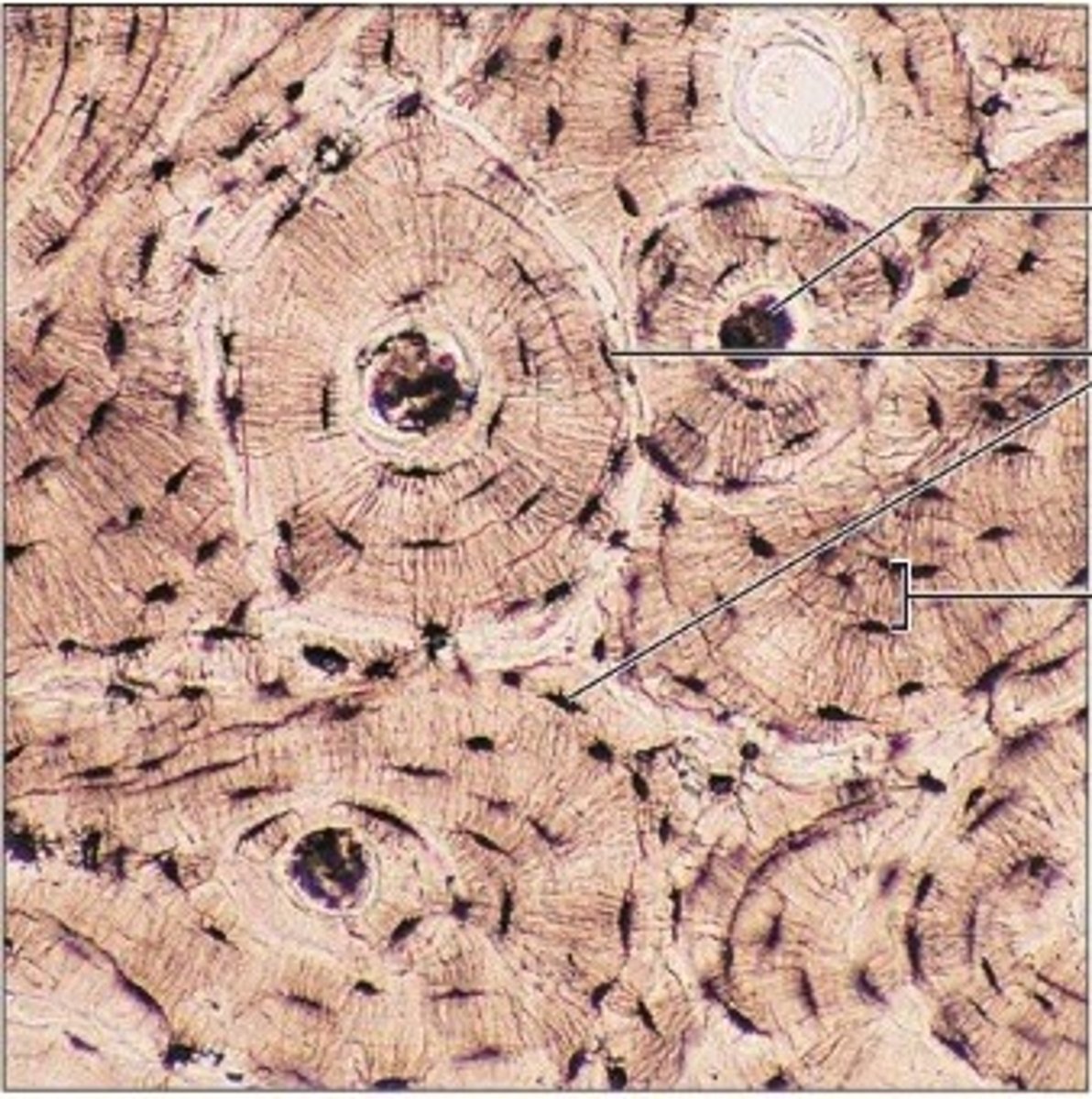
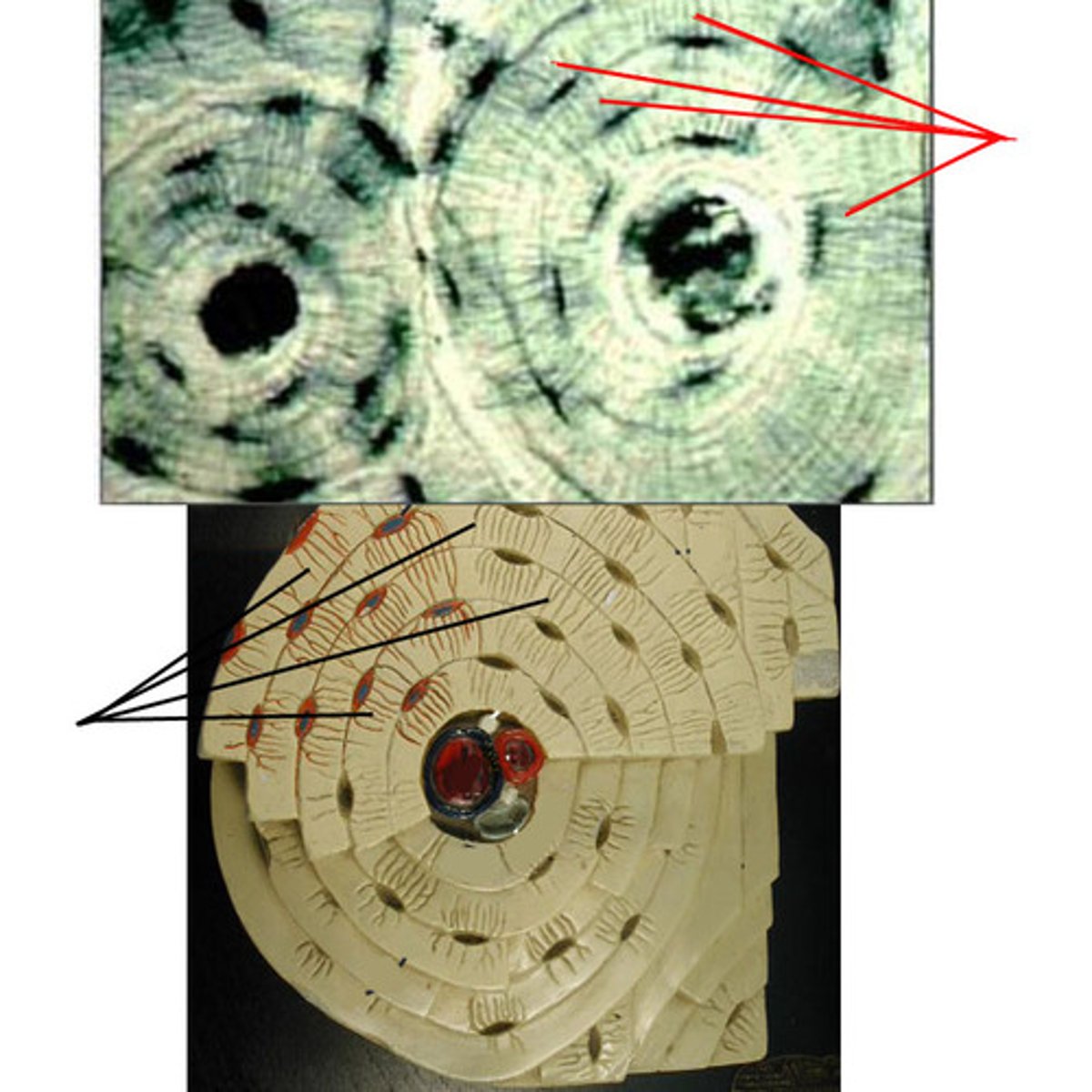
Lamellae
Concentric rings made up of groups of hollow tubes of bone matrix
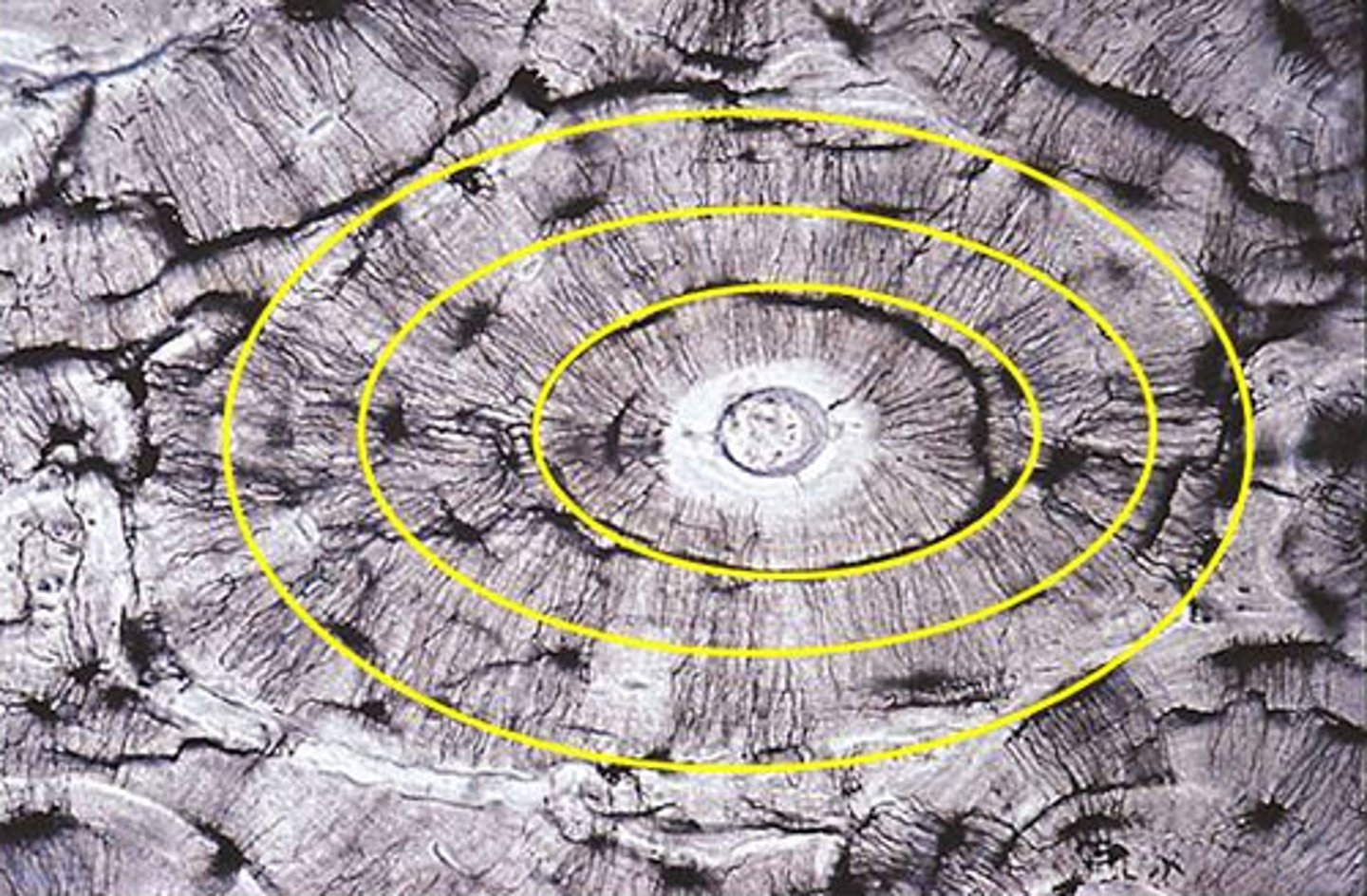
Haversian canal
one of a network of tubes running through compact bone that contains blood vessels and nerves; center dark spot in the osteoblasts
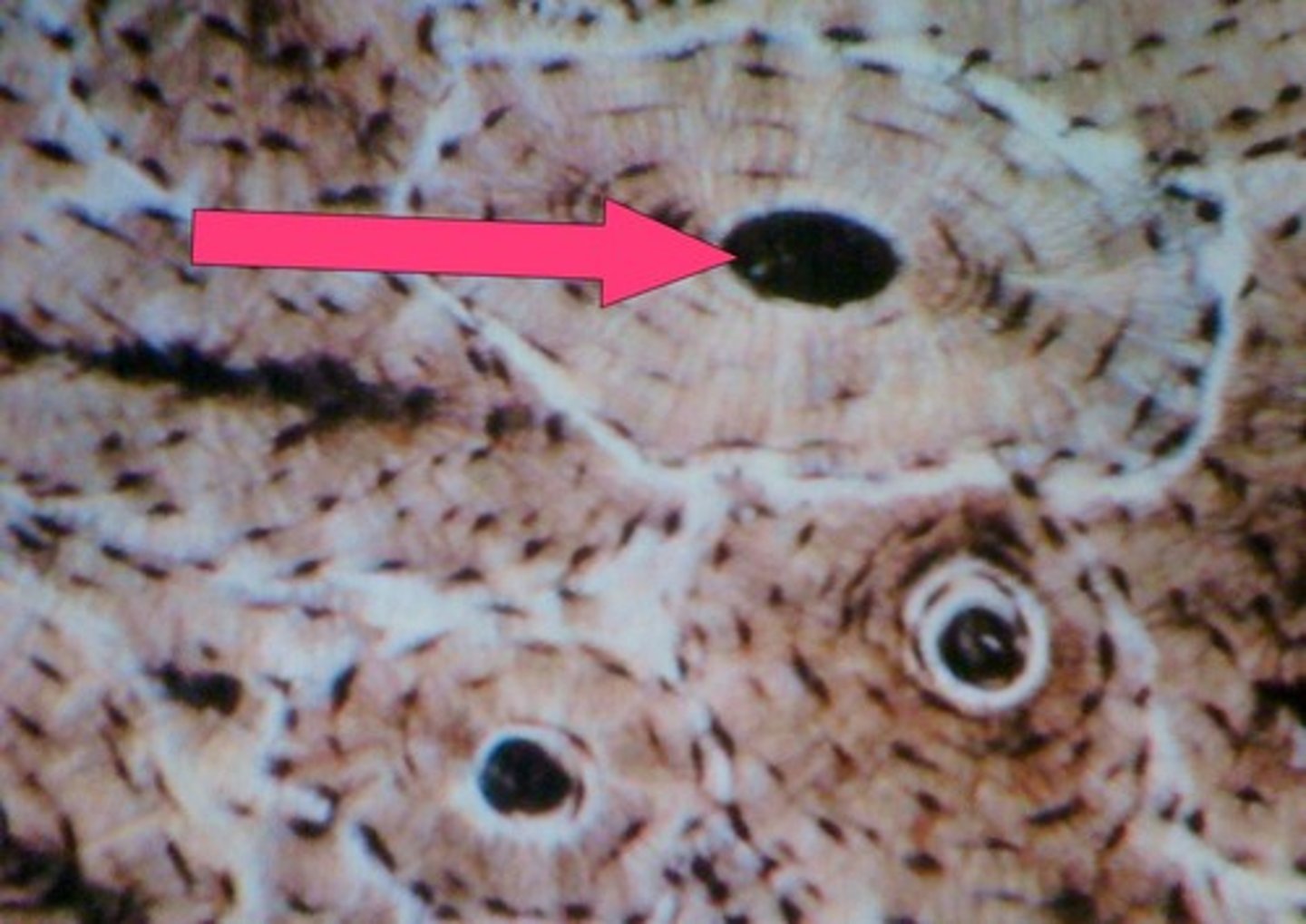
Canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
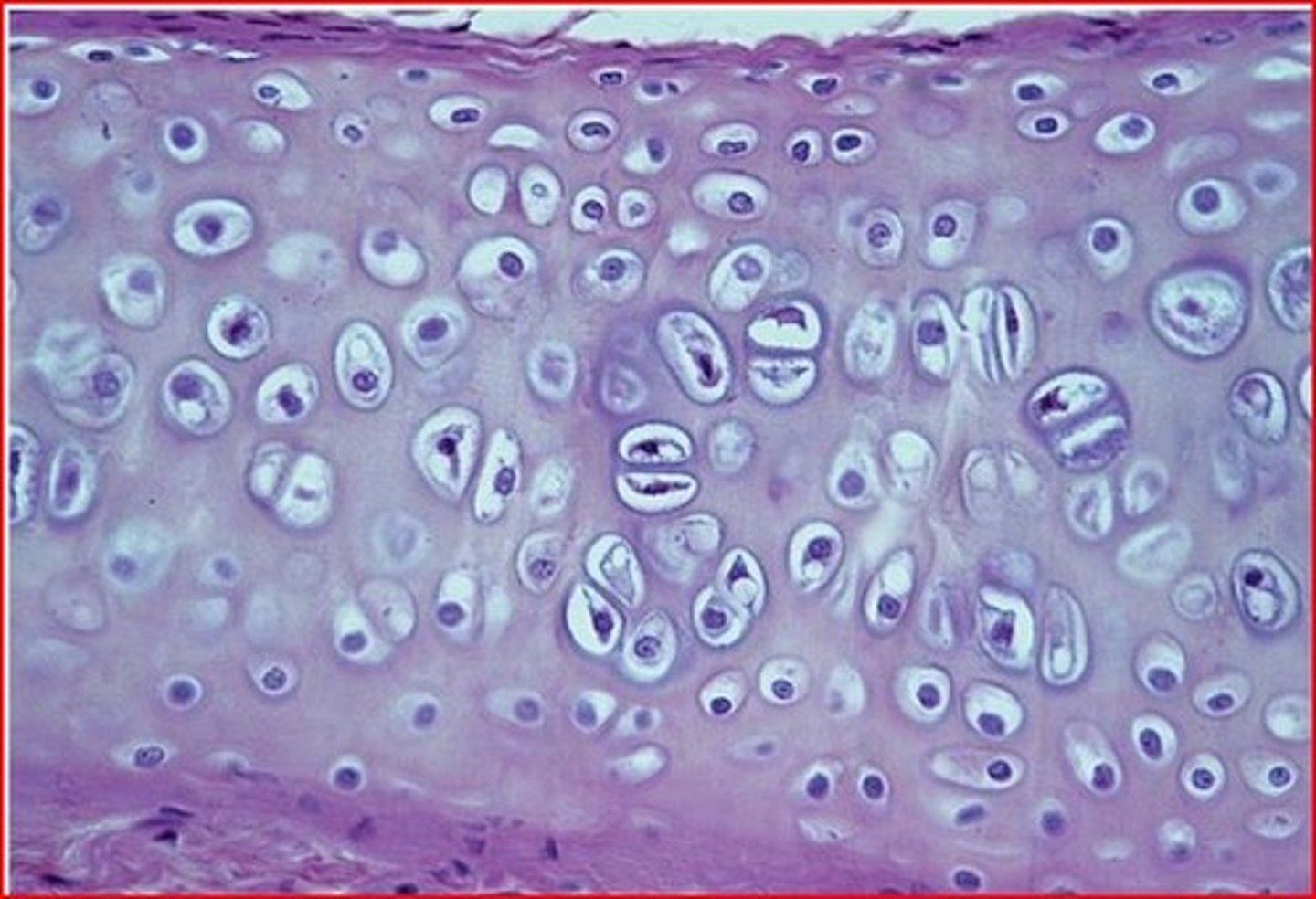
Description: Hyaline cartilage
amorphous but firm matrix; collagen fibers form an imperceptible network; chondroblasts produce the matrix and when mature (chondrocytes) lie in lacunae
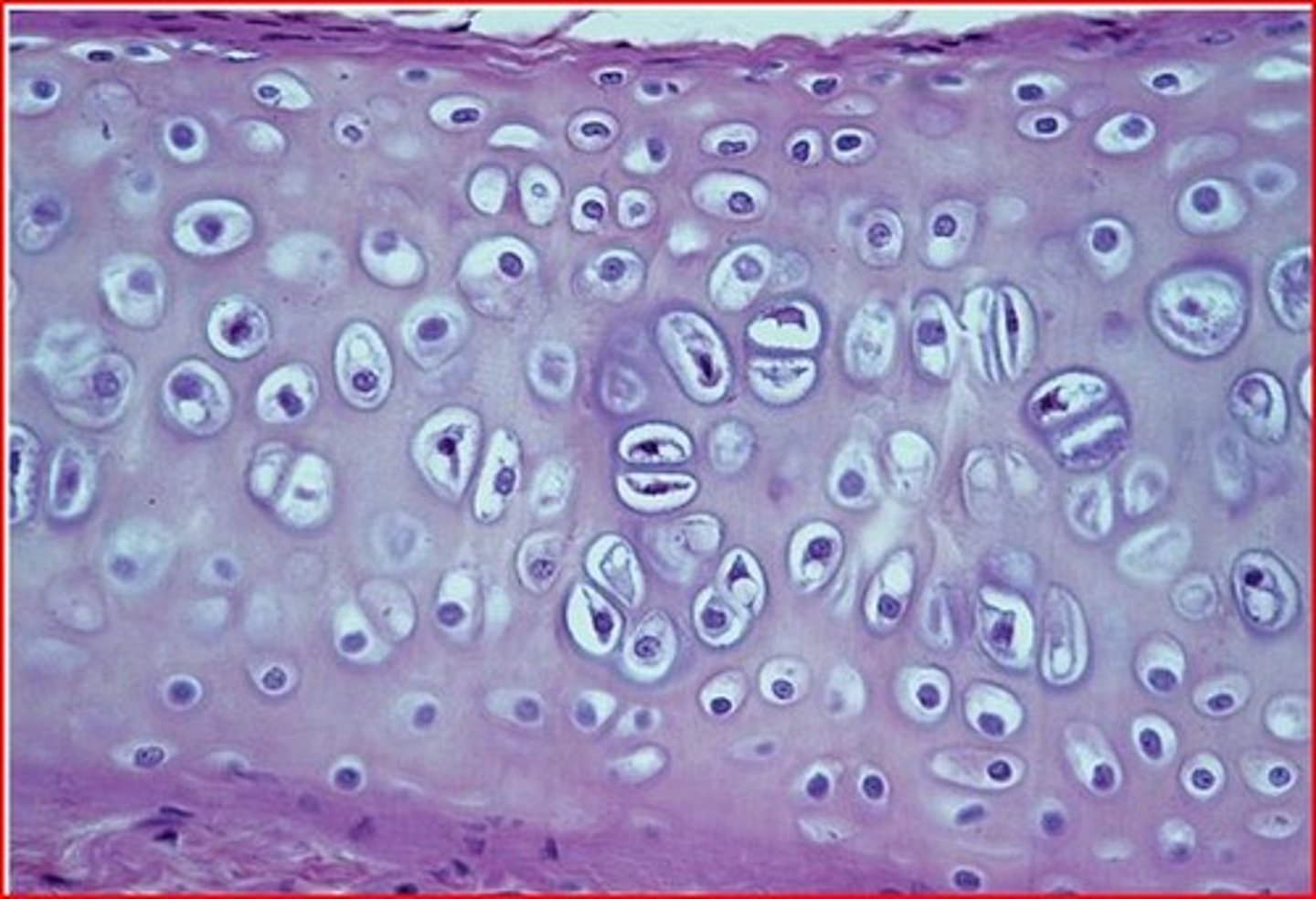
Function: Hyaline cartilage
supports and reinforces; serves as resilient cushion; resists compressive stress
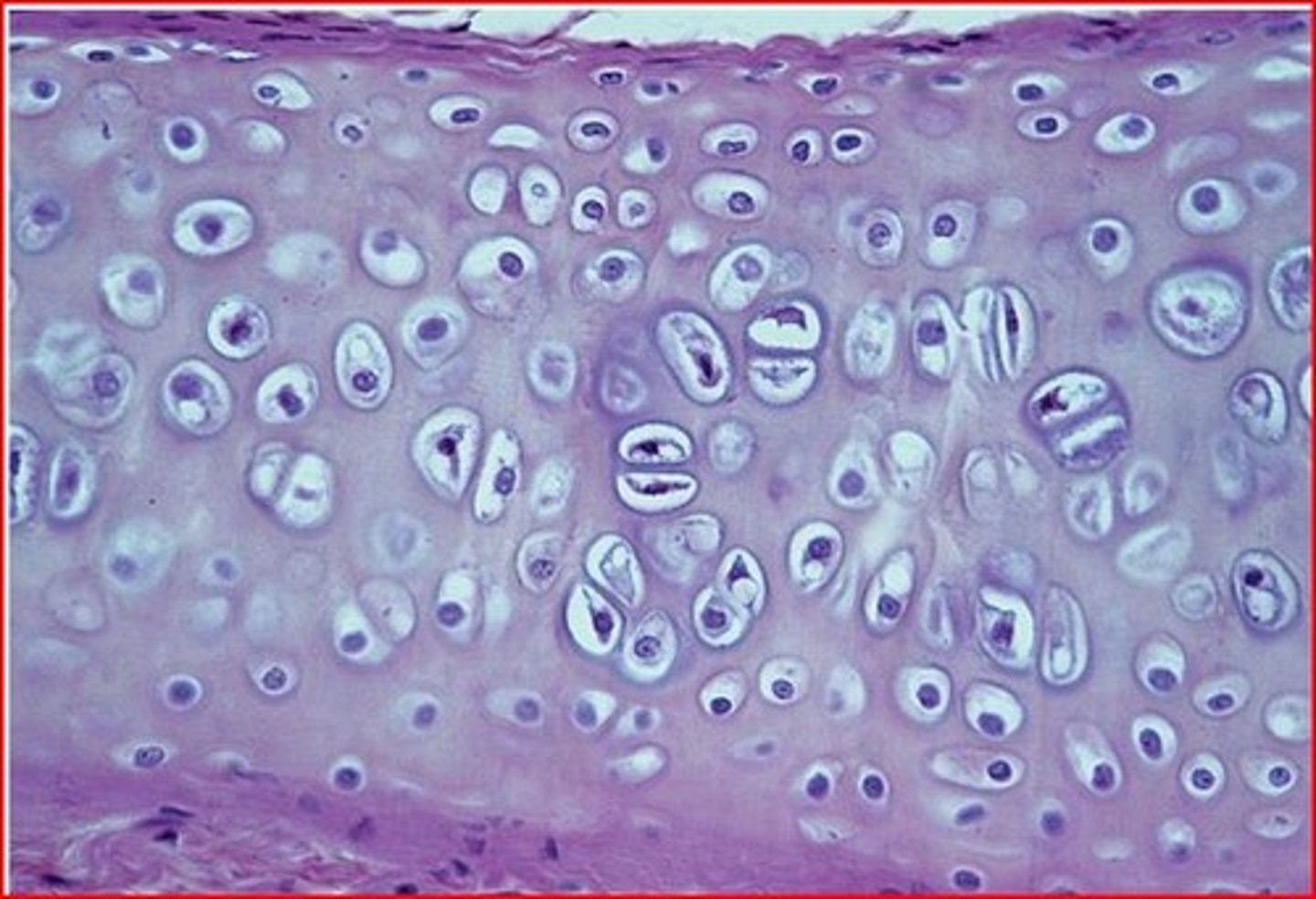
Location: Hyaline cartilage
forms most of the embryonic skeleton; covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities; forms costal cartilages of the ribs; cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx