Fungi
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are Fungi
-Eukaryotes, and multicellular
-Nuclei of fungal hyphae and spores are haploid, except for transient diploid
How do fungi eat
-Absorption
-exoenzymes
Exoenzymes
-Hydrolytic enzymes secreted by the fungus, digest food outside its body to simpler compounds
-saprobes
-digestion outside of body, decomposes organic substances
Saprobic fugi
-Absorb nutrients from nonliving organism
-outside of body digestion
Parasitic fugi
-absorb nutrients from the cells of living hosts (preying on animals)
-hyphae modified haustoria
Mutualistic fungi
absorb nutrients from a host organism, they reciprocate with functions that benefit their partner
Fugal hyphae
-cell walls are made of chitin
-multicellular with hyphae divided into cells by cross walls (septa)
-pores large enough for ribosomes
-vegetative body of fungus
Coenocytic fungi
-continuous cytoplasm mass
-hundreds or thousands of nuclei
-repeated nuclear division without cytoplasmic division
Mold
-rapidly growing, asexually reproducing fungus
-mycelia grow as saprobes or parasites on variety of substrates
-ONLY ASEXUAL STAGE, aesexual spores
-fugus may reproduce sexually, (zygosporangia, ascocarps, basildiocarps)
Yeasts
-unicellular fungi that inhabits liquid/moist
-simple cell division of budding off
-some reproduce sexually, forming sci (ascomycota), basidia (basidiomycota), no known sexual phase (imperfect fungi)
Lichens
-symbiotic association of photosynthetic microorganisms
-live in extreme environments
-fungal hyphae provides most of the mass/shape/structure
Mycorrhizae
-mutualistic associations of plant roots and fungi
-mycelium from the mycorrhizae greatly increase the absorptive surface of the plant roots
-mycor (fungus, rrhizae(root)
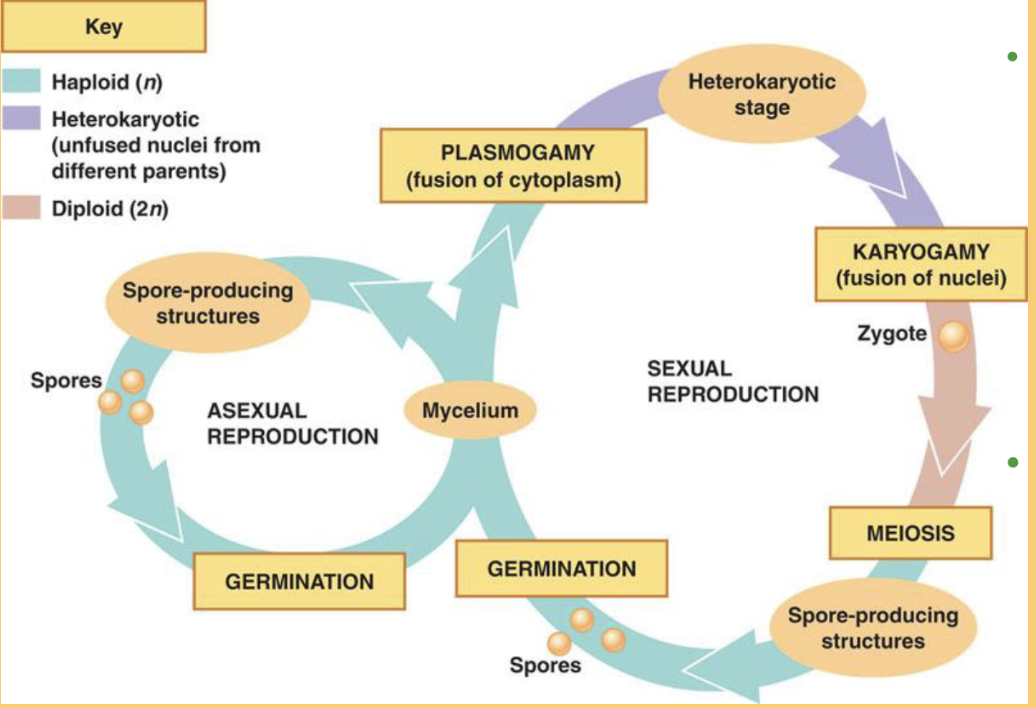
Karyogamy
-Fusion of haploid nuclei contributed by two parents
-karyo- (nucleus), -gamy (marriage)
plasmogamy
-cytoplasmic fusion by two parents
-plasmo- (cytoplasm), -ogamy(marriage)
Heterokayotic
-fusion of two hyphae that have genetically different nuclei
-nuclei may remain in separate parts of the same mycelium or exchange chromosomes and genes
-hetero-(different), -karyo- (nucleus)
Genetically heterogeneous
fusion of two hyphae that have genetically different nuclei
Phylum Chytridiomycota: Chytrids
-mainly aquatic
-saprobes, parasite protists, plants, and animals
-flagellated zoospores
-most primitive fungi
-absorptive mode nutrition have chitinous cell walls
-unicellular chytrids, form coenocytic hyphae
(coeno-(common, shared), -cyte(cell)
Phylum Zygomycota: Zygote fungi
-terrestrial - living in soil, decaying plant/animal material
-zygomycete (zygote fungi) hyphae are coenocytic with septa found in reproductive structures
-sexual stage
Phylum Glomeromycota
-arbuscular (arbuscul-small tree) mycorrhizae
-symbiotic with plant roots
-90% of plants have
-Glomero-(ball/mass), -mycota (fungus)
Phylum Ascomycota: Sac fungi
-unicellular yeasts —> morels
-plant pathogens
-saprobes of plant material
-sacs called asci
-half are mutualistic with algae to be lichens (mycorrhizae), or live between mesophyll cells to protect plant tissue from insects by releasing toxins
-extensive heterokayotic stage during formation of ascocarps
-Asco- (sac), -mycoya(fungi)
Ascomycetes
heterokaryotic during the formation of ascocarps
Ascocarps
sac-like structure that holds the spores of sac fungi
Phylum Basidiomycota: Club fungi
-eukaryotic mycelia
-dikaryotic mycelium (two nucleus)
-mushrooms, shelf, fungi, puffballs, rusts
-basidium, transient diploid stage (sexual reproduction)
-elaborate fruiting body called basidiocarp
-basid- (base), -id- (small), -mycota (fungus)
Haustoria
nutrient absorbing hyphae tips that penetrate the tissues of their host
Fungal reproductition