2.2 The Water Cycle and Oxygen-Demanding Waste
properties of water
composition of water molecules
- water molecules are cohesive, meaning that there are strong forces of attraction between molecules of water
water will remain a liquid over a wide variety of temperatures
- it has a high boiling point and a low freezing point
- it also has a high heat capacity, so liquid water changes temperature very slowly; it can store large amounts of heat without a change in temperature
- it has a high heat of vaporization, so it takes a lot of heat to evaporate liquid water
- water is the universal solvent and can dissolve a variety of compounds (eg. nutrients, waste, pollutants)
- has high surface tension, meaning that its surface behaves like a membrane (its surface is often similar to that of a solid)
- ice is less dense than liquid water — water expands when it freezes
causes for concern with water
- too much (flooding, eg. Pakistan)
- too little (droughts, eg. California)
- too poor of quality (contaminated, eg. Flint)
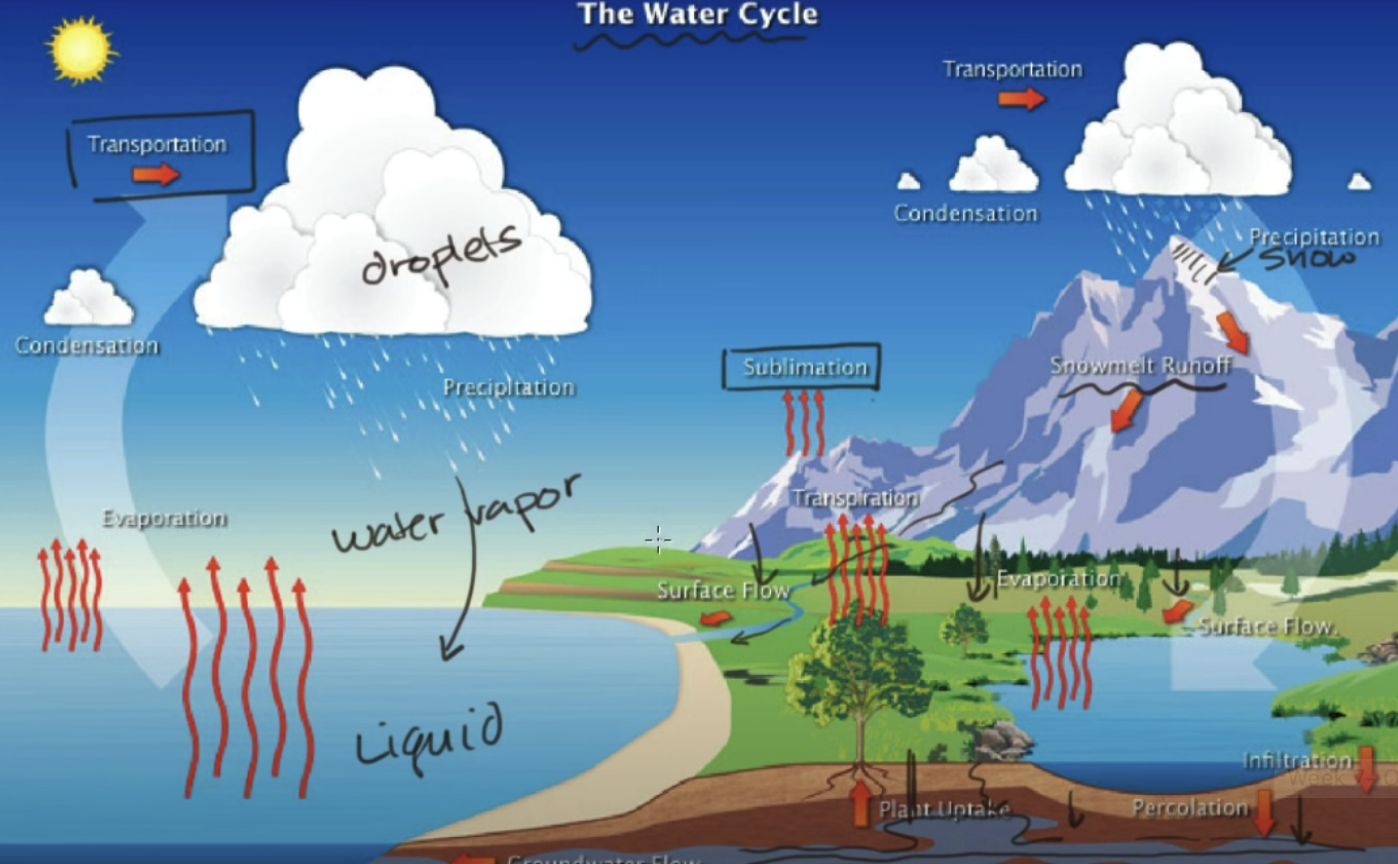
the water cycle
- the vast majority of water on earth is saltwater; of the freshwater, most of it is located in glaciers/permanent snow cover and groundwater
 oxygen-demanding waste
oxygen-demanding waste
- oxygen demanding waste: organic waste that can be decomposed by aerobic bacteria
- aerobic bacteria: bacteria that use oxygen
- because the bacteria use so much oxygen, the level of oxygen dissolved (DO) in the water decreases
- fish and other animals need high levels of DO to survive
- origins of oxygen demanding waste
- main cause — failing infrastructure
- eg. leaking pipes, failing/overflowing sewage systems
- results in the release of oxygen demanding waste, eg. raw sewage, manure, decomposing algae, paper factories, meat-processing plants
streams
- stream: a body of water that flows
- eg. rivers, creeks
- usually recover quickly from oxygen demanding waste, but if they are overloaded, the breakdown of degradable waste by bacteria depletes DO and produces an oxygen sag
- oxygen sag: the reduction in dissolved oxygen plotted over a distance along a water body from a point at which sewage or other pollutants have been discharged
- biochemical oxygen demand (BOD): the amount of oxygen consumed by bacteria while they decompose organic matter
sediment
- a pollutant
- sediment/suspended matter: insoluble soil particles which make water turbid
- turbid: cloudy, opaque, or thick with suspended matter