Sensing the world I
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:33 PM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
what is sensation?
the capacity to detect a particular physical or chemical stimulus
(involves the sensory organs and afferent nerves)
(involves the sensory organs and afferent nerves)
2
New cards
what is perception?
the conscious experience and interpretation of sensory information
(involves neurons in the central nervous system)
(involves neurons in the central nervous system)
3
New cards
what is a stimulus?
a thing or event that evokes a specific functional reaction in an organ or tissue (stimuli can be physical or chemical)
4
New cards
what are some physical stimuli?
* sound
* visible light
* heat
* magnetic field
* UV light
* visible light
* heat
* magnetic field
* UV light
5
New cards
what are some chemical stimuli?
* taste
* odour
* flavour
* pheromone
* odour
* flavour
* pheromone
6
New cards
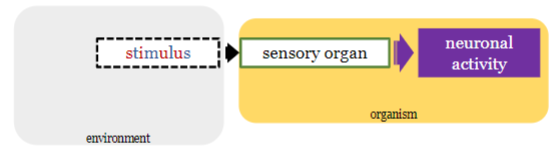
what is stimulus transduction?
converting the stimulus into the nervous system ‘language’ i.e. neuronal activity
(each sensory organ deploys a specific mechanism to transform chemical or physical attributes of stimuli to neuronal activity)
(each sensory organ deploys a specific mechanism to transform chemical or physical attributes of stimuli to neuronal activity)
7
New cards
which organ(s) and stimuli and related to somatosensation?
* organ: skin and other tissues
* stimuli: pressure, warmth, cold, pain
* stimuli: pressure, warmth, cold, pain
8
New cards
which organ(s) and stimulus and related to sight?
* organ: eyes
* stimulus: light
* stimulus: light
9
New cards
which organ(s) and stimulus and related to hearing?
* organ: ears
* stimulus: air vibration
* stimulus: air vibration
10
New cards
which organ(s) and stimulus and related to smell?
* organ: nose
* stimulus: volatile chemicals
* stimulus: volatile chemicals
11
New cards
which organ(s) and stimulus and related to taste?
* organ: mouth
* stimulus: soluble chemicals
* stimulus: soluble chemicals
12
New cards
how do pigeons use magnetoreception?
they use the magnetic field of the earth to navigate and find the direction they want to go
13
New cards
what do elephants (and other animals) use infrasound?
* infrasounds are sounds that humans can’t hear because the frequency is too low (they can also travel ling distances)
* they use it to communicate with each other and about things that are happening
* they use it to communicate with each other and about things that are happening
14
New cards
how do bats use ultrasounds?
* ultrasounds are sounds humans can’t hear because the frequency is too high
* they use it to navigate and localise everything that is around them including prey
* they use it to navigate and localise everything that is around them including prey
15
New cards
how do fish (e.g. elephant fish) use electrolocation?
* they can detect the electrical fields around them
* if the electrical field is disrupted they know an object is there
* they use electrical signals to communicate with each other
* if the electrical field is disrupted they know an object is there
* they use electrical signals to communicate with each other
16
New cards
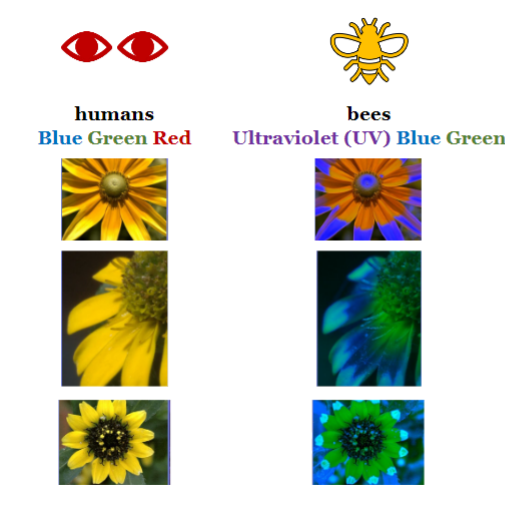
how does vision differ in humans and bees?
* humans have cones that detect blue, green and red
* bees have cones that can detect blue, green and ultraviolet
* bees have cones that can detect blue, green and ultraviolet
17
New cards
describe how asymmetric vision in the cockeyed squid works
* the large eye looking upwards detects predators against the dim sunlight
* the small eye looking downward detects prey’s bioluminescent signals
* the small eye looking downward detects prey’s bioluminescent signals
18
New cards
what are sensory receptors?
cells that specialise in converting external stimuli (physical or chemical) into neural (electrical) activity
types:
* photoreceptors
* mechanoreceptors
* chemoreceptors
* nociceptors
types:
* photoreceptors
* mechanoreceptors
* chemoreceptors
* nociceptors
19
New cards
what do photoreceptors do?
detect light (vision)
20
New cards
what do mechanoreceptors do?
detect movement (sound, texture, blood pressure, muscle stretch)
21
New cards
what do chemoreceptors do?
detect chemical compounds (smell. taste)
22
New cards
what do nociceptors do?
detect tissue damage (pain)
23
New cards
how do photoreceptors differ?
each photoreceptor points to a unique direction, sensing the light present in this two dimensional space
24
New cards
how do mechanoreceptors vary in the ear?
each inner hair cell responds to specific sound frequencies
25
New cards
how do odorant receptors differ?
each one detects only one chemical attribute
26
New cards
how are receptors distributed in sensory organs?
receptor distribution is not always homogenous (e.g. in the retina, tongue)
27
New cards
why does receptor sensitivity vary?
receptors have different thresholds (i.e. the minimum stimulus intensity that is detected)
28
New cards
what do neural relays do?
* all senses connect to the cortex through a series of neural relays
* sensory info is modified at each relay, allowing for the construction of different aspects of the sensory experience
* they also allow for sensory systems to interact (e.g. visual modification of sound - the McGurk effect)
* sensory info is modified at each relay, allowing for the construction of different aspects of the sensory experience
* they also allow for sensory systems to interact (e.g. visual modification of sound - the McGurk effect)
29
New cards
why is perception more complex than sensation?
the context, emotional state or memories can affect how we perceive the same sensory experience
30
New cards
why is the visual system important for our daily lives?
through seeing and perceiving the world around us we assess reality but can also produce adaptive behaviours
31
New cards
what is visible light?
the section of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can detect
(light can enter the eye from a source of light, or after bouncing on an object)
(light can enter the eye from a source of light, or after bouncing on an object)
32
New cards
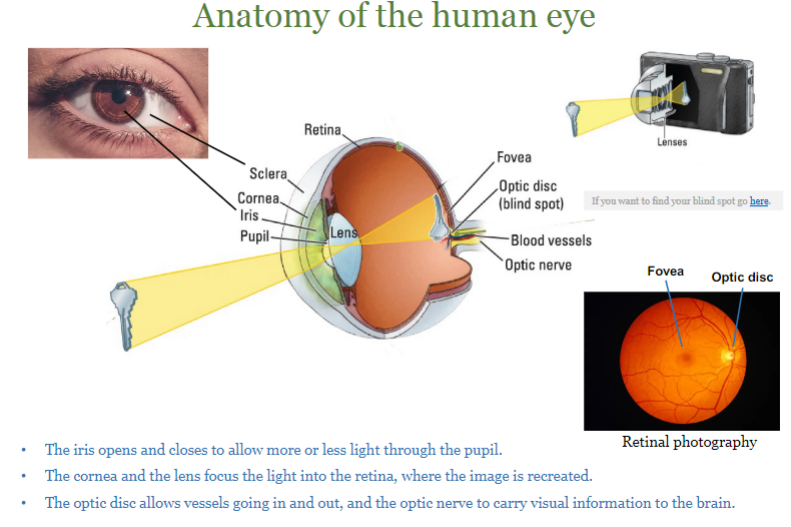
anatomy of the human eye
33
New cards
what are the two types of photoreceptors contained in the retina?
* cones (detect colour)
* rods (detect light)
* rods (detect light)
34
New cards
what type of photoreceptor is the fovea mainly covered in?
cones (actute vision during daylight)
35
New cards
what type of photoreceptor covers the periphery?
rods (which are more sensitive to light than cones)
36
New cards
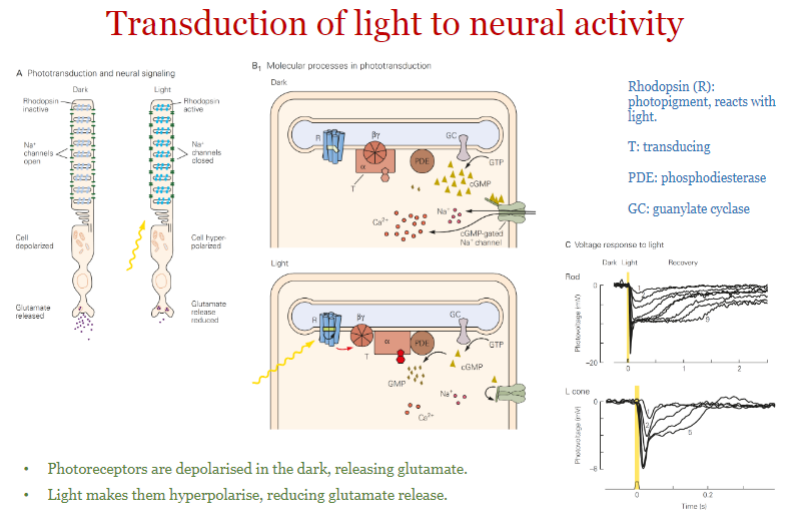
how does light affect the release of glutamate in photoreceptors?
* they are depolarised in the dark, releasing glutamate
* light makes them hyperpolarise, reducing glutamate
* light makes them hyperpolarise, reducing glutamate
37
New cards
what is a bipolar cell?
one of the main retinal interneurons and provide the main pathways from photoreceptors to ganglion cells
38
New cards
what affects the probability of neurotransmitter release?
photoreceptors and bipolar cells changing their membrane potential (they do not fire action potentials)
39
New cards
what are the two types of bipolar cells (in vertebrate retinas)?
on and off
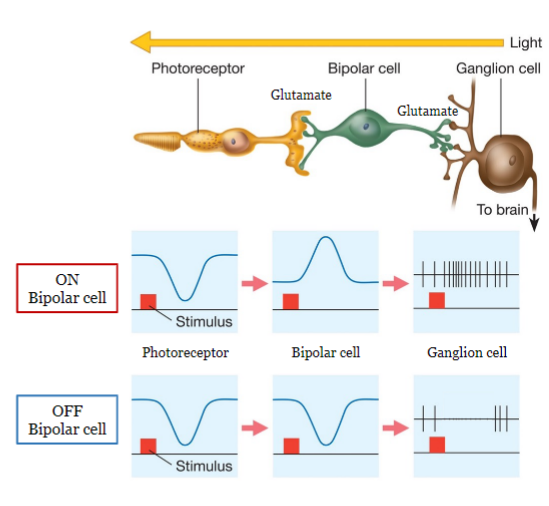
40
New cards
how many photoreceptors doe bipolar cells connect to in the fovea and the peripheral retina?
* fovea: one bipolar cell connects to one photoreceptor
* peripheral retina: one bipolar cell connects with several photoreceptors
* peripheral retina: one bipolar cell connects with several photoreceptors
41
New cards
where is visual information from each side of the visual field analysed?
* right side: left hemisphere
* left side: right hemisphere
* left side: right hemisphere
42
New cards
what are the three neural routes to the visual brain?
* retinohypothalamic tract
* geniculostriate pathway
* tectopulvinar pathway
* geniculostriate pathway
* tectopulvinar pathway
43
New cards
what is the retinohypothalamic tract involved in?
* regulating the circadian rhythm
* controls pupillary reflex that expands or contracts the pupil to regulate the amount of light reaching the retina
* controls pupillary reflex that expands or contracts the pupil to regulate the amount of light reaching the retina
44
New cards
what is the geniculostriate pathway involved in?
the conscious experience of vision
contains:
* dorsal stream: analyses *how*; guides movement to relative objects
* ventral system: analyse the *what*: object identification
contains:
* dorsal stream: analyses *how*; guides movement to relative objects
* ventral system: analyse the *what*: object identification
45
New cards
what is the tectopulvinar pathway involved in?
analyses spatial information of objects
* from ganglion cells from retina periphery, with no colour info
* explains the visual ability of patients with blindsight
* from ganglion cells from retina periphery, with no colour info
* explains the visual ability of patients with blindsight