1 Intro + 2 Anatomy
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
What was wrong with Trey?
brain filled with fluid - edema
5 yr old ran into a car. He started crying and ran to his mother, who took him to the hospital. He was alert at first, but then became lethargic. Neuroimaging was done (see picture), and he died 8 hours later.
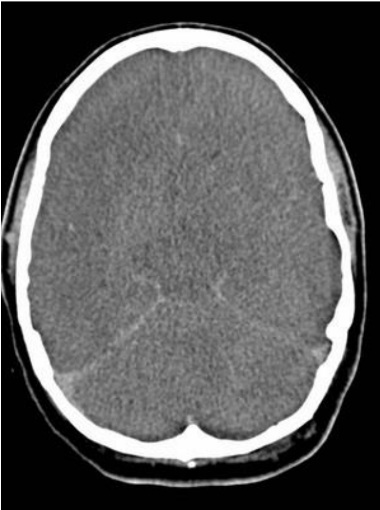
What did Aristotle think about brain function?
The heart was the seat of mental capacities; the brain’s job was to cool the blood
What did Hippocrates think about brain function?
Brain is the seat of thought and emotion
What did Galen discover about the brain?
reported behavioral changes in brain-injured gladiators
Phrenology
study of how the bumps on your skull correspond to attributes of personality - assigned seperate functions to cortical areas
What is Pick’s disease?
frontotemporal dementia - degeneration of front of brain, causing memory loss
degeneration in the front of the brain
Dementia/Pick’s disease
What were the pins used for in the picture of brain surgery we saw in class?
Epilepsy treatment
What was wrong with the 14 yo Vietnamese girl?
Stroke in her right brain first, then her left - caused paralysis of arms and difficulty seeing/hearing
14 yo Vietnamese girl at school had a seizure, and on arrival in ER could not move her right arm or see to her left. On exam, she was quite short and thin, and hard of hearing. A month later she was back in ER, this time unable to move her left arm, and her hearing was worse.
Reticular Theory vs Neuron Doctrine
Reticular Theory (Golgi)
everything in the nervous system is one continuous unit
was proven to be false after the discovery of the neuron doctrine
Neuron Doctrine
the brain is composed of independent cells - neurons are not connected
signals are transmitted from cell to cell across synapses (cell gaps)
Who were the scientists who discovered the Neuron Doctrine?
Camillo Golgi - stained brain cells
Santiago Ramon y Cajal - used Golgi’s cell stains to see individual neurons - credited with the Neuron Doctrine
(they shared 1906 Nobel prize because they had to)
Which way does a nerve impulse travel?
Down the axon (soma to axon terminal)
Parts of a neuron
Dendrites - accept signals
Cell body - houses nucleus and organelles
Axon hillock - place where axon meets cell body
Axon - delivers signals
Myelin Sheath - coverings of myelin around the neuron, insulates and helps signals pass through faster
Nodes of Ranvier - gaps in myelin sheath, signals jump from node to node
Axon Terminals - place where signals are transferred from one neuron to another, contains neurotransmitters
Synapse - gaps between neurons
What are the three types of neurons (classification is by # axons/dendrites)?
Unipolar, Bipolar, Multipolar
Unipolar neuron
a single extension branching in two directions, forming a receptive pole and an output zone
What is the place on a unipolar neuron that recieves signals called?
receptive pole
What is the place on a unipolar neuron that sends signals called?
output zone
What is the advantage of unipolar neurons?
Can send signals the fastest (ex: pain information)
What is the disadvantage of unipolar neurons?
Can only take one input
How many axons and dendrites do bipolar neurons have?
one axon, one dendrite
What kind of information do bipolar neurons facilitate?
sensory information, often visual
How many axons and dendrites do multipolar neurons have?
one axon, many dendrites
What is the most common type of neuron (unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar)?
multipolar
What is the advantage of multipolar neurons?
Can accept and comprehend multiple inputs
What is the disadvantage of multipolar neurons?
slowest
What are the 4 functional zones of a neuron?
Input zone, Integration zone, Conduction zone, Output zone
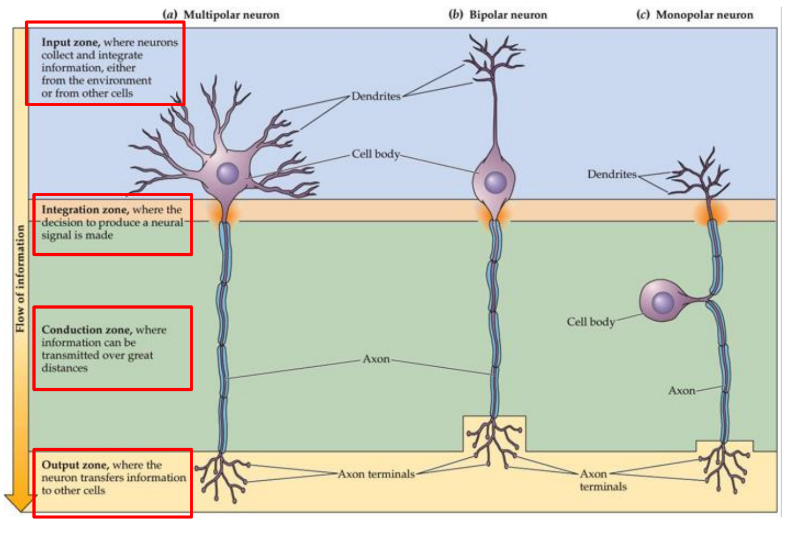
Input zone
neurons collect and integrate info
Integration zone
the decision to produce a neural signal is made, also decides which signal gets through
Conduction zone
where information can be transmitted over great distances
Output zone
where the neuron transfers information to other cells
What are the two kinds of brain cells?
Neurons and Glia/Glial cells
What are the three kinds of neurons? (classified by basic functions)
Sensory/Afferent, Motor/Efferent, and Interneurons
What is the function of sensory/afferent neurons?
Respond to environment (light, odor, touch), carries information to the brain, mostly bipolar neurons
remember: afferent = towards the brain
What is the function of motor/efferent neurons?
communicate with/signal muscles and glands, carries information away from the brain
remember: efferent = away from the brain
What is the function of interneurons?
integration - processes sensory impulses, then sends them to motor neurons
What kind of neuron are the most common (sensory/afferent, motor/efferent, interneurons)?
Interneurons
What is the basic function of glial cells, and what are the four kinds?
basic function: support the brain
four kinds: astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia
What is the function of the astrocyte?
structural support for neurons
provides blood-brain barrier
regulates composition of the extracellular space
provides nutrients to neuron
What common condition do astrocytes help cure?
headaches - astrocytes clears out any unwanted substances in the head
What is the most common type of glial cell?
astrocytes
A 36-year-old engineer at TI developed incoordination of left arm and tendency to fall to his left, along with headaches. What’s wrong with him?
Astrocytoma (cancer of the astrocytes, most common form of brain cancer)
Rolf is a 15-month-old boy whose astrocytes filled with GFAP. What is his diagnosis?
Alexander disease - astrocytes fill with GFAP (cytoskeleton fluid in glial cells)
What is the function of oligodendrocytes?
Make myelin, wrap axons with myelin sheaths inside brain and spinal cord
What are Nodes of Ranvier and how are they formed?
Nodes of Ranvier - gaps in the myelin where the axon membrane is exposed
Formed at the place where two oligodendrocytes meet
What is Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
Oligodendrocyte injury from autoimmune attacks
multiple attacks over several years/decades, over time the brain loses the ability to recover
What is this condition:
Oligodendrocyte injury from autoimmune attacks that occur over a long period of time
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
How is Multiple Sclerosis treated?
immunosuppressants
What is the function of microglia?
Cells move around, clean up debri from dying neurons and glia
What is the function of ependymal cells?
Line ventricles, secrete and absorb cerebral spinal fluid
What is AIDS Encephalitis?
neurons are accidentally killed while microglia try to get rid of neurotoxins
brain damage in pateint from the neurotoxins glutamate and nitric oxide from viral-activated microglia
(HIV/AIDS encephalitis virus activates viral-activated microglia → microglia produce neurotoxins → damages the brain)
What is this condition:
neurons are accidentally killed while microglia try to get rid of neurotoxins
AIDS Encephalitis
Why do more dendrites grow?
When you learn things, you get more dendrites
More dendrites = More surface area
What are the different shapes of neurons?
Double bouquet cell
Chandelier cell
Spiny stellate cell
Pyramidal cell
Large basket cell
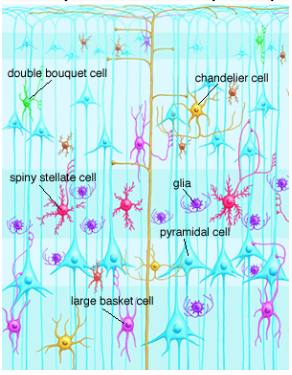
Do dendritic spines change?
Yes - they have neural plasticity, and their number/structure are rapidly altered by experience
What is a Synapse?
Gap between two neurons
What is the function of the mitochondria in a neuron?
axonal and dendritic development/regeneration, growth
How does a signal travel across the synapse?
Axon contains vesicles with neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters travel from the axon to the dendrite
Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the post-synaptic membrane, triggering an action potential in the recieving dendrite
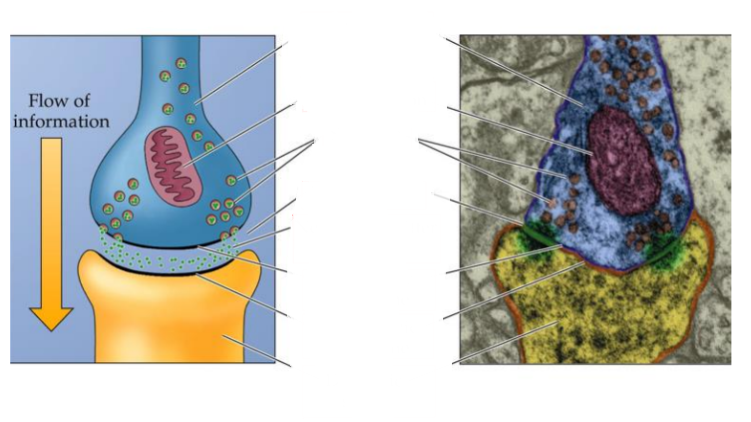
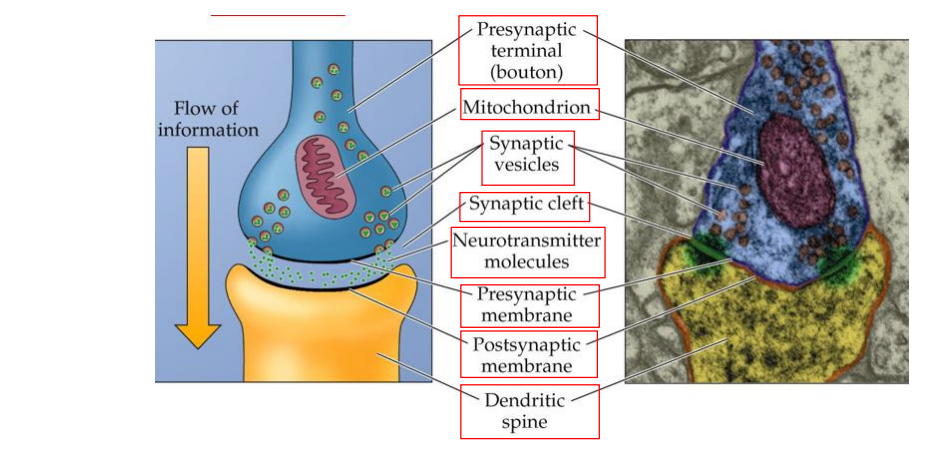
What are the parts of a synapse?
Presynaptic terminal (bouton)
Mitochondrion
Synaptic vesicles
Synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitter molecules
Presynaptic membrane
Postsynaptic membrane
Dendritic spine
What is the Central Nervous System (CNS) comprised of? What is the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) comprised of?
CNS - brain and spinal cord
PNS - cranial nerves and spinal nerves
What is the function of the autonomic nervous system?
Controls autonomous functions, involuntary
What are the divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic nervous system
both systems oppose each other
What does the Sympathetic Nervous System do?
Prepares the body for action (fight-or-flight)
What does the paraysmpathetic nervous system do?
rests and digests, calms the body down
What parts of the CNS activates the parasympathetic nervous system?
Brainstem - Preganglionic neurons in nuclei of III, IV, IX, and X cranial nerves
Spinal cord - Preganglionic neurons in S2-S4
What parts of the CNS activates the sympathetic nervous system?
ONLY SPINAL CORD
Preganglionic neurons in T1-T12, and L1-L2
What are the three planes?
Horizontal, Sagittal, Coronal
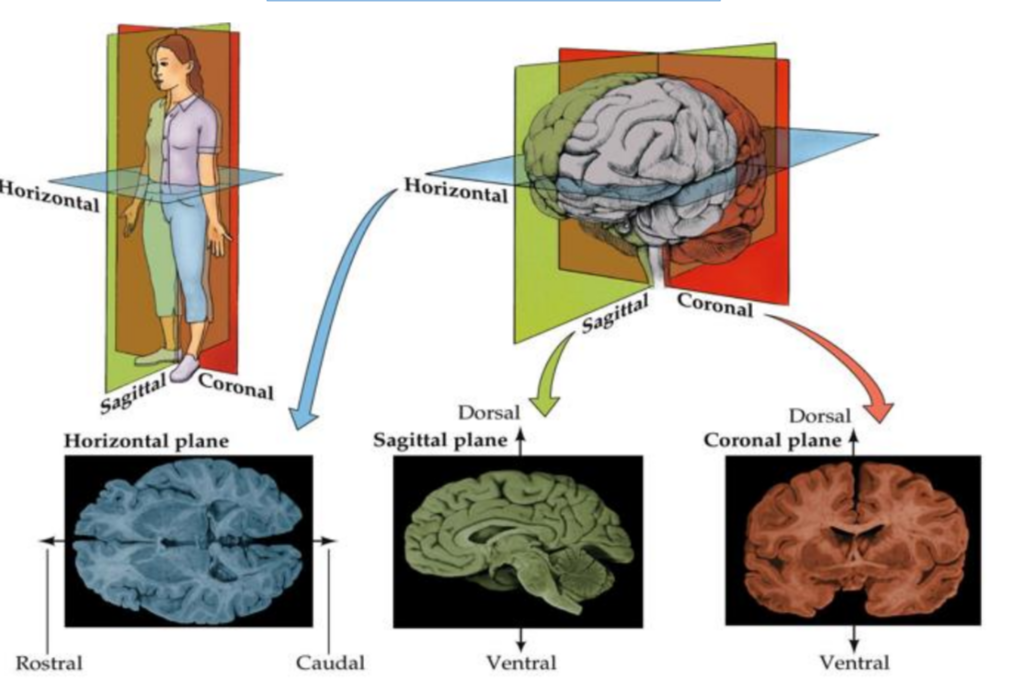
How does the coronal plane separate a brain?
Front to back - resembles a butterfly
How does the sagittal plane separate a brain?
side to side - midsagittal slices down the midline
How does the horizontal plane separate a brain?
separates brain from top to bottom
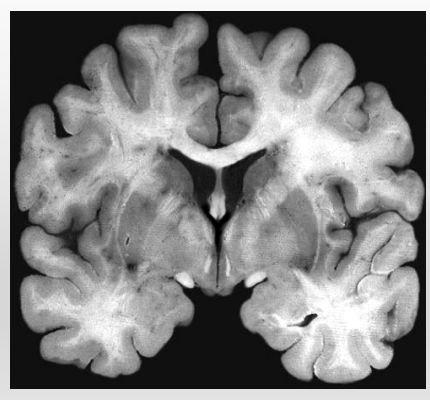
What plane is this?
coronal
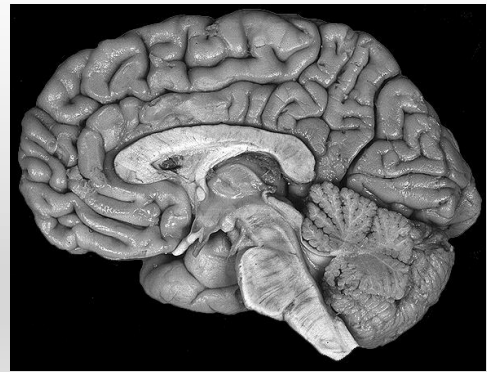
What plane is this?
sagittal
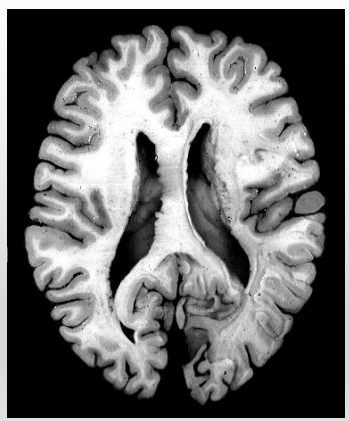
What plane is this?
horizontal
Medial
Towards the middle/midline
Ipsilateral
Same side
Anterior
Head end
Proximal
Near center
Dorsal
toward the back
Lateral
toward the side
Contralateral
opposite side
Posterior
tail end
Distal
toward periphery
Ventral
toward the belly
Afferent
carries impulses into a region of interest (sensory)
Efferent
carries impulses away from a region of interest (motor)
What is white matter composed of?
Axon bundles
Why is white matter white?
White matter is made of axon bundles, and the myelin sheaths that cover the axons are white.
What is gray matter made of?
clusters of neuron cell bodies
Why is gray matter gray?
It’s composed of clusters of neuron cell bodies, which are dark gray in appearance.
True or false: Our brain was built in layers due to evolution.
True
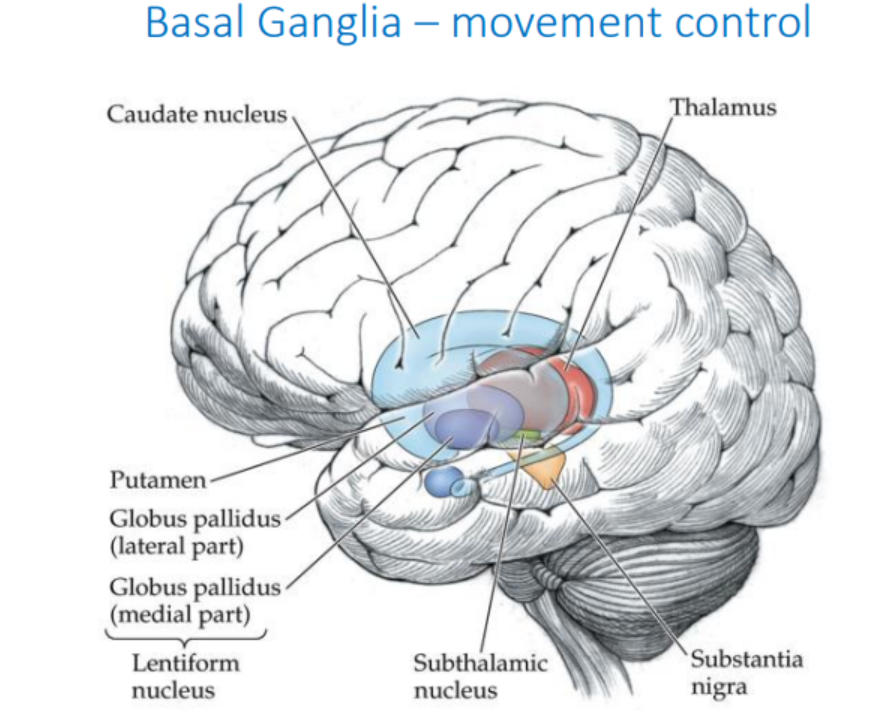
What is the function of the basal ganglia?
movement control
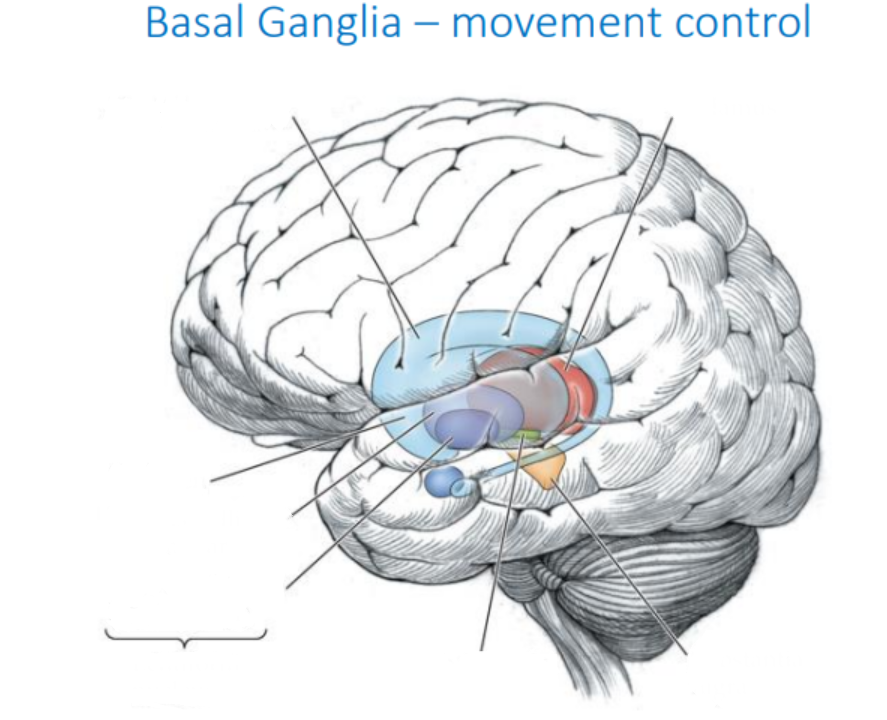
Identify the parts of the basal ganglia. (won’t be tested, but good to know)
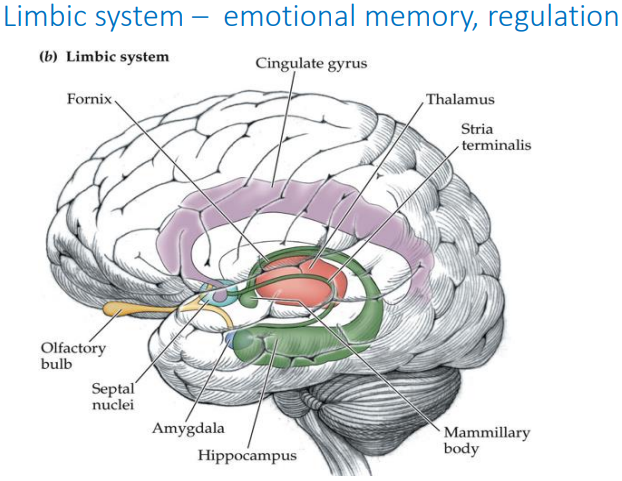
What is the function of the limbic system?
Emotional memory/regulation
parts of the limbic system diagram (won’t be tested, but good to know
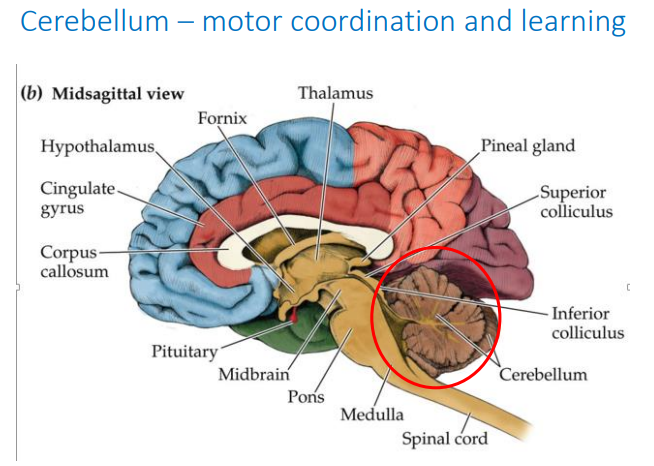
Function of the cerebellum
Motor coordination and learning
Identify the parts of the cerebellum. (won’t be tested, but good to know)
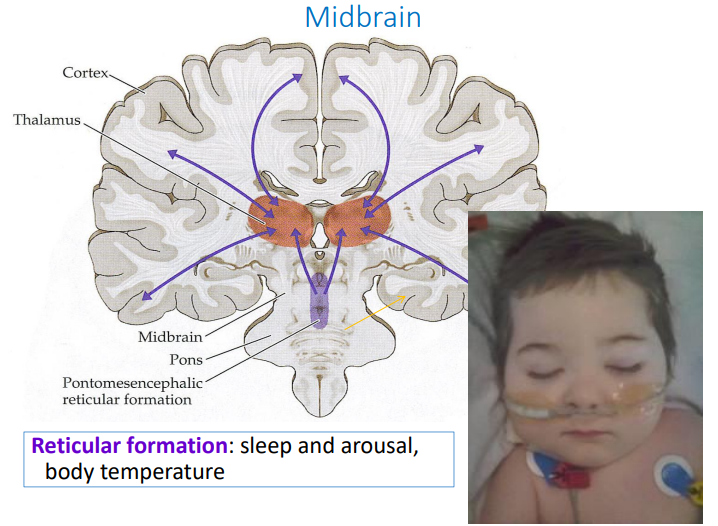
Function of the reticular formation
sleep and arousal, body temperature
damage/abnormalities can cause coma
Diencephalon
Intermediate between brainstem and
cortex
“First brain” involved in the
nervous system
Structures involved in the diencephalon
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Mammilary bodies
Identify the parts of the midbrain (will not be tested, but good to know)
What are meninges?
brain wrappings