Biol-1009 Major Lab Quiz #1 Review
1/38
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Scientific Method
Process in which scientists utilize in order to explain and gain knowledge about the physical and natural world.
Steps of the scientific method:
Observations
Hypothesis
Prediction
Test
Results
Results can support or not support hypothesis and can be revised/remade
Conclusions
Can lead to refinement of an existing hypothesis
Comprehensive model of Scientific Processes:
Exploration and Discovery: Aims to fill a knowledge gap in the field
How the scientific method aims to explore causation in activities and processes in the natural world
Conducted via making observations, asking ?’s, or being inspired to meet medical needs, or inspiration from other literature
Comprehensive model of Scientific Processes:
Forming and Testing Hypotheses
Determines if there’s support or not for a hypothesis
Hypotheses = tentative answer to tentative question that explains natural processes in the world
May be revised if not supported
Comprehensive model of Scientific Processes:
Community Analysis and Feedback
Allows for testing and review of studies to determine validity
Was the study conducted fairly? Reasonable conclusions based on evidence?
Society’s input = important
Because everyone can contribute ideas to science to strengthen knowledge and conclusions
Comprehensive model of Scientific Processes:
Societal Benefits and Outcomes
Studies conducted for solving problems or meet needs in society
Via: Finding new info, developing technology, or furthering knowledge
Science answers questions for society w/empirical backing
Hypothesis
Tentative answer to tentative question in which it explains natural processes and activities
Must be testable, predictable, and empirically supported w/given info
Can NEVER BE PROVEN, only supported or not supported
Independent and Dependent Variable
1. Variable manipulated by experimenter
2. Variable of interest that is measured by experimenter. Measured to determine causation due to IV
Control Group
Individuals who are not exposed to treatment and may go undergo placebo
Placebo
A “false” treatment is given to see if the idea of having an effect will make it happen
Control
Variables that remain the same throughout
Positive and Negative Control
Positive control = Expect an effect ex: Bleach in CURE
Negative control = No effect ex: Water in CURE
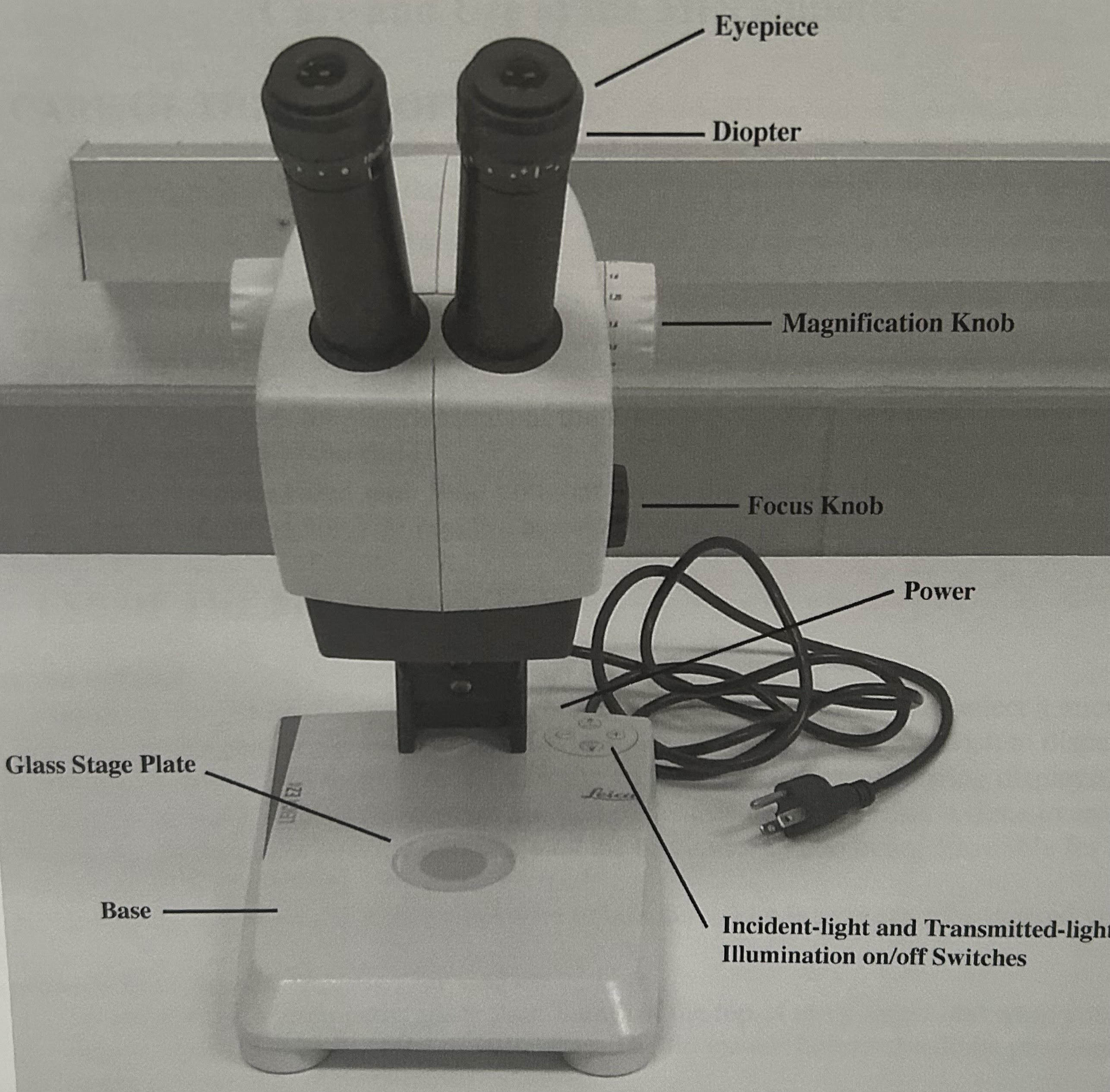
Dissecting Microscope
Low magnification microscope
Can see 3D object with higher detail using light from above
Compound Microscope AKA (Light Microscope)
Lenses let you see enlarged image of species
Magnification improves resolution, making the image sharper

Eyepiece
Contains ocular lens
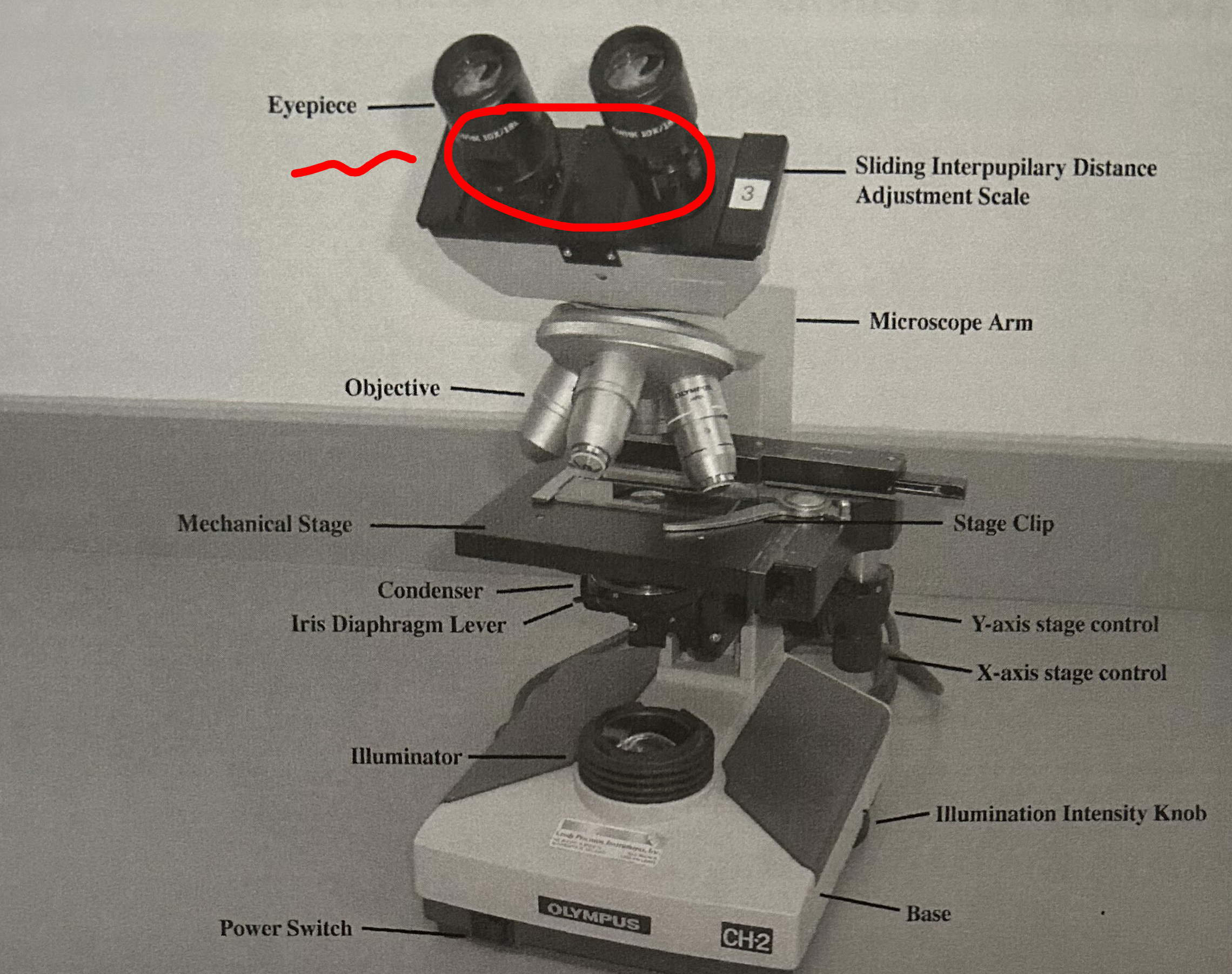
Pointer
Located in ocular lens
Indicates location of object

Sliding interpupillary distance adjustment scale
Adjusts distance between ocular lenses so it coincides w/distances between pupils
Ensures you only see one view when you look through eyepieces
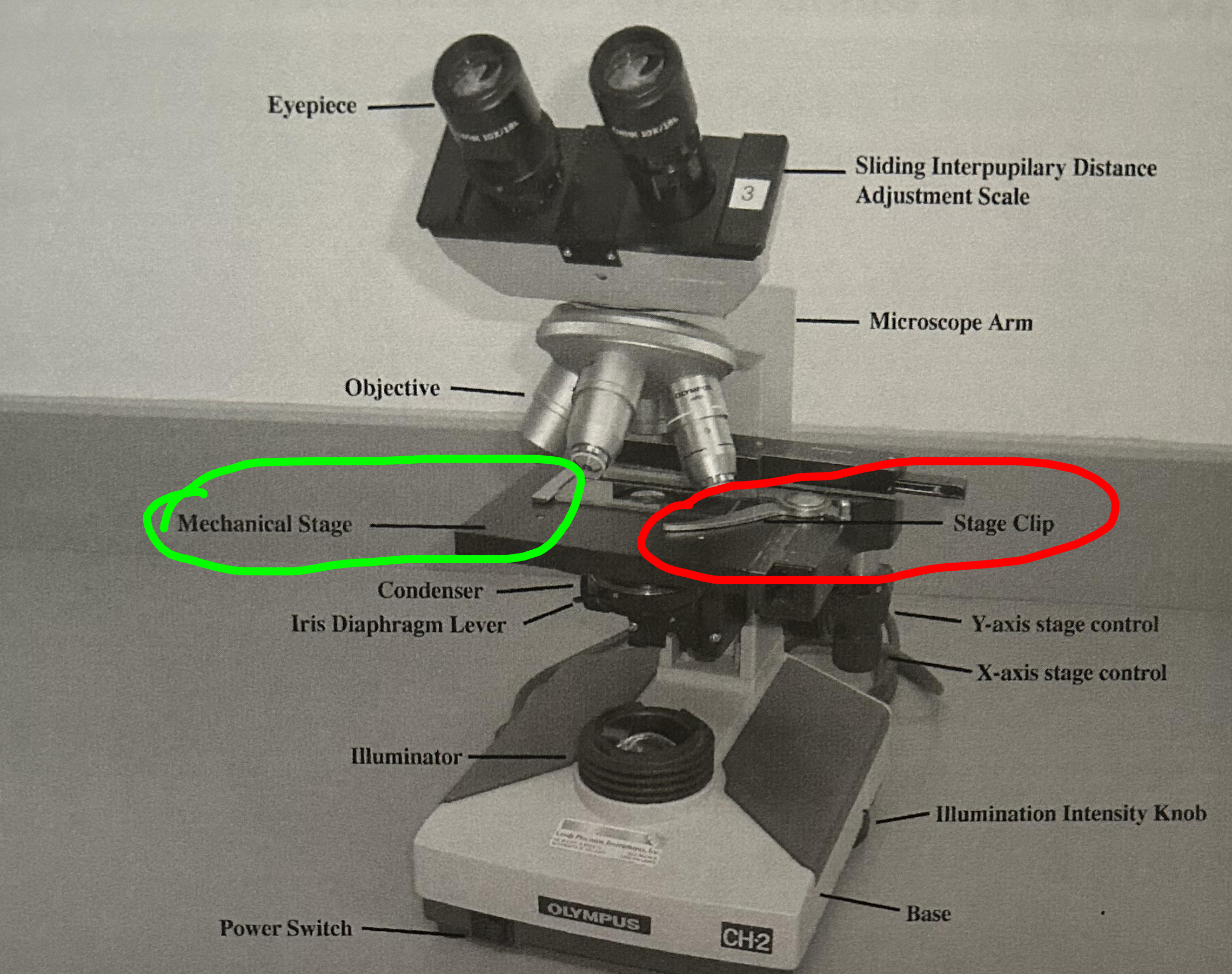
Mechanical stage and stage clip:
Holds the slide in place
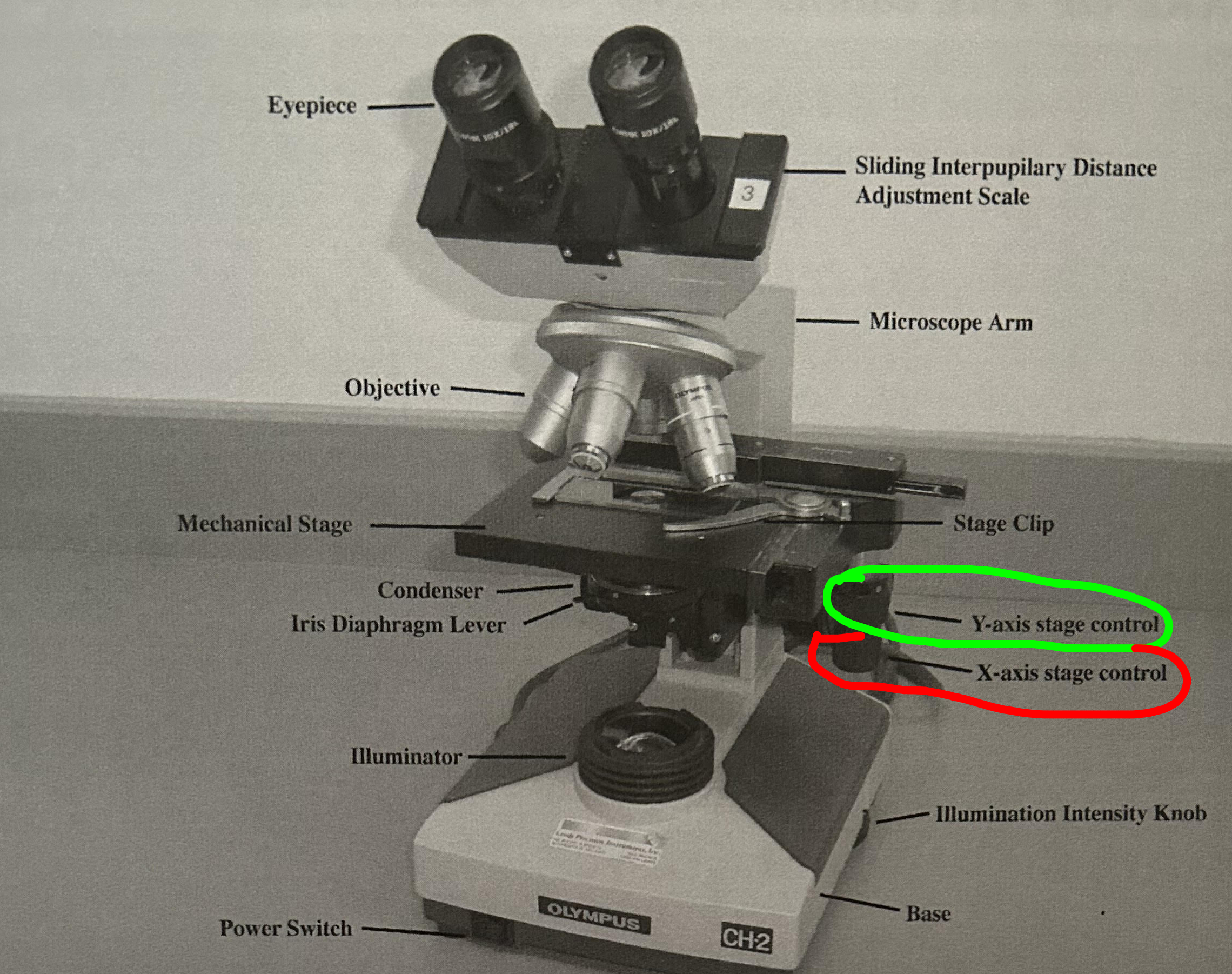
X & Y Stage Controls
Knobs that control horizontal and vertical movement of mechanical stage
Y is on top of the X
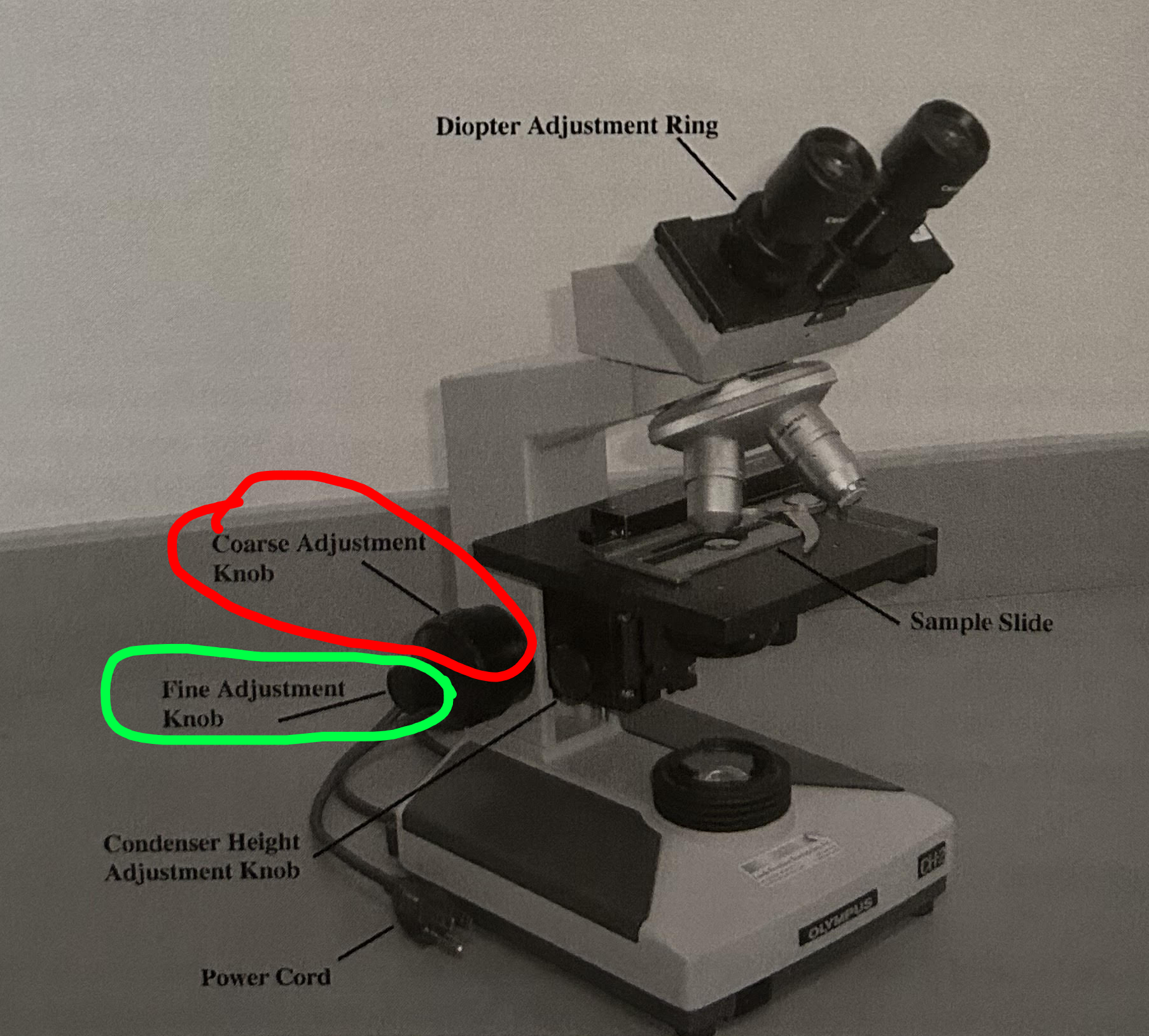
Coarse and Fine Adjustment Knobs:
Sharpen image of specimen
Coarse= Big one
Fine = Small one
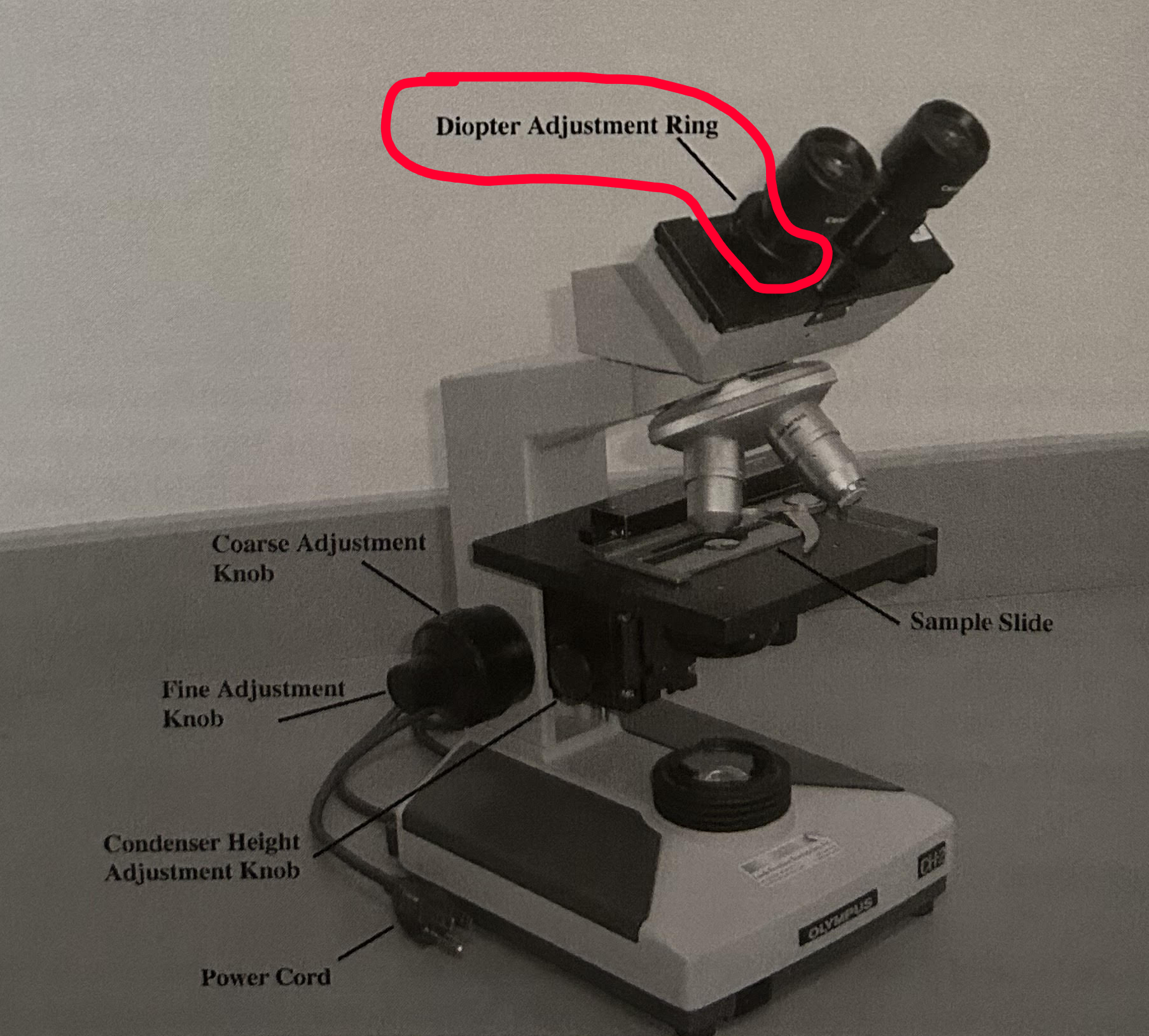
Diopter Adjustment Ring
Compensates for differences in your eye strength
Located on left eye piece

Illuminator
Light Source

Illumination intensity knob:
Regulates amount of light transmitted from illuminator

Iris diaphragm lever
Regulates amount of light that reaches specimen
Right under condenser

Condenser
Focuses light through specimen
Located under microscope slide typically
Better to focus the edges of FOV
May need to be rotated slightly downward
Objective and ocular lenses to total magnification
Objective x ocular = total magnification
AKA: (Obj.) Magnification strength x (Ocul.) 10 = total magnification
Ex: Objective lens 40x * 10 = 400x total magnif.
Diameter of field: Field of View
Circular illuminated area seen when you look through eyepiece of microscope
Negative relationship w/magnification
Center of Field
Objective lenses region where objects are in sharp focus
Fixed at each magnification
Depth of field
Vertical zone of center of focus
Not sharp in focus, but is still visible
Negative relationship w/magnification
Division per field, mm per field, and μm per field relationship
10:1:1000 ratio
Ex: Div.OF: 45. mm: 4.5 μm 4500
Enzymes
Organic catalyst that speeds rate of reaction
Via: Enzyme substrate complex
Enzyme and substrates are available
Substrate binds to enzyme’s active site
Substrate converted to products
Product released, and enzyme is unchanged and can be used again
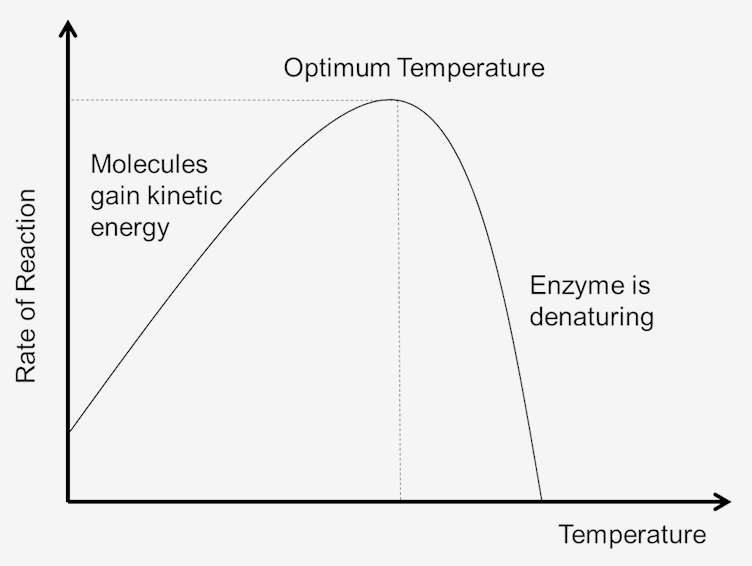
Temperature on enzymatic activity
There is an optimum temperature for each enzyme’s optimum activity
Going above it = chemical bonds of enzyme becomes denatured hence reaction is quickly reduced
Going below = reactants moving w/less kinetic energy hence not enough energy for reaction and rate of reaction is reduced
Decreasing temperature more gradual, increasing past optimum is a sudden drop
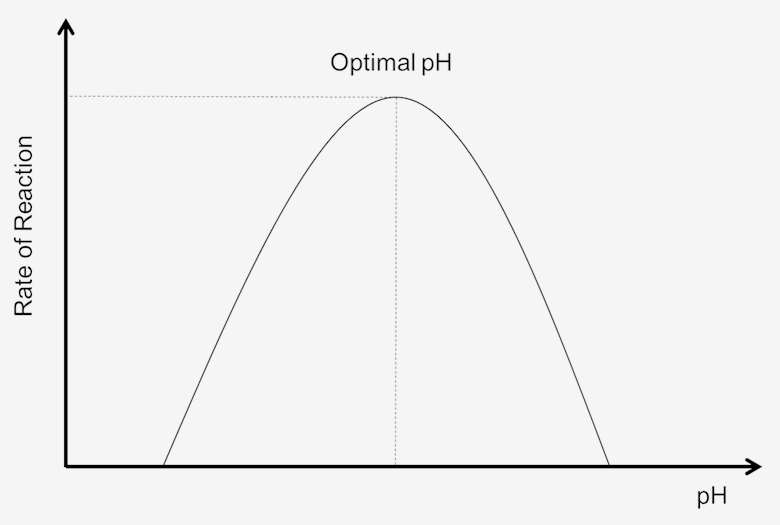
pH on enzymatic activity
Optimum pH where enzyme has optimal activity
Reduced and excess pH = disrupted chemical bonds in enzyme
Rate of reaction is inhibited and enzyme is less efficient
Bell curve
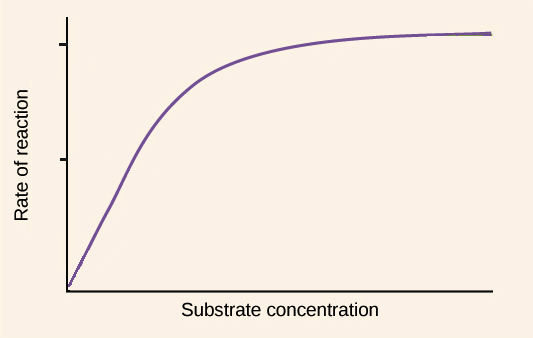
Substrate concentration on enzymatic activity
Substrate concentration increases enzymatic activity as more active sites get filled,
However all active sites will eventually be filled
Enzyme will be the limiting reactant at that point hence rate of reaction does not change after that point
Graph will top up at that point
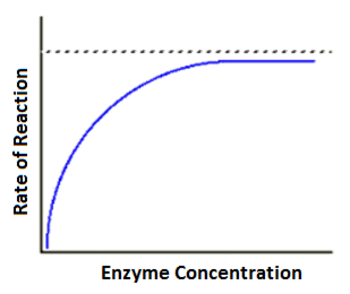
Enzyme concentration on enzymatic activity
Enzyme concentration increase enzymatic activity because more active sites are available for catalysis UNTIL
Substrate concentration will be limiting because there will be too many active sites to fill
Substrate = Limiting reactant
Graph tops up at that point as well
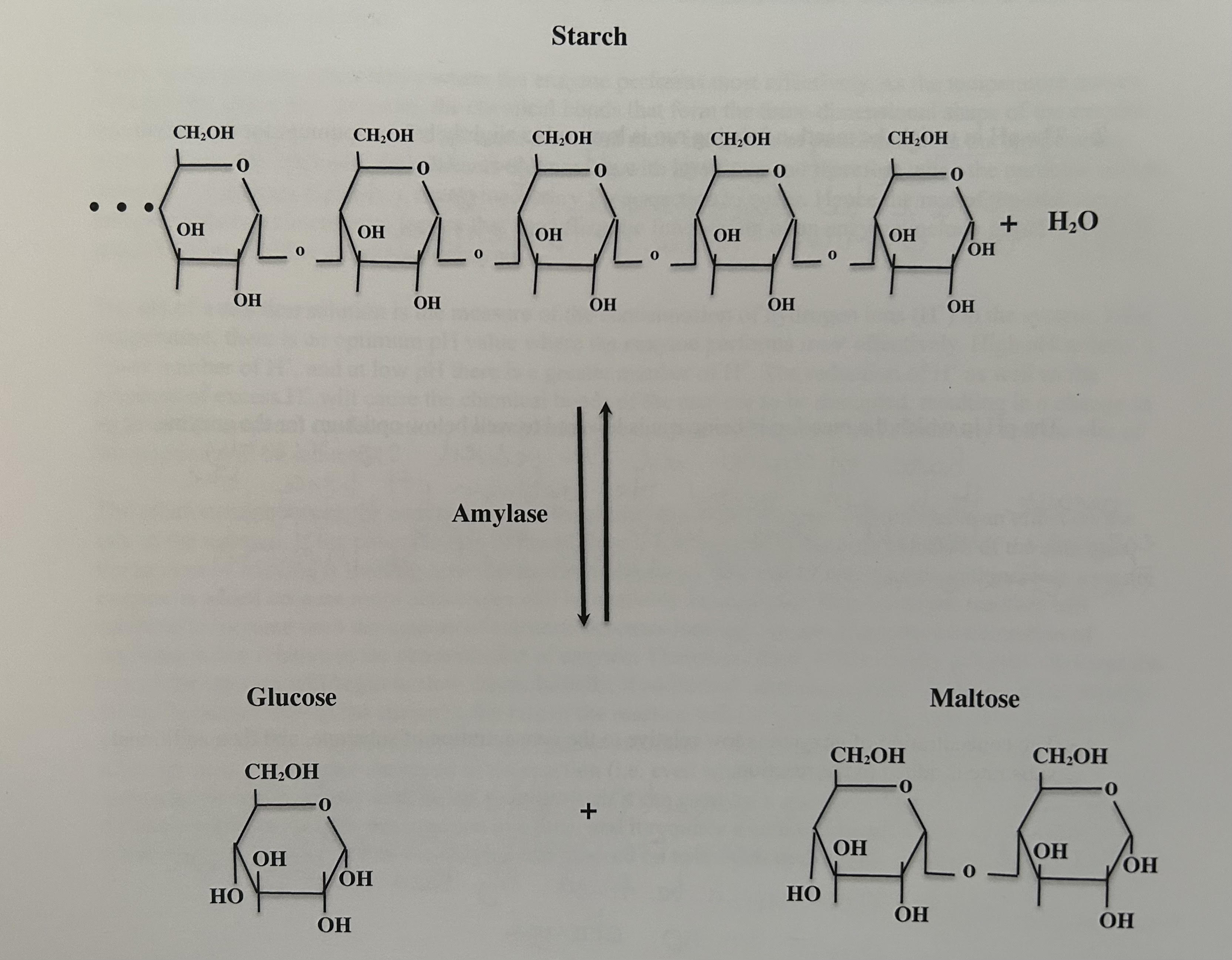
Starch Hydrolysis Reaction
Addition of water to break down starch
Catalyzed by amylase enzyme
Forms products: Glucose and maltose
Spectrophotometer
Detects amount of light absorbed by amber compound formed by reduction agents glucose and maltose
Displays absorbance value proportional to concentration of colored product
Is also proportional to concentration of glucose/maltose
Use of blanks
Ensures absorbance value in spectrometer is only tied to the sample material and not components of solution
Accuracy and reduces contamination for experiment
Detection Reagent
Glucose and maltose reduce it to 3-amino 5-nitrosalyicylic acid
An amber color compound, and intensity of color is directly proportional to quantity of glucose and maltose
Darker = higher concentration