Soil properties and its pollution
1/58
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Soil definition (Geologic)
Loose surface of the earth as distinguished from solid bedrock. Plant life support not required.
Soil definition (Traditional)
Material that nourishes and supports growing plants, including rocks, water, snow, and air.
Soil definition (Component)
Mixture of mineral matter (45%), organic matter (5%), water (25%), and air (25%). Example: Loam soil.
Basic Soil Properties (Physical)
Texture, structure, bulk density, moisture, infiltration, porosity.
Basic Soil Properties (Chemical)
Nutrient content, salinity, pH, organic matter, mineral content.
Basic Soil Properties (Biological)
Microbial activity, biomass, biodiversity, biological activity.
Soil Texture
Relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay. Determines feel: gritty (sand), soft/silky (silt), sticky (clay).
Sand Characteristics
Gritty feel, 2:0.05,particles visible to naked eye, low water/nutrient retention, high drainage.
Silt Characteristics
Soft/floury feel, medium particle size (0.002–0.05 mm), moderate water/nutrient retention.
Clay Characteristics
Sticky feel, smallest particles (<0.002 mm), high surface area (10,000x sand), high water/nutrient retention.
Hydrometer Method
Lab technique to determine soil texture. Measures relative particle density in liquid after settling.
Hydrometer Formulas
% Clay = (R1/Wt soil) × 100
% Silt = (Rsilt”R2-R1”/Wt soil) × 100
%Sand = 100 - (%clay+%silt)
Soil Aggregates
Secondary soil units held by organic substances, clays, etc. Stability indicates OM content, biological activity, and erosion resistance.
Soil Horizons (A)
Topsoil: high organic matter, biological activity, N/P content, granular structure.
Soil Horizons (B)
Subsoil: silicate clays, iron/aluminum oxides, less OM, sub
Soil Horizons (C)
Parent material layer, minimally weathered.
Nitrogen Deficiency Symptoms
Yellowing of lower leaves (inverted “V” in corn), stunted growth, small ears.
Phosphorus Deficiency Symptoms
Bluish
Potassium Deficiency Symptoms
Brown leaf margins (corn), yellowing lower leaves (soybeans), striped appearance.
Soil Erosion Definition
Process where soil is moved from its original location by wind, water, or human activity.
Sheet Erosion
Uniform removal of topsoil by wind/water.
Rill Erosion
Small channels formed by surface water flow.
Gully Erosion
Severe erosion with deep channels due to intense rainfall.
Splash Erosion
Caused by raindrop impact disrupting soil structure.
Tunnel Erosion
Subsoil washing away beneath stable topsoil, creating hollows.
Causes of Soil Erosion
Overgrazing, deforestation, poor farming practices, slope length, low vegetation cover.
Heavy Metals (Toxic)
Pb, Cd, Hg, As. Harmful even in small amounts.
Heavy Metals (Essential)
Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Zn. Required in trace amounts.
Bioremediation
Using plants/microorganisms to clean polluted soils. Example: Phytoremediation for heavy metals.
Phytoextraction
Plant
Effects of Soil Pollution
Reduced fertility, loss of nutrients, increased erosion, toxic dust, ecosystem imbalance.
Nitrogen Cycle Processes
Nitrification (NH4 → NO3), Denitrification (NO3 → N2 gas), Leaching, Volatilization (NH3 loss).
Control of Soil Pollution
Reduce chemical fertilizers/pesticides, recycle materials, afforestation, awareness programs.
Soil Salinity Impact
High salinity makes soil unfit for cultivation, often due to excessive fertilizers.
Organic Matter Role
Improves soil structure, water retention, nutrient cycling, and microbial activity.
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
Soil’s ability to hold cations (e.g., Ca, Mg, K). Higher CEC = higher nutrient retention.
Ideal Soil Balance
45% minerals, 25% water, 25% air, 5% organic matter.
Denitrification Conditions
Occurs in waterlogged, anaerobic soils. Converts NO3 to N2 gas.
Volatilization Triggers
High temperatures, windy conditions, surface
Soil Pollution Sources
Industrial waste, agrochemicals, oil spills, nuclear waste, deforestation.
Degrees of Erosion
Slight (surface loss), Moderate (surface removed), Severe (subsoil exposed), Extreme (deep subsurface loss).
Calcium Role in Plants
Strengthens cell walls, promotes root growth, improves soil acidity.
Magnesium Role in Plants
Key in chlorophyll production, activates enzymes, aids phosphorus mobility.
Zinc Deficiency Symptoms
Bleached leaf bands (corn), stunted growth, high pH exacerbates.
Iron Deficiency Symptoms
Interveinal chlorosis in young leaves, common in high
Bulk Density
Soil weight per volume. High density indicates compaction, poor porosity.
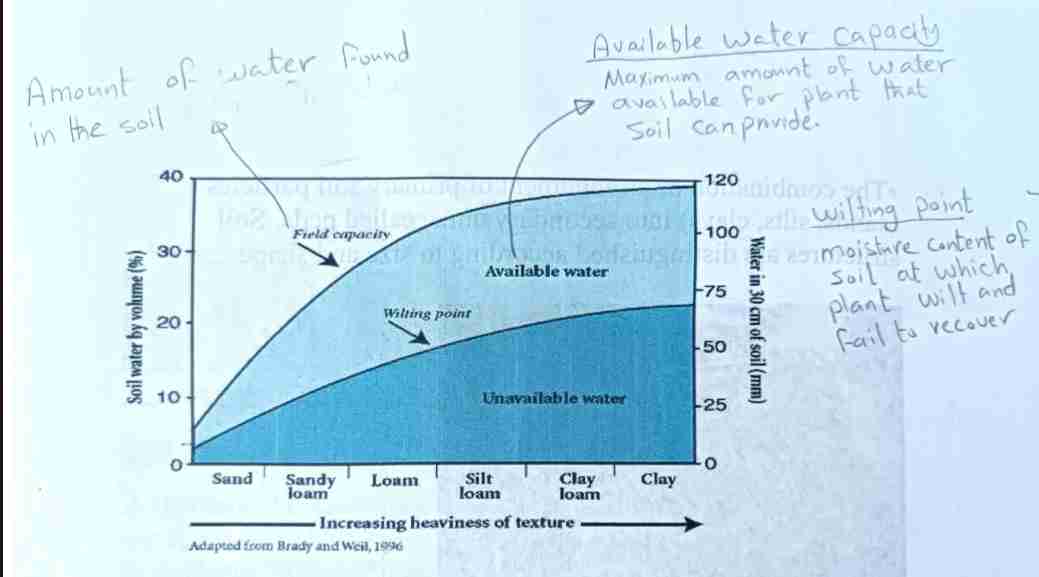
Field Capacity
Maximum water soil retains after drainage. Wilting point = moisture level where plants cannot recover.
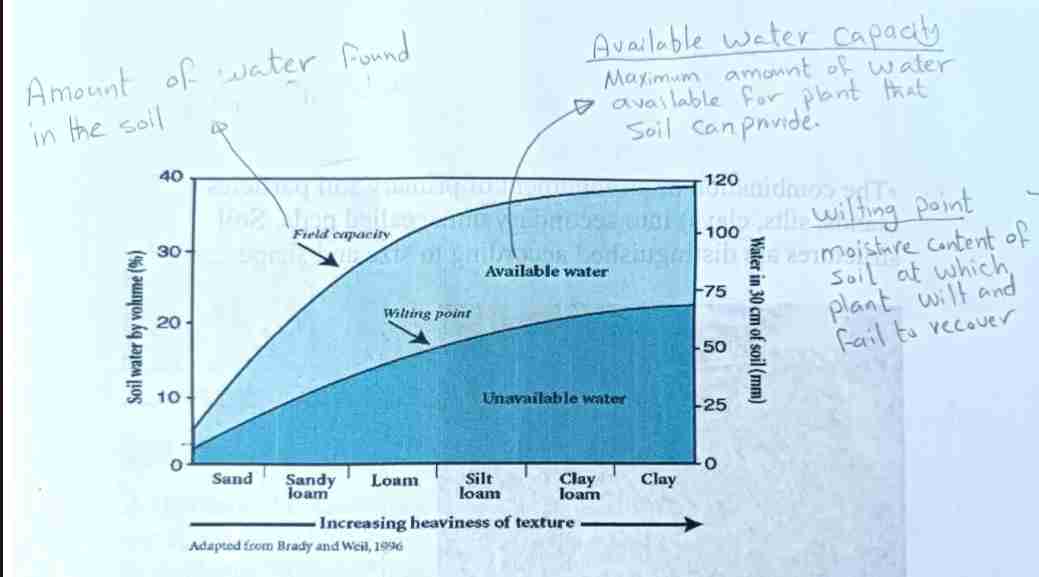
Available Water Capacity
Maximum amount of water available for plant that soil can provide
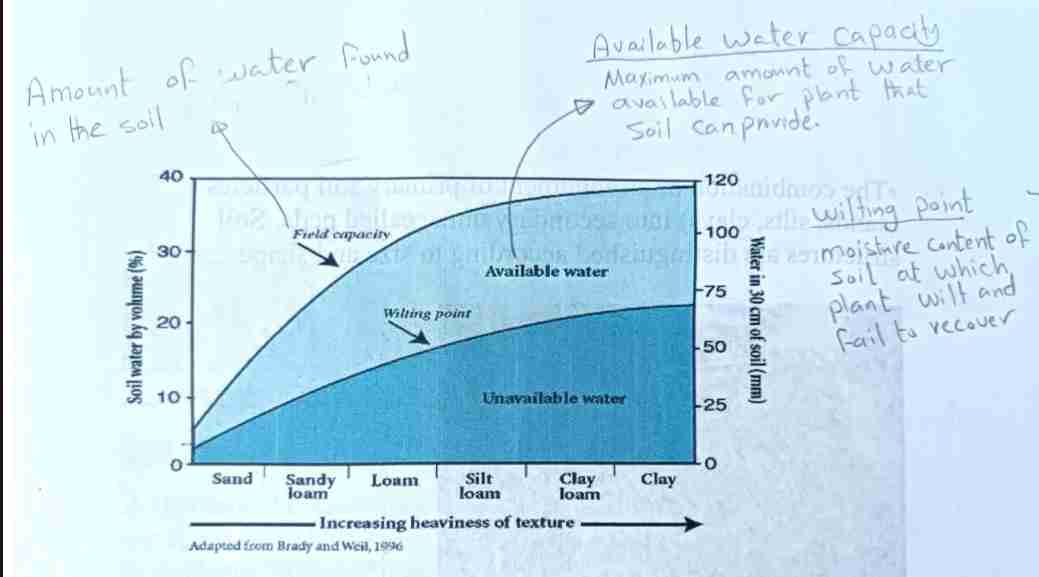
Wilting point
Moisture of soil soil at which plant wilt and failed to recover
Soil Pollution Human Health Effects
Kidney damage (Hg, Pb), liver changes (solvents), cancer risks (PAHs, pesticides).
Soil Conservation Methods
Contour farming, windbreaks, crop rotation, stabilizing roads with barriers.
Mycorrhizal Fungi Role
Symbiotic fungi aiding nutrient uptake, used in heavy metal remediation.
Sodic Soils
High sodium content displaces Ca/Mg, reduces fertility and structure.
Soil Pollution by Agrochemicals
Excess fertilizers alter pH, pesticides persist in food chain.
Soil Profile
Vertical section showing horizons (A, B, C). Indicates soil development over time.
Soil Texture Triangle
Classifies soil types based on sand, silt, clay percentages.
Humus
Decomposed organic matter enhancing soil fertility and structure.
Lateritic Soil Identification
High in iron oxides, reddish color, low fertility, suitable for crops like cassava.
Soil pH and Phosphorus
Availability highest near neutral pH (6.5–7.0). Fixed by Fe/Al (low pH) or Ca (high pH).