Chemistry_ Term 2 (2023)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics include: Matter and Material; Kinetic Molecular theory; The atom; The Periodic Table; Bonding
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
2
New cards
Properties of matter (SCaM BoreDoMM)
Strength.
Conductivity.
Malleability and ductility.
Brittleness.
Density.
Magnetism and non-magnetism.
Melting and boiling points.
Conductivity.
Malleability and ductility.
Brittleness.
Density.
Magnetism and non-magnetism.
Melting and boiling points.
3
New cards
Mixtures
Formed when two or more substances are combined and mixed physically, without chemically bonding
4
New cards
Properties of mixtures
Composition can vary and consist of two or more elements or compounds.
Properties are the same of those of the constituent substances.
Constituents can be separated by physical methods.
Properties are the same of those of the constituent substances.
Constituents can be separated by physical methods.
5
New cards
Homogenous mixtures
Have the same constant composition throughout the mixture.
- substances in the mixture can no longer be distinguished from each other and the mixture looks the same throughout.
- substances in the mixture can no longer be distinguished from each other and the mixture looks the same throughout.
6
New cards
Heterogenous mixtures
Non-uniform mixture of substances, of which the particles of the substances in the mixture remain separate.
- the particles are not evenly distributed and sometimes occur in more than one state.
- the particles are not evenly distributed and sometimes occur in more than one state.
7
New cards
Pure substances
Consist of one type of substance only.
8
New cards
Elements
Pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical methods.
9
New cards
Properties of elements
Consists of one kinds of atom.
Properties are unique.
Constituents cannot be separated by physical/chemical methods.
Properties are unique.
Constituents cannot be separated by physical/chemical methods.
10
New cards
Compounds
Pure substances made of the atoms of elements that are chemically bonded in fixed ratios.
11
New cards
Properties of compounds
Composition is constant.
Properties differ from those of the constituent elements.
Constituents can be separated by chemical methods.
Properties differ from those of the constituent elements.
Constituents can be separated by chemical methods.
12
New cards
Brownian motion
The random movement of microscopic particles suspended in a liquid or gas, caused by collisions between these particles and the molecules of the liquid or gas.
13
New cards
Properties of a solid
Not easily compressible.
Particles are bonded in a fixed position.
Strong forces between the particles.
Small spaces between the particles.
Particles vibrate in their rest position.
Particles are bonded in a fixed position.
Strong forces between the particles.
Small spaces between the particles.
Particles vibrate in their rest position.
14
New cards
Properties of a liquid
Not easily compressible.
Forces between the particles weaker than in solids.
Spaces between particles are slighter larger than in solids.
Particles move about more vigorously.
Exert pressure in all directions on all sides of the container.
Forces between the particles weaker than in solids.
Spaces between particles are slighter larger than in solids.
Particles move about more vigorously.
Exert pressure in all directions on all sides of the container.
15
New cards
Properties of a gas
Compressible.
Particles are far apart.
Virtually no forces between the particles.
Particles move around at high speed.
Exert pressure as a result of collisions of particles on objects.
Particles are far apart.
Virtually no forces between the particles.
Particles move around at high speed.
Exert pressure as a result of collisions of particles on objects.
16
New cards
Boiling point
Temperature at which the vapour pressure of a substance is equal to atmospheric pressure.
17
New cards
Melting point
Temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of a substance are at equilibrium.
18
New cards
Freezing point
The temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid by the removal of heat.
19
New cards
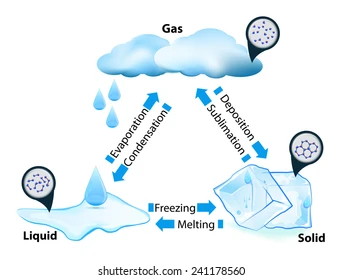
Phase changes
Solid to liquid = melting.
Liquid to solid = freezing.
Liquid to gas = evaporation.
Gas to liquid = condensation.
Solid to gas = sublimation.
Gas to solid = deposition.
Liquid to solid = freezing.
Liquid to gas = evaporation.
Gas to liquid = condensation.
Solid to gas = sublimation.
Gas to solid = deposition.
20
New cards
Kinetic molecular theory
Matter consists of small particles.
The particles are in constant motion.
There are forces of attraction between the particles.
Particles collide and exert pressure.
The particles are in constant motion.
There are forces of attraction between the particles.
Particles collide and exert pressure.
21
New cards
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles making up a substance.
22
New cards
The effect of temperature on the particles in a substanc e
If a substance is heated, the particles gain more energy, move faster and their average kinetic energy increases.
If the particles gain enough energy, they can overcome the intermolecular forces between them and move further apart (change phases).
If the particles gain enough energy, they can overcome the intermolecular forces between them and move further apart (change phases).
23
New cards
Kelvin (K)
SI unit for temperature.
To convert from ℃ to K, add 273,15 to the amount.
To convert from ℃ to K, add 273,15 to the amount.
24
New cards
Latent heat
The energy absorbed or released during a state change.
25
New cards
Cation
A positively charged ion.
Always named first in a compound.
Always named first in a compound.
26
New cards
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
If monatomic , change the end to -ide.
If monatomic , change the end to -ide.
27
New cards
Relative atomic mass
The weighted average of the mass of all the isotopes of an element.
28
New cards
Isotope
Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to differing numbers of electrons.
29
New cards
Orbitals
Region of space around the nucleus where there is a 90% chance of finding an electron.
30
New cards
S-orbitals
Spherical orbitals.
Only one per energy level.
Only one per energy level.
31
New cards
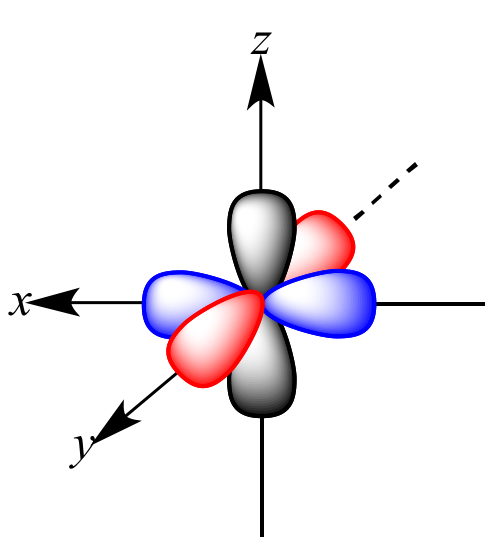
P-orbitals
Dumbbell shaped.
Three per energy level.
Three per energy level.
32
New cards
Aufbau's principle
Electrons occupy orbitals so that the atom's energy is minimized.
33
New cards
Hund's rule
When filling sub-levels of p-orbitals, electrons are placed in individual orbitals before they are paired up.
34
New cards
Pauli's Exclusion principle
Only two electrons can occupy an orbital and these electrons must spin in opposite directions.
35
New cards
Core electrons
Electrons that fill the inner energy level.
36
New cards
Valence electrons
The electrons that occupy the outermost energy level of an atom.
37
New cards
Valency
The number of electrons that need to be added or removed in order for an element to reach noble gas configuration.
- the number of bonds that an atom can form.
- the number of bonds that an atom can form.
38
New cards
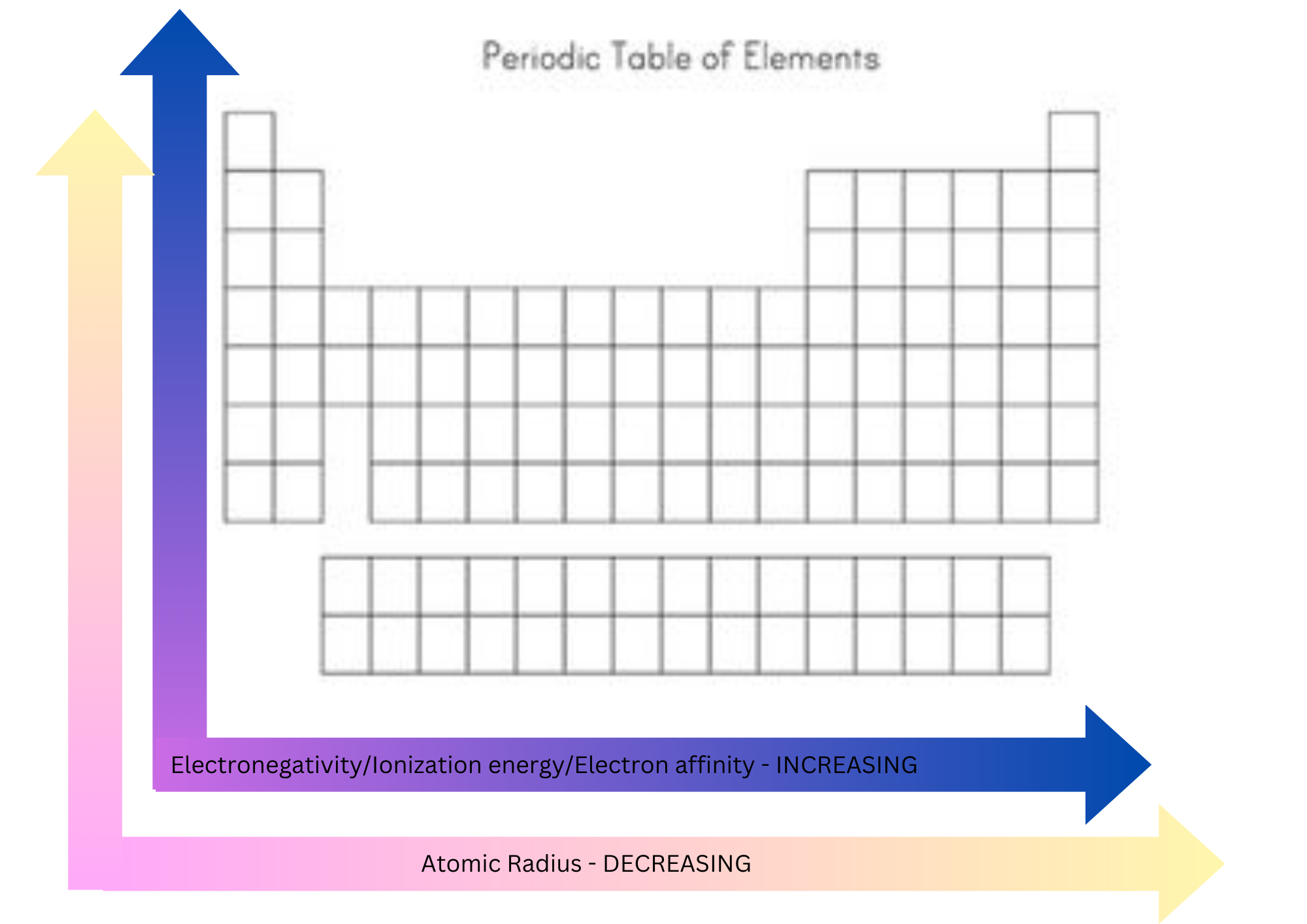
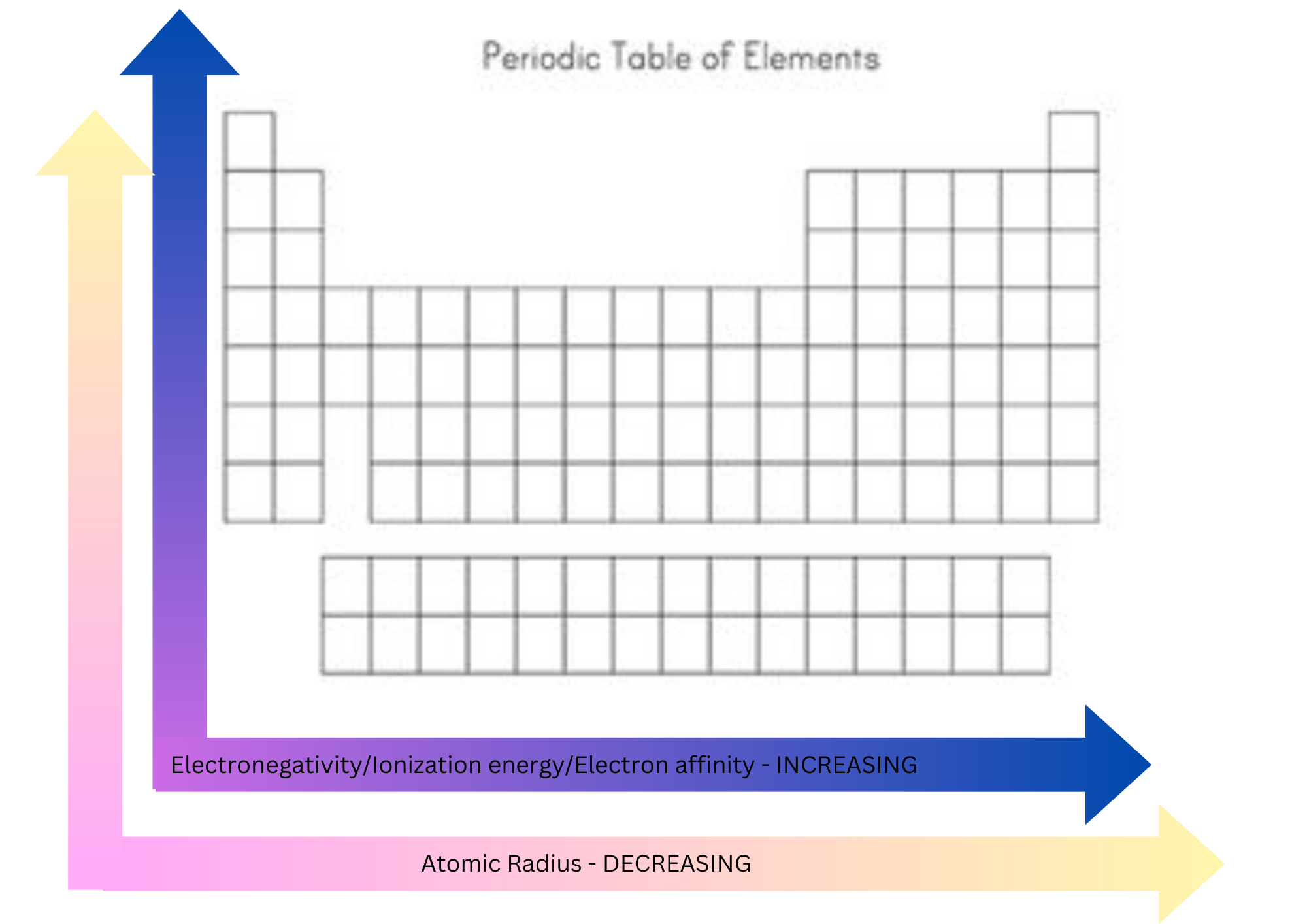
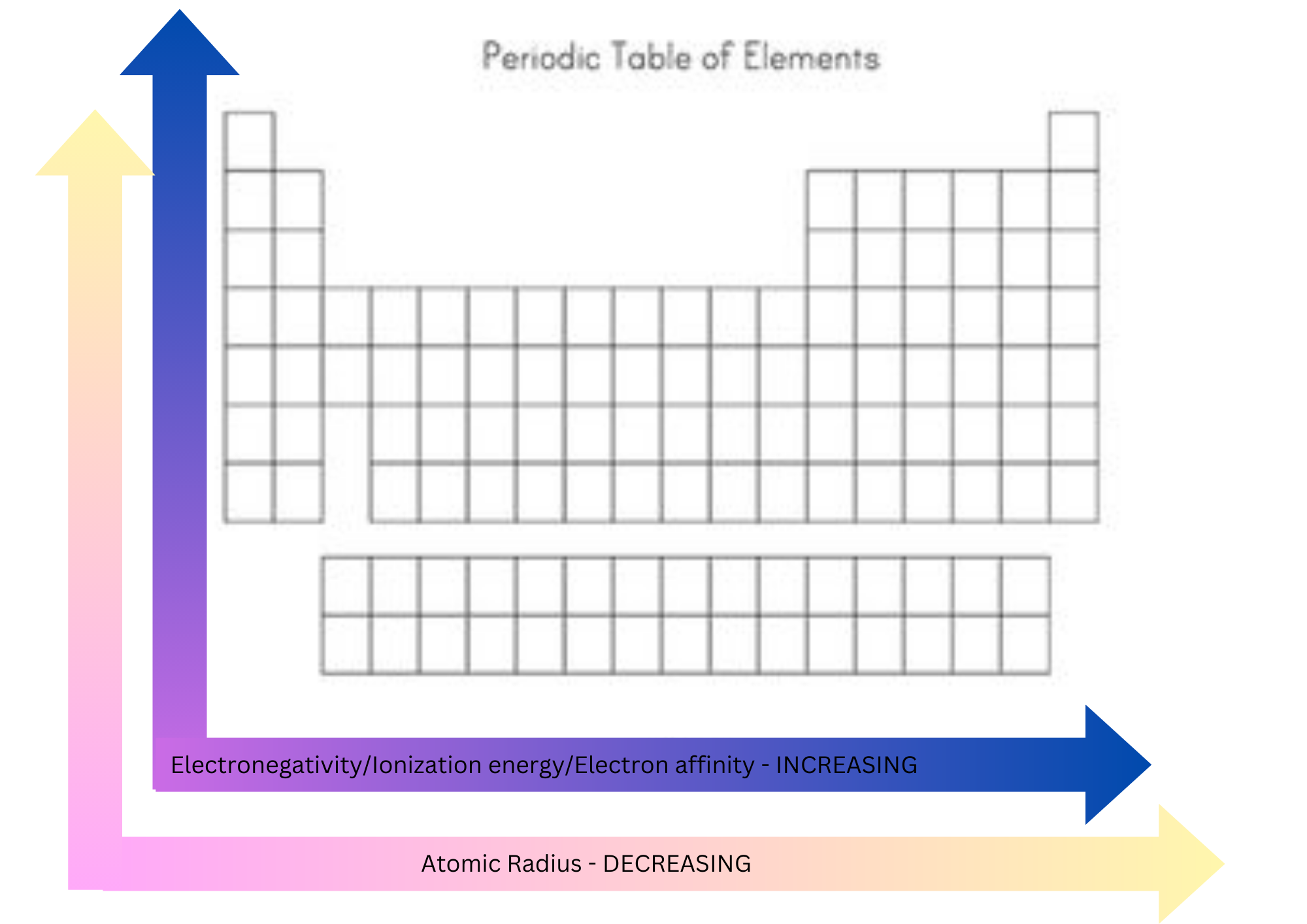
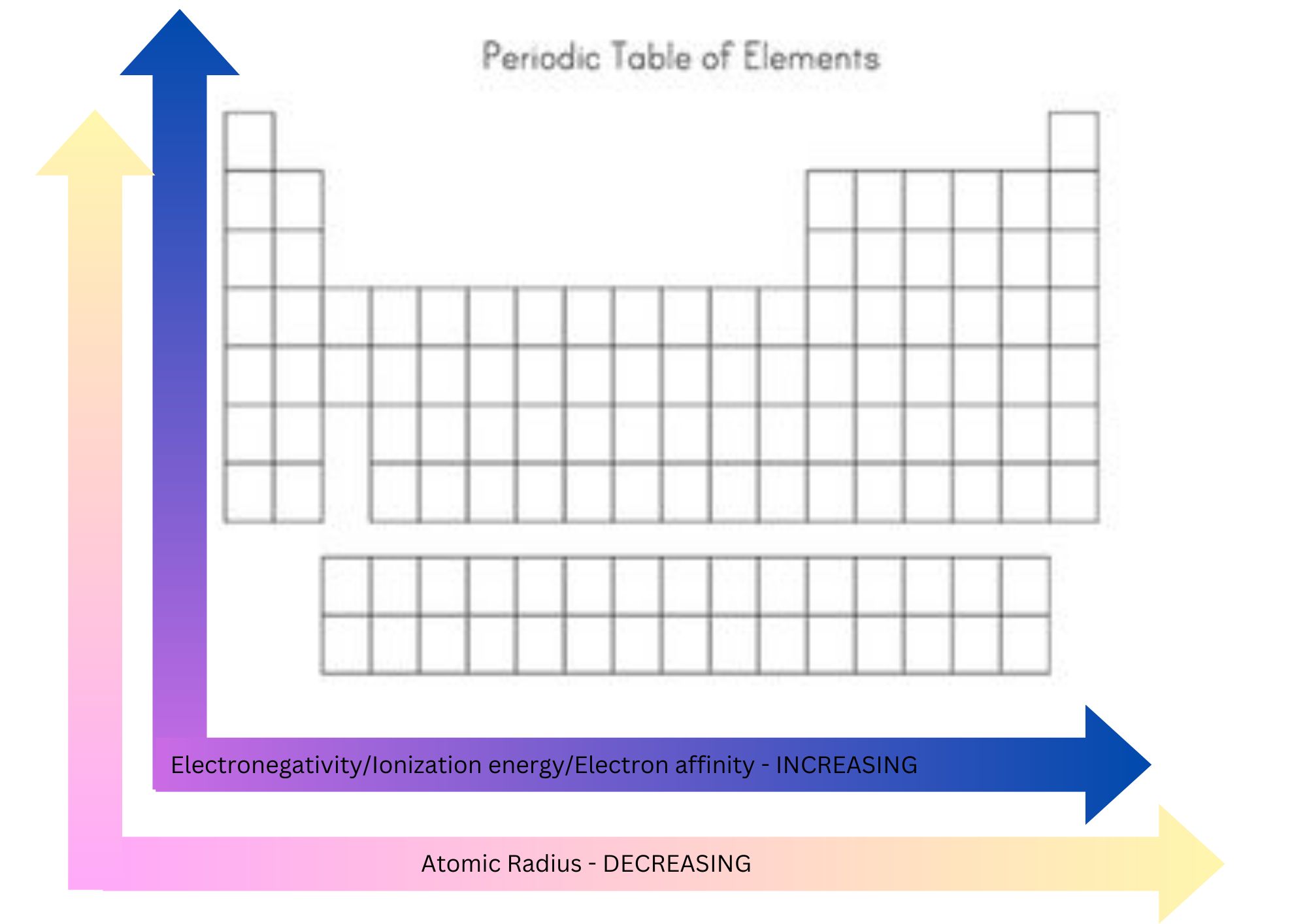
Electronegativity
A measure of how strongly the atom attracts the shared pair of electrons in a chemical bond.
Is affected by the atomic number and the distance of the valence electrons from the nucleus.
Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Is affected by the atomic number and the distance of the valence electrons from the nucleus.
Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
39
New cards
Ionization energy
The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an element in the gaseous phase.
Increases across a period - electrons are held more tightly by atoms because of the bigger positive charge in the nucleus.
Decreases down a group - electrons are further away from the nucleus.
Increases across a period - electrons are held more tightly by atoms because of the bigger positive charge in the nucleus.
Decreases down a group - electrons are further away from the nucleus.
40
New cards
Atomic radius
Distance from the nucleus to the outermost stable electron orbital.
Decreases across a period and increases down a group.
Decreases across a period and increases down a group.
41
New cards
Electron affinity
The energy released when an electron is accepted by an atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form an anion.
Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
42
New cards
Melting point, Boiling point and Density as a trend in the periodic table
All increase steadily from group 1 -14 and then suddenly drop in group 15. They then increase again from 16 - 18.
43
New cards
A chemical bond
A force that binds atoms together, formed when atoms are held together by attractive forces.
44
New cards
Octet rule
Atoms tend to form bonds so that they are surrounded by 8 electrons.
45
New cards
Covalent bond
Pairs of electrons are shared between atoms.
Occurs when two non-metals interact.
Valence electrons are distributed as shared or bond pairs and unshared or lone pairs.
Occurs when two non-metals interact.
Valence electrons are distributed as shared or bond pairs and unshared or lone pairs.
46
New cards
Ionic bond
Electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
Occurs when a metal and non-metal interact.
Occurs when a metal and non-metal interact.
47
New cards
Metallic bond
The electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalized electrons.
Occurs when two metals interact.
Occurs when two metals interact.
48
New cards
Metals
Solids that consist of atoms that are tightly packed together in a metallic crystal lattice.
Lose control over its valence electrons.
Lose control over its valence electrons.
49
New cards
Water of crystallization
Water molecules trapped inside ionic crystals.
Absorbed through the atmosphere.
Absorbed through the atmosphere.