Chapter 14
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Homologous Chromosome:
Chromosomes before replication and after
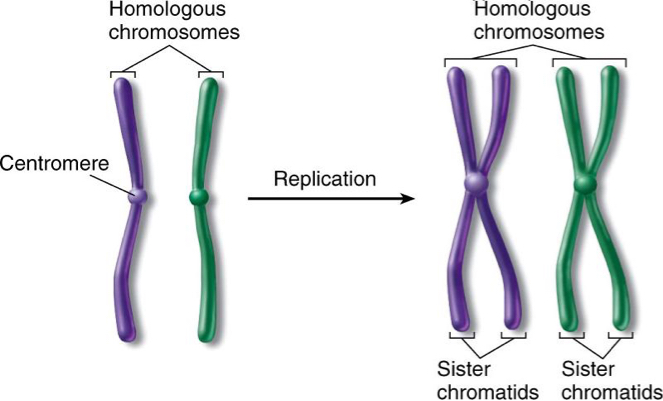
Replicative Chromosome:
Sister Chromatids:
Genetic Locus:
physical location of a gene
What is found at each genetic locus?
Allele; one from maternal and one from paternal
What is the difference between being a haploid and being a diploid?
What does a karyotype reveal?
G1:
Cell growth
S:
DNA replication
G2:
Cell growth + SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS
M phase:
Mitosis and cytokinesis occur
G1 Checkpoint:
-Determines if conditions are favorable for cell division and checks for DNA damage.
-G1 cyclin bind to CDK (cyclin dependent kinases) and allows advancement to the S phase
G2 Checkpoint:
-Checks for DNA damage, determines if all DNA has been replicated, monitors protein needed for M phase, mitotic cyclin binds to CDK.
Metaphase Checkpoint:
-Checks to see if spindle fibers are attached to centromere, mitotic cyclin is degraded
When is G1 cyclin degraded?
S phase
When is mitotic cyclin degraded?
M checkpoint
What happens during mitotic cell division?
Cell divides into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the original cell.
T or F? Mitotic divisions are used for asexual reproduction and for growth and development of multicellular organisms.
True
DNA is replicated in S phase, we know that!
In this phase, what is produced?
Replicative chromosomes
One replicated chromosome contains a pair of ____ _____!
sister chromatids
What does the spindle apparatus do? What is it composed of?
Organized and sorts chromosomes during cell division, composed of microtubules
In animal cells, microtubule growth and organization start at two ________.
centrosomes
During mitosis, what happens to the centrosomes?
Forms pole and spindle fibers
What is the big goal of mitosis?
Creation of two genetically identical daughter cells with each having the same chromatids
There are three stages that occur during mitosis.
1. Interphase:
2. Prophase:
3.. Metaphase:
4. Anaphase:
5. Telophase and cytokinesis:
1. Interphase: G1, S, and G2 phase occur
2. Prophase: Compaction of replicative chromosomes, nuclear envelope dissociates, nucleolus is no longer visible
3. Metaphase: pair of sister chromatids line along the metaphase plate
4. Anaphase: Spindle fibers shorten and separate sister chromatids apart, each going to a respective pole.
5. Telophase and cytokinesis:
telophase: sister chromatids decondense and nuclear envelope reforms. Cytokinesis: cleavage furrow separates cells creating 2 daughter cells
What happens before Meiosis I? (think about the G1 phase!)
What happens in Meiosis I? (think about the distinguishing feature of Meiosis I!)
There are 5 stages in Meiosis I:
Prophase I:
Prometaphase I:
Metaphase I:
Anaphase I:
Telophase I and cytokinesis:
Ultimately, what does Meiosis I produce?
When is synapsis and when does it occur?
What does Meiosis II separate? (It is the same as mitosis!)
There are 5 stages in Meiosis II:
Prophase II:
Prometaphase II:
Metaphase II:
Anaphase II:
Telophase II and cytokinesis:
Ultimately, what does Meiosis II produce?
Chromosome composition within a given species tends to be ______ (constant or different?), although composition is _____ (constant or different?) across species.
What are the three features that are used to classify and describe chromosomes?
____ _____ of eukaryotic chromosomes are used to detect changes in chromosome structure that occur as a result of mutation.
There are four different types of chromosomal mutations:
What does it mean to be euploid? What about aneuploidy?
What causes nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction in meiosis generates what types of gametes? What does this mean?