1B.20 Epi
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To do: 18, 19, 21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
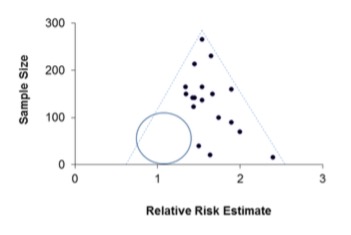
What is a funnel plot when considering systematic reviews?
A scatterplot that is used to visualise potential publication bias in meta-analyses
What can a funnel plot be used for outside of systematic reviews?
Comparing performance between organisations or clinical teams.
For meta-analysis, what variable is denoted along the x-axis?
The estimated treatment or intervention effect.
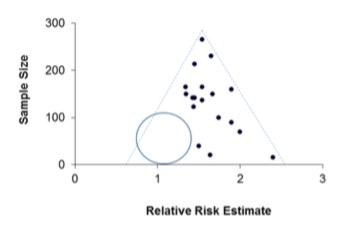
For meta-analysis, what variable is denoted along the y-axis? Give an example.
A measure of the study’s size or precision e.g. the inverse of standard error, the standard error, the study size
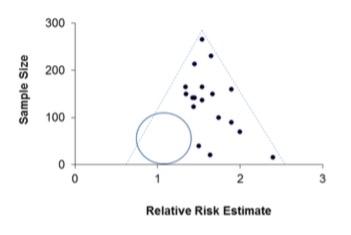
Why is a funnel plot wider at the base?
Because the precision of the estimate of the effect size increases with the size of the study, the smaller studies will have more widely scattered effect sizes towards the bottom of the scatterplot
Why is a funnel plot narrower at the top?
Because the precision of the estimate of the effect size increases with the size of the study, the variability will reduce while the precision increases as the studies get larger, so funnel towards the tip
If publication bias is present, how will the funnel plot appear?
Asymmetric, with a unilateral gap towards the bottom of the funnel where the results of the small, negative, unpublished studies should have been (blue circle)
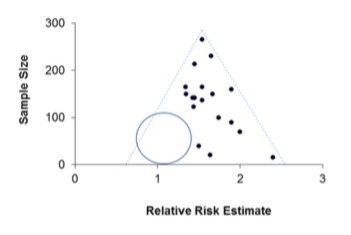
Where publication bias, or the small study effect, has occurred, a subsequent meta-analysis will result in ___?
…an overestimation of the true treatment effect.
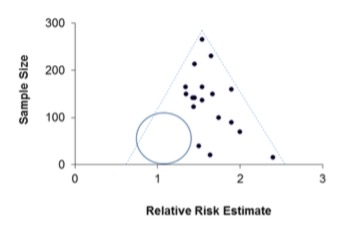
What does the dashed line of the triangle represent?
The region where 95% of studies would be expected to lie if there were no heterogeneity
If a funnel plot is asymmetrical at the bottom what does this indicate?
The small study effect
What is the small study effect in funnel plot asymmetry?
The phenomenon of small trials tending to report larger treatment benefits than larger trials.
What are some reasons for the prominence of small study effect outside of publication bias?
Studies targeting particularly high-risk patients tend to be smaller as there are far fewer high-risk patients from which to sample.