EKG Rhythms and Clinical Implications
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Junctional escape rhythm
Occurs in AV tissue when SA node fails (only passes impulse to bundle of his). Regular rhythm, 40-60 bpm. P-waves usually not there or inverted. Causes: digitalis toxicity, hypoxia, acute infections, etc. NEVER TERMINATED NATURALLY.
Premature junctional beats
Aka escape beat. Inverted P-wave prior or after QRS. Causes: Usually CAD.
Junctional tachycardia
3+ junctional escape beats in a row. HR: 120-200 bpm. P-waves before or after QRS.
Premature ventricular contractions (PVC)
Occurs below bundle of His. No failure of normal rhythm. Wide, bizarre QRS (b/c took longer for ventricles to depolarize) - no P-wave. Antiarrhythmic therapy needed if: Occur with ↑ frequency, occur in a pattern, fall close to a t-wave, R on T phenomenon. Uni or multifocal. 2 occurring together: couplet. Every other beat: bigeminy; every 3 beats: trigeminy; 3+ PVC's: v-tach.
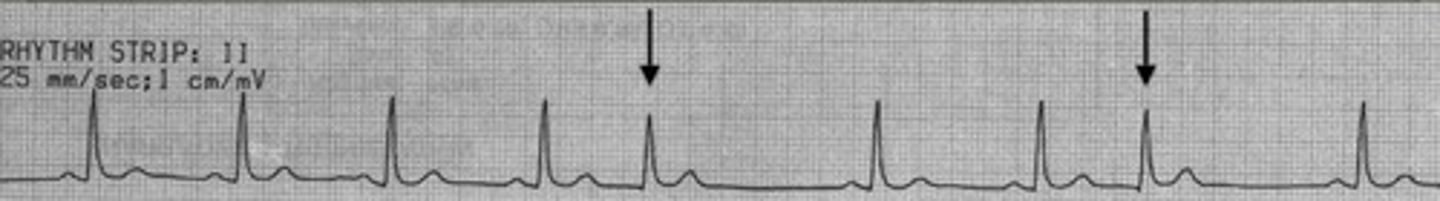
Fusion beats
Sinus and ectopic impulses occur at the same time. P-wave with wide, bizarre QRS (less wide than PVC). p-p interval constant. p-r interval abnormally short if visible.
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach)
Life threatening. 140-200 bpm. No p-waves. Wide and bizarre QRS. R-R is regular. Usually initiated by single PVC. Might see a capture beat (normal sinus beat sneaks through). 3 or more PVCs in a row = V-tach.
Ventricular flutter
TRANSITION RHYTHM from v-tach to v-fib. 200+ bpm. Usually unconscious. Shockable.
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib)
Chaotic, no PQRST noticeable. Ventricles are quivering. Fatal. Shockable. Epinephrine may be used to convert fine v-fib to coarse v-fib for better response from defibrillator.
Pulseless electrical activity
When a person has some electrical impulses but no pulse.
Ventricular escape beats
When sinus node can't maintain a rhythm. Life saving mechanism. SA node 60-100 bpm. AV node 40-60 bpm. Purkinje fibers 20-40 bpm. QRS widened. Looks like it goes backward.
Hypokalemia
Potassium levels below 3.6 mEq/L. Depressed ST segment. Prominent U wave. Prolonged QT/QU interval. May be associated with: starvation, vomiting, diarrhea, diuretic therapy, steroid use, etc. May also cause: PVC's. Mainly affects repolarization, so look for changes near T-wave.
Hyperkalemia
Potassium levels greater than 5.2 mEq/L. Usually has tall, peaked, narrow T-waves that are symmetrical. Diminished height of R wave. Small P waves. Widened QRS. Mainly associated with: burns (2nd/3rd degree), crushing injuries, excessive amounts of K+ solutions, kidney damage, etc. Depresses normal electrical activity of the myocardial cells. May also cause: sinus bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia, first degree AV block, V-tach, V-fib, asystole.
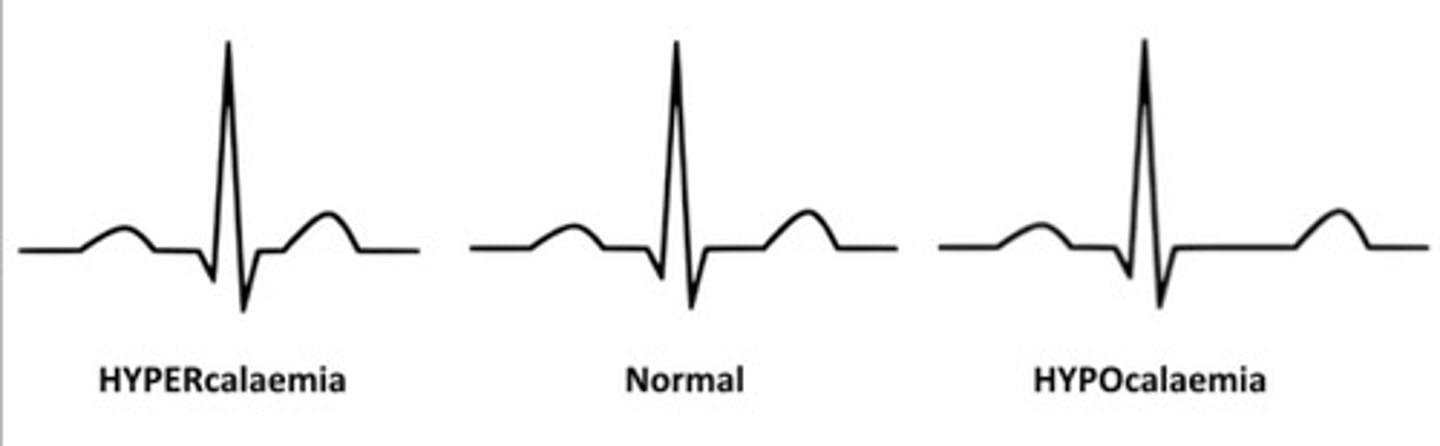
Hypocalcemia
Calcium levels below 9 mg%. Changes noted in ST segment (lengthening). No change in QRS or T-wave. Usually an upset in the acid-base balance due to hyperthyroidism.
Hypercalcemia
Calcium levels more than 11 mg%. Causes increased contractility of the heart. Has a shortened ST segment (may even be absent). Watch for acidosis.
Hypomagnesemia
May occur in tandem with hypokalemia (low K+). May result from: diarrhea, hypoparathyroid disease, pancreatitis, ulcerative colitis, SEVERE alcoholism.
Hypermagnesemia
May result from: renal failure, dehydration, diabetic acidosis, oliguria (diminished urine output).
Junctional escape rhythm
Premature junctional beats
Junctional tachycardia
Unifocal PVC
Multifocal PVC
v-tach
v-flutter
v-fib
ventricular escape beat
hypocalcemia