B17: Organisation of an ecosystem
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Biomass
The mass of living material in a living organism. Measures in g/m^-2 or kg/m^-3
Substances that make up an organisms biomass
Cellulose to form cell walls
Starch for storage
Proteins, made up from amino acids using nitrates from the soil
Respiration Equation
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Food Chain
Producer → Primary Consumer → Secondary Consumer → Tertiary Consumer/Apex Predator
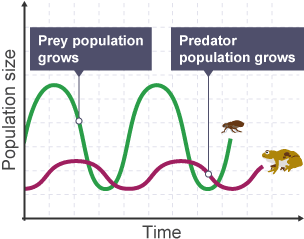
Predator-Prey Relationships
Cyclical Fluctuation
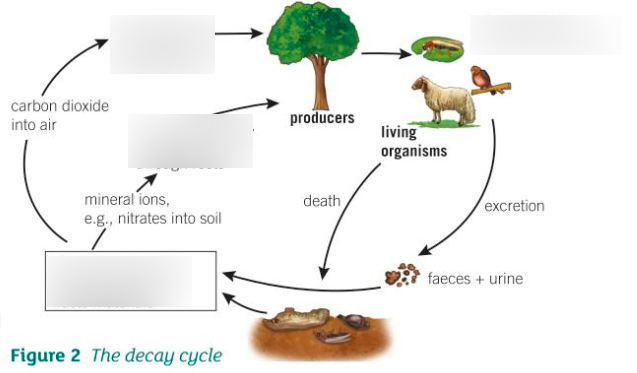
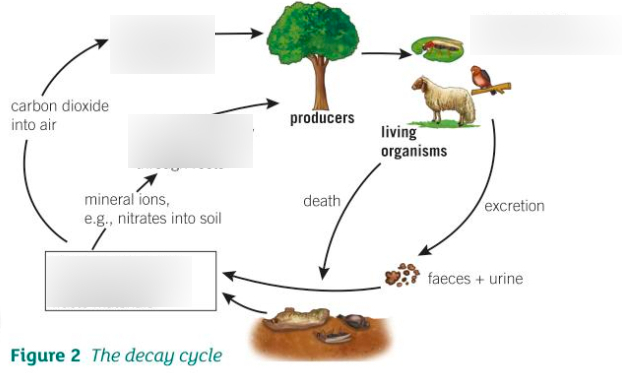
Decay Cycle (fill in the blanks)
1 - Photosynthesis
2 - Plant material eaten by consumers
3 - Mineral ions e.g nitrates go into the plant through the roots
4 - Decomposers break down dead bodies + waste materials
Carbon-containing molecules in plants, animals, the atmosphere, and faeces
Plants: Starch, Cellulose
Animals: Glycogen
Atmosphere: Carbon Dioxide
Faeces: Proteins, DNA
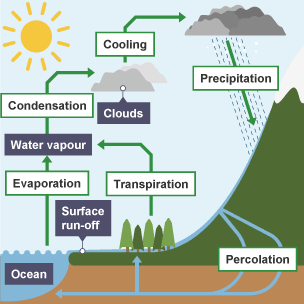
Water Cycle
Why is water needed in living organisms?
Turgidity in plant cells, chemical reactions (photosynthesis), chemical reactions in solution, transpiration, blood plasma to transport blood cells and platelets, sweating to maintain core body temperature.
Process of transpiration
Water is taken through the roots by osmosis and absorbed into the plant. The water then travels up the plant via the xylem tissue. It travels up into the leaves then exits the leaf through the stomata.
How and why might the water obtained from plants via respiration be different on a sunny day?
They lose more water than they gain. A plant would respire the same depending on the day. If it is sunnier, they will photosynthesise more, so the stomata will be more open, and the plant loses more water through transpiration.
Molecules that contain carbon
Fats, Carbohydrates, Nucleic acids (DNA), Proteins, CO2, Glycogen
Carbon Cycle
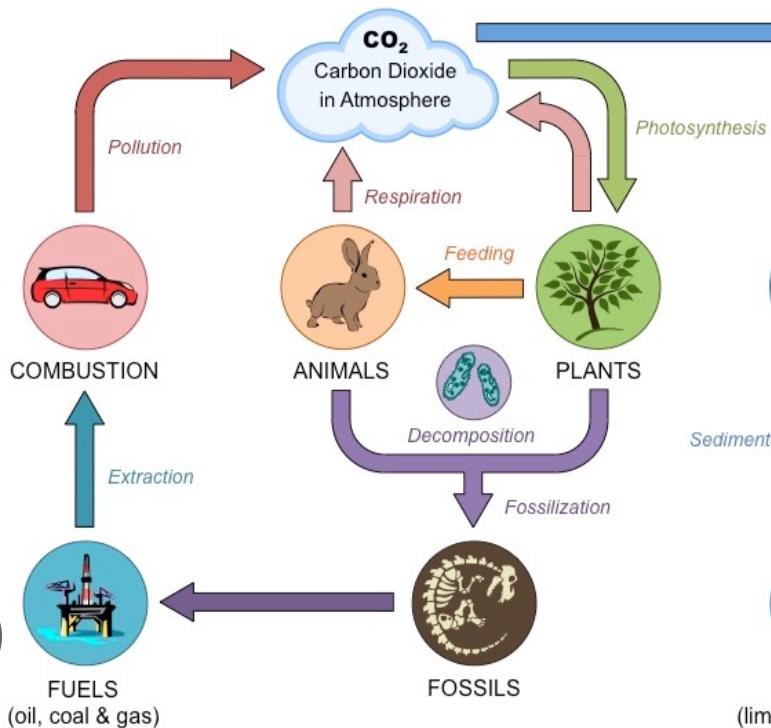
Decomposition is carried out by
Detritivores (woodlice, maggots, earthworms)
Decomposers (saprotrophic feeders (bacteria, fungi))
Factors that affect decay
Warm Temperature ↑
Moist conditions ↑
Presence of bacteria ↑
Lots of oxygen ↑
Cold temperature ↓
Dry conditions ↓
Lack of oxygen ↓
Lack/Lots of carbon dioxide (no effect)
How does temperature affect decomposition
Enzymes have optimum temperatures.
If it is too hot/cold, enzymes will denature.
Lower temperature means less kinetic energy, which means less collisions will happen, so less reactions will happen.
How does moisture affect decomposition
Water transports mineral ions
Water is needed for chemical reactions
Water is a crucial metabolite
How does oxygen affect decomposition
Oxygen is needed for respiration, which is necessary for digestion
Biogas Generators
Anaerobic decay produces methane gas. Biogas generators can be used to produce methane gas as a fuel for cooking heating, and burning. There are two types: Fixed dome design and Floating dome design.
Fixed Dome Design
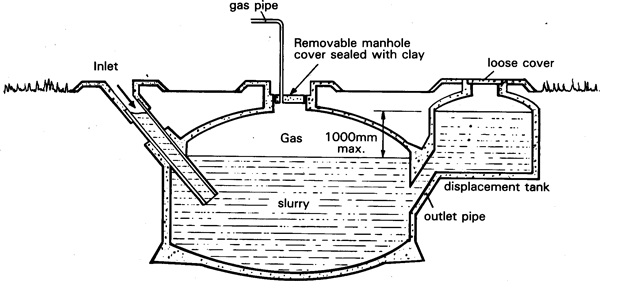
Fixed Dome Design: Advantages and Disadvantages
Fewer metal parts
Less expensive to set up
Does not rust
Can be used by single families or communities
Gas pressure fluctuates
Less straightforward to control
Gas leakage is more likely
Production of methane is low
Floating Dome Design
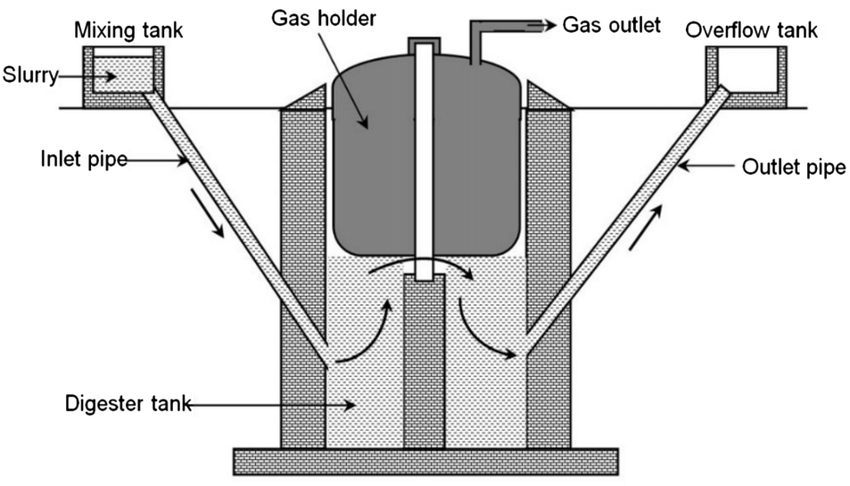
Floating Dome Design: Advantages and Disadvantages
Floating dome stabilises the gas pressure
Gas production can be monitored more easily
Can be used on a larger scale
For large villages or for commercial production of methane
Expensive to set up and maintain
Requires more management
Metal construction: rusts easily