Concept 12.2: The mitotic phase alternates with interphase in the cell cycle
1/19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Walther Flemming
The German anatomist who developed dyes to observe chromosomes during mitosis and cytokinesis in 1882
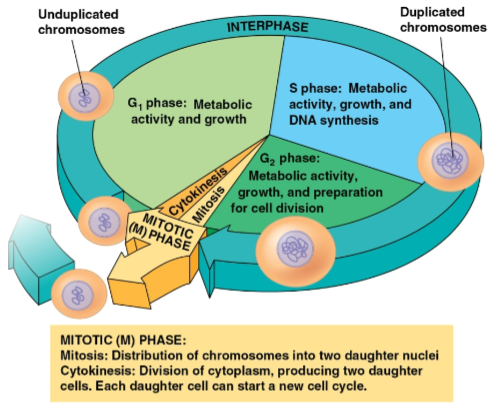
Cell cycle
Consists of:
The mitotic (M) phase (mitosis and cytokinesis)
Interphase (cell growth and copying of chromosomes in preparation for cell division)
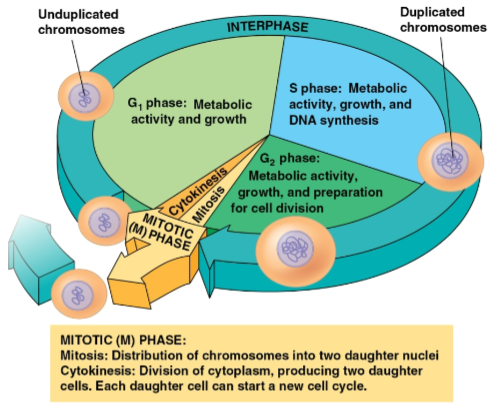
Mitotic phase
Phase of the cell cycle that includes mitosis and cytokinesis
Divided into five stages:
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
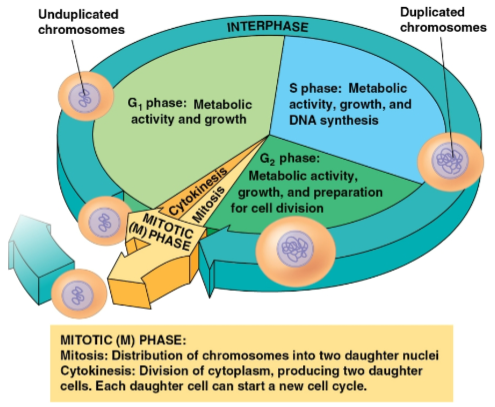
Interphase
Phase of the cell cycle where cell growth and chromosome duplication occurs in preparation for cell division
Divided into three phases:
G1 phase (first gap)
S phase (synthesis)
G2 phase (second gap)
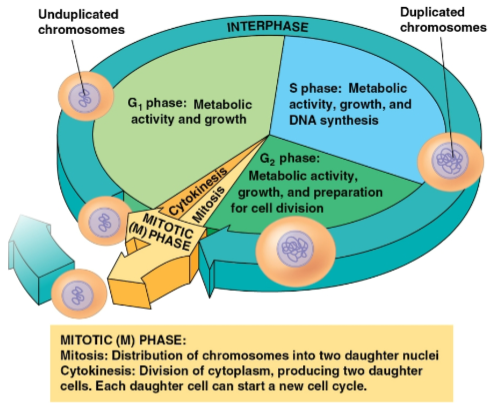
G1 phase
Phase of interphase where metabolic activity and growth occurs
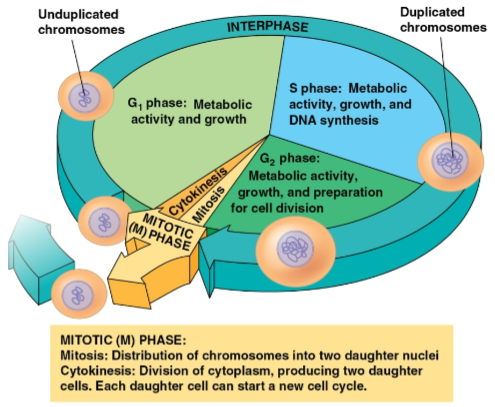
S phase
Phase of interphase where chromosomes are duplicated
G2 phase
Phase of interphase where metabolic activity, growth, and preparation for cell division occurs
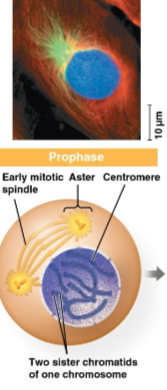
Prophase
Phase of mitosis where sister chromatids joined by a centromere become visible as the mitotic spindle develops
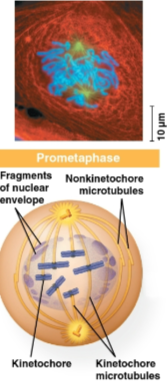
Prometaphase
Phase of mitosis where the nuclear envelope dissolves and kinetochore microtubules extend over the chromosomes
Centrosomes are at opposite ends of the cell by the time of this phase’s completion
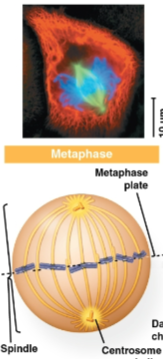
Metaphase
Phase of mitosis where the mitotic spindle is developed with centrosomes at the pole and centered chromosomes
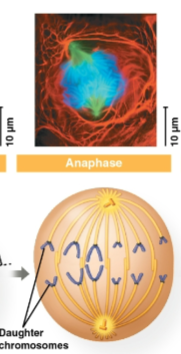
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis where daughter chromosomes are pulled apart towards the poles of the cell by centrosomes
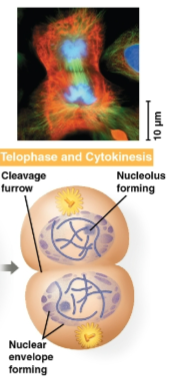
Telophase
Phase of mitosis where cytokinesis starts to occur as the nucleus reforms and the cell divides
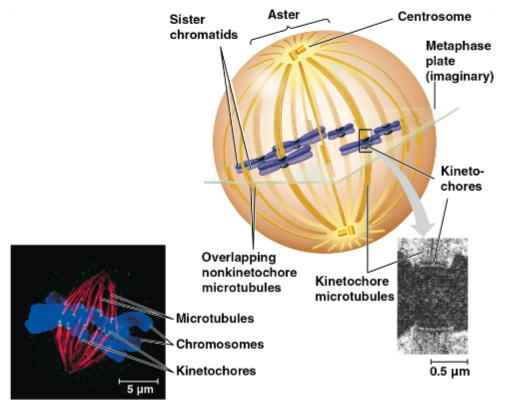
Mitotic spindle
A structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement during mitosis
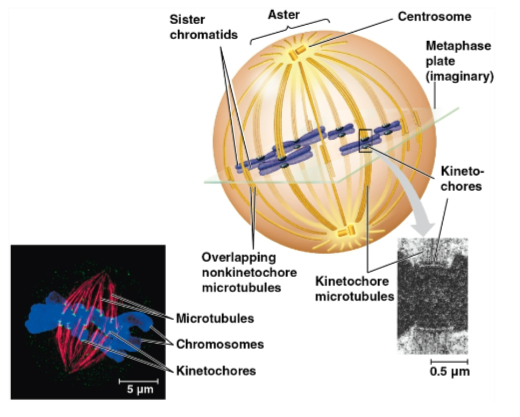
Centrosome
An assembly of spindle microtubules at the poles of each cell for organization
Replicates during interphase and migrates during prophase and prometaphase
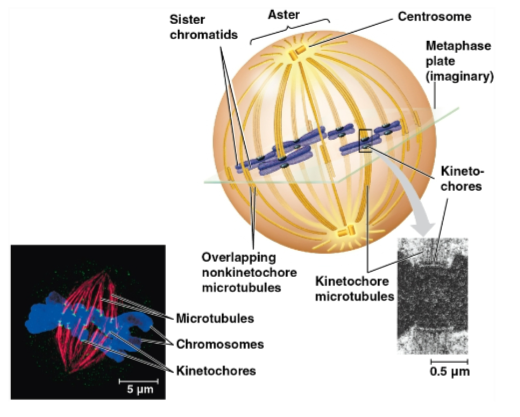
Kinetochore
A protein complex associated with centromeres, assigned to each sister chromatid
Spindle microtubules attach to these during prometaphase
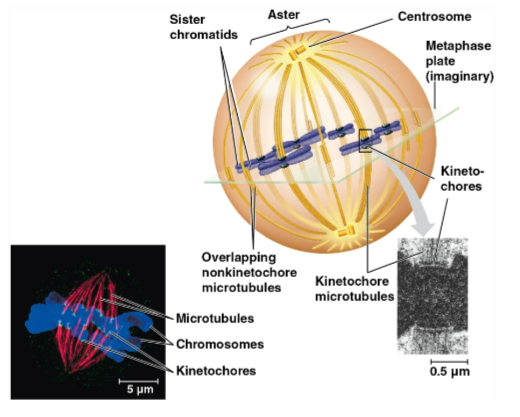
Metaphase plate
Plane midway between the spindle’s two poles where the chromosomes are all lined up
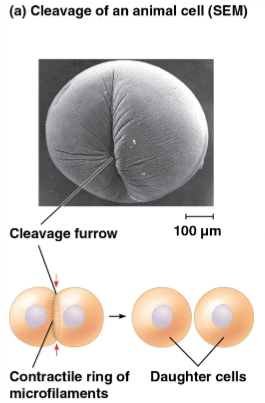
Cleavage
Process that causes cytokinesis in animal cells
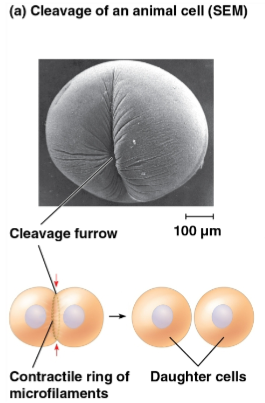
Cleavage furrow
The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell, marked as a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate
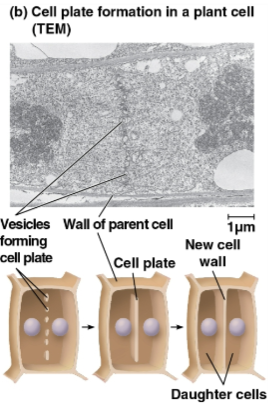
Cell plate
Sign of cytokinesis in plant cells after cell division
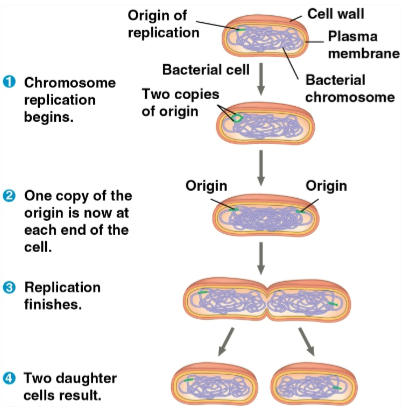
Binary fission
The type of cell division conducted by prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea
Replicates the chromosome, then actively moves them apart as the plasma membrane pinches inward for division
Likely the basis for mitosis in eukaryotes through evolution