Protein synthesis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
what is transcription
the synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA as a template, production of mRNA
where does transcription take place (euk/pro)
eukaryote: in the nucleus
prokaryote: in the cytoplasm
describe the three stages of transcription
initiation: RNA polymerase binds to DNA at the start of the gene and unwinds the DNA in the section
elongation: RNA polymerase builds a strand of mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction using complementary base pairing
termination: a terminator sequence is detected, and mRNA releases and the DNA closes together
what strand does mRNA build onto
The template/ antisense strand
what happens when the right RNA nucleotide is placed?
it forms a temporary hydrogen bond with the complementary base on the template strand
adenine and thymine : two bonds
guanine and cytosine: three bonds
why is it important that DNA is stable and doesn’t degrade
because if it degraded, proteins wouldn’t be able to be produced from it which would stop cell functions
what is translation?
the synthesis of polypeptides (proteins) from reading mRNA
mRNA is read by the ribosome and amino acids are added to build a polypeptide
where does translation occur
once the mRNA moves into the cytoplasm, it is translated at ribosomes which catalyze reactions
ribosomes brings mRNA and tRNA together which makes the process happen
what is tRNA
a single stranded RNA molecule that fold on itself to make to a clover shaper with three loops
each tRNA attaches to an amino acid
what is an anticodon?
region at the end of the tRNA that pairs to the mRNA because it is the opposite of the codon on the mRNA (complementary)
what is a codon
any three RNA bases in a sequence that codes for the placement of a specific amino acid
how many possible combinations are their of codons
4³ (64)
what happens during initiation in translation
the mRNA binds to the small subunit of the ribosome
tRNA charging: it collects the right amino acids in the cytoplasm (enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA sythesase catalyses the binding)
mRNA has a start codon that links to initiator tRNA that carries methonine
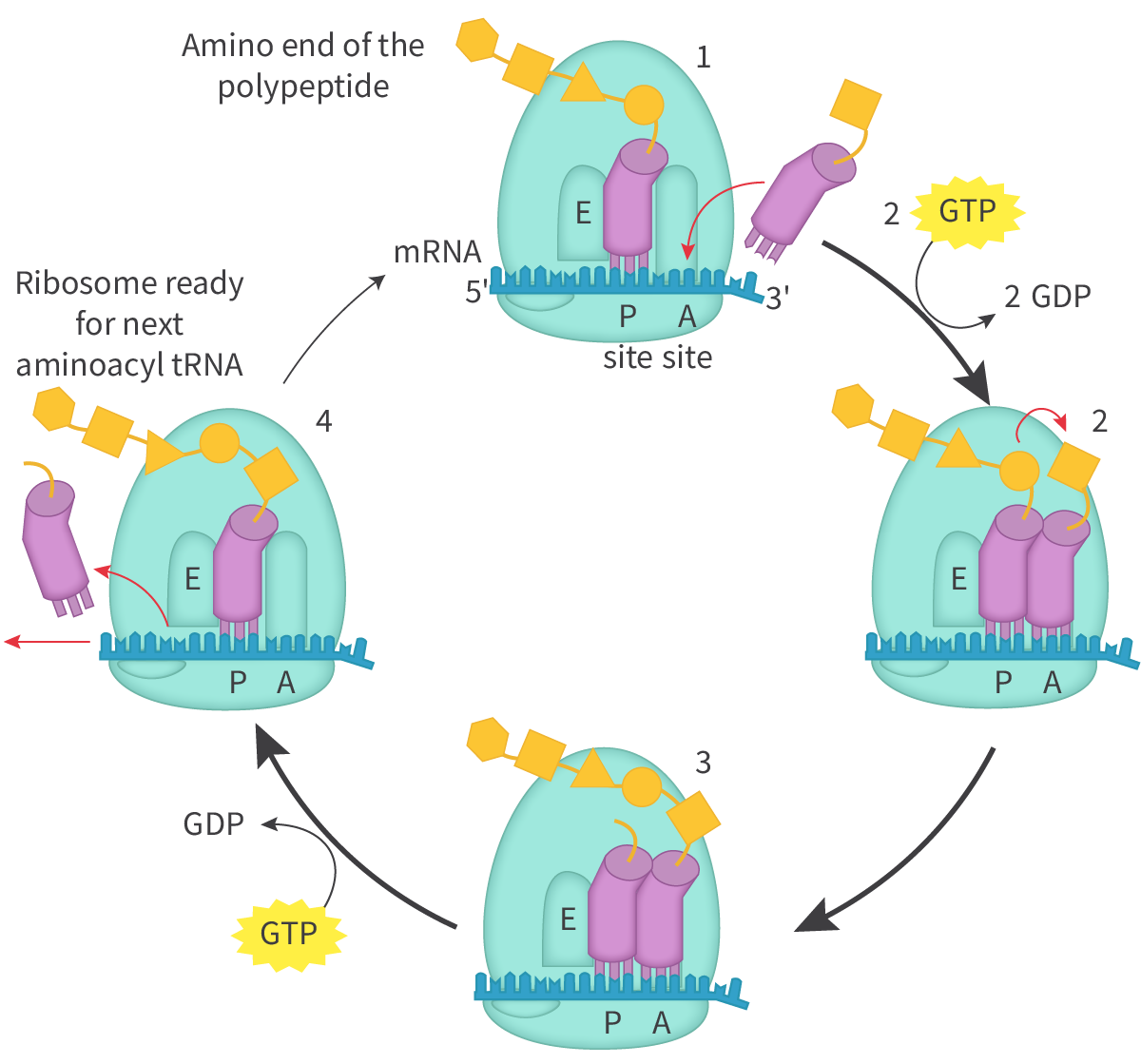
translation - elongation
ribosome moves along the mRNA one codon at a time
tRNA attaches at the P site on the start codon
new tRNA attaches at the A site and a peptide bond forms between the amino acid and transfer to the new tRNA
the new tRNA moves to the P site
the old tRNA moves to the E site and exits
what reaction causes bonds in the polypeptide chain
condensation reaction forms the chain of polypeptides (protein)
what is a point mutation
swapping of one base during transcription or translation
example of a point mutation
sickle cell anaemia: point mutation in the gene that produces a polypeptide in haemoglobin
where does silent mutation occur/ wobble hypothesis
most likely at the third base in the codon
some codons code for the same amino acid so it doesn’t matter
a tRNA molecule can bind to the to the codon based on the first 2 out of 3 bases
what direction do transcription and translation occur in
transcription
RNA polymerase can only build in a 5’ to 3; direction and catalyze the bond between the 3’ end and 5’ end of another
translation
mRna moves through the ribsome in a 5’ to 3’ direction and it only fits to the biding site of the ribsome if oriented that way
what is the promoter
the region just before a gene
where RNA polymerase binds in transcription at initiation
called the TATA box, which only has 2 hydrogen bonds so its easier to break apart and expends less energy
what are transcription factors
proteins that bind to the promoter
RNA polymerase can’t bind without them and the. gene wouldn’t be expressed
what are enhancers/ silencers
DNA regions that don’t code for proteins
they act as biding sites to increase/ decrease rate of transcription
what is an intron
a DNA base sequence only in eukaryotes that gets removed after transcription
non coding DNA
they can have controlling sequences
telomeres
repetitive sequences of DNA that protect the ends of chromosomes and ensure DNA is replicated correctly
they fall off a bit each cell division
non coding DNA
genes for tRNA and rRNA
non coding DNA
code for RNA molecules that fold to form tRNA or rRNA (part of ribosome structure)
exons
gene regions that code for polypeptides
what are some post TRANSCRIPTIONAL modifications?
synthesis of pre-mRNA (transcrition)
addition of a 5’ cap and a poly-A-tail to protect from degradation
splicing intons and ligating exons to make mature mRNA
what is a spliceosome and how does it work
snRNP
base pairs with ends of introns
cuts out introns by making a loop out of them and then exising it
ligating (joining) the exons together
what is an example of alternative splicing
different exons can be ommited and combined
produces various proteins
genes that produce troponin T which is for muscle contraction
in babies the protein in spliced on way which gives it a high sensitvity ro CA2+ but after a few weeks it becomes spliced differently and loses the sensitivity
what is the large ribosomal subunit
it joins in initiation to complete the assembly of the translation complex
POSt-translation modification
after polypetides are created they are sent in vesicles to the golgi apparatus
describe how insulin is post-translationally modified
it begins as pre-proinsulin
when it is on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (bond ribosome) the signal peptide is removed
disulfide bridges form between the A and B chain
proinsulin is moves to the golgi apparatus which removes the c-peptide
proteasomes
hydrolises proteins by breaking peptide bonds between amino acids
breaks apart used or damaged proteins to maintain a constant supply of amino acids
when does transcirption occur
interphase
what is the central dogma
dna can make more dna (replication)
dna can make rna (transcription)
rna can make proteins through translation
is mature mRNA shorter or longer?
shorter because you cut out all the introns
translational termination
a stop codon is detected by a protein release factor and the translational apparatus comes apart and releases the finished polypeptide
what is a framshift mutaion
insertion or deletion of one base that changes all subsequent codons