Week 11 - Aggression
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Aggression
physical or verbal behaviour intended to hurt someone
- can be physical, social, or emotional
Hostile Aggression
- directing aggressive behaviour to person who directly wronged you
- driven by anger and performed as an end in itself
- ex: most murders, bullying
Instrumental Aggression
- aggression that is a means to some other end
- aggressive behaviour for a greater cause
- ex: most acts of war or terrorism
3 Theories of Aggression
1. aggression as a biological phenomenon
2. aggression as a response to frustration
3. aggression as learned social behaviour
Biological Theory
- aggression as instinct
- aggression as biologically adaptive
- helps us be more competitive
Biological Theory: Instinct Theory
- from Freud
- humans have some self-destructive impulses
- then expanded
Biological Theory: Neural Influences
- no center of aggression in the brain, but involves amygdala and hypothalamus
- more aggressive men have smaller amygdala
Biological Theory: Genetic Influences
- sensitivity to aggression cues: things in environment that trigger aggression
- ex: facial expressions, tone of voice, weapons
- temperament
Biological Theory: Biochemical Influences
- Alcohol
- Low serotonin
- Testosterone
- Poor diet
- Biology and behaviour interact
Frustration Theory
- frustration-aggression theory: frustration triggers a readiness to anger
- displacement: redirection of aggression to a target other than the source
Frustration Theory: Simplified Frustration-Aggression Theory
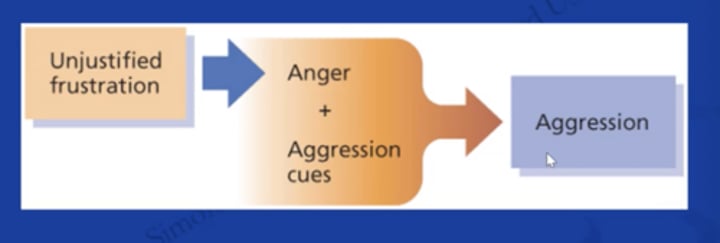
Frustration Theory: Relative Deprivation
- perception that one is less well off than others to whom one compares onself
- RELATIVE- what is perceived
Learned Behaviour Theory
- the rewards of aggression
- social learning theory
- learn social behaviour by observing and imitating, by being rewarded and punished
Learned Behaviour Theory: Observational Learning
- Bandura (1977): Bobo doll experiments
- Family: violence produces violence
- Culture: certain cultures support aggression more
Learned Behaviour Theory: Social Learning Theory
- we learn aggression from models: media, culture, family etc.
aversive experiences -> emotional arousal
rewards and costs -> anticipated consequences
arousal + consequences -> dependency, achievement, withdrawal and resignation, aggression, bodily symptoms, constructive problem solving, coping with drugs
Influences on Aggression: Aversive Incidents
pain
- rat experiments: delivering shocks, the greater the shock the more violent they got
heat
- intense heat as an environmental factor
- students felt more tired and aggressive in hot conditions
attacks
- if insulted or attacked, we are more likely to retaliate
Influences on Aggression: Arousal
- given state of bodily arousal feeds one emotion or another
- dependent on how person interprets and labels arousal
Influences on Aggression: Arousal Study (1962)
- made men physiologically aroused by injecting them with adrenaline
- some were told drug effects
- some were not told
- shown picture of either a hostile or happy person
- those informed had no reaction
- those not informed felt aggressively to hostile person and attracted to happy person
Aggression Cues
- violence more likely if there are aggressive cues in environment
- certain stimuli that are associated with aggression
- ex: weapons, prime us for aggression
Aggression Cues: Weapon Study at University of Wisconsin
- had either non-weapon or weapon item placed on table
- participant "gave" more electric shocks to a confederate when they had seen the gun
Media Influences
- pornography and sexual violence
- television and the internet
- video games
Media Influences: Pornography and Sexual Violence
- distorted perceptions of sexual reality, like of rejection and consent
- aggression against women
- media awareness education is important
Media Influences: Pornography and Sexual Violence Study
- assigned men to watch either normal movie, erotic movie, or aggressive erotic movie
- had them teach either a male or female confederate some syllabus
- if confederate gets it wrong, participant can shock them
- after watching aggressive erotic movie, female confederates were shocked more
Media Influences: Television and the Internet, Effects on Behaviour
- one type of arousal energizes other behaviours
- viewing violence disinhibits because repeatedly exposed to violent behaviour
- decreased perception of consequences and severity
- study: girls who observed more gossiping were more likely to gossip
- longitudinal study: positive correlation between children who watched more tv and likelihood of committing crime in the future
Media Influences: Television and the Internet, Effects on Thinking
- desensitization
- social scripts
- less realistic depiction of behaviour in tv, believe this is more acceptable than actually is
- the more sexual content that adolescents watched, they had more permissive attitudes towards sexual behaviour
- altered perceptions
- cognitive priming
Media Influences: Video Games
- identifying with, playing role of, a violent character (first person shooter games)
- adolescent men, lots of hormones
- active rehearsal of violence instead of passive watching
- engage in whole sequence of enacting violence
Group Influences
- diffusion of responsibility
- social contagion
- group polarization
Reducing Aggression
- need for catharsis (aristotle)
- misconception of venting: it actually increases subsequent aggressive behaviour, not letting go arousal
- social learning approach: reward cooperative behaviour, reduce media influence, reduce aggression triggers