Management Skills Final Rutgers
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Two Types of Influence Tactics
1. Interpersonal- influencing individuals and or group members
2. Procedural- managing rules or procedures used to exchange information and combine individual preference
Cialdini's 6 principles of influence
1. Liking
2. Reciprocity
3. Social Proof
4. Consistency
5. Authority
6. Scarcity
1. Liking
Similarity and Praise
individuals comply with requests from individuals or friends
examples: similarities (shared interests), compliments or praise, cooperation
2. Reciprocity
people repay in kind
people feel obligated to give back the form of behavior they receive
managers can elicit desired behavior by modeling it
examples: trust, a spirit of cooperation, pleasant demeanor
3. social proof
people follow the lead of similar others
People feel obligated to comply with request for behavior if it is consistent with what others are similarly doing
4.Consistency
People align with their clear commitments
people commit....
1. Actively- choice spoken out loud, written down, or made explicitly
2. Publicly- choice shared with others either spoken or written
3. Voluntarily - personal ownership
example: emailing or signing off of something
5.Authority
people defer to experts
people follow suggestion of people of legitimate authority
6.Scarcity
people want more of what they cant have
people see items and opportunities more valuable as they become less available
ex: exclusive info is better than widely available information
Additional tactic for interpersonal information ....establish
1. Establish your credibility
demonstrate expertise, integrity, trust
need to take an honest assessment of where you stand before you begin to persuade
Additional tactic for interpersonal information ....frame
2. Frame for common work
describe advantaged of your perspective and highlight shared benefits
Additional tactic for interpersonal information... Ev
Evidence
provide data, vivid examples, and stories
compelling and tangible quality
Additional tactic for interpersonal information....connect
Connect emotionally
show emotional commitment to your position and be in sync emotionally with your audience
Additional tactic for interpersonal information....build
Build coalitions
identify and form strategic alliances
persuasion involves compromise
Procedural Influence
•influencing the way that the group as a whole makes decisions or gets things done
•Techniques for influencing the rules or procedures used to exchange information and aggregate individual preferences - that is, for managing the group as a whole
Procedural Influence tactic #1
Controlling what goes on in the agenda
-what issues to consider?
-amount of time spent on each topic?
Procedural Influence tactic #2
influencing group norm
-allow criticism?
-limit talking time?
Procedural Influence tactic #3
Who speaks when
-speak early to frame discussion?
- pick an ally to speak first
Procedural Influence tactic #4
Shaping how decisions are made
-decision rule
-voting format
Procedural Influence tactic #5
Who sits where
-seating position determines leadership
-table configuration encourages collaboration
Group decision making
1. Conformity
2. Group Polarization
3. Groupthink
4. Social Loafing
1. conformity
a change in belief or behavior to fit in with the group
2. group polarization
tendency for group decisions or opinions of a group to become more extreme
the tendency for individuals' opinions within a group to become more extreme in the direction of the group's average opinion after discussion
3. Group think
Tendency for members of a group to value group consensus and cohesion over the critical evaluation of the decision.
-Extreme reluctance to communicate disagreements; no dissent
remedies
-Voice objectives and doubts
-Form subgroups to discuss critical issues before they are raised
-Use outside experts
-Have someone play the role of devil's advocate
-Leader impartiality
5. Social Loafing
tendency for individual effort to decrease as group increases
-Task perceived as being unimportant or uninteresting
-Group members feel their individual output is not identifiable
-Shared reward so no incentive to contribute more
-Coordination loss as more people perform the task
remedies
-Ensure tasks are challenging and important
-Emphasize personal accountability
decision making
identifying, evaluating, and choosing between alternatives that lead to desired results
Three models of decision making
1. the rational model-managers use a rational approach to decision making
2. bounded rationality-people are restricted in the information they possess, conduct a limited search for solutions, and settle for less than optimal solutions
3. garbage can model -decision making is haphazard, chaotic, unpredictable, and sometimes depends on luck
the rational model
Goal is to identify the optimal decision
Assumes that all information is available and complete
Benefits of using this model:
The quality of decisions may be enhanced
It makes the reasoning behind a decision transparent
bounded rationality
decision-makers are "bounded" or restricted by a variety of constraints when making decisions ( time, money, technology, resources)
results in not identifying all solutions
satisficing
-Satisfactory over optimal solution generated
satisficing
choosing a solution that meets some minimum qualifications, one that is "good enough"
Garbage Can Model
decision making is sloppy and unorganized
decision results from complex interaction of factors, including problems, solutions, participants and choice opportunities—all floating randomly inside an organization
Act swiftly short cuts
why might managers not follow the rational model?
All information may not be available, assumptions, may not have all the resources, inferior, time consuming to way in all options its costly, stubborn and biased
What are the root causes of poor decision-making?
•Capital
•Time
•Tech
•Bias like over confidence
Obstacles to decision making #1 Biases
A preference of inclination for or against someone/something that can inhibit impartial judgment
Obstacles to decision making #2 Heuristics
mental shortcuts or rules of thumb that people use to make quick judgments and decisions, especially when faced with complex situations or limited information
-Can help decision makers reduce uncertainty but can lead to errors that erode the quality of decisions
obstacles to decision making -self serving bias
view self in positive light; attribute success to internal qualities and failures to circumstances beyond our control
•(locus of control) we blame the world point fingers
obstacles to decision making-Egocentric bias
see self as contributing more (give ourselves more credit than others give us and more credit than we give others) (LoC , fundamental...)
obstacles to decision making - False uniqueness
see self as favorably; as unique from others
obstacles to decision making - illusion of control
tendency to believe that we exert more influence over situations than we actually do
obstacles to decision making - overconfidence
unwarranted confidence in judgment; overestimate accuracy of estimates or forecasts
Halo effect
one attractive trait = other attractive traits
occurs when our positive impressions of people, brands, and products in one area lead us to have positive feelings in another area
Forked tail effect:
opposite of halo effect: one undesirable trait = other negative traits
primary effect
first info we learn alters impression
Fundamental attribution error:
attribute behavior to personality traits rather than situational factors
a cognitive bias where individuals tend to overestimate the influence of personality traits and underestimate the role of situational factors when explaining the behavior of others
assuming someone is lazy for being late to work without considering that they might have had traffic issues or an unexpected family emergency
Obstacles to Effective Decision Making : Faulty perceptions about others- negative effects
once we learn negative info about someone, tend to put a lot of weight on that info
confirmation bias
•subconsciously seek information that confirms our expectations and discount information that does not (e.g., reinforce what we already know)
Availability bias
make decisions based on information readily available
Hindsight bias:
believe something was inevitable after it happened
Base rate fallacy
choose to rely on single, vivid data point rather than more reliable data
The base rate fallacy happens when people ignore general statistical information (the base rate) and focus too much on specific information. In decision-making, this leads to incorrect conclusions because the broader context is overlooked.
Insensitivity to sample size:
assume small samples not representative
People tend to treat results from small samples as more representative of the entire population than they actually are.
is a cognitive bias where people fail to account for the impact of sample size on the reliability of results
Representativeness-
make judgments on basis of stereotypical cues or information rather than more deliberate processing
where people judge the likelihood of something based on how much it resembles a typical case, rather than on actual probability.
Example: In hiring, a manager might assume a candidate from a prestigious school will perform better, simply because they “fit” the image of a successful employee, even if other evidence suggests otherwise.
Anchoring and Insufficient Adjustment
•: influenced by the first information received, even if it's irrelevant (e.g., first impressions anchor our decisions)
•Framing:
tendency to consider risks about gains differently than risks pertaining to losses
Escalation of commitment
continue to irrationally invest in an ineffective course of action due to sunk costs
Three Strategies to Enhance Decision Making
1. Decisional Balance Sheet
2. Problem Definition/Framing
3. Pre-Mortem Exercise
1. Decisional Balance Sheet
•Consideration in four different areas:
1.Gain/losses for self (e.g., income, free time)
2.Gain/losses for others (e.g., how does this decision affect family, friends, coworkers, customers, etc)
3.Self-approval or disapproval (e.g., pride, shame, alignment to ideals/values, etc.)
4.Approval or disapproval of others (e.g., will my friends feel I made the right choice, will I be criticized or ridiculed, will I be praised and respected, etc.)
•Evaluate the positive and negative aspects of each area
•Answers can be influenced by informational inputs and persuasive arguments
•Completeness and accuracy when filling in the decisional balance sheet before implementing a decision is critical
Technique #2: Bazerman's Problem Definition
•Obtaining a broader perspective of the problem through a wider search of information
1.Define the problem
•Selecting the right graduate school
2.Identify the criteria necessary to judge the multiple options
•Location, prestige, faculty, etc.
3.Weigh the criteria
•Rank #2 in terms of importance to you
4.Generate alternatives
•The schools that admitted you
5.Rate each alternatives against each criterion
•Rate each school on each criteria that you identified
6.Compute the optimal decision
Technique #3: Osland's Pre-Mortem Exercise
1.Preparation: Individuals thoroughly review the plan
2.Imagine a fiasco: Decision-makers imagine that the project or plan is a complete and utter failure. What could cause this?
3.Generate reasons for failure: Individuals write down all the reasons why they think the failure occurred.
4.Consolidate lists: Each individual states one reason for failure until all reasons have been shared.
5.Revisit the plan: Individuals address two or three issues of major concern. Another meeting is scheduled to discuss all remaining issues.
6.Review the list: Individuals review the list of concerns to make sure that all concerns have been addressed.
Problem solving
•The essence of management is problem defining and problem solving
-Empowering employees and gaining their commitment
-Developing employee skills
-Final decisions are better understood by the group
-Generating more alternative solutions/ideas
programmed decisions
are routine, repetitive decisions that follow established rules, procedures, or guidelines. They are typically made in situations that occur regularly and have predictable outcomes.
Example: Approving standard employee vacation requests or reordering office supplies when inventory runs low.
Non programmed decisions
-New, novel, complex decisions having no proven answers
The Stages of Decision Making
•Stage 1: Situational Analysis What's the most important problem?
•Stage 2: Problem Analysis
What are the causes of the problem?
•Stage 3: Solution Analysis
What's the best solution?
•Stage 4: Implementation Analysis
How do we implement the solution?
The Kolb Model of Group Problem Solving
Kolb says problem solving is not linear but wave-like. Groups move outward to explore ideas (expansion) and inward to focus decisions (contraction).
Key concepts:
Green Light / Red Light:
Green light = free idea generation (no judgment).
Red light = critical evaluation and decision-making.Believing / Doubting:
Believing = openly explore ideas (divergent thinking).
Doubting = test and challenge ideas (convergent thinking).Divergence / Convergence:
Divergence = gather many ideas and perspectives.
Convergence = narrow down to the best solutions.
This cycle repeats as needed to fully solve complex problems.
•Green Light/Red Light - The Kolb Model
•Green mode = Expansive Phases
•Creative imagination
•Sensitivity to the immediate situation
•Empathy with other people
•Red mode = Contraction Phases
•Analysis
•Criticism
•Logical Thinking
Coping with the External Environment
Think of the green mode as diverging to gather information and ideas, and the red mode as converging on a decision that allows the group to proceed to the next stage.
situation analysis
•Role: LEADER
•Visioning/Exploration
•Priority Setting
whats the most im
Problem Analysis
What are the Causes of the Problem?
•Role: DETECTIVE
•Information Gathering
•Problem Definition
Solution Analysis
What's the Best Solution?
•Role: INVENTOR
•Idea Getting
•Decision Making
Implementation Analysis
How do we Implement the Solution?
•Role: COORDINATOR
•Participation
•Planning
Group Decision Making in Organizations
1. consultative
2.consensus
3. democratic
Consultative
leader consults with members
consensus
1.: leader shares problem and together they generate/evaluate problem/solutions
democratic
problem given to group and members empowered to make the decision
Nominal Group Technique:
Generating and evaluating alternative solutions to a problem
Delphi Technique:
A method of reaching expert agreement through anonymous, multi-round questionnaires with feedback after each round.
Devil's Advocate:
assigning someone the role of critic
why?forcing the other team members to justify their decision. Avoids groupthink.
higher quality decision
The Dialectic Method:
calls for managers to foster a structured debate of opposing viewpoints prior to making a decision
method is a discourse between two or more people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing to establish the truth through reasoned arguments.
higher quality decision
Conflict
when one party believes another party has or is about to do something that will negatively effect something they care about
Helpful Conflict
C-type conflict, "cognitive conflict" or "task conflict" is conflict about task-related issues
encourages open communication enables people to learn from each other, and to consider each other's views ... then they'll be more likely to accept whatever the final decision is, too. This benefits team effectiveness because teams will be focused, creative, integrative and open.
Harmful Conflict
A-type, "affective conflict" or "relational conflict" is about
individual issues.
Blocks communication and draws the focus from the
team to the individuals.
Limits communication to a few people and decreases
the quality of work.
Decreases the likelihood that people will accept final
decisions and work together well in the long-term.
Teams LESS focused, creative, integrative and open.
Stage 1: Potential Opposition
Three conditions for conflict
1. communication
2. Structure
3. personable variables
Personal barriers to communication
individual attributes that hinder communication
physical barriers to communication
physical noise, time zone differences, physical distance, office design, etc.
Semantic Barriers to communication
words themselves
Jargon - language, acronyms, or terminology specific to a profession, group or company
Buzzwords - overused words, faddish phrases (e.g., "transparency")
structure
Conflict can occur when the organization or team structure creates ambiguity in who is responsible for what
•Conflict between groups --- COMPETE
-Competition for limited resources
-Differing priorities and goals
-Asserting their ideas
•Conflict within groups --- ROLE FORMALIZATION
-Overlapping or unclear job boundaries
-Unreasonable or unclear policies, standards, or rules
-Unreasonable deadlines or extreme time pressure
-Collective decision making
Personable Variables
Different personal styles or personality can create tension
•Incompatible personality traits
-E.g., introvert vs. extrovert; Type A vs Type B
•Differing value systems
-E.g., shop floor vs. c-suite
Stage 2: Cognition & Personalization
•The perception of conflict arises between the parties
•Emotions begin to get involved. In order for personalization to occur, the parties must feel that there is conflict via stress, anxiety, anger or frustration, resulting in emotional involvement
•Once conflict arises, individuals must make a decision on how to handle the problem
Stage 3: Intention to Manage Conflict
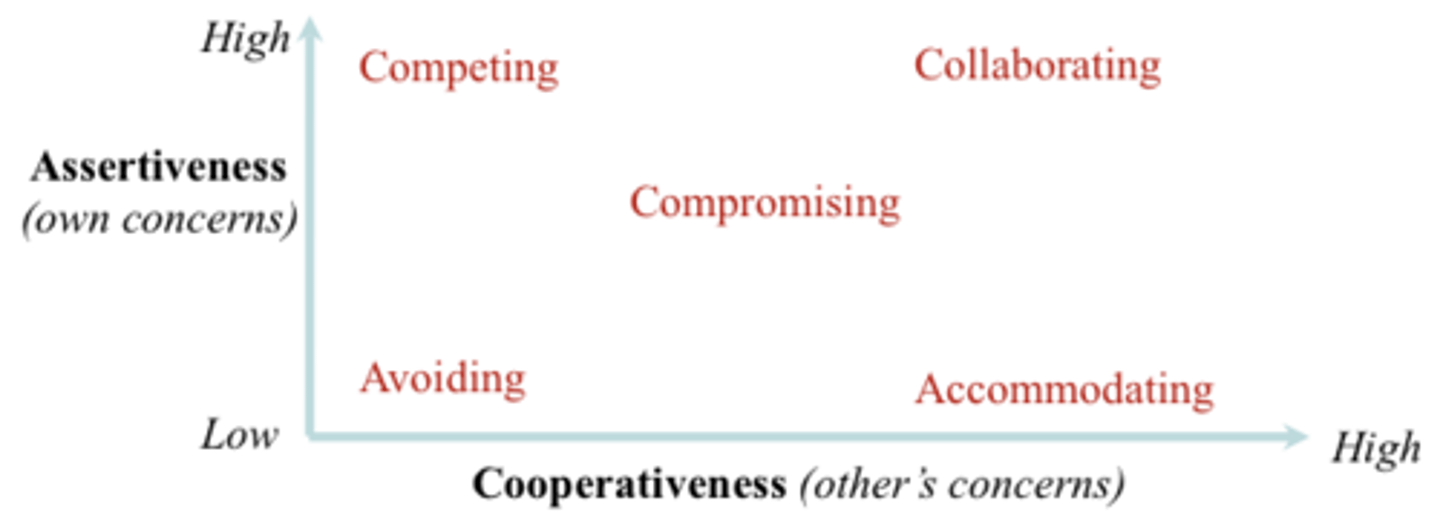
Each conflict category reflects varying levels of the following two dimensions:
1.Assertiveness à the extent to which the individual attempts to satisfy his or her own concerns
2.Cooperativeness à the extent to which the individual attempts to satisfy the other person's concerns
Stage 3: Intention to Manage Conflict - 5 Styles
•Competing: Assertive and uncooperative; all about you
•Accommodating: Unassertive and cooperative (the opposite of Competing); self sacrifice, yielding
•Avoiding: Unassertive and uncooperative; avoiding the conflict; withdrawing
•Collaborating: Assertive and cooperative (the opposite of Avoiding); working together to find a solution that fully satisfies the concerns of both
•Compromising: Intermediate in both Assertiveness and Cooperativeness - finding a mutually acceptable solution that partially satisfies both parties; seeking middle ground
Stage 4: Behavior
Intention to manage conflict--> Individual's behavior/other's behavior.
Stage 5: Outcomes
functional and dysfunctional
functional
-Improves the group's performance
-Improves the quality of decisions
•Stimulates creativity and innovations
•Encourages interest and curiosity among group members
•Provides the medium through which problems can be aired and tensions released
•Fosters an environment of self-evaluation and change
dysfunctional
-Hinders group performance
•Poor communication
•Reduces group cohesiveness
•Ignores group goals
•Infighting between members
-Could lead to the destruction/dissolution of the group
Why Negotiate?
-Interdependence
-People need to be able to work together across business units and divisions
-Dynamic nature of business
-People must continually create possibilities, integrate their interests with others, and recognize the inevitability of competition both within and between companies
-An increasingly diverse set of customers/clients/partners
-Increased inter/intra-organizational competition
What is negotiation?
-A process in which two or more people or groups share their concerns and interests to reach an agreement of mutual benefit
Positions
one party's stance regarding the issue (stated agenda)
Interests
•underlying concerns that would be affected by the resolution (hidden agenda)
•The private interests of the negotiator behind the positions
BATNA:
•Best Alternative To a Negotiated Agreement
-Alternative if no agreement reached
-The better the BATNA, the more power you have in negotiating
Reservation (Resistant) Price:
Least favorable point to accept an agreement
-"Bottom line" price
-For the Buyer, it's the most they are willing to pay
-For the Seller, it's the least they are willing to sell for
Bargaining Zone (ZOPA):
•Zone of Possible Agreement
-Range between reservation prices
Target Price
Realistic view of getting the highest achievable outcome from a negotiation
Distributive Bargaining
A negotiation strategy in which one person gains and the other person loses