Chapter 9: Aggression (hurting others)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
+ Lecture content from March 11th & 14th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
T or F: Aggression is defined by its intentions NOT by the form it takes
TRUE
Agression
Physical, verbal, and nonverbal behaviour that is intended to hurt others
What are 3 main types of aggression
Hostile
Instrumental
Relational
Hostile aggression
Hurting someone else because we are angry
Driven by anger → performed as an end in itself
Instrumental aggression
Hurting someone else to achieve some other purpose
A means to someone other goal
*Linked to terrorism
Relational aggression
Aggression that harms someone else through the manipulation of friendships
*Leverages the knowledge that everyone wants to be included
Ex. cyberbullying, in-person bullying
What are 2 challenges that pose studying this aggression question: “Kids who watch more violent TV are more aggressive on the playground”
Reverse causality → opposite relationship
Maybe it is not the violent TV shows that cause aggression
Perhaps it is just that aggressive kids tend to watch more violent TV
3rd variables
Perhaps there is another variable that is causing both the aggressive behaviour AND The TV show tendencies
E.g., lack of TV supervision at home OR parents fight at home
How is aggression operationalized in the lab?
Self-report & scenario complete
Shocks, noise blasts, hot sauce, demanding yoga poses
Costly punishment in an ultimatum game
Is aggression based on nature or nurture?
Nature
Evolutionary instincts
Genes → males = more aggressive (esp. hostile aggression)
Testosterone
Nurture
Social learning theory
Culture of honour
Social learning theory (aggression)
We learn how to behave by behaving and experiencing consequences
AND we learn how to behave by observing others behaving and observing the consequences of their behaviour
E.g., Bobo doll experiment
*We can learn to be aggression simply by watching other people aggressive and seeing whether they are rewarded
Culture of honour
Southern US states are classified as “culture of honour”
Strong concerns about reputation caused a this culture of honour
Responses to insults are often returned with violence
Insults deserve retaliation
Willingness to use violence to avenge perceived wrongs or insults
Murder rates x culture of honour
U.S Southern states = increased argument-related murders (in comparison to North)
*Felony-related murders are relatively similar → but South is still higher
Aggression hallway experiment
(1) Participants from Northern and Southern states were asked to carry a box of supplies down an office hallway → on the way a confederate purposefully bumps into them and calls them an “asshole”
Facial expressions observed
RESULTS = Southerners → more angry faces & Northerners → more amused faces
(2) Participants then completed different scenarios describing threat to honour
Cortisols and testosterone measured
RESULTS = Southerners → increased cortisol ; answered scenarios stories with violence
Culture of honour in Canada
If you live farther away from Mountie forts (you have less local Mountie authority) = more likely to have a culture of honour because you have to fend for yourself
Frustration-aggression hypothesis
Frustration = anything that blocks us from attaining goals
Frustration → leads to aggression
We aggress when our goals are block (AKA when we are frustrated)
Critiques of frustration-aggression hypothesis
Frustration & goal blocking = does not always cause aggression
Valid excuses
Apologies
Frustration & goal blocking = causes different responses → learned helplessness
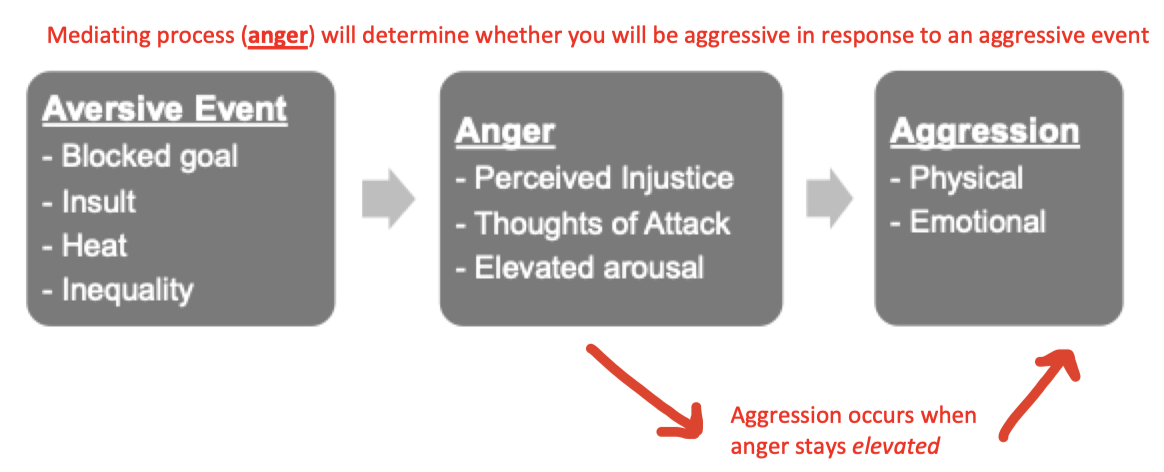
Neo-associationistic account of aggression
Aversive event → anger → aggression
Mediating process (anger) = determines whether you will be aggressive in response to an aggressive event
Aggression occurs when ager stays elevated
Relative deprivation theory
When you think that you (or your social group) has less than you deserve → associated with aggression
Believing you are less well off when comparing yourself to others
Income inequality and aggression
Countries with lower income inequality = lower aggression
E.g., Norway, Denmark, Sweden
Examples of situational causes of aggression
Relative deprivation theory
Frustration-aggression theory
Neo-associationistic account of aggression
The weapons effect
Hot weather
Alcohol
Video games
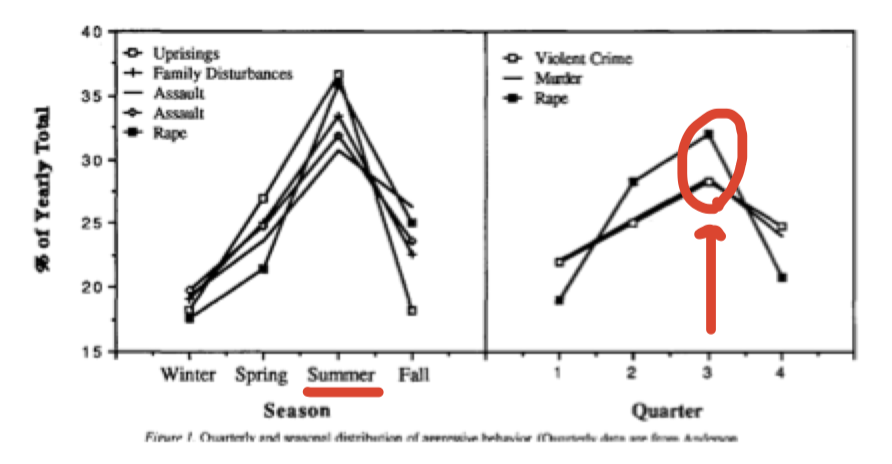
Heat x aggression
Heat = environmental irritant → naturally frustrating
Hotter weather = more aggression
More road rage
More violent crime
More bad batters
Heat causes aggression because it make you uncomfortable → increases arousal
Misattribution arousal → to other people RATHER than the weather
Alcohol x aggression
Alcohol = increases aggression
Reduces anxiety & inhibitions against aggression
Interferes with info processing that would override aggressive impulses → makes us forget to think about future consequences
Interpreting ambiguous acts as provocations
“Alcohol myopia” → reduces self-awareness and enhanced de-individualization
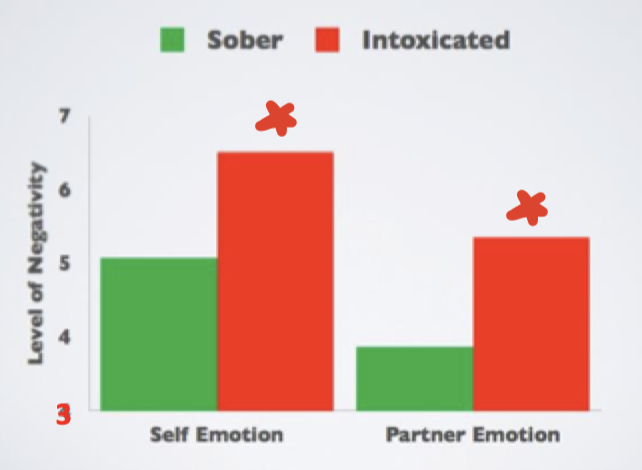
Alcohol x aggression in relationships study
Participants asked to recall an argument in their relationship → asked how both they and their partner felt about the aggression
RESULTS = Increased negative self-emotions and partner emotions when drunk
Alcohol made negative emotions worse

The weapons effect
The mere presence of weapons acts as a cue that can cause violence
Priming effect → guns and weapons associated with violence and aggression
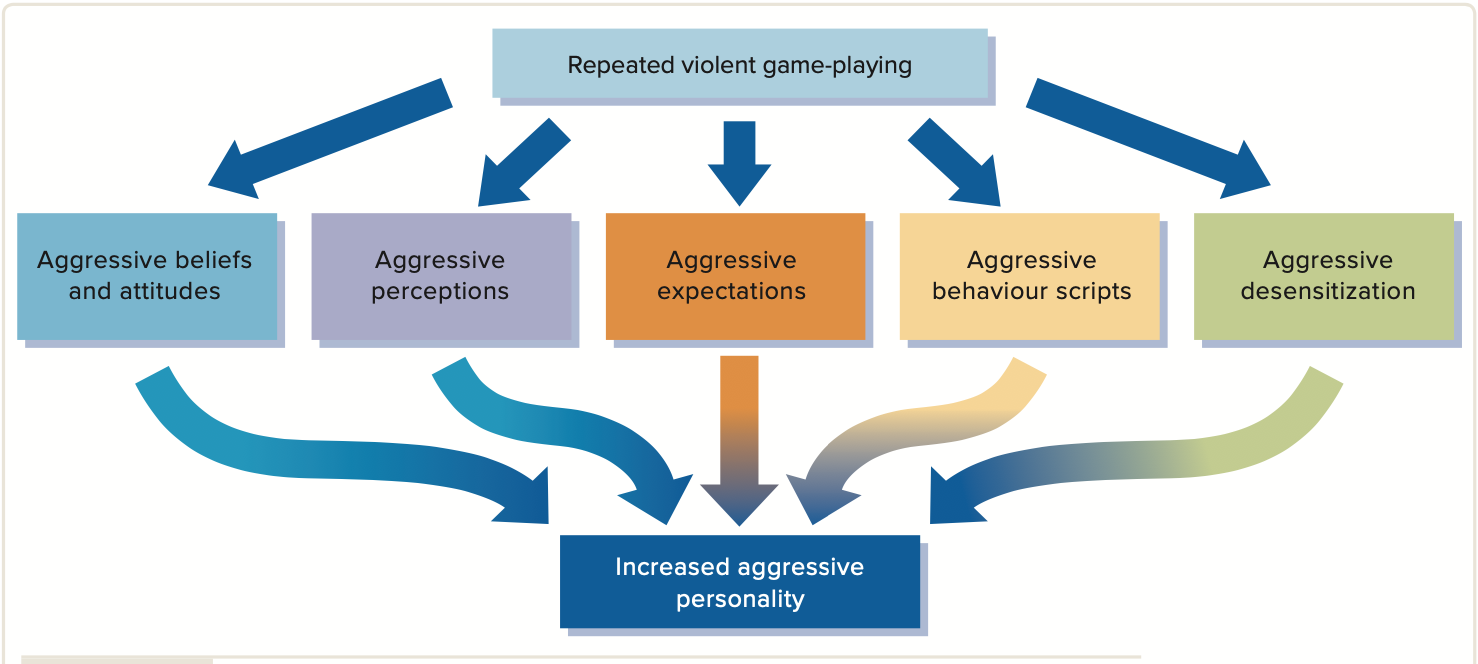
Video games x aggression
Increased aggressive behaviour, thoughts, & emotions
*Decreased prosocial behaviour
Catharsis
Venting emotions→ emotional release
Aggression
Physical or verbal behaviour intended to cause harm
Comes in many different forms
Ex. physical → hurting someone’s body
Ex. relational → hurting someone’s feelings or status
Ex. hostile → stems from emotions such as anger
Ex. instrumental → aims to injure
Social leaning theory x aggression
Aggression = learned behaviour
Ex. Bandura Bobo doll experiment
What are the effects of viewing violence?
Increased aggressive behaviours → esp. in provoked people
Desensitizes viewers to aggression
Alters viewers perceptions of reality
*Linked to the finding that violent porn can increase men’s aggression towards women
T or F: heavy exposure to televised violence correlates with aggressive behaviour
TRUE
Why might playing violent video games increase aggression more than TV or movies?
Playing video games = requires more active participation
Aggression as an instinctive behaviour
Instinctive behaviours = innate, unlearned, universal
Aggression is adaptive > self-destructive
T or F: aggression correlates with testosterone in men
TRUE
Displacement
When we redirect our aggression to a target OTHER than the source of the frustration
Typically new target = safer or more socially acceptable
According to Bandura, when do we aggress?
When we are aroused → frustration, pain, insults
When it seems safe and rewarding to aggress → based on the consequences we anticipate
Catharsis view of aggression
Aggression is reduced when we “release” aggressive energy either by:
Acting aggressively
Fantasizing aggression
What are some factors that predict aggression
Being male
Aggressive or anger-prone temperaments
Alcohol use
Violence viewing
Anonymity
Provocation
Weapons effect
Group interaction