Biology - Chapter 3: Proteins | Quizlet
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
protein
an organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids linked together with a peptide bond
peptide bond
the chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
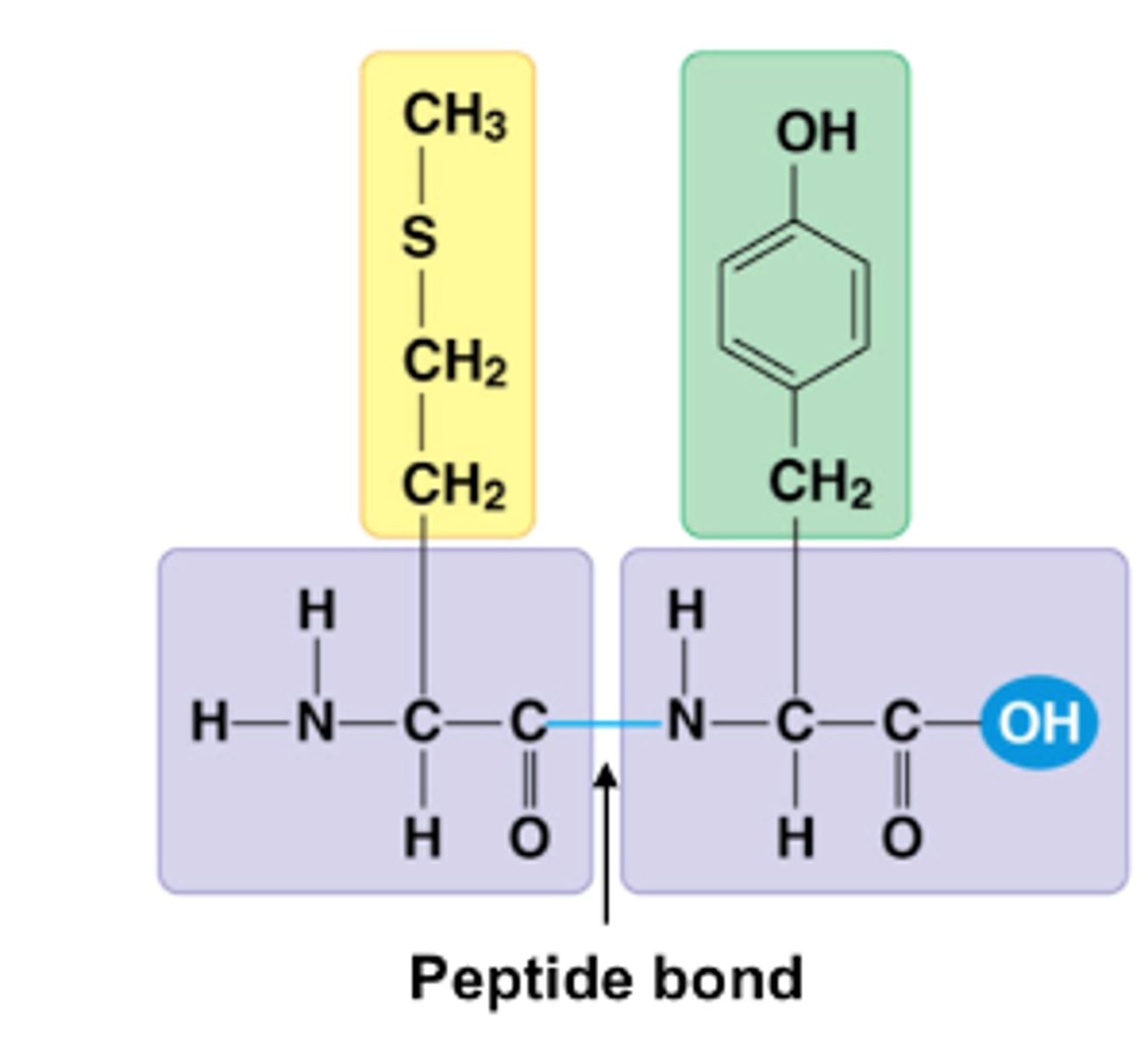
polypeptide backbone
repeating sequence of atoms along the core of the polypeptide chain
side chains give proteins
unique properties
noncovalent bonds between side chains determine
folding of the protein
polarity of side chains (hydrophobic repulsion)
folds the protein so that the nonpolar side chains are not in contact with water/polar side chains are in contact with water
denaturation of a protein
unfolding of the protein's tertiary and secondary structure
proteins will fold into conformation of ______ energy
lowest
molecular chaperones
special proteins that assist in the protein folding
protein domains
structural units that fold more or less independently of each other
primary structure of protein
amino acid sequence
secondary structure of protein
Stretches of polypeptide chain that form α helices and β sheets
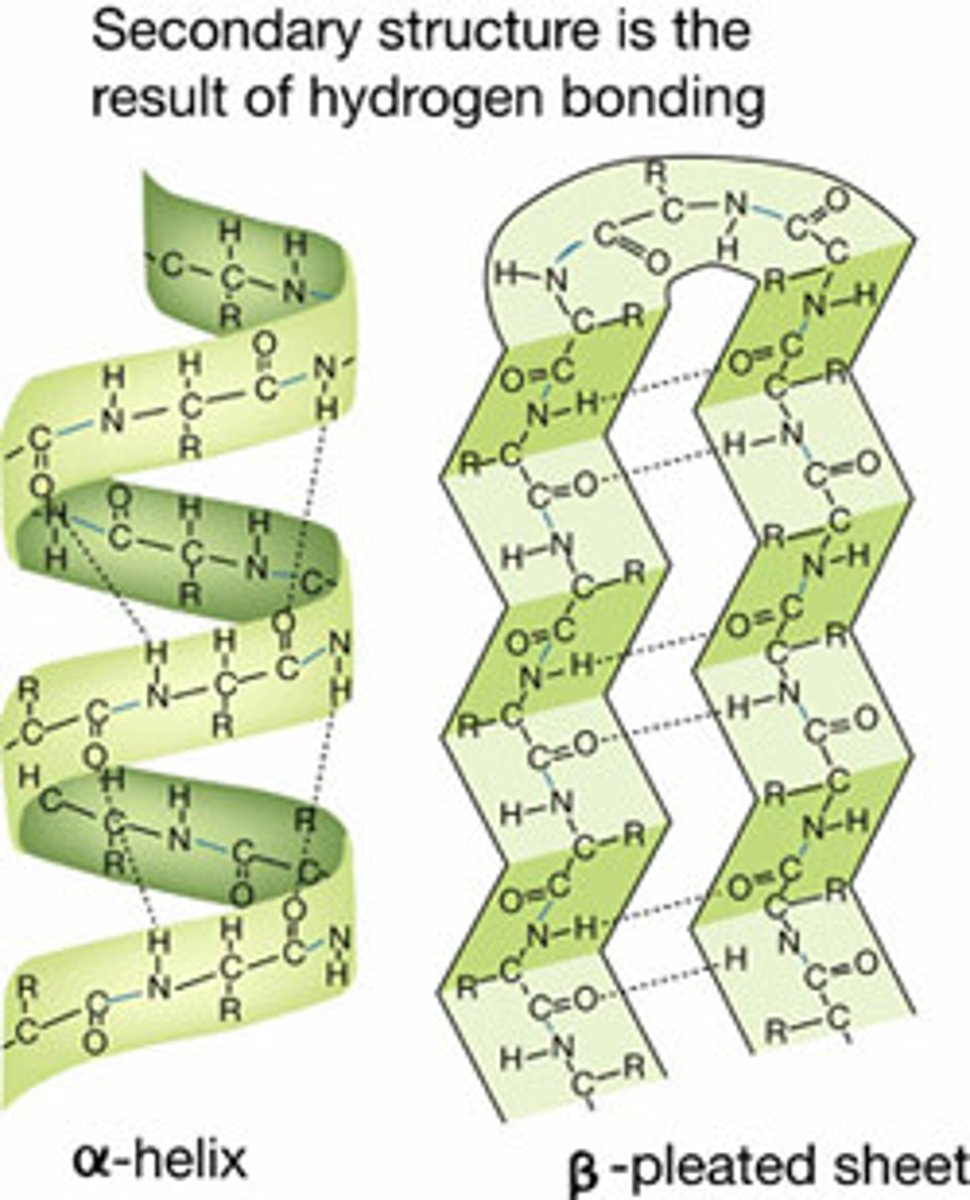
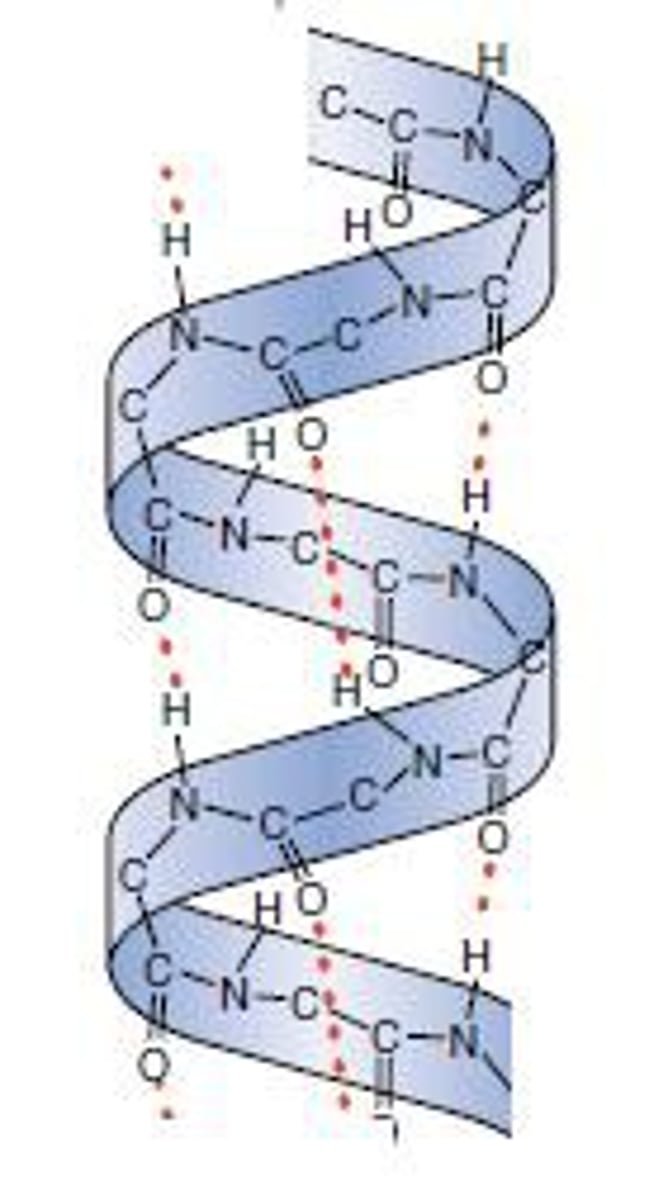
α helix
forms when a single polypeptide chain twists around on itself to form a rigid cylinder
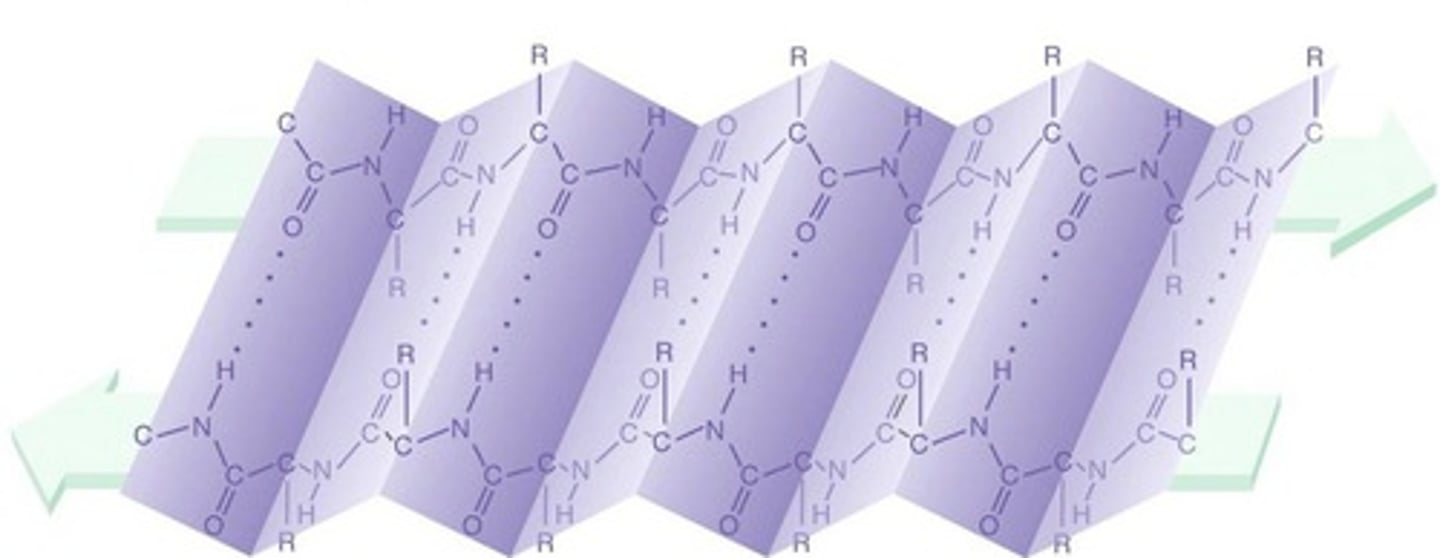
β sheet
forms either from neighboring segments of the polypeptide backbone that run in the same orientation (parallel chains) or from a polypeptide backbone that folds back and forth upon itself, with each section of the chain running in the direction opposite to that of its immediate neighbors (antiparallel chains)
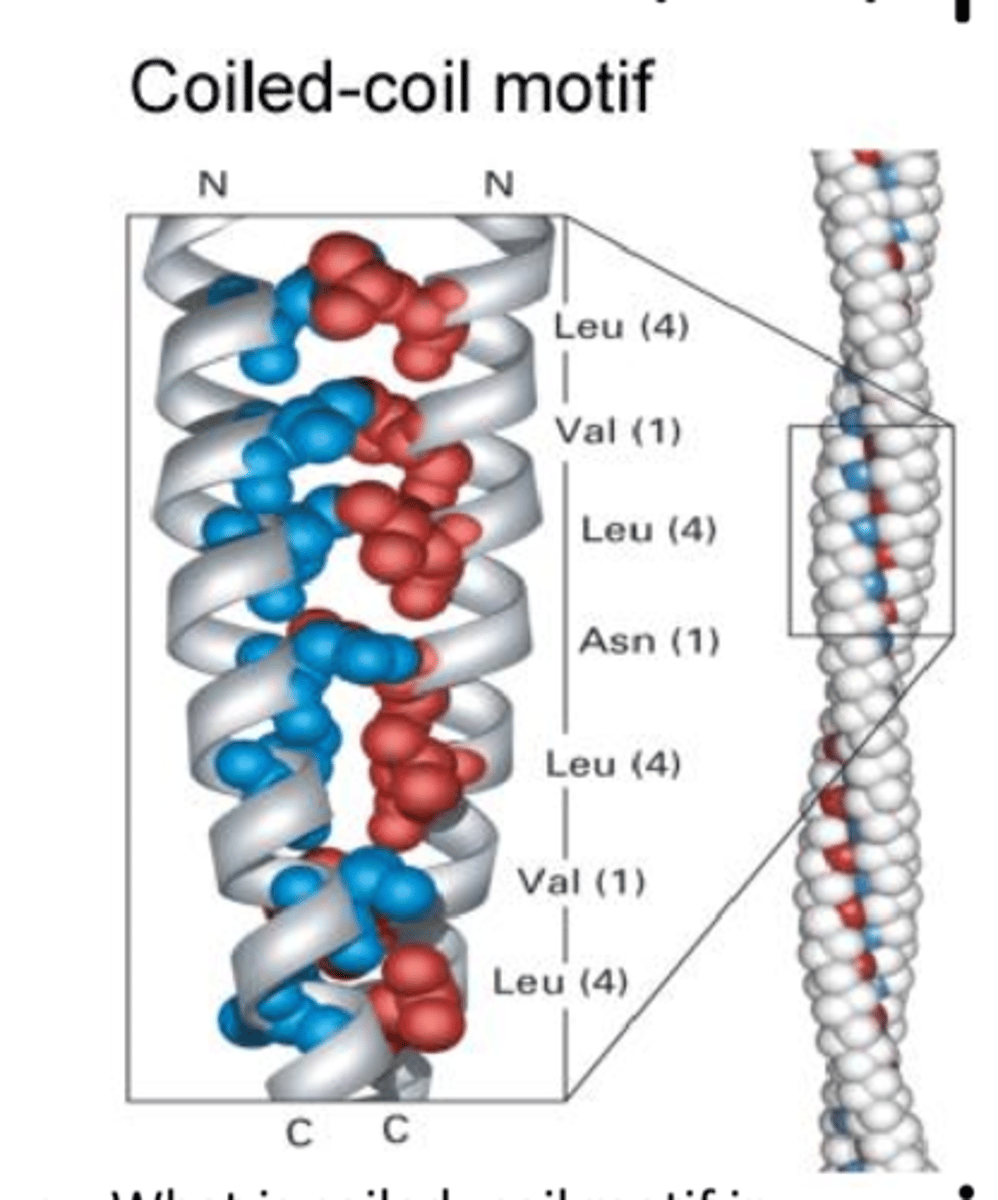
coiled-coil structure
a secondary structure where a pair of alpha helices that are coiled around each other; hydrophobic strip in the center
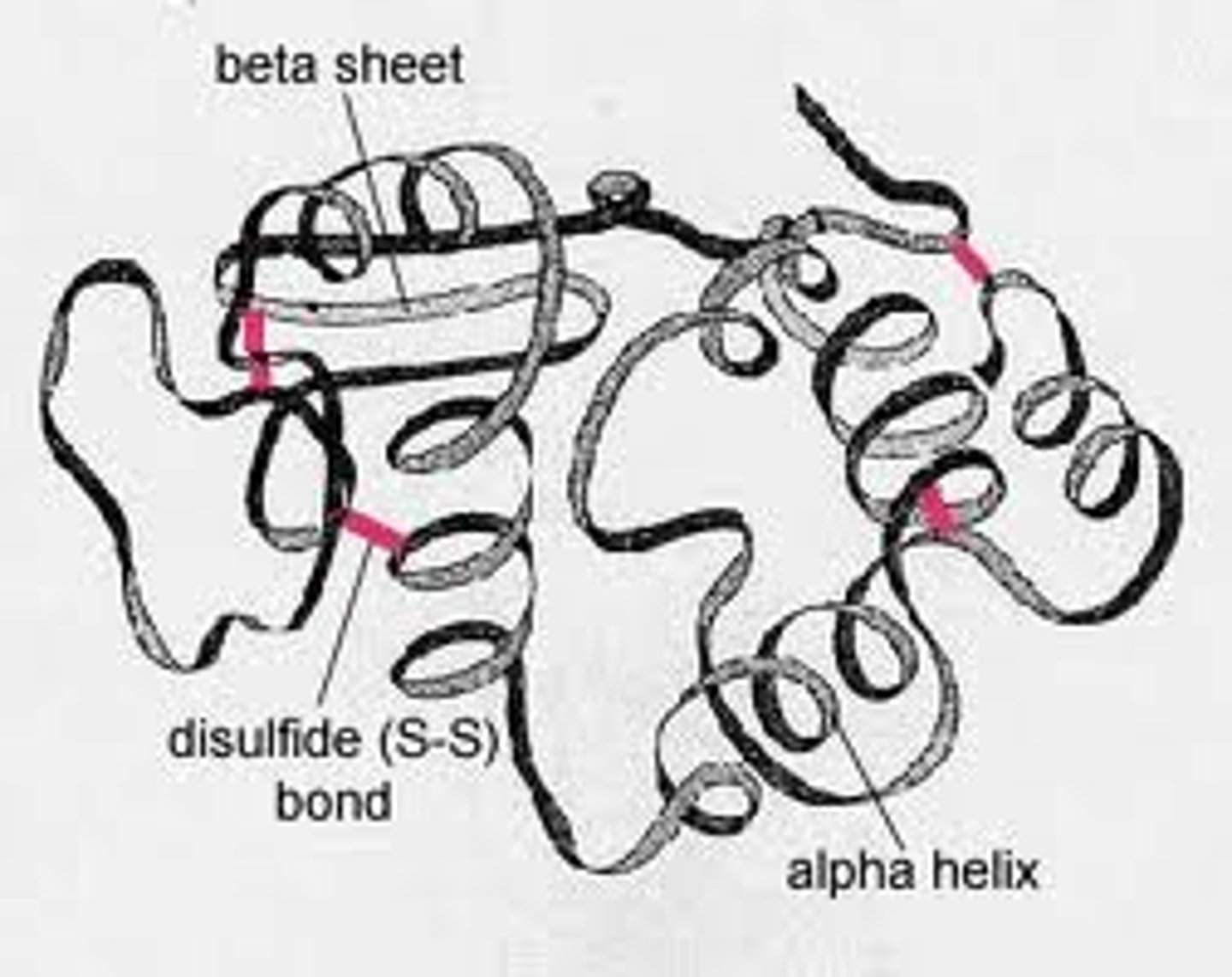
tertiary structure of protein
full three-dimensional structure
quaternary structure of a protein
if a particular protein molecule is formed as a complex of more than one polypeptide chain
protein family
a group of proteins that are structurally and functionally related
protein module
structural or functional units that are common to many different proteins
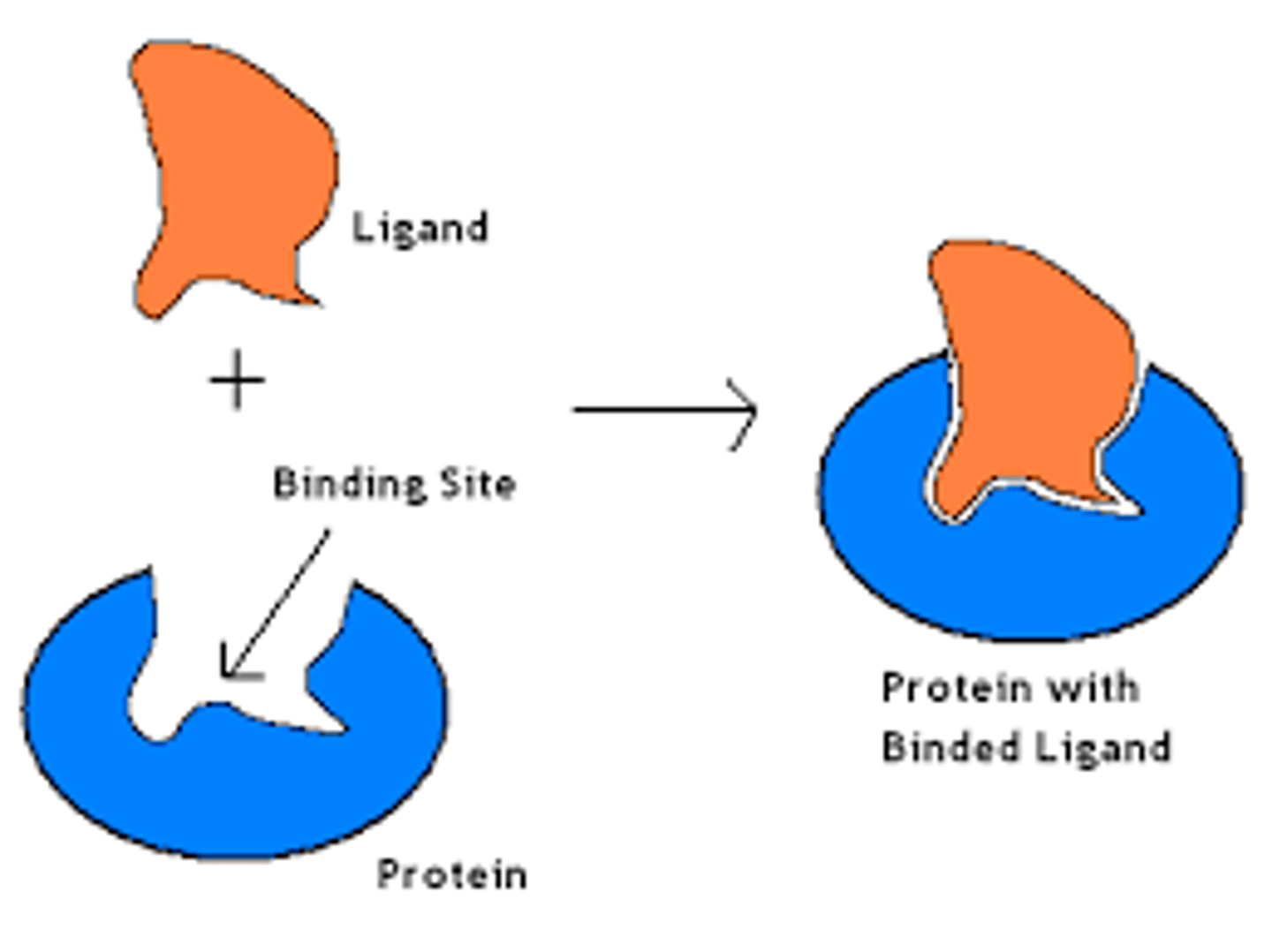
binding site
any region of proteins surface that can interact with other molecule through sets of noncovalent bonds
protein subunit
polypeptide chain in a multi-protein complex
globular proteins
spherical, water-soluble proteins
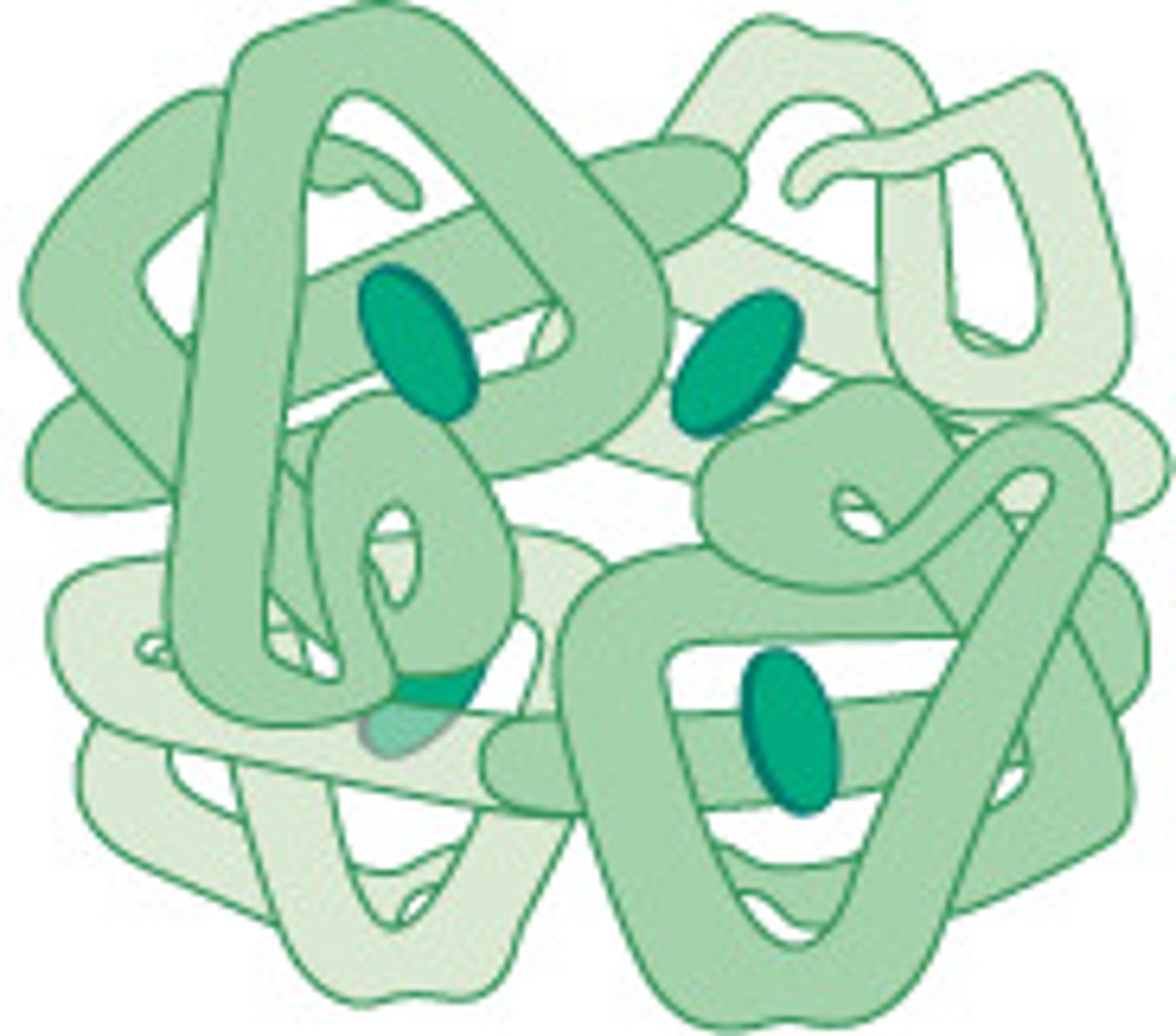
globular proteins can form
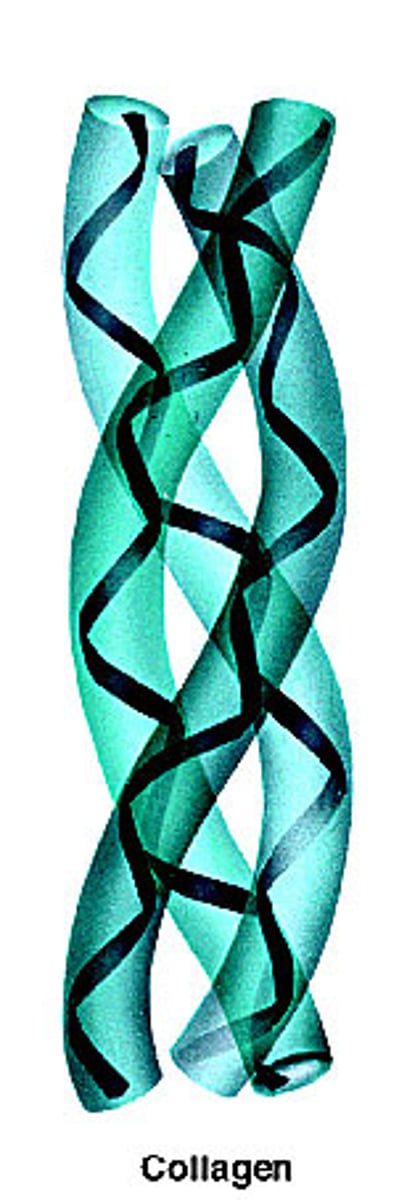
long helical proteins
fibrous proteins
long, insoluble, structural proteins

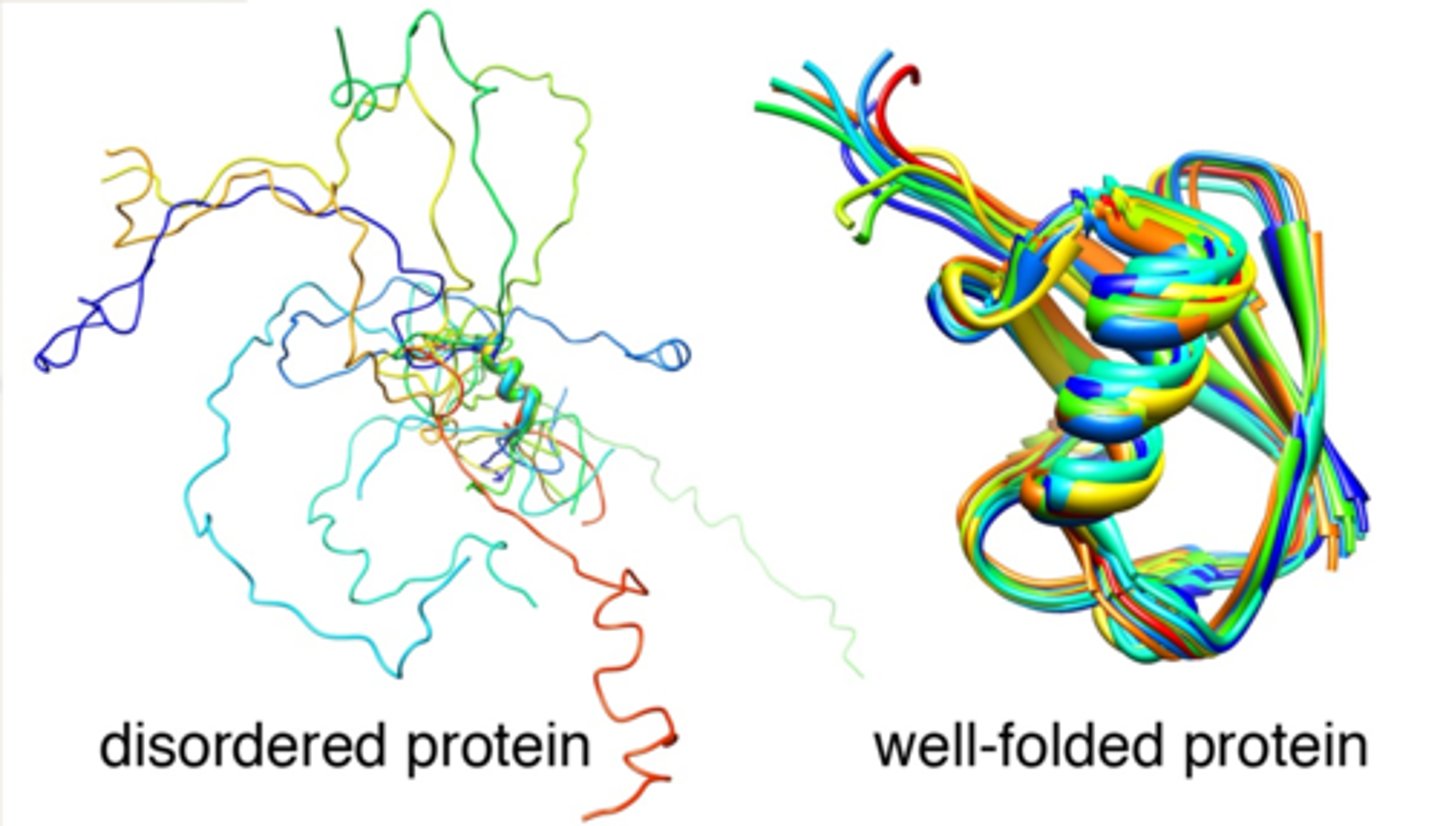
disordered proteins
rubberlike, elastic meshwork (elastin in EM)
covalent cross-linkages
stabilize extracellular proteins (disulfide bonds)
reasons why large structures are formed by subunits (proteins)
1. small genetic information is needed
2. easy assembly and disassembly
3. errors in synthesis can be more easily avoided
assembly factors
proteins that are required for formation of a macromolecular structure but are not themselves part of that structure
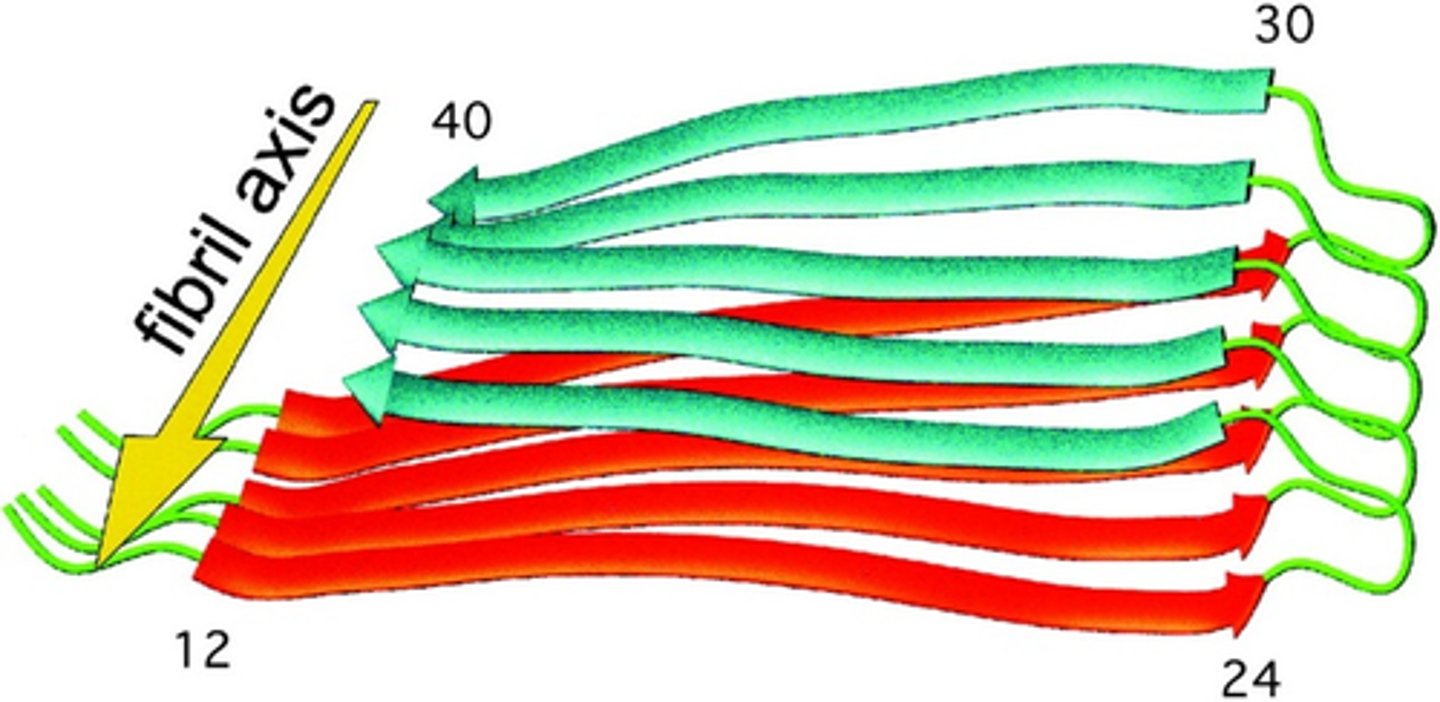
amyloid fibrils
Self-propagating, stable β-sheet aggregates (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and prion diseases)
ligands
any molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule
three ways of two proteins binding
1) surface-string
2) helix-helix (coiled coil)
3) surface-surface
hydrolase
hydrolytic cleavage
nuclease
breaking down nucleic acid by hydrolysis
protease
breaking down proteins by hydrolysis
synthase
synthesizing two molecules in anabolic reactions by condensation
ligase
joining two molecules in energy-dependent process
isomerase
rearrangement of bonds
polymerase
catalyzing polymerization reactions
kinase
catalyzing addition of phosphate groups
phosphatase
hydrolytic removal of phosphate groups
oxido-reductase
catalyzing redox reactions
ATPase
hydrolyzing ATP to ADP
GTPase
hydrolyzing GTP to GDP
phosphorylation
the addition of a phosphate group to a molecule
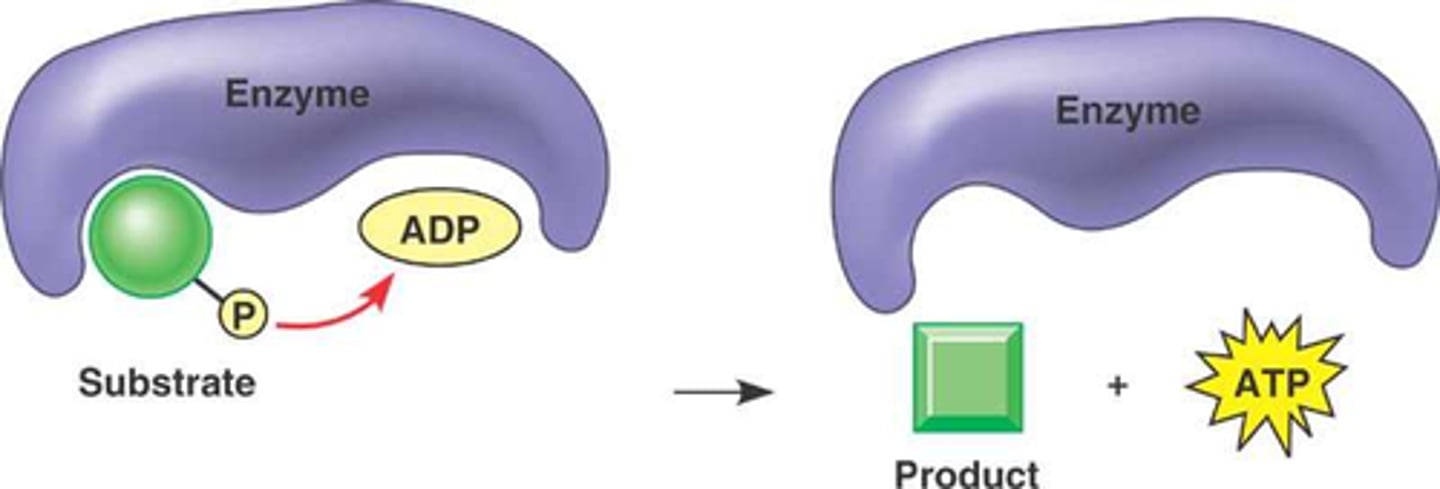
regulation by phosphorylation
-two negative charges on a phosphate group can greatly change proteins conformation
-phosphate group can be recognized by other proteins' binding sites
-can disrupt protein-protein interactions
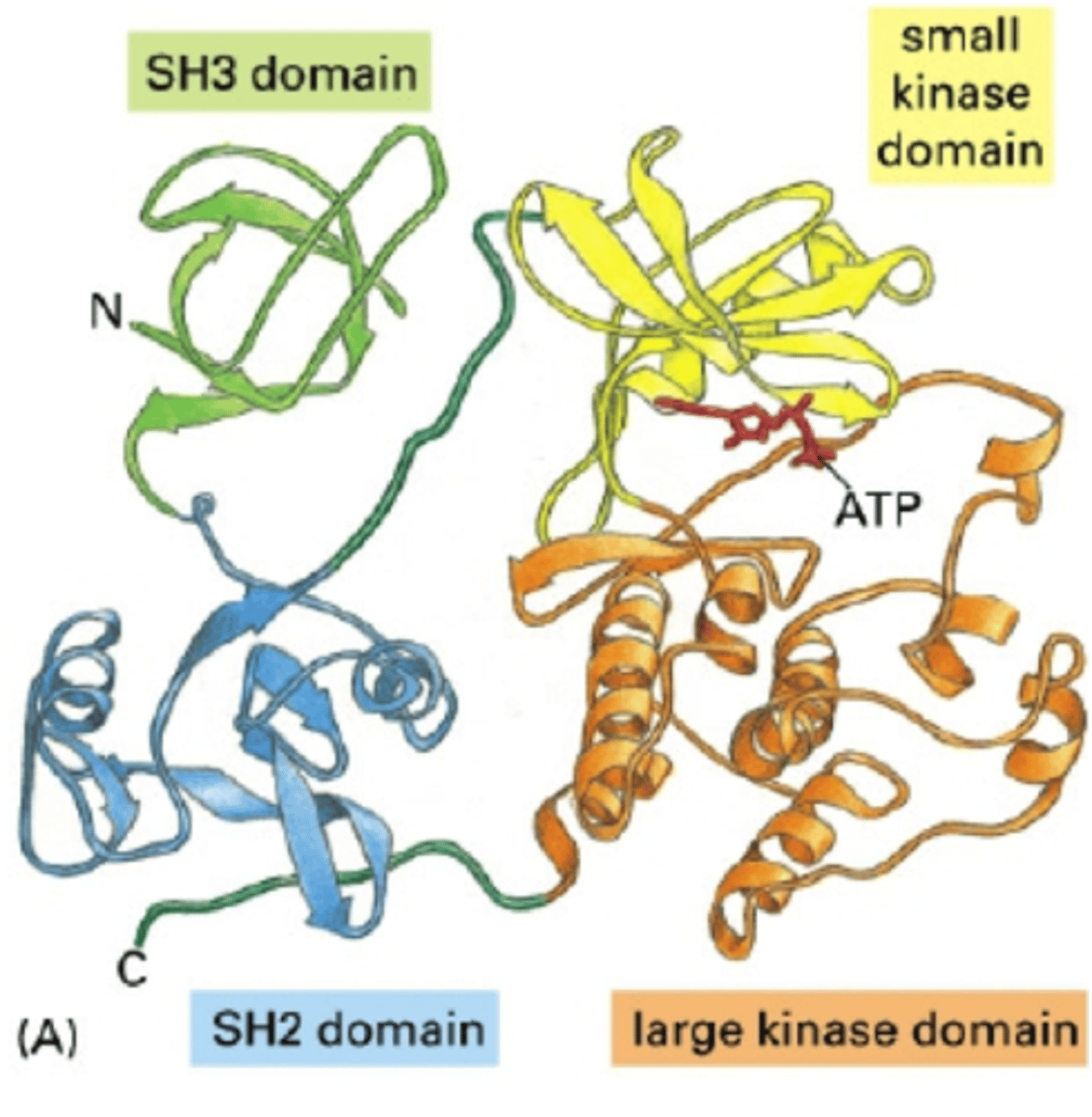
Src family of protein kinases
controlling signal-processing proteins by adding phosphates and removing them
Ras protein
monomeric GTPase that drives the growth, proliferation, and migration of cells
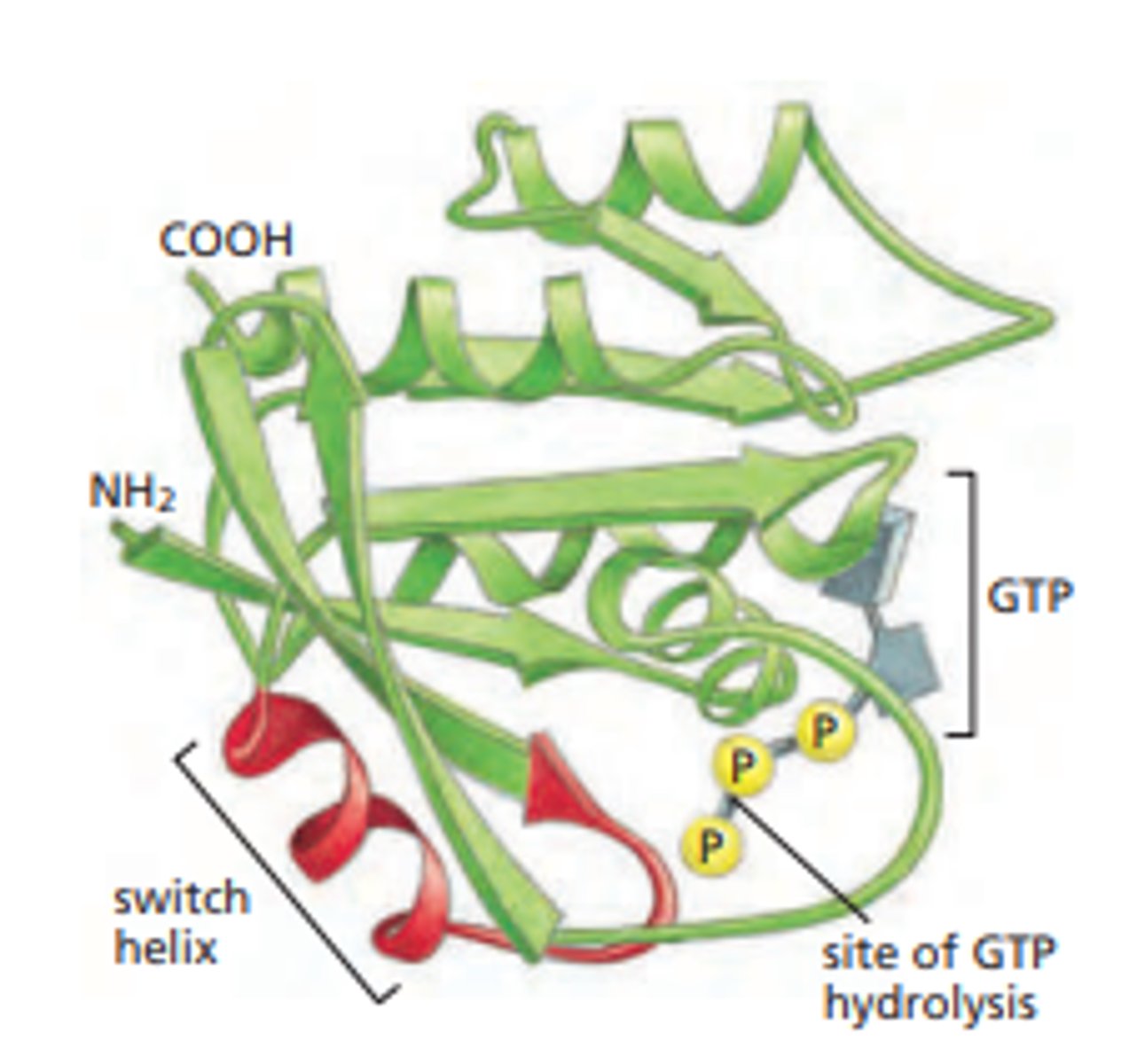
GTP-binding proteins
proteins which are 'on' (actively signaling) when GTP is bound, and 'off' when GDP is bound
GAP
GTPase activating protein binds to Ras and induces hydrolysis of GTP
GEF
guanine nucleotide exchange factor binds to GAP-Ras causing the release of GDP
ubiquitination
targets a protein for degradation by a proteasome
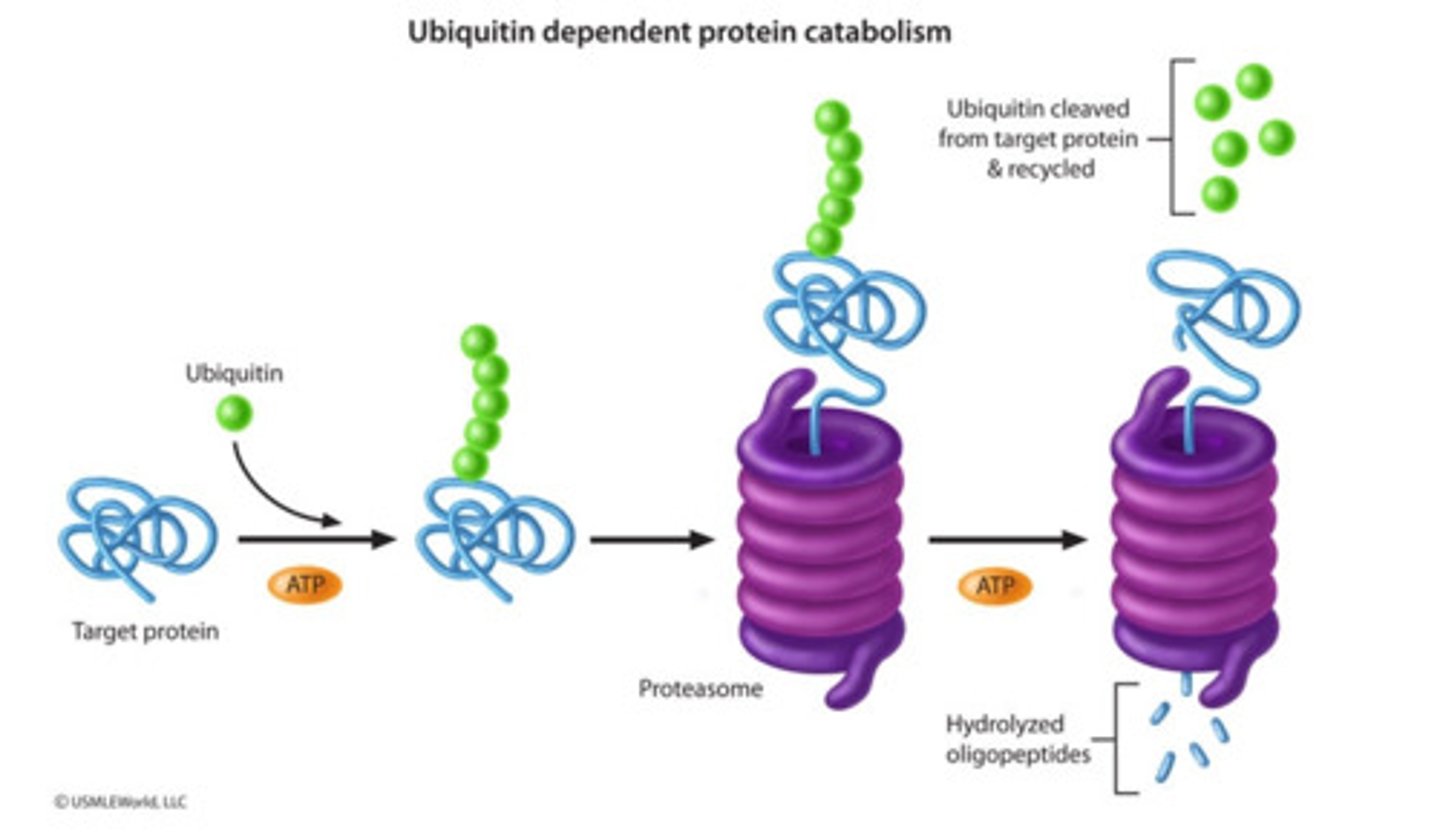
ubiquitination process
1. E1 (ubiquitin-activating enzyme) uses ATP hydrolysis to bind ubiquitin to itself
2. E1 passes ubiquitin to E2 (ubiquitin conjugating enzyme) that works in conjunction with E3 (ubiquitin ligase)
3. E3 binds to degradation signals (degrons) in protein substrates
motor proteins
specialized proteins that use energy to change shape and move cells or structures within cells
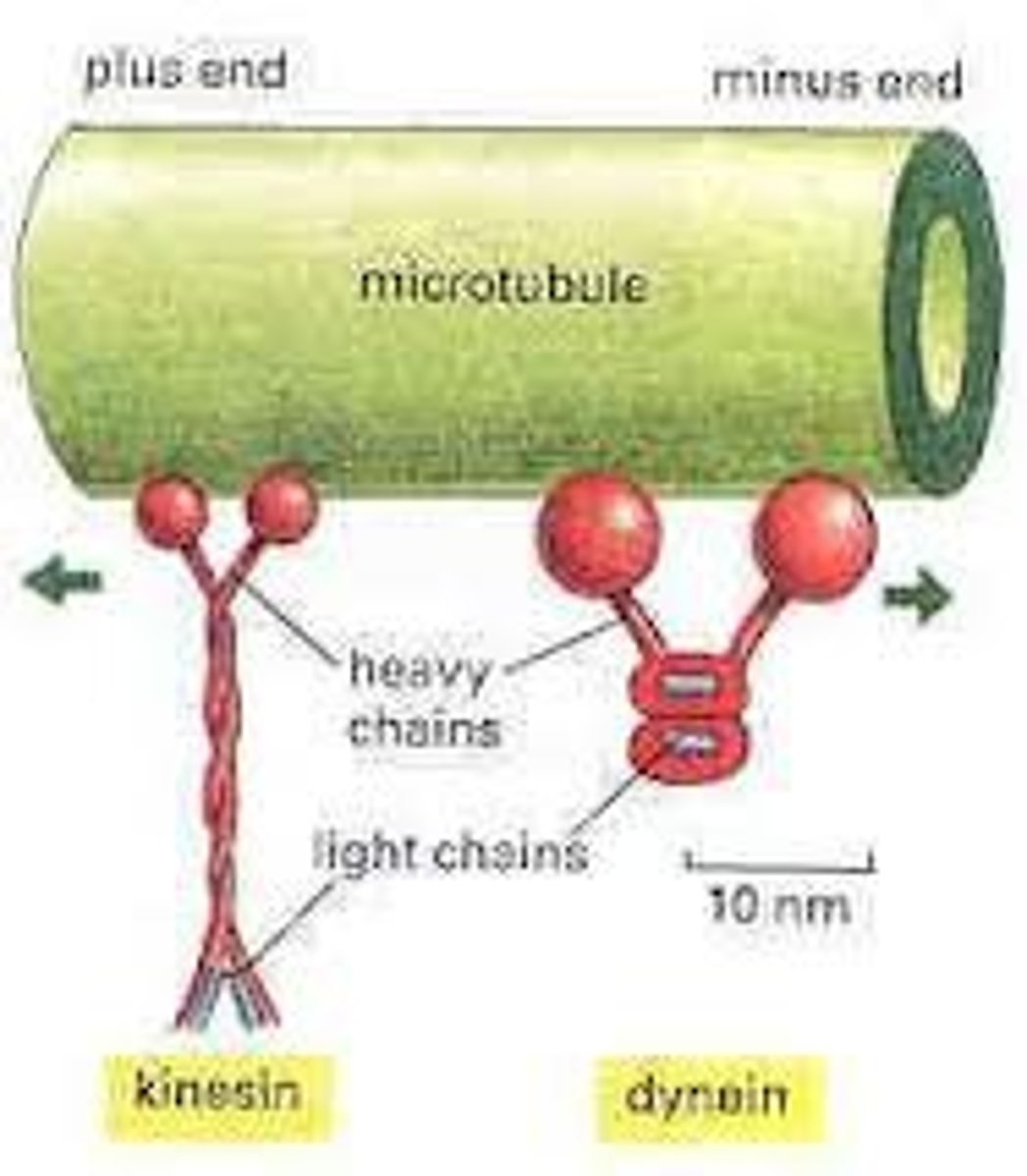
How is unidirectional movement of motor proteins achieved?
By coupling one of the conformational changes to ATP hydrolysis.
transport proteins
a transmembrane protein that helps a certain substance or class of closely related substances to cross the membrane
ABC transporters (ATP-binding cassette)
carrier proteins that use energy from ATP to transport solutes (mostly hydrophobic molecules out of the cell)
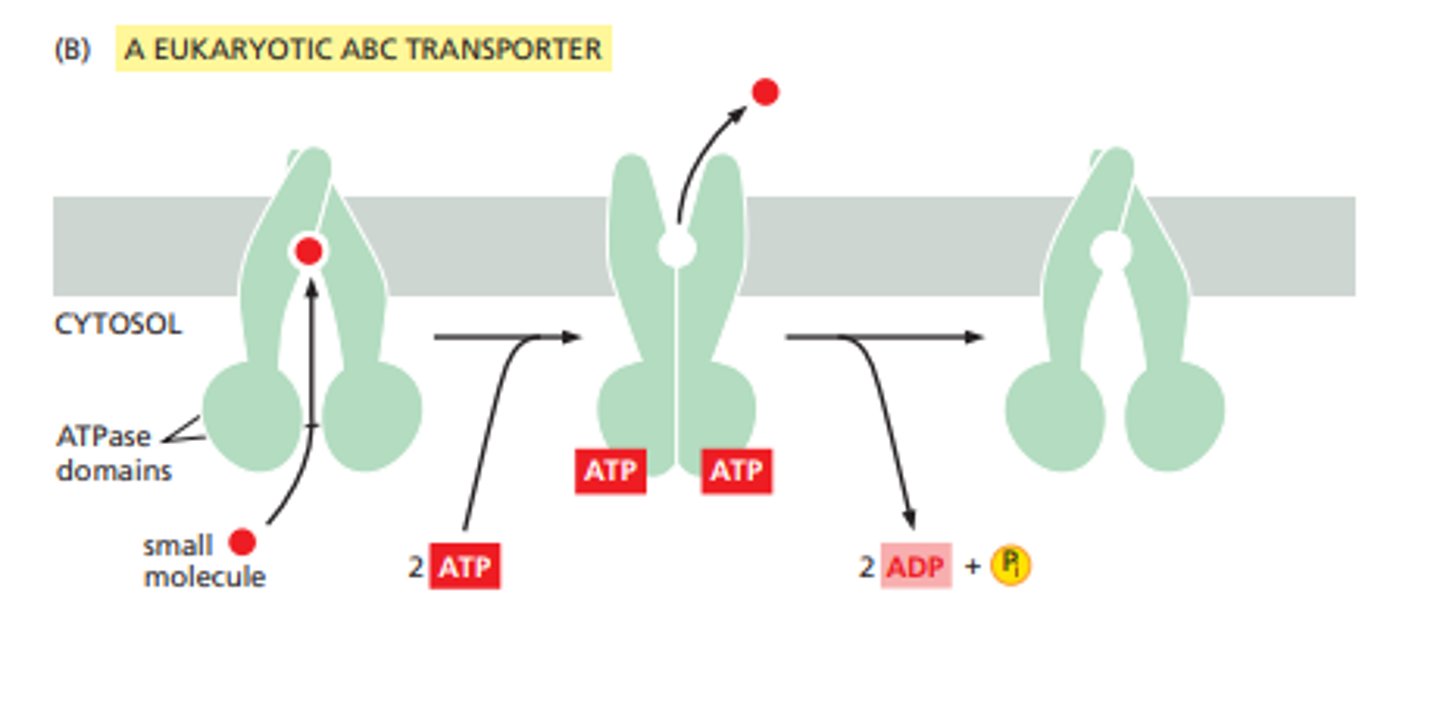
rotary pumps
membrane-bound pump
-couple ATP hydrolysis to the H+ transport
-acidify the interior of lysosomes
-can function in reverse to catalyze the phosphorylation of ADP
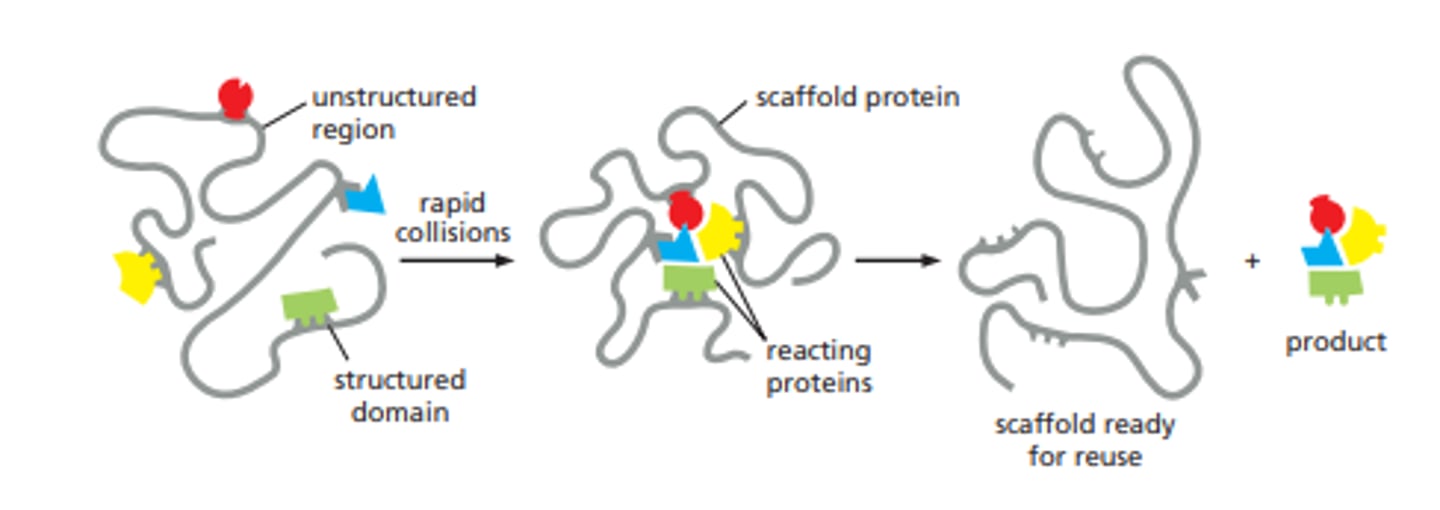
scaffold proteins
proteins with binding sites for multiple other proteins (link and position the proteins)