APES Midterm
1/94
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Tragedy of the Commons
suggests that individuals will use all the shared resources in their own self-interest
sustainability
humans living on Earth and their use of resources without depletion of resources for future generations
nonrenewable
finite supply, fossil fuels, minerals
renewable
can replenish naturally
ecological footprint
measure of biological productive land and water needed to produce resources and absorb waste of individual
Observe
Hypothesize
Collect data
Interpret results
Disseminate findings
Scientific Process
Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
photosynthesis
CO2 —> glucose + O2
Cellular Respiration
glucose + O —> CO2 + H2O + ATP
chemosynthesis
bacteria and archaea using energy to create food
food webs
graph that shows all trophic eating
Rule of tens
only 10% of energy transfer from 1 trophic level to the next
Gross Primary Productivity - R
What is the Net Primary Productivity formula?
Net Primary Productivity + R
What is the Gross Primary Productivity formula?
hydrologic/water cycle
movement of water through the biosphere
transpiration, evaporation, runoff, infiltration, percolation
What are the steps of the water cycle?
Nitrogen Cycle
Important compound of 1. amino acids (make up protein) 2. component of nitrogenous bases of DNA and RNA
phosphorus cycle
major component of DNA, RNA, and ATP
weathering of rocks
Where is phosphorus found on land?
forms sediment at the bottom of the ocean; not water soluble
Where is phosphorous found in water?
False
True or False: Phosphorous has an atmospheric form
Phosphorous
________ causes algae blooms
eutrophication
over-enrichment of a water body with nutrients leading to excessive plant and algae growth, which then dies, depletes the oxygen in the water and creates a dead zone
thermal pollution
when water is used as a coolant and causes sudden changes in temperature and depletion of oxygen, harming marine life
sediment pollution
pollution in water from soil and dirt; comes from construction and deforestation
wetlands
where land meets water; crucial for acting as filters to prevent floods and pollution
Swamps, marshes, bogs
What are the three types of wetlands?
watersheds
all land in a given landscape that drains into a particular stream, river, lake, or wetland
riparian zone
interface between land and a river on stream
carrying capacity
max population size of a species that a given environment can support
density dependent
stronger effects on large populations than smaller ones
disease, competition for resources, predation
What are examples of density dependent limiting factors?
density independent
some effect regardless of population size
Natural disasters
What is an example of a density independent limiting factors?
logistic growth
strains population growth, S shaped
exponential growth
unregulated population growth, J shaped
biotic potential
max reproductive growth of a population under ideal condition (highest birth lowest death)
K species
less kids, longer lives
elephants and humans
What are examples of K-selected species?
r species
many kids, short lives
spiders
What is an example of a r-selected species?
specialist
particular and picky for food and habitat
panda and bamboo
What is an example of a specialist?
generalist
broad and can live off many habitats and foods
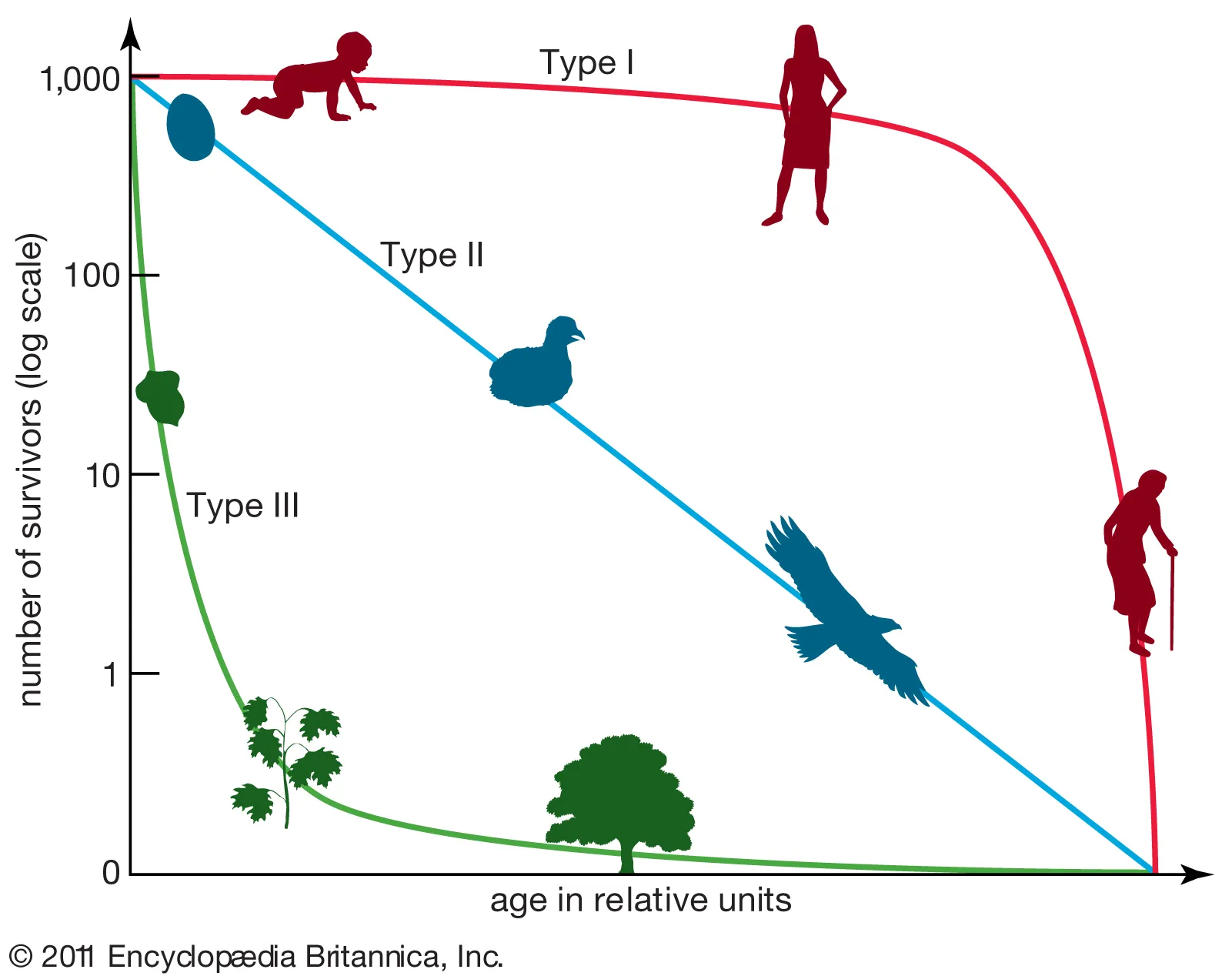
survivorship curve
organism → population → community → ecosystem → biosphere
What is the order for organization of life?
intraspecific competition
competition between 2 or more species
interspecific competition
competition within species
Competitive Exclusion Principle
two species competing for same limiting resources cannot coexist
resource partitioning
differation of niches
keystone species
a species whose removal would cause drastic changes
mutualism
intraspecific interaction where both species benefit
commensalism
one species benefits and other is neutral
parasitism
one lives on or in another organism
abiotic
non-living physical with chemical elements
biotic
living components of an ecosystem
primary succession
pioneer species colonize newly exposed area
secondary succession
community change after an event
invasive species
non-native, exotic organisms that spread widely, dominate, and have harmful effects on ecological communities
natural selection
individuals that have certain genetic traits survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals
genetic drift
variation in relative frequency of different genotypes in small populations
bottleneck effect
when a population size drastically shrinks because natural disasters cause a severe loss of genetic diversity
founder effect
occurs when few individuals become isolated from a large population and affect allele frequencies
endemic species
limited geographic range and habitat
genetic diversity
differences in DNA among individuals
species diversity
variety of species in a given area
habitat diversity
variety of habitat, ecosystems, communities
species richness
number of species in a given area
species evenness
measure of whether a particular ecosystem is numerically dominated by one species
Habitat loss, Invasive species, Pollution, Climate change, Overharvesting
What does HIPCO stand for?
wildlife corridor
connection between fragmented habitats that allow wildlife to move safely between them
provisioning, regulating, cultural, supporting
What are the 4 ecosystem services?
provisioning services
benefits that can be extracted from nature, like food, water, and timber
regulating services
benefit provided by ecosystem processes that moderate natural phenomena, like air quality, soil, floods
cultural services
non-material benefits which contribute to development and culture of people, like swimming, hiking, skiing
supporting services
helps sustain consistency of underlying natural processes, like photosynthesis, water cycle, creation of soil
Endangered Species Act
passed 1973
US Fish and Wildlife must maintain list of endangered and threatened species and develop recovery plan for each
forbids government and citizens from harming listed species and habitats
forbids trade in products made from listed species
CITES
bans international trade of body parts of endangered species
captive breeding
raising and breeding organisms in controlled conditions like zoos and aquariums
Species Survival Plan
program to save individual species by captive breeding, education, and research
ecosystem approach
collaboration of managing land, water, and living resources
biodiversity hot spots
focuses attention on areas where the greatest number of species can be protected with the least effort
ecological restoration
process of assisting the recovery of ecosystems that have been degraded, damaged, or destroyed
endangered species
species threatened by extinction
island biogeography
distance from the mainland and size affects colonization
biodiversity distribution
species not evenly distributed globally within a given geographic area
equator
Biodiversity increases toward ______
Demographics
Population size
Density and distribution
Age structure
Sex ratio
Birth, death, immigration, emigration
India, China, USA
What are the top 3 largest populations?
Quote from Thomas Matthus
If we kept producing, we would run out of resources because of war, famine, and hardship.
Gross domestic product
What does GDP stand for?
\frac{\left(CBR+imm\right)-\left(CDR+emi\right)}{10}
What is the growth rate formula?
\frac{\left(CBR-CDR\right)}{10}
What is the global growth rate formula?
\frac{70}{GR}
What is the formula for Doubling Time?
\frac{\vert new-old\vert}{old}\cdot100
What is the percent change formula?