Problem Solving
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
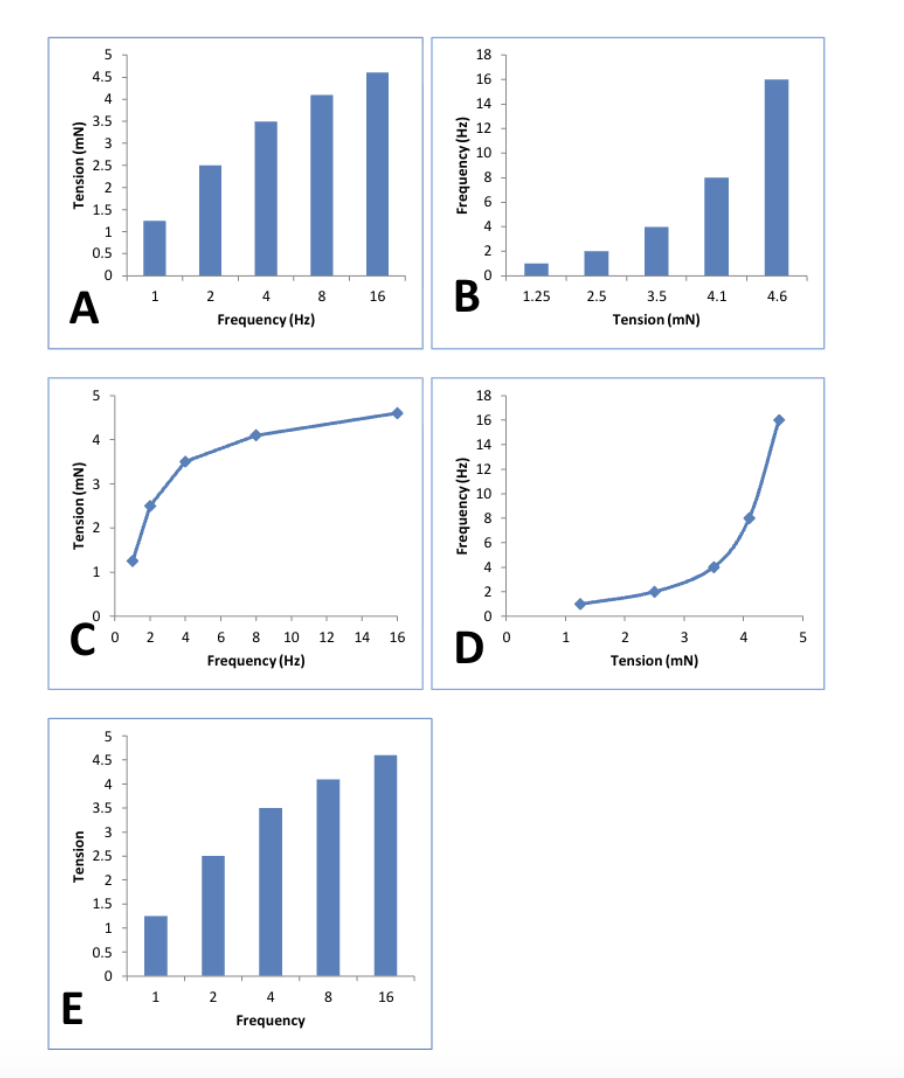
Which of the following graphs correctly represents the data shown in figure 1?
C
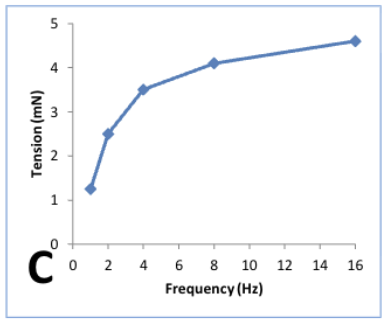
Describe the relationship between stimulation frequency and smooth muscle
tension
an increase in stimulation frequency leads to an increase in smooth muscle tension. the relationship is non linear
Looking at figure 2, what type of ion channel is involved in the generation of the
recorded response, is it voltage or ligand gated and are these channels located in
the muscle or nerve?
sodium voltage gated ion channel, located in the nerve
What can you conclude from figures 3, 4 and 5 regarding the type of receptors
involved in generating muscle tension in this muscle preparation?
Alpha adrenoceptors that contract smooth muscle
Why do you think the authors chose 4Hz for the experiments carried out in figures
2-5?
4 Hz produced the most consistent response
Why do you think the authors chose different stimulation frequencies for the
desipramine experiments (figure 6) compared to the adrenoceptor antagonist
experiments (figures 3-5)
steep stimulus response frequency curve, thought different stimulation frequency would be more likely to show potentiation
Can we conclude that adrenoceptors are the only receptors mediating smooth
muscle contraction in this preparation? Justify your answer
No, there is still a tension response when the adrenoreceptors are knocked out/inactive
(Figure 7) The authors are investigating the potential involvement of which type of
receptor?
cholinergic
(Figure 7) Are these receptors present in this preparation?
No
(Figure 7) By choosing a stimulation frequency of 4 Hz, what effect on muscle tension
are the authors predicting atropine will have?
predict that atrophine will decrease the amount of smooth muscle tensio
(Fig 8 prediction is wrong) his suggests the neurotransmitter in question actually
increases/decreases smooth muscle tension?
increases
(Fig 8 prediction is wrong) to confirm this you would repeat the experiment using a higher/lower frequency than 4hZ?
lower
What are the most accurate conclusions you can draw from the data presented
in figure 8?
an increase in 5-HT leads to a decrease in contraction frequency, meaning that 5-HT is generally inhibitory
From figures 9 and 10, which receptor subtype(s) may be involved in inhibiting
contraction of lymphatic vessels?
Subtypes 1,2, 4
Which 5-HT receptors could be responsible for the responses observed at
300nM and 1000nM 5-HT in figure 10 and are these receptors excitatory or
inhibitory?
subtype 4, inhibitory
Why might the responses observed at 300nM and 1000nM 5-HT in figure 10 only
be seen in the presence of DAU6285?
contractions at concentrations of 300 nM 5-HT are mediated by 5-HT4
What can be concluded from figures 11 and 12 regarding the receptor sub-type
involved in stimulating contraction of lymphatic vessels and (from figure 12) the
effect on magnitude and significance of contraction frequency?
subtype 2 is invovled in stimulating increased contraction
It is observed that addition of pertussis toxin in a pharmacological experiment
decreases the recorded response. What type of G protein is involved and does the
associated effector protein generate an excitatory or inhibitory downstream
response?
Gai subunits, inhibitory downstream response
Intravenous injection of potassium chloride (KCl) solution causes cardiac arrest
and for this reason potassium chloride has been used, in combination with other
drugs, to terminate the lives of prisoners on death row. What is the
neurophysiological basis of the lethal action of potassium chloride on the
myocardium
KCl makes RMP more positive → too much electrical activity → increased extracellular K+ → myocites depolarize → seizures
The drug fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Describe its
mechanism of action and state whether it is an antidepressant or anti-psychotic
antidepressant. blocks serotonin reuptake → acts longer in synapse → more binding to serotonin receptors → increased serotonin
A drug which causes widespread autonomic dysfunction of both parasympathetic
and sympathetic divisions is mostly likely binding to which type of receptor?
nicotinic (neuromuscular junction)
blood test on a hospital patient reveals their plasma urea level to be 10 mmol/l.
The normal value is 30mg/dl. By how much is the patient out with the normal value?
You should be able to state whether they are over or under the normal value too.
1dl =0.1L
Molecular weight of urea: 60.06
patient value: 10 mmol/L
normal value: 5 mmol/L
patient is 2x over the normal concentration