Bio Unit 8
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Heredity
**passage of traits from parent to offspring**
2
New cards
Chromosomes
Condensed form of DNA
3
New cards
Diploid
Organisms like humans, contain chromosomes in pairs, one half of each chromosome pair comes from the male parent and the other half of the pair comes from the female parent, it has two matching (but not identical) homologues per set
4
New cards
Homologous Pairs
it is known as two matching (but not identical) __________ per set,
5
New cards
Humans Chromosomes
have 2 sets of 23 chromosomes, therefore 46 in total
6
New cards
Karyotype
picture of an individual’s chromosomes
7
New cards
Sex Chromosomes
23rd pair and they determine the sex of the offspring
8
New cards
Nondisjunction
causes chromosomes to not separate properly, can result in an abnormal chromosome number. An abnormal chromosome number is damaging to the offspring
9
New cards
Monosomy
an individual has only one chromosome when it should have a pair, would have 45 total chromosomes
10
New cards
Trisomy
when an individual has an extra chromosome in a pair, have 47 total chromosomes
11
New cards
Downs Syndrome
Trisomy 21
12
New cards
Trait
any characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring
13
New cards
Heredity
the passing of traits from parent to offspring
14
New cards
Genetics
the scientific study of heredity
15
New cards
Gregor Mendel
Pea plant experiment, father of genetics
16
New cards
Gene
a DNA sequence that determines a particular trait for an organism
17
New cards
Locus
gene for a trait is always found in a specific location on a specific chromosome
18
New cards
Alleles
Genes can have different forms, dominant, recessive, represented by single letters
19
New cards
Roses
2/8 white roses, 6/8 red/pink roses
20
New cards
Dominant Allele
the stronger variant of a gene, it is usually expressed more often. Represented by a capital letter (ex: R or T), If an individual has two ______ alleles (ex: RR or TT), they will show ______ trait, If an individual has one _____ allele & one ______ allele for a trait (ex: Rr or Tt), they will display the _______ trait
21
New cards
Recessive Allele
the gene that is displayed less often in a cross. Represented by a lowercase letter (ex: r or t), If an individual has two ______ alleles (ex: rr or tt), they will show the ______ trait, If an individual has one ______ allele & one ______ allele (ex: Rr or Tt), they will not show the ________ trait
22
New cards
Genotype
allele combination for a trait, or the organism’s actual genetic makeup, codes for proteins, which code for traits, represented by two letters, one for each allele, homozygous or heterozygous
23
New cards
Homozygous genotype
gene combination of 2 dominant or recessive alleles Ex: AA or aa
24
New cards
Heterozygous genotype
gene combination of one dominant and one recessive allele, called hybrid Ex: Aa
25
New cards
Phenotype
is the physical trait resulting from a genotype, Ex: yellow or green coat color
26
New cards
Punnett Square
Offspring inherit alleles from their parents. The probability that an offspring will inherit a specific combination of alleles (and therefore a particular trait) can be predicted
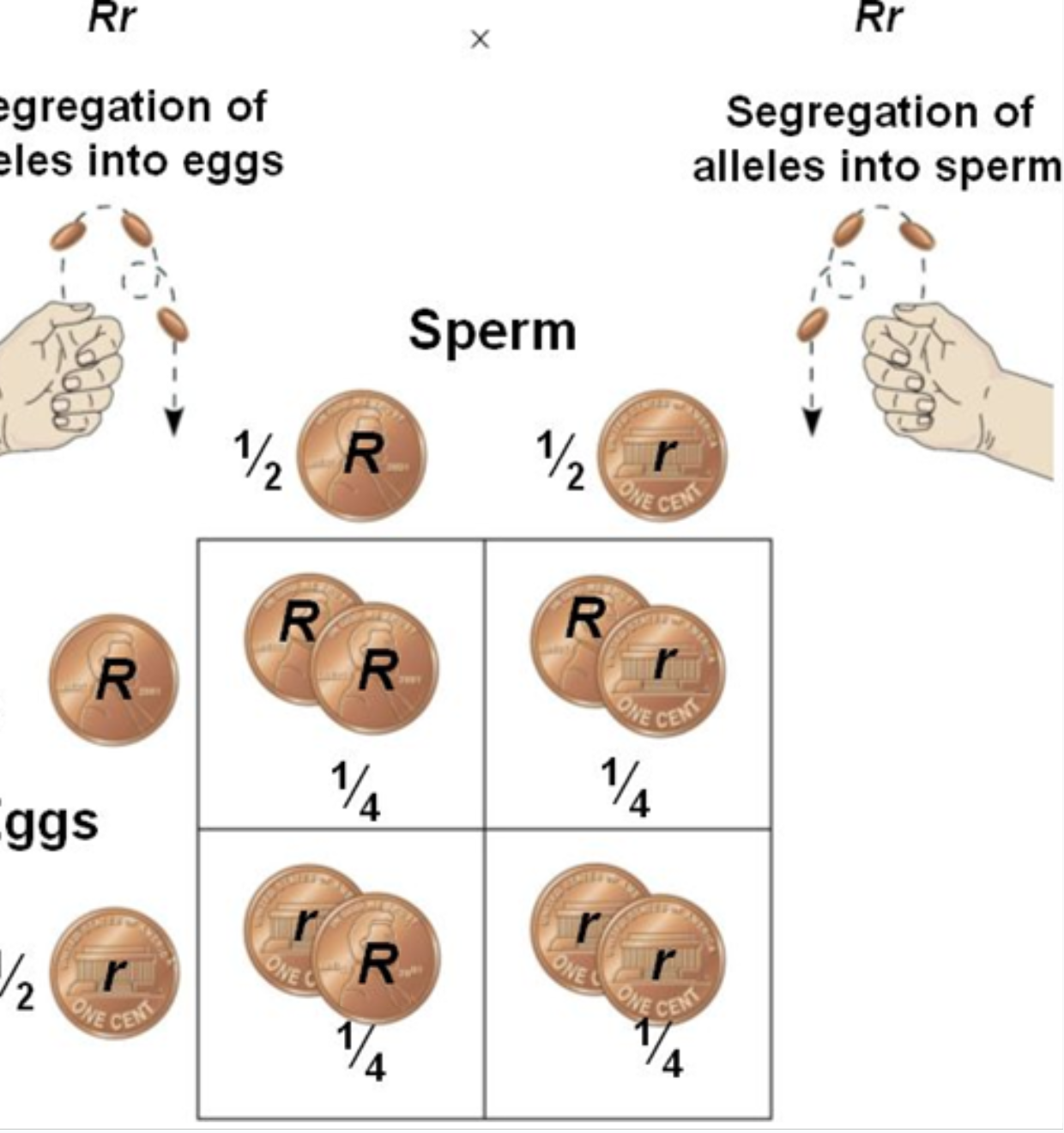
27
New cards
Monohybrid cross
determine the probability that an offspring will inherit a single trait using a Punnett Square
28
New cards
Non-Mendelian traits
Some traits do not follow the patterns that Mendel observed
29
New cards
Incomplete Dominance
neither allele is completely dominant over the other and a blend of traits is observed
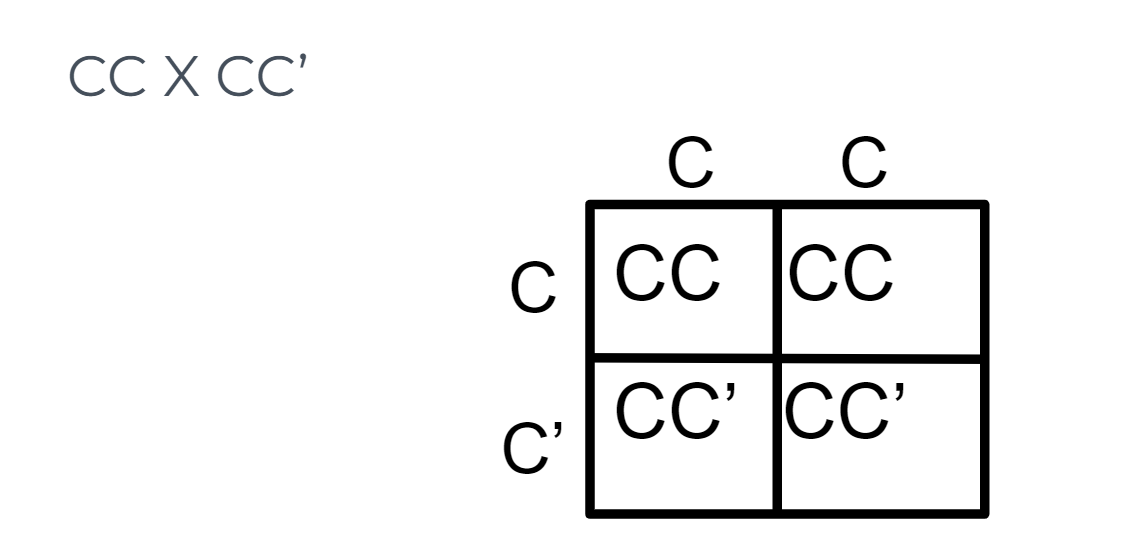
30
New cards
Codominance
in which both alleles are dominant and both are expressed equally, A capital letter represents one of the codominant alleles. A different capital letter represents the other codominant allele so that the two are easily differentiated. Example: *Roan cattle exhibit codominance; they are brown and white spotted*
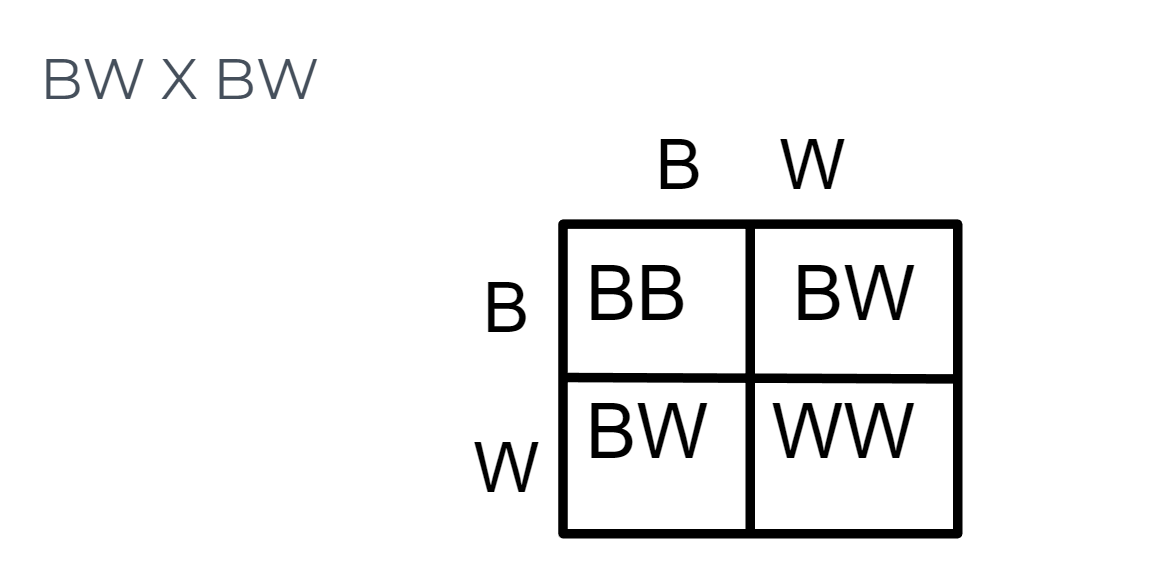
31
New cards
Multiple Alleles
(specifically **ABO Blood Types**), in which three alleles (two codominant and one recessive) determine human blood type,
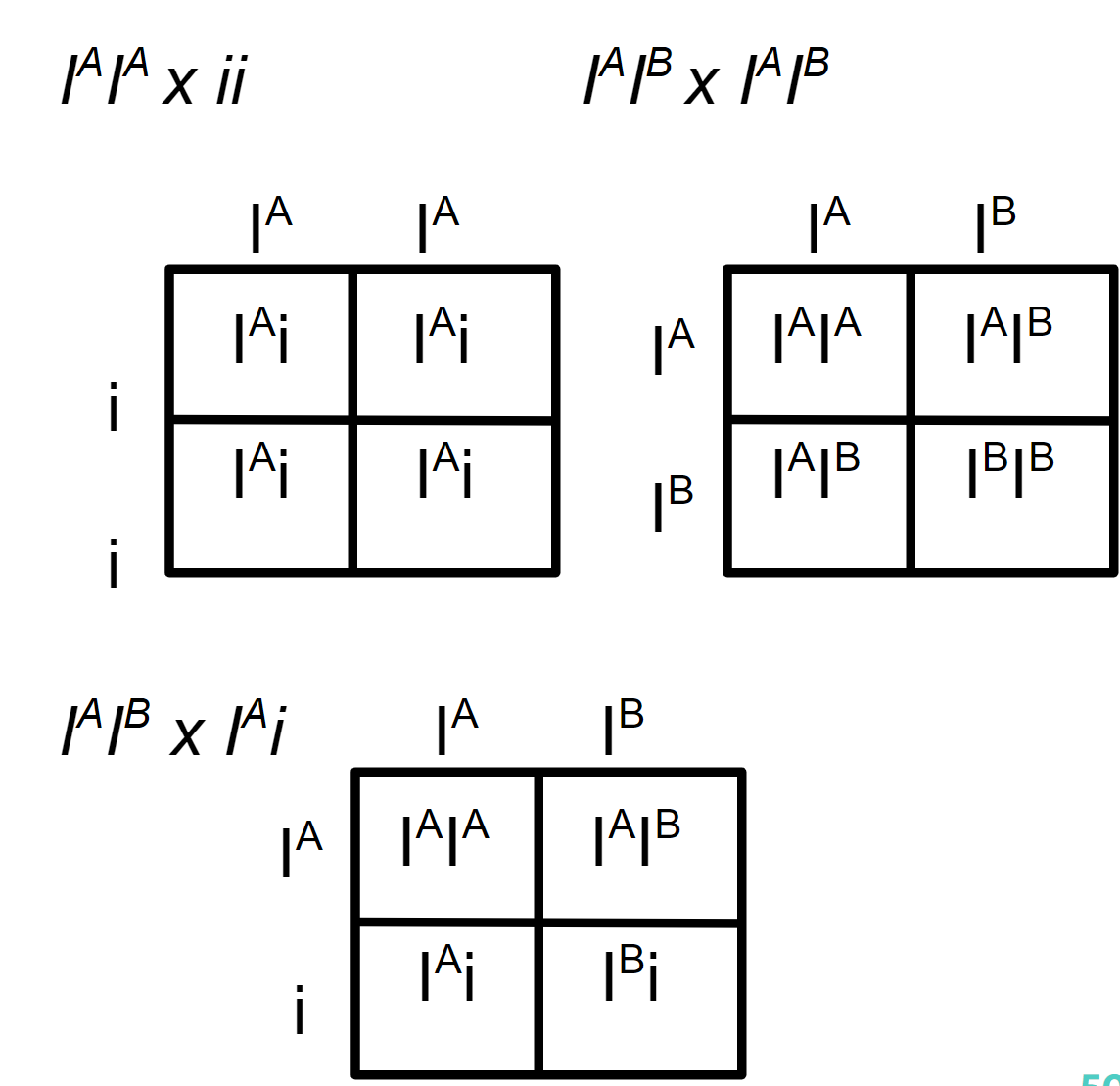
32
New cards
Letter Prime (P’)
A capital letter represents one of the two incompletely dominant alleles. The same capital letter, represents the other incompletely dominant allele
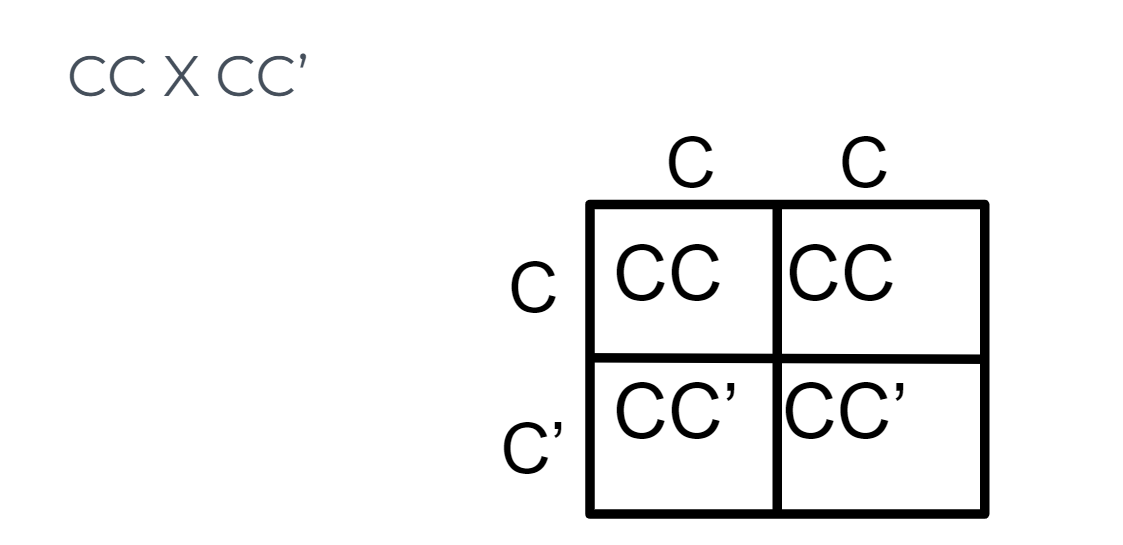
33
New cards
ABO Blood Types
Blood types are distinguished by the presence (or absence) of certain antigens, called A and B. on the surface of red blood cells, ABO blood type in humans is determined by *three* alleles: IA, IB, i, IA and IB are codominant alleles, Both IA and IB are dominant to the allele i, In this case, there are four different phenotypes (blood types): A, B, AB, and O
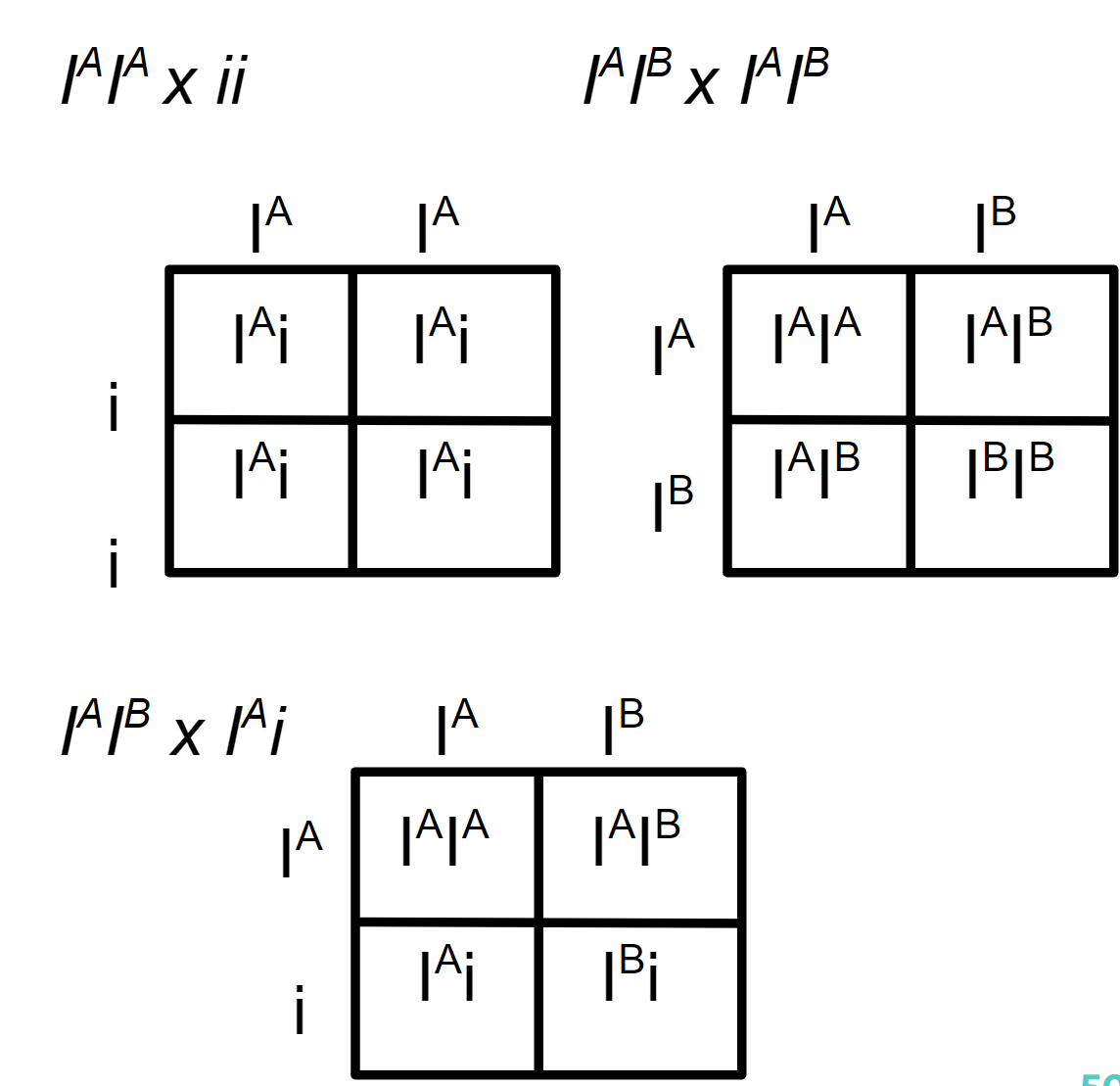
34
New cards
Type A can donate to
Type A and AB
35
New cards
Type B can donate to
Type B and AB
36
New cards
Type AB can donate to
Type AB
37
New cards
Type O can donate to
Type A, B, AB, and O
38
New cards
X-linked gene
one that is present on the X chromosome but not the Y chromosome. This can lead to different patterns of inheritance, Due to the inheritance pattern of x-linked disorders in humans, certain conditions are much more common in men
39
New cards
Color Blindness and Hemophilia
two X-linked diseases that are more common in men than in women because of their pattern of inheritance, a mother who is heterozygous for one of these disorders: one of her X chromosomes has the allele and one does not
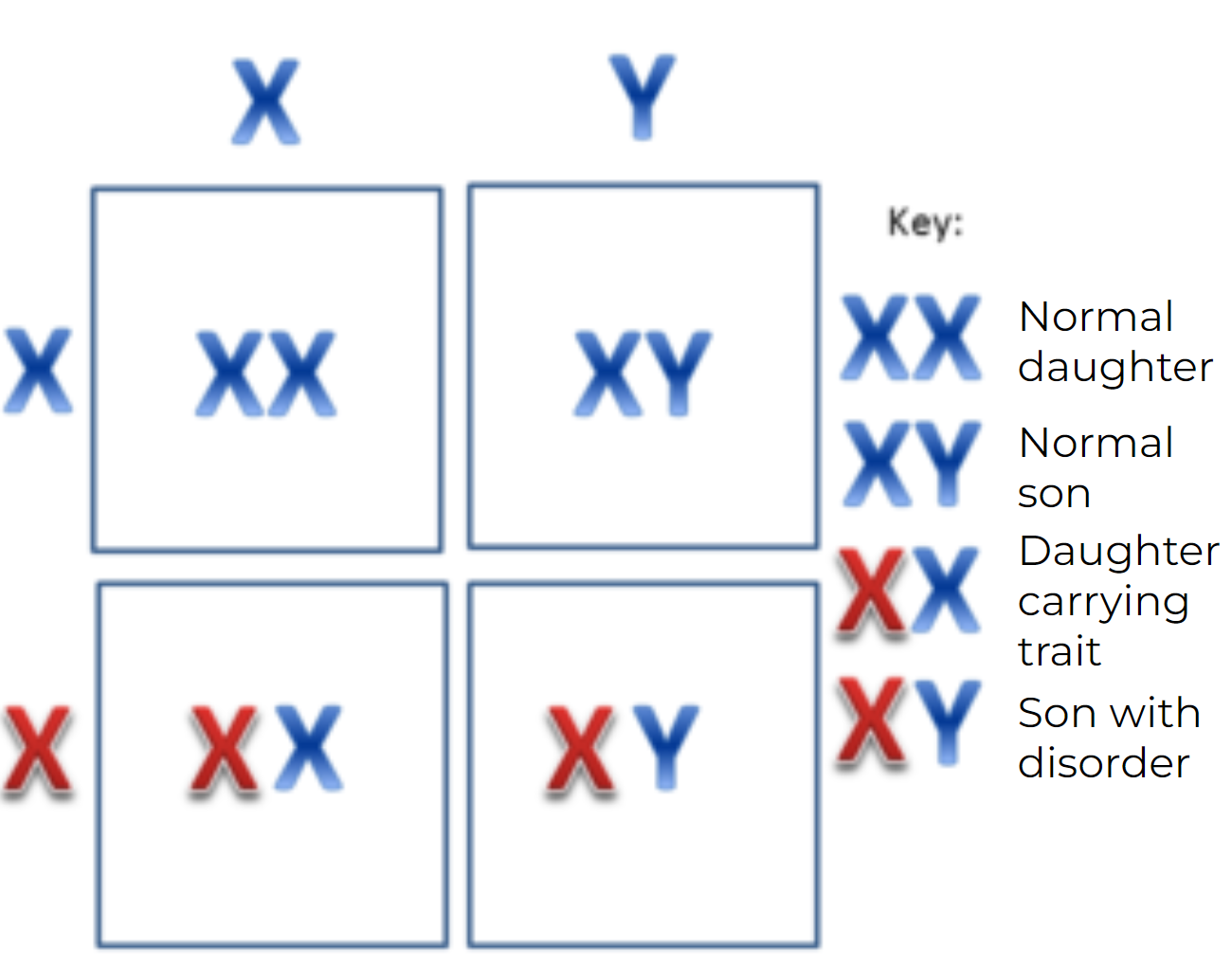
40
New cards
Hemophilia
blood clotting disorder in which the body has difficulty stopping bleeding. Small cuts can be very dangerous for sufferers of hemophilia
41
New cards
Pedigree
to show the passing of traits in families, Circles represent females, squares represent males. Whether or not a box is shaded is an indication of phenotype (recall that this is a physical trait). *Shading indicates that a trait is shown*
42
New cards
Marriage Lines
Lines directly between individuals
43
New cards
Line of Descent
A vertical line from a marriage line
44
New cards
Sibling Lines
Branches off of the line of descent
45
New cards
When a pedigree is used, it is often to
Determine if a trait is dominant or recessive, Determine if a trait is autosomal or sex-linked, Infer the genotype of an individual