Chapter 11 - Respiratory System and Gas Exchange
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
What does metabolism require?
ATP
What does ATP synthesis require?
O2 and generates CO2
Respiratory system delivers air to lungs by?
O2 diffuses into blood, CO2 diffuses out.
What are the four processes for gas exchange?
- pulmonary ventilation
- pulmonary gas exchange
- gas transport
- tissue gas exchange
gas exchange is known as?
external respiration
external respiration
bringing air into the lungs (inhalation) and releasing air into atmosphere (exhalation); gas exchange between lungs and blood
internal respiration
exchange of gases (o2 & co2) between blood and body cells
Pulmonary Ventilation
breathing
Pulmonary Gas Exchange
gas diffusion across alveoli; oxygen moves from alveolar air to blood, while CO2 moves from blood to alveolar air
Gas Transport
gas travels in blood
Tissue Gas Exchange
gas exchange at the tissues; O2 from blood to cells and CO2 from cells to blood
Functions of the respiratory system
gas exchange, regulation of blood pH, voice production, olfaction, protection
Regulation of blood pH
altered by changing blood carbon dioxide levels
voice production
movement of air past vocal folds makes sound and speech
Olfaction
smell occurs when airborne molecules are drawn in nasal cavity
Protection
against microorganisms prevents entry and removing them from respiratory surfaces
Seven principle organs
1. nose
2. pharynx
3. larynx
4. trachea
5. bronchi
6. lungs
7. diaphragm
Upper respiratory tract location
airway from nose to larynx
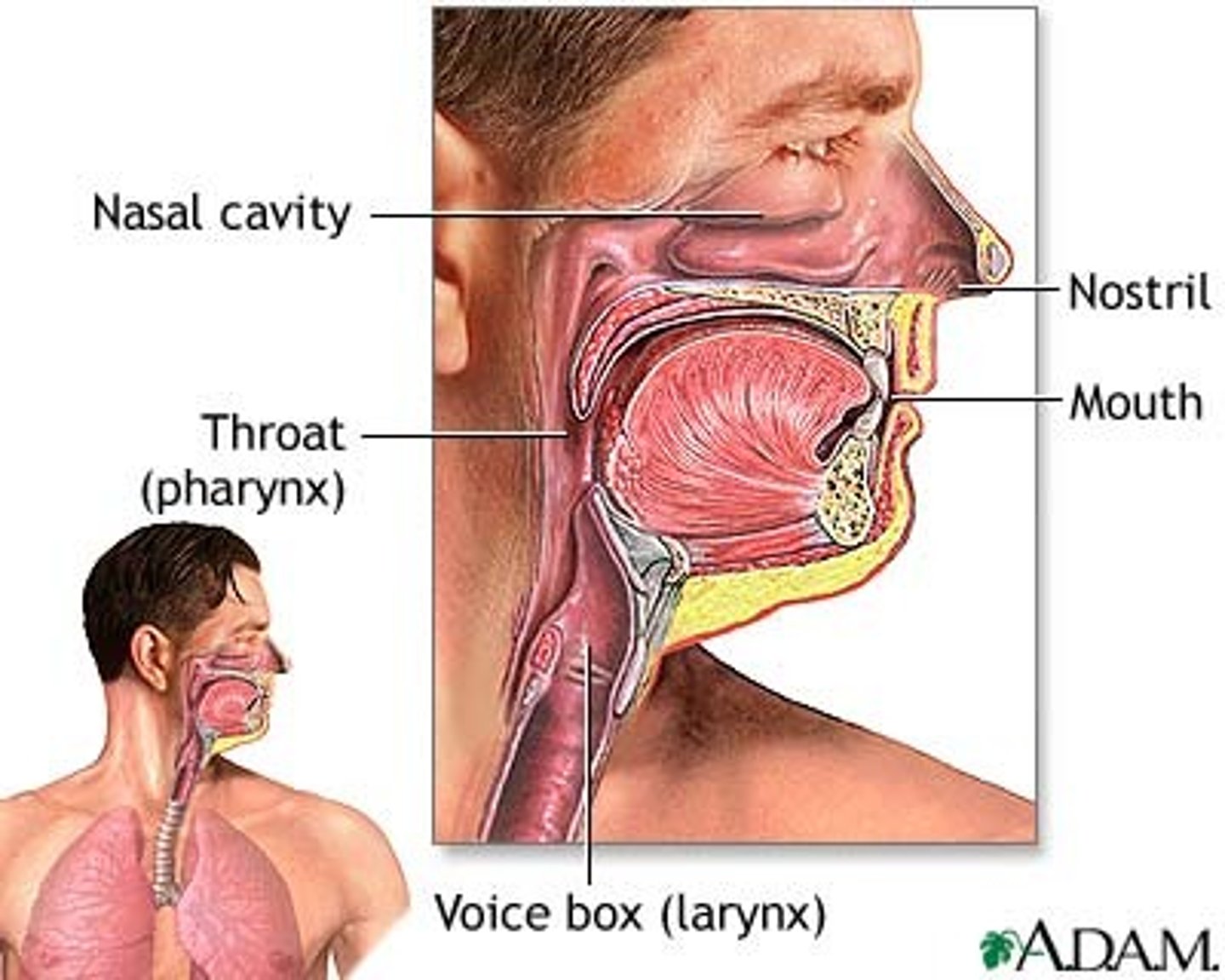
Upper Respiratory Tract consists of what?
respiratory organs in head and neck
Lower Respiratory Tract location
airway from trachea to lungs
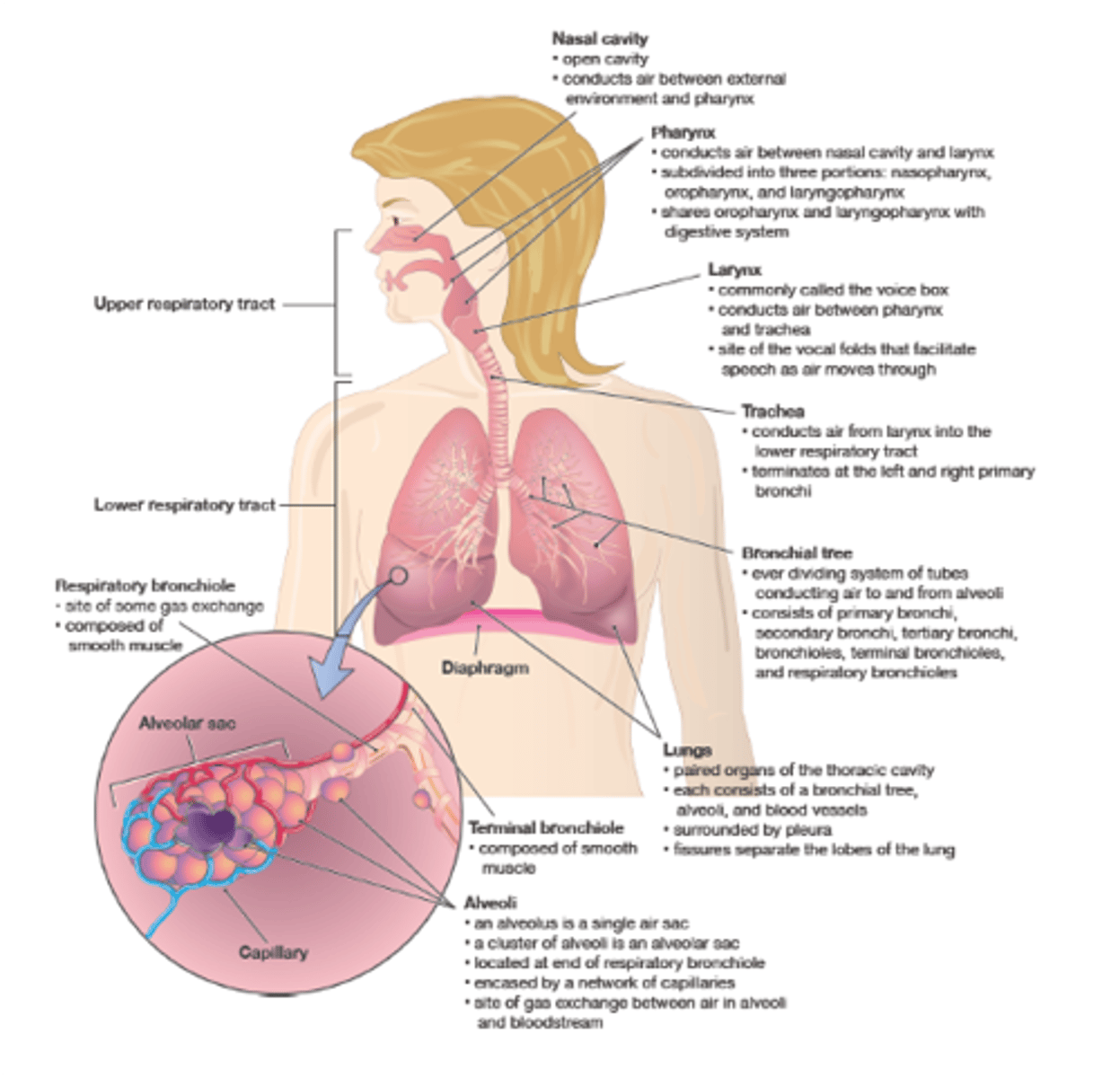
What does the lower respiratory tract consist of?
respiratory organs of thorax
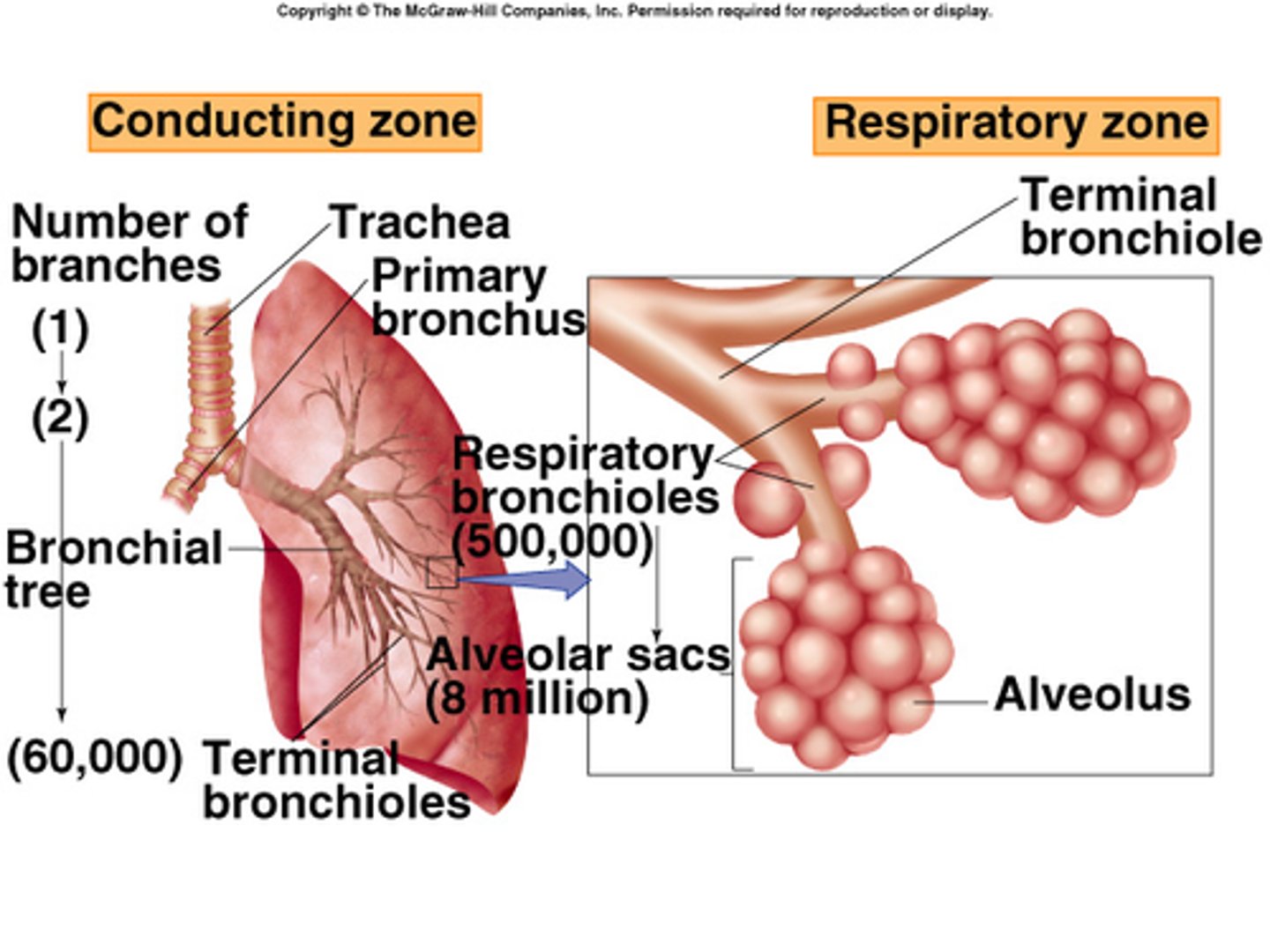
Conducting Zone
passages for airflow
Airflow starts and goes where?
from nostrils to bronchioles
Airflow is too thick for what?
for O2 diffusion into blood
Respiratory Zone
gas exchange
Alveoli
air sacs in the lungs
Conducting Zone vs Respiratory Zone (image)
Nose does what?
warm, cleanses, humidifies, inhaled air detects odor, amplifies voice
Olfactory Epithelium
sensory cells, detects odors; in nasal cavity
Respiratory Epithelium
contains goblet cells; in respiratory tract
What does the respiratory epithelium secrete?
mucus
Where is mucus moved too?
ciliated cells move mucus to pharynx
What gets swallowed by respiratory epithelium?
inhaled dust, pollen, bacteria, and foreign matter
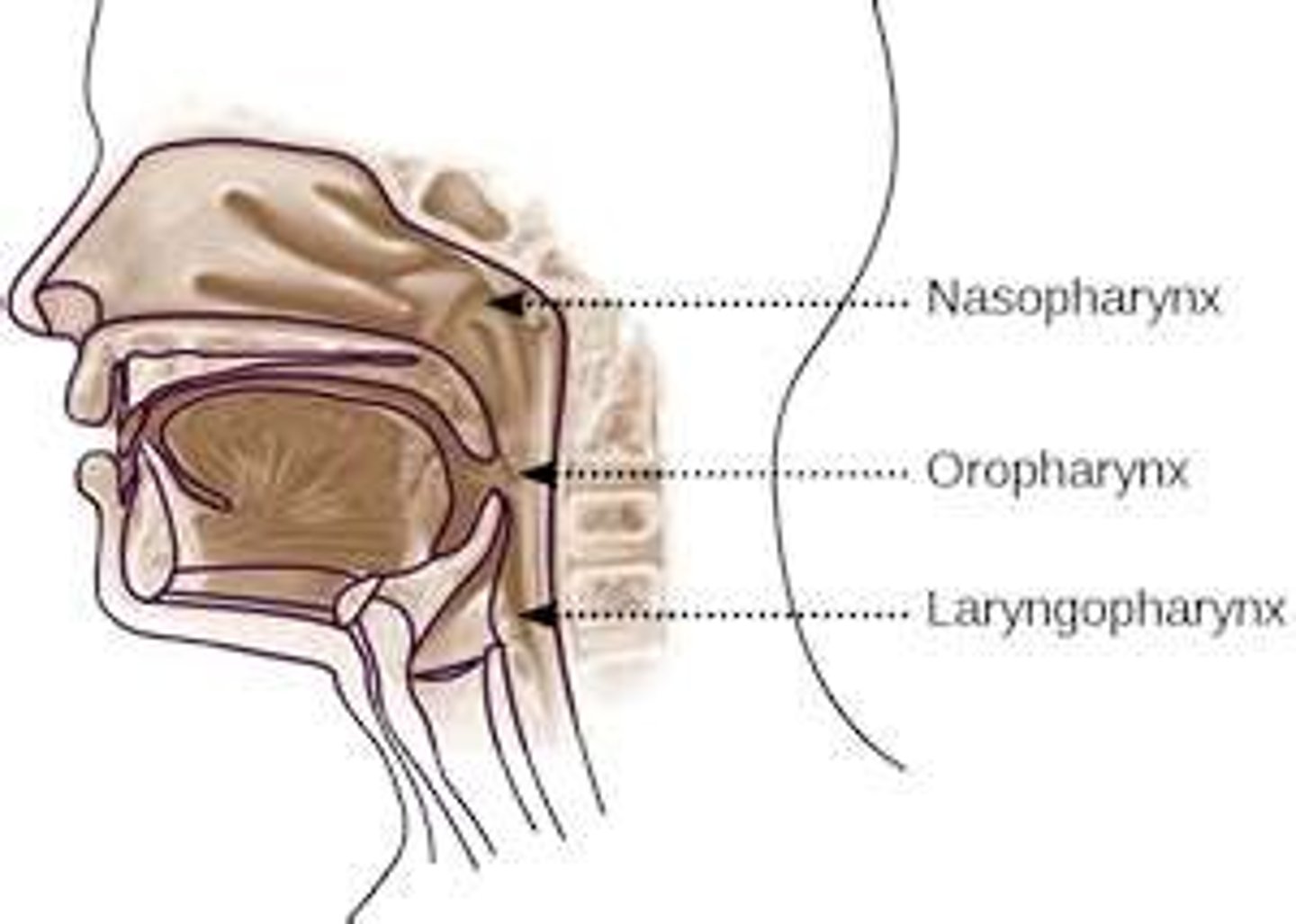
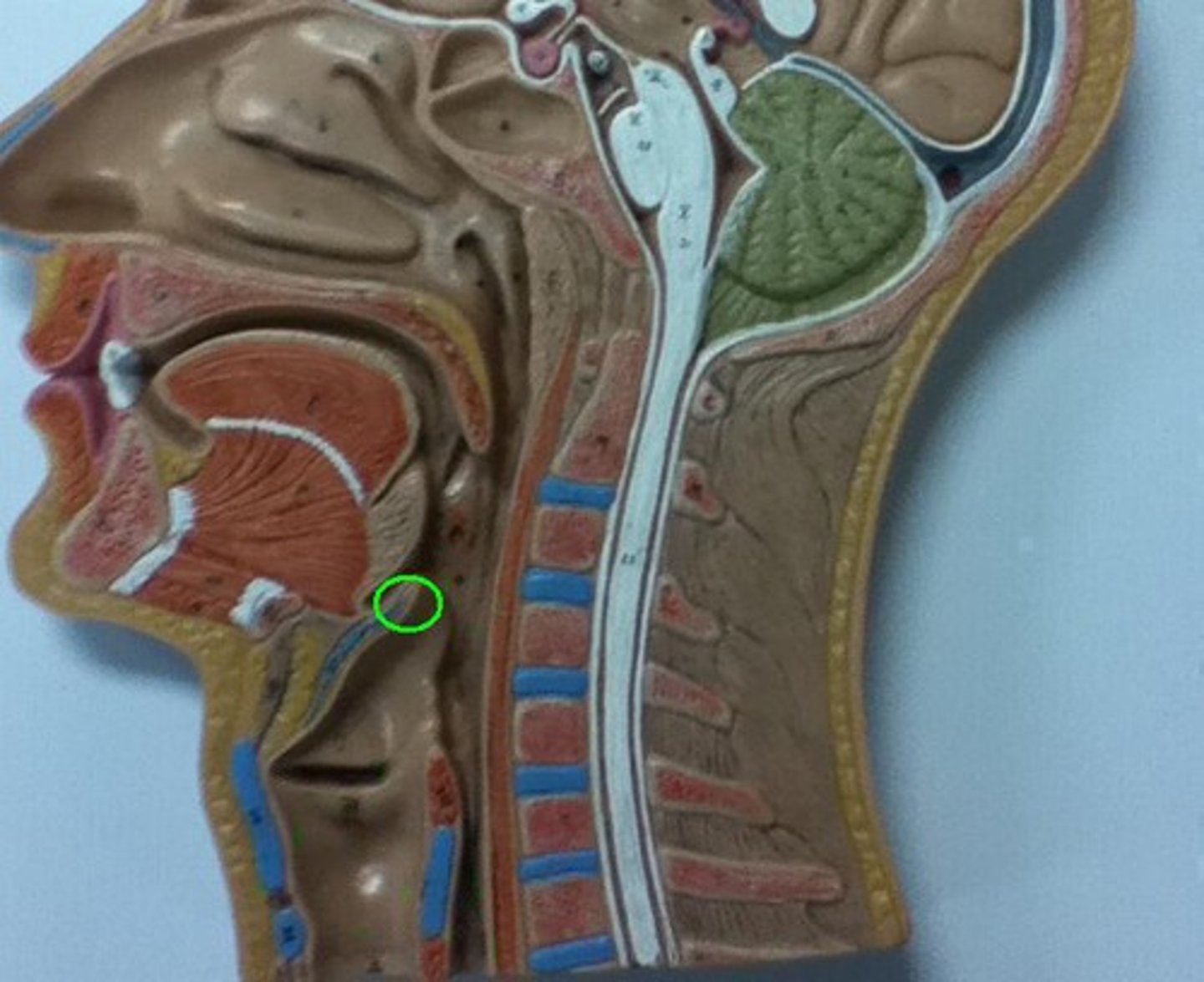
What is the pharynx made of?
nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx
Nasopharynx
inhaled air makes 90 degree pass, large particles get caught in mucus
Oropharynx
posterior of soft palate and epiglottis, where air arrives if breathing through mouth
Laryngopharynx
posterior to larynx, esophagus begin at this point
Pharynx (image)
What is the primary function of the larynx?
keep food and drink out of ariway
What is another role of the larynx?
sound production "voice box"
Vocal Cords
produces sounds when air pass through
Epiglottis
in larynx is the opening guarded by flap
Larynx (image)
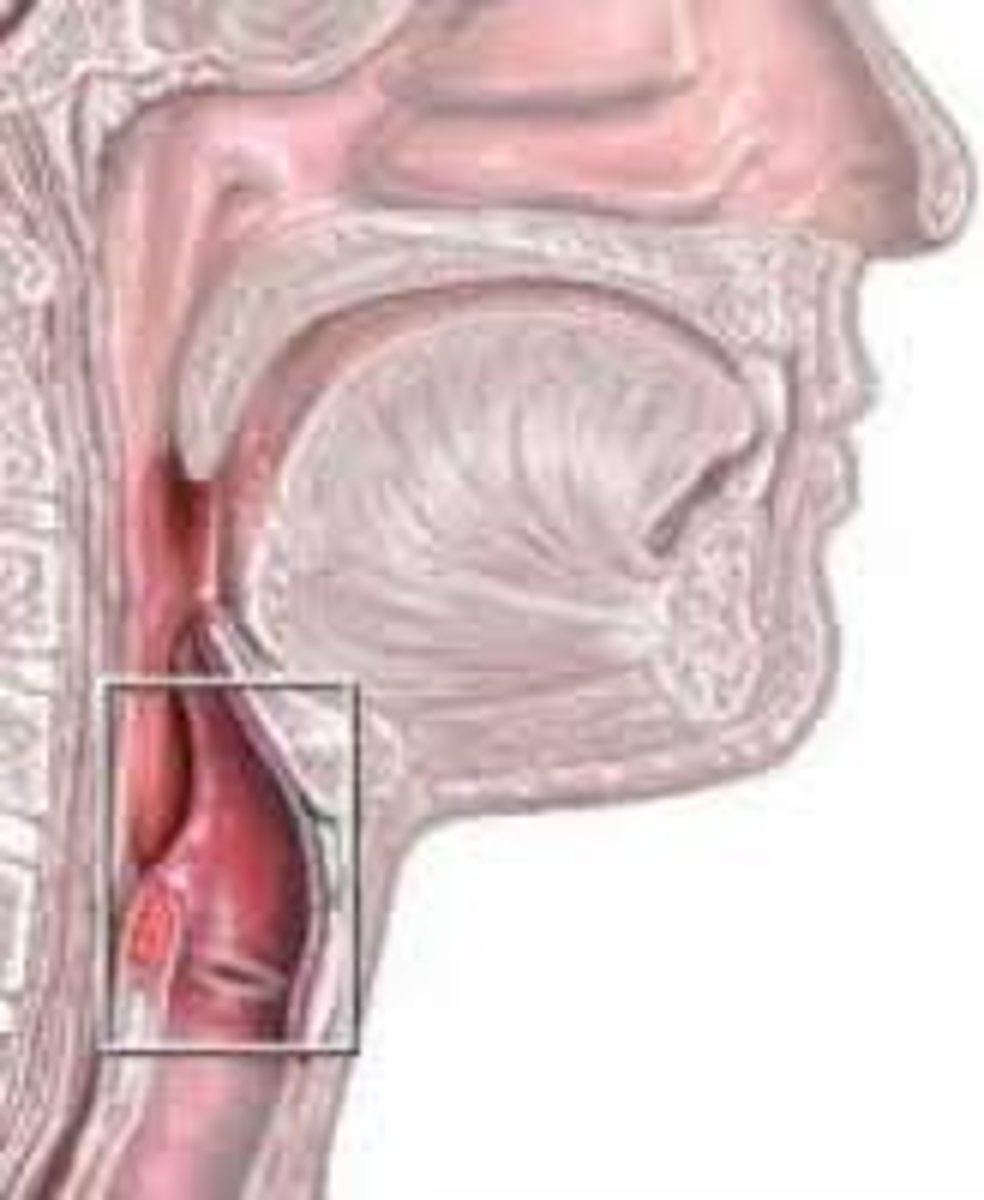
Epiglottis (image)
Functions of Epiglottis?
stands vertical at rest to allow airflow
What does the epiglottis do while eating?
closes airway
What is another function of the epiglottis?
directs food and drink into esophagus
Trachea is aka?
windpipe
What is the trachea supported by?
C-shaped rings of cartilage
Bronchii?
reinforce trachea, prevent collapsing
What is the inner lining of the trachea and bronchi composed of?
columnar epithelium (mucus secreting goblet cells and cilia)
mucociliary escalator
mucus traps particles and move debris up to pharynx to be swallowed (inner lining of trachea)
What is inferior to the lungs and diaphragm?
liver, spleen, and stomach
Position of right and left lungs?
right lung is shorter than left lung.
Why is the right lung shorter?
the liver rises higher on the right
Why is the left lung taller?
narrow and heart tilts to left
How many lobes does the right lung have?
3
3 Lobes of Right Lung
superior, middle, inferior
Horizontal Fissure
deep groove, separates superior and middle lobes
Oblique Fissure
separate middle and inferior lobe
Fissures of Right Lung
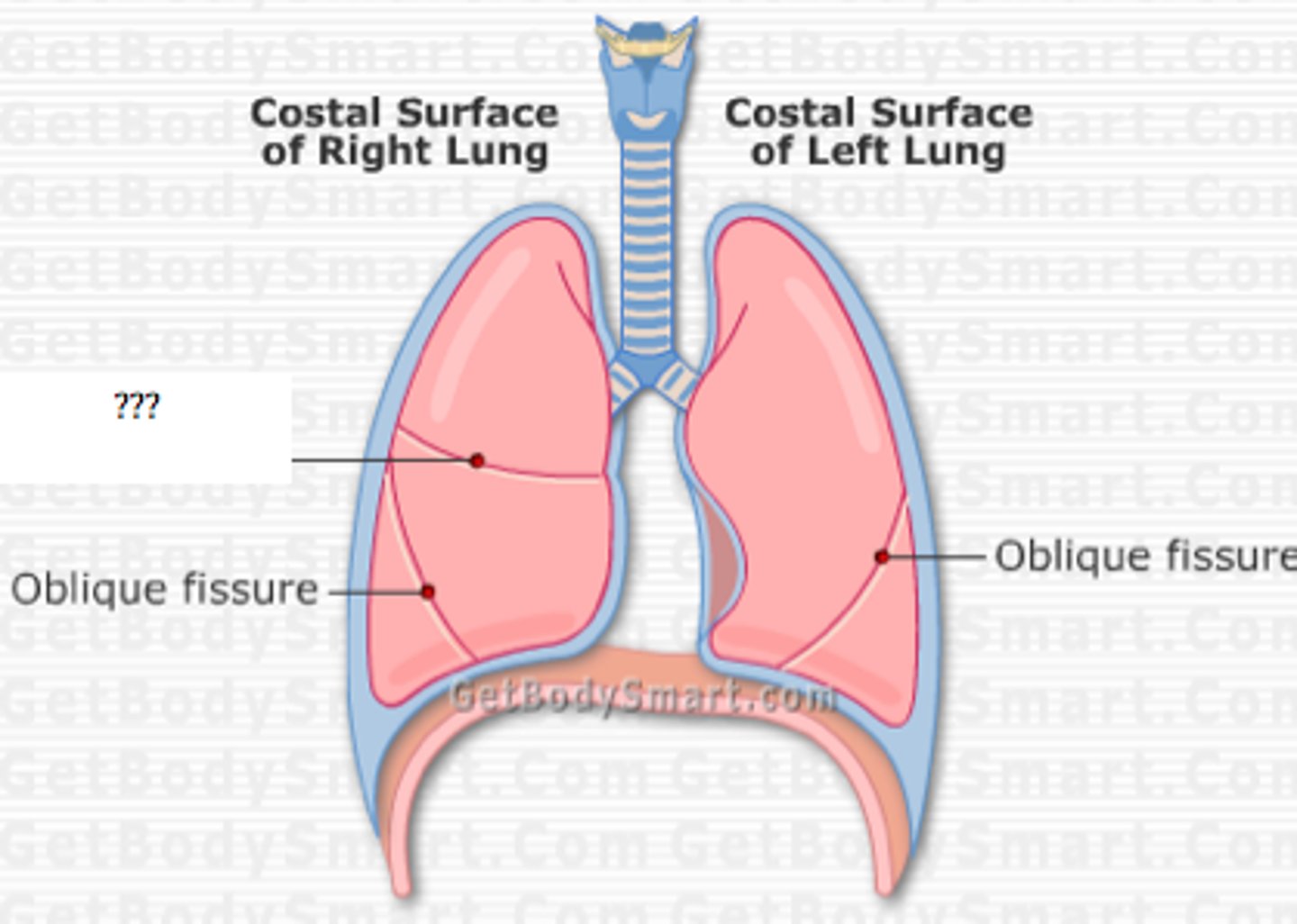
Left Lung consists of how many lobes?
2
Lobes of left lung
superior and inferior
What is the single fissure in the left lung?
oblique fissure
Source of blood to lungs:
pulmonary artery brings deoxygenated blood to lungs from right side of heart to be oxygenated in capillary beds that surround alveoli. Blood leaves via pulmonary veins and returns to left side of heart
Two lymphatic supplies?
superficial and deep lymphatic vessels
Superficial lymphatic supplies?
drain superficial lung tissue and visceral pleura
Deep Lymphatic Vessels supplies?
drain bronchi and associated C.T.
Do any lymphatics drain alveoli?
no
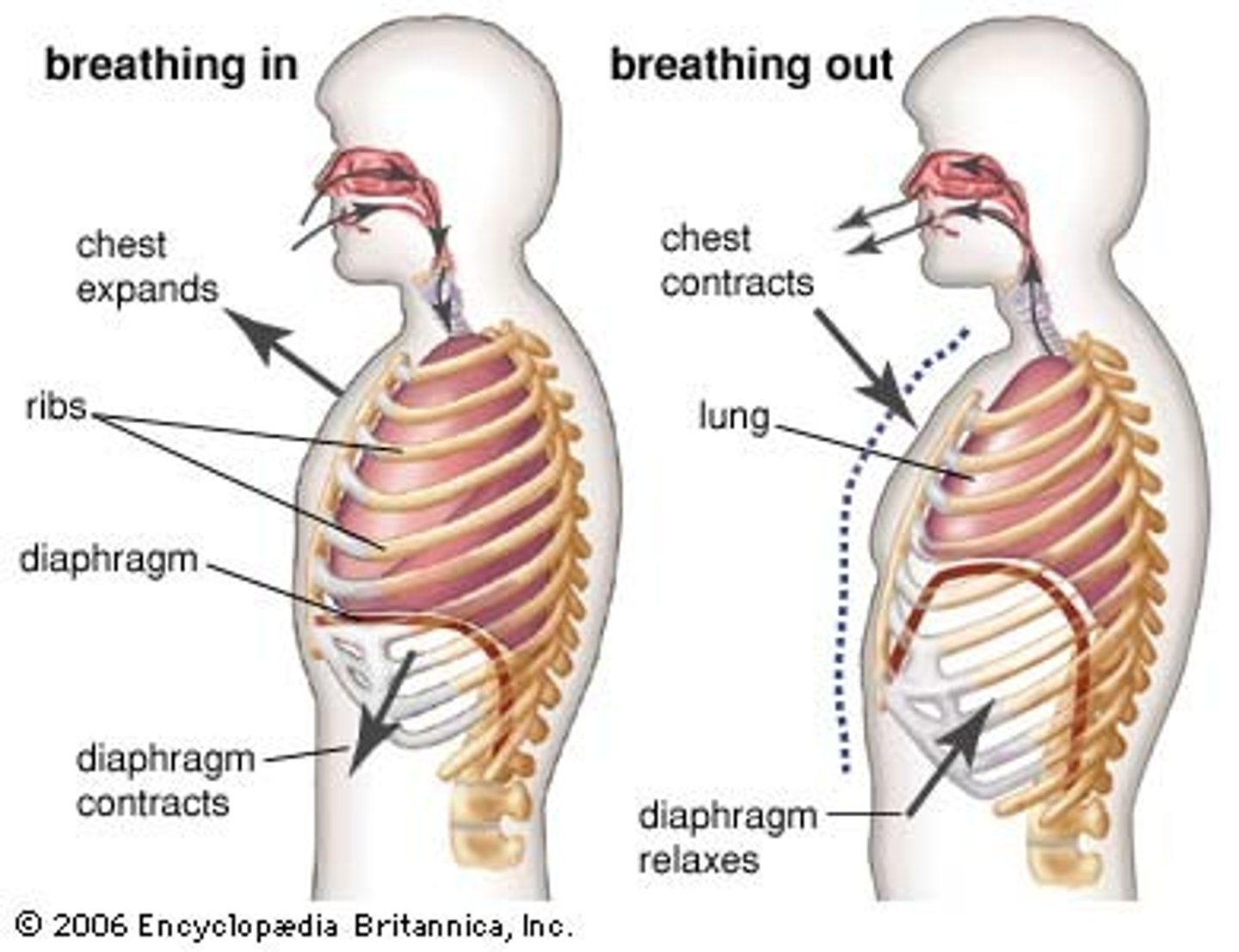
Diaphragm
dome shaped, muscular, separates thoracic and abdominal cavities
Principle of respiration for diaphragm
provides 2/3 of pulmonary airflow
What does the diaphragm do when we breathe?
contracts when we breathe in and relaxes we we exhale
Diaphragm inhalation and exhalation
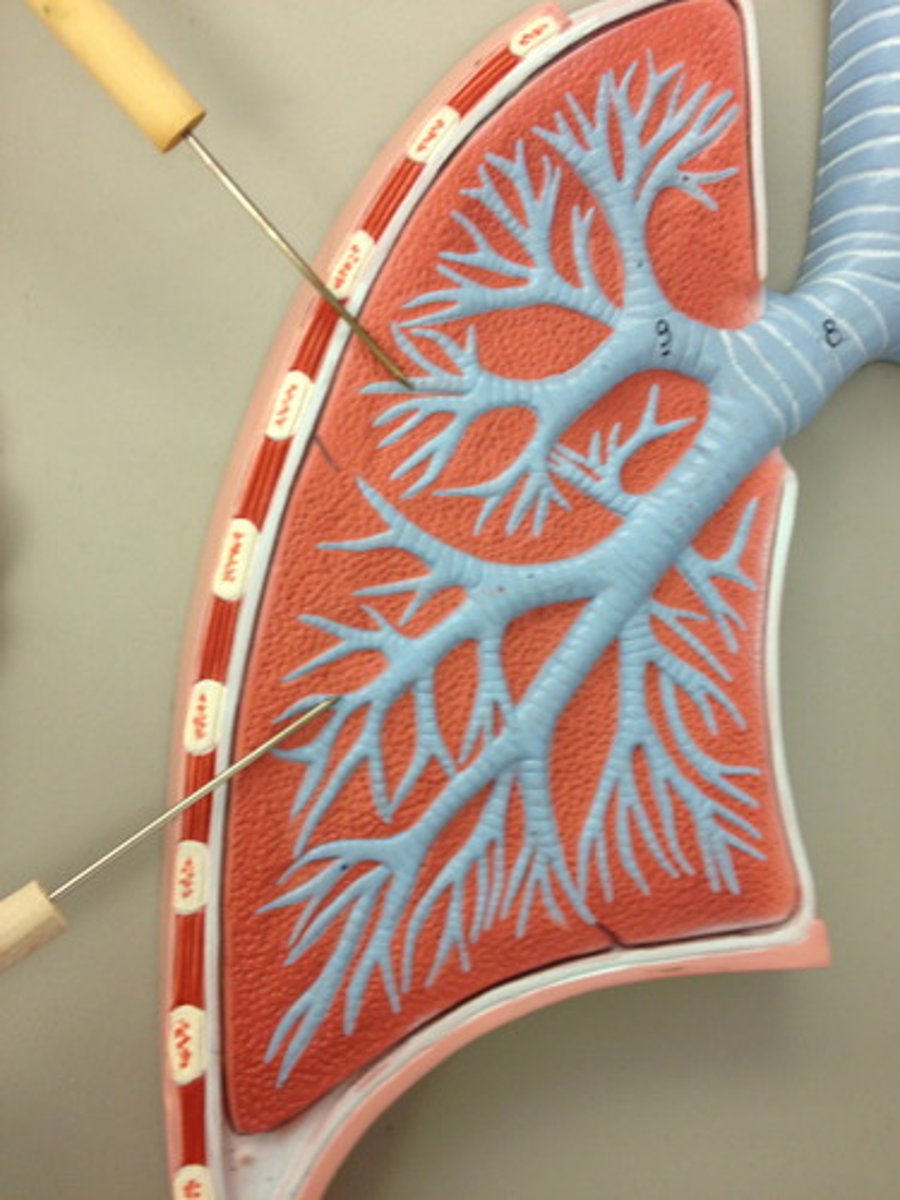
Bronchial Tree
branching system extends from main bronchus
How many bronchioles are in the bronchial tree?
~65,000 terminal bronchioles
Bronchial Tree (image)
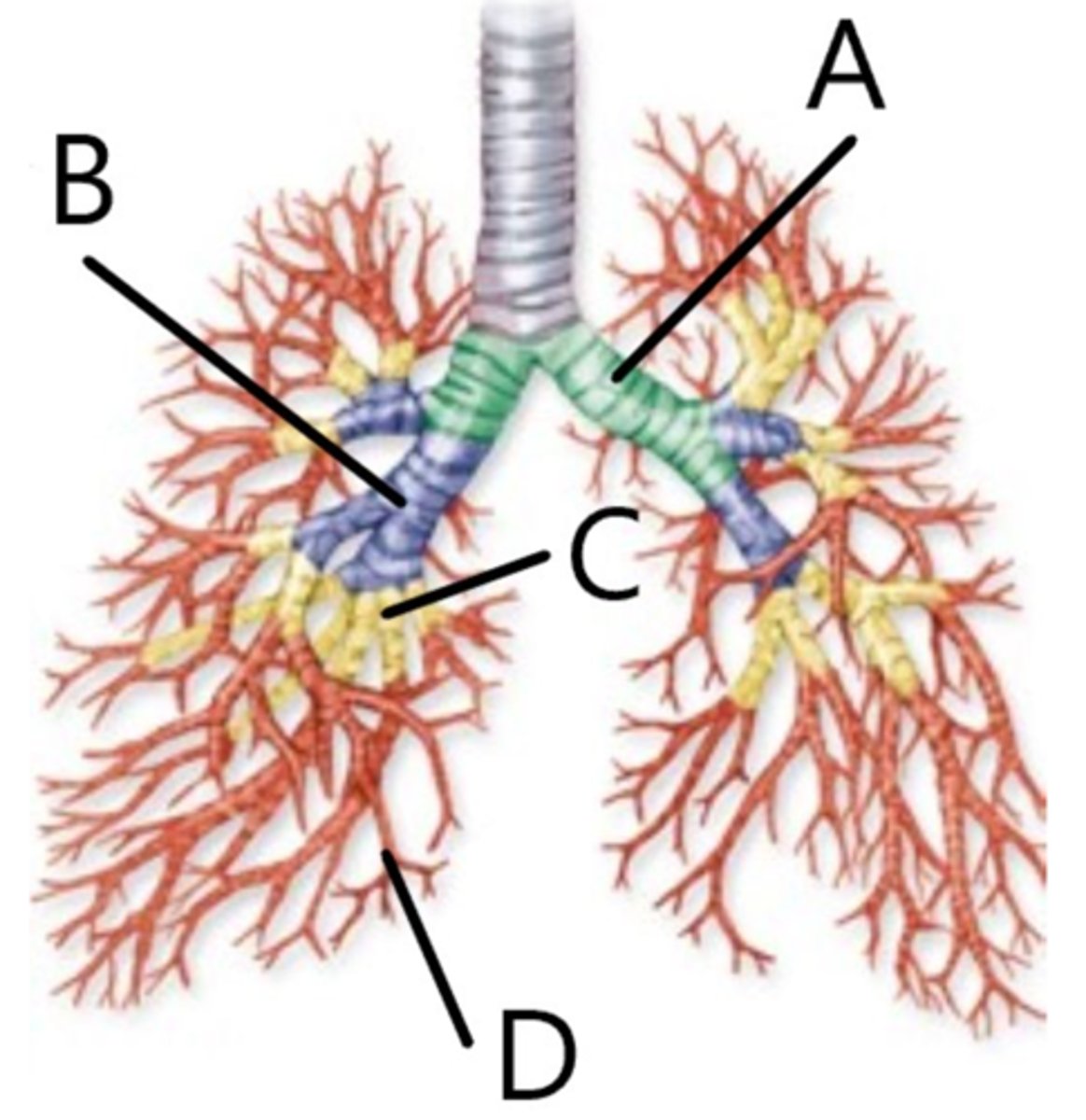
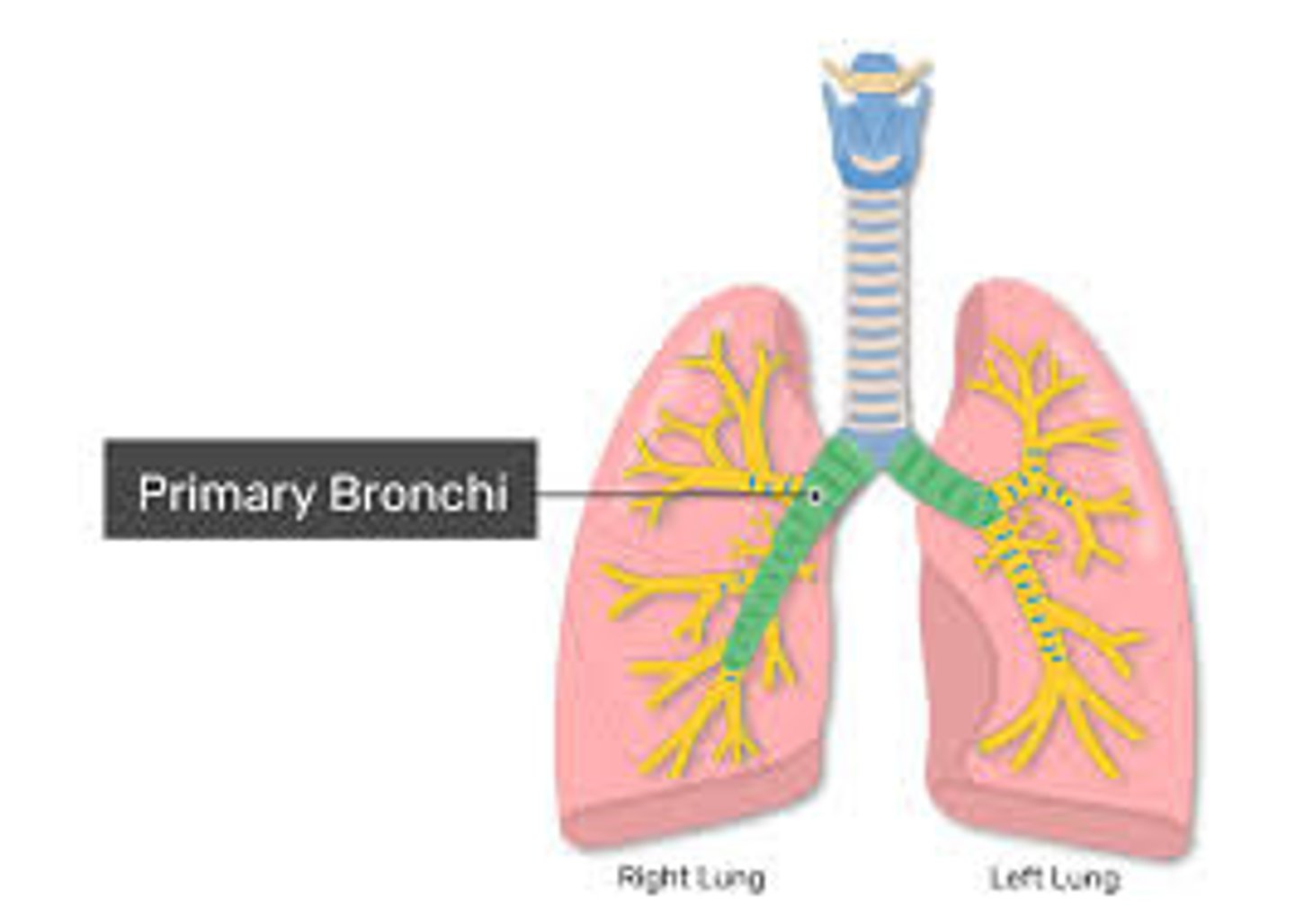
Main (Primary) Bronchi
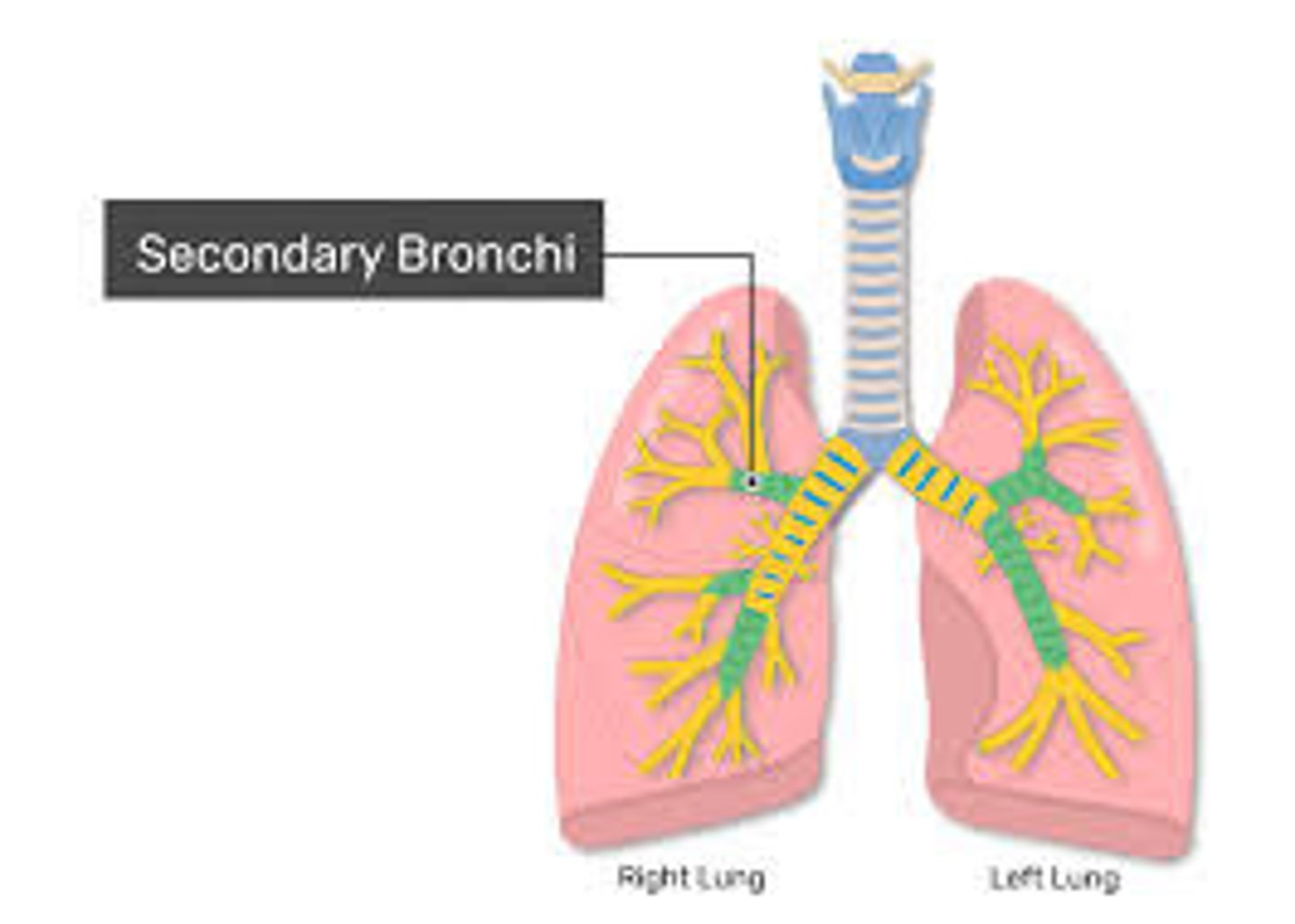
Lobar (secondary) bronchi
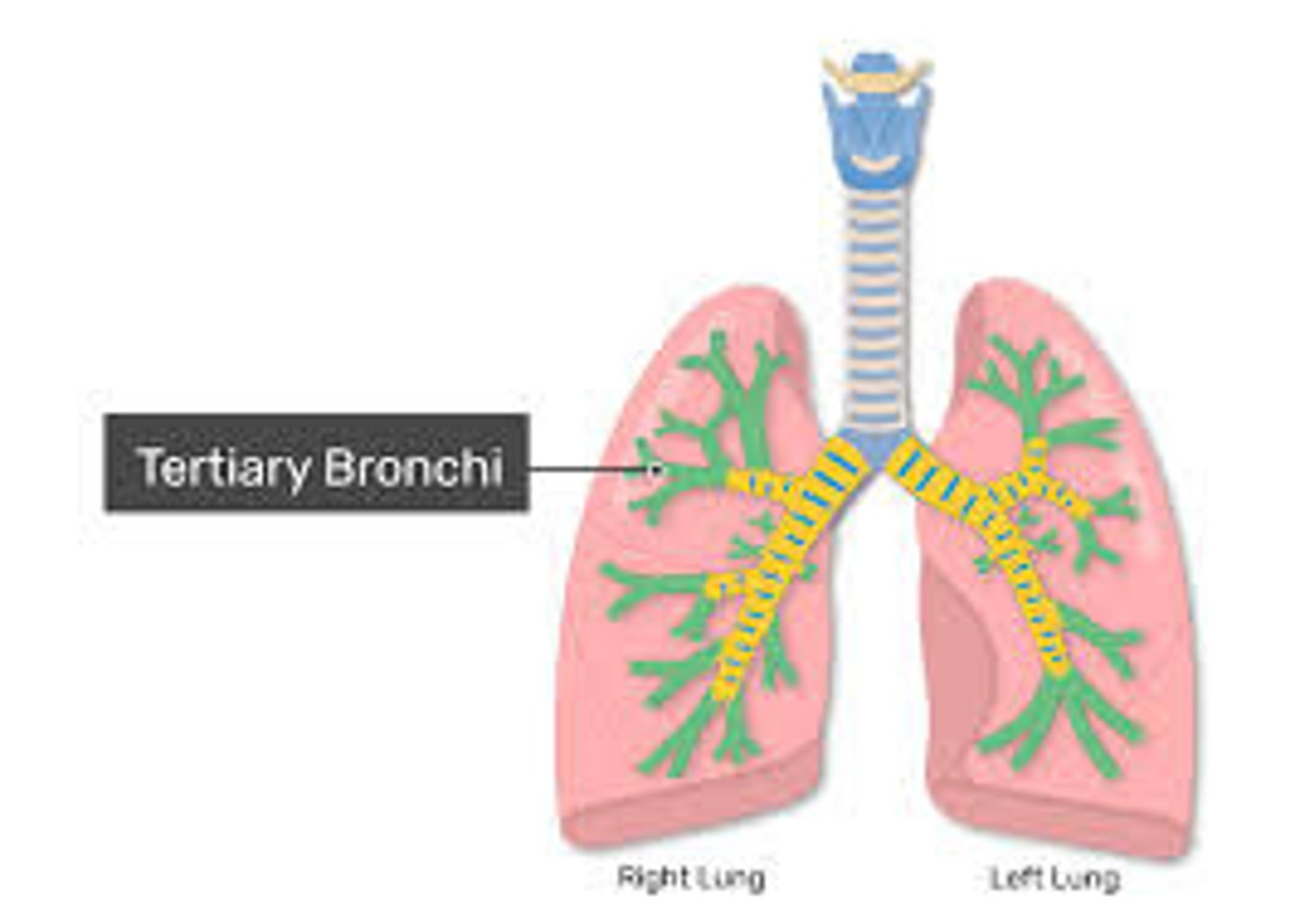
Segmental (tertiary) bronchi
Bronchioles
Terminal Bronchioles
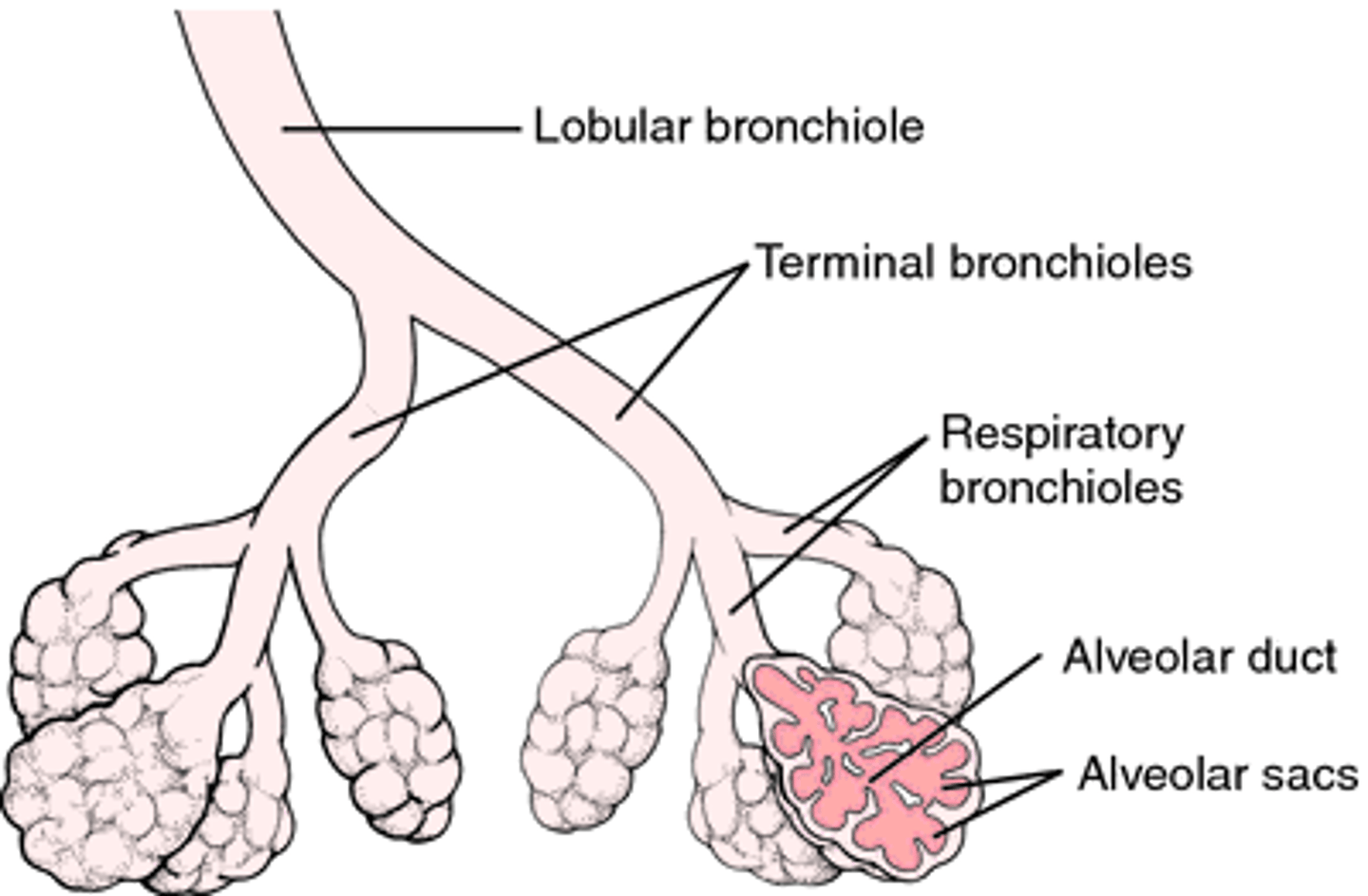
Alveoli
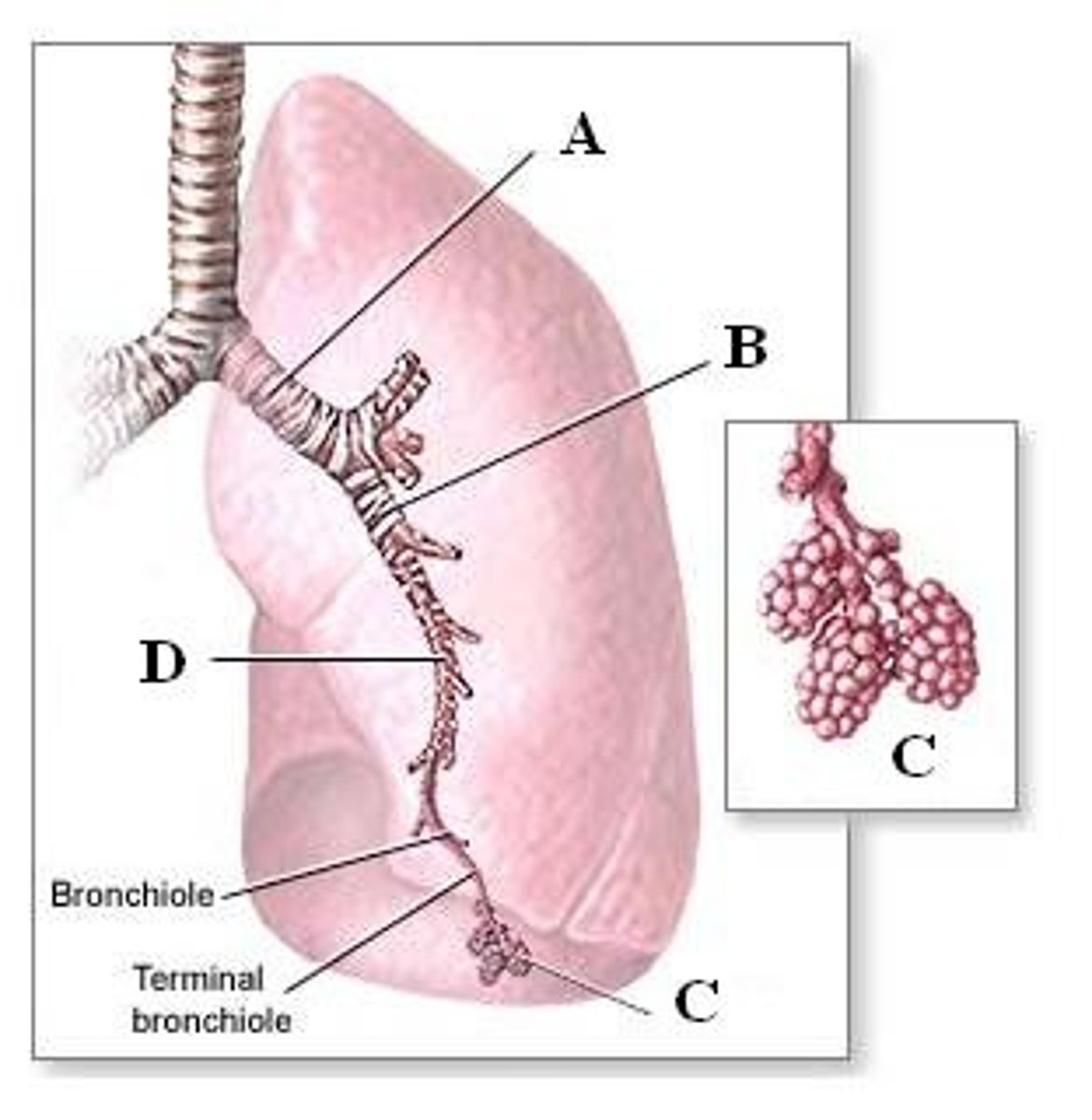
Tracheobronchial Tree
Trachea and network of air tubes in lungs
Four Classes of Tracheobronchial Tree
Lobar (secondary) bronchi, segmental (tertiary) bronchi, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles
Lobar Bronchi
(secondary), arise from main bronchi, each seres as lobe of lungs
What does the lobar bronchi contain?
cartilage plates and lined with pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Amount of Lobar Bronchi
three of right and two on left
Segmental Bronchi
(tertiary) supply bronchopulmonary segments
Bronchioles size
less than 1 mm in diameter
What are larger bronchioles lined with?
ciliated simple columnar epithelium
Terminal Bronchioles have?
no cartilage in walls, but prominent in smooth muscle, lined with ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium
Alveoli
small, spongy sacs in lungs, where exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs
Squamous Alveolar Cells
cover 90-95% surface
Cuboidal Great Cells
~5% , repair epithelium, secrete pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary Surfactant
phospholipids and protein coat
Alveolar Macrophages
dust cells, phagocytize dust particles
Pleura
lines thoracic wall, forms surface of lungs
What is pleural fluid for?
lubrication
What are the two layers of the pleura?
visceral (inner) and parietal (outer)
Visceral Pleura
(inner) surface of lung and extends to fissure between lobes