Midterm Marketing
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:15 PM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
1
New cards
Business model
Architecture of value creation by defining the entities, factors, and processes involved in delivering and capturing value in the marketplace.
2
New cards
Narrow business model
Describes fairly generic value creation strategies related to a particular marketing activity, such as pricing, promotion, and distribution.
3
New cards
Franchising model
Describes the strategy of adopting (leasing) an already existing business model.
4
New cards
3 important aspects of Business model
Value focused Intangible Universal
5
New cards
Value focus aspect of B.M.
Central to any business model and can be associated with both monetary and non monetary outcomes.
6
New cards
Intangible aspects of B.M.
A subjective representation of reality. Represent the way in which the organization conceptualizes the value-creation process.
7
New cards
Universal aspect of B.M.
A viable model is essential for the success of any organization, be it a start-up or an established market leader.
8
New cards
Strategy
Identifies the market in which the company operates, defines the value exchanges among the key market entities, and outlines the ways in which an offering will create value for the relevant participants in the market exchange. Defining the target market and the value exchange among the relevant market entities.
9
New cards
Tactics
Describe a set of activities (marketing mix) employed to execute a given strategy by designing, communicating and delivering specific market offerings. Describe the particular aspects of the offering that will ultimately create market value.
10
New cards
Marketing strategy 2 key components
Target market and value proposition
11
New cards
5 key factors of target market (five Cs)
• customer • company • collaborators • competitors • context
12
New cards
Customers
Are potential buyers defined by the needs the company aims to fulfill with its offering. Can be B2B or B2C
13
New cards
Company
The organization managing the offering. Could be a business unit or strategic business unit.
14
New cards
Collaborators
Entities that work within the company to create value for target customers.
15
New cards
Competitors
Are entities with offerings that target the same customers and aim to fulfill the same customer need. Competition can be in the same industry or not, is any entity that fullfil the needs same customer need.
16
New cards
Context
Involves the relevant aspects of the environment in which the company operates. Economic ( growth, money supply, inflation, r) Business (emergence of new business models) Technological ( diffusion of existing technologies) Sociocultural (demographic trends) Regulatory ( import/export teriffs) Physical (natural resources)
17
New cards
6 context factors
Economic ( growth, money supplyinflation, r) Business (emergence of new business models) Technological ( diffusion of existing technologies) Sociocultural (demographic trends) Regulatory ( import/export teriffs) Physical (natural resources)
18
New cards
Value proposition
The value that an offerings aims to create for relevant participants in the market.
19
New cards
Value exchange
Refers to the value-based relationships among the different entities in a given market. Entities: customer , company, collaborators and competition acting in a context.
20
New cards
Value exchange
Process of giving (creating) and receiving (capturing) value. Company creates value for → Customer Customer creates value → companies capture it same with collaborators.
21
New cards
3 value propositions for optimal value propositions
• defining the value for target customers • defining the value for its collaborators • defining the value for the company
22
New cards
Optimal value proposition
The … is balancing the value among its stakeholders, customers and collaborators.
23
New cards
Marketing mix: tactics
• product • service • brand • price • communication • distribution
24
New cards
Product aspect
Reflects its key functional characteristics. Change ownership during purchase. Can be distributed to buyers via multiple Chanels.
25
New cards
Service aspect
Reflect its functional characteristics but do not imply a change in ownership; customers obtain the right to use it for a period of time.
26
New cards
Brand
A set of unique marks and associations that identify the offering and create value beyond The product or / and service aspects of the offering.
27
New cards
Price
The amount of money the company charges its customers and collaborators for the benefits provided by the offering.
28
New cards
Incentives
Tools used to selectively enhance the value of the offering for its customers, collaborators and or employees. Can be monetary or non-monetary.
29
New cards
Communication
Refers to the process of informing current and potential buyers about the specifics of the offering.
30
New cards
Distribution
Defines the channels through which the offering is delivered to customers.
31
New cards
Marketing tactics as processes
• process of designing • process of communicating • delivering value
32
New cards
Top-down analysis of A Business model
Broader consideration of the target market and the relevant value exchange which is followed by designing a specific offering. Starts with the strategy then tactics.
33
New cards
Bottom-up analysis of - Business model
Starts with designing the specific aspect of the offering, which is then followed by identifying the target market and developing an optimal value proposition From tactics to strategy.
34
New cards
Targeting
The process of identifying customers for whomthe company will optimize its offering.
35
New cards
One-for-all strategy
Develop same offering for different customers Might not be effective for customers with different needs because the offering will end up not creating value for at least one.
36
New cards
One-for-each strategy
Develop different offerings based on the needs of each one (customers). Might not be effective because the company might not have the resources to develop offerings that meet the needs of both customers.
37
New cards
Customer segments
Group of customers that share similar characteristics.
38
New cards
Functionally of segmenting
Enables the company to improve the cost efficacy of its marketing activities by not having to customize the offering for individual customers.
39
New cards
Customer characteristics
Value-based factors and profile factors-based
40
New cards
Value based factors
Reflect customers needs and their willingness and ability to pay for the company's offerings
41
New cards
Profile-based factors
That reflect customers observable characteristics like age, gender, income, social status, geographical location, and buying behavior
42
New cards
Strategic targeting
Focuses on the value defined by customer needs and the potential to create value for the company. Can the company create superior value for those customers? Can these customers create vale for the company and the collaborators?
43
New cards
Tactical targeting
Focuses on customer profile, including factors like age, gender, income, social status, geographical location and buying behavior, to identify effective and cost efficient ways to reach customers.
44
New cards
2 key targeting criteria
Target attractiveness and target compatibility
45
New cards
Target attractiveness
Reflects the ability of a given segment to deliver superior value to the company. Could be monetary or strategic
46
New cards
monetary value (ch.4)
Ability to generate profits for the company.
47
New cards
Strategic Value
Customers ability to create non monetary benefits that are of strategic importance for the company.
48
New cards
Target compatibility
Reflects the company's ability to fulfill the needs of target customers better than the competition.
49
New cards
Target-specific
Resources compatible with one segment might not be compatoble with another segment.
50
New cards
Tactical targeting
Aims to determine which customers to target and which to ignore Aims to identify an effective and cost-efficient approach to communicate and deliver the offering to already selected target customers.
51
New cards
Two aspects of devleoping value propisition
1. Intangible
2. idiosyncratic
52
New cards
Intangible
A customers subjective evalutation of the worth (utility) of the company’s offering does not physically exists in the marketplace.
53
New cards
Idiosyncratic
The same offering can have different value for different customers.
54
New cards
Functional value
Th benefits and costs directly related to an offering’s performance.
55
New cards
Psychological value
The psychological benefits and costs associated with the offering.
56
New cards
Monetary value (ch.5)
Monetary benefits and costs associated with the offering.
57
New cards
Three factors of an offering’s ability to create value
1. The attributes defining the company’s offering.
2. The relative importance of these attributes for target customers.
3. The offering’s performance on these attributes.
58
New cards
Customers valuation of a market offering formula
\
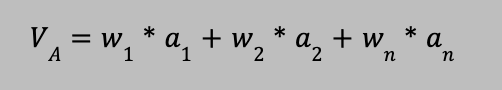
59
New cards
Reference-point dependence
Aspects of the value function reflects the fact that consumers often do not have well-articulated preferences and that their evalutations of market offereings depend on the decision context.
60
New cards
Loss-aversion aspect
Extends the principle of reference point dependence to assert that people value the positive (gains) and negative (lossess) deviations from the reference point in a different fashion, placing more weight on losses than gains.
61
New cards
Principle of diminishing marginal value
Implies that the utility from improving an offering’s performance on the same dimension does not increase in a monotonic fashing, and that after a certain point improving the offering’s performance will produce marginally diminishing increases in the subject valuation of the offering.
62
New cards
Satisficing (one popular decision heuristic)
Involves selecting the first option that meets the buyers’ criteria without necessarily considering all of the available options. Buyers might end up choosing different options depending on the order in which they evaluate the options.
63
New cards
Equal-weight heuristic
Buyers might evaluate only the most important attributes, without taking into account the performance of the options on all attributes.
64
New cards
Lexicographic heuristic
Buyers might consider only the most important attribute describing the choice options and select the option with the highest value on that attribute.
65
New cards
Two factors of an offering’s competitive advantage
1. Points of difference
2. Points of parity
66
New cards
Points of difference
Involve attributes that are important for target customers and on which the company’s offering is percieved to be different from that of its competitors.
67
New cards
Points of parity
Refer to attributes on which an offering’s performance matches that of the competition.
68
New cards
Three strategies for increasing the offering’s value
1. Improve the offering’s performance on a given attribute.
2. Add new attribute on which the offering has an advantage.
3. Increase the perceived importance of an attribute on which the offering has an advantage.
69
New cards
Positioning
Reflects the company’s view of how its offering should be thought of by customers; it is the process of creating a distinct image of the company’s offering ina customer’s mind. Customer valuation of market offerings is influenced by the refrence points used to assess the attributes of individual offering.
70
New cards
Five types of frames of reference
1. Need-based framing
2. User-based framing
3. Category-based framing
4. Competitive framing
5. Product-line framing
71
New cards
Need-based framing
Directly links the benefits of the offering to a particular customer need.
72
New cards
User based framing
Defines the offering by associating it to a particular type of buyer.
73
New cards
Category-based framing
Defines the offering by relating it to an already established product category.
74
New cards
Competitive framing
Defines the offering by explicitly contrasting it to competitor’s offerings and typically highlighting those aspects of the offering that differentiate it form the competition.
75
New cards
Product-line framing
Defines the offering by comparing it to other offerings in the company’s product line.
76
New cards
Three positioning strategies
1. Positioning on functional benefits.
2. Positioning on psychological benefits.
3. Positioning on monetary benefits.
77
New cards
Positioning on functional benefits
Aims to create functional value by emphasizing a particular aspect of an offering’s performance.
78
New cards
Positioning on psychological benefits
Emphasizes the psychological value associated with the offering.
79
New cards
Positioning on monetary benefits
emphasized the monetary value associated with the offering.
80
New cards
Products
Anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisify want or need. Once created, they can be physically seperated from the manufacturer and distributed to end users via multiple channels.
81
New cards
Durable goods
Consumed over multiple occasions and over an extended period.
82
New cards
Nondurable goods
Typically consumed on a single occasion or over a short period.
83
New cards
Three catogories of product uncertainty
Search, experience, and credence.
84
New cards
Search products or services
Associated with the least amount of uncertainty and are typically identifiable through inspection before purchase.
85
New cards
Experience products and services
Carry greater uncertainty and are revealed only through consumption.
86
New cards
Credence products and services
Have the greatest amount of uncertainty, and their quality is not truly revealed even after consumption.
87
New cards
Specific decisions concerning factors of managing products and services
Performance, consistency, reliability, durability, compatibility, ease of use, technological design, degree of customization, form, style, and packaging.
88
New cards
Performance
Products vary in their performance on different attributes.
89
New cards
Consistency
An important aspect of designing an offering is ensuring that in-kind products and services are identical and consistent with specification.
90
New cards
Reliability
Refers to the probability that the product or service will operate according to its specifications and willl not malfunction for the duration of its projected life cycle.
91
New cards
Durability
Another important consideration in product design involves the expected length of the offering’s life cycle.
92
New cards
Ease of use
An important aspect of many products and services is their ease of use.
93
New cards
Two technological design methods
Product-innovation aproach
Product-variation aproach
Product-variation aproach
94
New cards
Product-innovation aproach
Involves technology-based innovations and innovative use of existing technology to design new offerings.
95
New cards
Product-variation approach
Leads to offerings characterized by relatively minor variations in their functionality, such as adding different colors, flavours, tastes, sizes, designs, or packaging variations.
96
New cards
Degree of customizations
When designing its offerings, a company needs to decide on the degree to which these offerings will be customized for target customers.
97
New cards
Mass-production strategy
Offering the same products and services to all customers.
98
New cards
One-to-one customization
The company’s products and services are customized for each individual customers.
99
New cards
Segment-based customization
A compromise between the mass-production approach and the one-to-one customization approach.
100
New cards
Form
Product design typically involves decisions concerning the physical aspects of the offering, such as its size and shape.