Lecture 9: Pain and Brain Development
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Stress and Trauma:
T/F: Stress and Trauma can be POSITIVE and NEGATIVE
True
What is the downstream consequences?
Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE) has been associated with nearly how much of psychiatric disorders?
Adults w more that what ACE score have higher likelihood of dying 20 years earlier than anticipated?
1/3 of psych disorders
6 ACE
Childhood Brain Development:
The newborn’s brain weight about how much of the adult brain?
Adult’s brain are relativley ____, BUT children’s brains are developing and evolving rapidly and thus always _____.
25%
Adult: Set, Child: Changing
Are there times in a child’s development when trauma and injuty have larger impacts on brain development and pain?
Children who were sexually abused AFTER the age of 12 were 10x more likley to develop PTSD then those BEFORE 12.
Pain chronicity increases w age in children peaking in adolescents at 16 yo. F > M.
Network Changes w Chronic Pain:
Increase or Decrease:
Salience Network
Central Autonomic Network
Emotion Regulation Network
Default Mode
Salience Network
Increase
Central Autonomic Network
Increase
Emotion Regulation Network
Increase
Default Mode
Decrease
Changes in Cortical and Subcortical Regions:
Key Point:
Pain is about what?
Chronic Pain and Trauma Response are what?
Pain = Memory
CP and TR = Memory Disorder
Changes in Cortical and Subcortical Regions:
Knowing the function of the areas of the brain helps understanding of what?
What is common function of the Cortical and Subcortical Regions? (3)
What are the 2 Levels of Processing?
Nature of Pain
Function
Memory and Learning
Emotions
Autonomic Response
Level of Processing
Subconsious and Unconsious
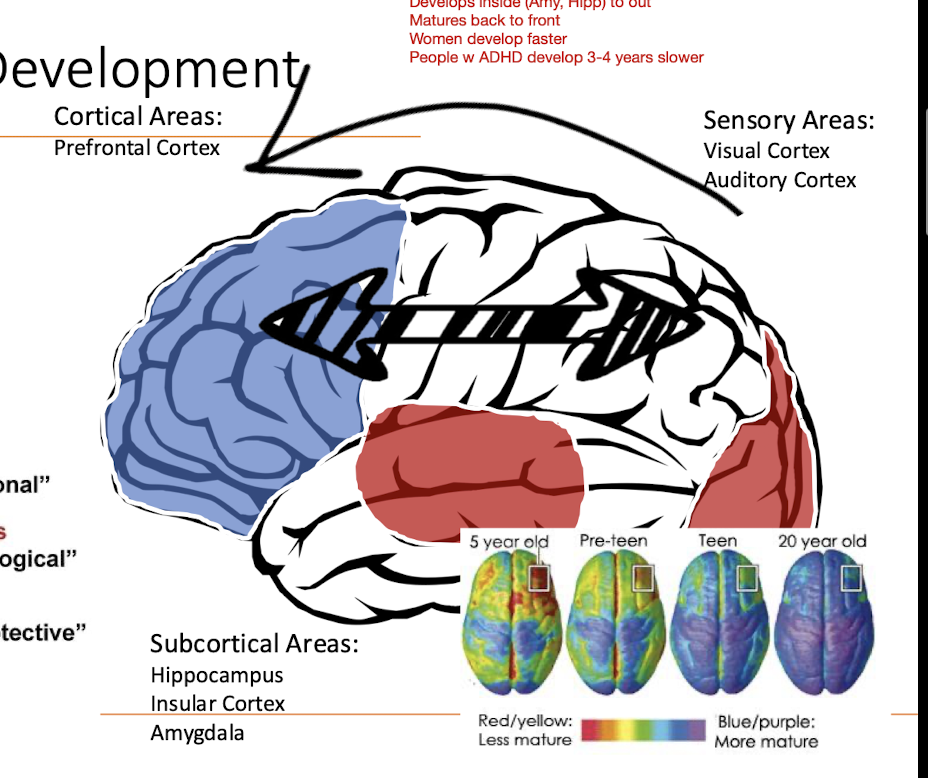
Childhood Brain Development:
Towards which direction does the brain DEVELOP?
Towards which direction does the brain MATURE?
What gender does the brain develop faster?
People w ADHD, their brains develop how many years slower?
Dev: Inside Out
Mature: Back to Front
Female
3-4 years slower
Childhood Brain Development:
Myelination proceeds from what directions?
Back to Front of Brain
From Center to Sides
Trauma and Pain in Child’s Brain: AMYGDALA
L or R Amygdala develops quicker?
L Amygdala has been associated with what?
R Amygdala is associated with what?
L development is impacted by trauma at what age?
R development is most impacted by trauma at what age?
L quicker than R
L = Positive Experiences
R = Avoidance
L development impacted at:
Early Childhood (0-3 yrs)
R Development impacted at:
Middle Childhood (10-11 yrs)
Trauma and Pain in the Child’s Brain: HIPPOCAMPUS
What months are the KEY milestone of hippocampal development and continues to adolescence?
Spikes seen when?
18-24 mo
Spike at Early Adolescence
Trauma and Pain in the Child’s Brain: PREFRONTAL CORTEX
Activity may correspond to what?
Ages?
Intense periods of growth
7-9 yo
11 - Adult (greatest impact)
Subconscious: Amygdala
When does Amygdala develop?
Assesses threat by assessing what?
(0-10 yrs)
Importance of incoming information w memory
Subconscious: Hippocampus
When does Hippocampus develop?
Influences new what?
Storage of what before it moves to Long Term Memory?
Informs ____ and stores information about what?
(2-7 yrs)
Influences new memory formation and consolidation
Short Term Memeoru
Behavior; space and time of events
Subconscious: Insular Cortex
When does Insular Cortex develop?
The Insula filters and interprets what type of information taken by what?
Insular Cortex function:
Example:
(7 yrs to Teens)
Filters and Interprets Interceptive Info taken by senses
Sound, Smell, Taste, Sight, Touch (Autonomic Reg)
Fx:
Threat Decision Making
Emotion and Empathy
Craving, Addiction, Desires
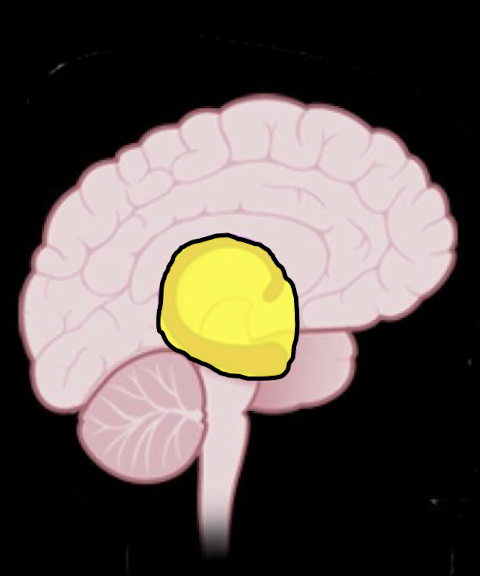
Subconscious: Insular Cortex
L Posterior Insula develops when?
R Posterior Insula develops when?
L: 7-9 yrs
R: Teens
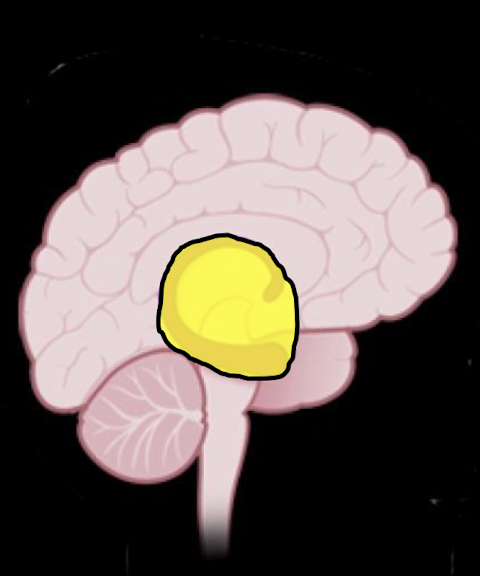
Subconscious: Anterior Cingulate Cortex
When does ACC develop?
Critical role in what?
Involved in interpreting what?
Recieved from where?
(7 yrs to Teens)
Delegating areas of the brain to perform specific tasks
Interp: Sensory, Social, Contextual Info
Received from Physical Env
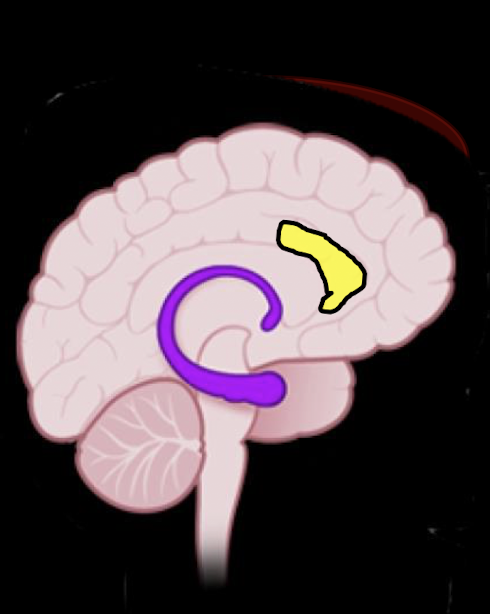
Subconscious: Anterior Cingulate Cortex
ACC is involved in what of emotion?
Wave of activity at what age?
Active when?
Perception, Eval, and Experience of Emotion
7-9 yrs
Adolescence
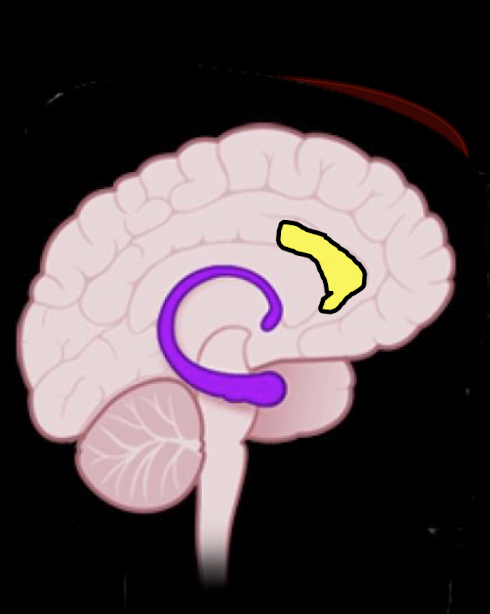
Conscious: Prefrontal Cortex
When does PFC develop?
Main function:
Teens
Fx:
Problem Solving
Integ of Emotion
Interp and Integ Info
Predicting and Adjusting Behavior
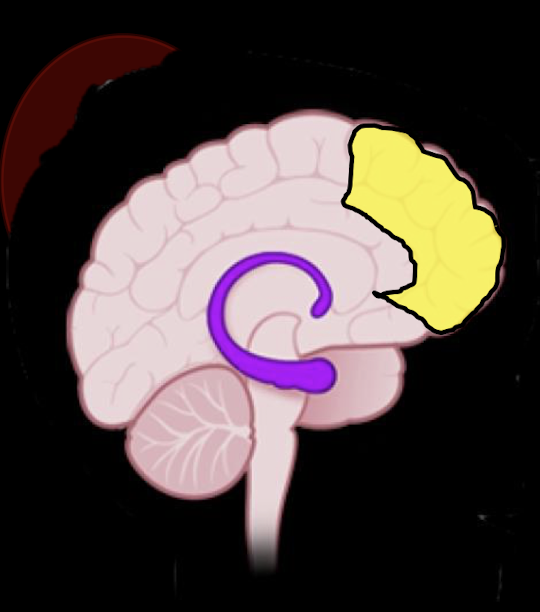
Conscious: Prefrontal Cortex
____ and ____ behavior
Helps determine social relevance of what?
Predicting and Adjusting Behavior
Social Relevance of:
Info
Integrating Affect
Controlling Impulses
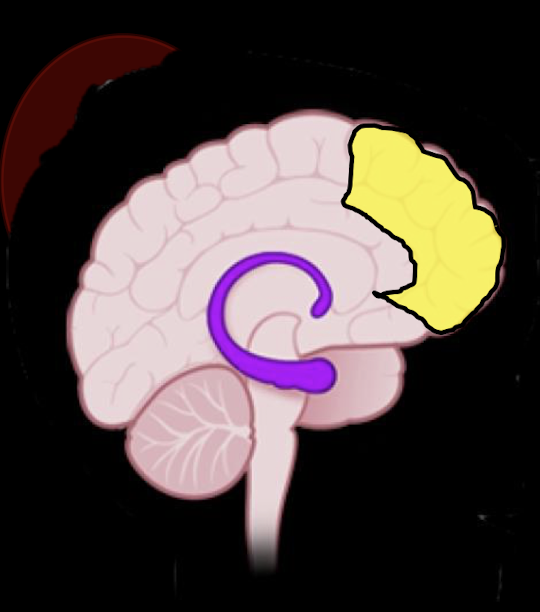
Subconscious: Corpus Callosum
When does Corpus Callosum develop?
Allows for communication between what structures and is involved in what?
Neuroimaging research has identified reduces overall size and reduced gray and white matter of the CC in what?
3-12 years
Communication btwn L and R brain; Lateral Processing
Traumatized Children
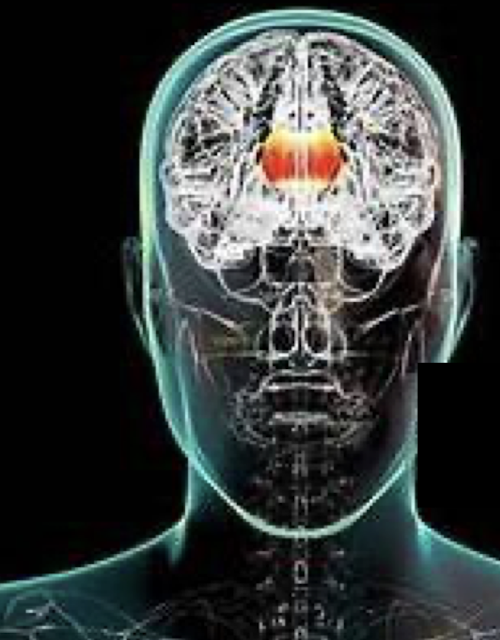
Subconscious: Corpus Callosum
CC undergoes significant development in children of what age?
This dev relates to what?
In children from 6-12 yrs, the CC develops significantly in relation to what?
3-6 years
Attention and Behavioral Planning
Language and Memory
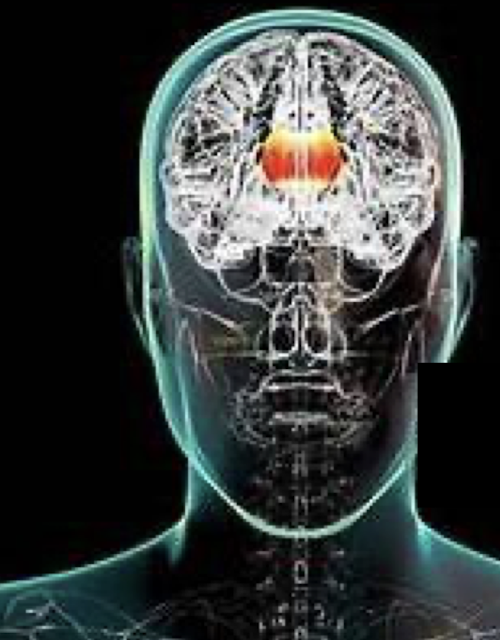
Other: Cerebellum
When does Cerebellum develop?
Cerebellum is involved in diverse processes such as:
There is consistent evidence of ____ Cerebellum Volume in children w histories of trauma exposure
Adulthood
Diverse Processes such as:
Classical Conditioned
Motor Control
Language
Working Memory
Cognition
Emotion
Decreased
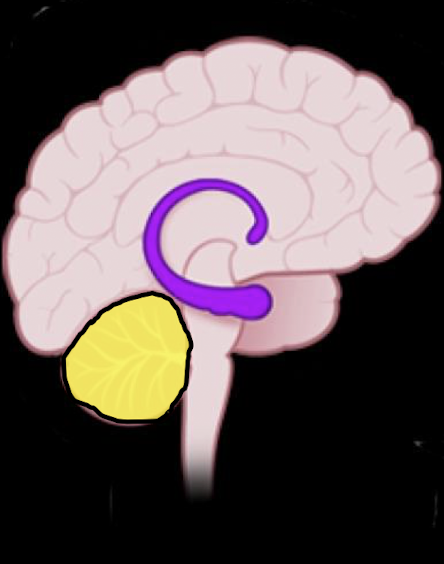
Other: Cerebellum
_____ related circuitry found in Cerebellum w CP
Inverse relationship between what?
Cerebellum also has prolonged what?
Potentially making it vulnerable to what?
Aversion
Limbic Activity and Cerebellar Activity
Prolonged Dev Period
Vulnerable to Env Stress
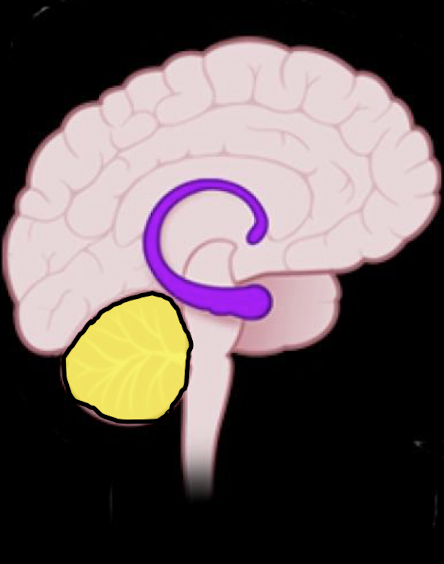
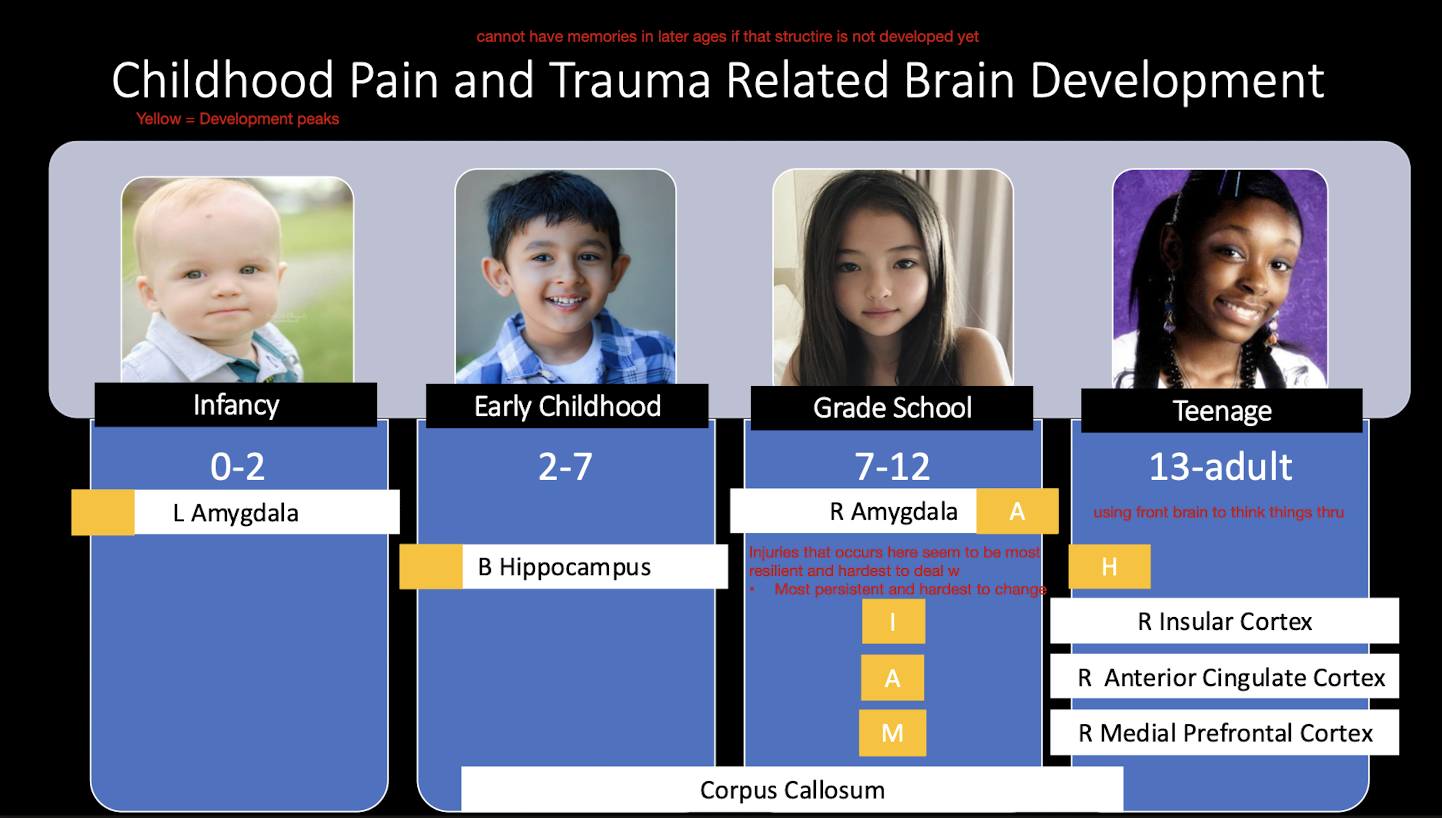
Childhood Pain and Trauma Related Brain Dev:
What brain structures develop during ages:
Infancy (0 - 2 yrs)
Early Childhood (2 - 7 yrs)
Grade School (7 - 12 yrs)
Teenage (13 - Adult)
Infancy (0 - 2 yrs)
L Amygdala
Early Childhood (2 - 7 yrs)
Bilat Hippocampus
Grade School (7 - 12 yrs)
R Amygdala
Teenage (13 - Adult)
R Insular Cortex
R ACC
R mPFC
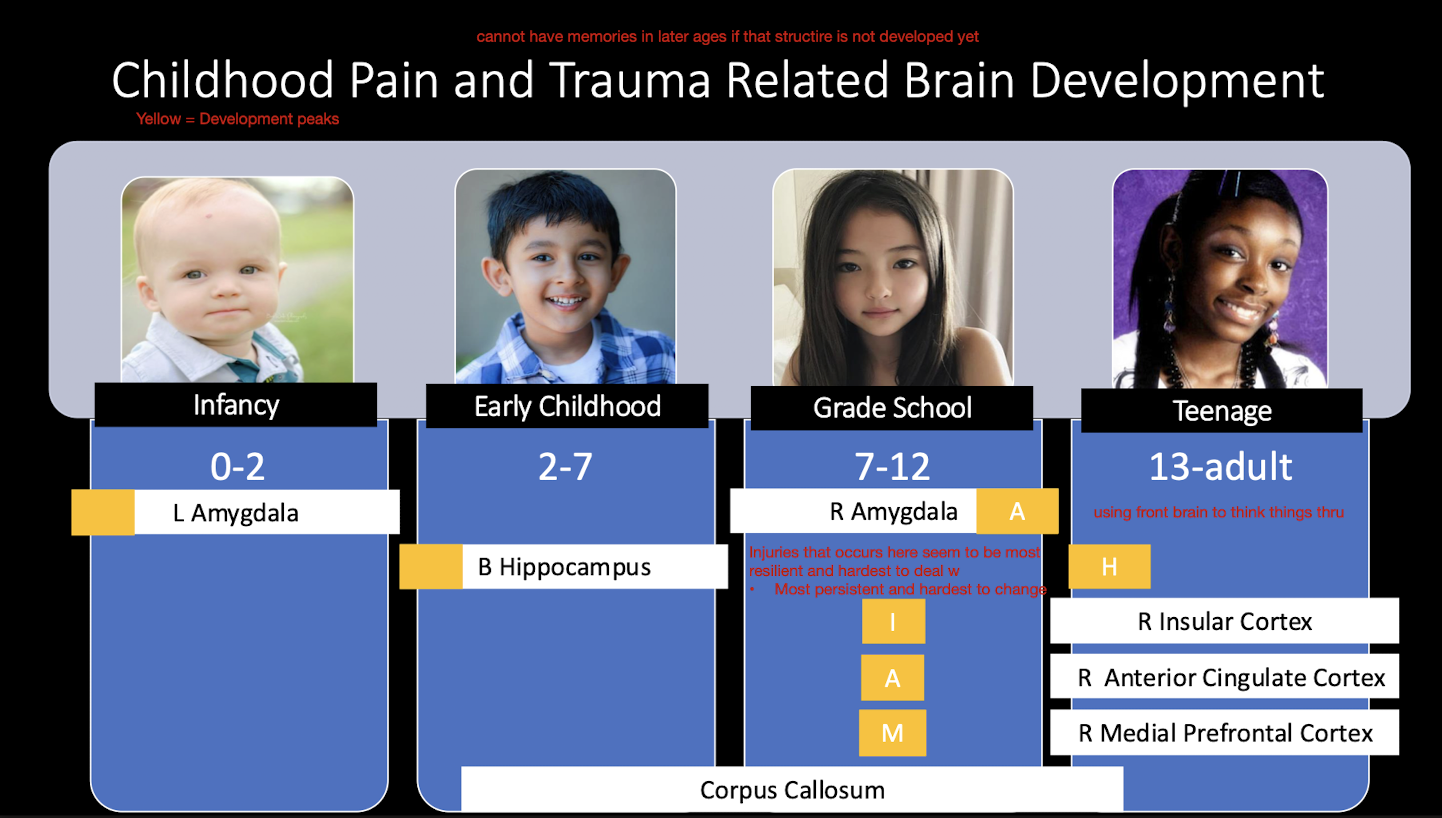
Childhood Pain and Trauma Related Brain Dev:
When does the Corpus Callosum develop?
Early Childhood to Teenage
What type of response is Pain?
Pain is a response that can be _____ and ____ learned
Protective threat response
Subconsciously and Associatively
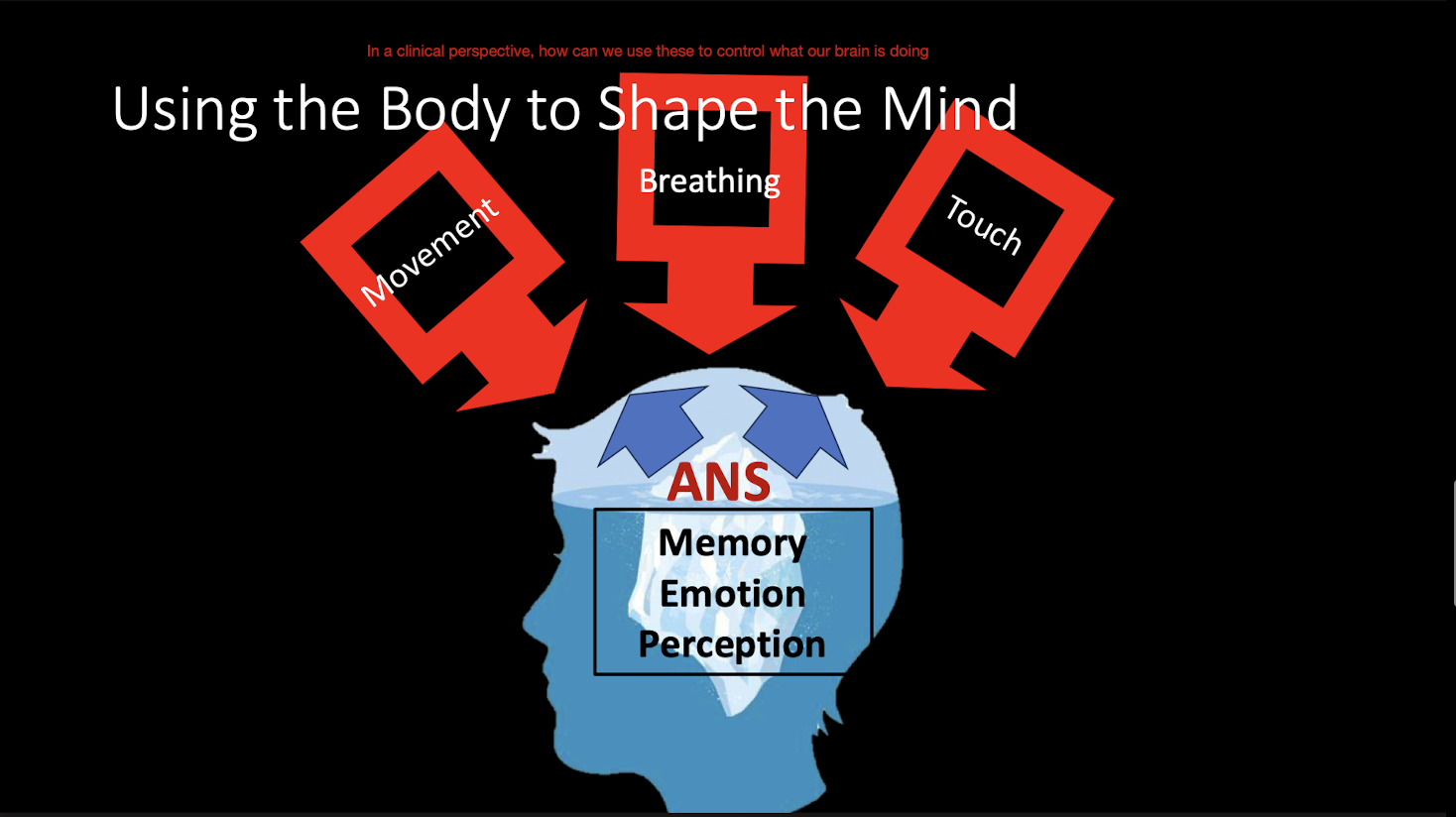
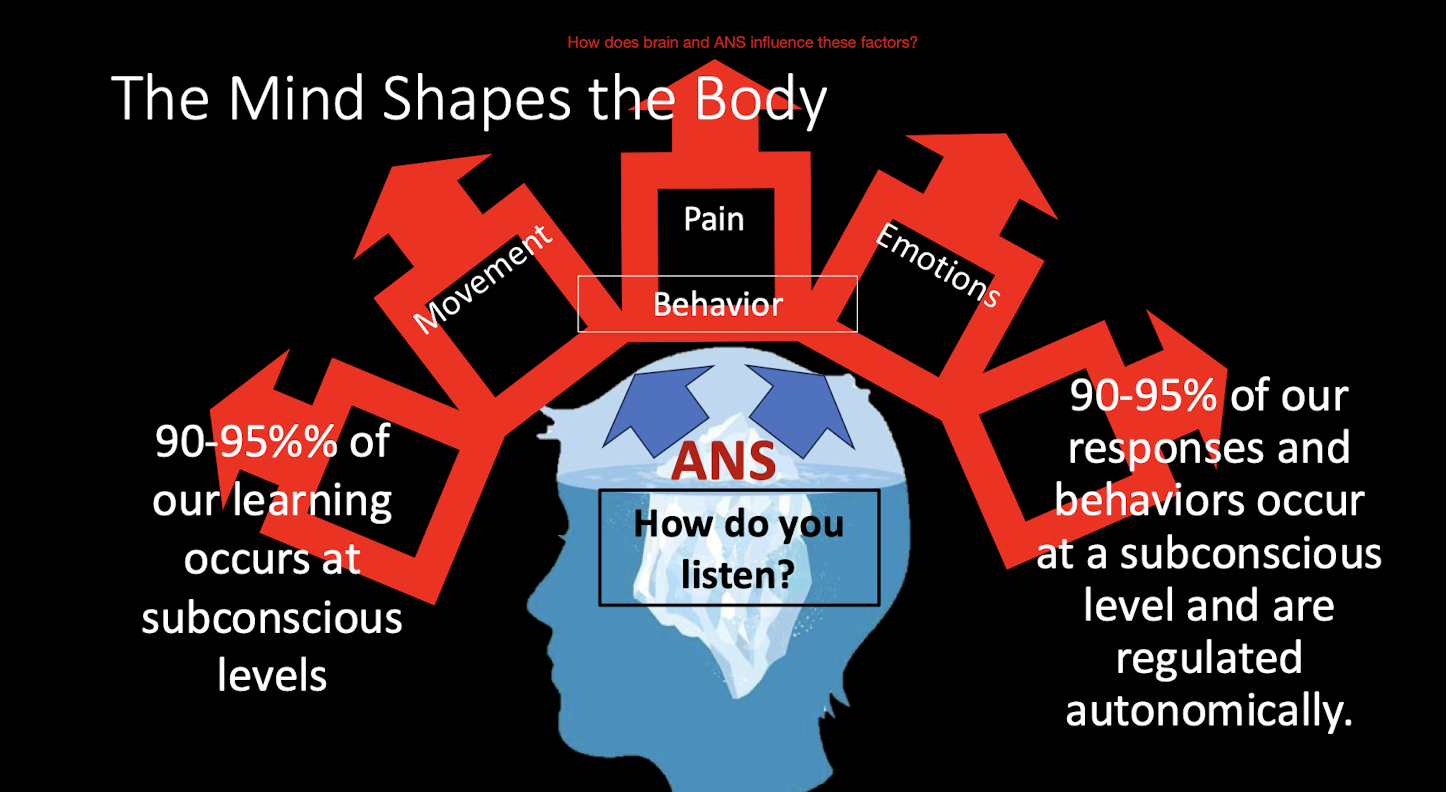
Mind Shapes the Body:
90-95% of our responses and behaviors occur at:
What level?
Regulated how?
Subconscious Level
Autonomically
Using the Body to Shape the Mind