Mustafa - ophthalmic, nanomedicine, semisolid dosage forms
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Pharmaceutical nanotechnology: the _______, _________ and ________ of pharmaceutical materials, structures and products that have one or more dimensions (diameter) between approximately ___ to ____ nm
Frequently, particles in larger size ranges are also considered as nanotechnology (sizes up to ______ nm)
design, characterization, production, 1-100, 1000
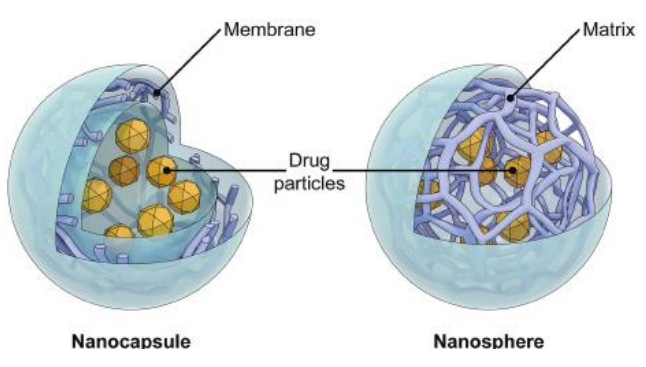
Colloidal particles - size range of ________ nm
Nano-capsules =
Nano-spheres =
Mainly developed for ________ administration
advantages (3)
commonly used materials (4)
1-1000
core shell structure
matrix system
parenteral
protect from degradation, control drug release, targeted delivery
PLGA, polysaccharide (chitosan, alginate), solid lipid, albumin
Classification of Dispersed Systems
Molecular dispersion
Size
characteristics
Examples
Colloidal dispersion
size
characteristics
examples
Coarse dispersion
size
characteristics
examples
< 1 nm
pass through membrane, invisible in e- microscope
ions, glucose
1-500 nm
pass through filter paper but not membrane, visible under e- microscope
nanoparticles, viruses, liposomes, polymers, paint
> 0.5 micrometer
do not pass through either, visible under optical microscope
emulsions, susp, rbcs
Nanoparticles for Paclitaxel (cancer treatment drug)
Abraxane → paclitaxel ________-bound nanoparticle formulation, ___ ______ ______, can be delivered into body at ____ higher dose within ___ minutes
Taxol → conventional paclitaxel formulation, organic solvent IS used to increase the _______ of paclitaxel, pre-medication is needed to avoid ____ _____; infusion for ____ hours
albumin, no organic solvent, 50%, 30
solubility, side effects, 3
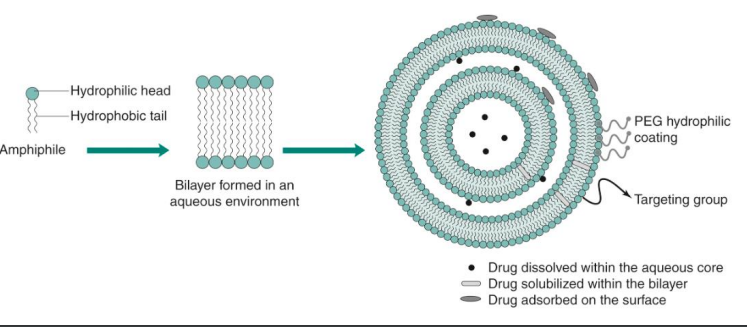
Liposome nanoparticle example
small spherical vesicle composed of a _____ bilayer
______ core + ______ sphere
________ in diameter
_______ or ______ structure
surface can be _______
water soluble drug is encapsulated in the _______
water insoluble drug is encapsulated in the ________
lipid
aqueous, lipid
20 nm - 10 micrometer
unilamellar, multilamellar
modified
core
lipid bilayer (sphere)
Preparation of Liposome
_________ is a technique where the liposome suspension is passed through a membrane filter of defined pore size
Lipid dispersion is forced through ______ with different pore sizes
result → _______ and _______ size
_______ is usually used as the membrane for liposome extrusion
extrusion
filters
homogenous, uniform
polycarbonate
Mononuclear phagocytic system MPS
is a part of the _____ system → a collection of ______ cells
mainly exists in the …. (4)
Rapid clearing of nanoparticles by phagocytes via ________
Surface characteristics affect the uptake of nanoparticles by MPS
Particles with more hydrophobic surface is preferentially taken up by the ______, ______, and ______
Hydrophilic nanoparticles show ___% less uptake by the _____ and ______
Surface modification with flexible _______ polymer ______ PREVENTS plasma protein absorption and consecutive uptake by the MPS
immune, phagocytic
liver, spleen, lungs, lymph nodes
phagocytosis
liver, spleen, lungs
1%, liver, spleen
hydrophilic, PEG
Types of liposomes (4)
conventional → neutral or - charged
stealth → sterically stabilized, polymer coatings, prolonged circulation time
immunoliposome → antibody modified
cationic → + charged for nucleic acid delivery
What kind of liposome are PEG modifed? (conventional, stealth, immuno, or cationic?)
stealth
Stealth liposome → liposome coated with inert biocompatible polymers such as _____ → ______ circulation in blood can lead to higher uptake by ______ cells
2 examples
^
These improved _______ for solid tumors and decreased ____ ______
PEG, longer, tumor
Doxorubicin → 20 min circulation t1/2
Doxil → 55 hours circulation t1/2
targeting, cardiac toxicity
disadvantages of liposomes (4)
expensive
poor shelf life, lipid prods may break down in presence of H2O
poor encapsulation efficiency for some drugs
difficulty in scale up
Preparation of Liposome → Thin Film Hydration Method Steps (8)
lipids + hydrophobic drugs in organic solvent
rotary evaporation
dry lipid film
hydration
stirring
downsizing (extrusion)
purification
final liposome
Similarities of Liposome & cell membrane (3)
similar lipid bilayer
high biocompatibility
no toxicity (immunogenicity)
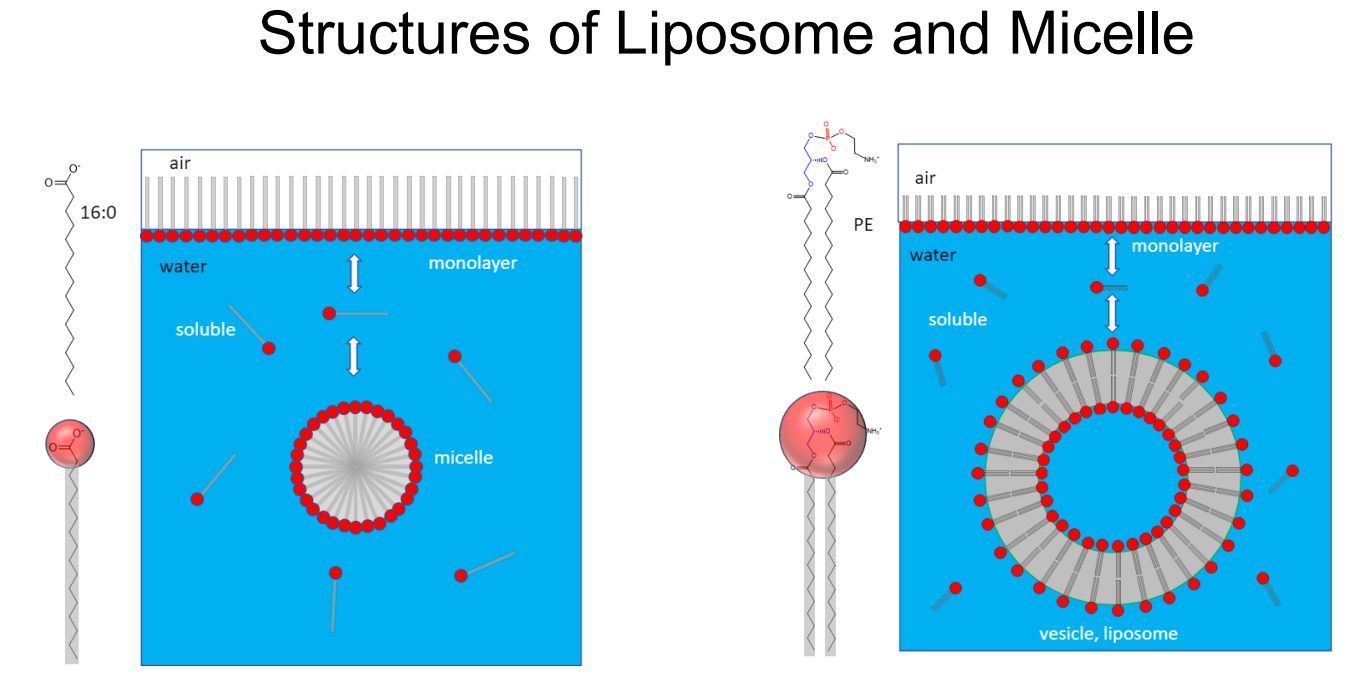
Liposome vs micelle
micelle = single chain amphiphile, liposome = double chain amphiphile
Applications of Liposome (3)
cosmetics
diagnostic imaging of tumors
drug delivery
advantages of liposomes
________ and ________
can _______ drugs w diverse properties
__________
_______ drug release
surface can be _______ w targeting ______ for targeted drug delivery
biocompatible, biodegradable
encapsulate
protection
prolong
modified, ligands
__________ ________ ____ ________ effect when molecules (liposomes/nanoparticles) with certain size ______ in tumor tissue much more than they do in normal tissues → tumor cells grow quickly
the newly formed tumor vessels are usually _______
the neovasculature is ….
and the endothelial cells are ….
enhanced permeability and retention EPR, accumulate
abnormal
irregular, dilated, leaky, defective,
poorly aligned, large fenestrations
cellular uptake of liposomes (6 steps)
specific absorption
nonspecific absorption
fusion w membrane
destabilize and release
exchange of lipid components w cell memb
endocytosis
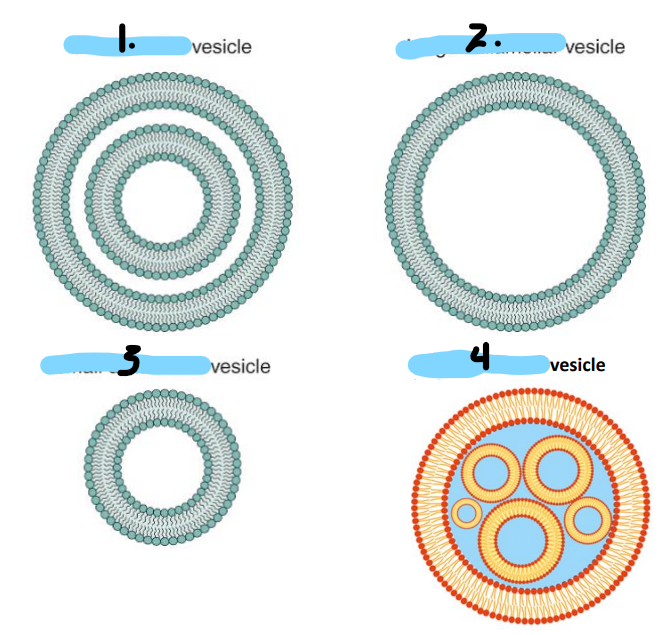
Name the configurations of lysosomes
multilamellar
large unilamellar
small unilamellar
multivesicular
Most anterior part of eye → target membrane
Posterior inner layer of eye
Liquid that fills anterior and posterior chambers
Cornea
Neural retina
Aqueous humor
Highly efficient _____ ______ system that contribute to LOW ocular drug bioavailability via the topical route
Lacrimal drainage
The ______ route of drug delivery is the most common way of treating the anterior segment
More than ____% of the ophthalmic medicines on the market are in the form of ____ _____
Topical ophthalmic preparations can be classified into ….
Topical
90%, eye drops
Solutions, suspensions, ointments, gels
3 Factors affecting ocular drug delivery
Physiological, drug properties, formulation
The ocular bioavailability of aqueous ophthalmic solutions is usually LOW owing to the barrier properties of the _____ and ______
conjunctiva, cornea
Loss of drug can happen due to several processes such as
________ loss of drug due to tear turnover
_______ by the naso-lacrimal apparatus
In situ _______
Systemic _______ (conjunctival and nasal mucosae)
Pre corneal
Drainage
Metabolism
Absorption
Max volume at one time that the eye can accommodate
30 microliters
Cornea
Outer epithelial and endothelial layer is _______
Middle stromal layer is ________
Log P of _____ is optimal (more lipophilic or hydrophilic?)
T or F: hydrophilic molecules can pass lipophilic layers
Lipophilic
hydrophilic
2-3, lipophilic
F
Ophthalmic ______ generally produce GREATER ocular bioavailability bc of the greater contact time, drug absorption is increased
Ointments
enhancing ocular drug bioavailability by 2 strategies:
Sustained drug del systems (3)
Enhancing drug absorption (2)
implants, inserts, colloids
viscosity enhancing agents, penetration enhancers
Ophthalmic preparations require special considerations regarding … (5)
Sterility
Preservation
Isotonicity
Buffering
Viscosity
Methods of sterilization (4)
Autoclave
Filtration → for heat sensitive
Gas sterilization → ethylene oxide
Gamma irradiation → $$, for heat sensitive
Microbial preservatives used in ophthalmic formulations (4)
Benzalkonium cl, benzethonium cl, chlorobutanol, phenyl mercuric acetate
Ophthalmic preparations must be formulated at a pH equivalent to tear fluid pH = ____
Eye can tolerate a range of tonicities _______% NaCl solution
Tonicity agents (6)
Hypotonic causes _______
Hypertonic causes ______ and is more or less severe than hypo?
7.4
0.6-1.8%
NaCl, KCl, buffering salts, dextrose, mannitol, glycerol
oedema
Dryness, less
Viscosity enhancers enables the formulation to remain in the eye ________ and gives ________ ______ for the drug to exert its therapeutic activity
Acceptable viscosity of ophthalmic preparations is up to ____ mPa
Commonly used viscosity enhancers (4)
longer, more time
15
MCC, HPMC, HEC, PVA
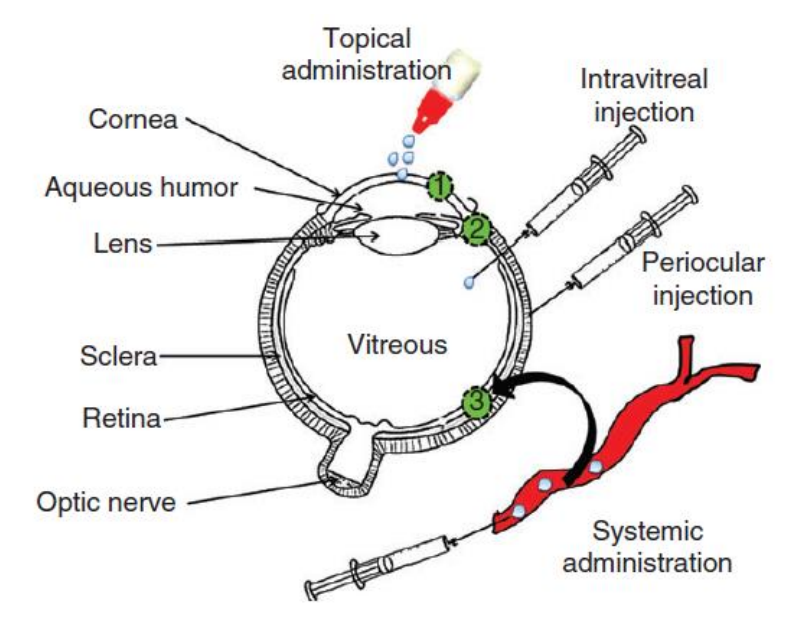
Routes of Ocular Drug Administration
Topical administration - may deliver drugs to ______ segment of eye (______ and _____), high patient compliance
Intravitreal and periocular injections - deliver drug to the ______ segment (______)
^ Which injection is more invasive, intravitreal or periocular?
Systemic administration - delivers drug into ______ segment, still not a successful route due to limited _____ into ocular tissues
anterior, cornea, conjunctiva
posterior, retina
intravitreal
posterior, absorption
2 types of ophthalmic preparations + examples
conventional systems → soln, susp, gel, ointments
non-conventional → implants, collagen shields
Conventional delivery systems
Drugs are commonly applied to the eye for the _____ effect of the medication on the surface of the eye or on its interior
________ solutions are most frequently employed
localized
aqueous
Ophthalmic solutions
Ophthalmic solutions are most often administered in the form of ________.
Ophthalmic solutions must be ______ and contain adequate preservatives.
Disadvantage of ophthalmic solutions is the short _________ of drug with the absorbing tissues of the external eye mainly cornea (_____ ocular bioavailability).
eye drops
sterile
contact time, low
Ophthalmic suspensions
employed to a much ______ extent than are ophthalmic solutions
may be prepared when the API is _______ in the desired vehicle OR _____ in solution form
drug particle size is ________ (reduced) to prevent ________ of the cornea
particles in suspension should be _______ μm which will not cause irritation to the eyes
the suspended particles can NOT agglomerate into larger particles upon storage, _______ agents are added to prevent agglomeration
may also be desired to provide a ______ release of drug from the vehicle
lesser
insoluble, unstable
micronized, scratching
<10
flocculating
slower
Ophthalmic ointments
ointments are cleared from the eye more _______ than solution
ophthalmic ointments, in contrast to dermatological ointments, MUST be _______
ointment base for an ophthalmic ointment must be nonirritating to the eye, with melting/softening point close to _______ temperature
Primary advantage of ointment over solution → increased drug ocular _______ _____
Disadvantage → ______ vision which occurs as ointment base melts and is spread across the lens
slowly
sterile
body
contact time
blurred
Ophthalmic Gels
divided into 2 categories →
gelling agents are polymers such as _____ and ______
can provide improved __________ by increasing the corneal contact time
gel/gel eye drops → gel before application, in situ gels → form gel upon application
MC, CMC
bioavailability
Ophthalmic preparations are mostly packaged in soft ______ containers holding 2, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, and 30 mL of product with a fixed built-in _______
Ophthalmic solutions used as eyewashes are generally packaged with an ____ ____, which should be cleaned and dried thoroughly before and after each use
plastic, dropper, eye cup
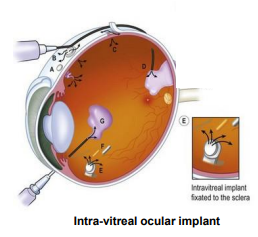
Ocular Implants
implants made from ______________ polymers which are _________, can result in drug release over ______ months period
mainly treat ______ segment eye disorders
__________ _______ delivers the drug over a 6 month period (manage Cytomegalovirus retinitis, a complication of ____)
use associated with _________ (inflammation of the intraocular fluids)
poly lactide/glycolide, biodegradable, 5-6
posterior
ganciclovir GCV implant, AIDs
endophthalmitis
________ _______ are designed to be a __________, _______-term therapeutic bandage lens for cornea
these shields can be used in patients who underwent ______ surgery for delivery of ______ agents without disturbing the eye
utility of collagen shields for _______ segment drug delivery is still under investigation
collagen shields, disposable, short
corneal, therapeutic
posterior
Disadvantages of ocular drug delivery
intraocular implants →
systemic admin →
intravitreal injections →
topical application →
risk of retinal detachment and intravitreal hemorrhage, invasive
limited penetration, systemic toxicity
risk of retinal detachment, intravitreal hemorrhage, endophthalmitis, cataracts, rapidly diluted, need to repeat
limited penetration, rapid tear washout, poor patient compliance
Pharmacologic categories of ophthalmic drugs
___________: tetracaine, cocaine, proparacaine
____________ agents: steroidal and nonsteroidal
________ and _______ agents: gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin
________ agents: amphoterecin B, natamycin
________ agents: trifluridine, idoxuridine, vidarabine
___________: cause cell contraction → zinc sulfate
anesthetics
anti-inflammatory
antibiotic, antimicrobial
antifungal
antiviral
astringents
Pilocarpine ocusert system is advantageous over pilocarpine eye drops because ….
a. it is more invasive
b. increased drug eye contact time and bioavailability
c. decreased patient compliance
d. less expensive
b
A ________ dermatological product is designed to deliver drug into the skin for treating dermal disorders, with the skin as the target organ (LOCAL DELIVERY)
topical
A ________ product is designed to deliver drugs through the skin (percutaneous absorption) to the general circulation for systemic effects, with the skin not being the target organ (SYSTEMIC DELIVERY)
transdermal
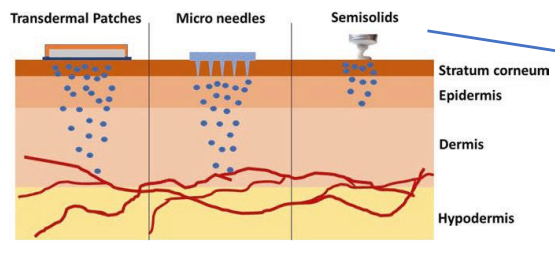
Example of products that interact with stratum corneum
Example of products that remain on skin surface
Example of products that reach the dermis or epidermis layers
moisturizers
sunscreens, barrier creams
antimicrobial agents, local anesthetics
Properties of Topical Formulations
Topical semisolid preparations may or may not contain a drug substance dissolved and/or dispersed in a simple or multi-component base (main component)
The base may consist of _______ or ________ substances
preparation may have _______ or ________ properties
Topical semisolid preparations may contain excipients such as …. (6)
Topical dermatological semisolid preparations for use on broken or severely injured skin must be _________
natural, synthetic
hydrophilic, hydrophobic
antimicrobial preservatives, antioxidants, stabilizers, emulsifiers, thickeners, penetration enhancers
sterile
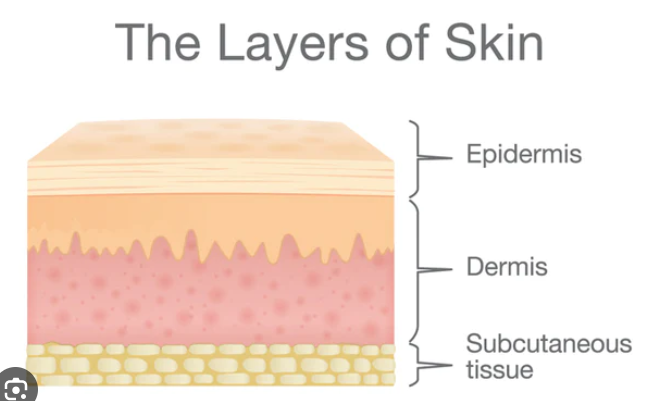
Topical formulations
Emollients form a _______ on the skin surface and fill in any _____
Occlusives form a _________ ______ and prevent transepidermal ______ ______
Humectants attract _____ from the dermis and the environment into the ______
film, gaps
protective barrier, water loss
water, epidermis
4 categories of semisolid preparations
creams, ointments, pastes, gels
4 main groups of ointment bases
hydrocarbon, absorption, emulsion, water soluble
Hydrophilic petrolatum USP is an example of an _________ base
absorption
Hydrophilic ointment USP is an example of an _______ base
emulsion
________ are in the emulsion class of ointments
Vanishing creams are ________ _______ containing large percentages of water and stearic acid or other oleaginous components
Many patients and physicians prefer creams to ointments because they are easier to ______ and _____
Example of W/O cream
Example of O/W cream
Creams are generally described as either ___________ or _________
creams
O/W emulsions
spread, remove
cold cream
hydrophilic ointment
nonwashable, washable
Emulsions are two-phase systems in which one liquid is dispersed throughout another liquid in the form of small ______, the two phases are ________ → two types: oil in water O/W and water in oil W/O
droplets, immiscible
Pharmaceutical gels are semisolid preparations where macromolecules (_______ _____) at low concentration are uniformly distributed throughout a liquid
If the liquid is in water, aqueous gels are formed which are also called ________
gelling agents, hydrogels
________ contain a large amount (20-50%) of finely powdered solids dispersed in a _______ base
They are more ________ in consistency and ____ greasy than ointments
pastes, hydrophobic , stiff, less
Ointments and other semisolid preparations are packaged either in large-mouth ________ _____ or in ________/________ ______
ointment jars, metal/plastic tubes
Which topical dermatological dosage form is used for example in the treatment of nappy rash or for skin lesions where there is oozing or crusting?
paste
Which drug involves nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel?
Abraxane or Taxol?
abraxane
T or F:
Ointments are more greasy than pastes
T
Which ophthalmic preparation has to be micronized + add flocculating agents (to prevent agglomeration) ?
suspension
Summary: Name the materials used for …
Colloidal particles
Viscosity enhancers
Liposome extrusion membrane
Tonicity agents
Gelling agents
Ocular implants
Microbial preservatives
PLGA, polysaccharides (chitosan, alginate), solid lipids, albumin
MCC, HPMC, HEC, PVA
polycarbonate
NaCl, KCl, buffering salts, dextrose, mannitol, glycerol
MC, CMC
poly lactide/glycolides
Benzalkonium cl, benzethonium cl, chlorobutanol, phenyl mercuric acetate