4. Pulpal and Periapical Pathology & Inflammatory Lesions of Jaws (Dr. Pabla & Dr. Lerman)
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
What is the most common disease process that a dentist encounters?
inflammation
What play a key role in identifying and determining the extent of involvement in bone?
imaging/radiographs
What is an inflammatory response to pathogenic microorganisms and necrotic pulp (caries, trauma) that is restricted to the root apex?
periapical inflammatory disease
What are two extensions of inflammation into bone from soft/gingival tissue?
- Periodontal disease
- Pericoronitis
Periodontal disease is inflammation of what?
supporting structures of tooth
Pericoronitis is inflammation of what?
crown of partially erupted tooth
What is an extension of inflammation into bone marrow?
osteomyelitis
Caries and trauma can develop into what?
necrotic pulp
Necrotic pulp can develop into what?
periapical inflammatory disease
Periapical inflammatory disease can develop into what?
osteomyelitis
What is an example of acute periapical disease?
periapical abscess
What is an example of chronic periapical inflammatory disease?
periapical granuloma
What two things can a periapical granuloma develop into?
- Osteomyelitis
- Periapical cyst
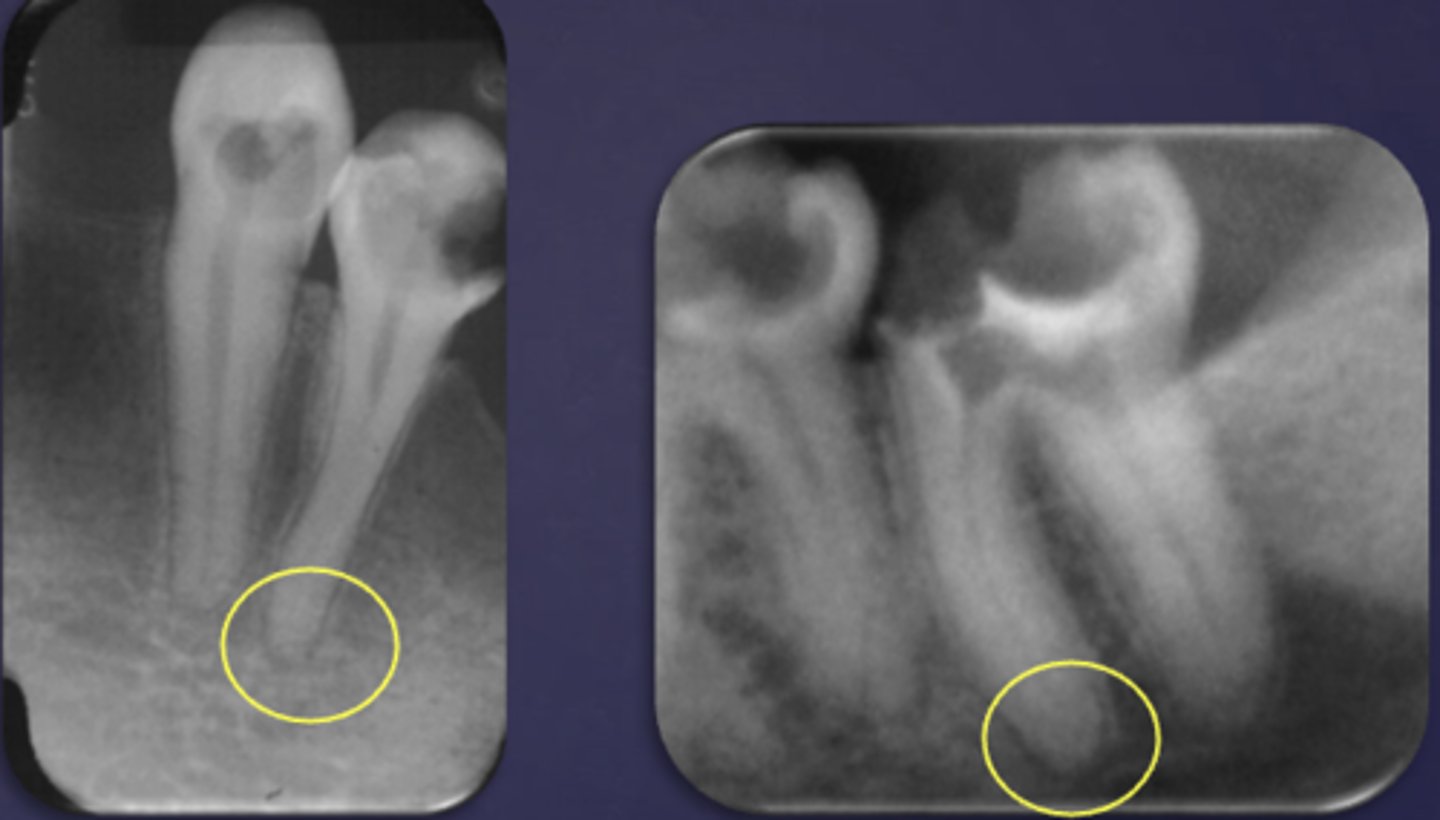
What are two radiographic signs of apical periodontitis?
- Widened PDL space
- Loss of lamina dura
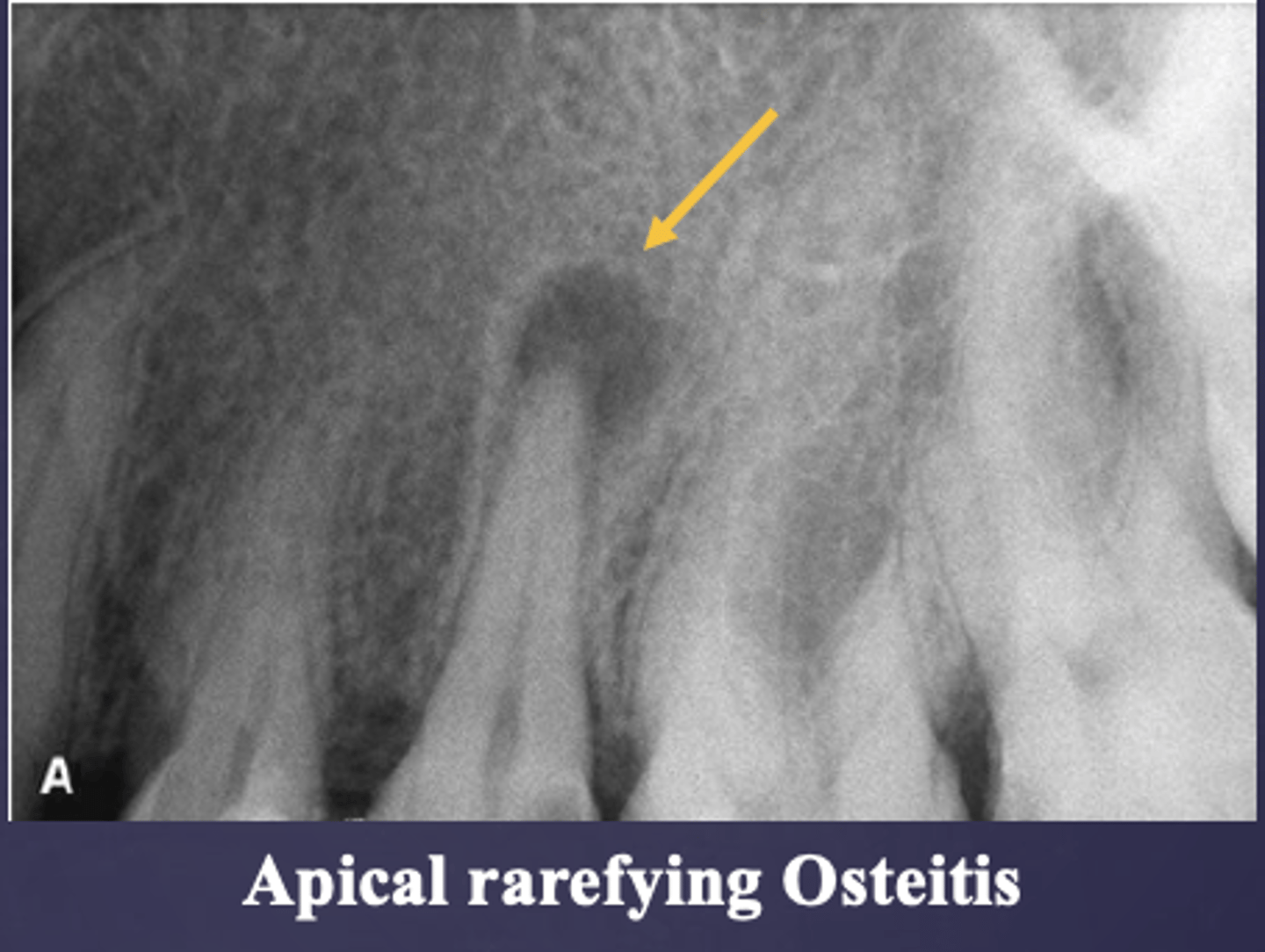
Rarefying osteitis leads to what radiographically?
increased radiolucency
What condition?
- Chronic inflammation associated with a
NON-VITAL TOOTH
- Radiolucent presentation due to removal of bone
- Sequela of an acute episode
- Includes abscess, granuloma or radicular cyst
rarefying osteitis
Rarefying osteitis has what radiographic presentation?
radiolucent
What condition?
rarefying osteitis
How do you differentiate abscess, granuloma, or radicular cyst?
Cannot differentiate on a radiograph --> need histology section
Sclerosing osteitis has what other two names?
- Focal sclerosing osteitis
- Condensing osteitis
What means "hardening" of bone?
sclerosis
Sclerosis leads to what radiograph changes?
increase in radiopacity of bone
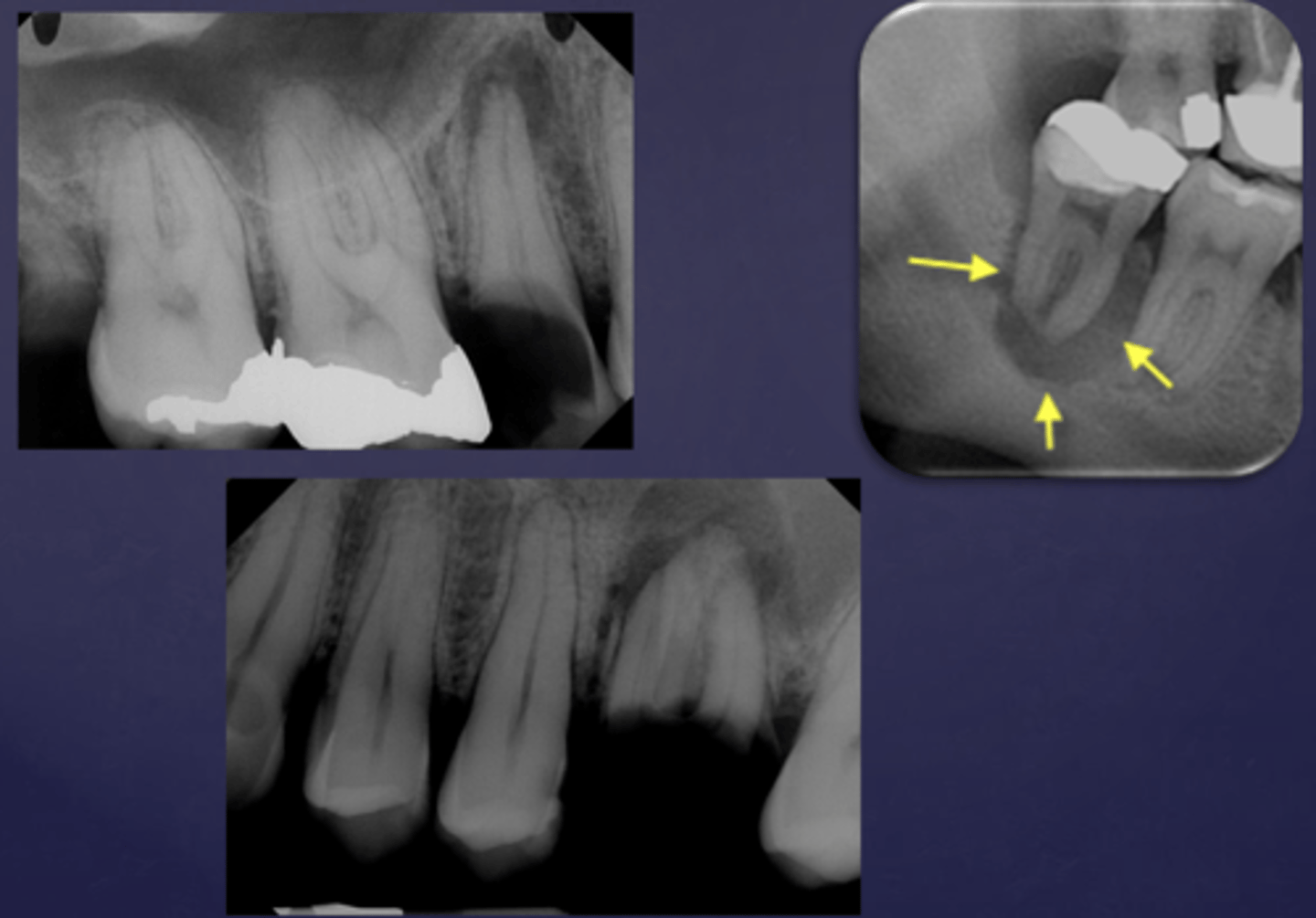
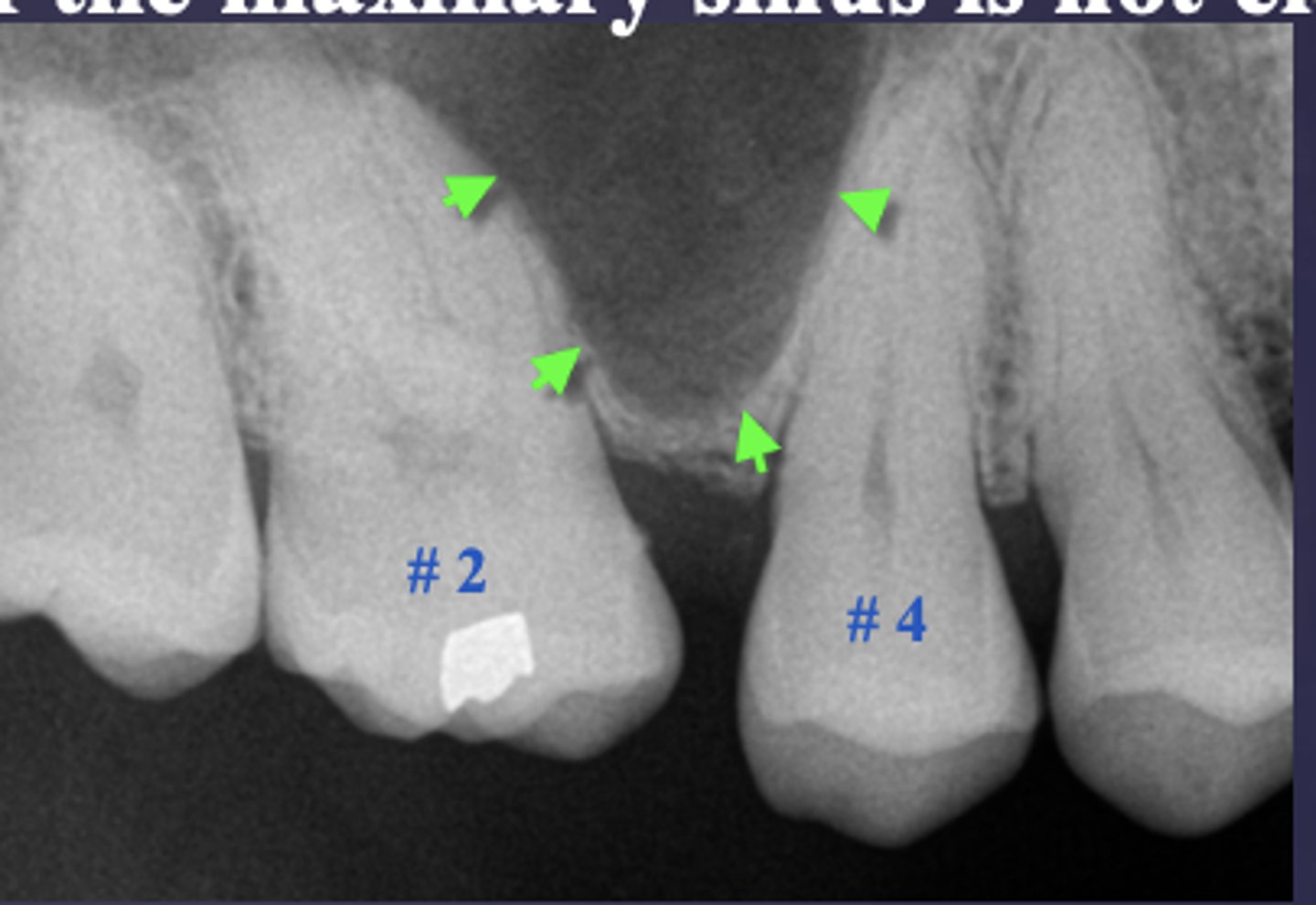
What are two defects that the arrows are pointing to?
- Widened PDL
- Sclerosis
ID the condition:
Carious exposure of pulp
ID the condition:
Root fracture
Very early lesions show no radiographic evidence because there is inadequate time for changes in calcified content (i.e.1-2 weeks, or 12%- 15% to 2/3rd of bone turnover).
How can you make a diagnosis of an early lesion?
Diagnosis is based on clinical signs and symptoms
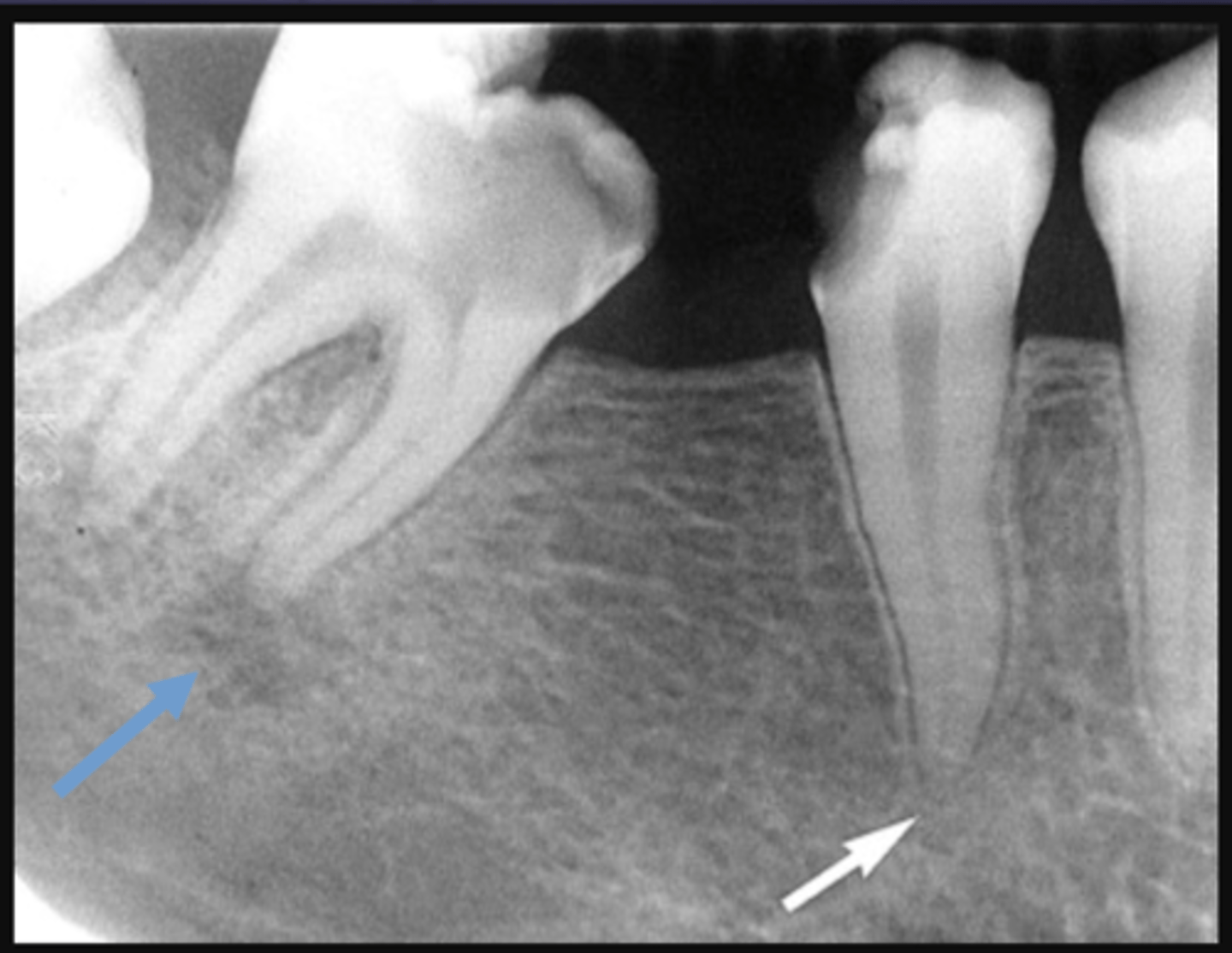
The white arrow is showing what stage of lesion?
early (involving pulp, no changes in bone)
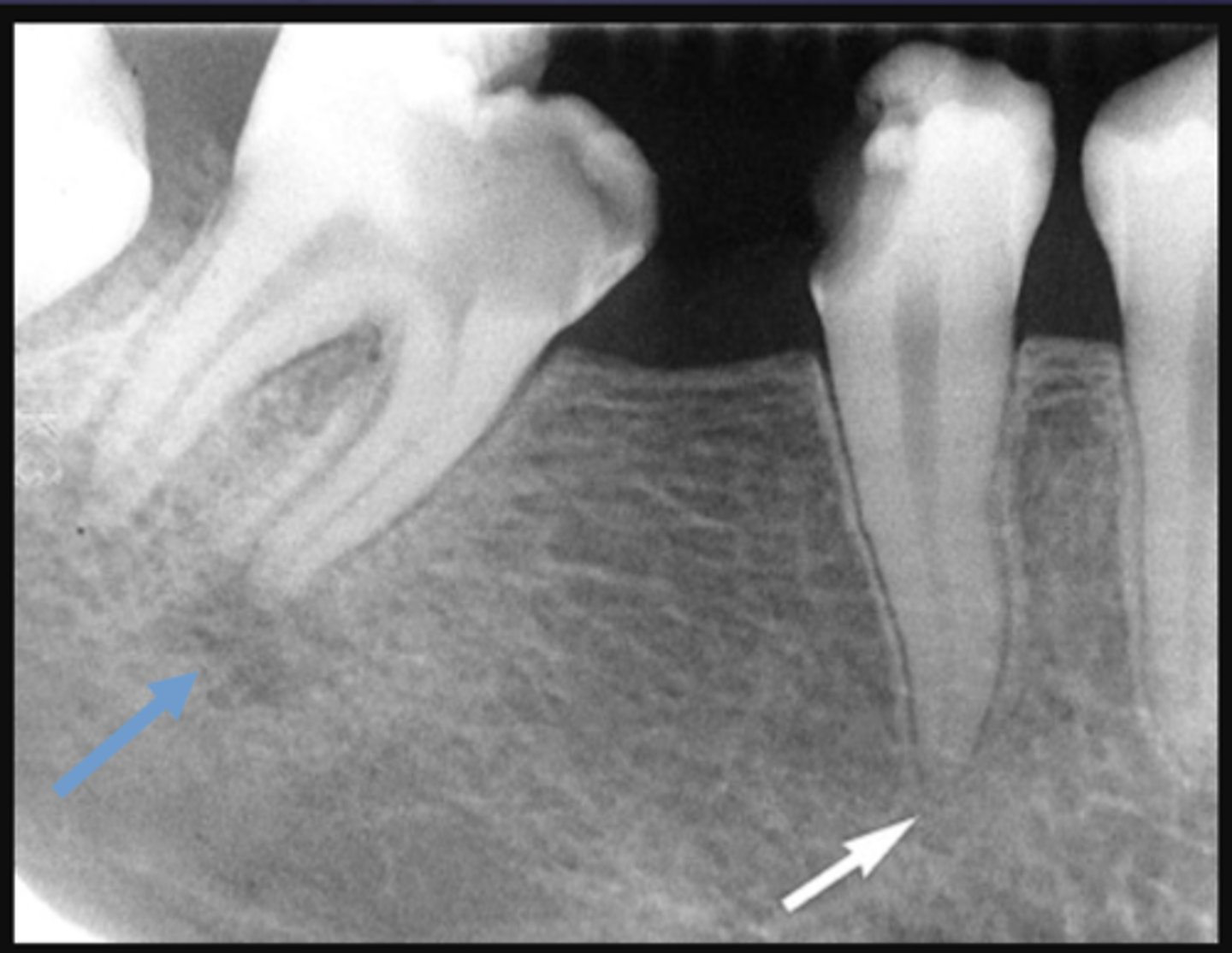
The blue arrow is showing what type of lesion?
chronic (loss of lamina dura, apical radiolucency and surrounding sclerotic bone reaction)
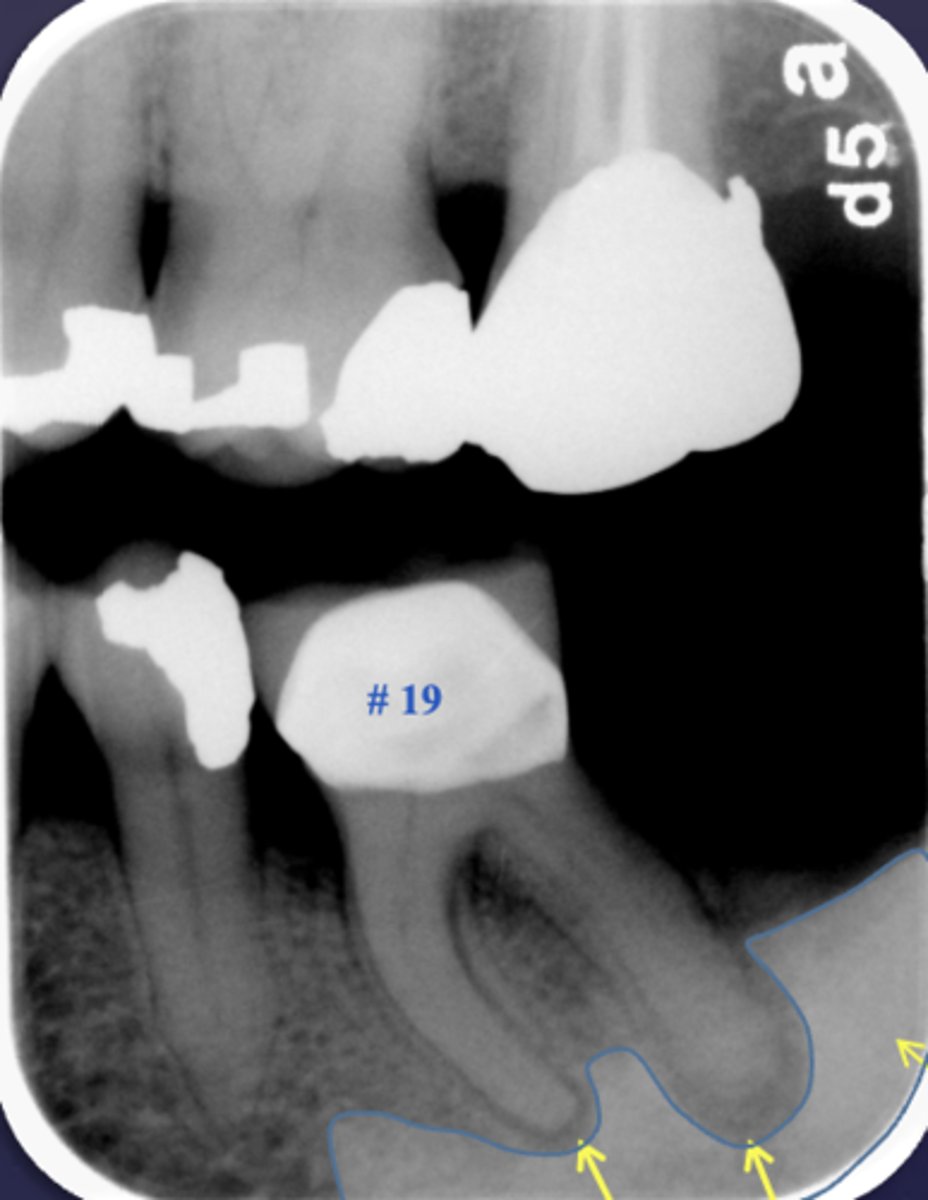
What are two early changes in periapical inflammatory disease?
- Loss of apical lamina dura
- Widening of apical PDL space

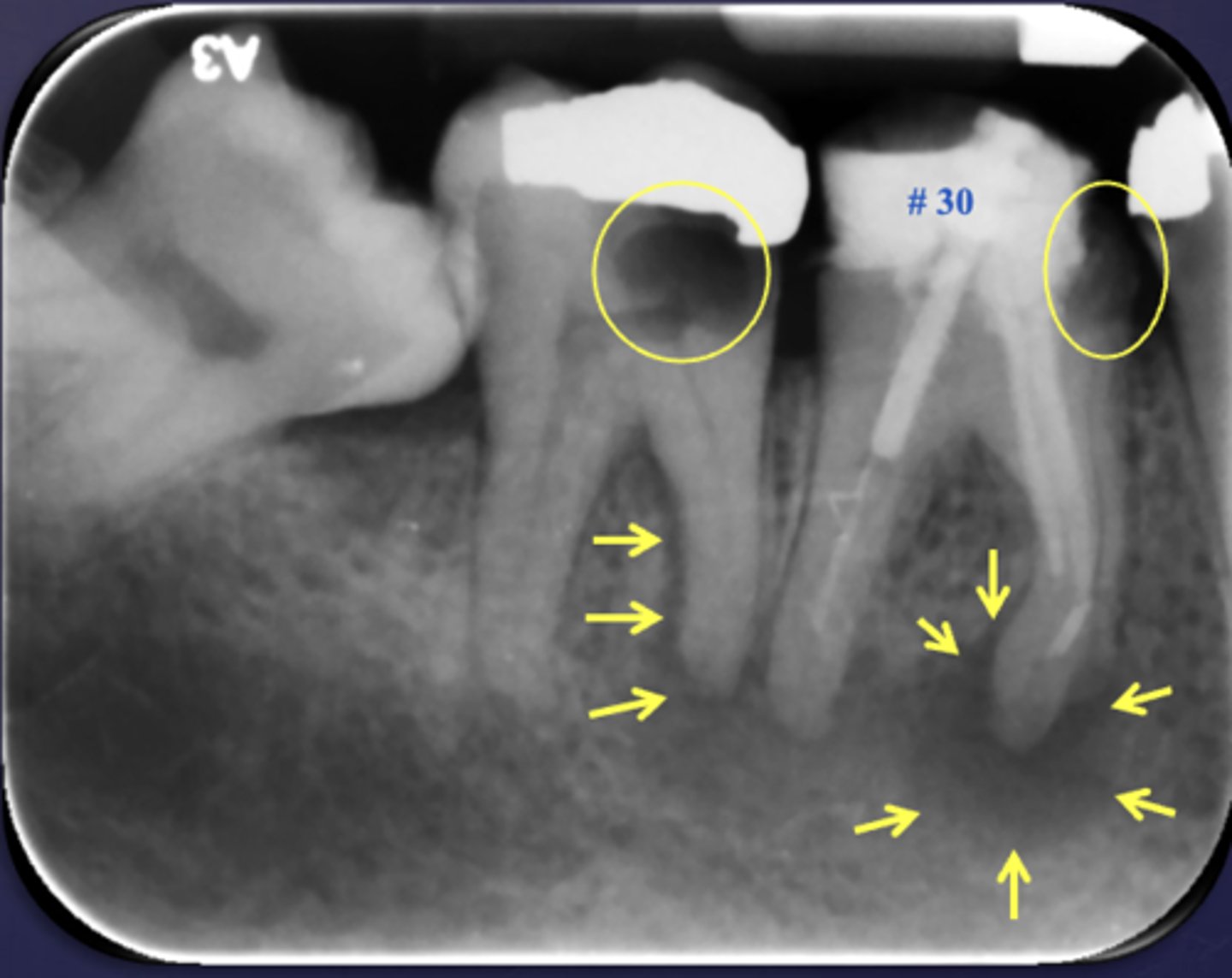
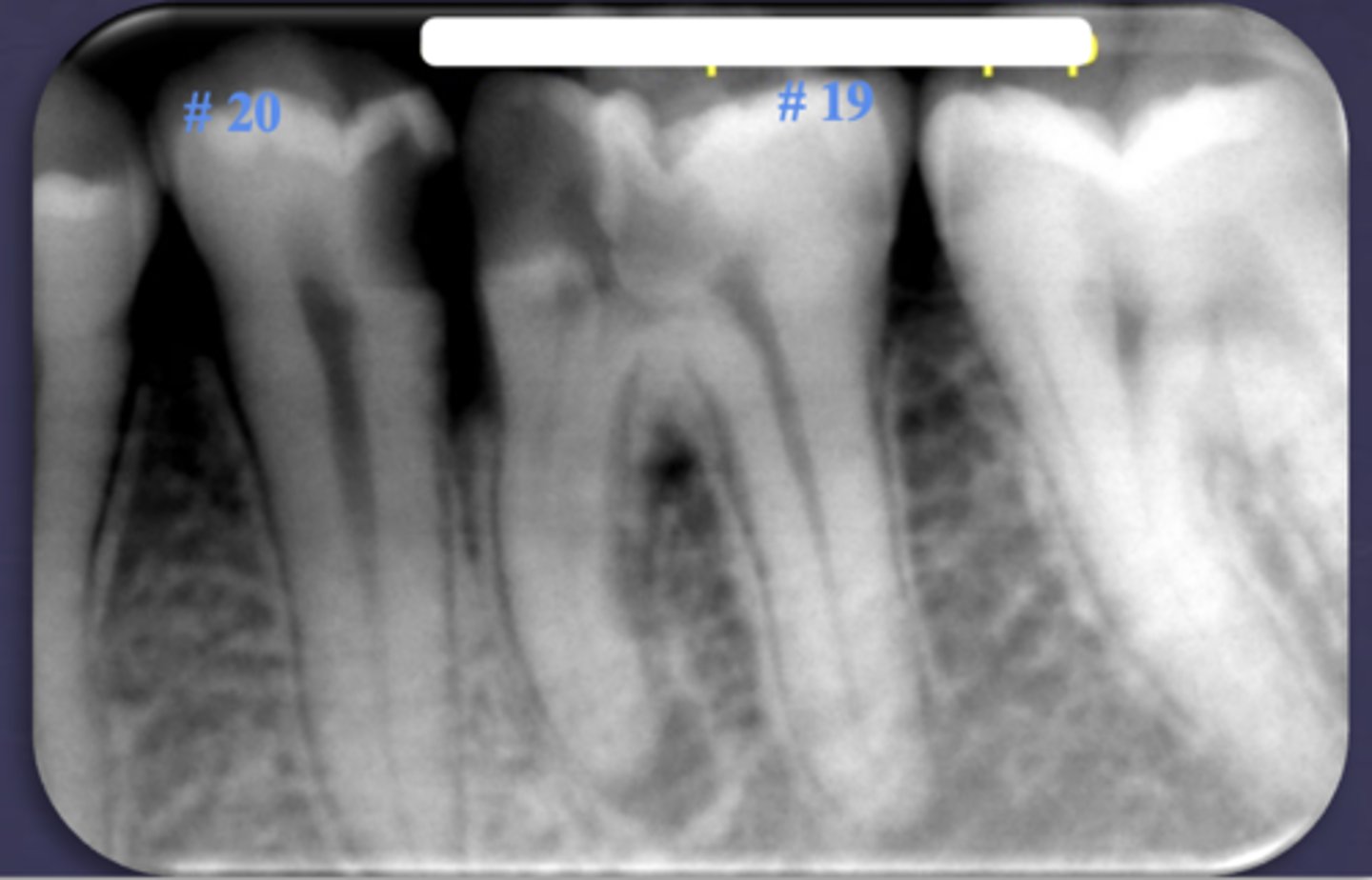
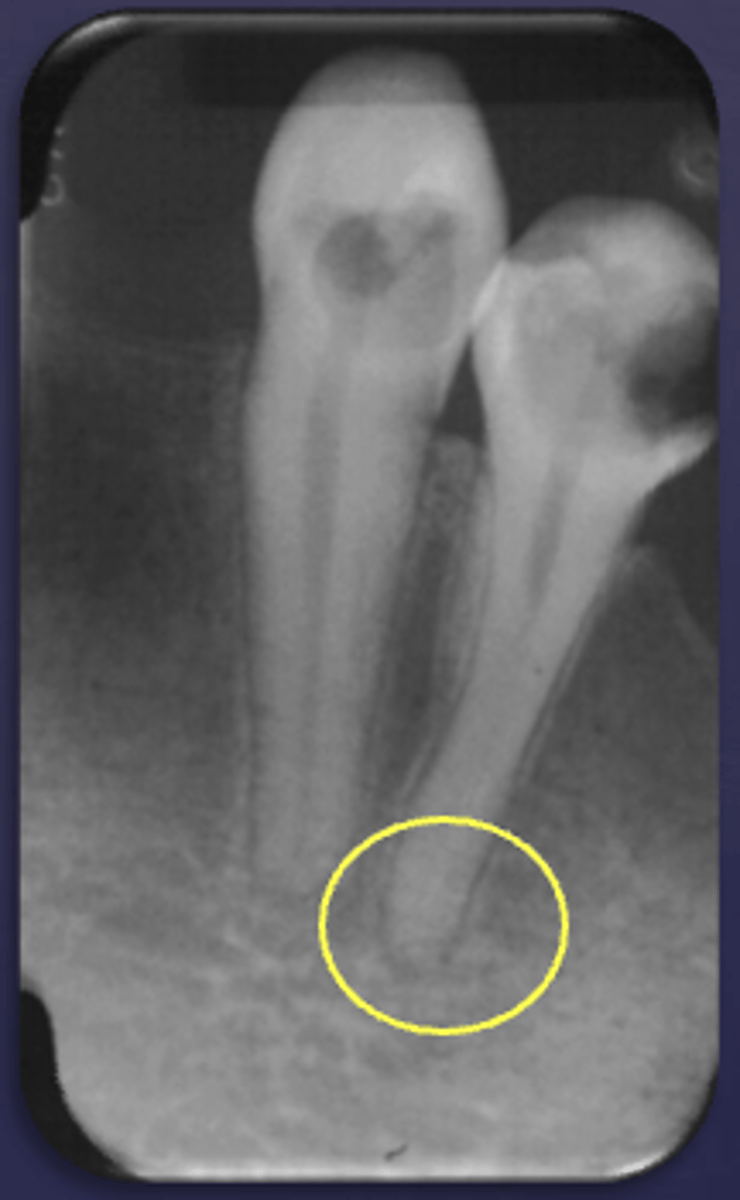
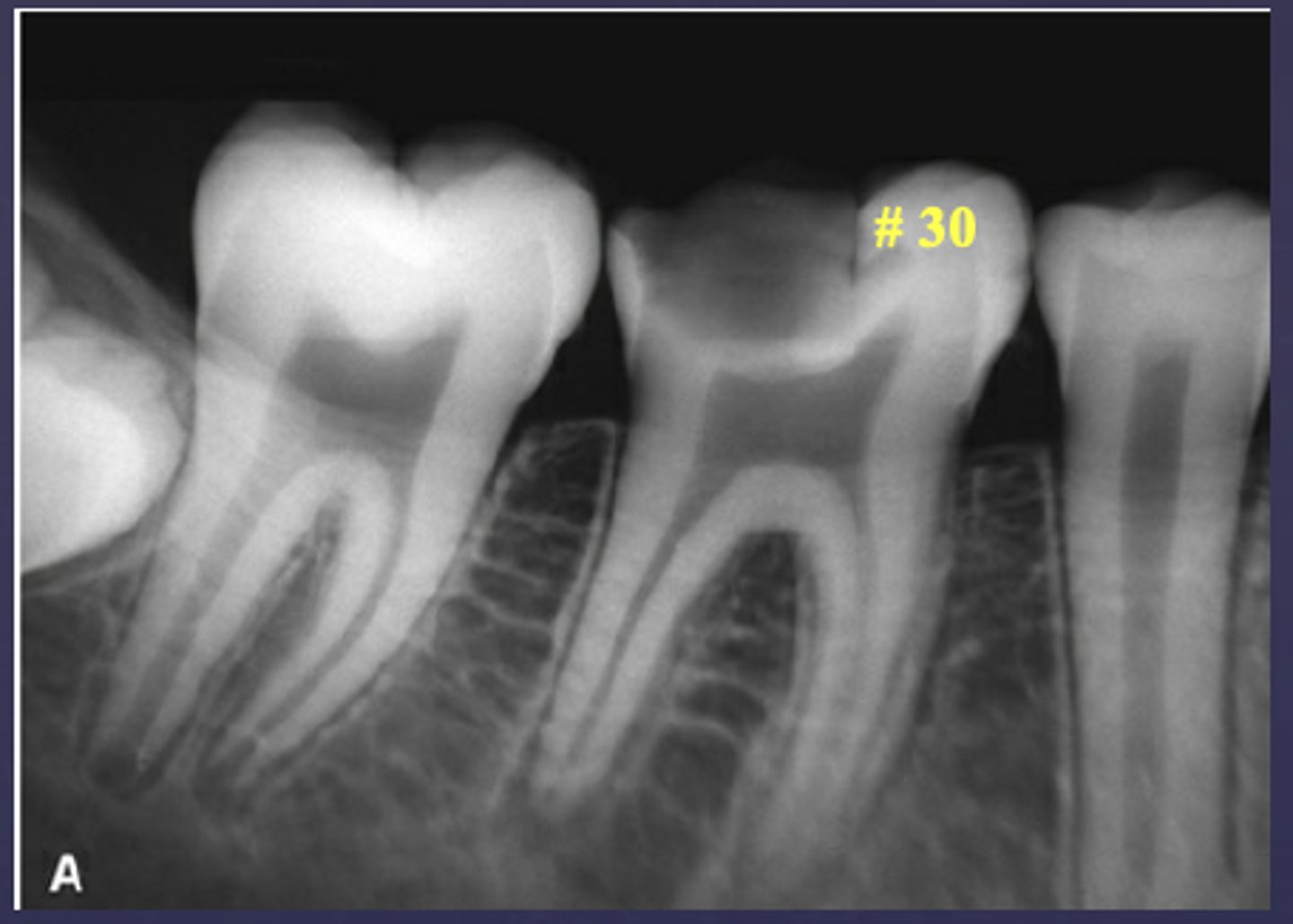
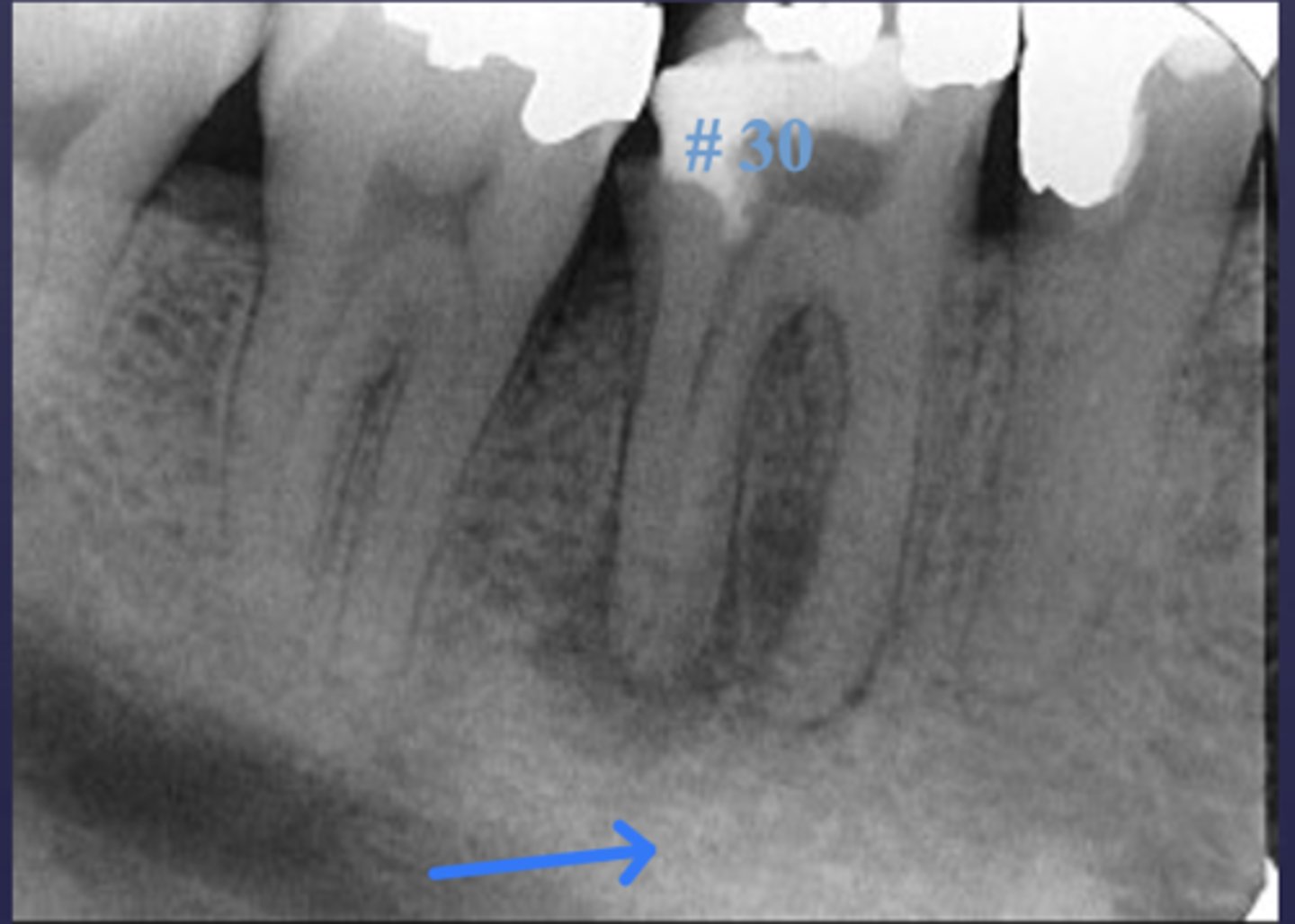
What type of change is seen in this radiograph?
early change (apical periodontitis #30)
What type of change is seen in this radiograph?
early change (apical periodontitis #21)
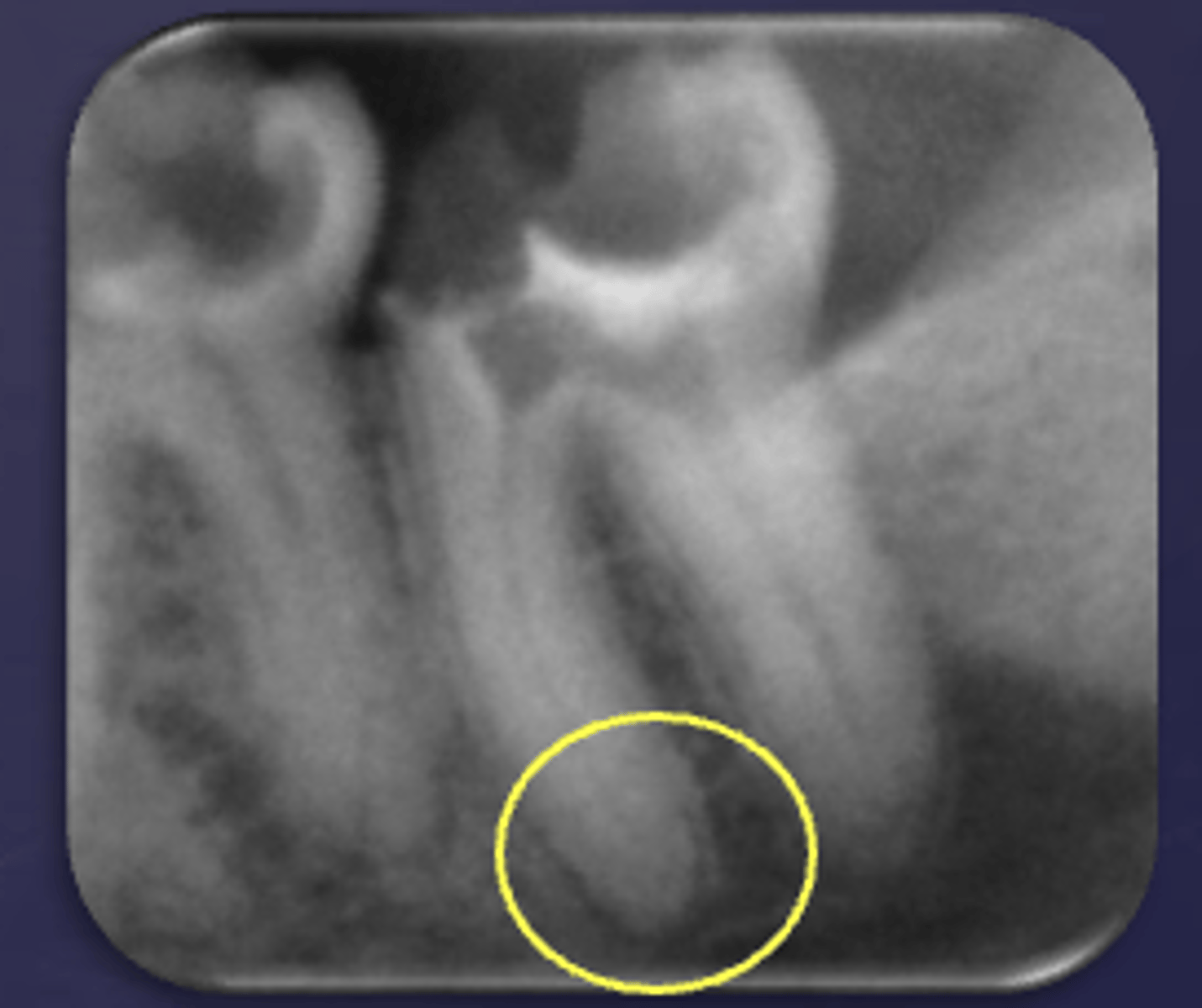
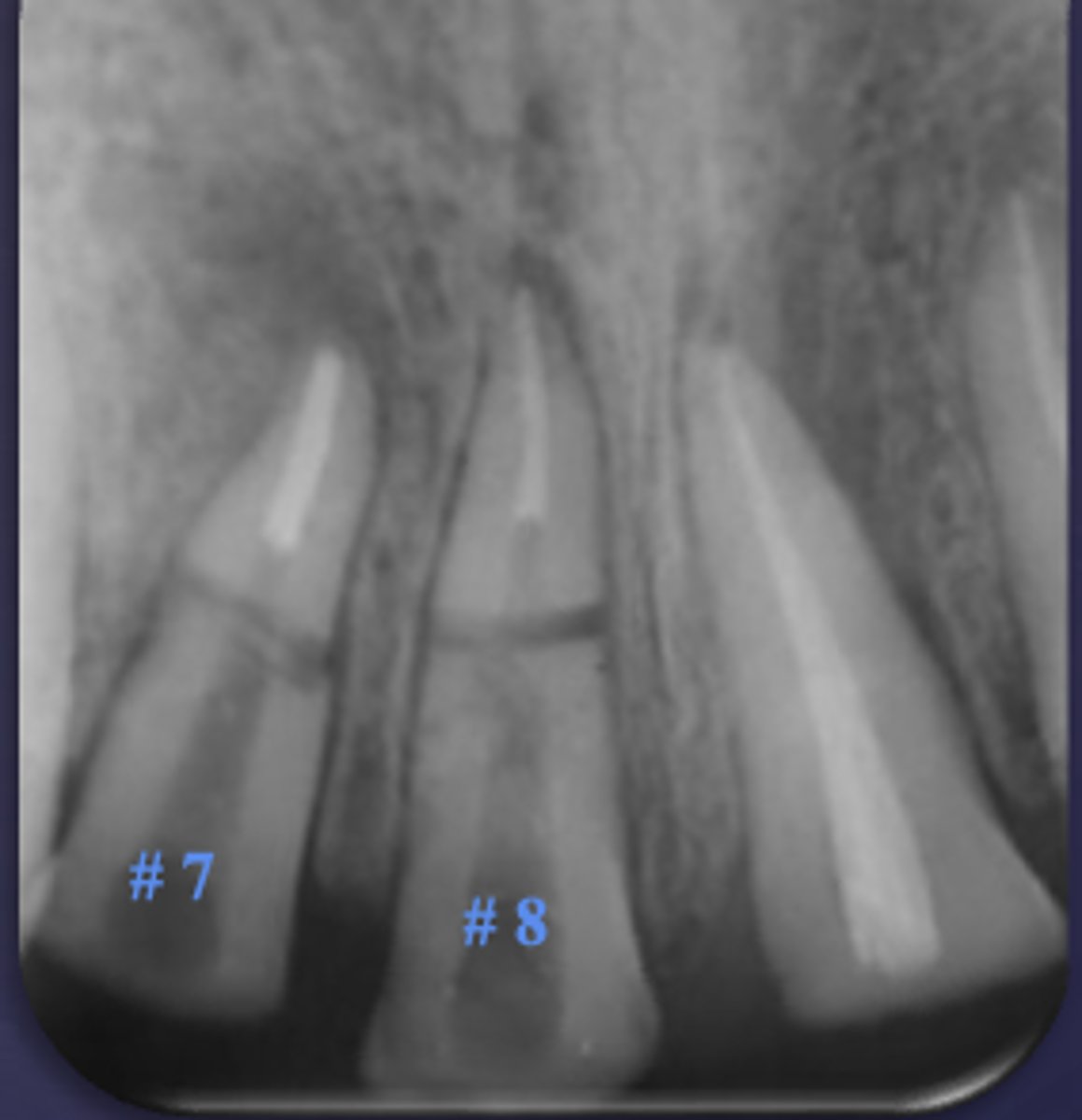
What type of change is seen in this radiograph?
early change (apical periodontitis #17-18)
What type of change is seen in this radiograph?
early change (apical periodontitis #14)
Periapical inflammatory disease can be located where?
- Apical to root apex
- Adjacent to accessory canal/root fracture/perforation
If a periapical lesion enlarges, the epicenter moves where?
away from root apex
What condition is present in this radiograph?
apical rarefying osteitis
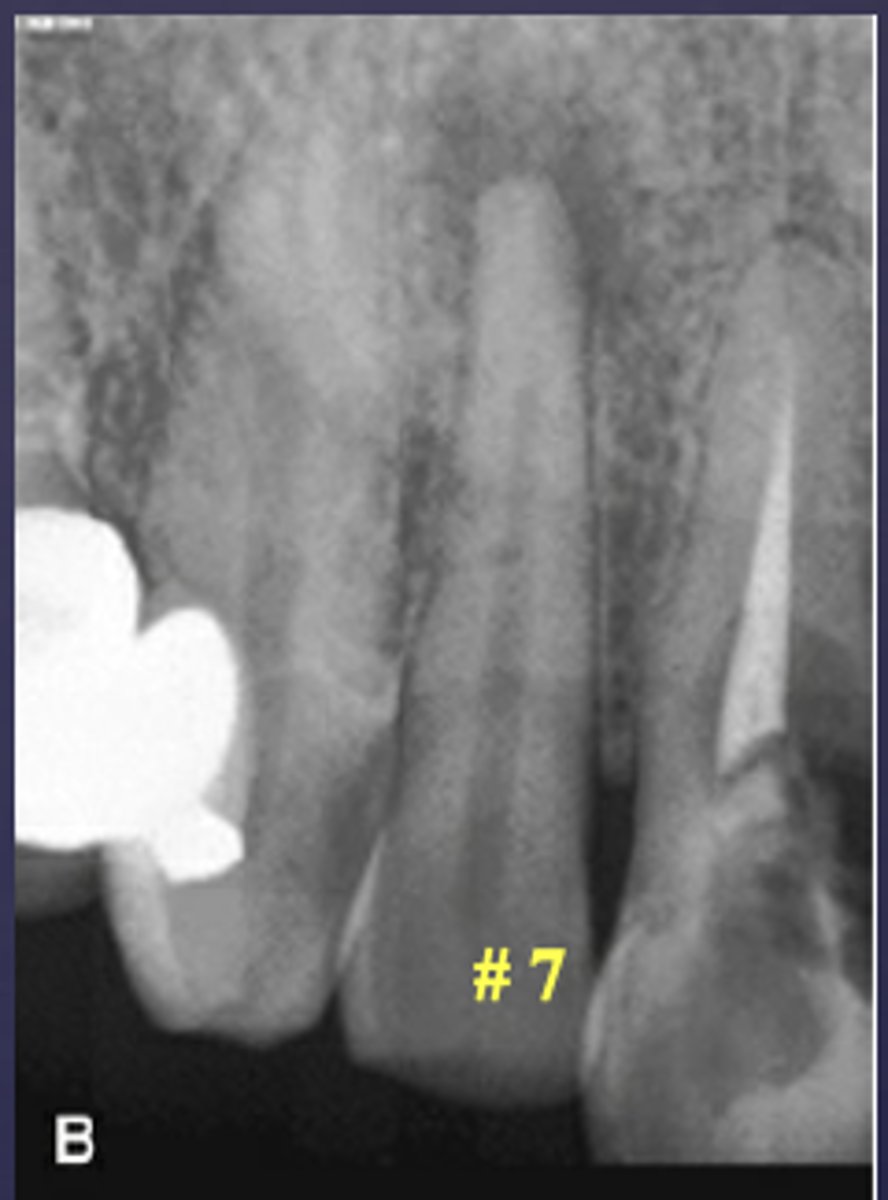
What condition is present in this radiograph?
apical rarefying osteitis
Well defined or poorly defined?
well defined

Well defined or poorly defined?
poorly defined
Early stages of periapical inflammatory disease has what effect on adjacent bone?
little
What is bone deposition around area of rarefaction called?
sclersoing osteitis
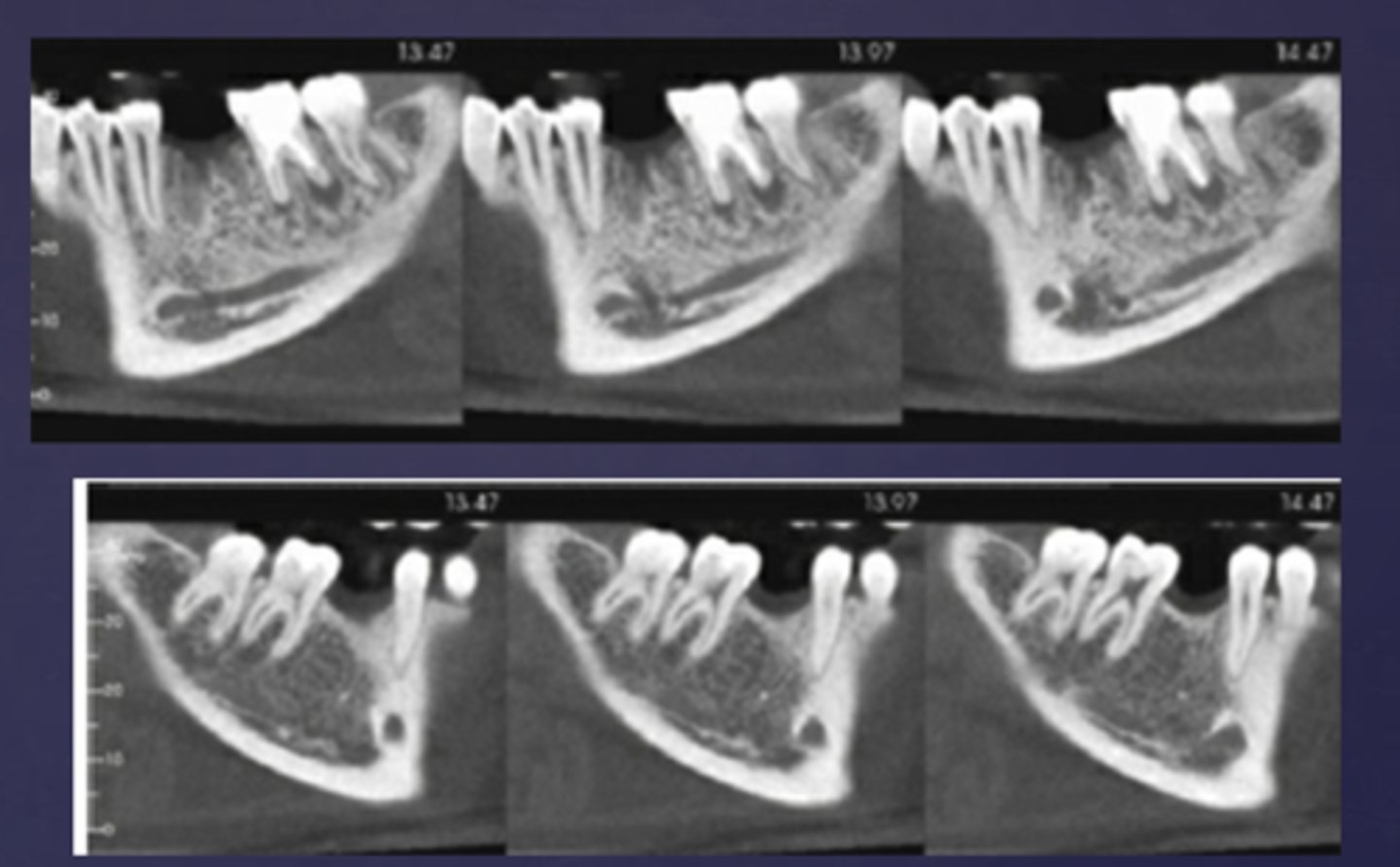
Periapical inflammatory disease alters trabecular bone pattern and marrow spaces in what ways?
- Thicker trabeculae
- Increase in marrow spaces
T/F: Periapical inflammatory disease can cause periosteal new bone formation and perforation of bone border
true
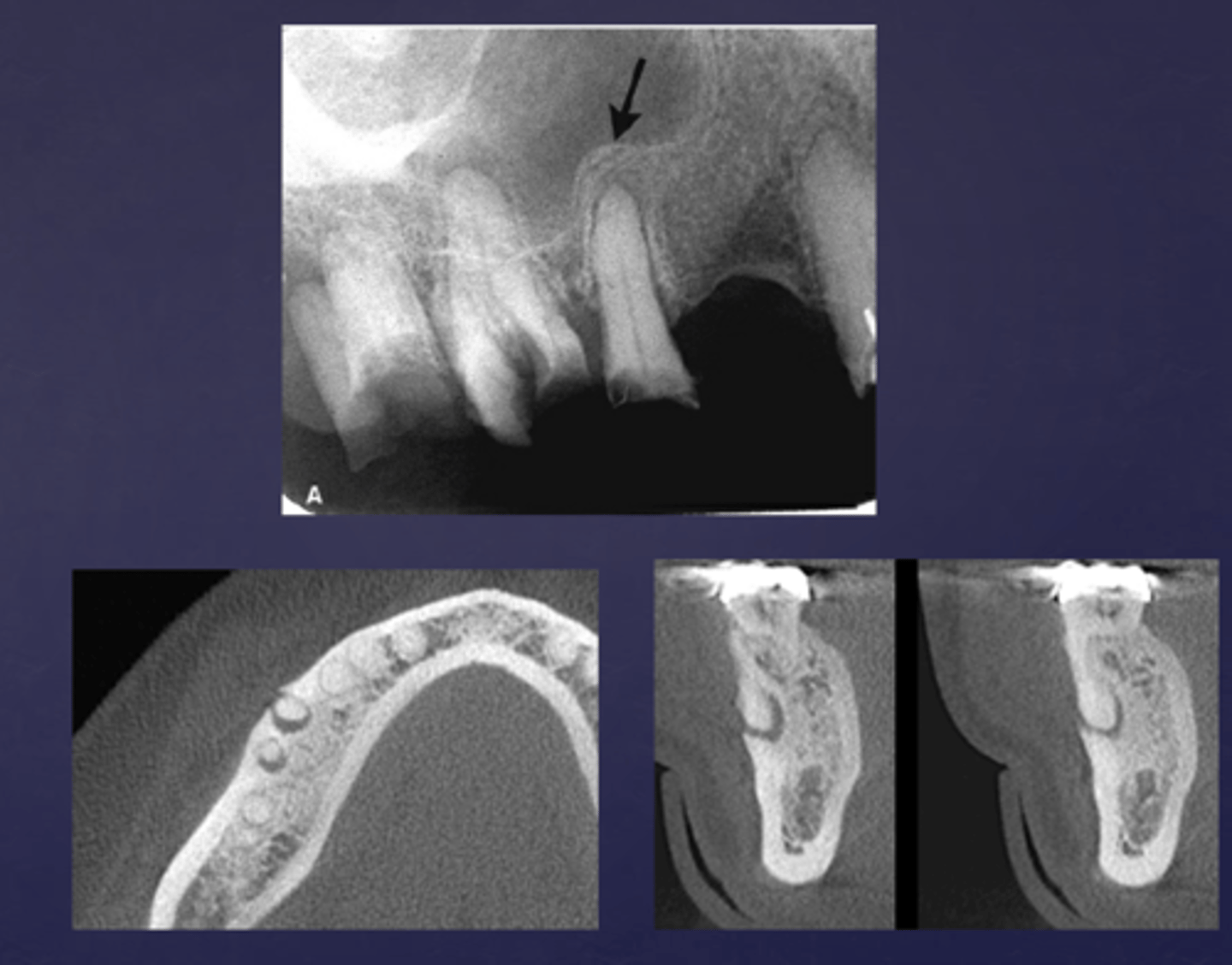
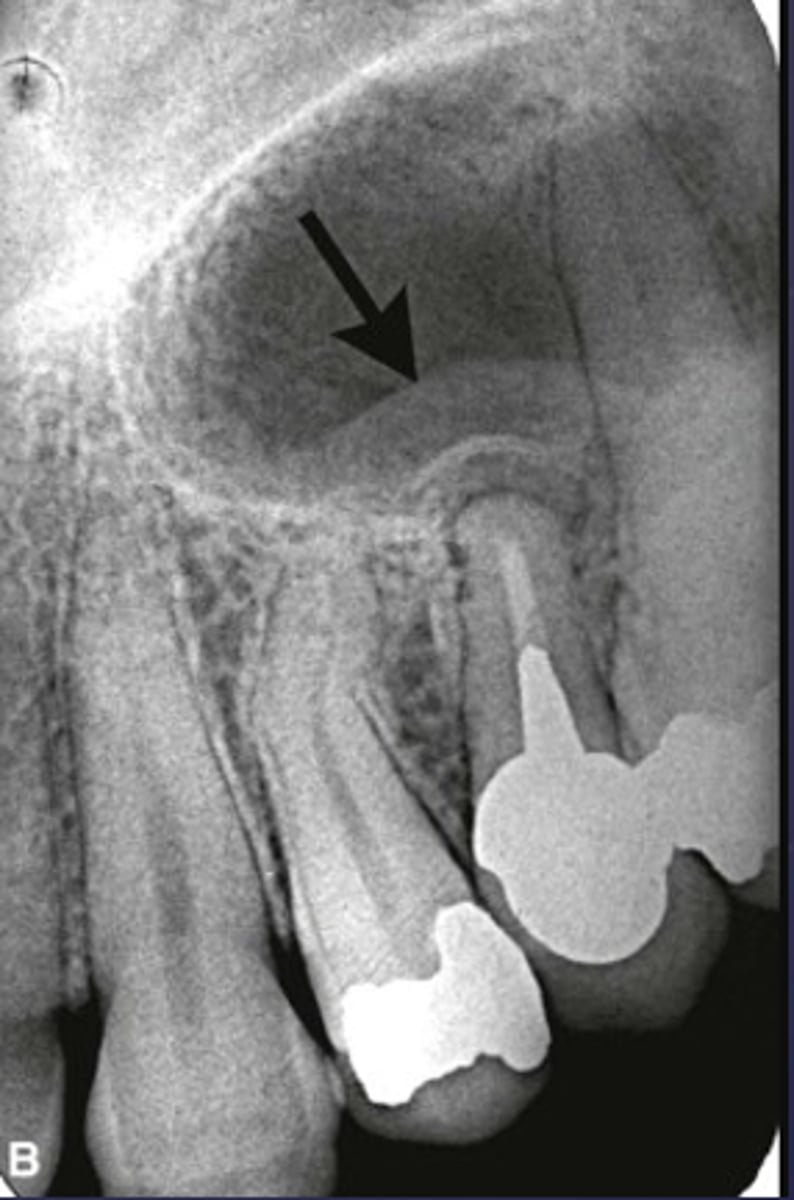
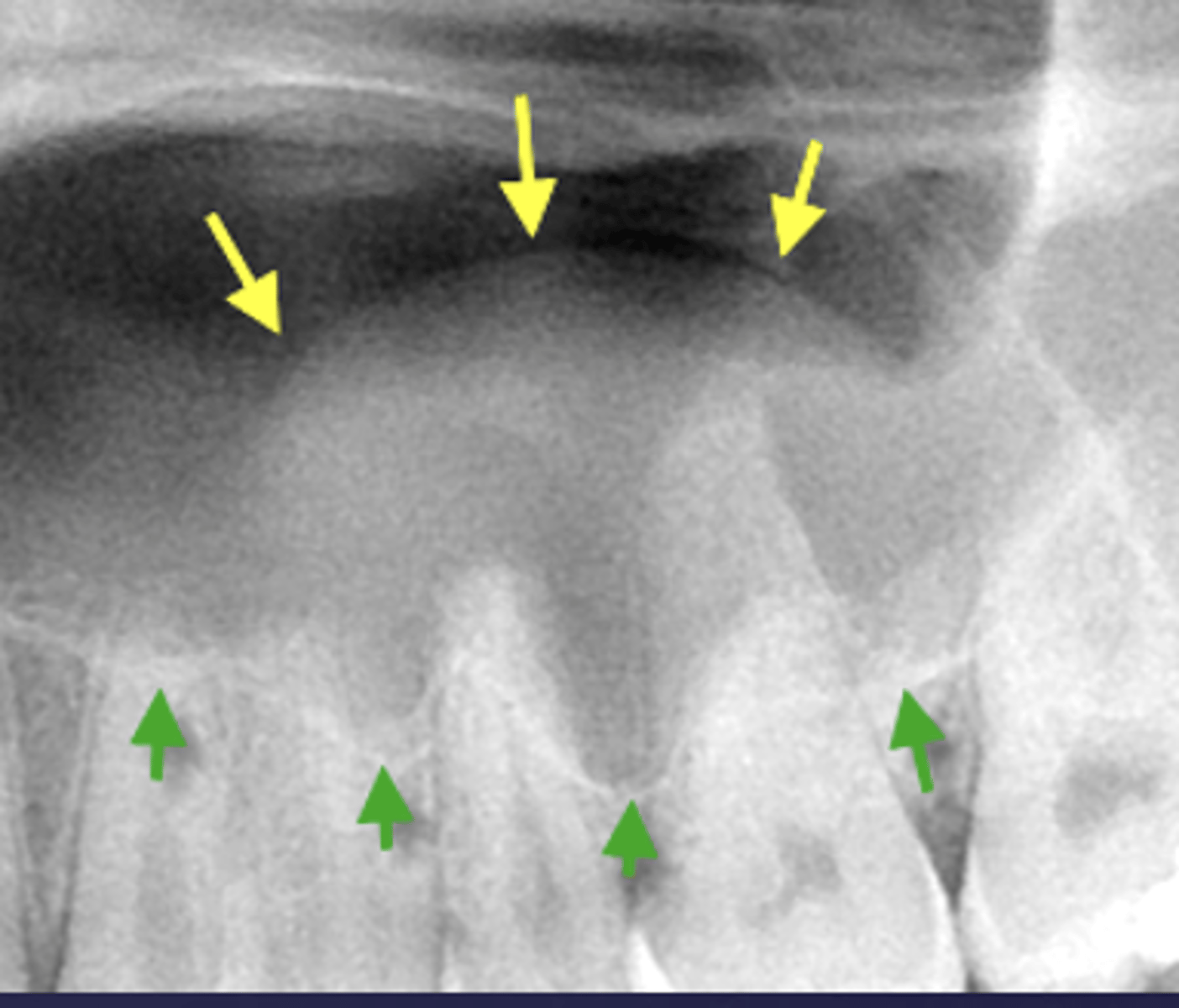
What is a key sign of periapical inflammatory disease where there is an elevation/displacement of the floor of the maxillary sinus usually affecting maxillary posterior teeth?
halo sign
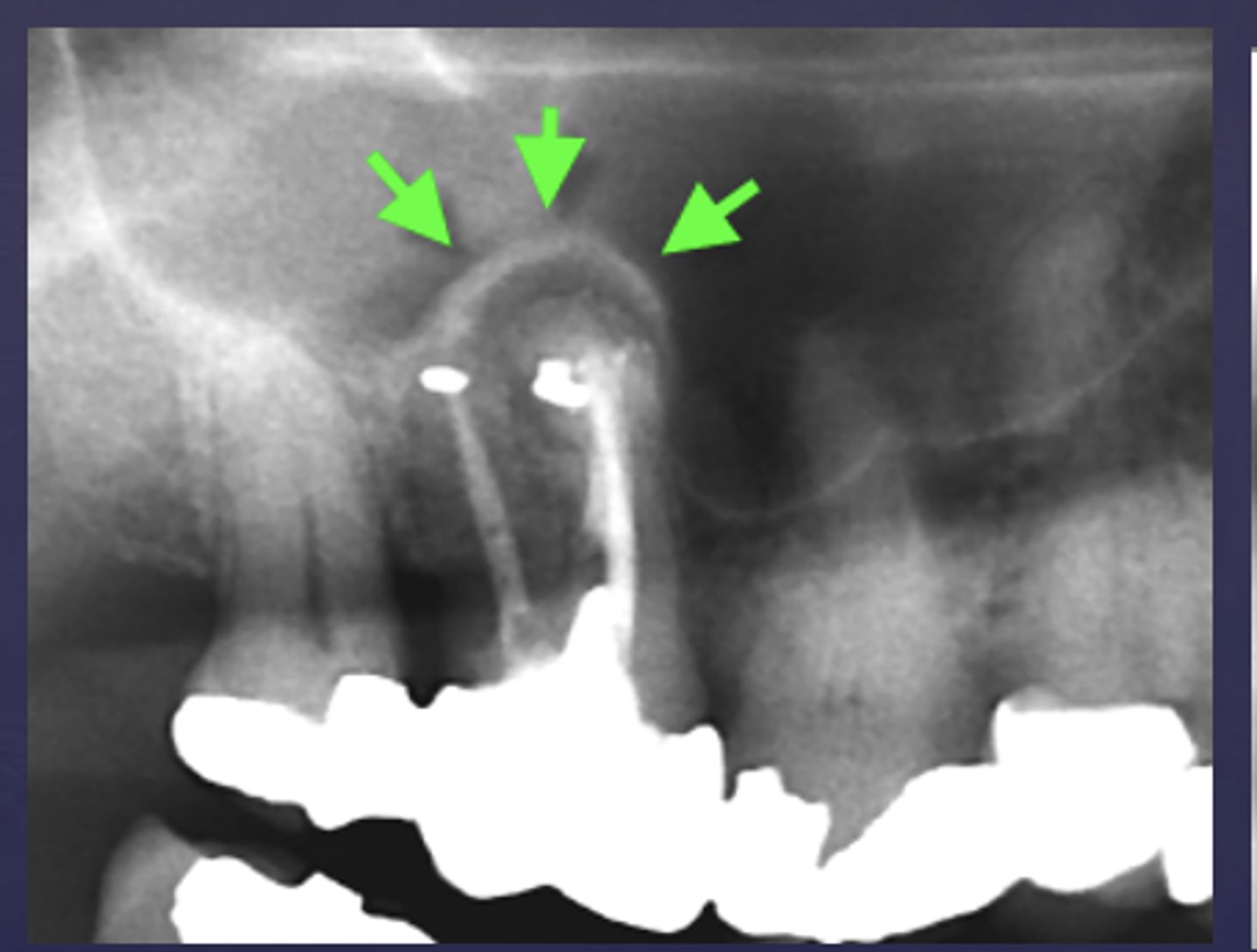
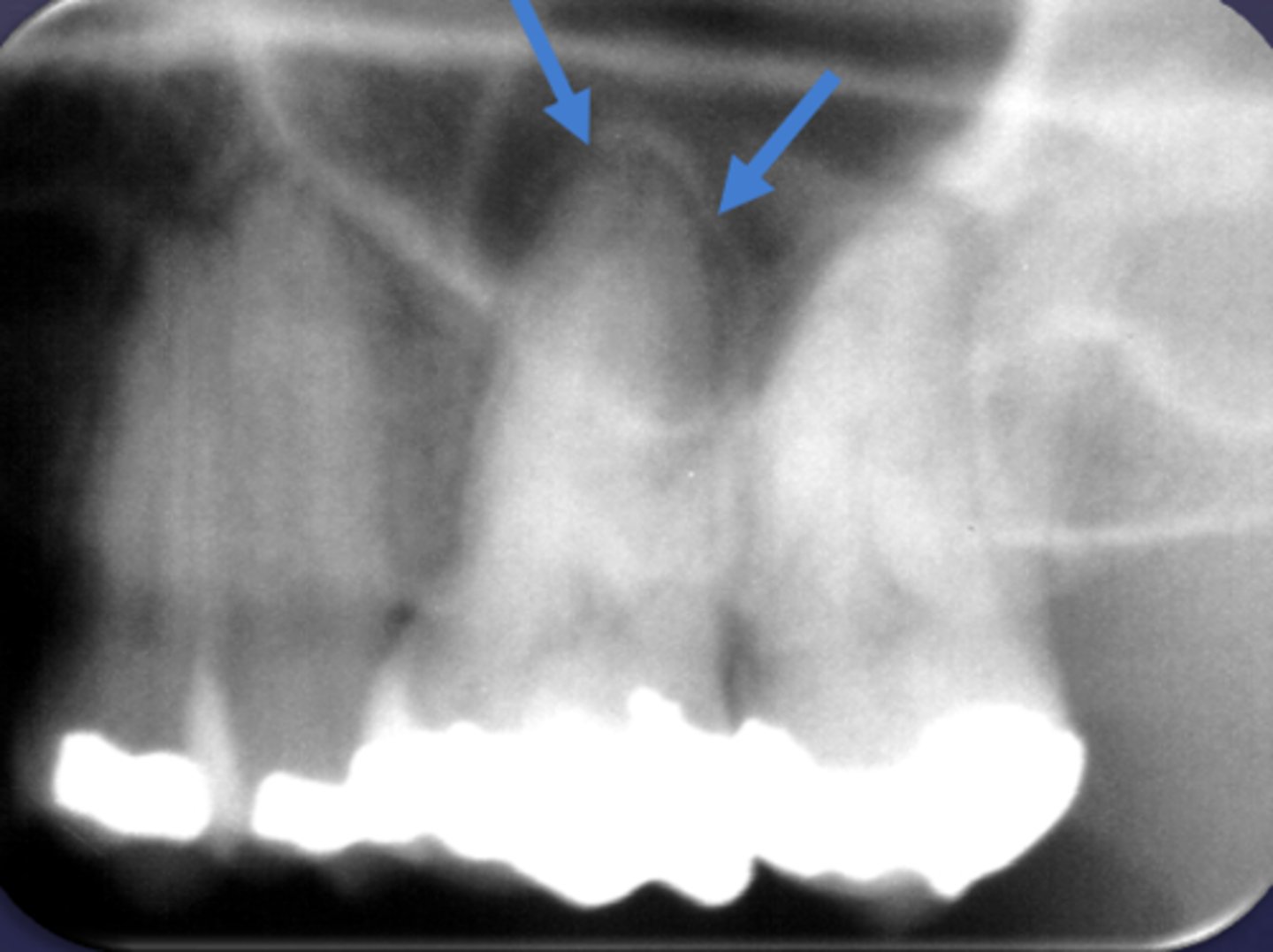
What are the arrows pointing to?
halo sign
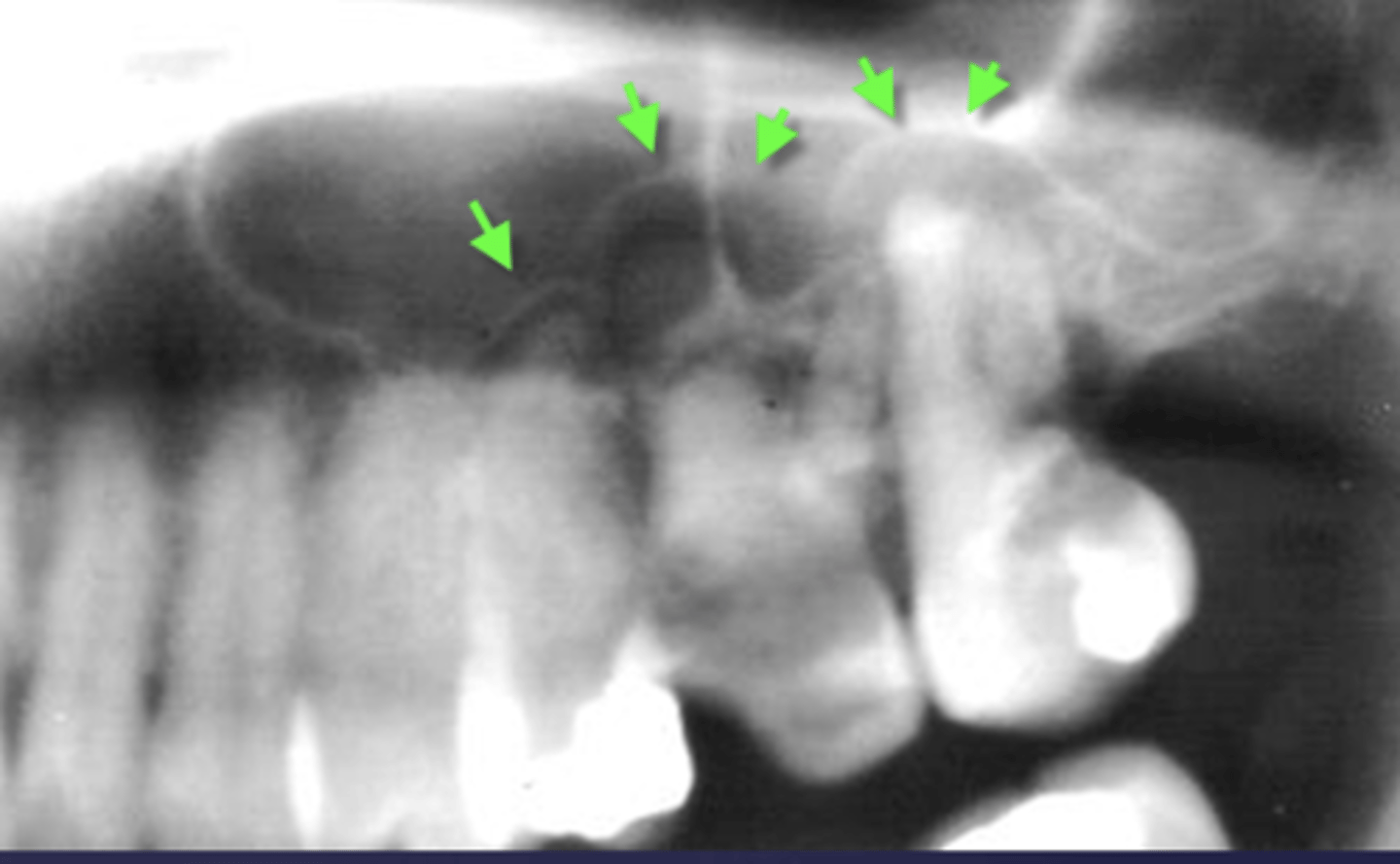
What are the arrows pointing to?
halo sign
What are the arrows pointing to?
periostitis/onion skin
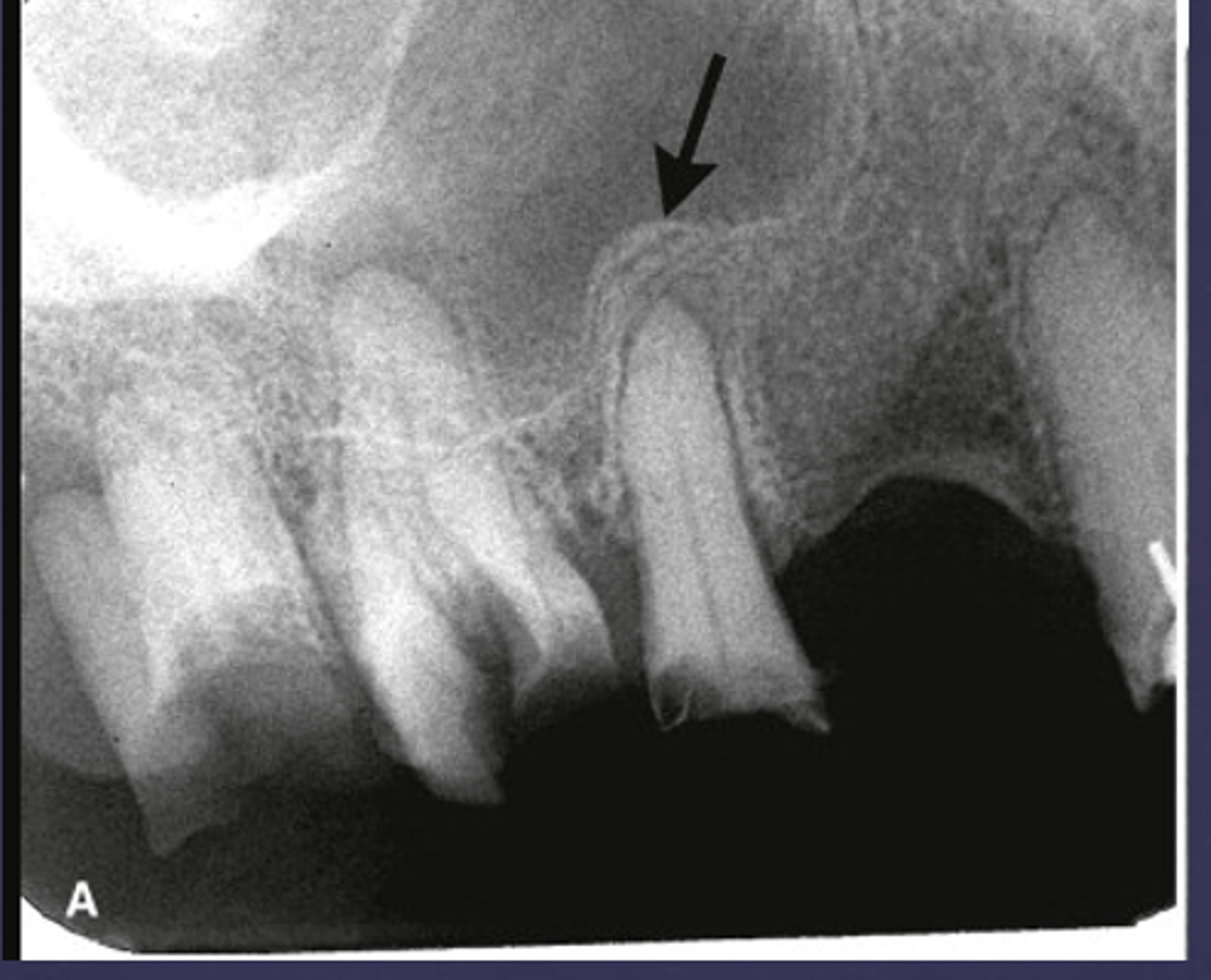
What are the arrows pointing to?
Periostitis and mucositis
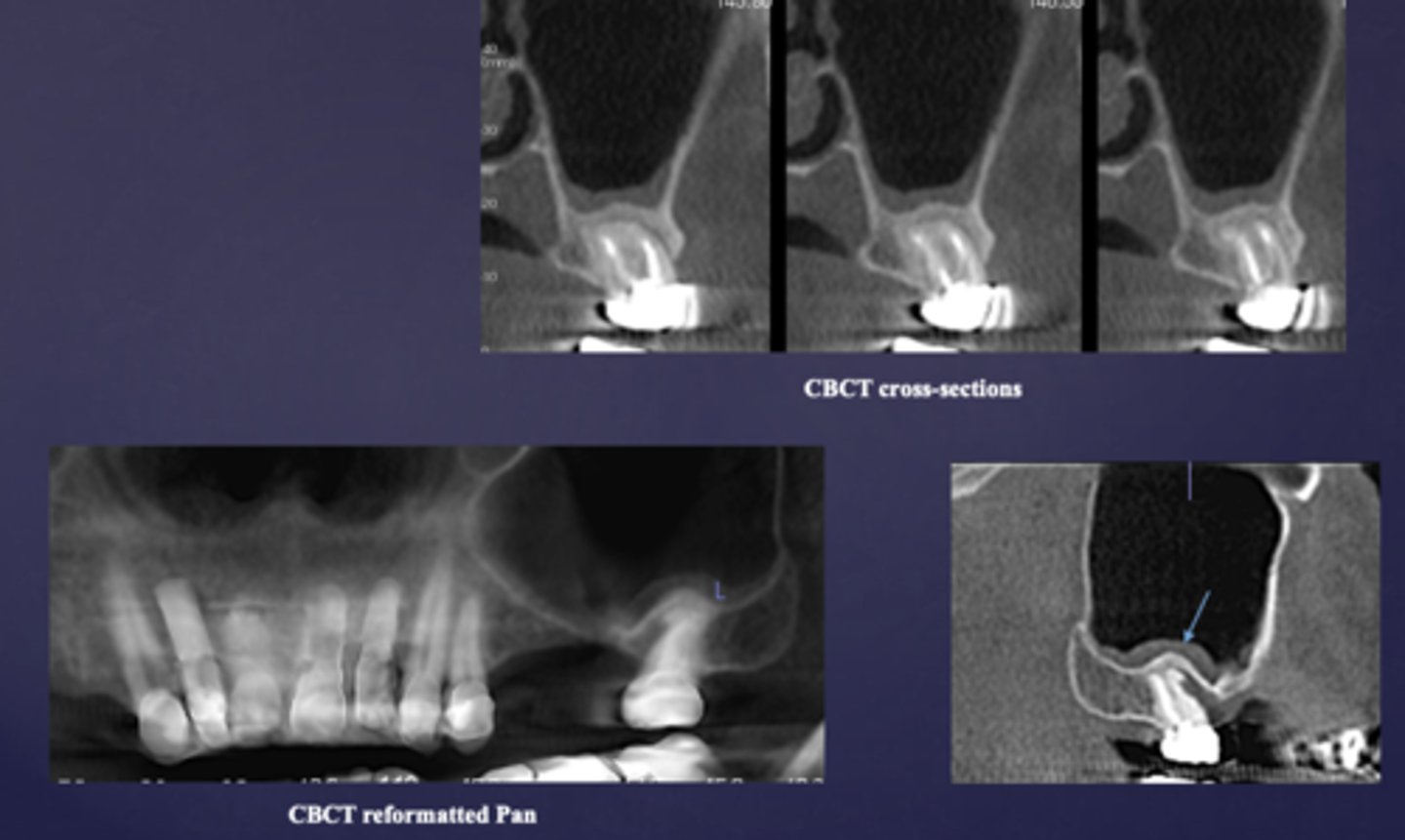
What condition?
maxillary sinus floor periostitis/mucositis

Majority of periapical inflammatory disease show a combination of what?
rarefying and sclerosing osteitis
Is this radiolucent inflammation classified as rarefying or sclerosing?
rarefying
This radiopaque area is classified as rarefying or sclerosing?
sclerosing (added bone)
Is this radiolucent inflammation classified as rarefying or sclerosing?
sclerosing (added bone)
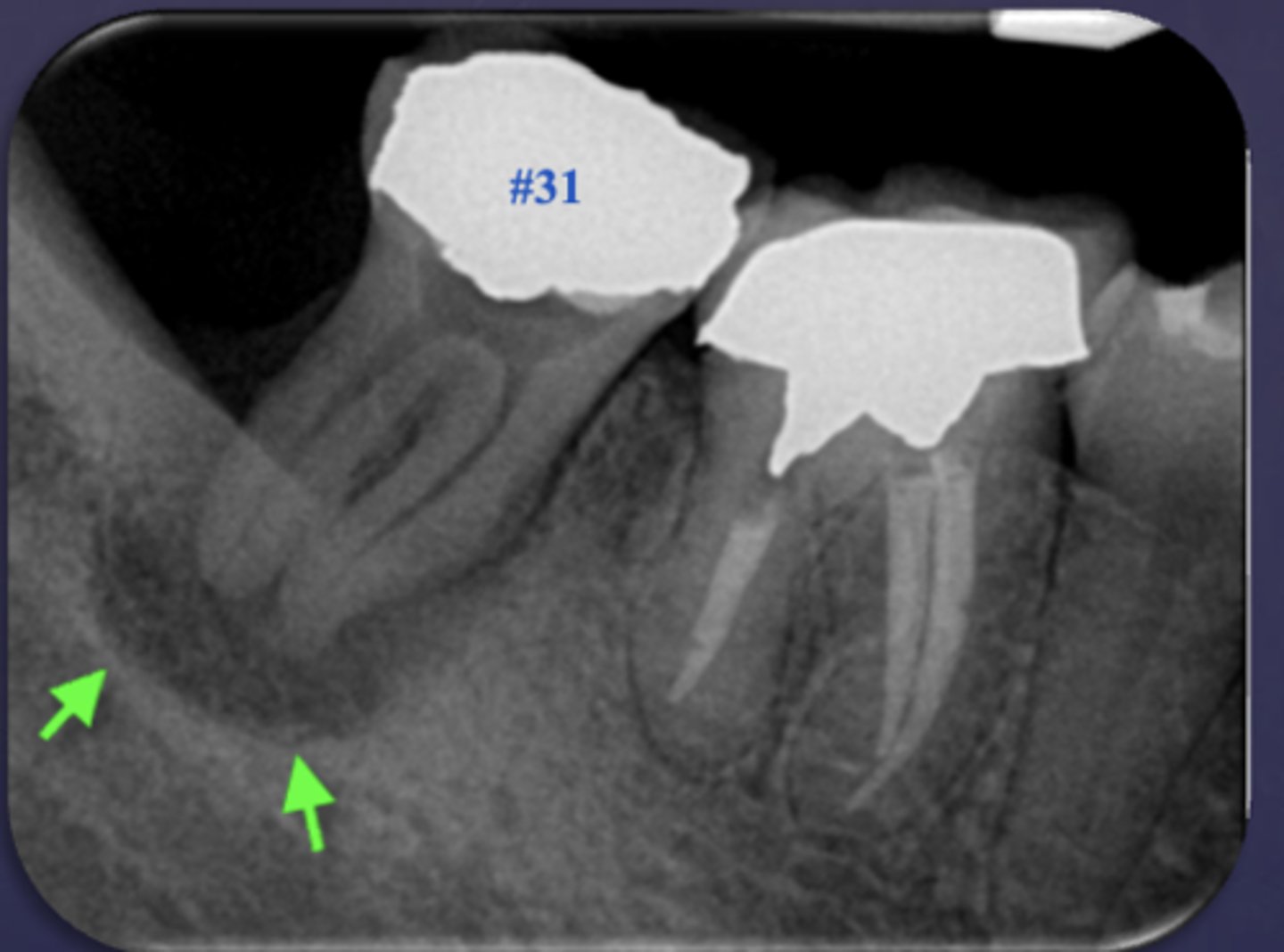
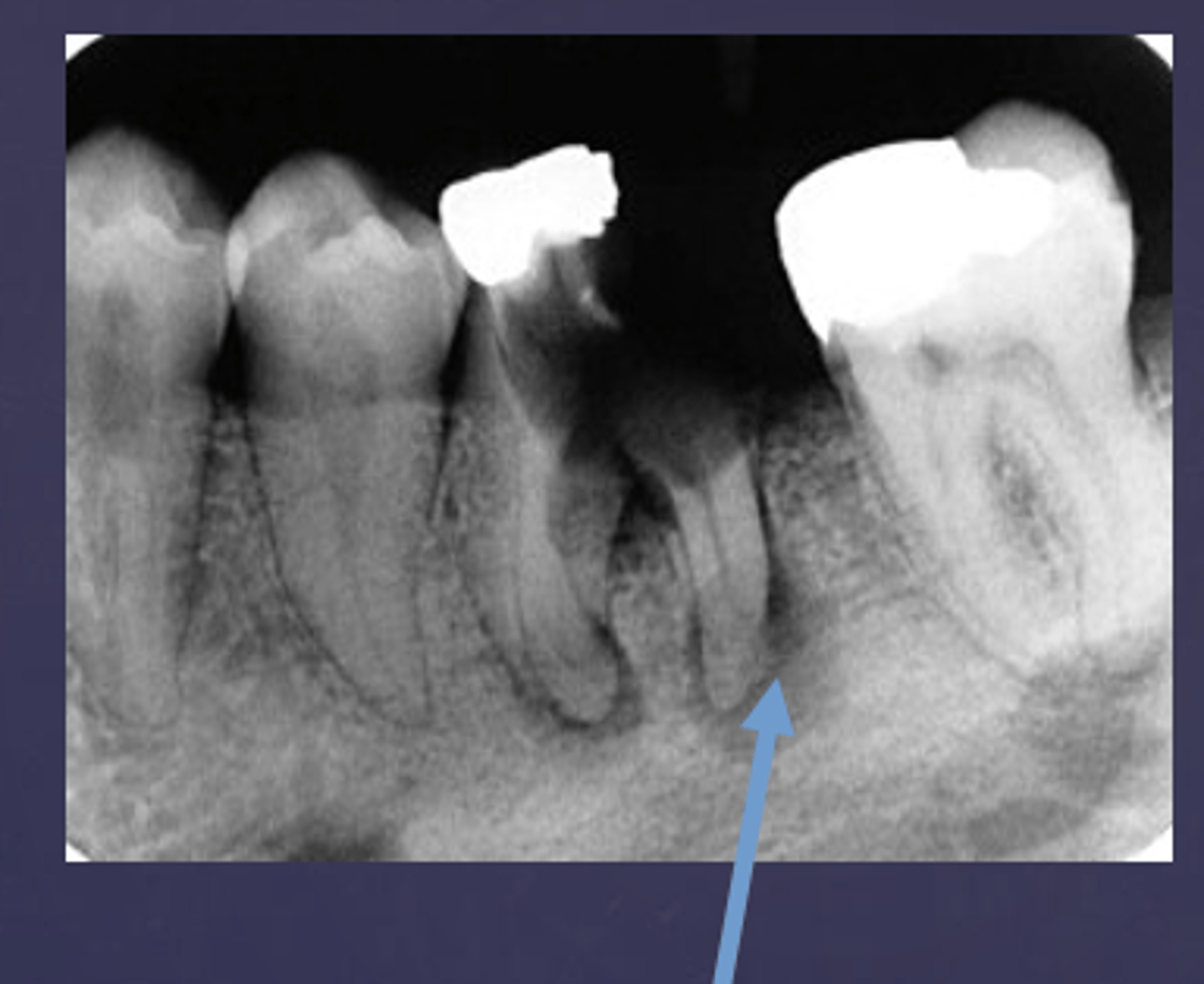
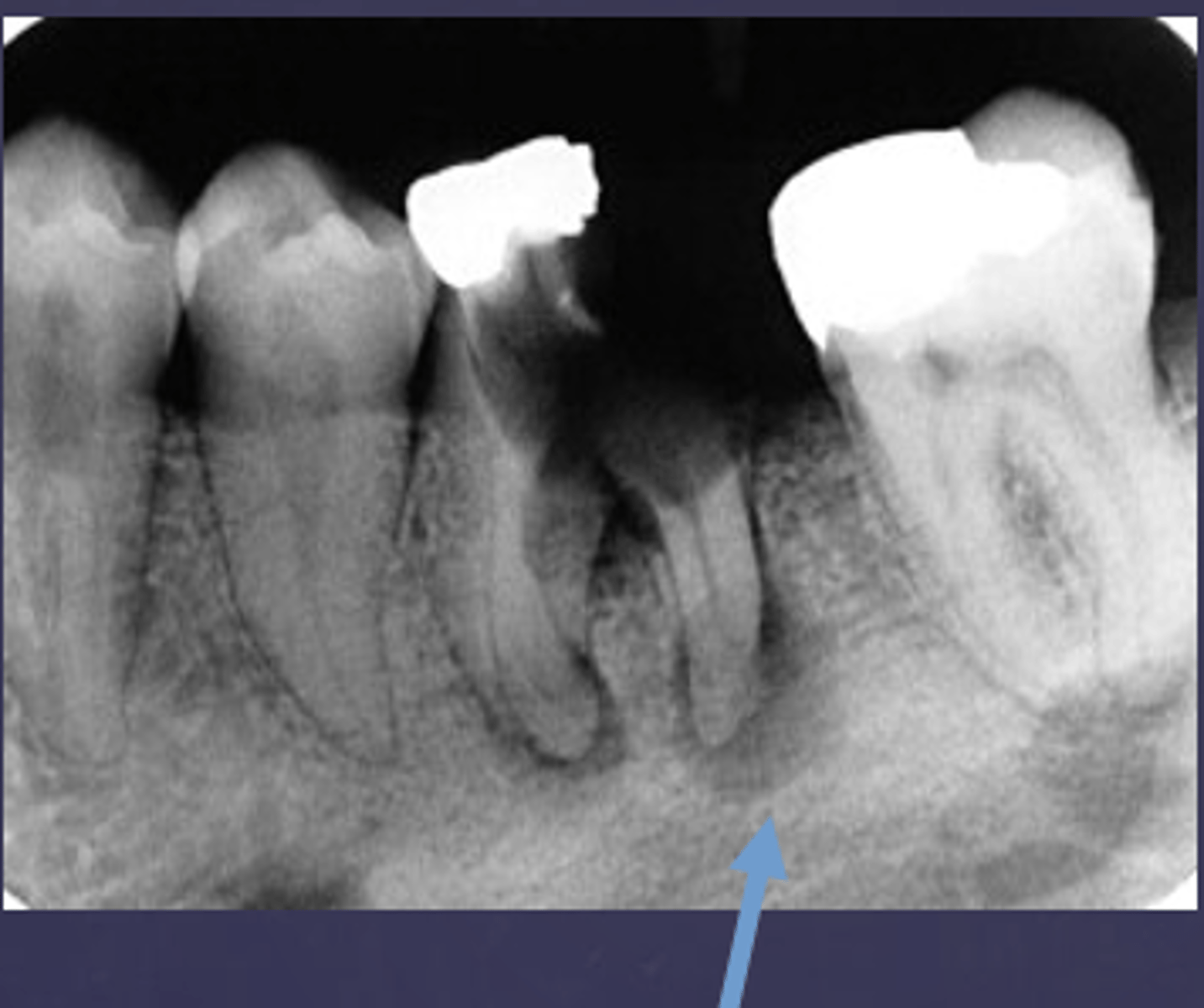
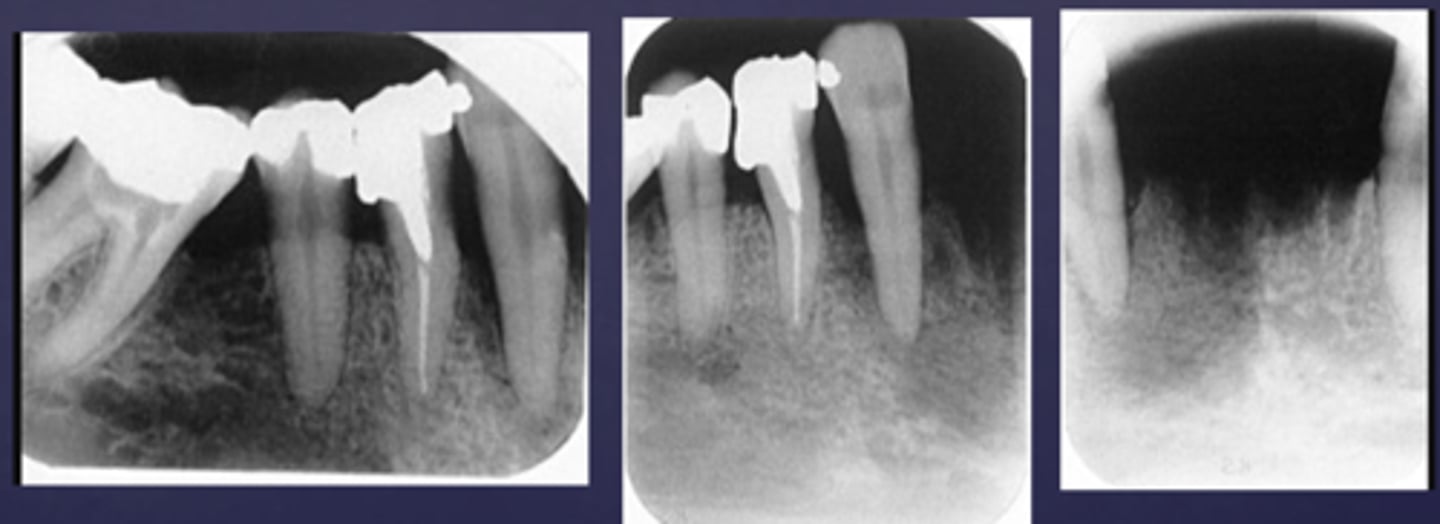
The arrows are pointing at the loss of apical lamina dura and periapical radiolucency, what is the differential diagnosis?
apical rarefying osteitis
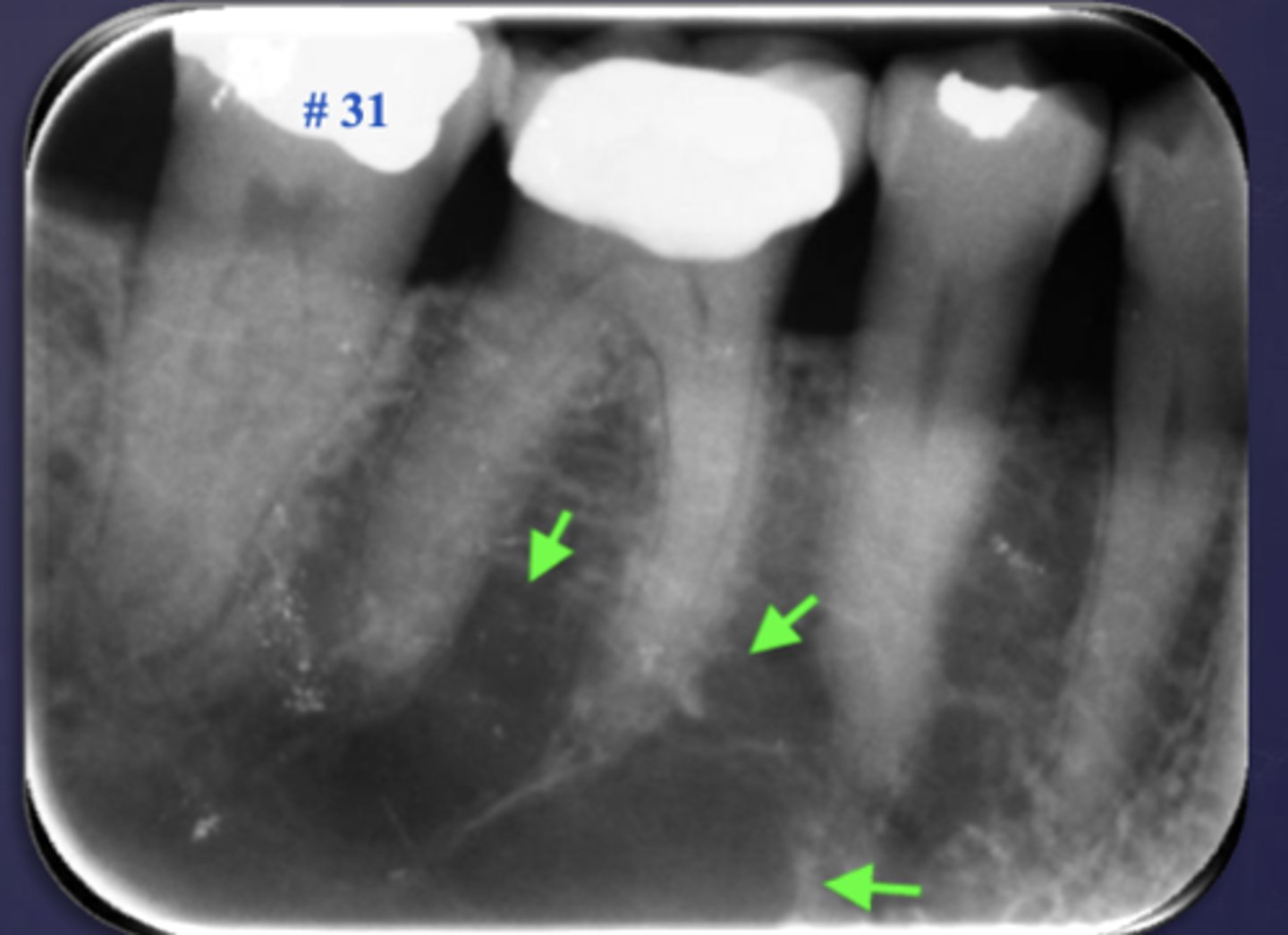
What is the differential diagnosis?
healthy (no loss of lamina dura, submandibular gland fossa- normal anatomy)
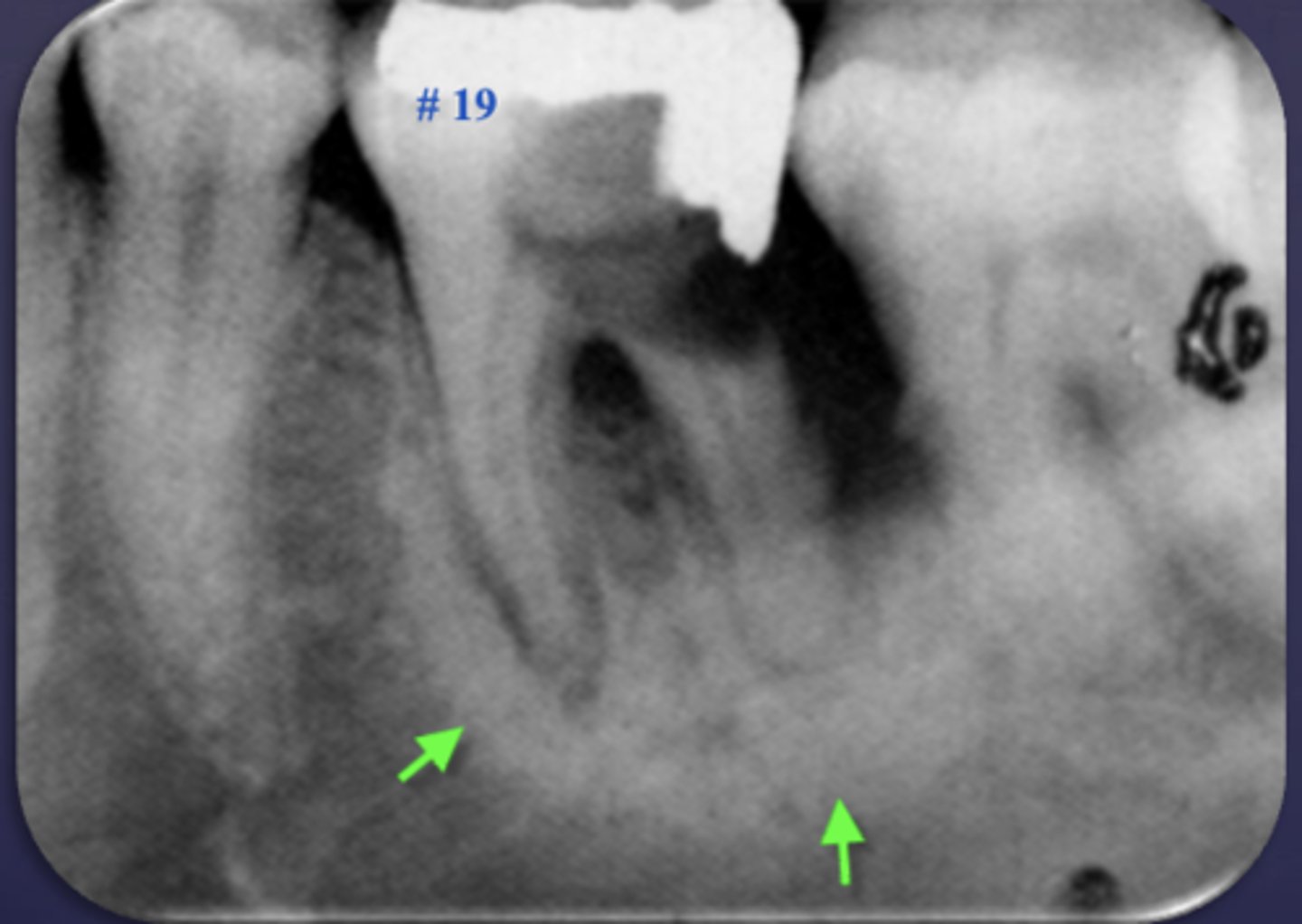
Sclerosing osteitis or dense bone island?
Sclerosing osteitis
(Widening of PDL space, Periapical radiopaque area, Non vital tooth)

Sclerosing osteitis or dense bone island?
Dense bone island
(No widening of PDL space, Periapical radiopaque area, Vital tooth)
Sclerosing osteitis or dense bone island?
- Widening of PDL space
- Periapical radiopaque area
- Non vital tooth
Sclerosing osteitis
Sclerosing osteitis or dense bone island?
- No widening of PDL space
- Periapical radiopaque area
- Vital tooth
Dense bone island
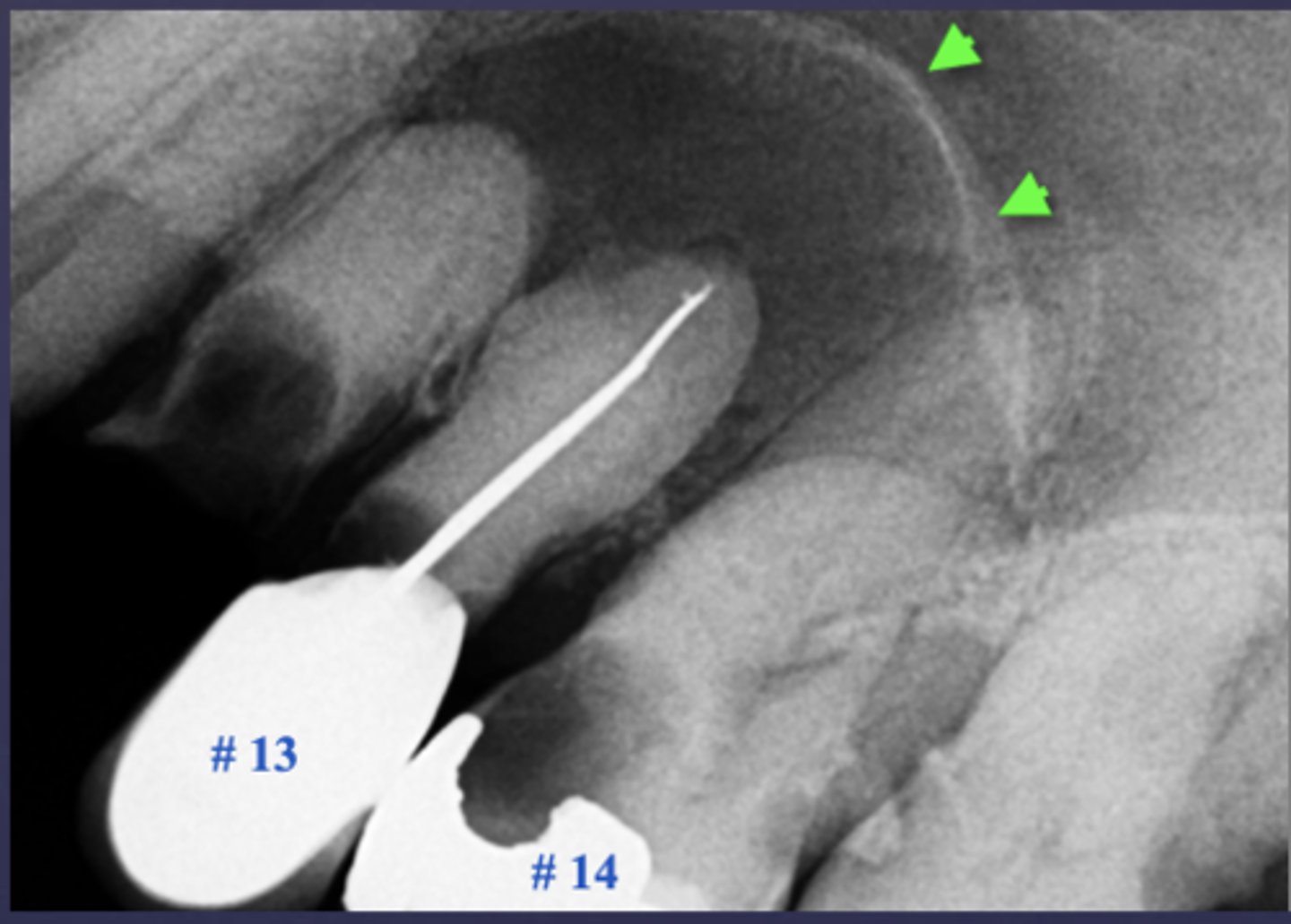
What is the differential diagnosis?
A) Rarefying osteitis
B) Maxillary sinus pneumatization
C) Mucus retention pseudocyst
D) Sclerosing osteitis
A) Rarefying osteitis
What is the differential diagnosis?
A) Rarefying osteitis
B) Maxillary sinus pneumatization
C) Mucus retention pseudocyst
D) Sclerosing osteitis
B) Maxillary sinus pneumatization
What is the differential diagnosis?
A) Rarefying osteitis
B) Maxillary sinus pneumatization
C) Mucus retention pseudocyst
D) Sclerosing osteitis
C) Mucus retention pseudocyst
What condition?
- Inflammation of bone
- Extension of inflammation from periapical region to the marrow space, cortex, cancellous portion of bone & periosteum.
Pyogenic organisms can reach bone marrow:
- Abscessed teeth
- Post- surgical infection
- Trauma
- Hematogenous spread
osteomyelitis
These are predisposing conditions of what?
- Malnutrition
- Diabetes
- Leukemia
- Anemia
- Alcoholism
- HIV
- Diseases with reduced vascularity in bone:
- - Paget disease of bone
- - Florid osseous dysplasia
- - Osteopetrosis
- - Fluorosis
osteomyelitis
All of the following are synonyms for osteomyelitis EXCEPT...
A) Acute osteomyelitis
B) Acute suppurative osteomyelitis
C) Garre's Osteomyelitis
D) Acute pyogenic osteomyelitis
E) Proliferative periostitis
F) Periostitis Ossificans
C) Garre’s Osteomyelitis
Which type of osteomyelitis is most common in the mandible, premolar-molar area?
acute osteomyelitis
The following are characteristic clinical features of what?
- Pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Fever
- Purulent discharge
- Mobility in involved teeth
acute osteomyelitis
Characteristic features of what?
- Sequela of inadequately treated acute phase
- May arise de novo
chronic osteomyelitis
What type of osteomyelitis also occurs in long bones of children, has pain and swelling?
CRMO (chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis)
What does SAPHO syndrome stand for?
- Synovitis (inflammatory arthritis)
- Acne (pustulosa)
- Postulosis (psoriasis)
- Hyperostosis (acquired)
- Osteitis
CRMO and SAPHO are what types of osteomyelitis?
chronic
A 35-year-old woman presents with pustular lesions on her palms and chronic pain near the sternoclavicular joint. Imaging reveals hyperostosis and osteitis. Which condition is most likely?
A. SAPHO syndrome
B. Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis
C. Rheumatoid arthritis
D. Chronic bacterial osteomyelitis
A. SAPHO syndrome
T/F: Clinical features of chronic osteomyelitis are intermittent recurrent pain and swelling
True
What type of osteomyelitis? Radiographic features :
- No radiographic manifestation in early stages
- Imaging features vary depending on the stage of disease
acute osteomyelitis
What phase of osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis
(periphery: poorly defined, non-corticated, gradual transition to normal trabeculae)
What phase of osteomyelitis?
- Decrease in density of bone, loss of sharpness of trabeculae
- Localized or scattered regions of radiolucency, ill defined periphery
acute osteomyelitis (internal structure)
A periapical radiograph of the right mandible shows an ill-defined radiolucent area with loss of trabecular pattern and decreased bone density. The patient reports pain, swelling, and fever. Which condition is most consistent with these findings?
Acute osteomyelitis
In the early radiographic stage of acute osteomyelitis of the mandible, what is a characteristic finding?
Initial blurring of bony trabeculae
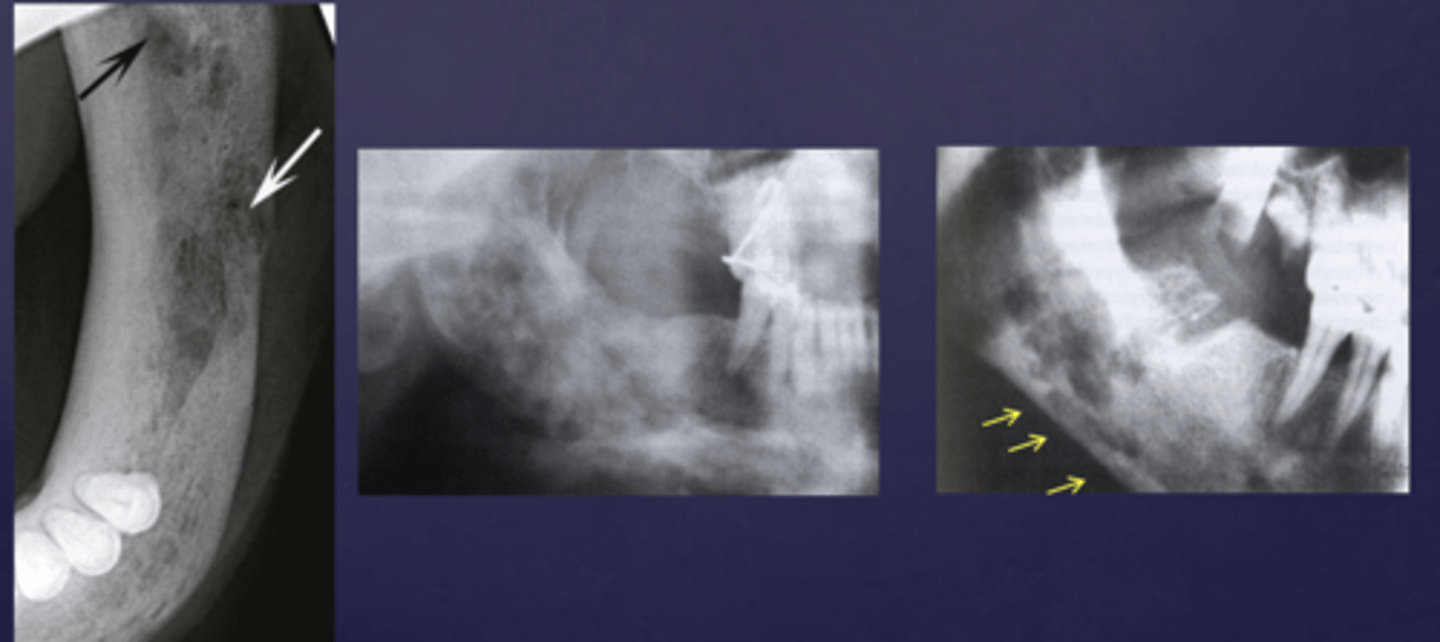
These arrows are pointing at what?
moth-eaten appearance of acute osteomyelitis
The moth eaten appearance is associated with what?
acute osteomyelitis, mixed radiolucent/radiopaque areas
What are islands of necrotic bone that vary in size?
sequestrae
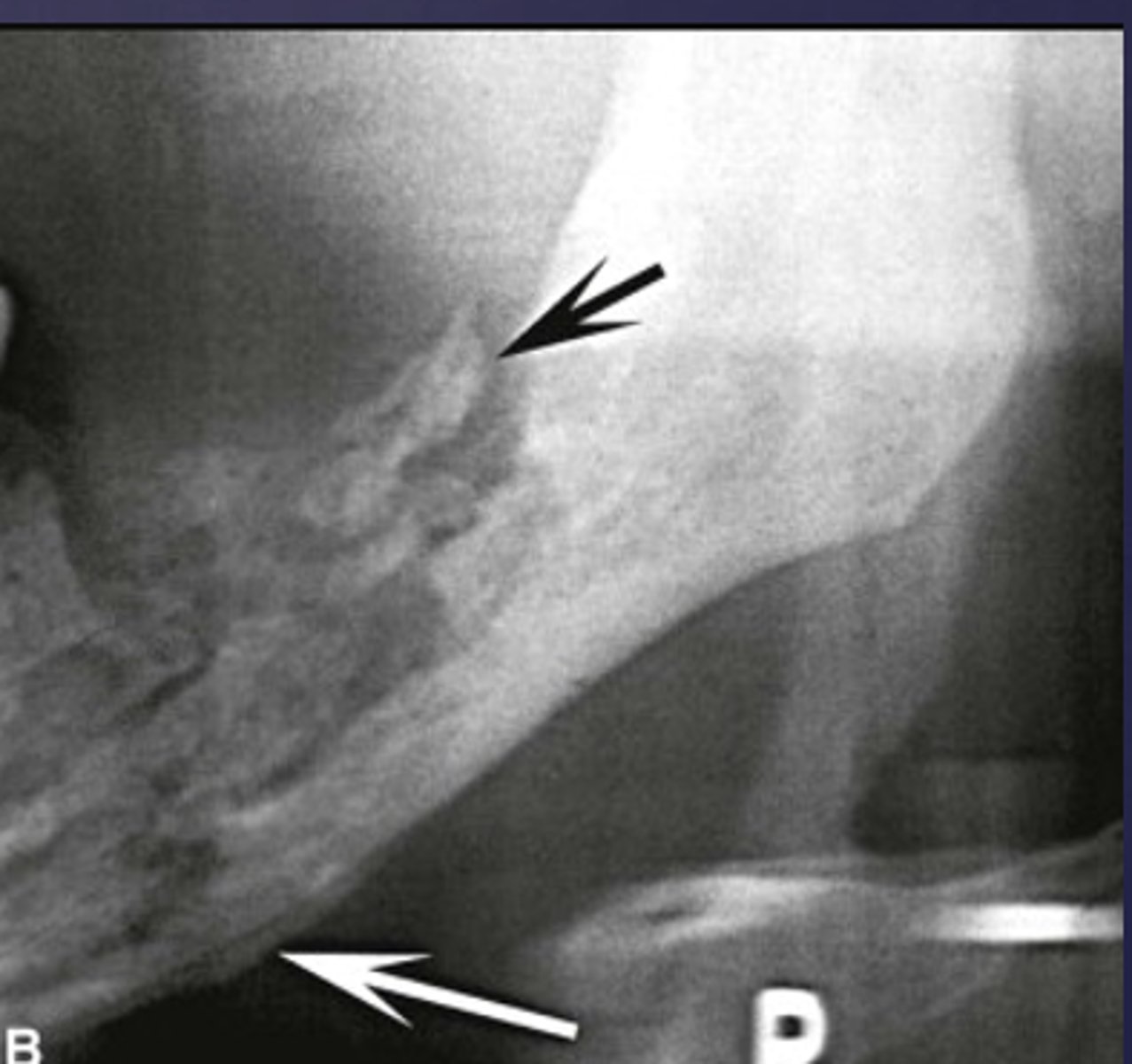
What is the black arrow pointing at?
sequestrae

What is the white arrow pointing at?
periosteal reaction
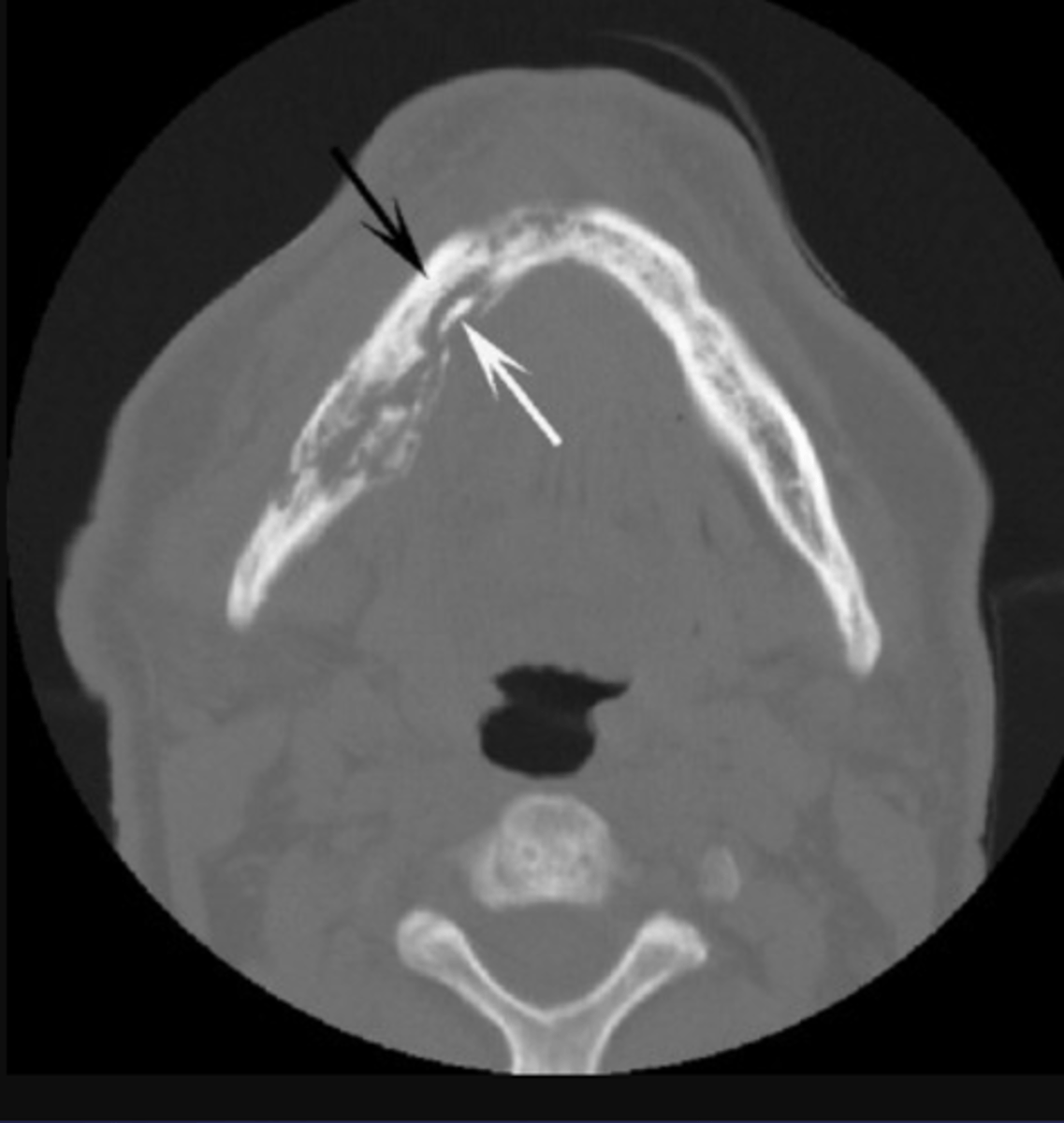
What is the black arrow pointing at?
periosteal reaction (increased bone density)

What is the white arrow pointing at?
sequestra
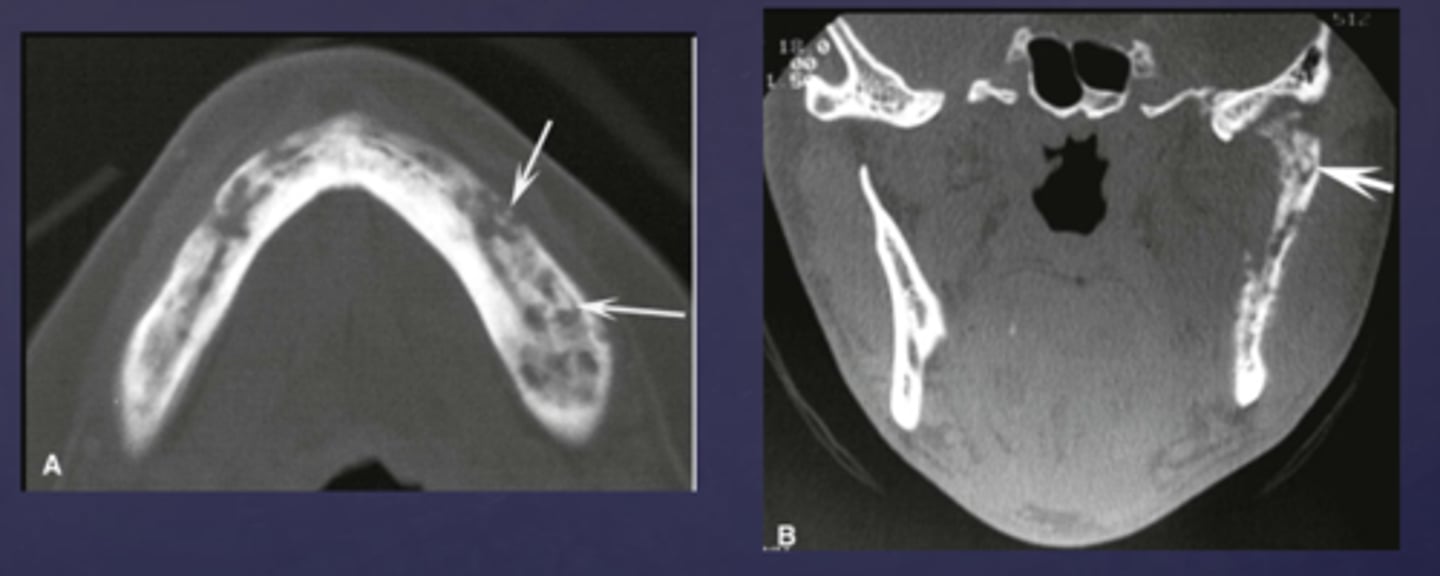
What phase of osteomyelitis does this show?
acute (multiple sequestrae)
What is the imaging method of choice for osteomyelitis
CBCT
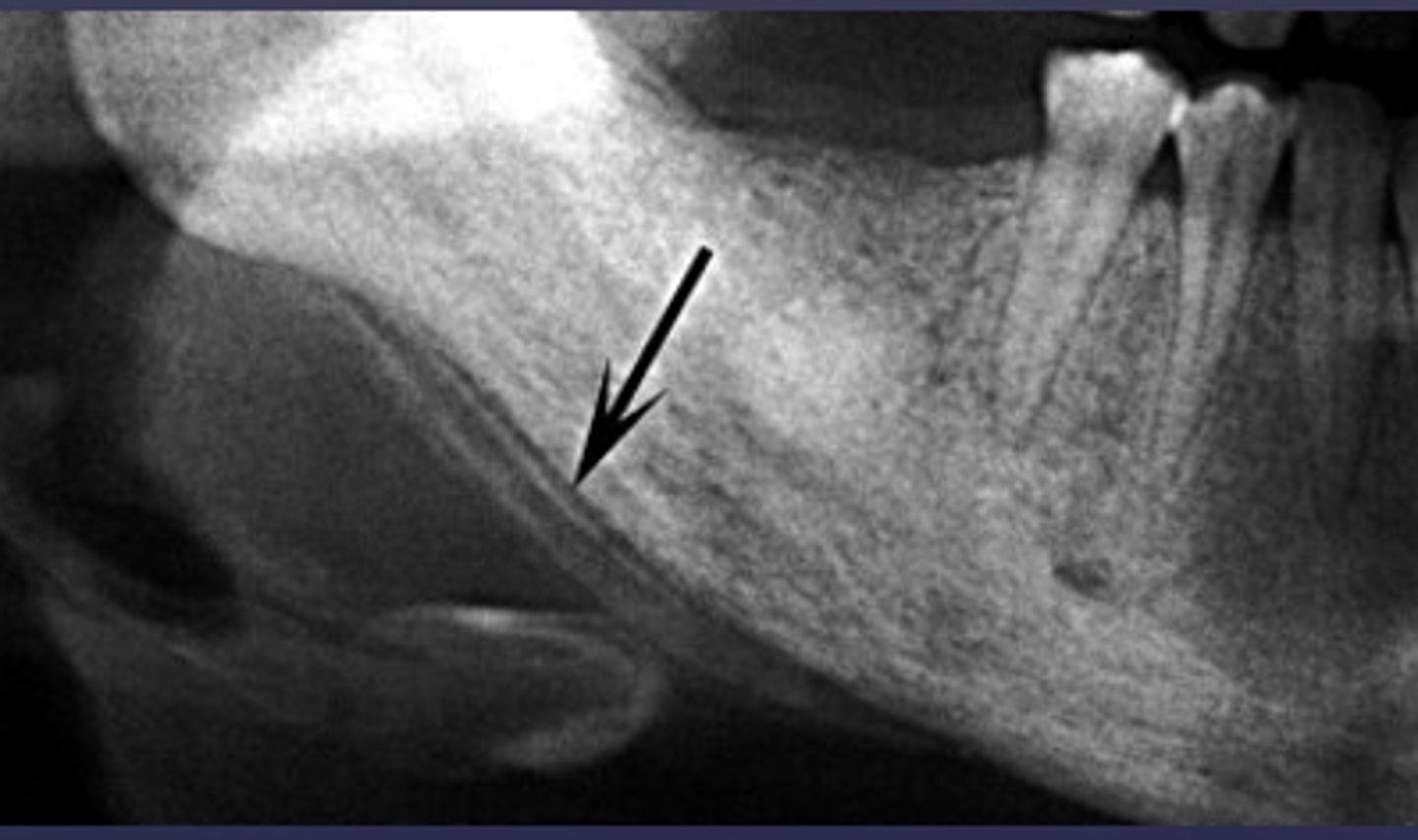
A radiograph of the mandible shows concentric layers of new bone formation parallel to the cortex, producing an "onion-skin" appearance. What is the diagnosis?
Periosteal reaction (acute osteomyelitis)
The "onion-skin" appearance seen in acute osteomyelitis results from which process?
Alternating cycles of periosteal bone deposition and resorption
How does early periosteal involvement in acute osteomyelitis form in relation to the cortex?
New bone formation parallel to the cortex
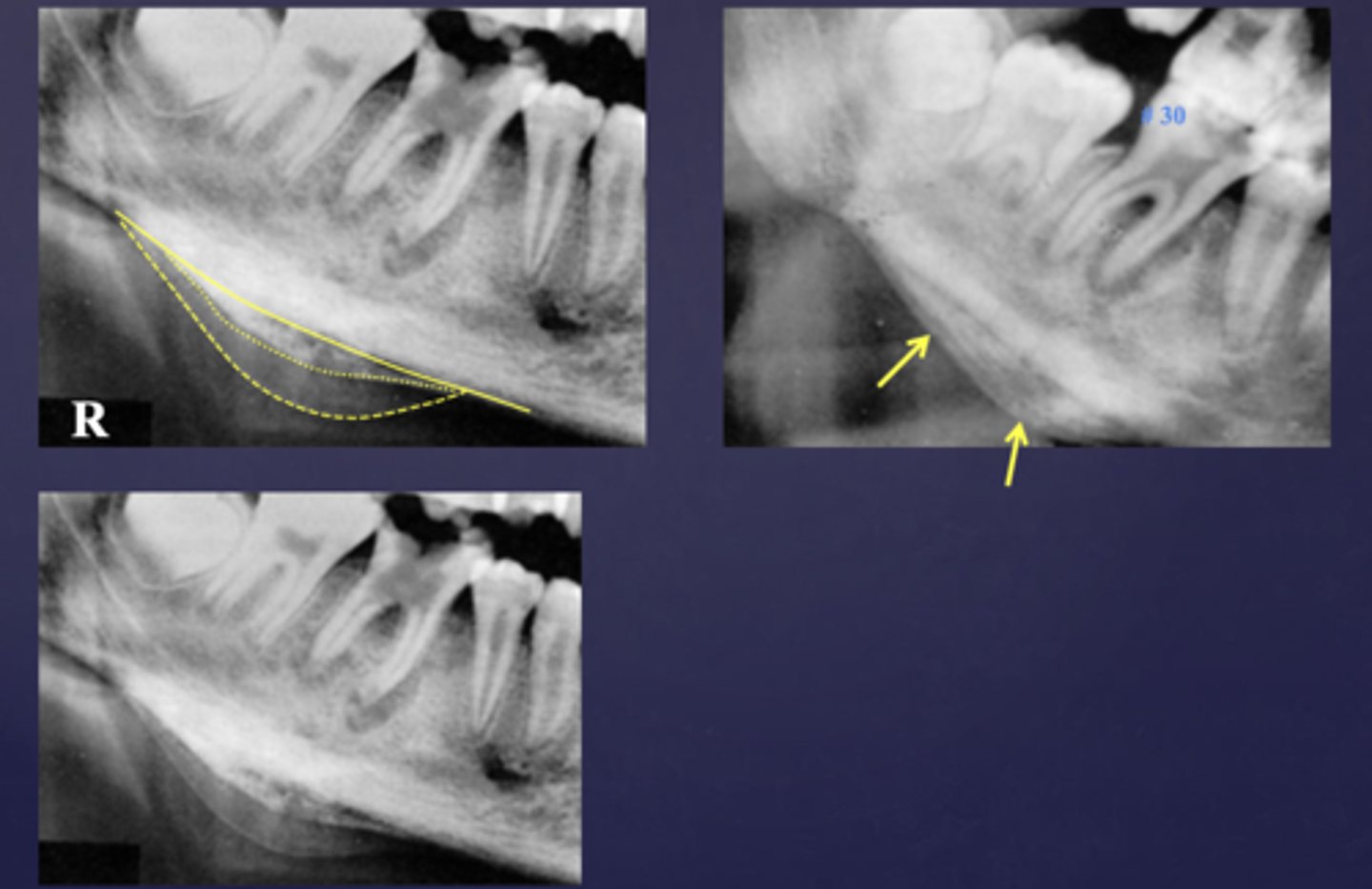
What is happening here?
periosteal reaction
Proliferative periostitis is also known as what?
onion skin
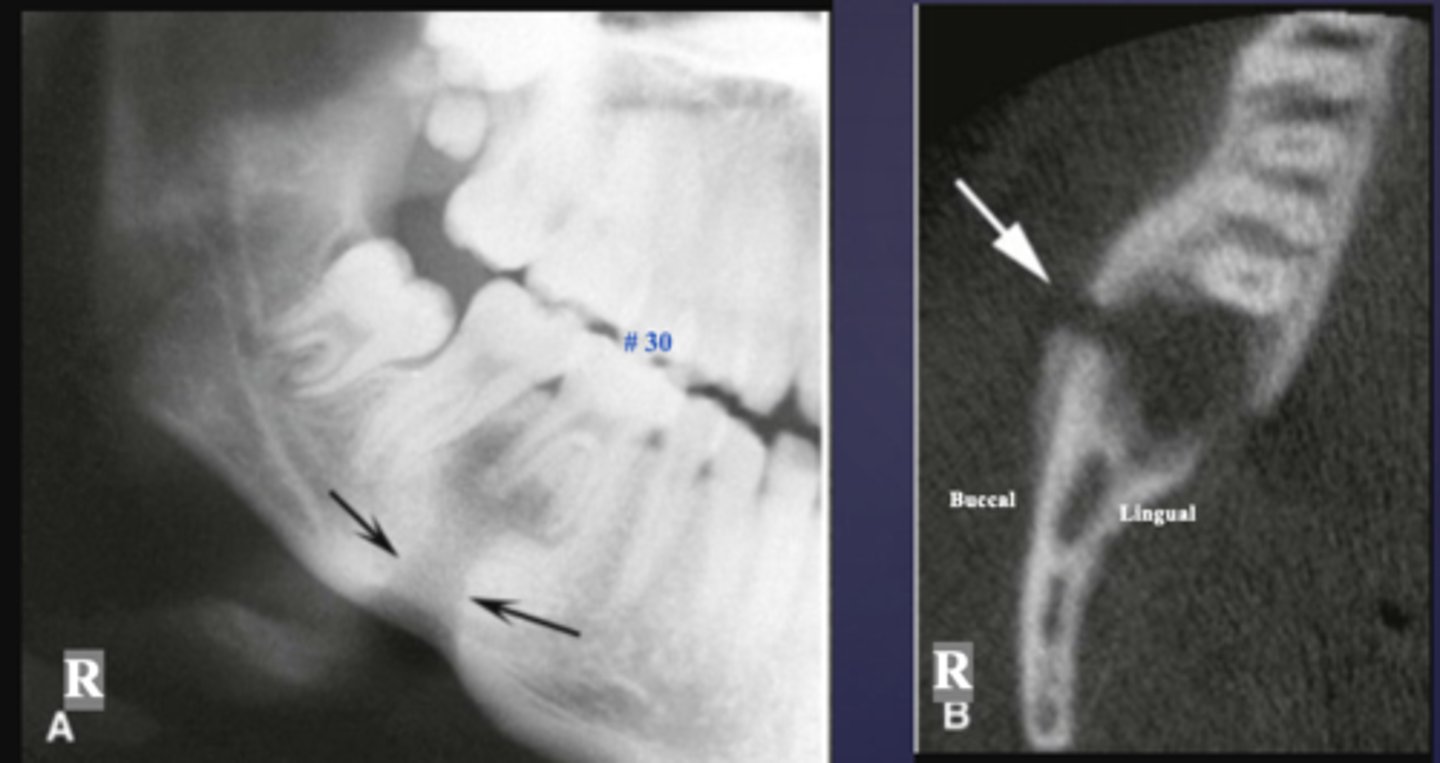
What defect?
fistula
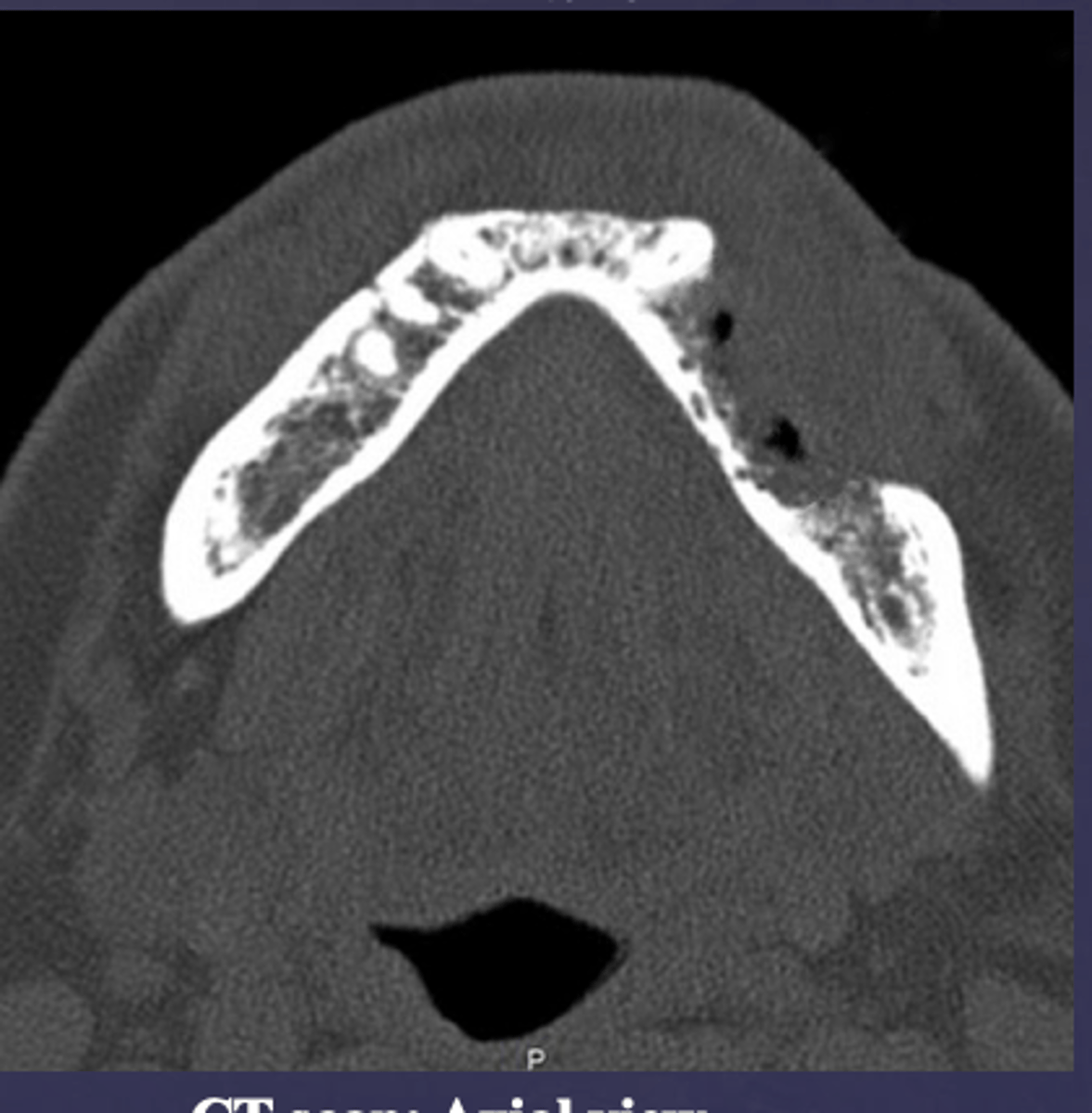
What occured?
Destruction of buccal cortex (ill defined radiolucent area in the mandible)
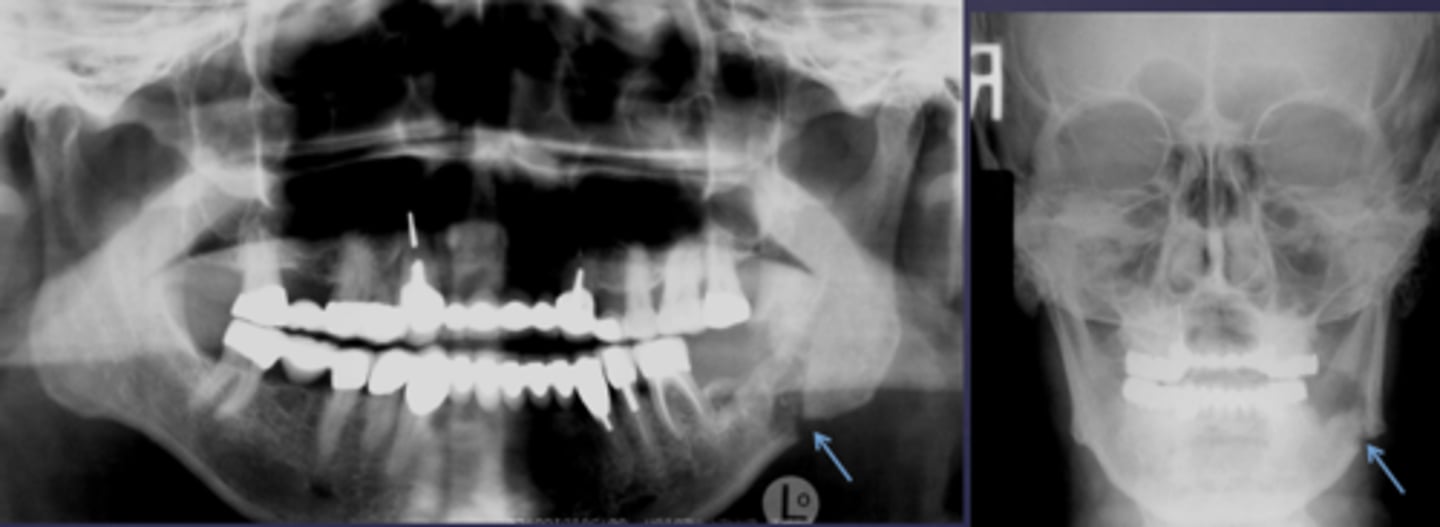
Osteomyelitis caused what to occur?
Pathologic fracture
What is the primary response of diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis?
proliferation reaction
What type of osteomyelitis?
- Sclerotic appearance of involved bone
- Subperiosteal bone deposition
- Slight jaw enlargement
- Involves large segment of jaw
diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis (chronic osteomyelitis)
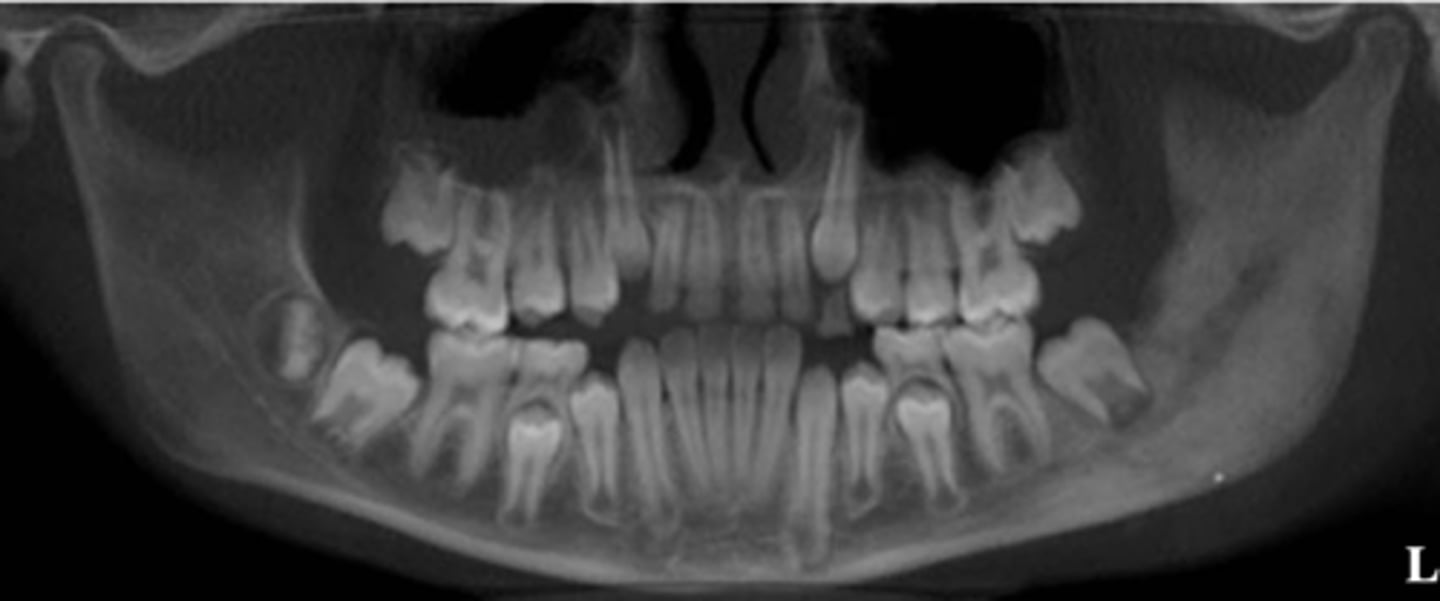
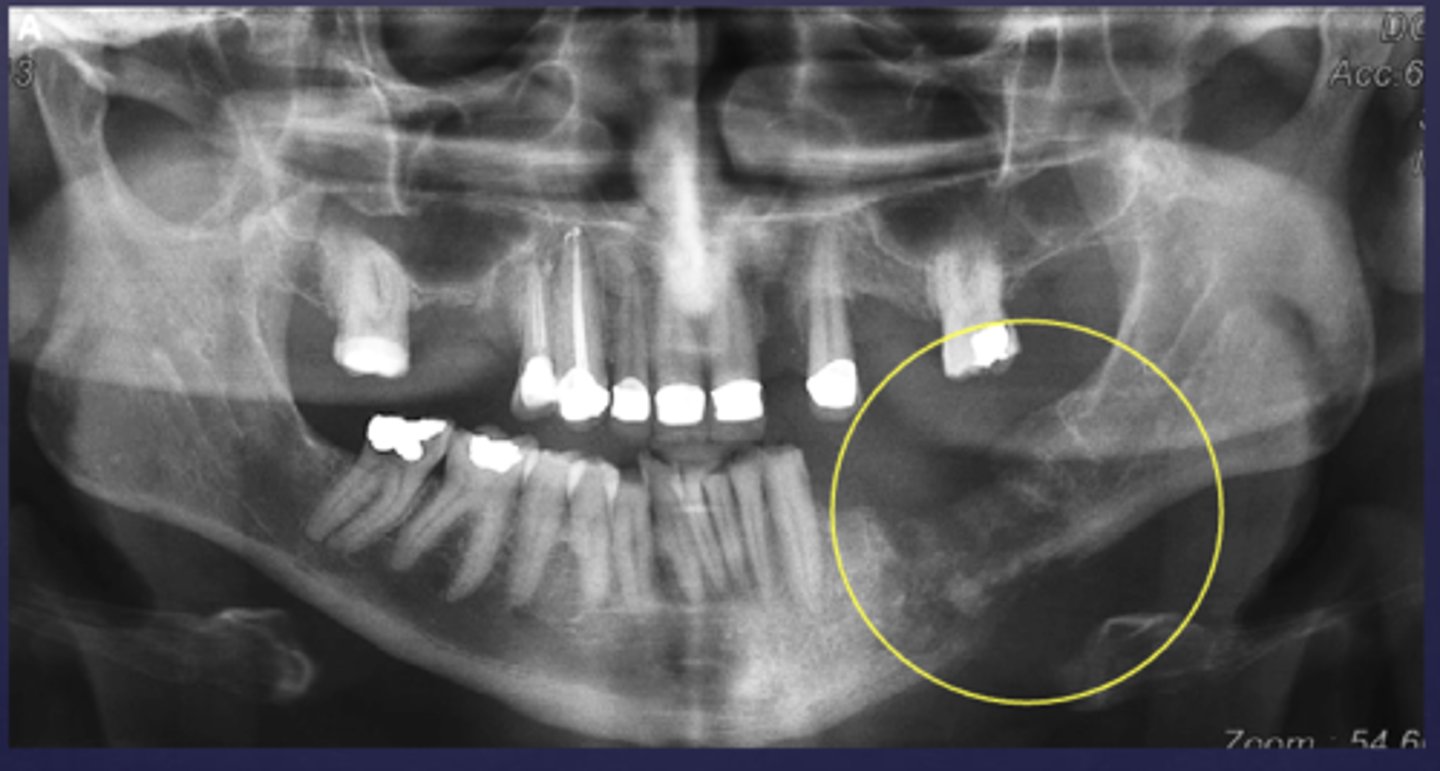
What is the differential diagnosis of the left angle-ramus of mandible?
diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis (chronic osteomyelitis)
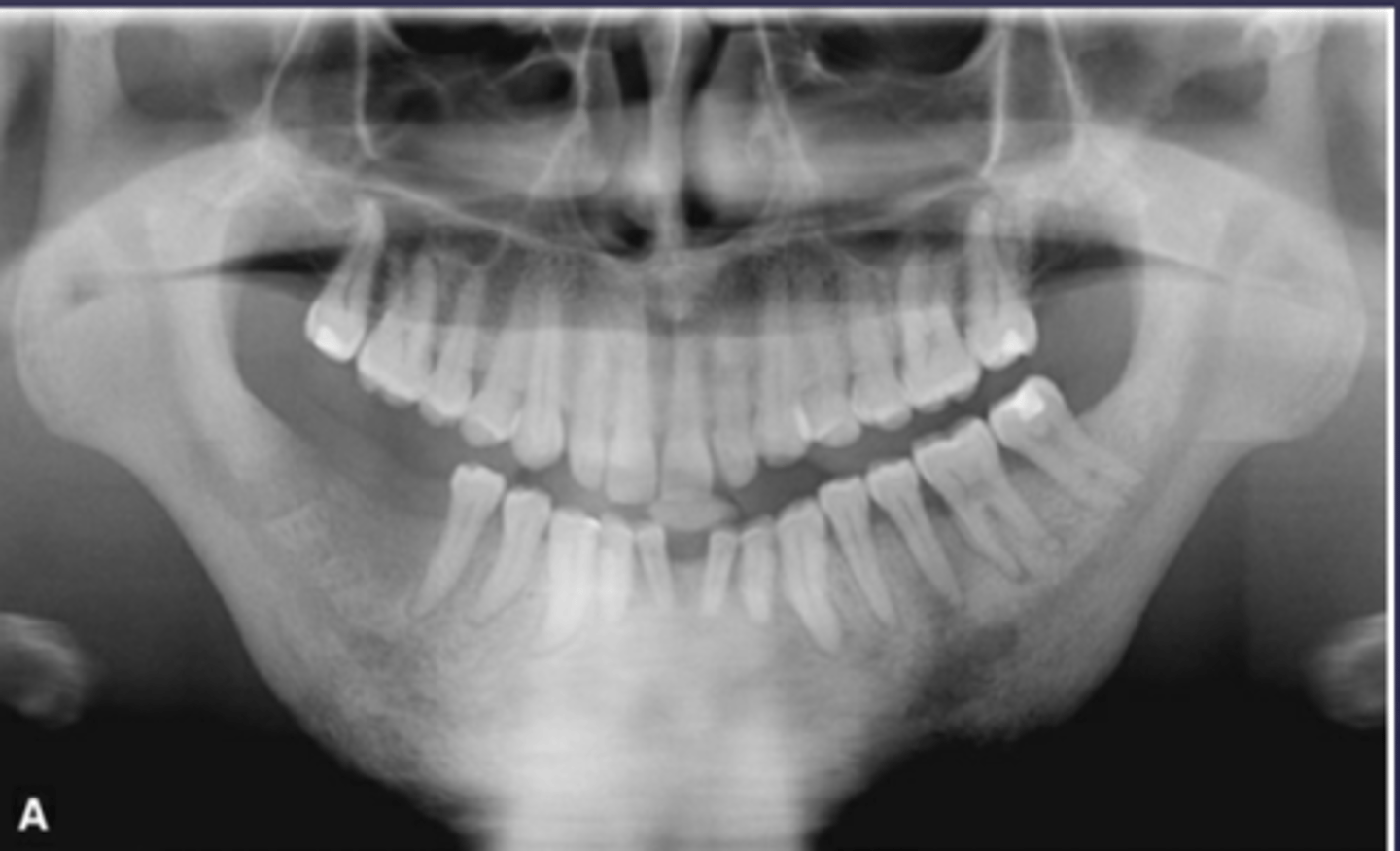
A patient's pano is shown and presents with wrist symptoms. What is the differential diagnosis?
SAPHO Syndrome
What is the condition?
- Radiation induced damage to bone : resulting from exposure to therapeutic doses of radiation
- Doses above 50 Gy cause hypocellularity and hypovascularity
- Clinically exposed necrotic bone
- Radiologic changes similar to Osteomyelitis
osteoradionecrosis (ORN)