Clin Med L3 CBC - WBC portion
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are Granulocytes? Give Examples
cells that digest microorganisms
ex: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils
What are Agranulocytes? Give Examples
cells that cannot digest microorganisms
ex: Monocytes and Lymphocytes.
What is the function of WBCs in host defense?
Phagocytosis (granulocytes and monocytes)
Immune response (lymphocytes).
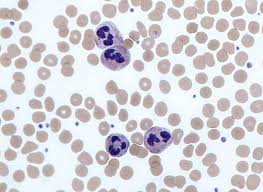
What is the function of Neutrophils?
phagocytize and destroy microbes, increased in bacterial infection
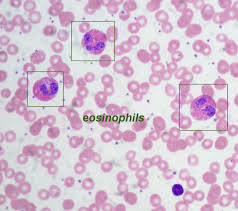
what is the function of Eosinophils?
combat the effects of histamine in allergic reactions, destroy certain parasitic worms
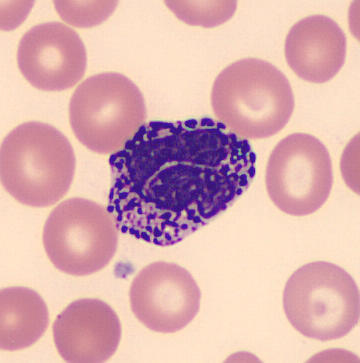
what is the function of Basophils?
release heparin, histamine, and serotonin to intensify the inflammatory response in allergic reactions
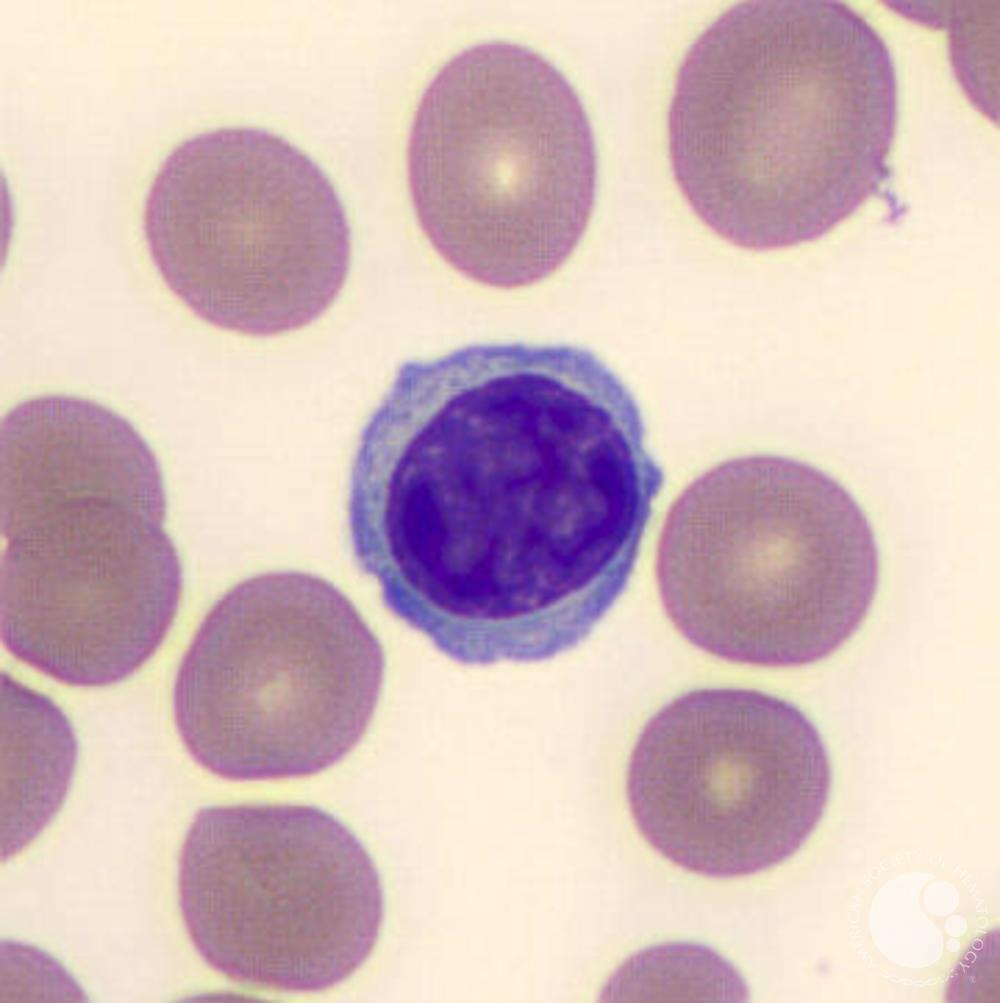
what is the function of Lymphocytes?
essential component of the immune defense system, interact with antigens and mount an immune response (T and B lymphocytes), increased in viral infections
What is the function of Monocytes?
differentiate into macrophages and phagocytize debris and microbes
strep is what kind of infection?
mono is what kind of infection?
bacterial
viral
what type of WBC fights parasitic worms?
eosinophils
what type of WBC fights viral infections?
lymphocytes
blue cytoplasma
what type of WBC deals with inflammatory allergic reactions?
basophils
what type of WBC fights bacterial infections?
neutrophils
what type of WBC deals with histaminic allergic reactions?
eosinophils
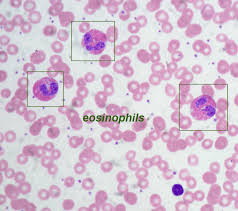
What is the difference between Neutrophils and Eosinophils?
Eosinophils are larger and richer in color when stained, and typically are bi-segmented unlike neutrophils
R: Neutrophil L: Eosinophil
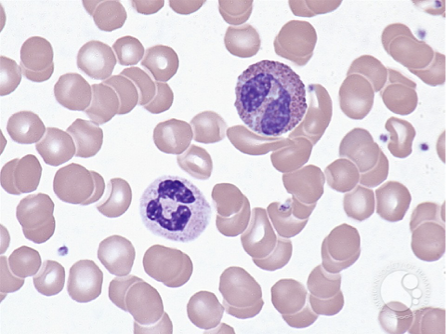
neutrophils have how many segments?
color?
more than 2 segments
pale
eosinphils have how many segments?
color?
only 2 segments
vibrant
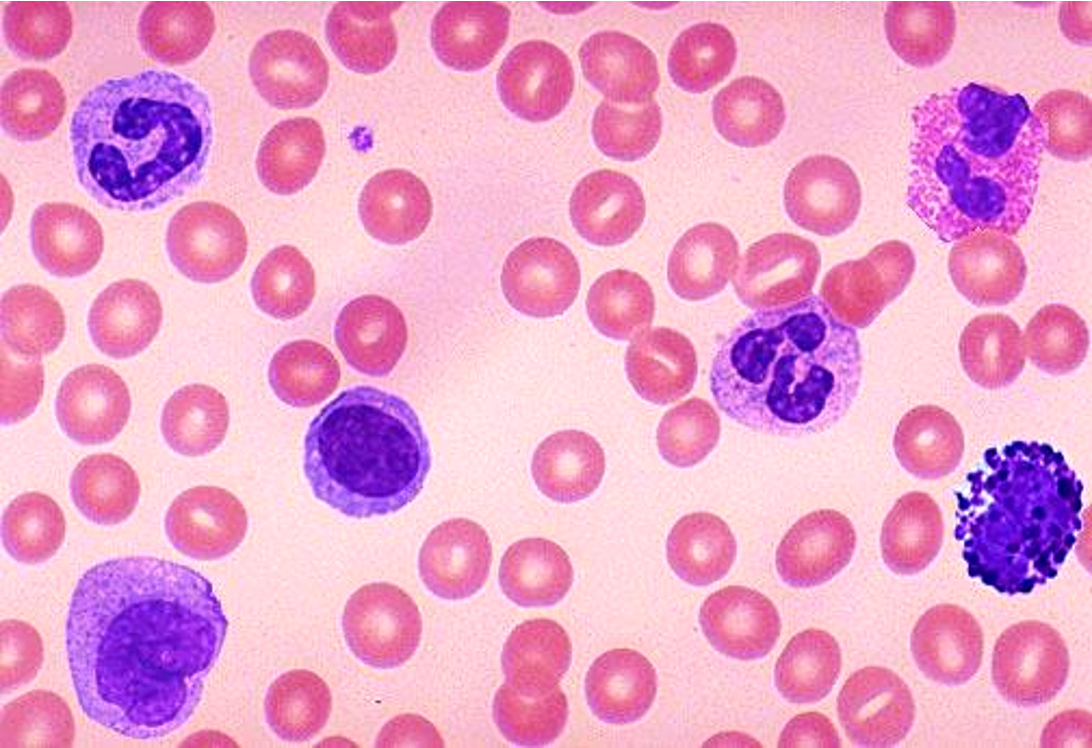
identify all these WBC
top R
middle R
bottom R
top L
middle L
bottom L
top R: neutrophil with band
middle R: T cell
bottom R: plasma B cell (lymphocyte)
top L: eosinophil
middle L: neutrophil
bottom L: basophil
what is hypersegmentation?
what anemia do we see this in?
neutrophils with MORE than 6 segments
commonly seen in
megaloblastic anemias (B12 and folate deficiencies)
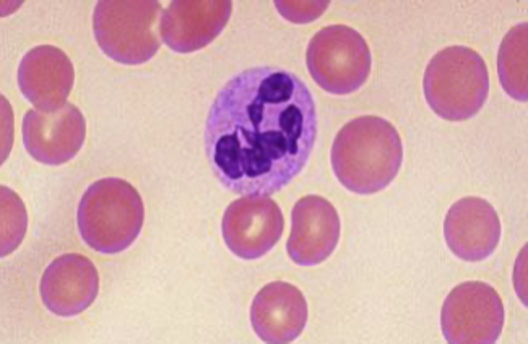
what is hyposegmentation (Pelger-Huet anomaly) ?
neutrophil has 2 segments or LESS
congenital or acquired (ex. CML).
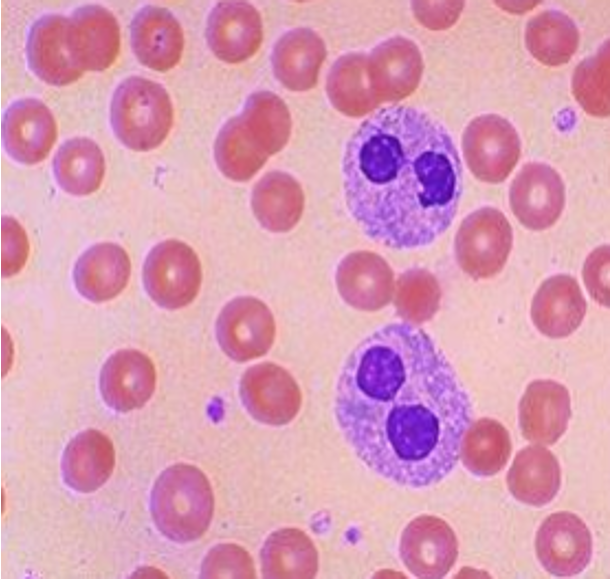
What is Toxic Granulation?
more inclusions in the cytoplasm of WBC seen as darker staining of neutrophils
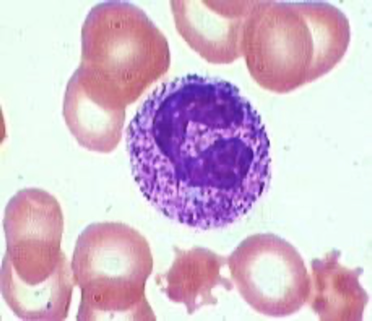
What is Vacuolization?
Commonly seen in?
“holes” in the cytoplasm; frequently seen in association with toxic granules
Commonly seen in acute infections – usually bacterial.
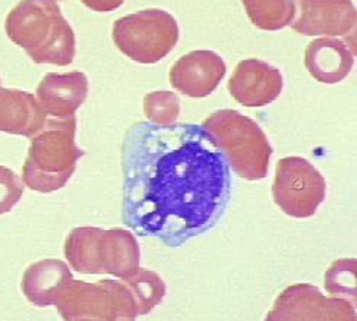
what WBC can have hypersegmentation, hyposegmentation, toxic granulation and vacuolization?
neutrophils
What are Döhle Bodies?
What do they indicate?
Seen as large, gray-blue structures in cytoplasm, often located next to the cytoplasmic border
Structures are aggregates of rough endoplasmic reticulum
Indicate rapid cell maturation
What are Reactive Lymphocytes?
large lymphocytes
nucleus appears elongated
cytoplasm is abundant, pale blue, and often staining unevenly
what illness do we see reactive lymphocytes in?
viral infections
What information does the WBC Count provide?
provides a count of the number of WBCs
does NOT tell you why they are elevated
is the WBC count specific or non-specific?
non-specific
What is a WBC Differential?
tells you different counts of the different WBC
What does 'Shift to the Left' mean in the context of WBCs?
Indicates that the neutrophils present in the blood are at a slightly earlier stage of maturation than usual
results in an increased number of band neutrophils
what does a left shift indicate?
bacterial infection; also known as “bandemia”
early response to infection
What does a WBC count of 100,000 – 400,000 indicate?
a new onset WBC of 100,000 – 400,000 indicates acute or acute on chronic leukemia
What does a Reticulocyte Count indicate?
how well your bone marrow is producing RBCs
how well the body is compensating while having anemia
what usually causes an increase in Retic Count?
any disease that is destroying your RBCs that forces the body to make more RBC
When would you see an Increased Retic Count?
Hemolytic anemias
Acute or chronic bleeding
Following treatments for iron def anemia or factor def anemia
what does a Decreased Rectic count mean?
ineffective production of RBCs in the bone marrow
aka body CANNOT make RBCs well (erythropoiesis)
When would you see a Decreased Retic Count?
aplastic anemia
other various types of deficiency anemias
Thalassemia
when you have a Decreased Retic Count what is the next diagnostic test you will order?
bone marrow biopsy
What is Bone Marrow Biopsy?
Examination of bone marrow tissue to diagnose
Polycythemia vera
Acute and chronic leukemias
Myelodysplastic syndromes
Aplastic anemia
What is Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)?
means of detecting any inflammatory conditions
is the ESR specific or non-specific?
non-specific
How do increased protein levels affect ESR?
the increased protein levels decrease the tendency of RBCs to repel each other and enhances rouleaux formation
stacked RBC
What is G6PD Deficiency?
genetic abnormalities which cause decreased in G6PD activity
G6PD protect RBC
when is G6PD deficiency tested?
patient with symptoms or risks of hemolytic anemia without any other cause