Honors Biology: EOC Review
1/291
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
292 Terms
organic molecules
molecules that contain carbon
carbohydrate
compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; type of nutrient that is the major source of energy for the body
Monosaccharide
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate?
disaccaride and polysaccaride
What is the polymer of a carbohydrate?
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Monosaccharides
What kind of molecule is glucose?
starch, cellulose, glycogen
What is an example of a polysaccharide?
carbohydrate
What macromolecule is a plant cell made of?
cellulose
What is a plant cell made of?
chitin
What if the fungi cell wall made of?
peptidoglycan
What is a bacteria cell wall made of?
short term energy
What is the function of a carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates
made of rings of C,H, and O; and OH's on all carbons except one
amino acid
What is the monomer of a protein?
protein
What is the polymer of a protein?
protein
What macromolecule are these; enzyme, insulin, hemoglobin?
enzymes, structure, growth and repair, transport
What is the function of a protein?
protein
contain N and have N-C-C backbone
long chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Nucleotide
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid?
DNA and RNA
What is the polymer of a nucleic acid?
carries and transfers genetic information
What is the function of a nucleic acid?
to reduce the number of chromosomes in half so the resulting zygote formed from fertilization with have the correct number of chromosomes
What is the main purpose of meiosis?
amount of oxygen in the atmosphere
Which factor does not affect the rate of photosynthesis?
enzyme
The enzyme amylase breaks down starch. Which term best describes amylase?
nucleic acid
made up of sugars, phosphates, and nitrogen bases.
fatty acid
What is the monomer of a lipid?
Glycerol
What is an example of a fatty acid?
lipid
What is the polymer of a lipid?
steroids, hormones, insulation, and wax oils
What are examples of lipids?
lipids
head with fatty acid tail
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information.
adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
What are the nitrogen bases of DNA?
Thymine
What nitrogen base goes with Adenine?
Guanine
What nitrogen base goes with Cytosine?
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
ribose
What kind of sugar does RNA contain?
Deoxyribose
What kind of sugar does DNA contain?
Adenine
What pairs with Uracil?
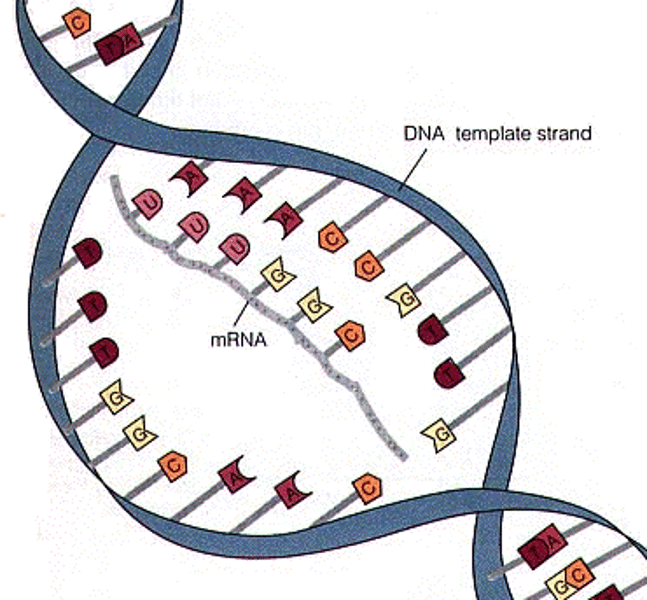
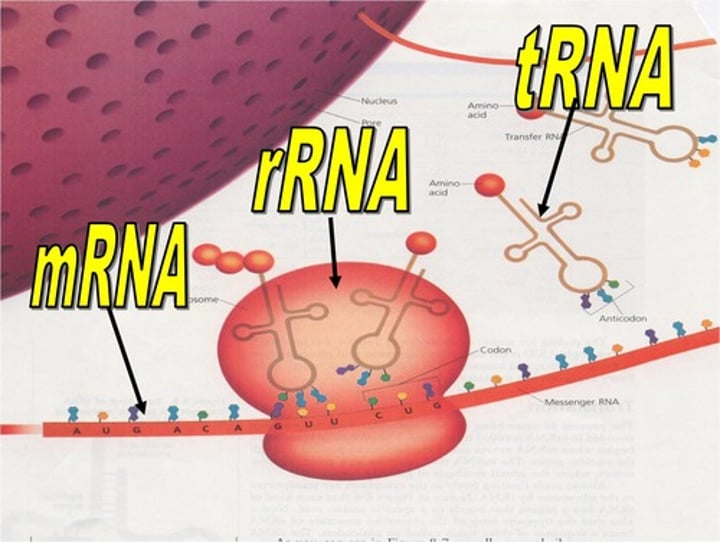
Messenger RNA
carries DNA code from nucleus to ribosome
Transfer RNA
carries amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome
Ribosomal RNA
What the ribosome is made of
3
How many nitrogen bases codes for an amino acid?
Mutation
What is a error in a nitrogen base called?
protein synthesis
the formation of proteins by using information contained in DNA and carried by mRNA
transcription, translation
What are the steps on protein synthesis?
transcription
copying DNA code onto the mRNA
translation
making protein in the ribosome
transcription
What is this describing? DNA unwinds and unzips
mRNA nucleotides match up to the complementary DNA nucleotide
single strand of mRNA is made with the DNA code
mRNA leaves the nucleus and carries the code to the ribosome
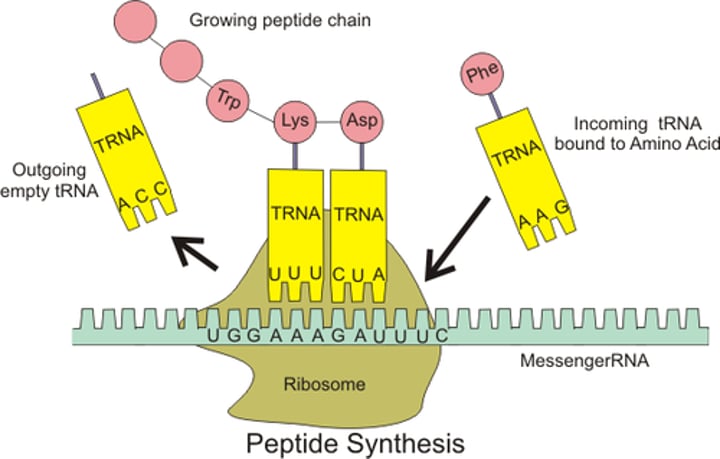
translation
What is this describing? mRNA lines up in the ribosome
mRNA triplet codes match up with tRNA triplet codes and bring amino acids
amino acids are put in the correct sequence
peptide bonds forms between amino acids
polypeptide folds into protein
protein
What macromolecule is an enzyme?
lowers activation energy
What does a catalyst do?
substrates
Different enzymes work with specific _________, depending on their shape
damages it
What does denaturing an enzyme do?
temperature and pH
How are enzymes denatured?
-ase
What do most enzymes end in?
Adenine Triphosphate
What does ATP stand for?
Adenine Diphosphate
What does ADP stand for?
ATP
What does ADP turn into during respiration?
ADP
What was ATP before respiration?
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen
aerobic respiration
What is the most efficient form of respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
What is the formula for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6
glucose
6O2
Oxygen
6CO2
carbon dioxide
6H2O
water
glucose and oxygen
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
carbon dioxide and water
What are the ending molecules of cellular respiration?
glycolysis
What does all cellular respiration start with?
Anerobic
What kind of respiration is glycolysis?
anerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen
2 pyruvate
What does glucose get split into during glycolysis?
fermentation begins
What happens during respiration if there is no oxygen present?
lactic acid fermentation
the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates that produces lactic acid as the main end product
lactic acid is made
What happens during lactic acid fermentation?
animals
Where does lactic acid fermentation occur?
yeast and some prokaryotes
Where does alcoholic fermentation happen?
Alcohol and lactic acid
What is made during alcoholic fermentation?
Cytoplasm
Where does glycolysis occur?
matrix
Where does the Krebs Cycle occur?
Cristae
Where does the Electron Transport Chain occur?
38
How many ATP is gained during the entire process of cellular respiration?
2
How many ATP are produced during glycolysis?
4
How many carbon dioxides are released into the air after BOTH turns of the Krebs Cycle?
matrix
What is the fluid inside the mitochondria that contains the enzymes and coenzymes required for respiration?
2
How many ATP are gained during anaerobic respiration?
36
How many ATP are produced during aerobic respiration?
Krebs cycle
Where does most of the carbon dioxide evolved during respiration come from?
citric acid cycle
what is the krebs cycle also called?
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
what are the reactants for photosynthesis?
avaliability of carbon dioxide and water, temperature, and pH, and light
What can affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
Homeostasis
What is your body trying to maintain at all times?
3
What is the minimum amount of trials in an experiment?
control group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment.
manipulated variable
the thing that you change in the experiment