Neuroanatomy with images
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
inferior
under
superior
over
anterior
front
posterior
back
lateral
side
medial
middle
dorsal
north of brain stem
ventral
south of brain stem
rostral
toward the beak
caudal
toward the tail
sagittal
perpendicular to bread cut
coronal
bread cut
mid-sagittal
through the middle
somatic nervous system
facilitates motor and sensory communication between the CNS and rest of body by innervating the skin joints and muscles
spinal nerves
communication between the CNS and the periphery of the body via dorsal sensory input and ventral motor output
autonomic nervous system
regulates internal organs
sympathetic nervous system
prepares body for action in response to threats via increase in heart rate, respiration, and blood flow to muscles. Flight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
energy conservation and restoration of body, rest and digest
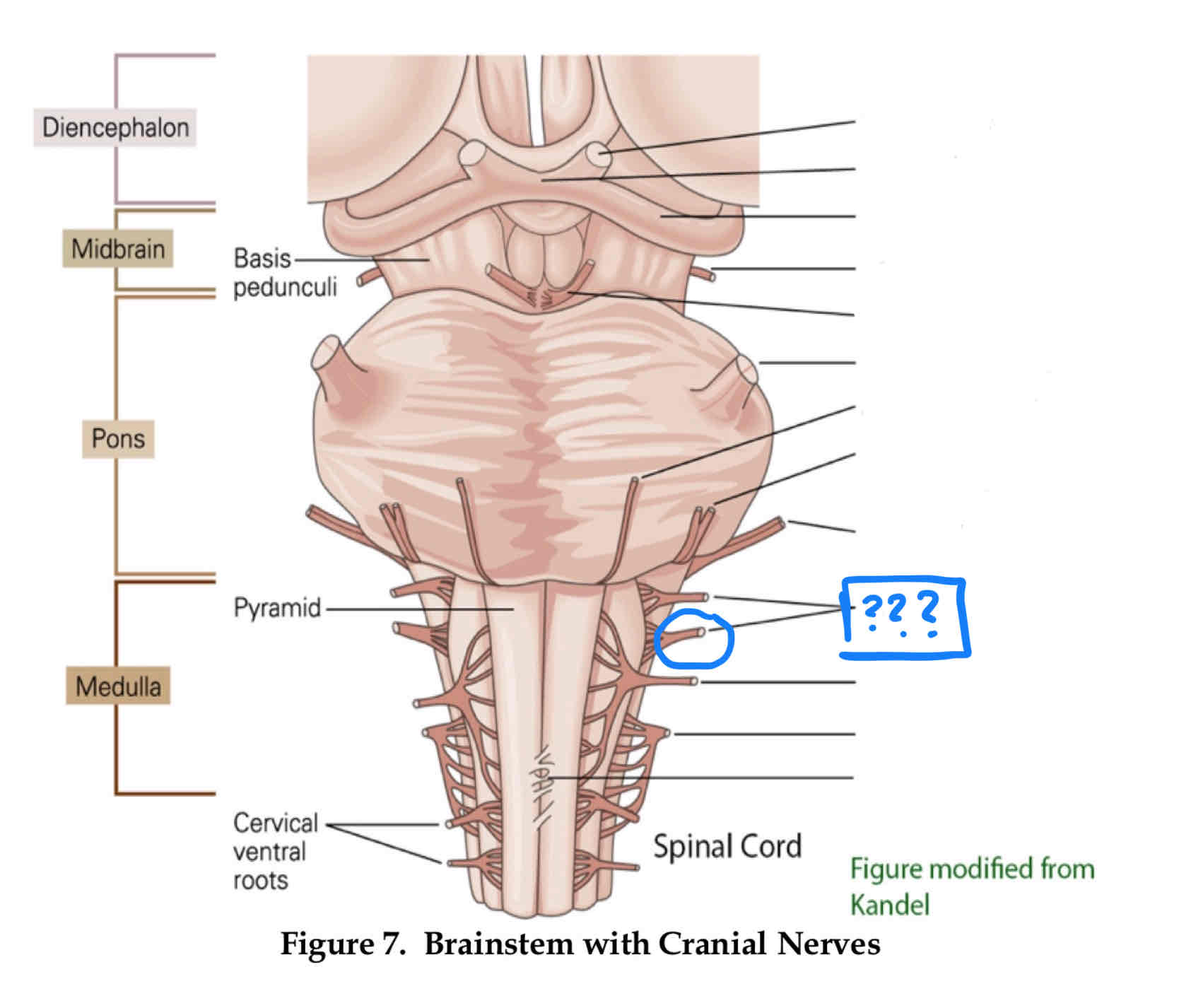
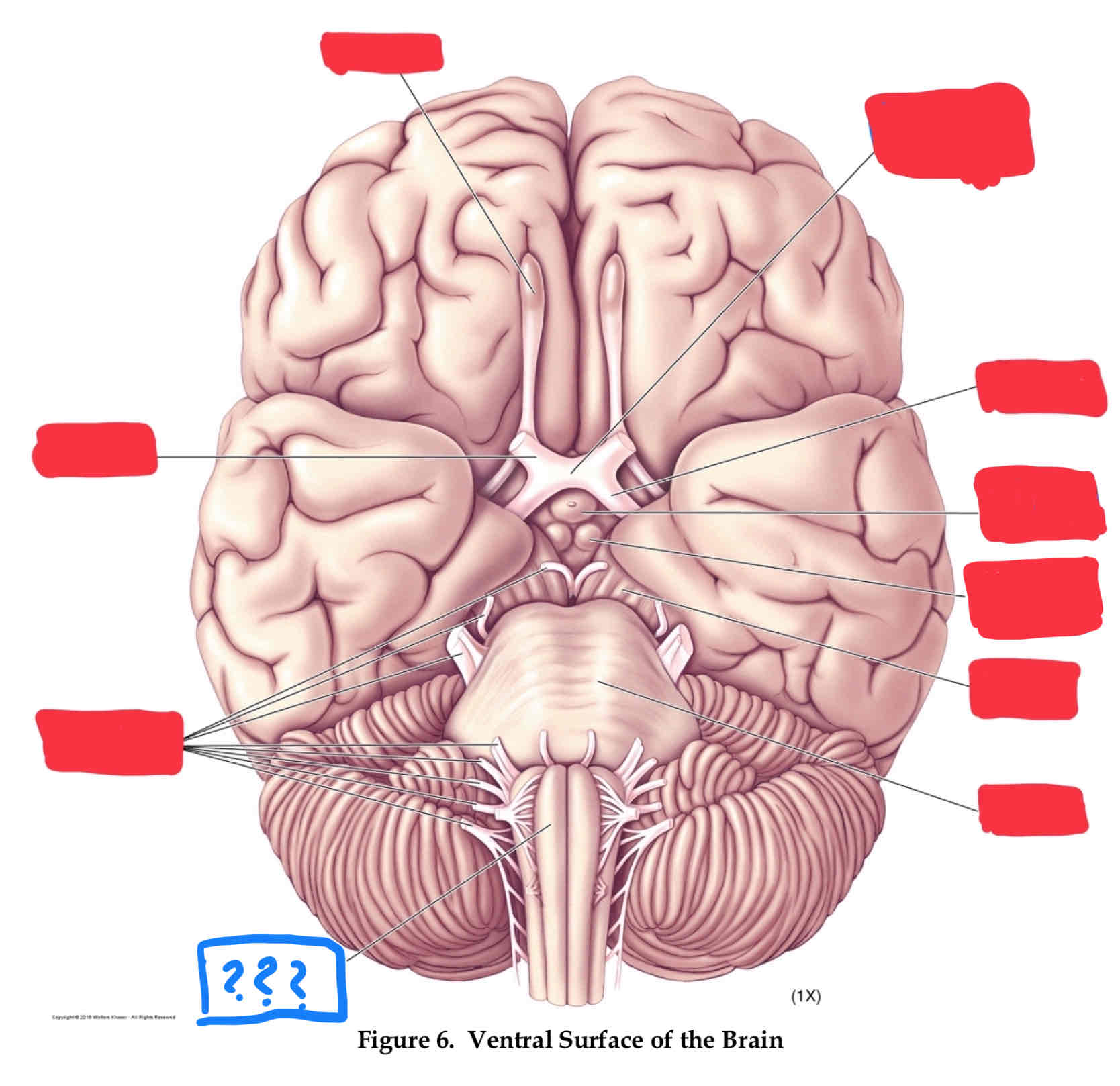
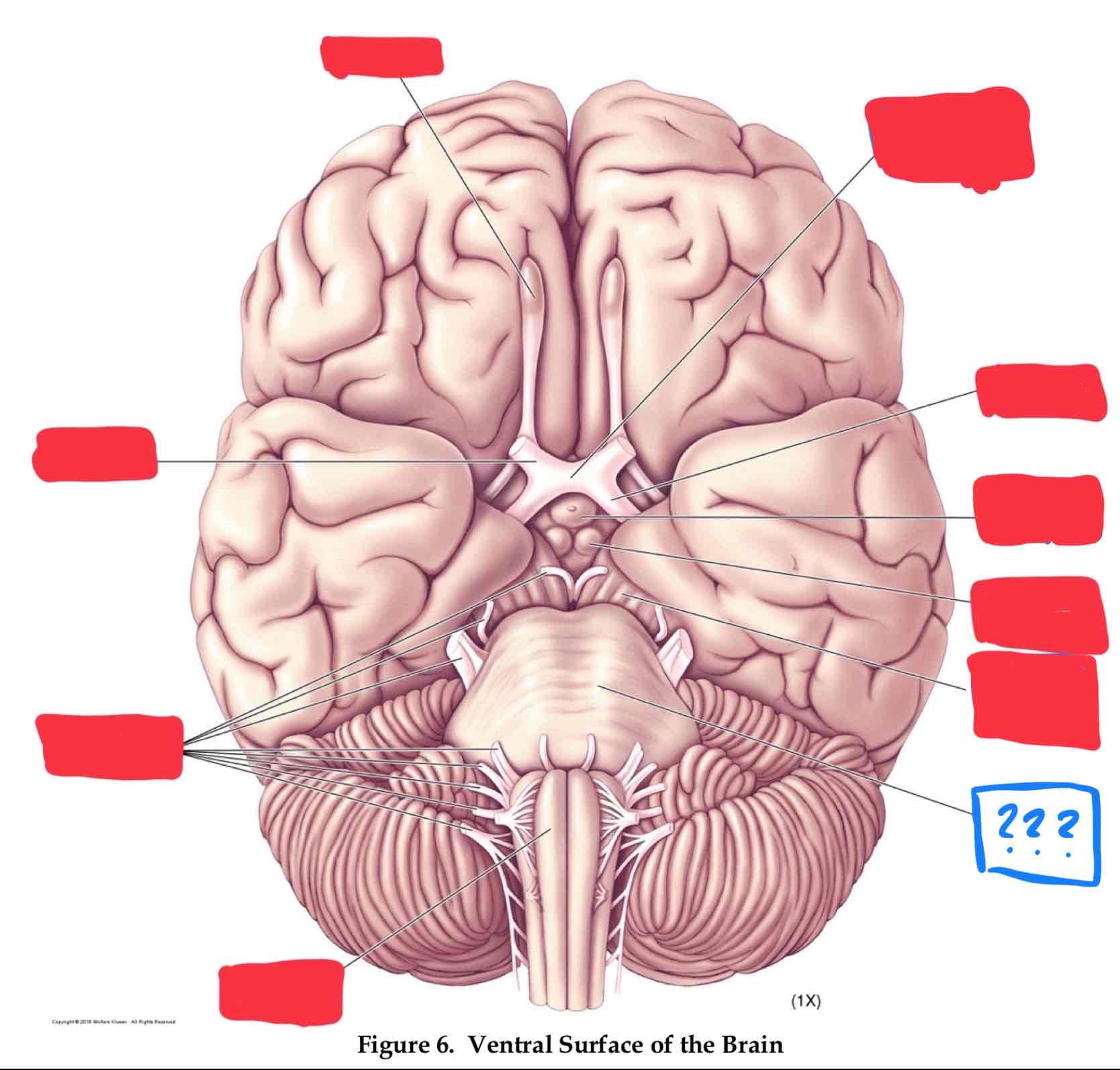
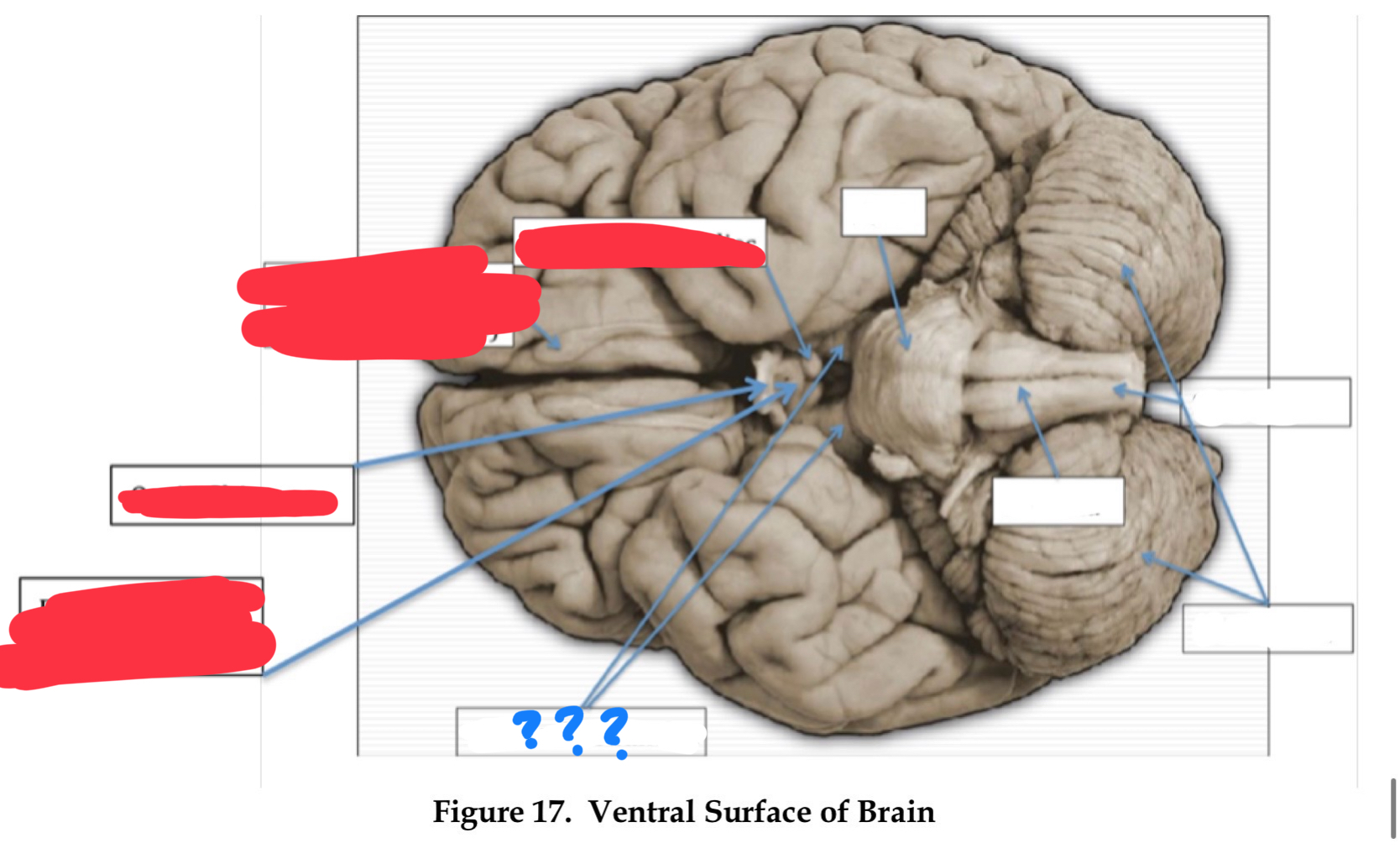
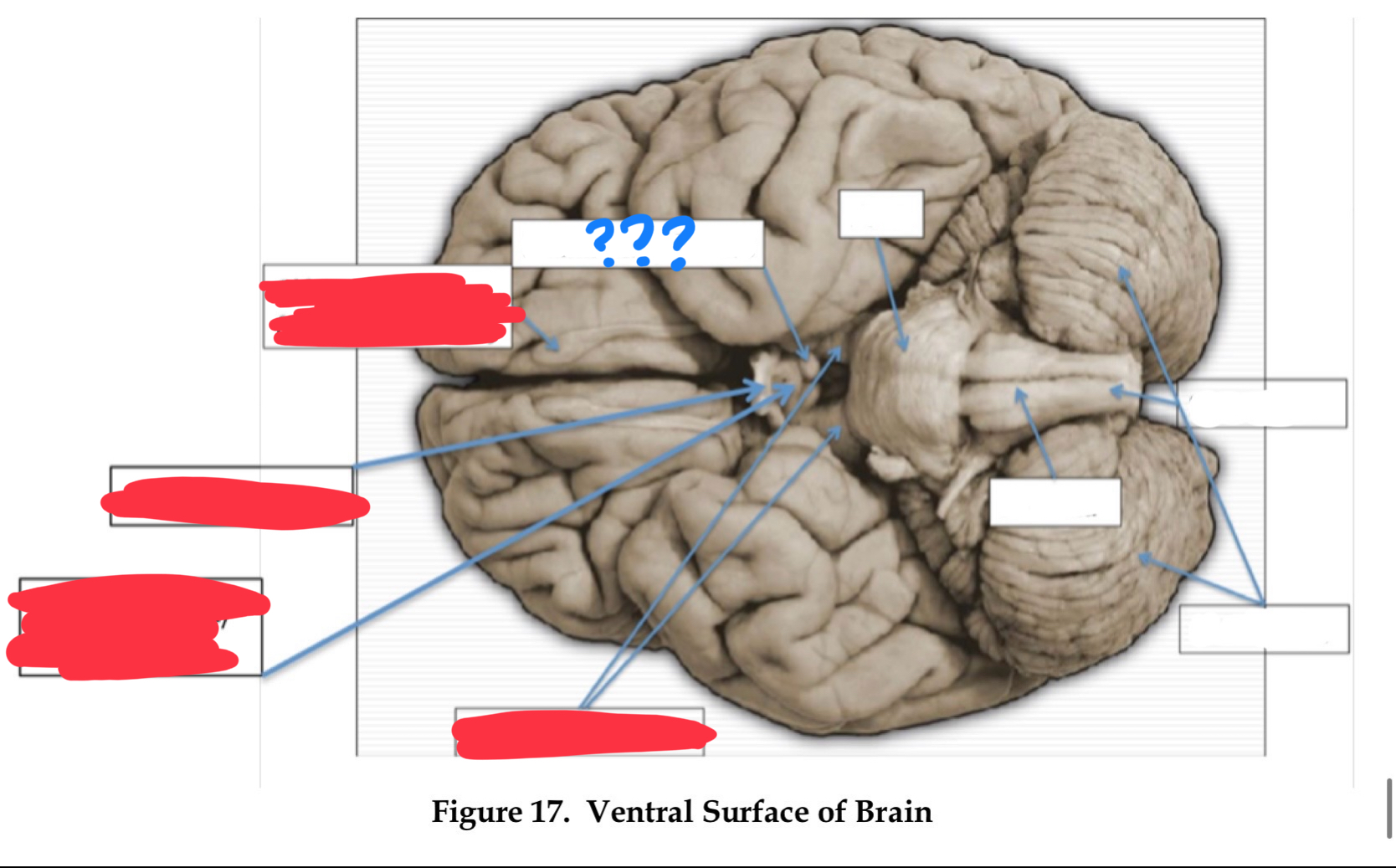
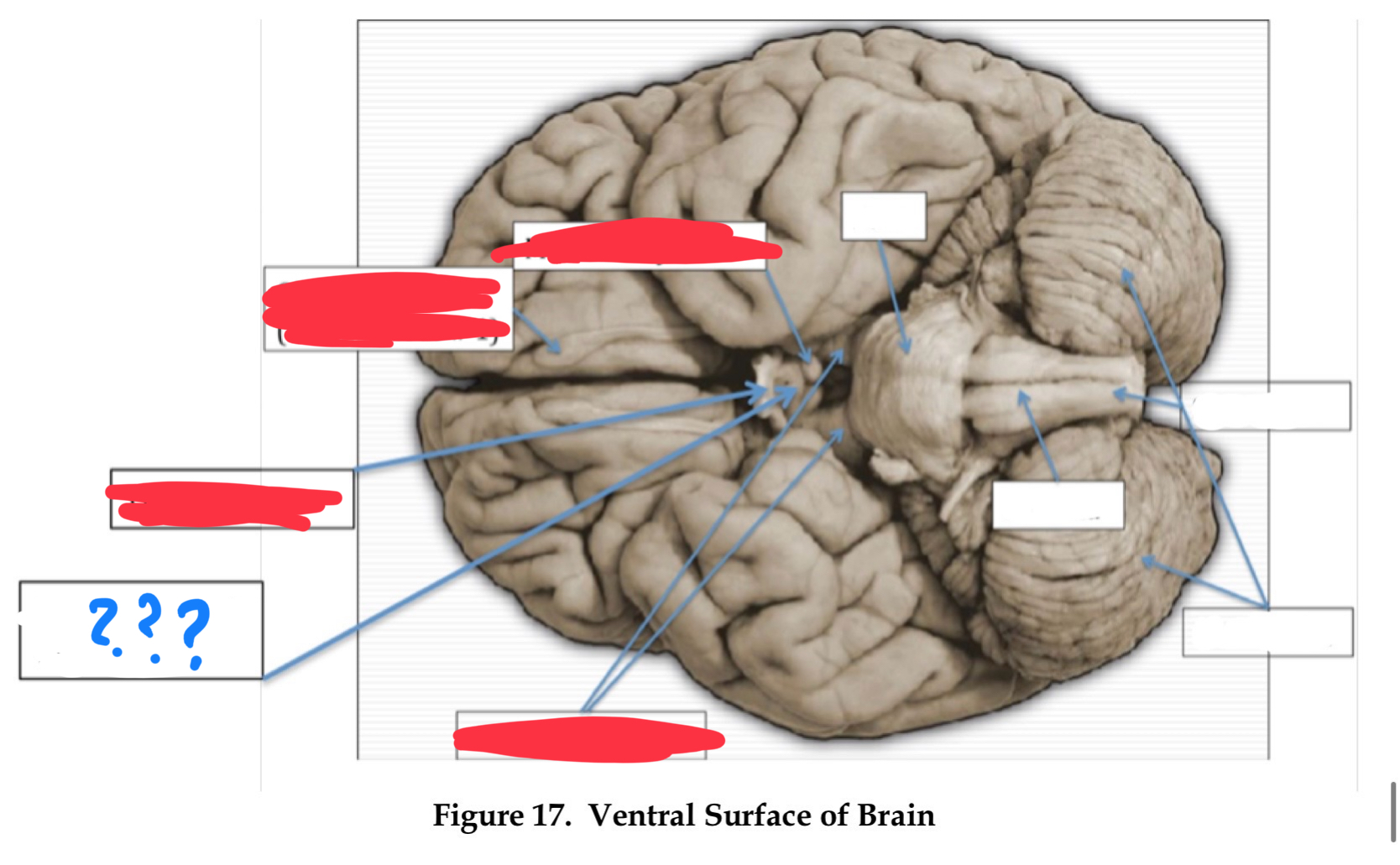
olfactory nerve I
olfaction
olfactory bulb
olfaction
optic nerve II
vision
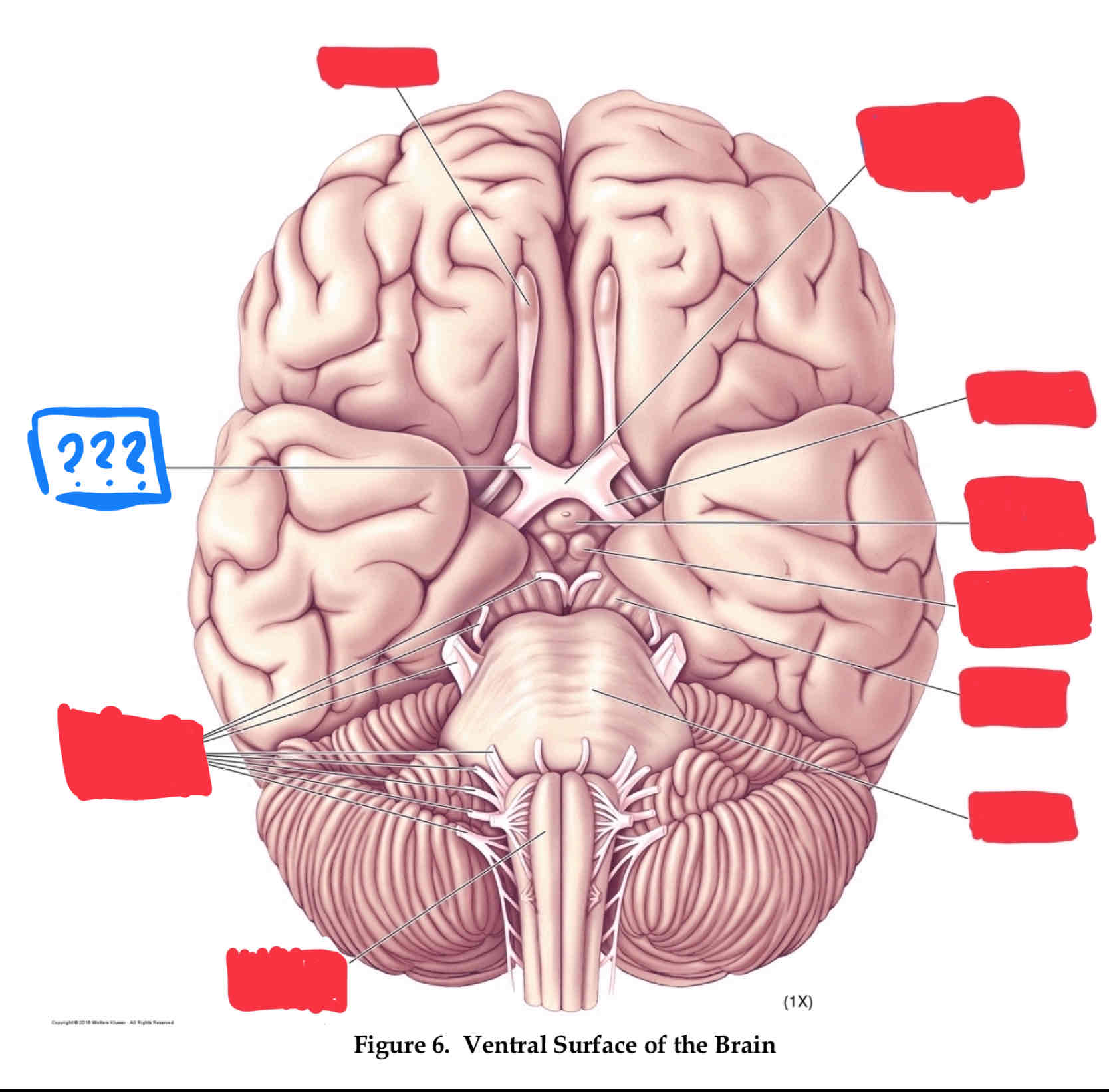
optic chiasm
vision
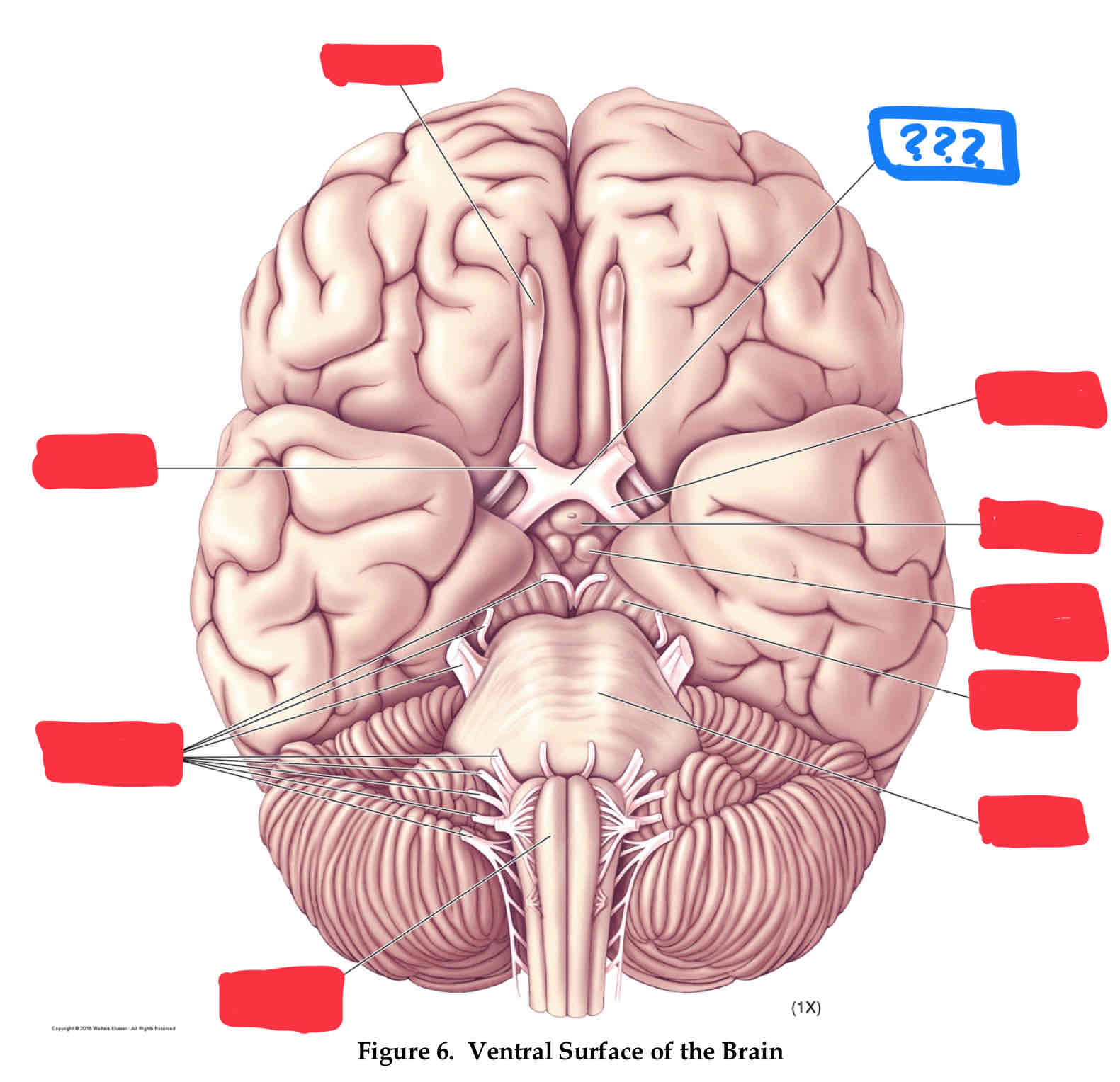
optic chiasm
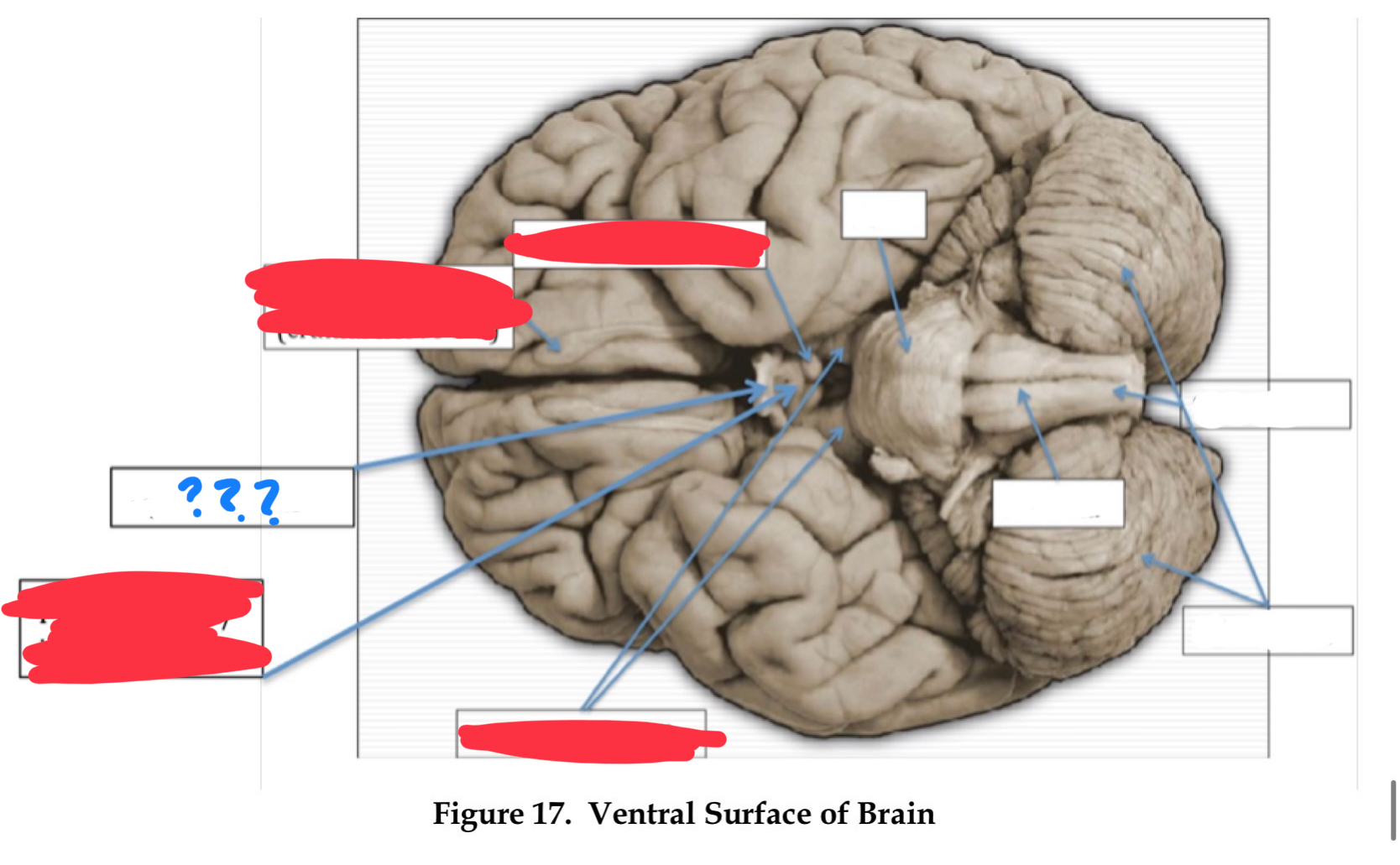
optic tract
vision
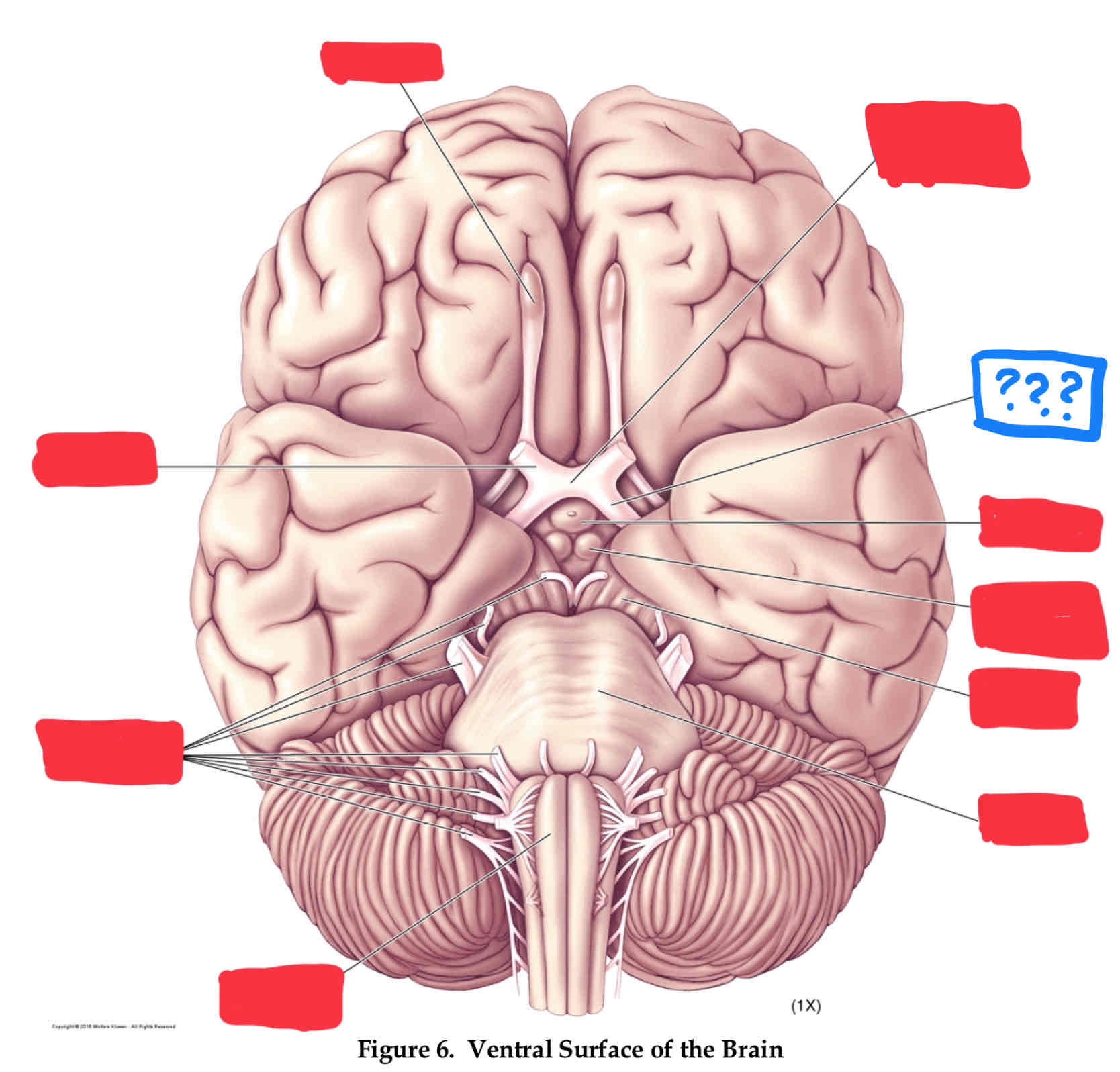
oculomotor nerve III
involved in eye and eyelid movement and pupil size
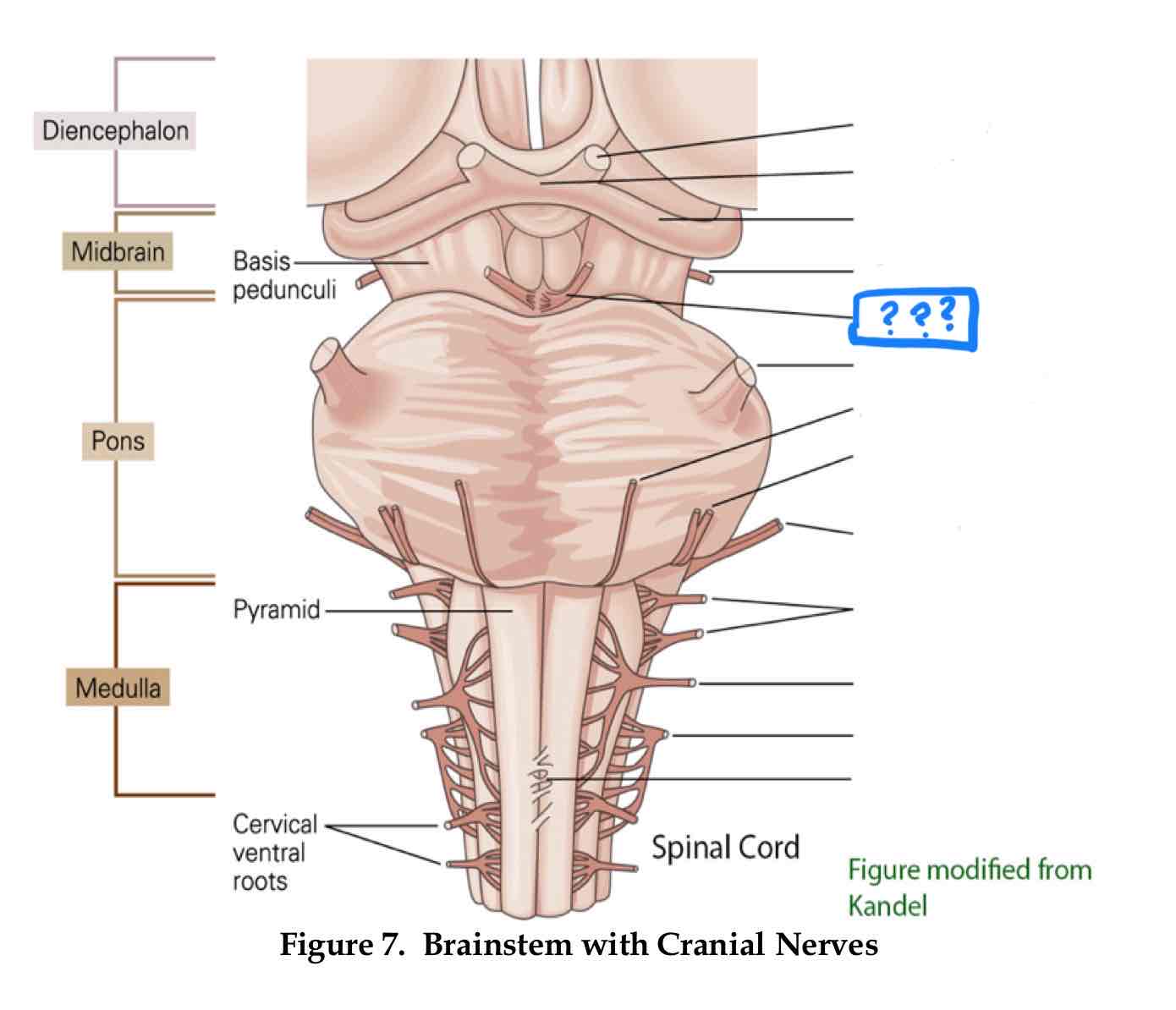
trochlear IV
eye movement (up and out movement)
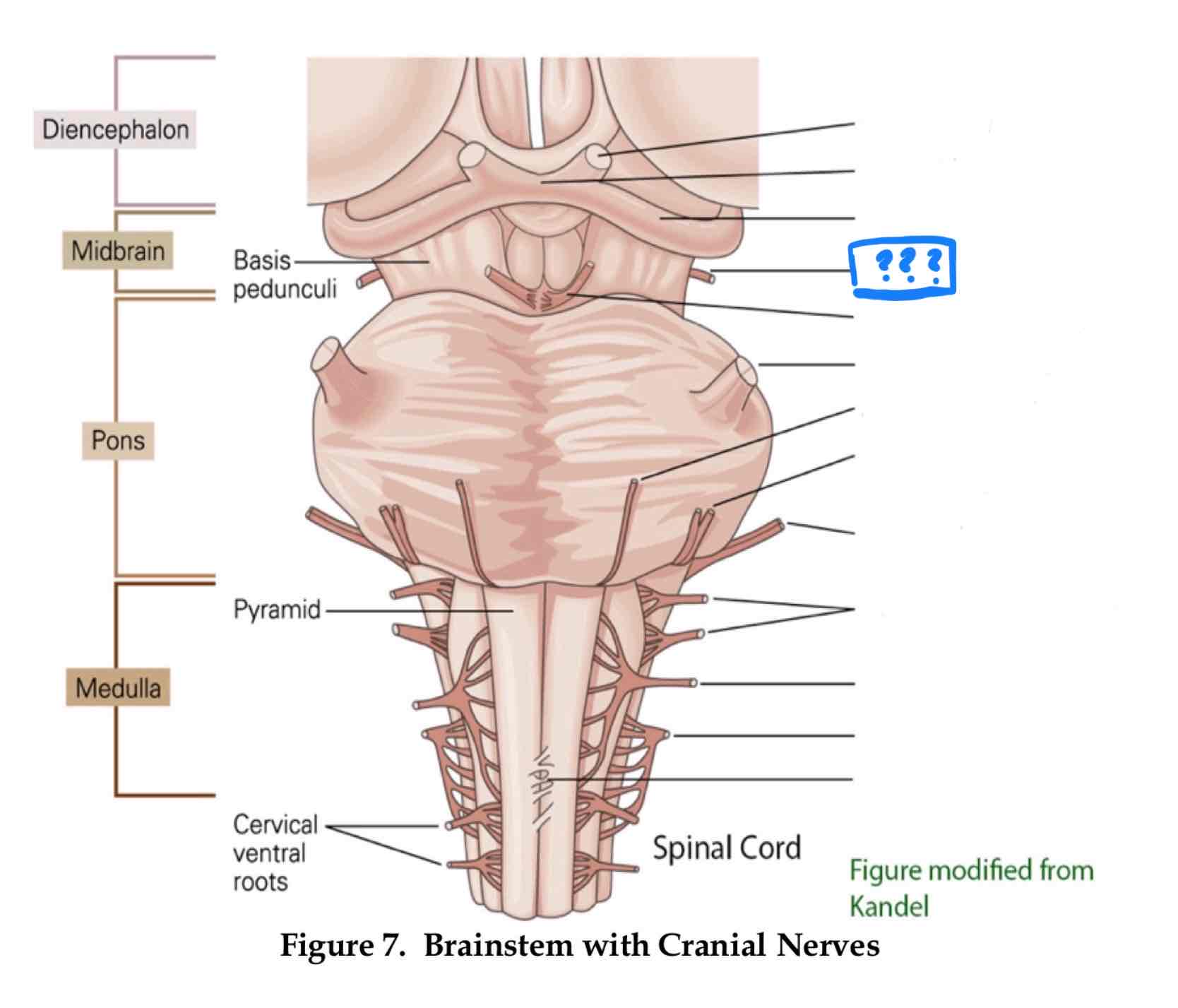
trigeminal V
transmission of oral pain/ control of chewing and biting
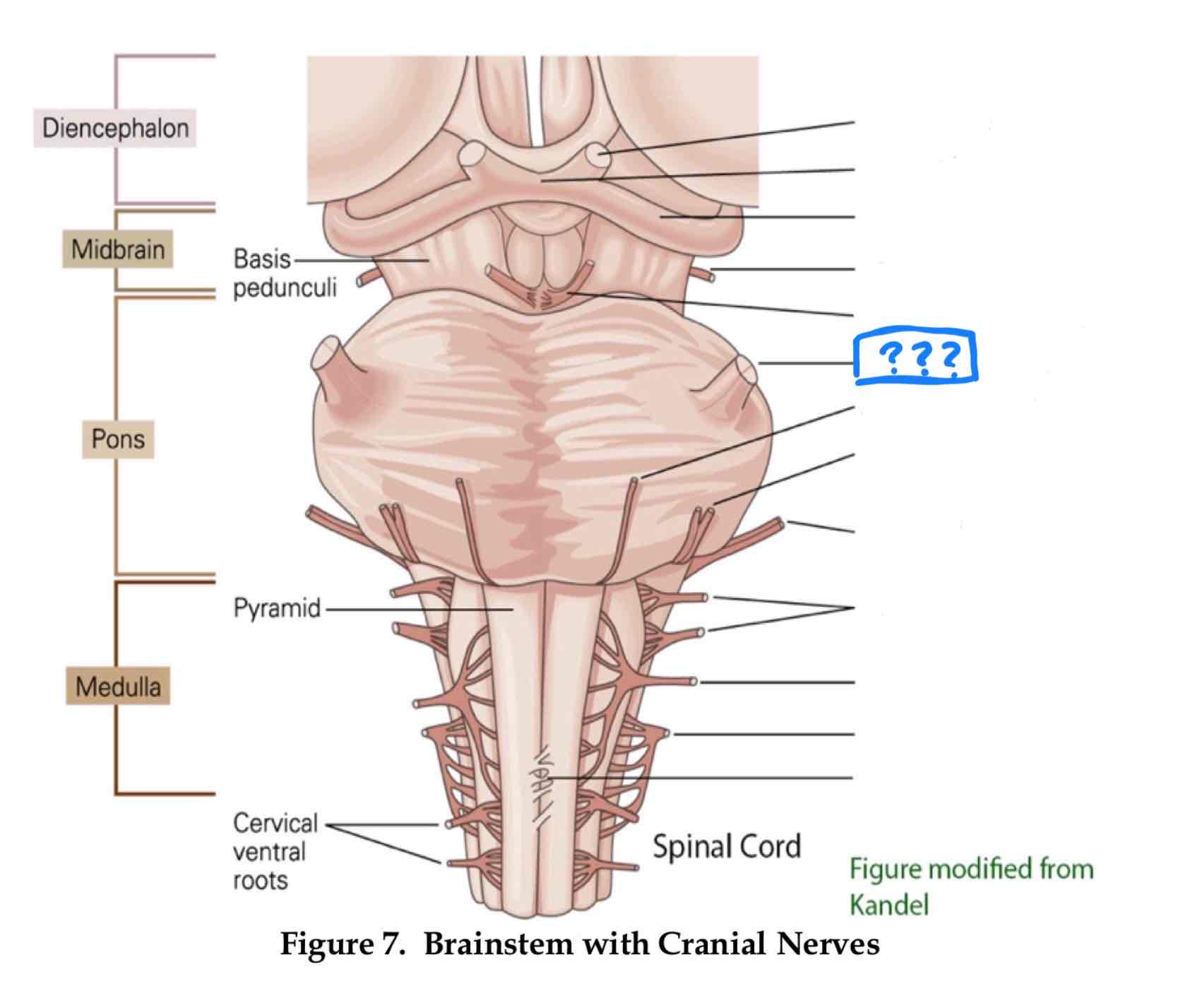
vestibulocochlear VIII
audition and vestibular balance functions
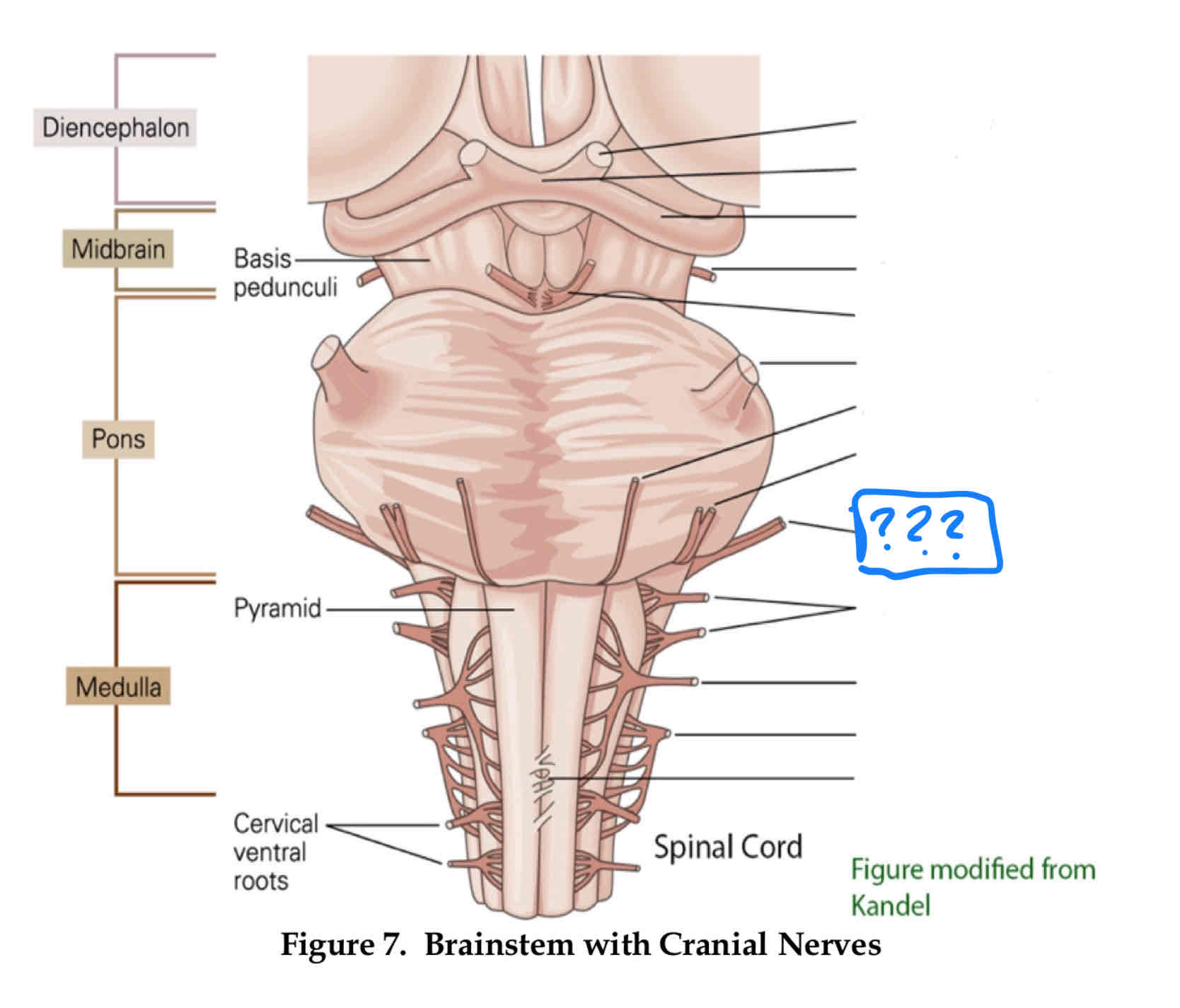
vagus X
sensation of visceral pain and the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract
dura mater
outter most layer
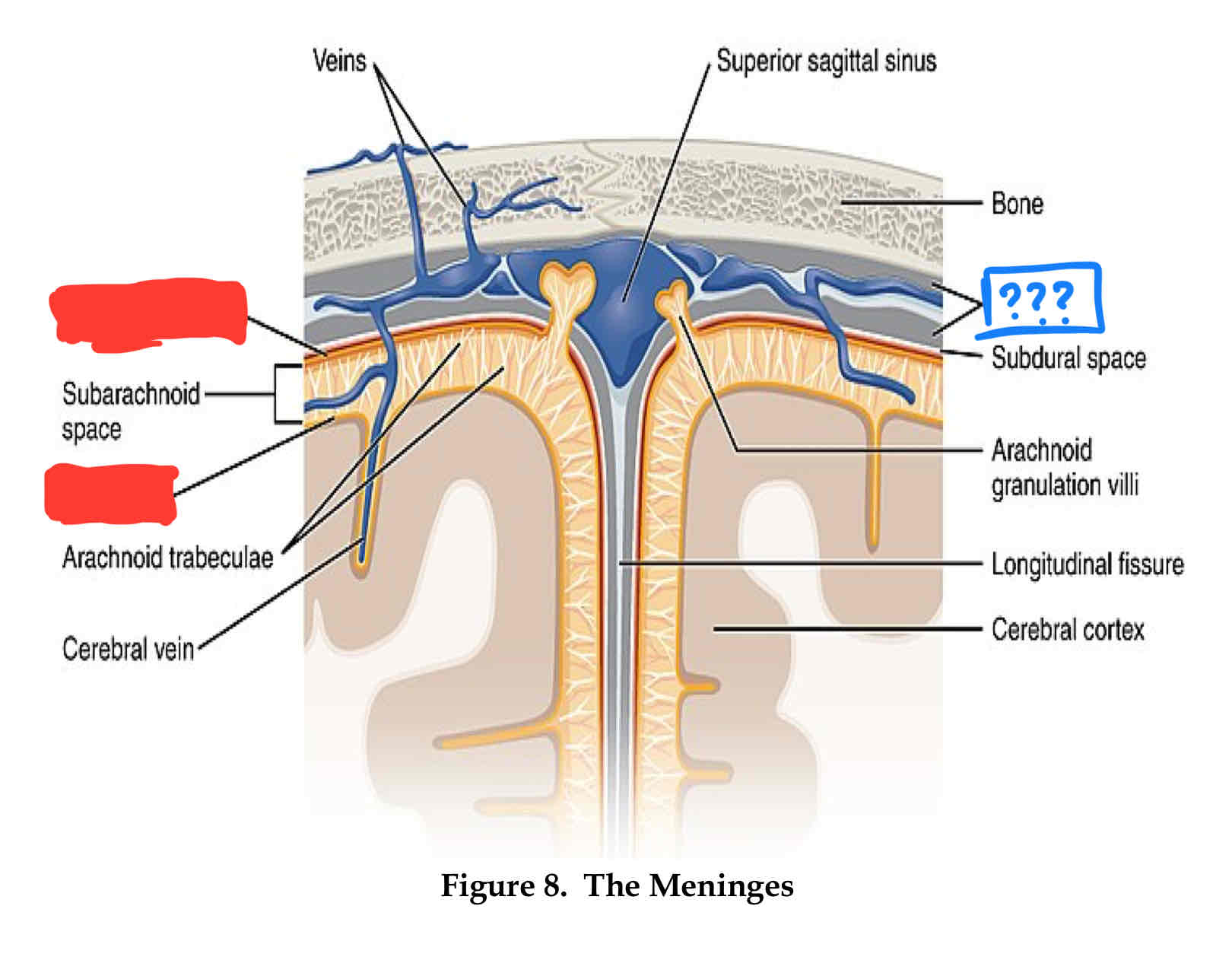
arachnoid layer
middle layer, csf flows between this layer and pia layers
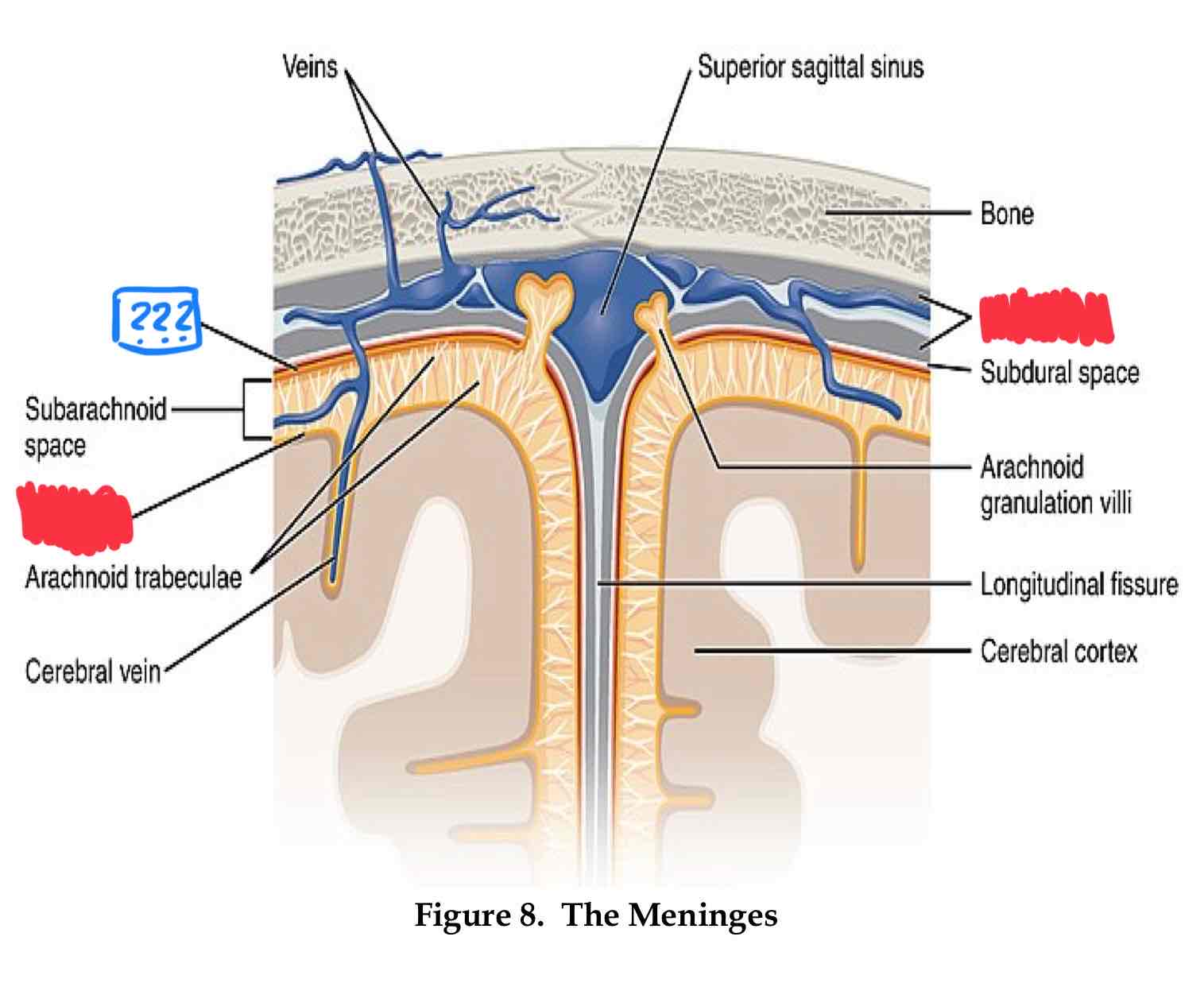
pia mater
inner most layer, follows sulci and gyri
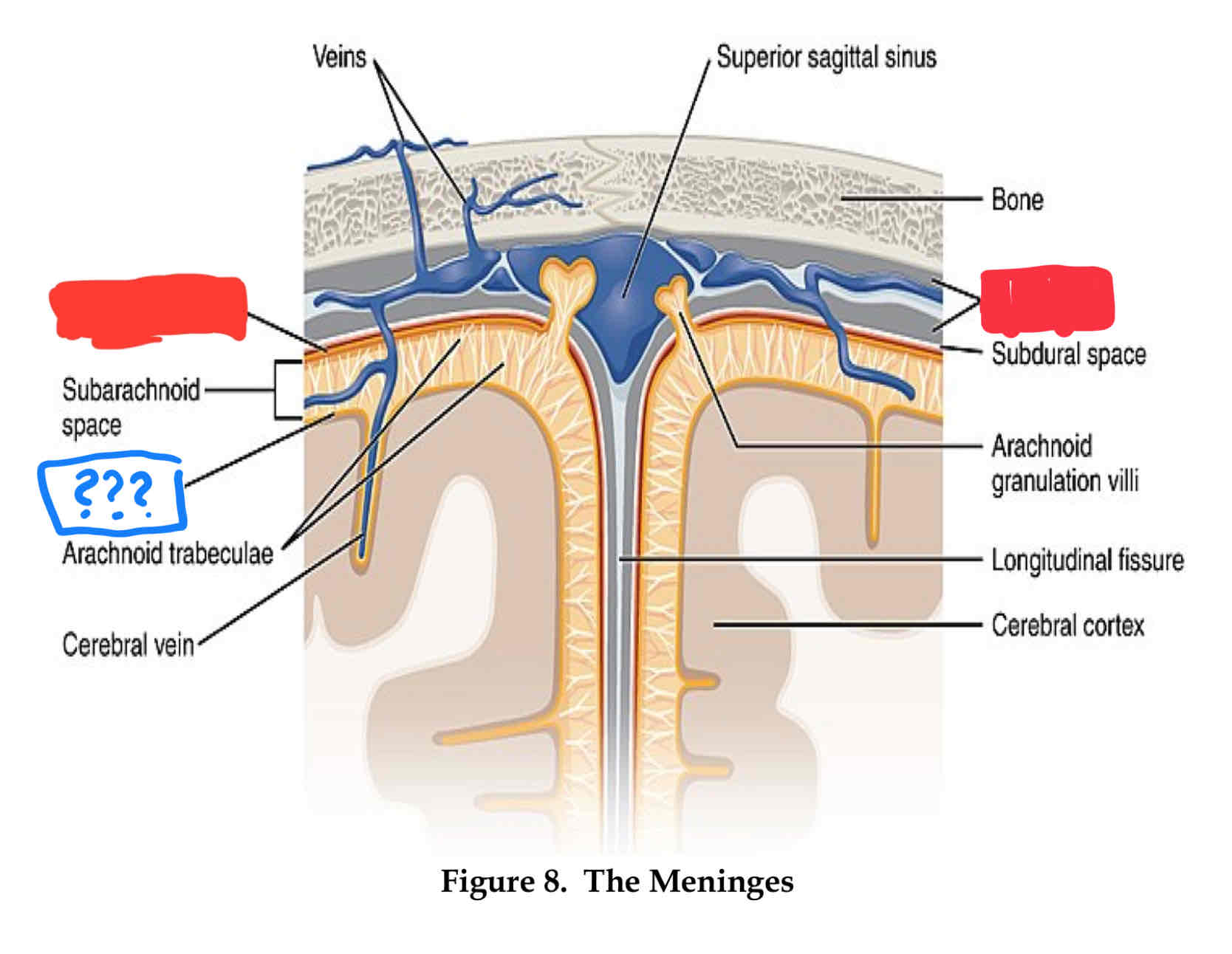
where does cerebrospinal fluid (csf) flow?
Subarachnoid space
lateral ventricle
side ventricle
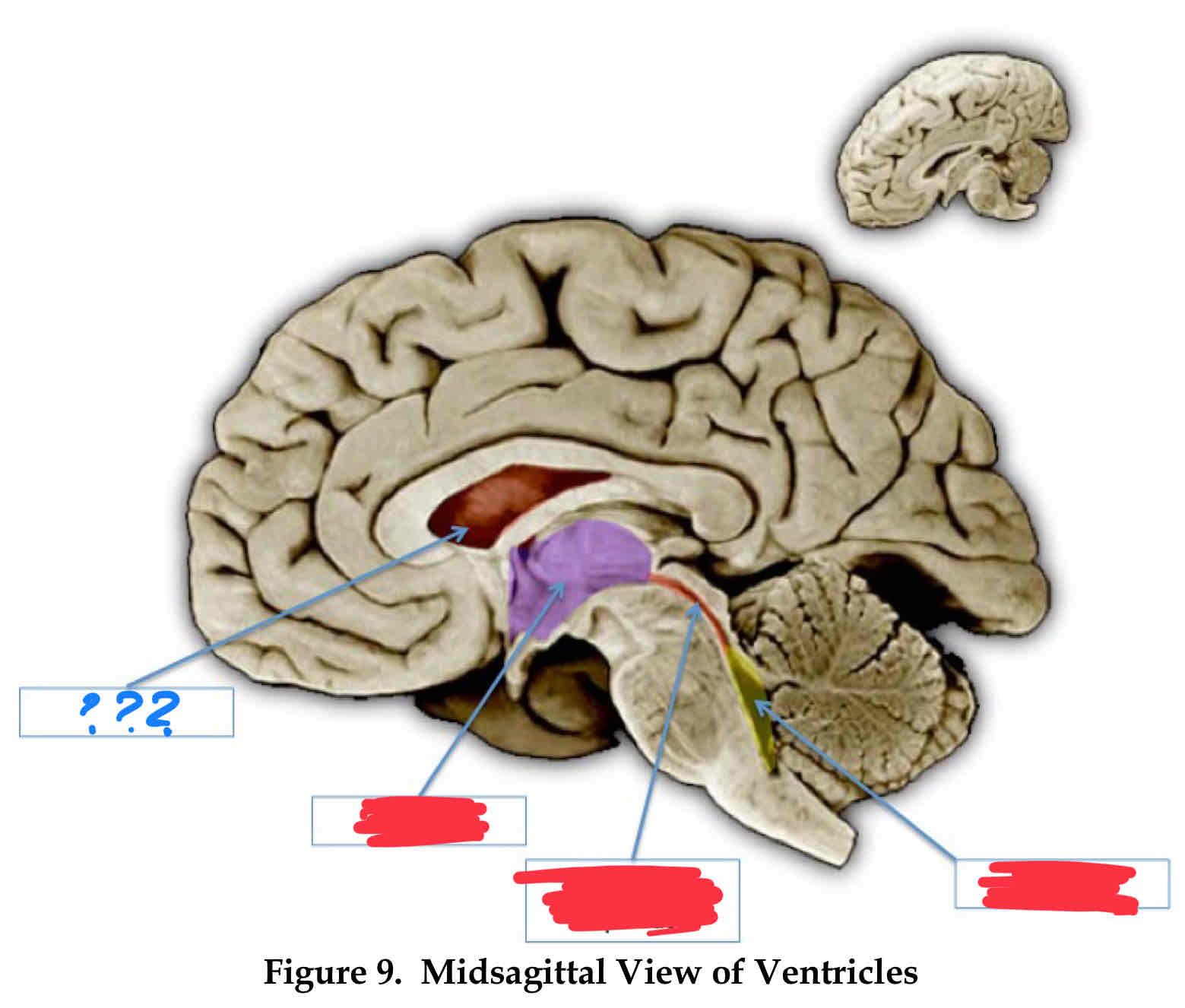
third ventricle (III)
central
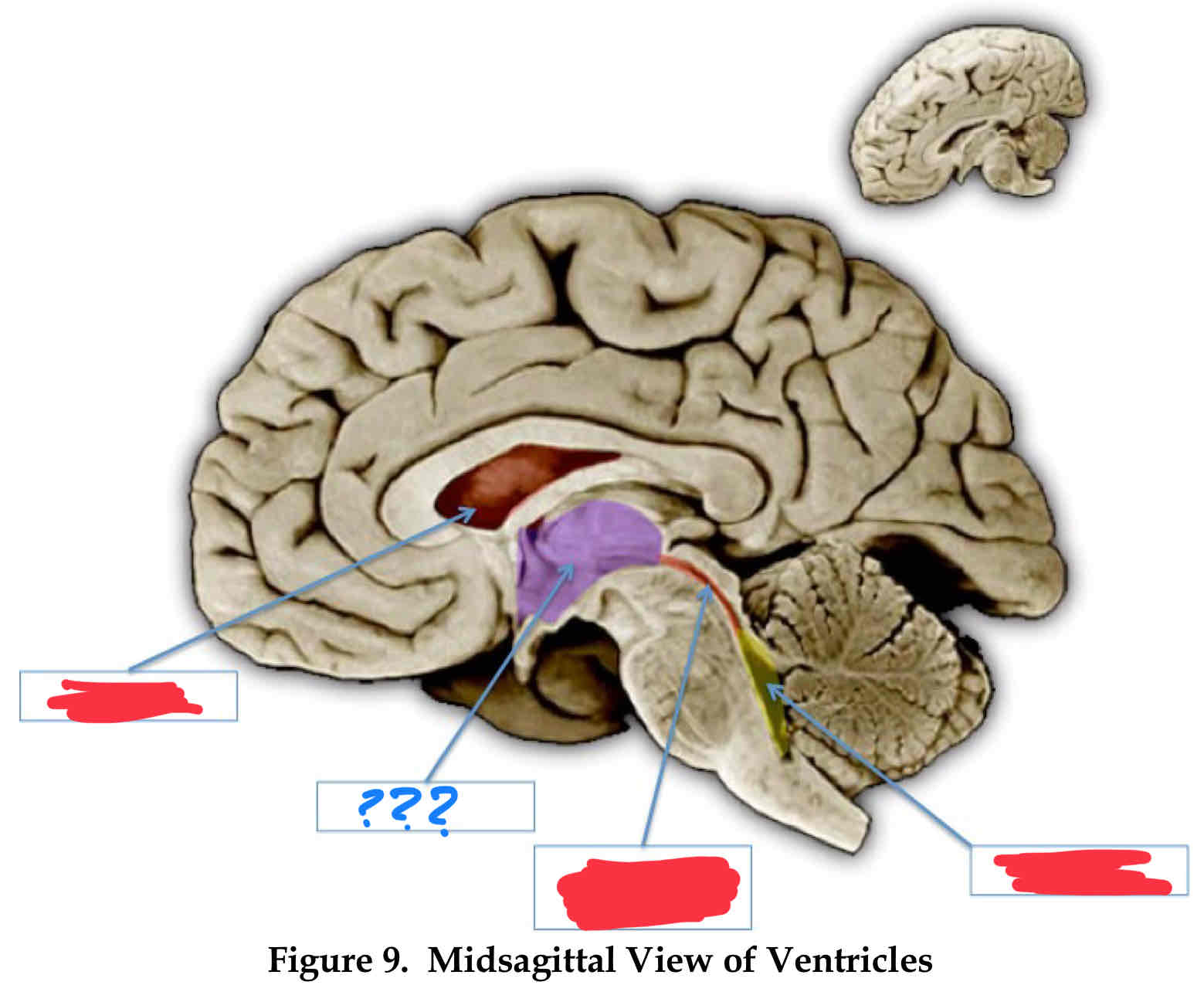
cerebral aqueduct
below third
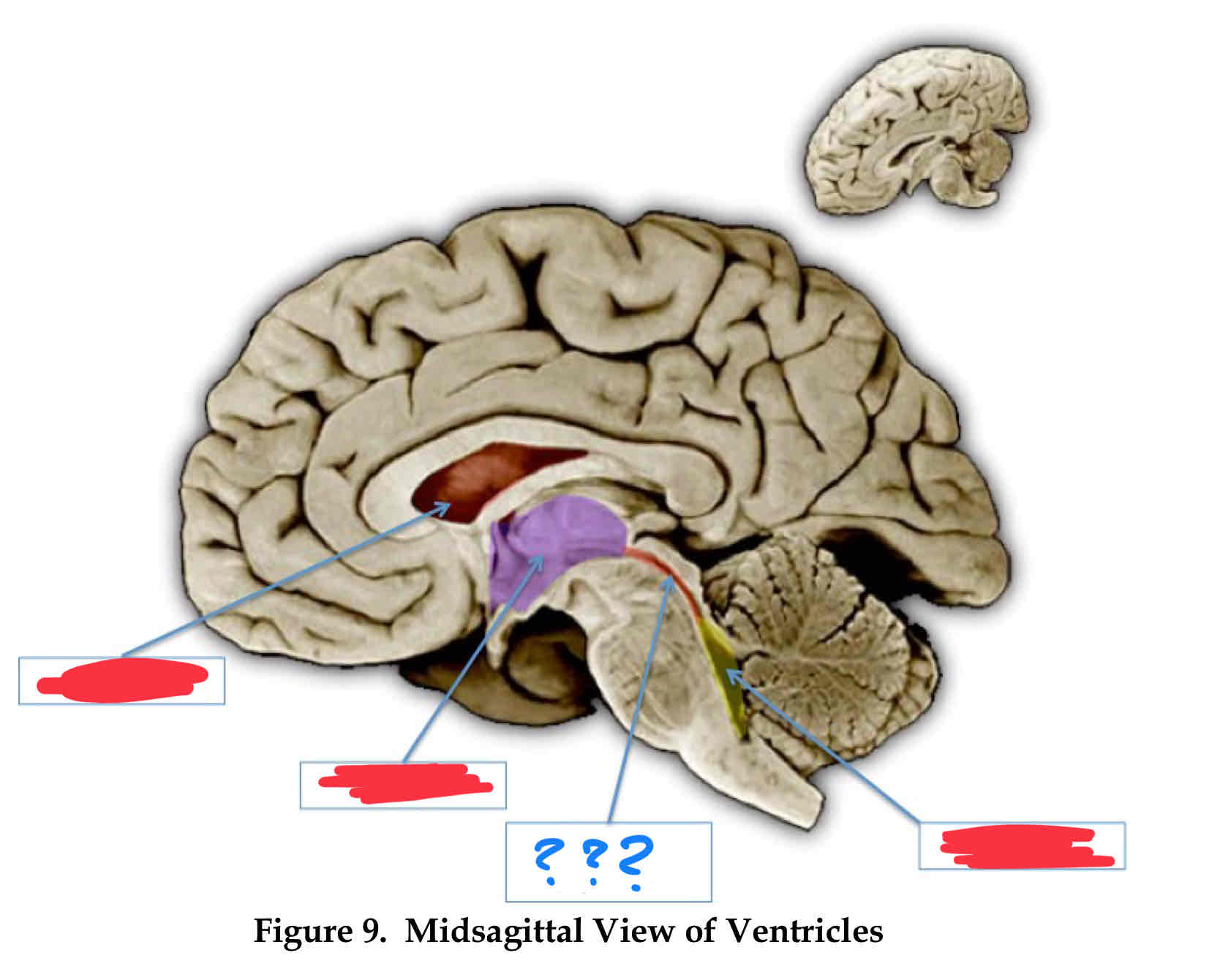
fourth ventricle
between the cerebellum and pons
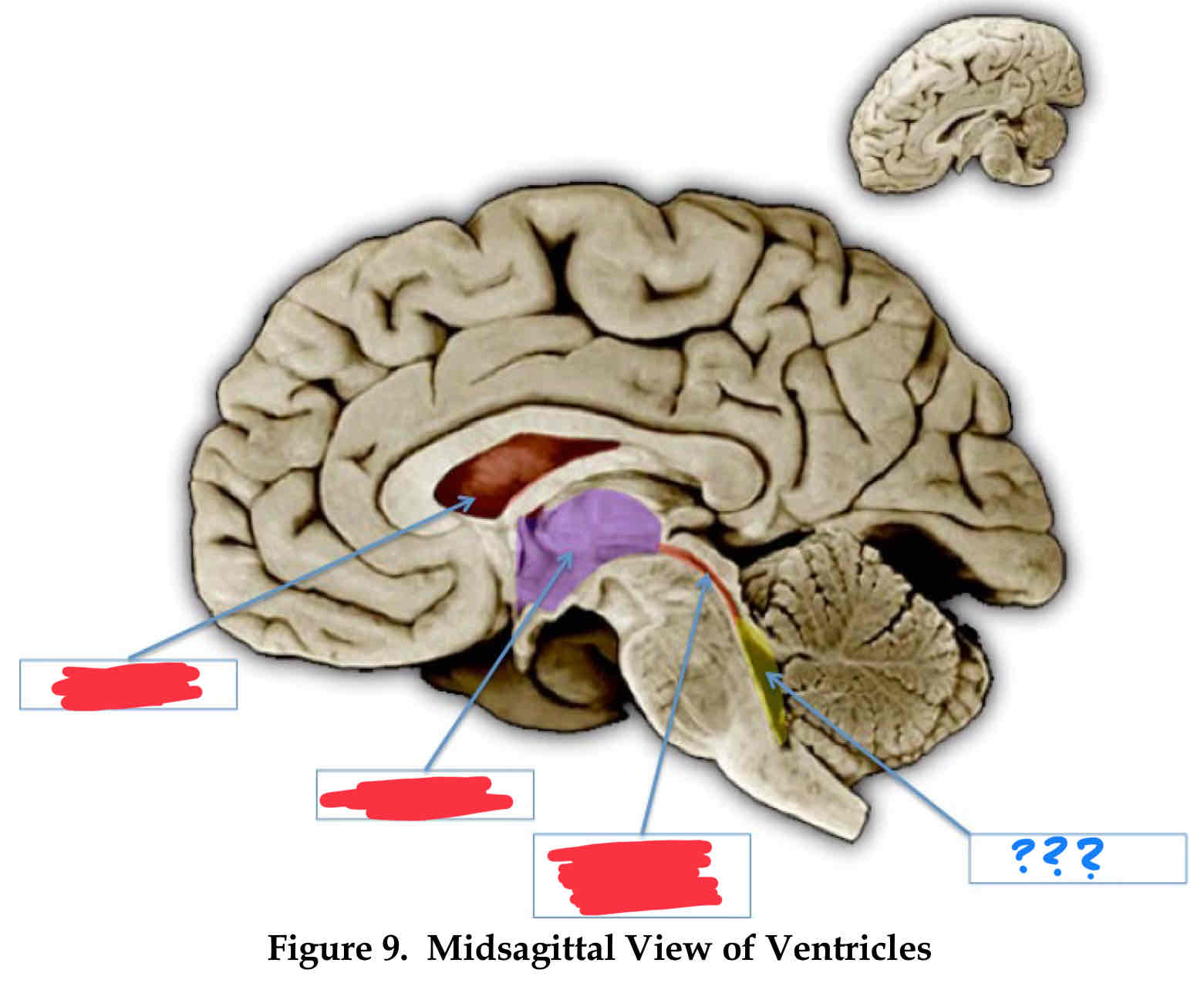
vertebral-basilar system
supplies blood to brainstem
internal carotid artery
supplies blood to the cortex and deep nuclei
anterior cerebral artery
supplies blood to the medial surface of the cerebral hemispheres
middle cerebral artery
supplies blood to the lateral cerebral hemispheres (mostly frontal, temporal, and parietal)
posterior cerebral artery
supplies blood to the midbrain and the inferior portion of the posterior cerebral hemispheres (occipital and temporal lobes)
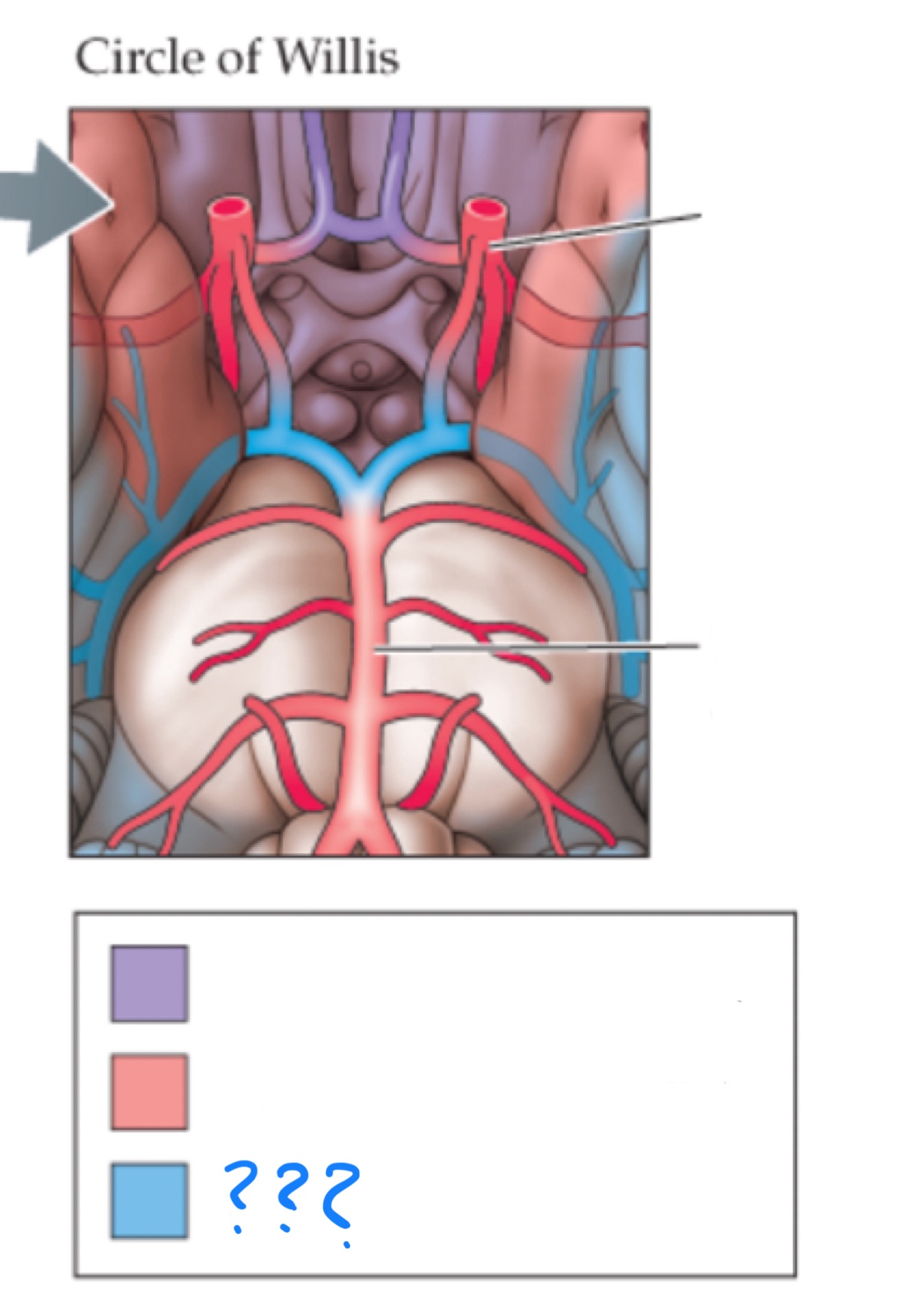
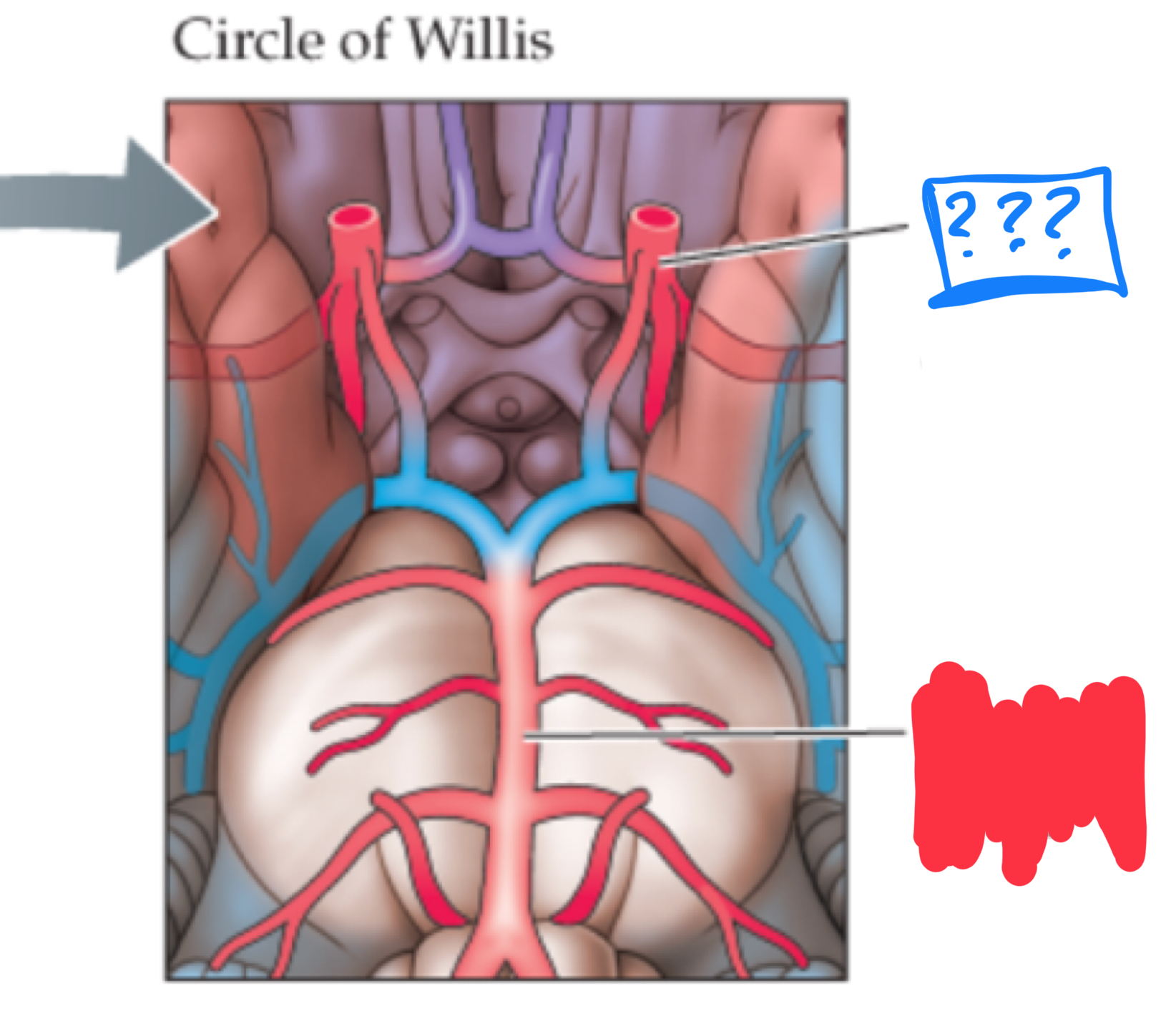
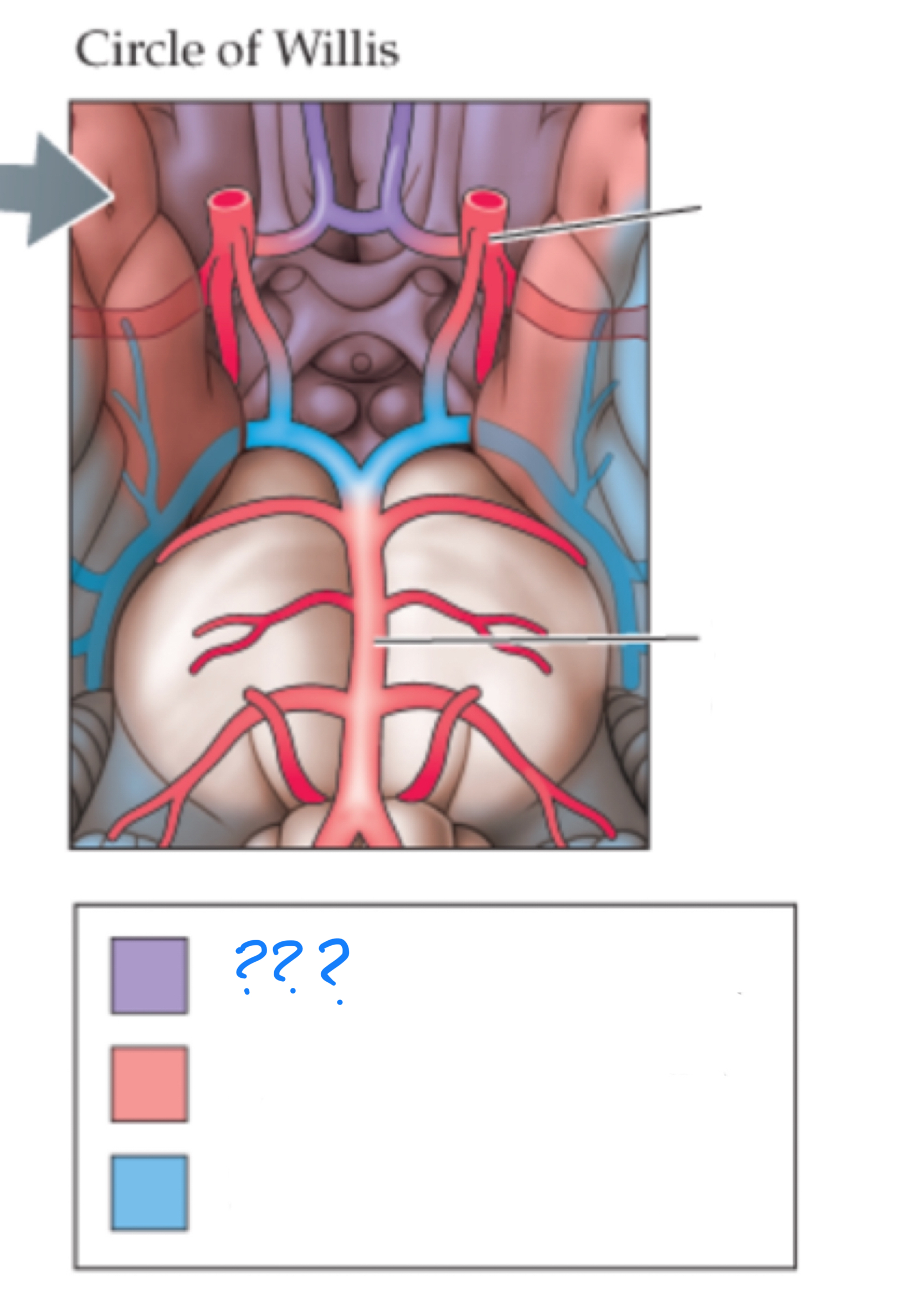
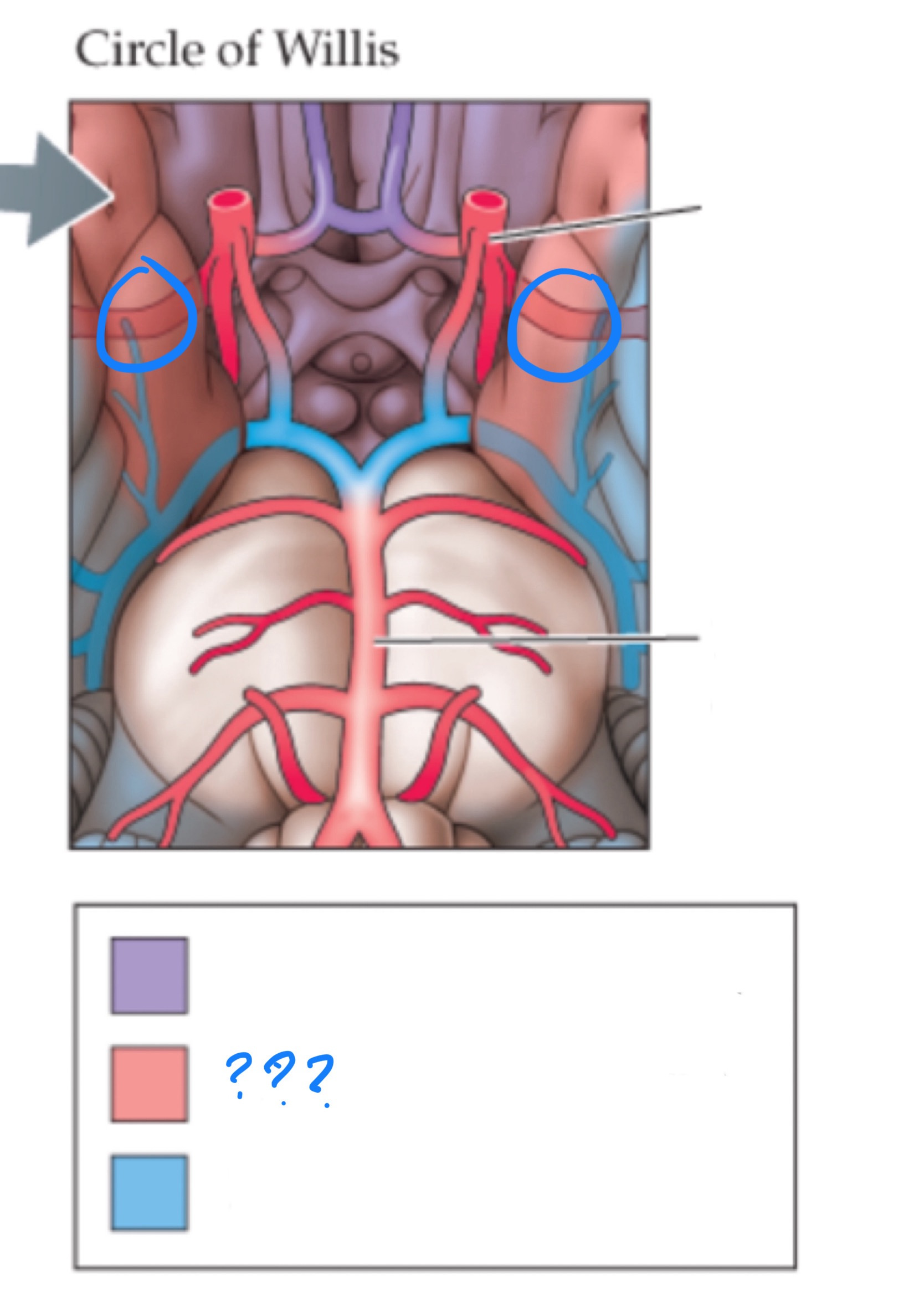
circle of willis
anastomosis of the anterior and posterior arterial systems
venous system
sends blood to be re-oxygenated by the lungs
glymphatic system
removes waste from the brain
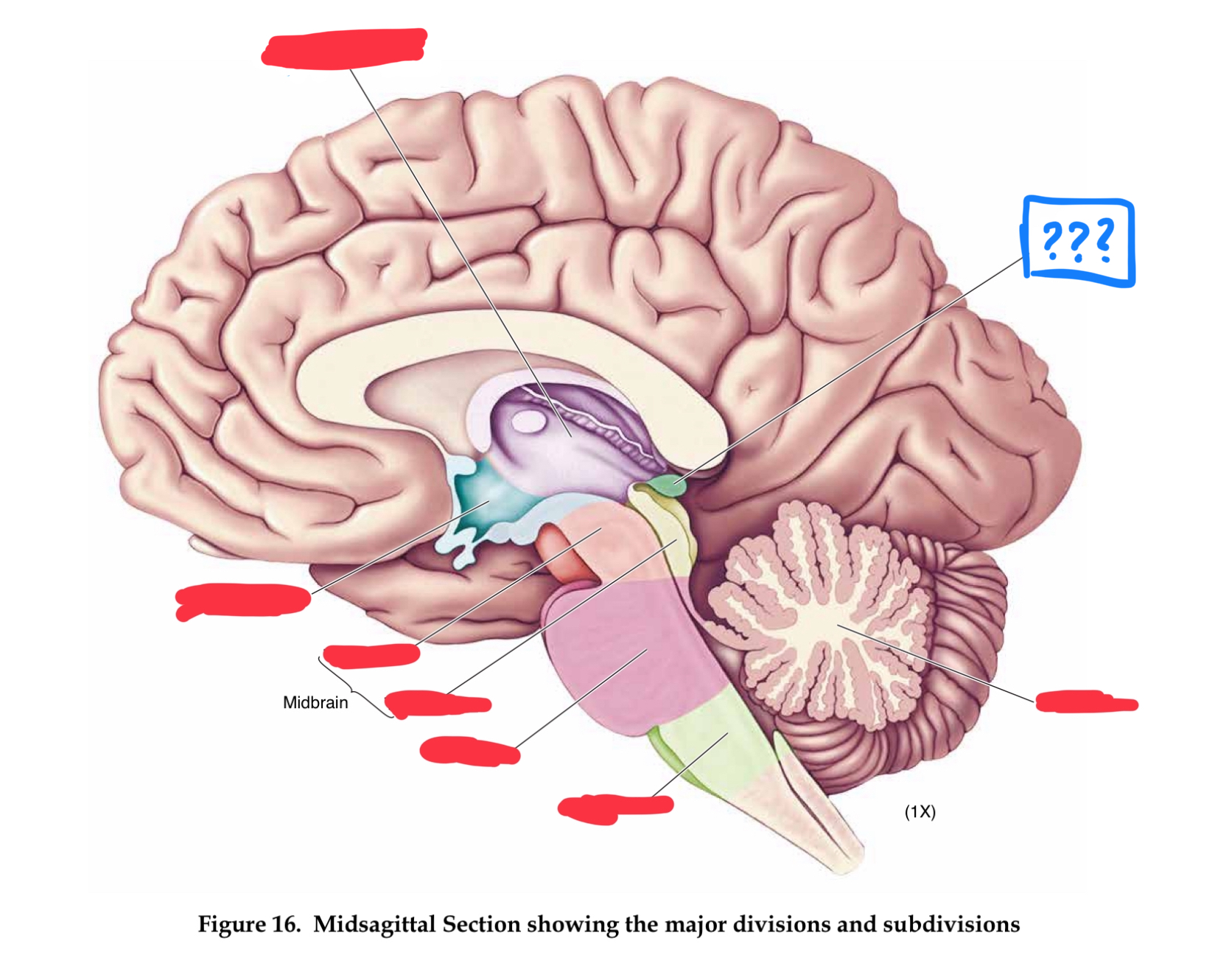
major divisions of the brain
hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain
Forebrain
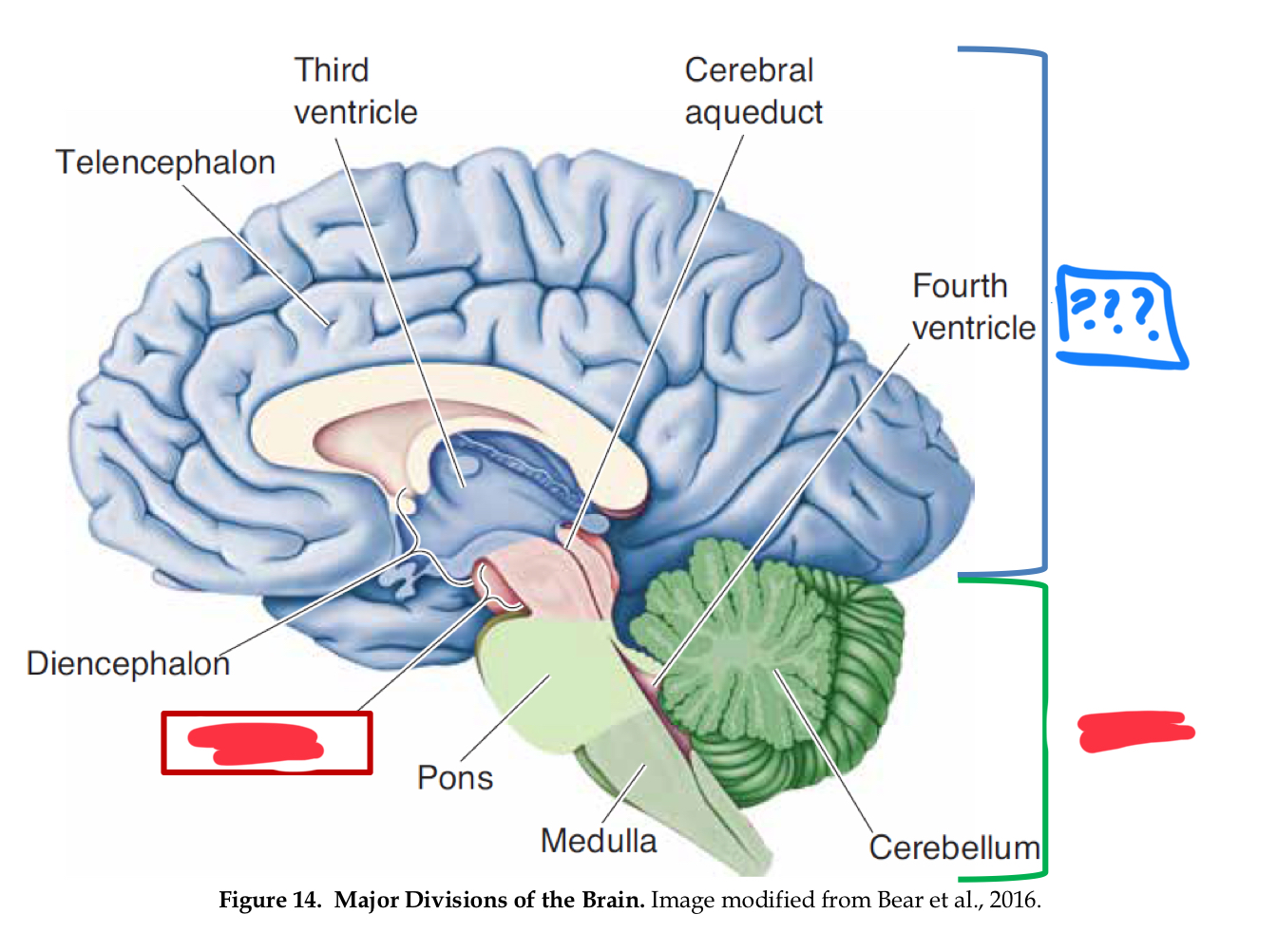
Midbrain
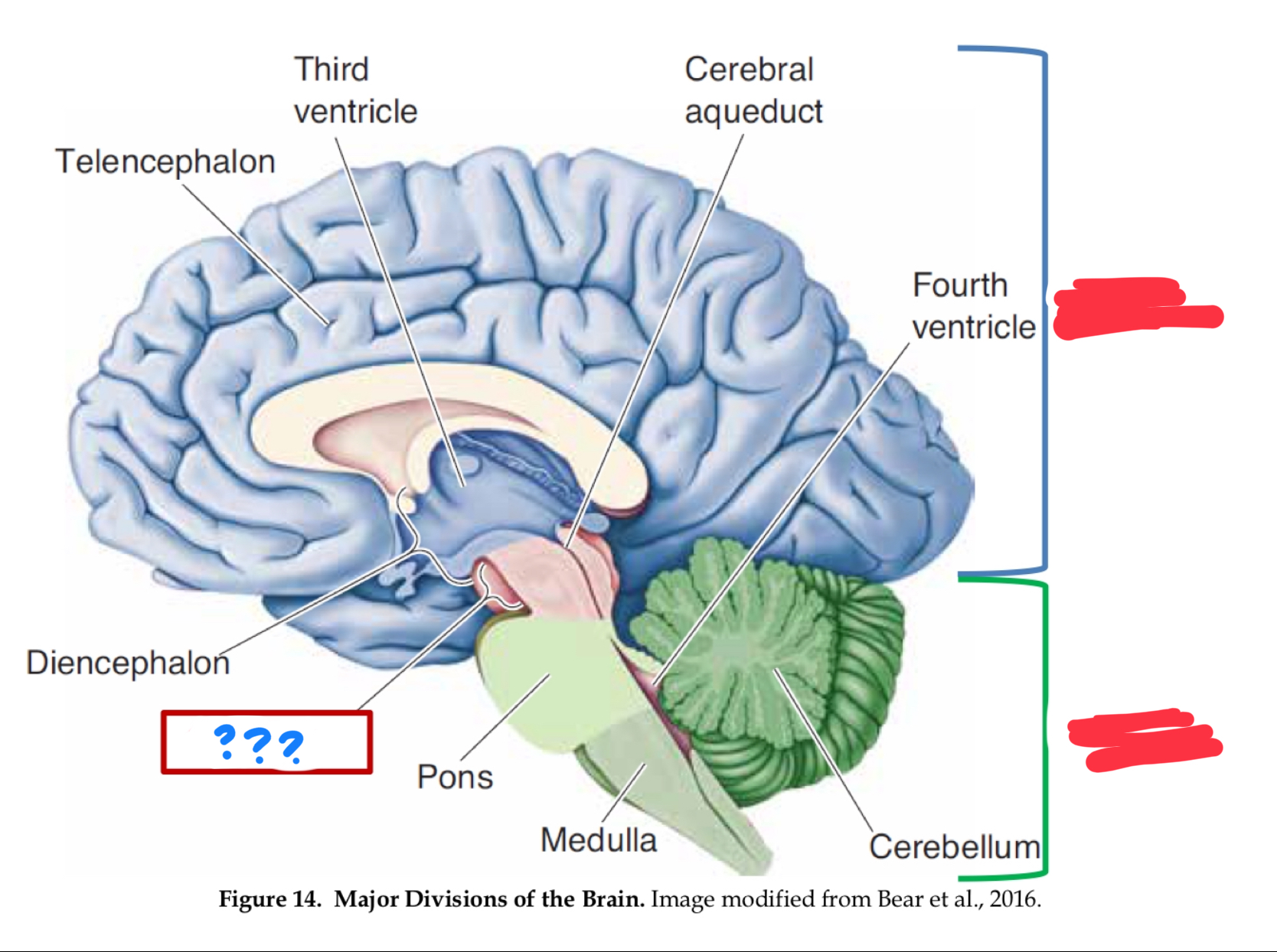
Hindbrain
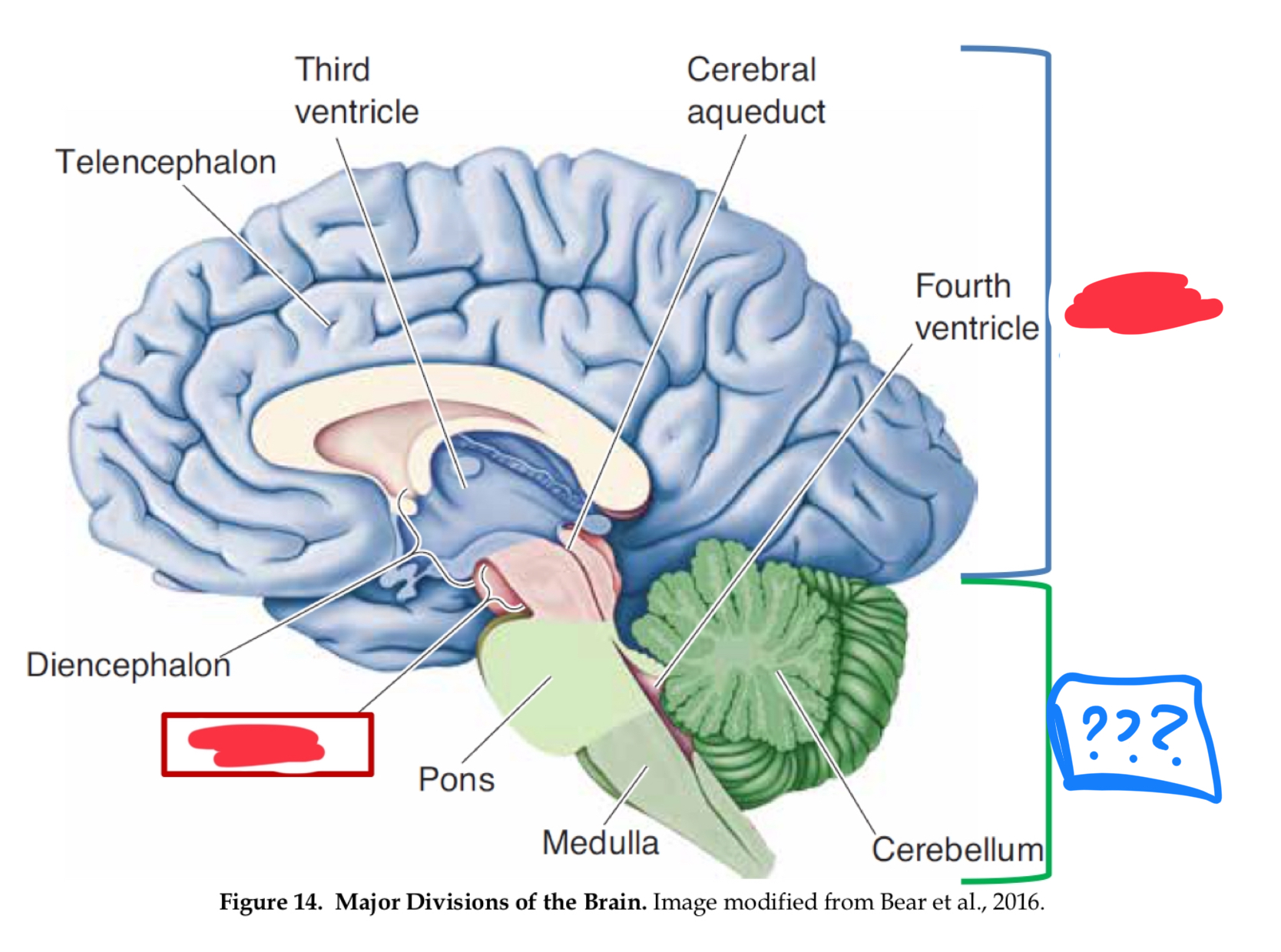
myelencephalon (mesencephalon also)
in hindbrain
medulla
control of vital functions such as respiration, heart regulation, and general muscle tone (in myencephalon)
medulla
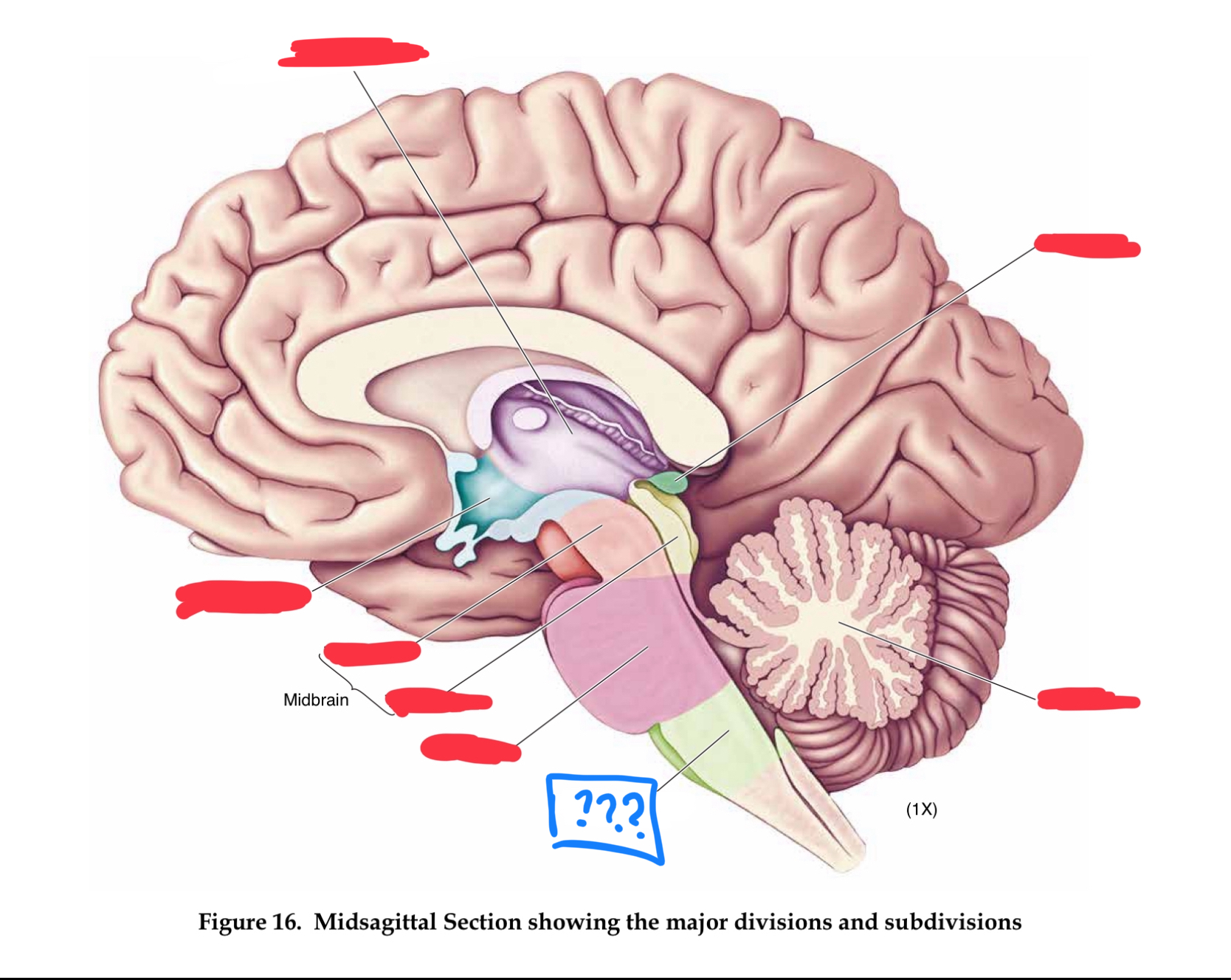
metencephalon
in hindbrain
pons
transmits information between cerebellum and rest of brain (in metencephalon)
cerebellum
regulates timing and coordination of complex muscle activity such as limb and eye movements, maintenance of muscle tone, and postural balance. Also involved in classical conditioning of some motor responses (eg conditioned eye blink response) (in metencephalon)
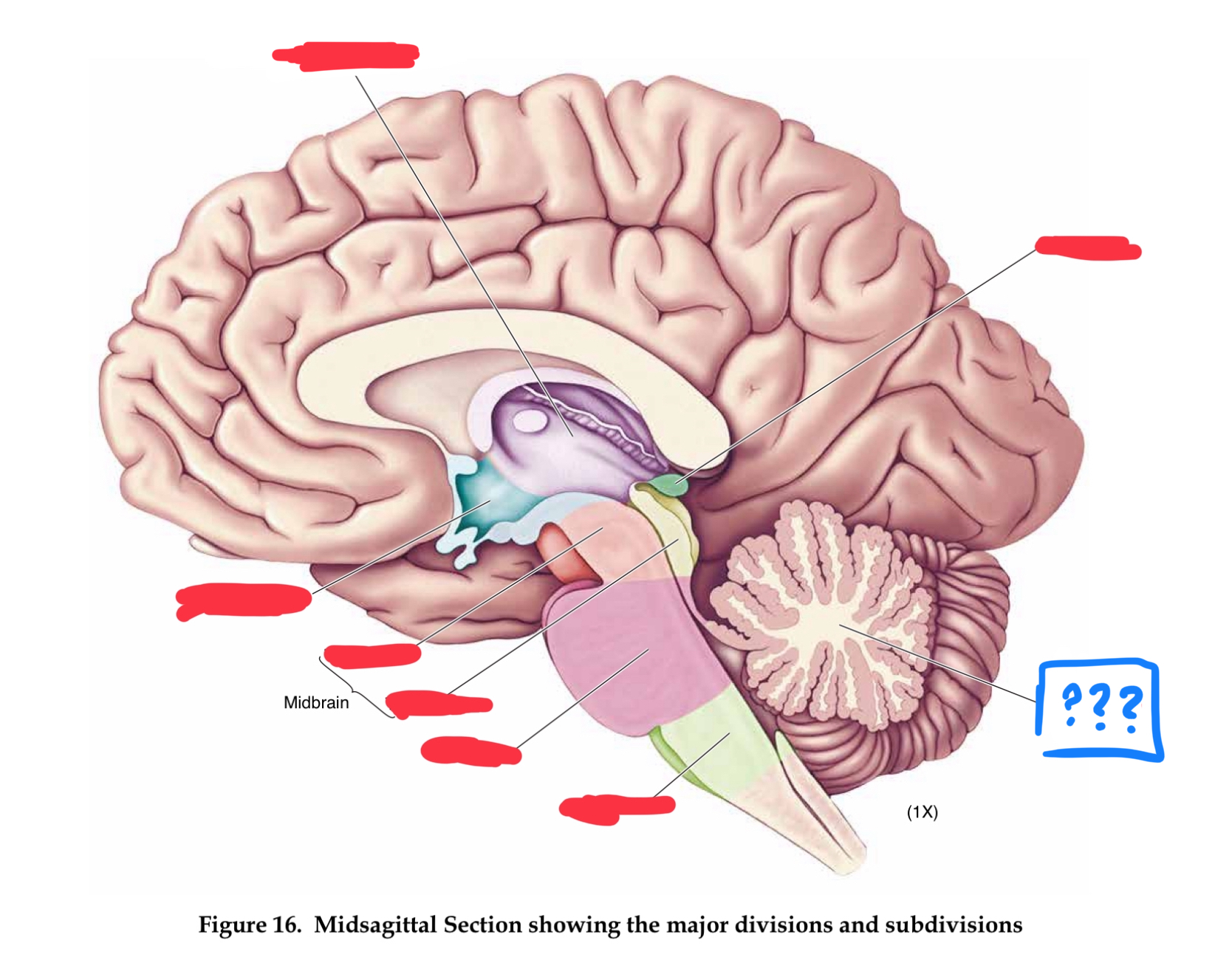
mesencephalon
midbrain
tectum
roof of midbrain cerebral aqueduct, contain superior and inferior colliculi (in mesencephalon)
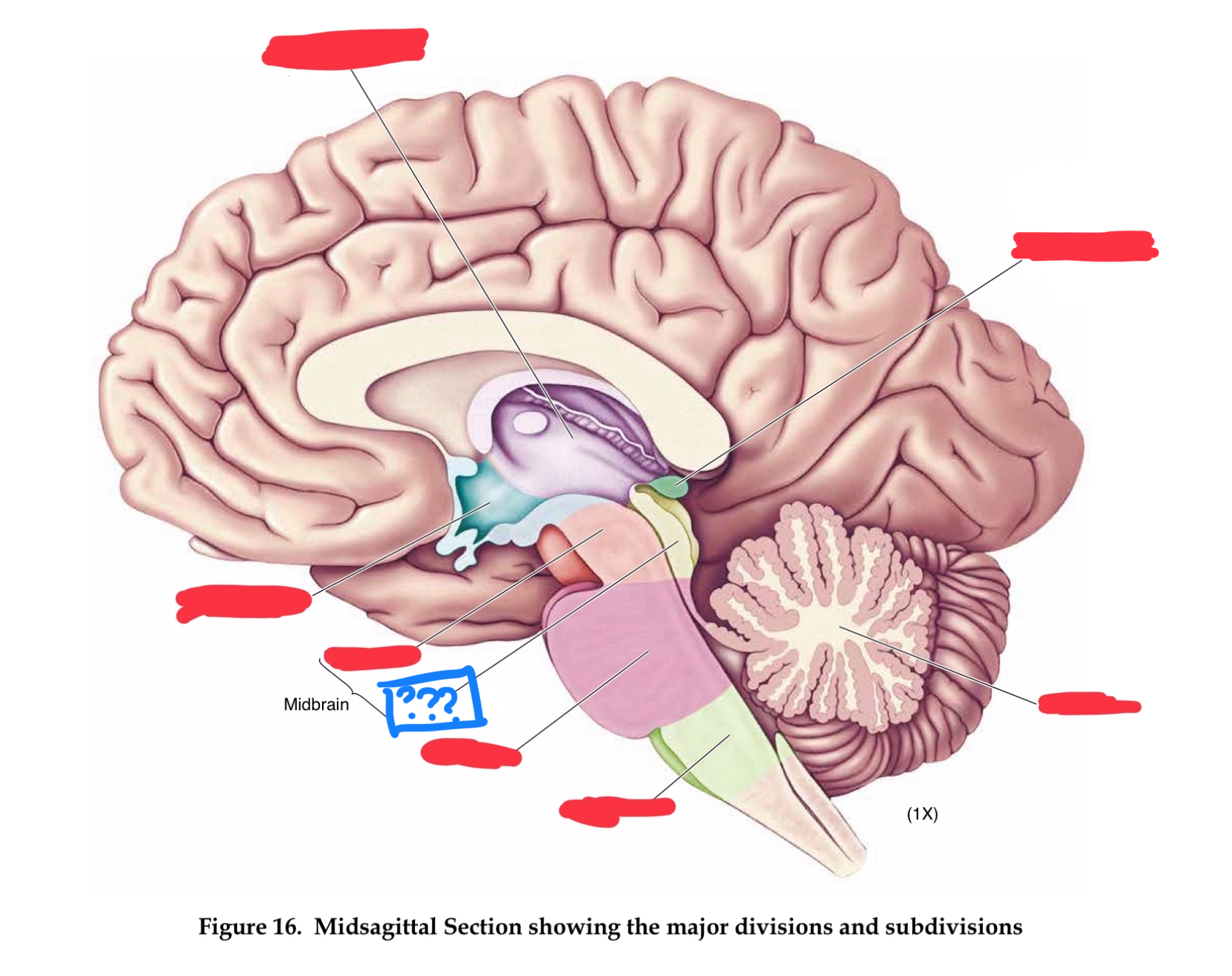
superior colliculus
controls orientation of head and eyes toward visual stimuli (in tectum)
inferior colliculus
relays auditory information from the brainstem to the thalamus (in tectum)
tegmentum
contains cell bodies for dopaminergic projections to the basal ganglia and the frontal lobe (in mesencephalon)
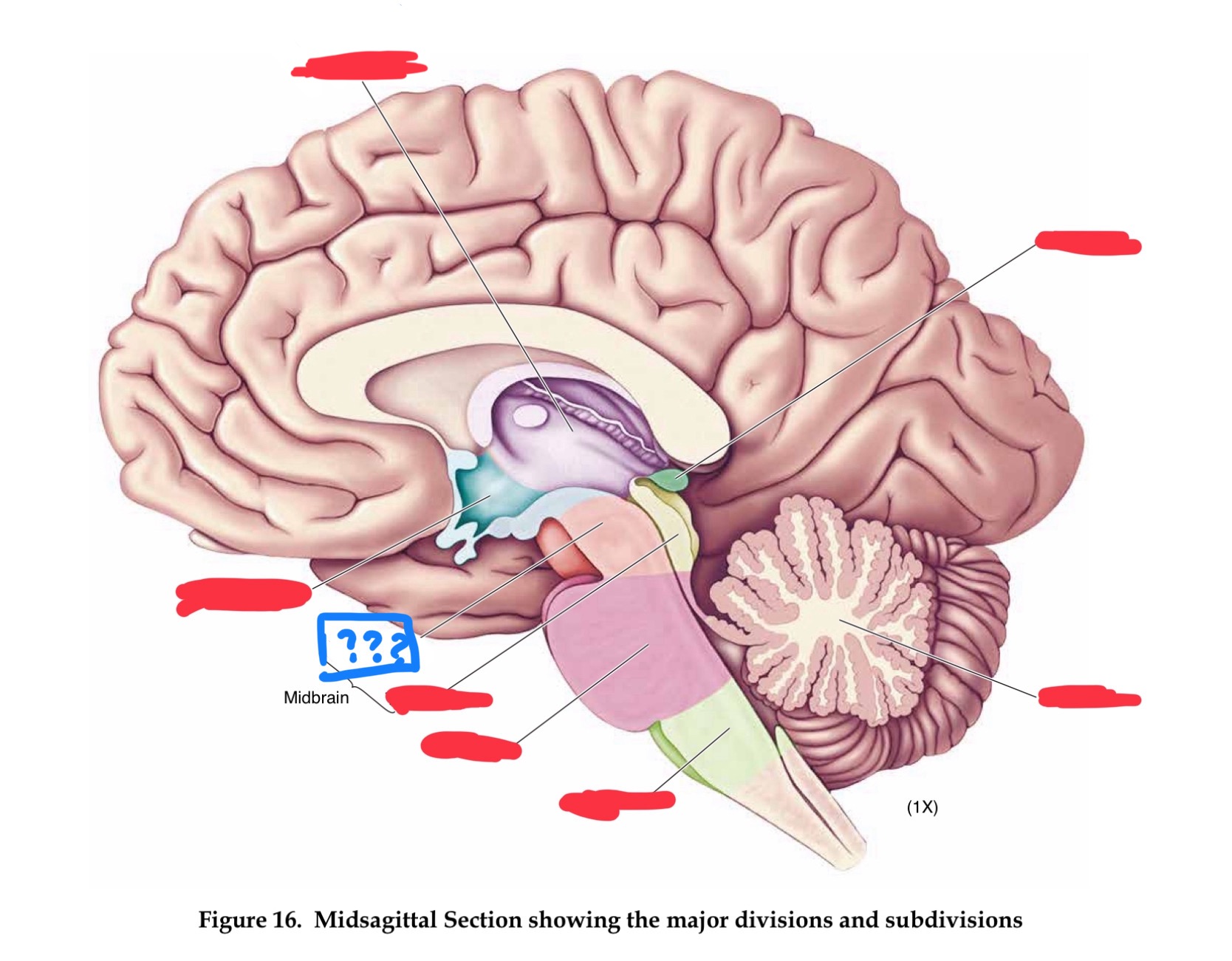
cerebral peduncles
in mesencephalon
diencephalon
part of forebrain
thalamus
responsible for relaying information between the cerebral cortex and the rest of the brain (in diencephalon)
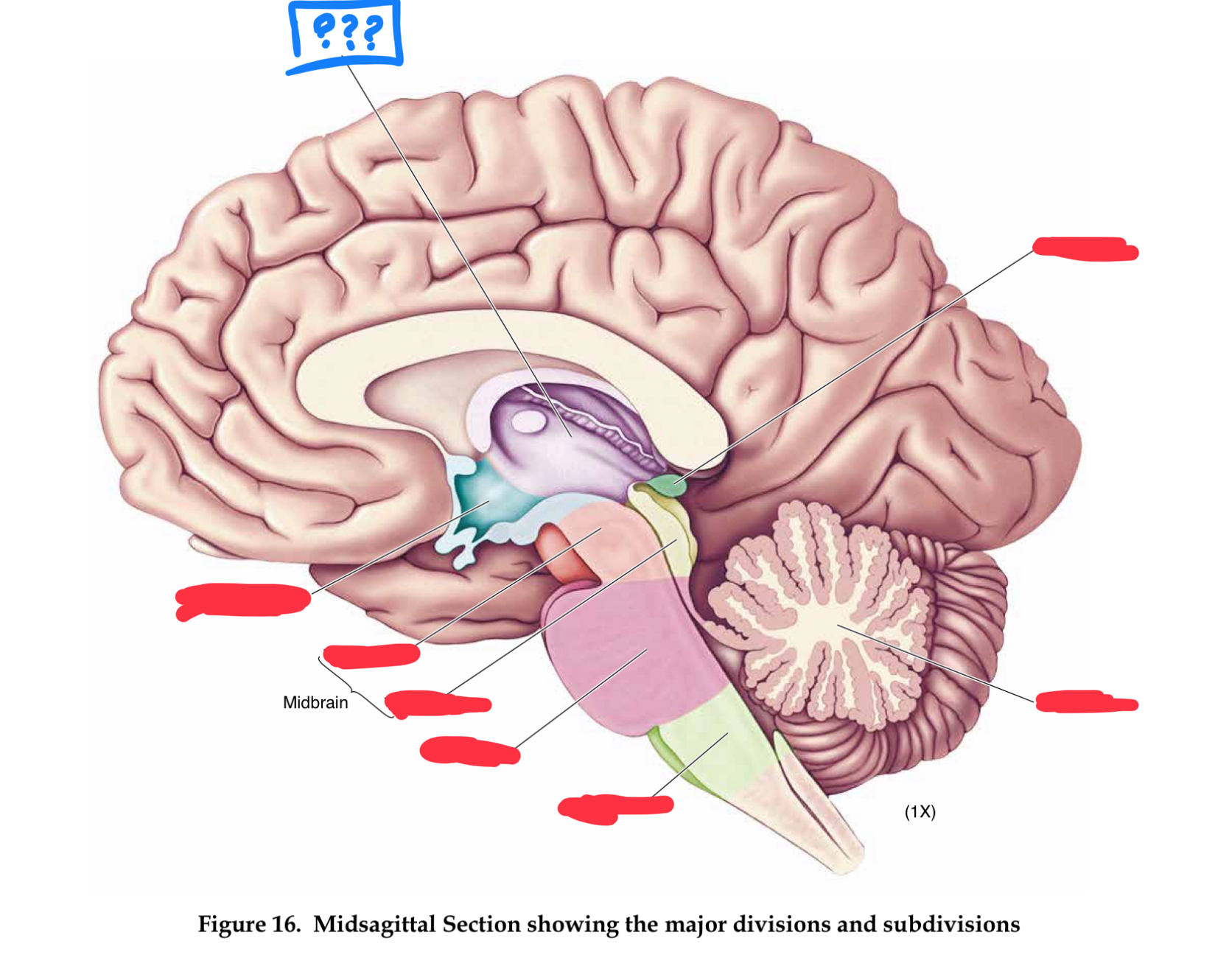
pons
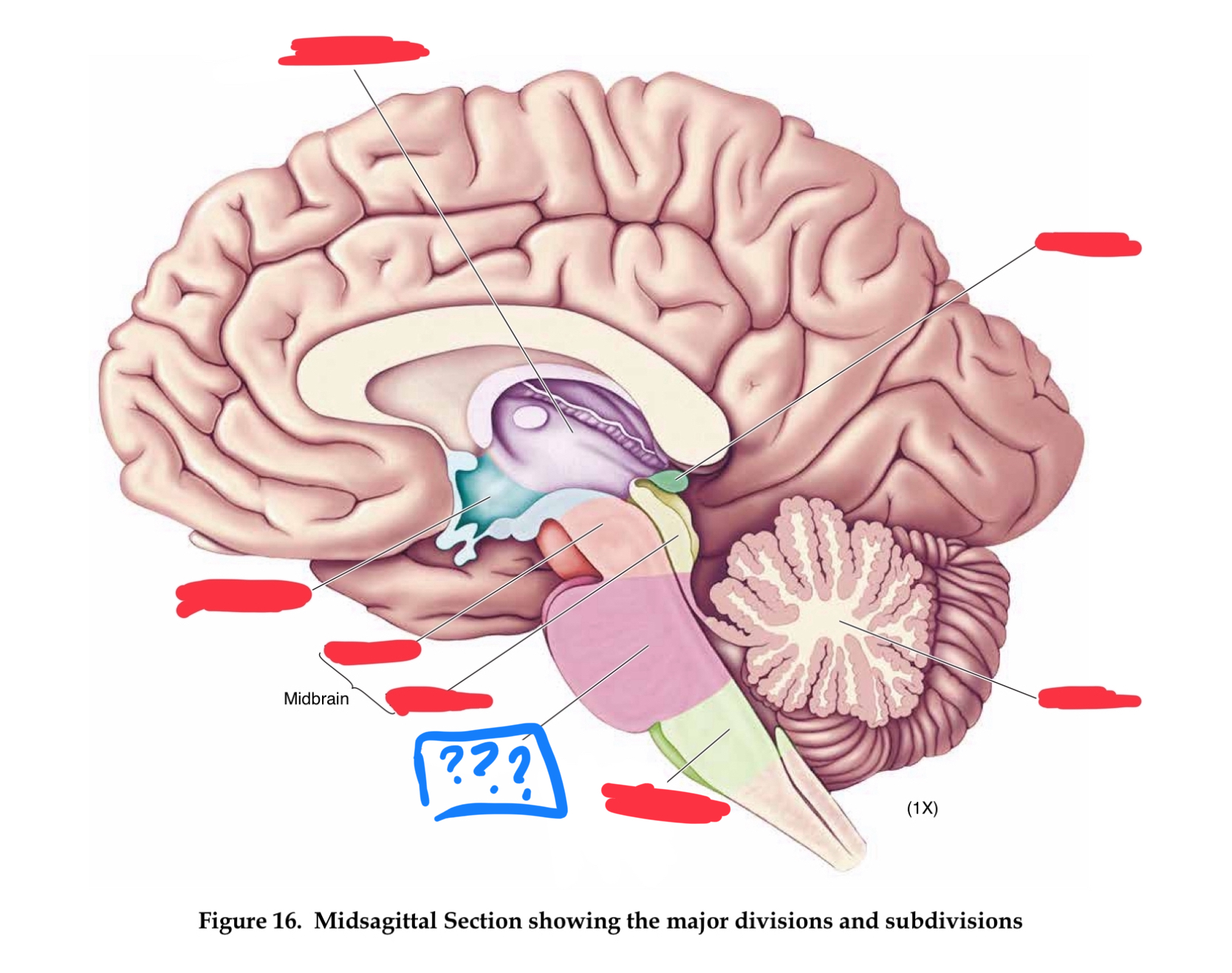
hypothalamus
maintaining homeostasis through regulation of the four Fs: feeding, fighting, fleeing, and fornication (in diencephalon)
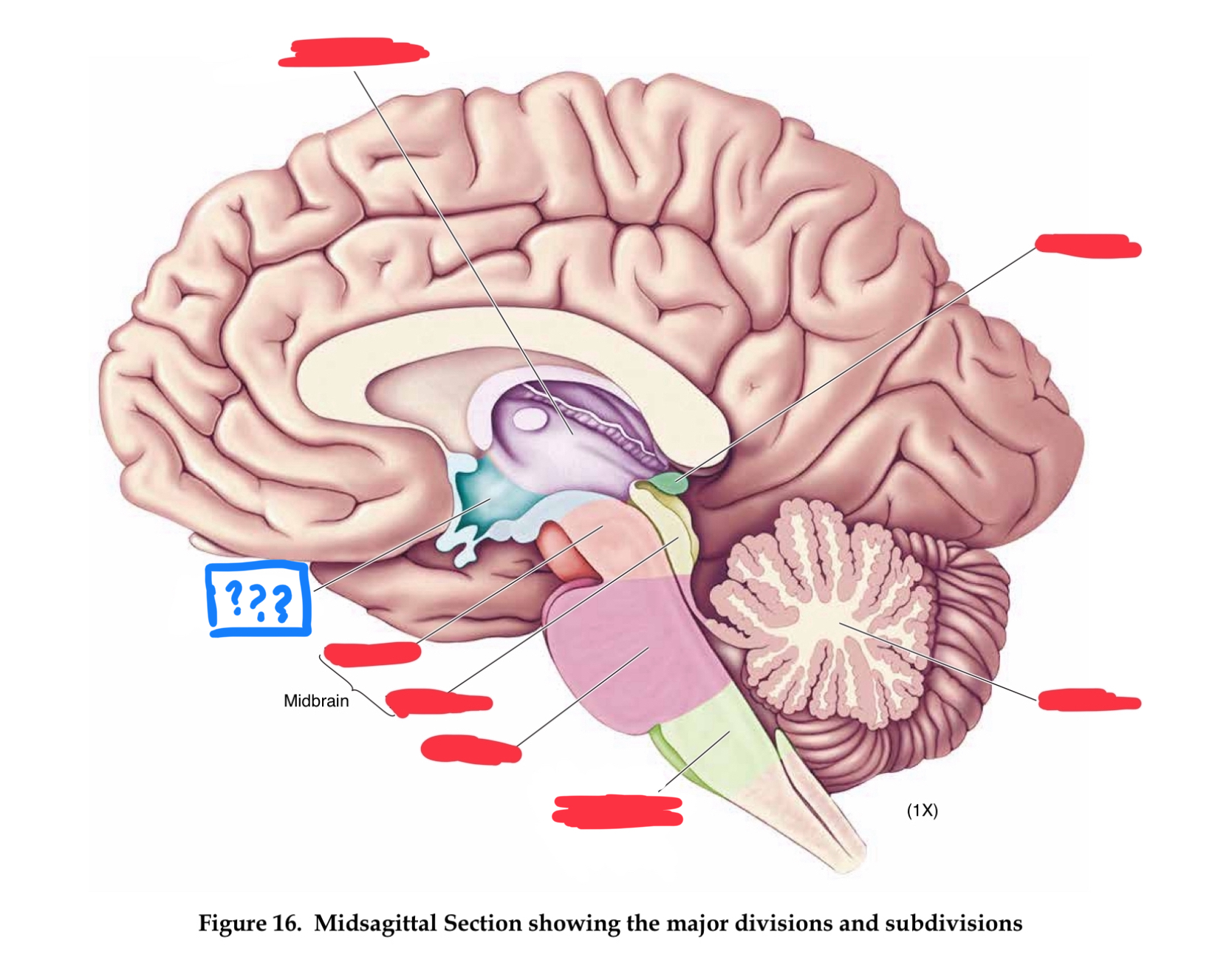
mammilary bodies
receives input from hippocampus and amygdala, implicated in memory (in diencephalon)
infundibulum
pituitary gland
contains posterior and anterior portions (in diencephalon)
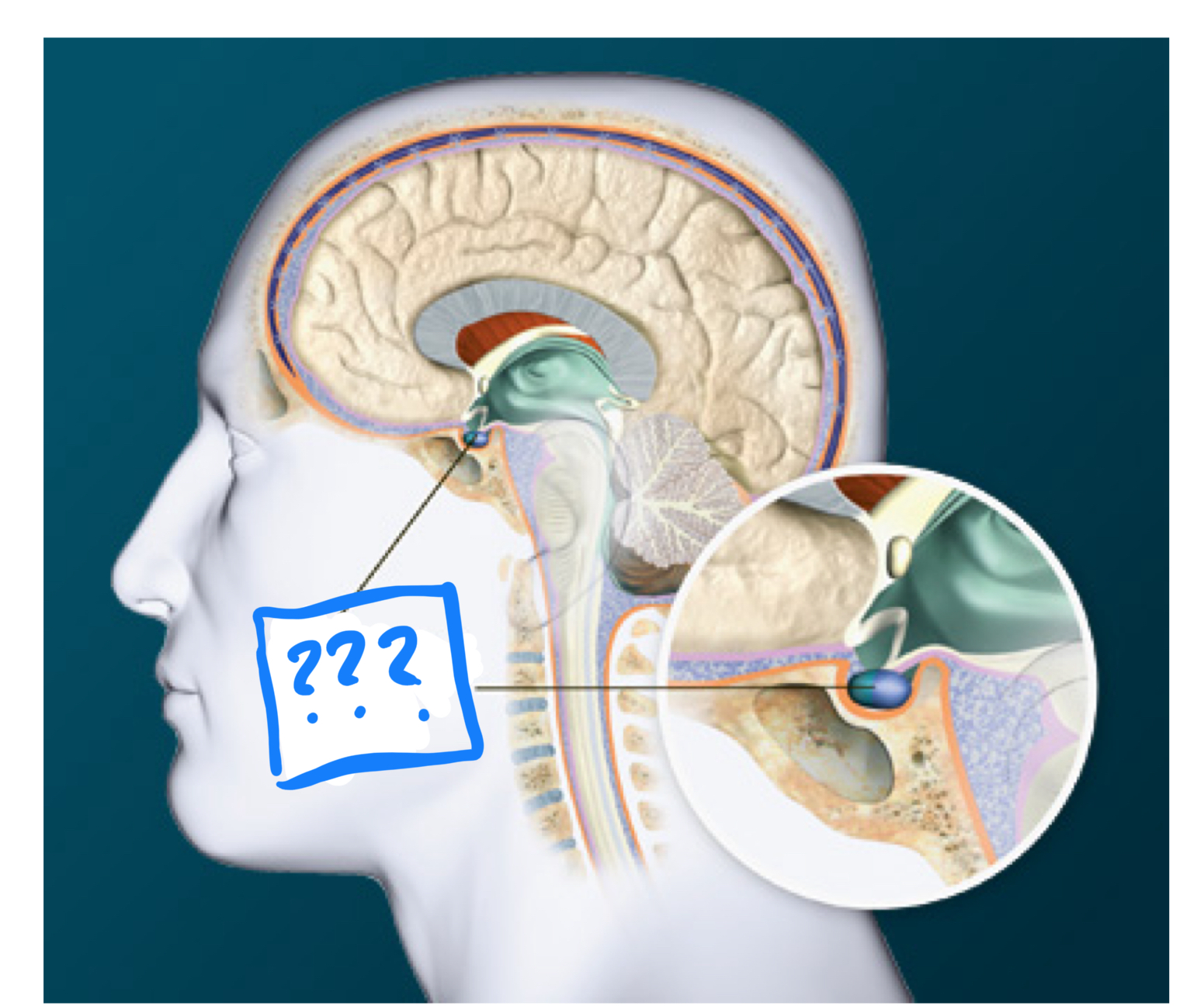
posterior pituitary
(area of pituitary) receives direct neural connections from the hypothalamus, it control the release of the antidiuretic hormone vasopressin, and oxytocin
anterior pituitary
(area of pituitary) connected to the hypothalamus which releases hormones into the system and stimulates the release of other hormones such as growth, acth, and gonadotropic hormone
pineal gland
secretes one hormone, melatonin which is involved in sleep
telencephalon
in forebrain
gyri
pre-central and post-central gyrus
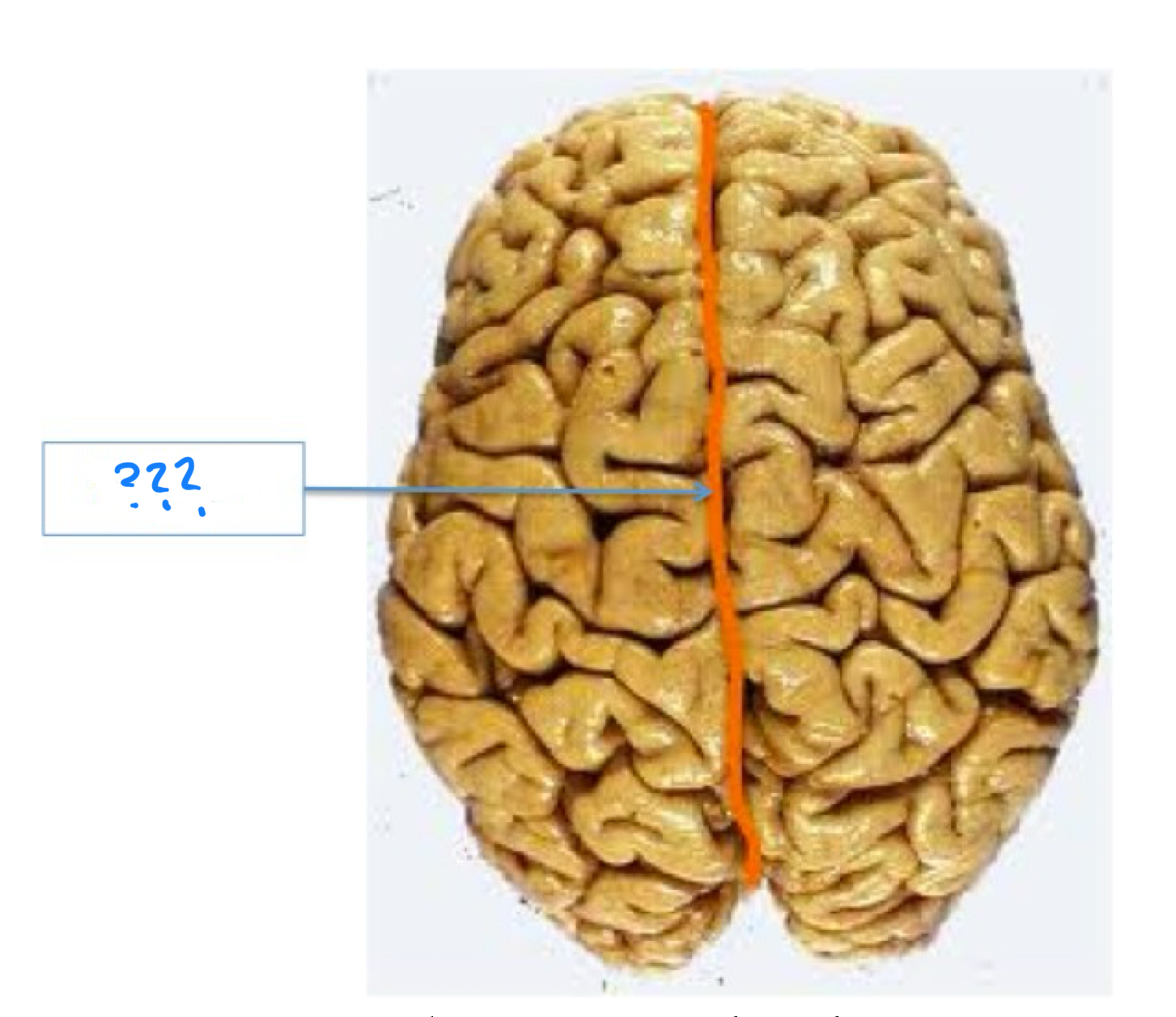
central sulcus
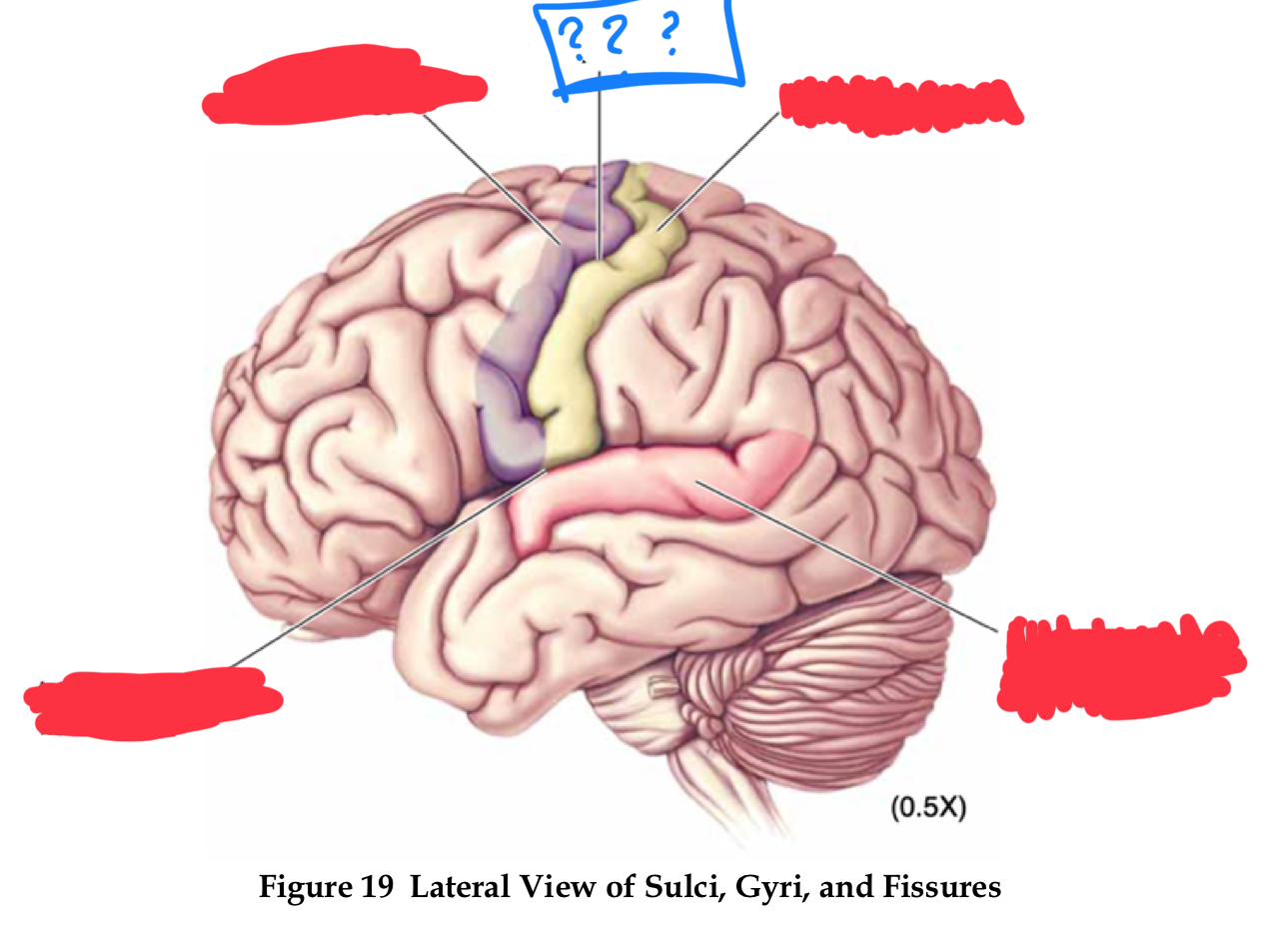
pre-central gyrus
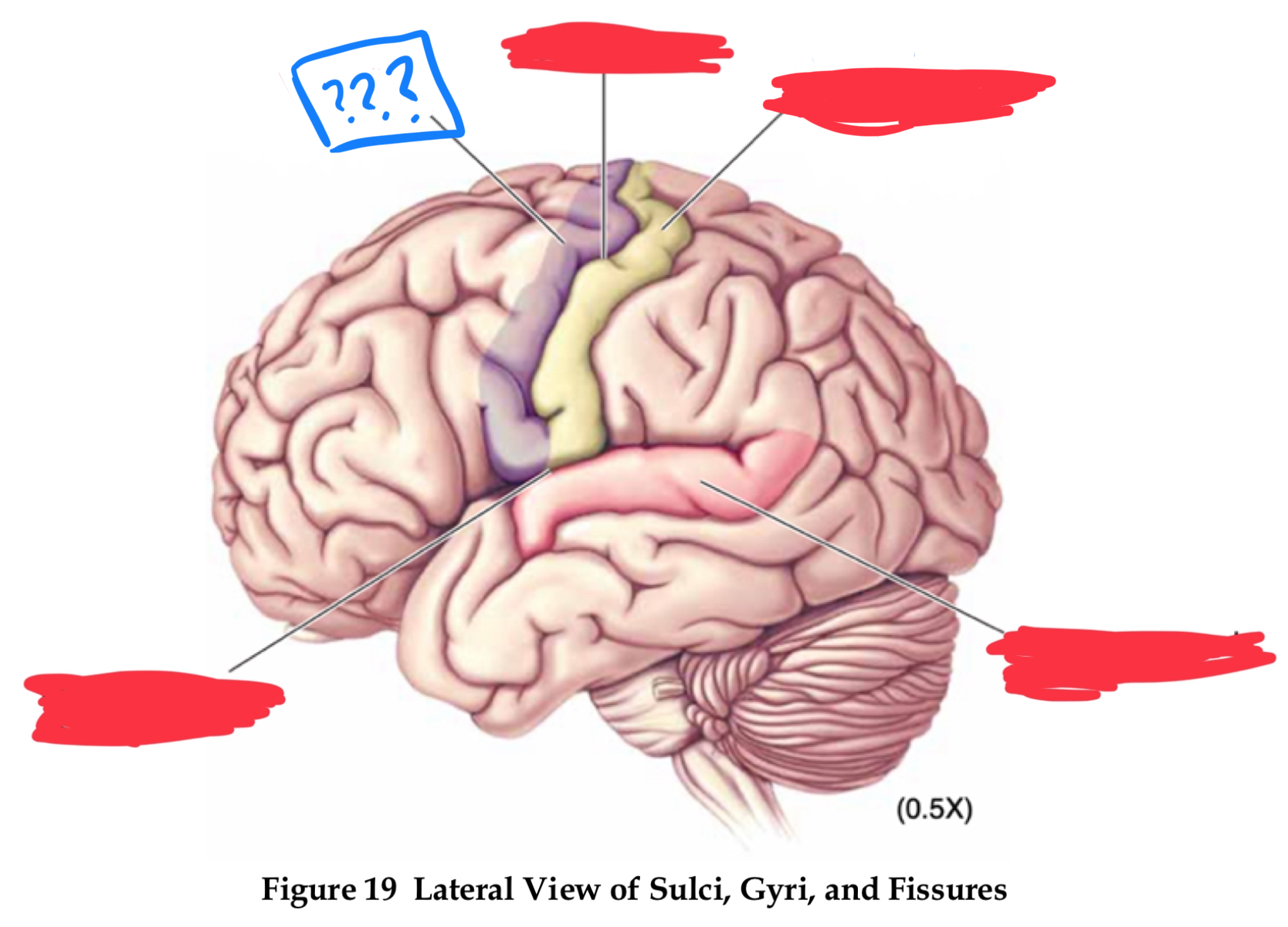
post-central gyrus
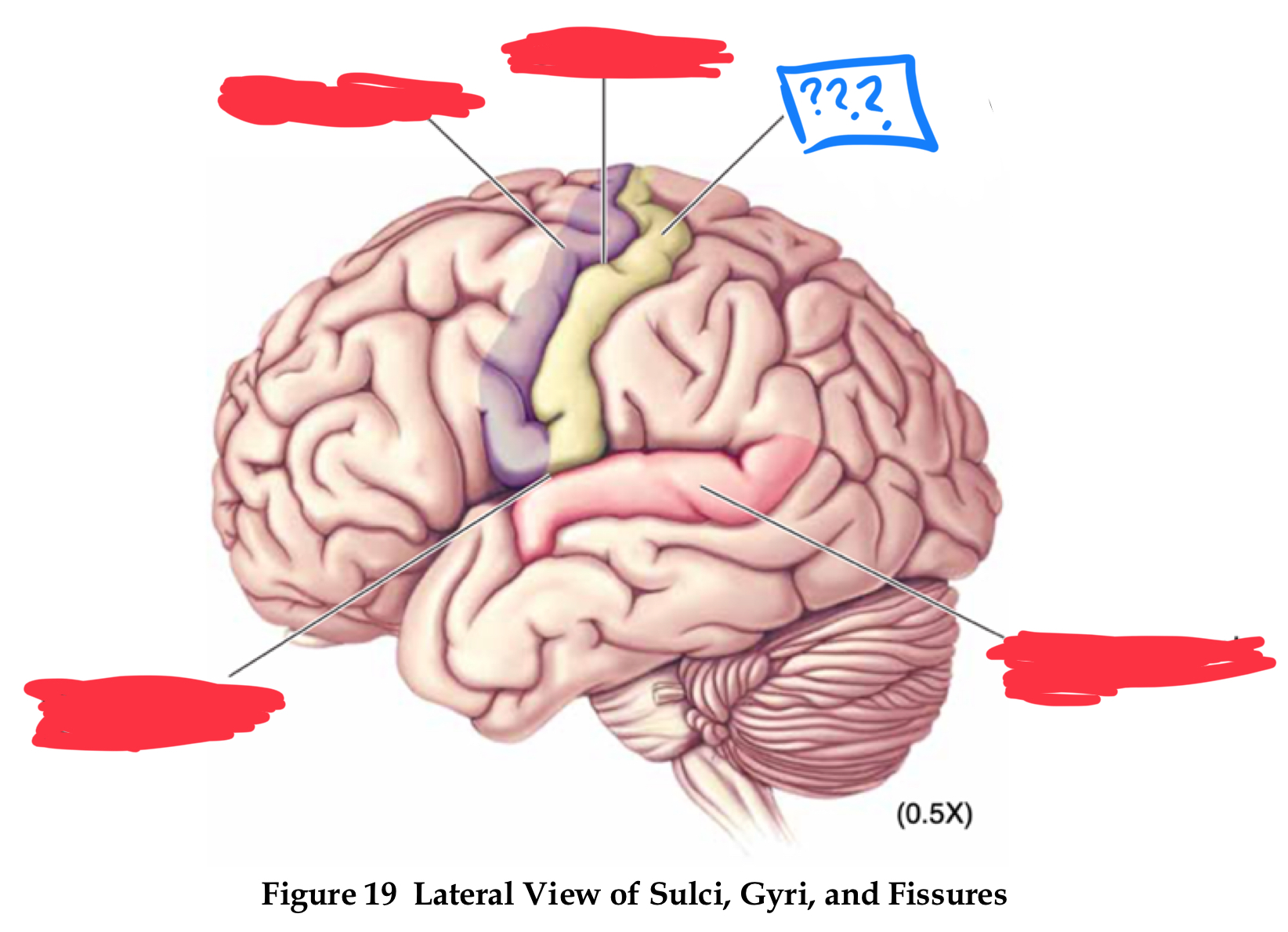
superior temporal gyrus
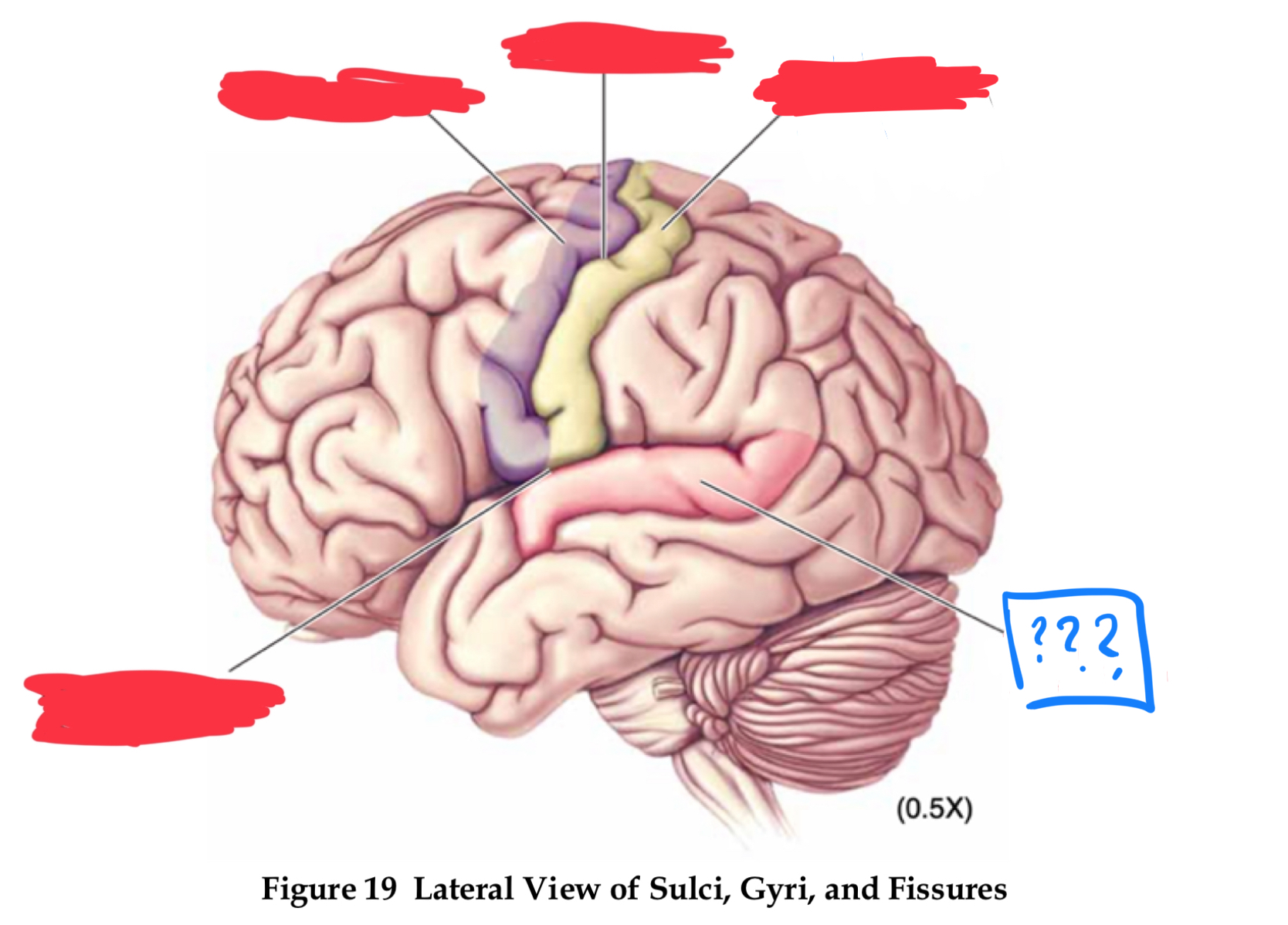
lateral fissure
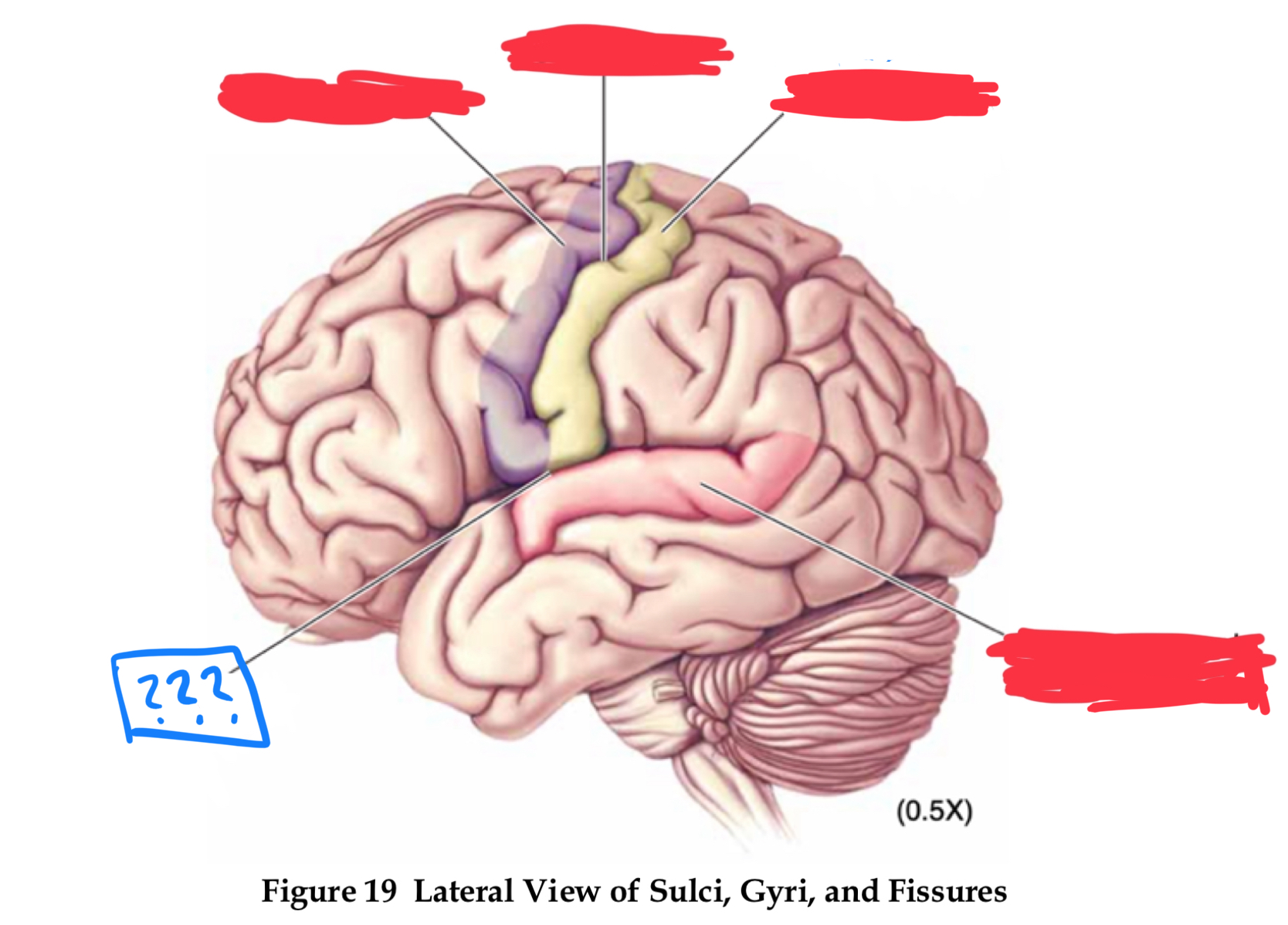
longitudinal fissure
sulci
central sulcus, lateral fissure (sylvian), longitudinal fissure
frontal lobe
lobe that controls movement, executive functions, eg planning, organization, goal directed behavior, cognitive control and self referential thought
temporal lobe
lobe that controls audition and visual object and face recognition
parietal lobe
lobe that controls somatosensory functions, eg touch, pain, temp, and proprioception, and multi-sensory functions such as spatial processing
occipital lobe
lobe responsible for vision
primary visual cortex
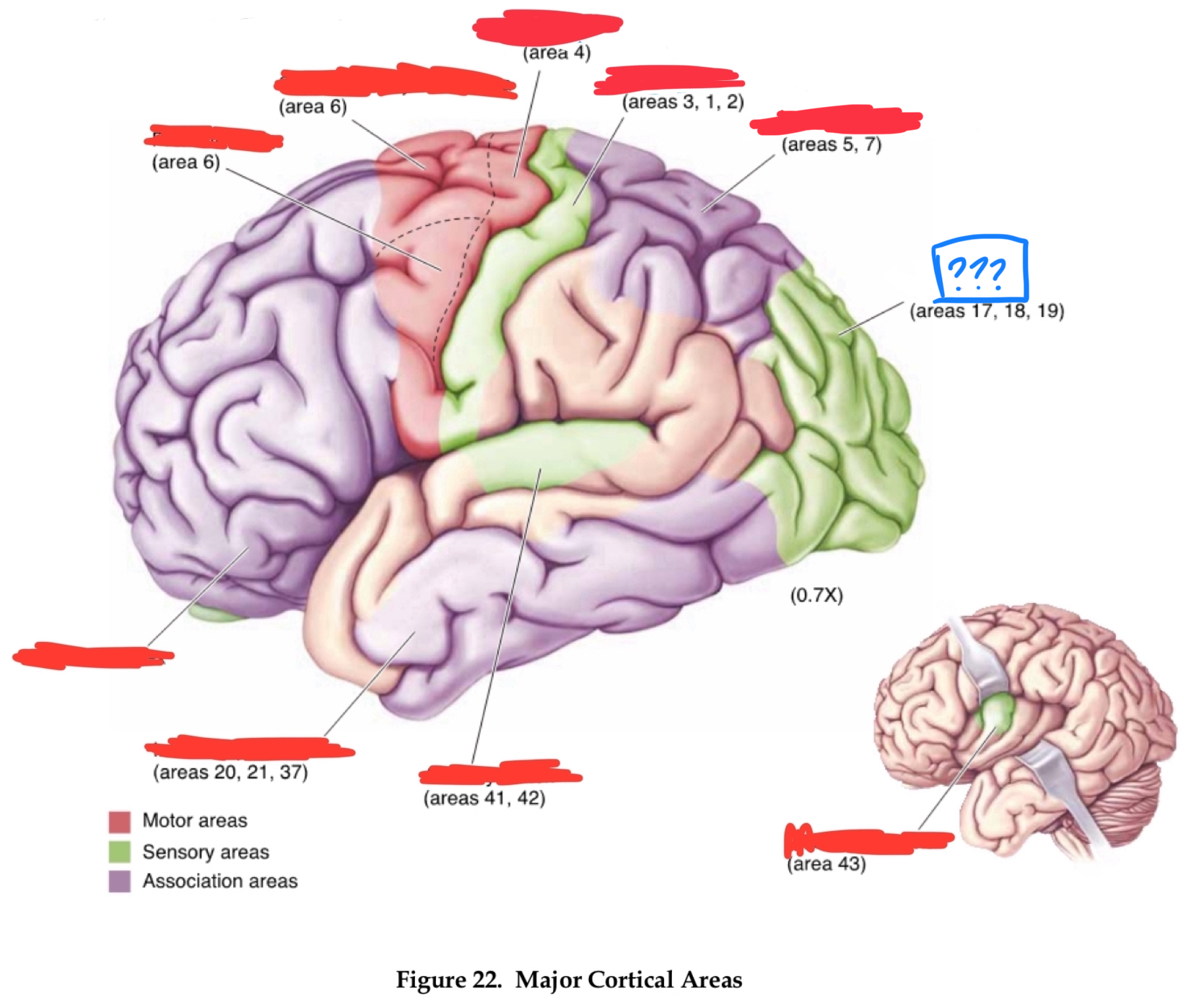
gustatory cortex
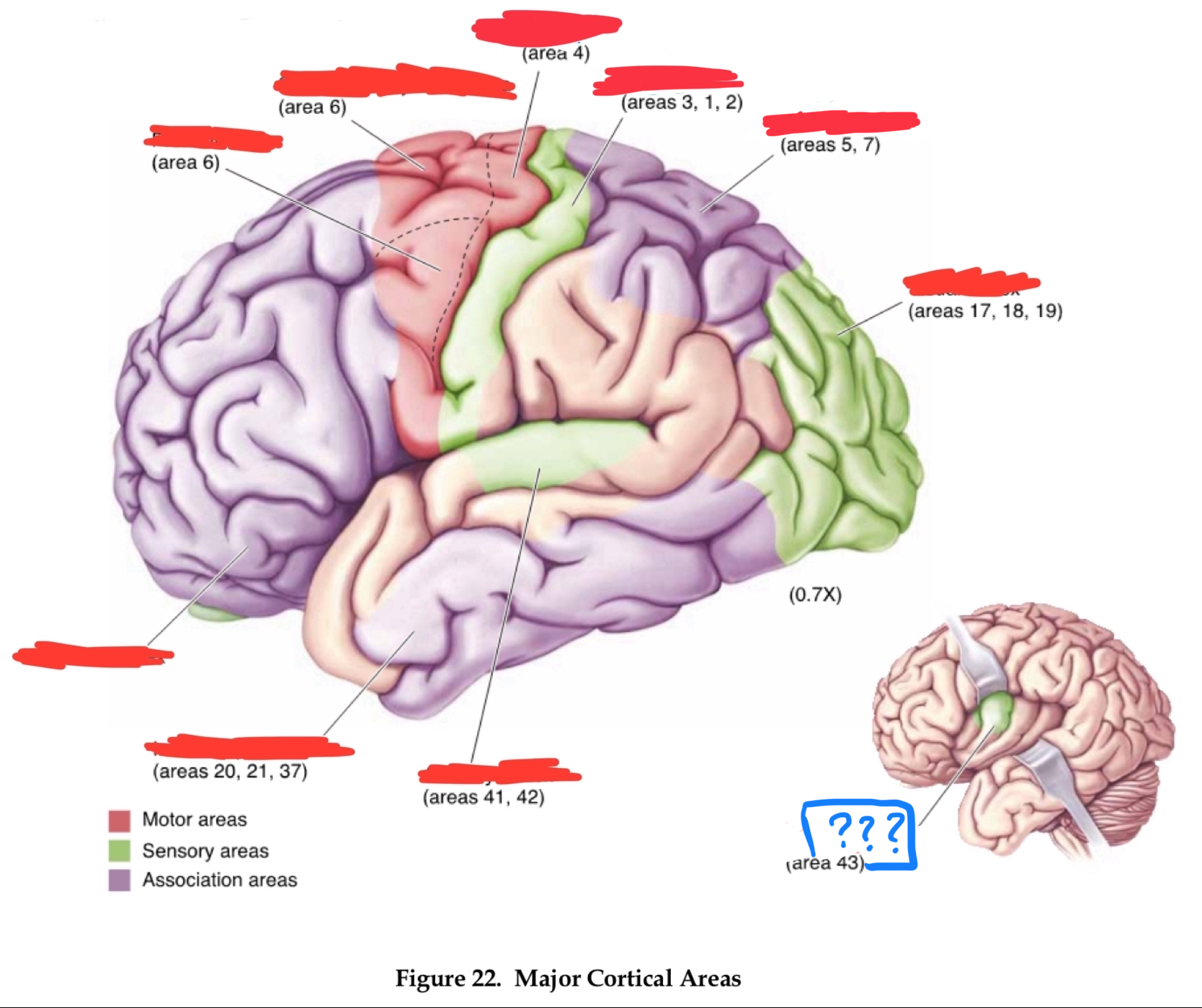
primary auditory cortex
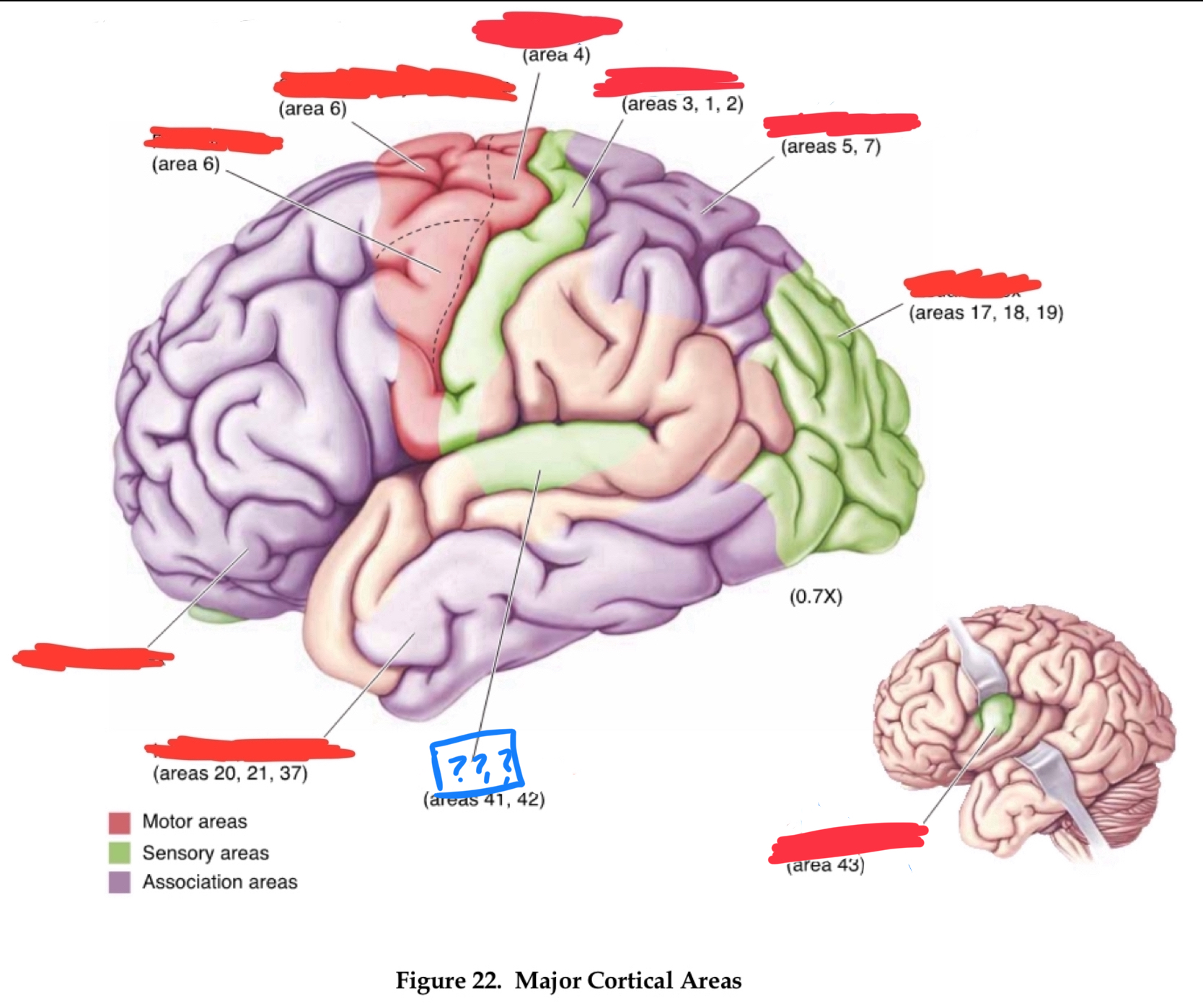
temporal association cortex
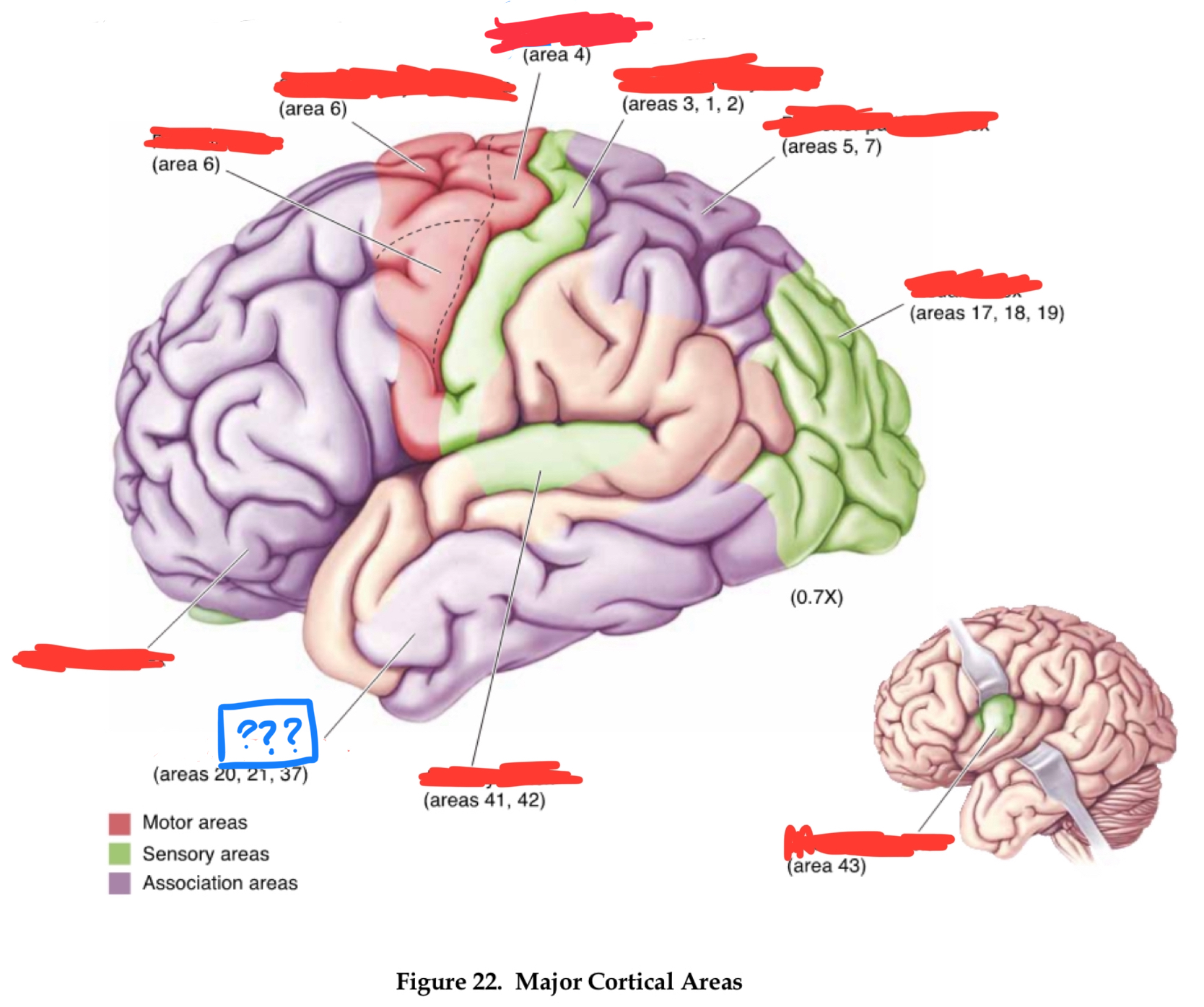
primary somatosensory cortex
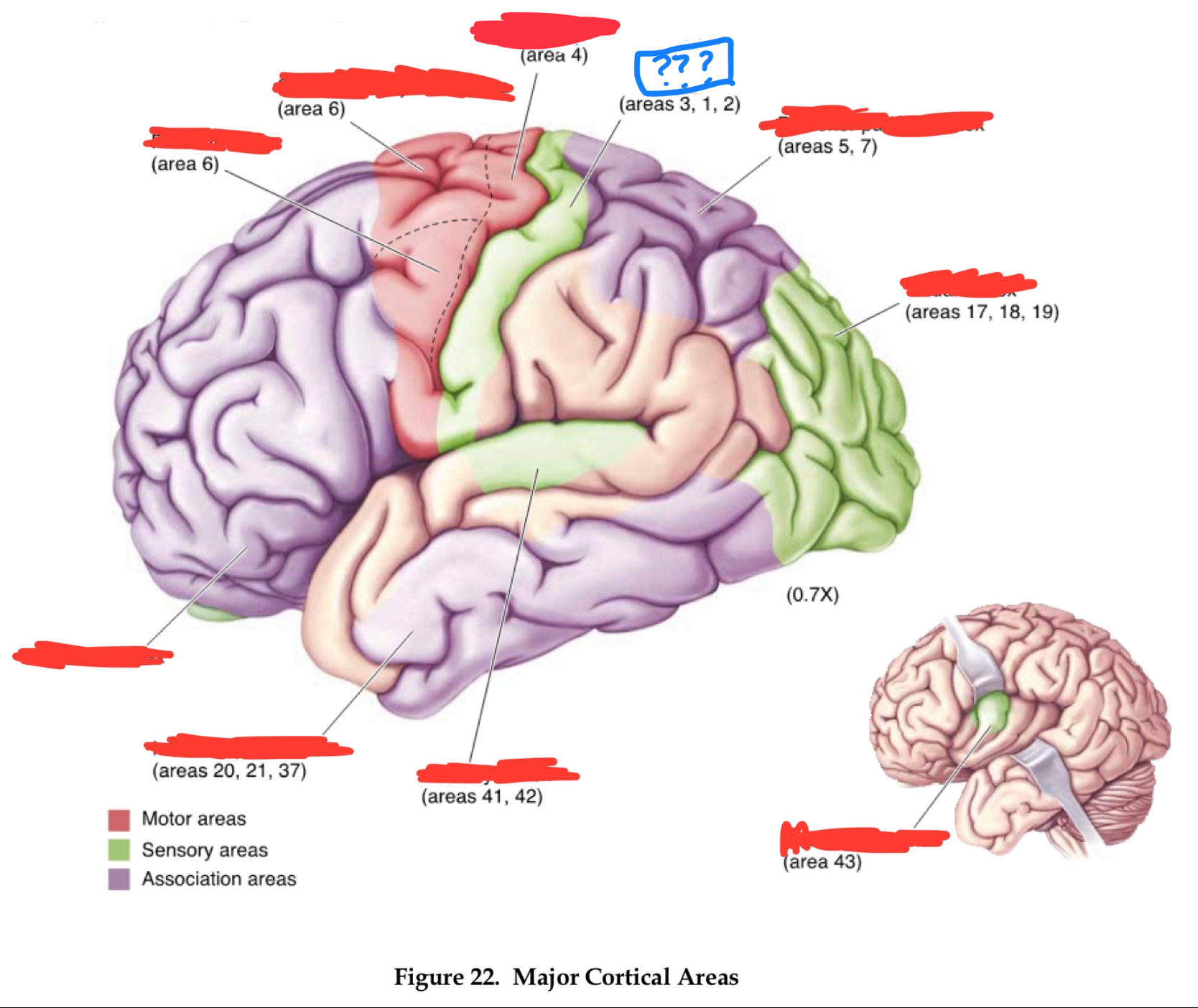
posterior parietal associational cortex
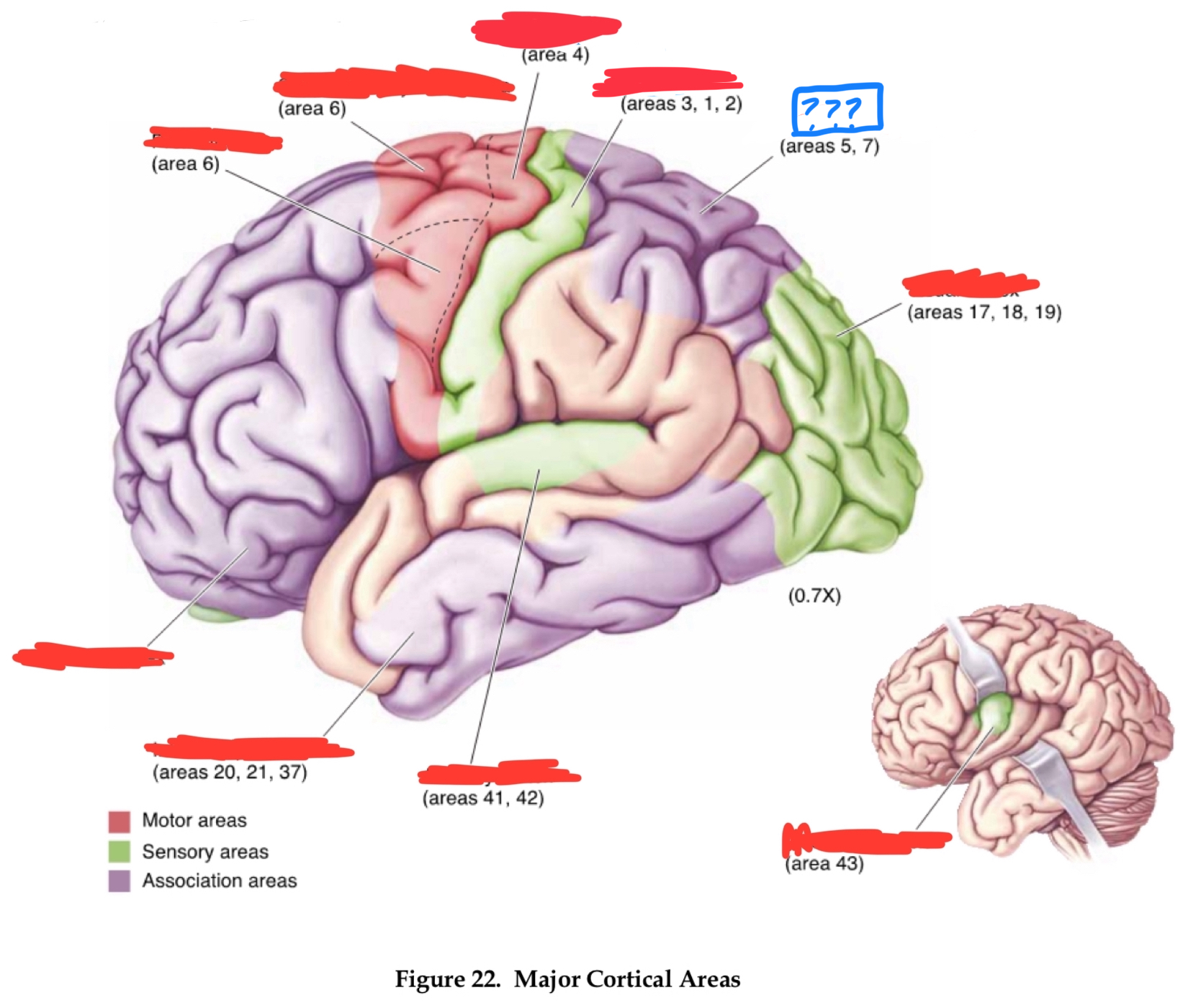
primary motor cortex
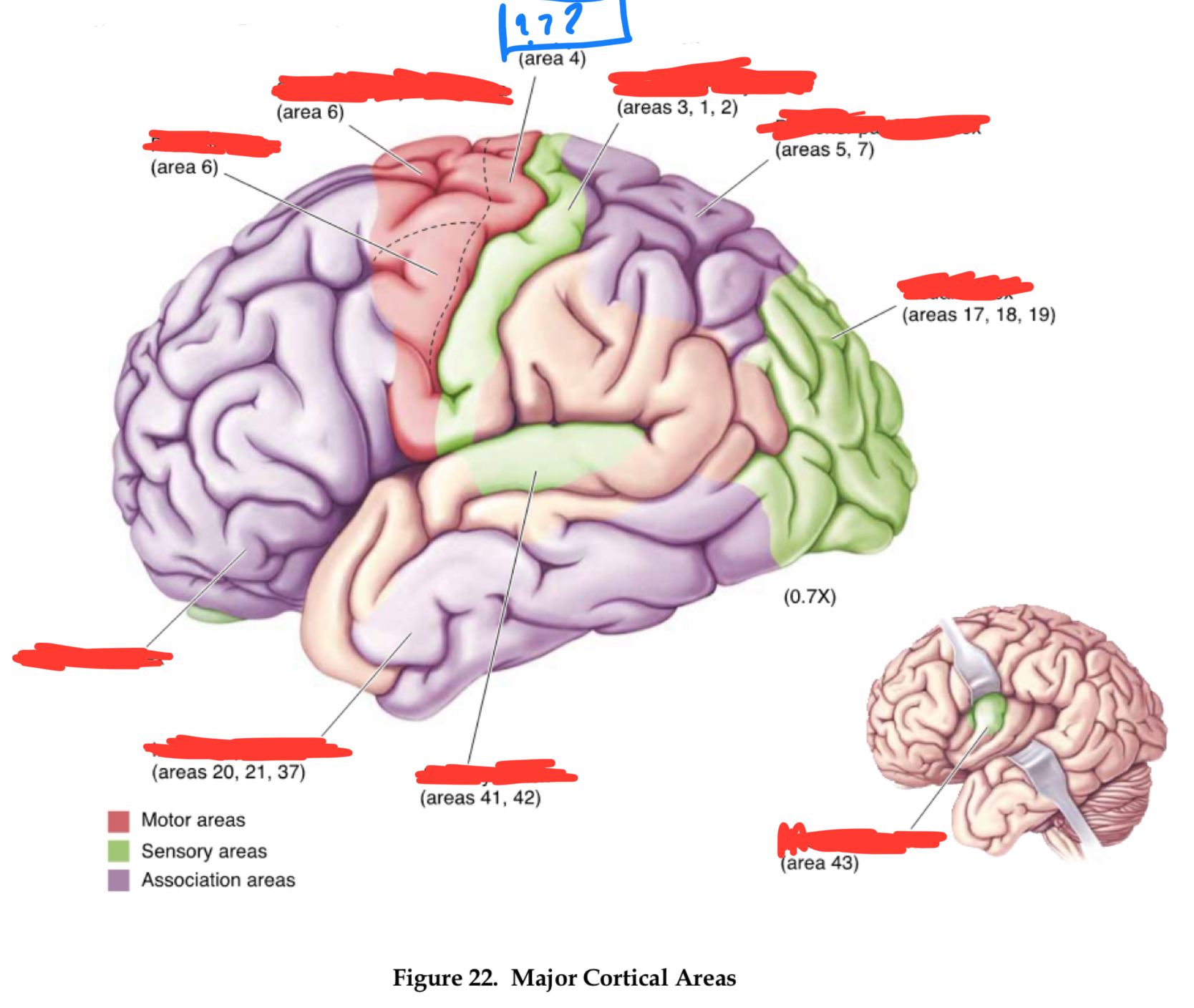
premotor cortex
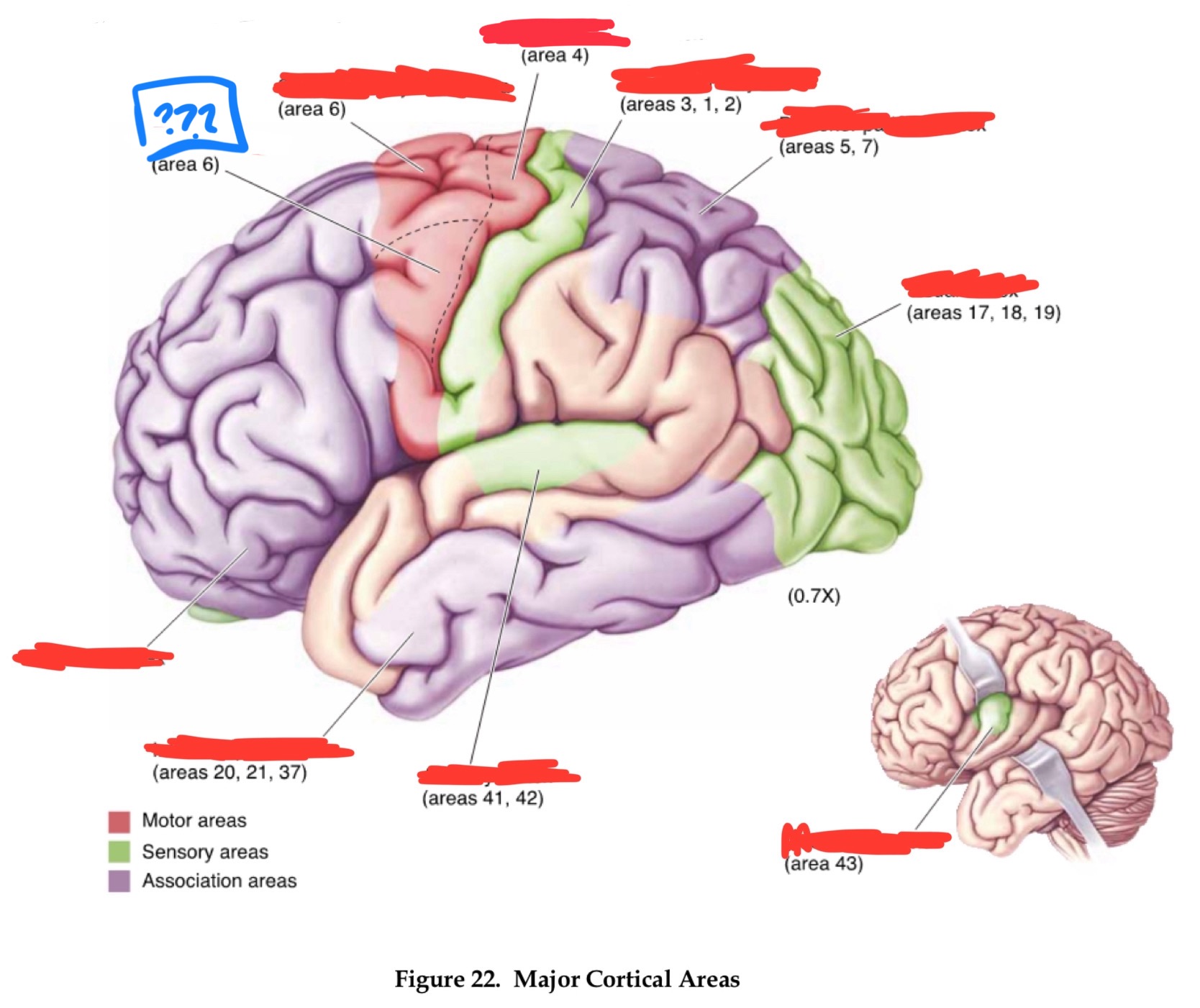
prefrontal cortices
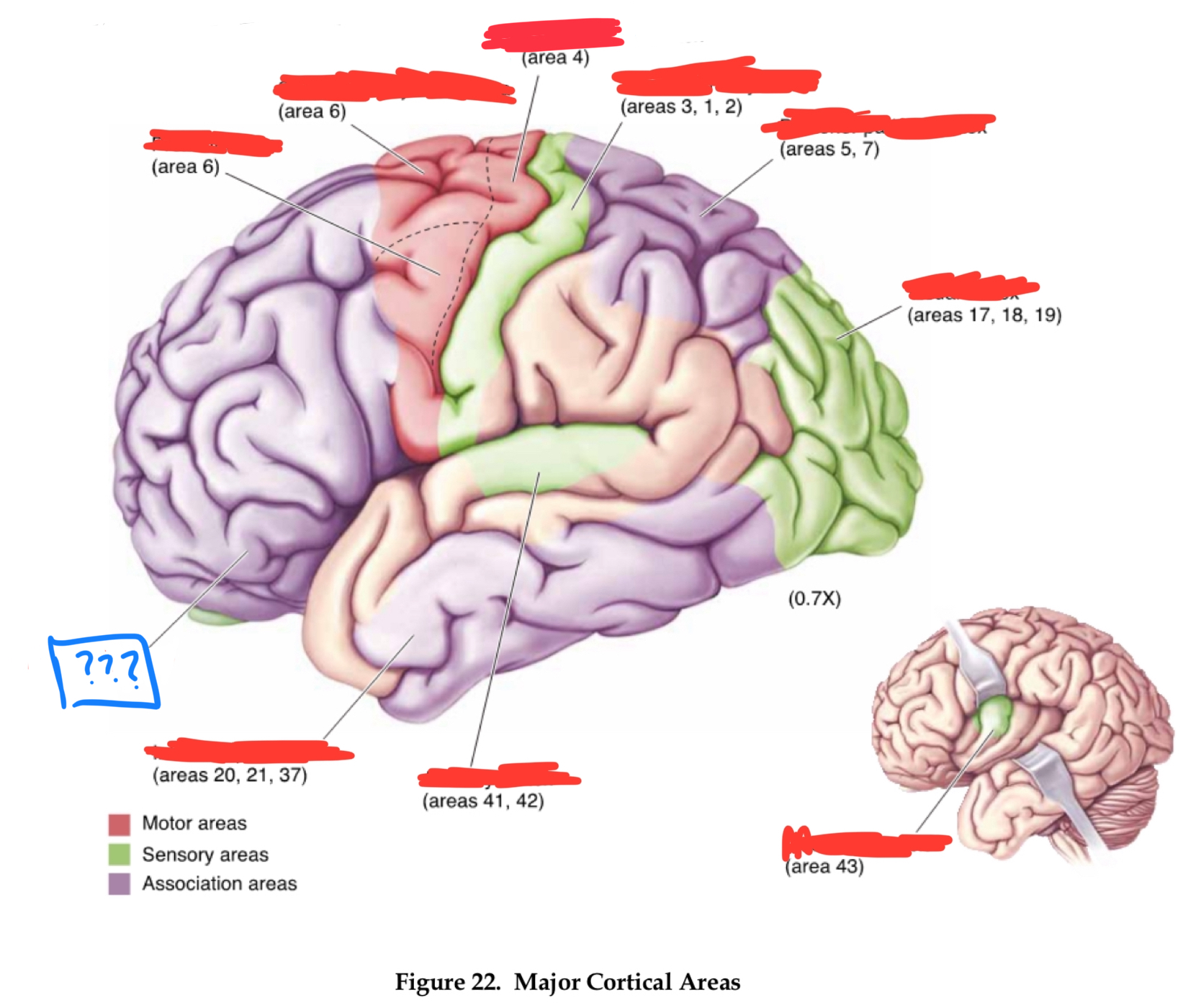
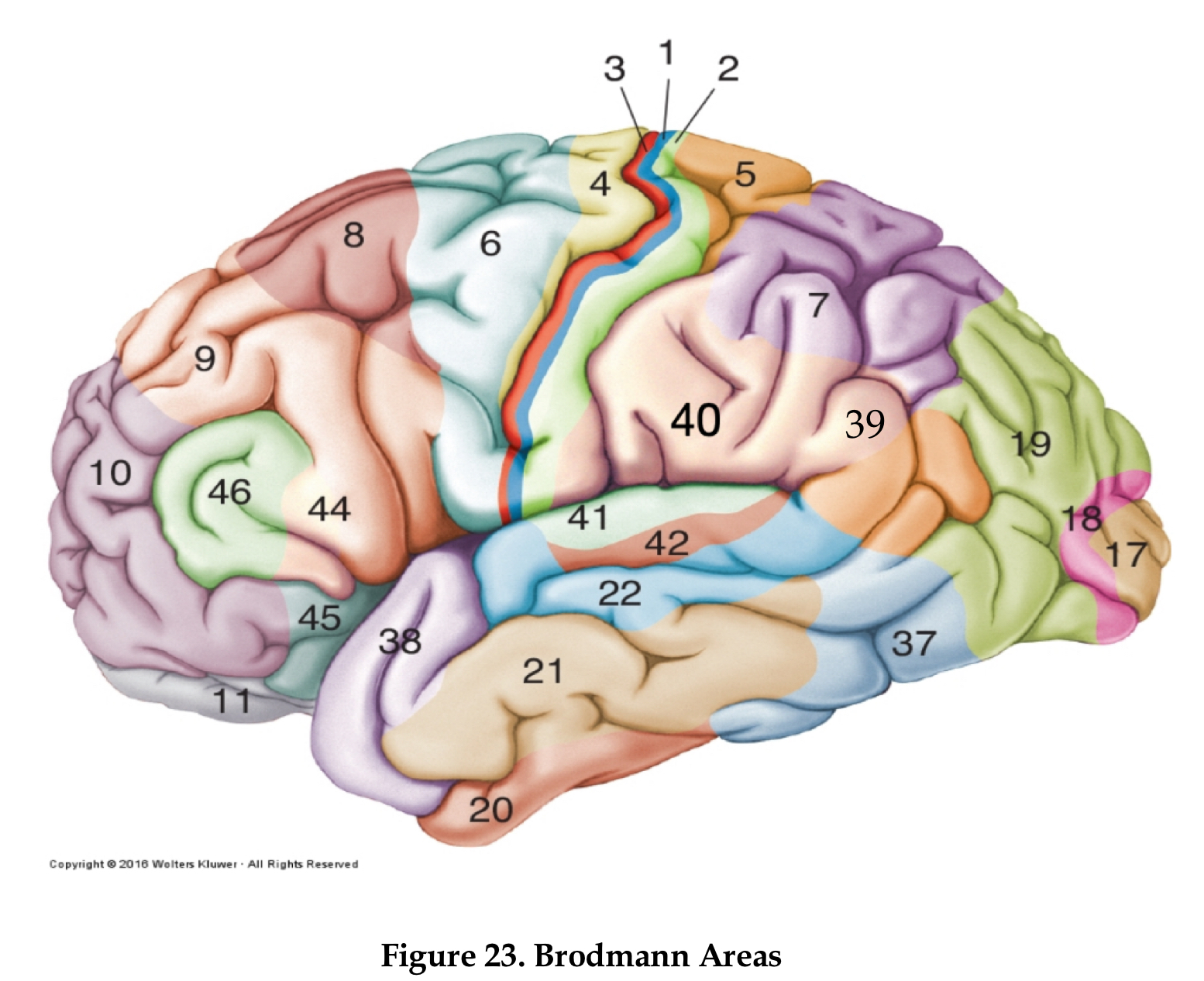
Area 10
frontal pole
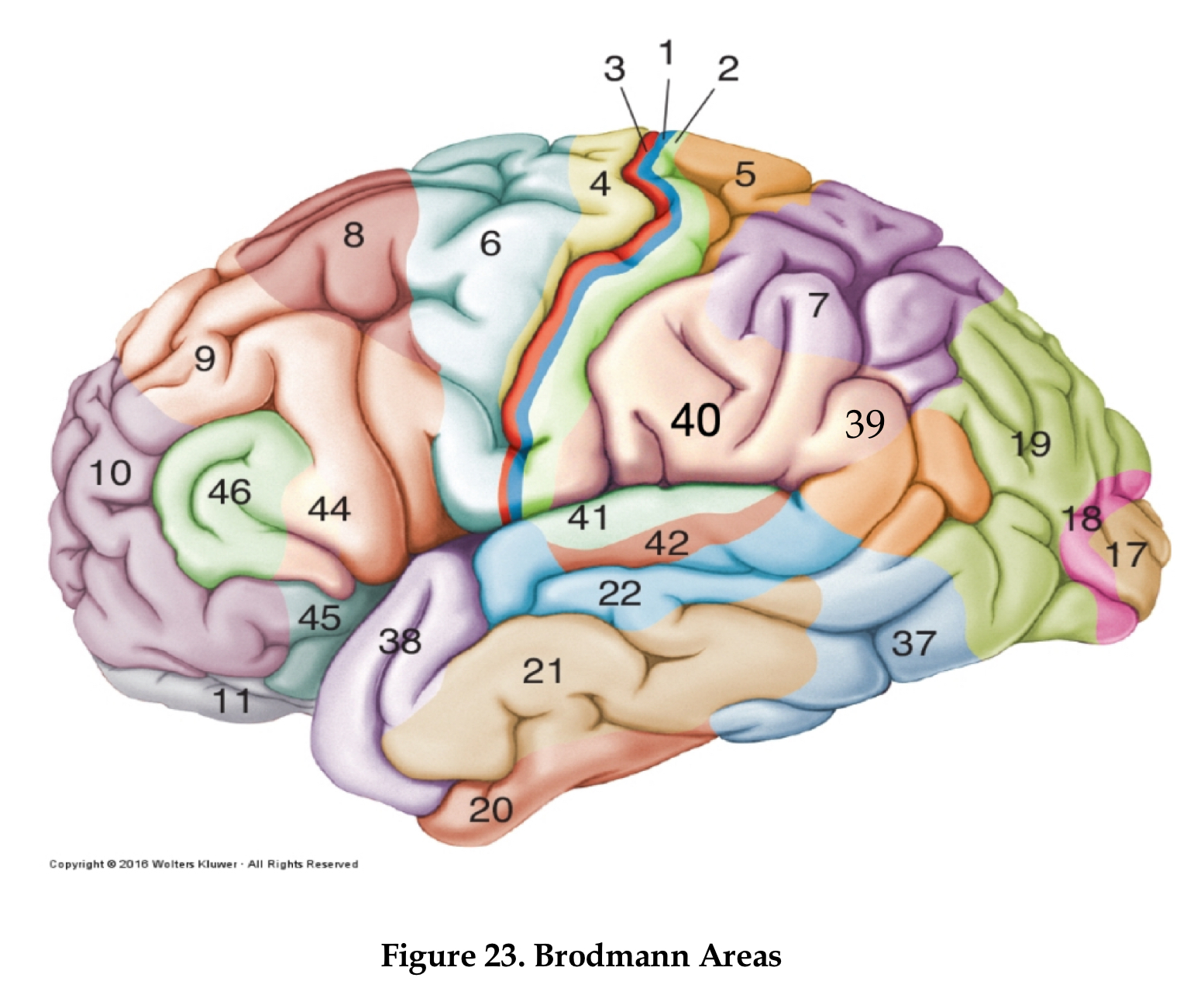
area 4
primary motor cortex
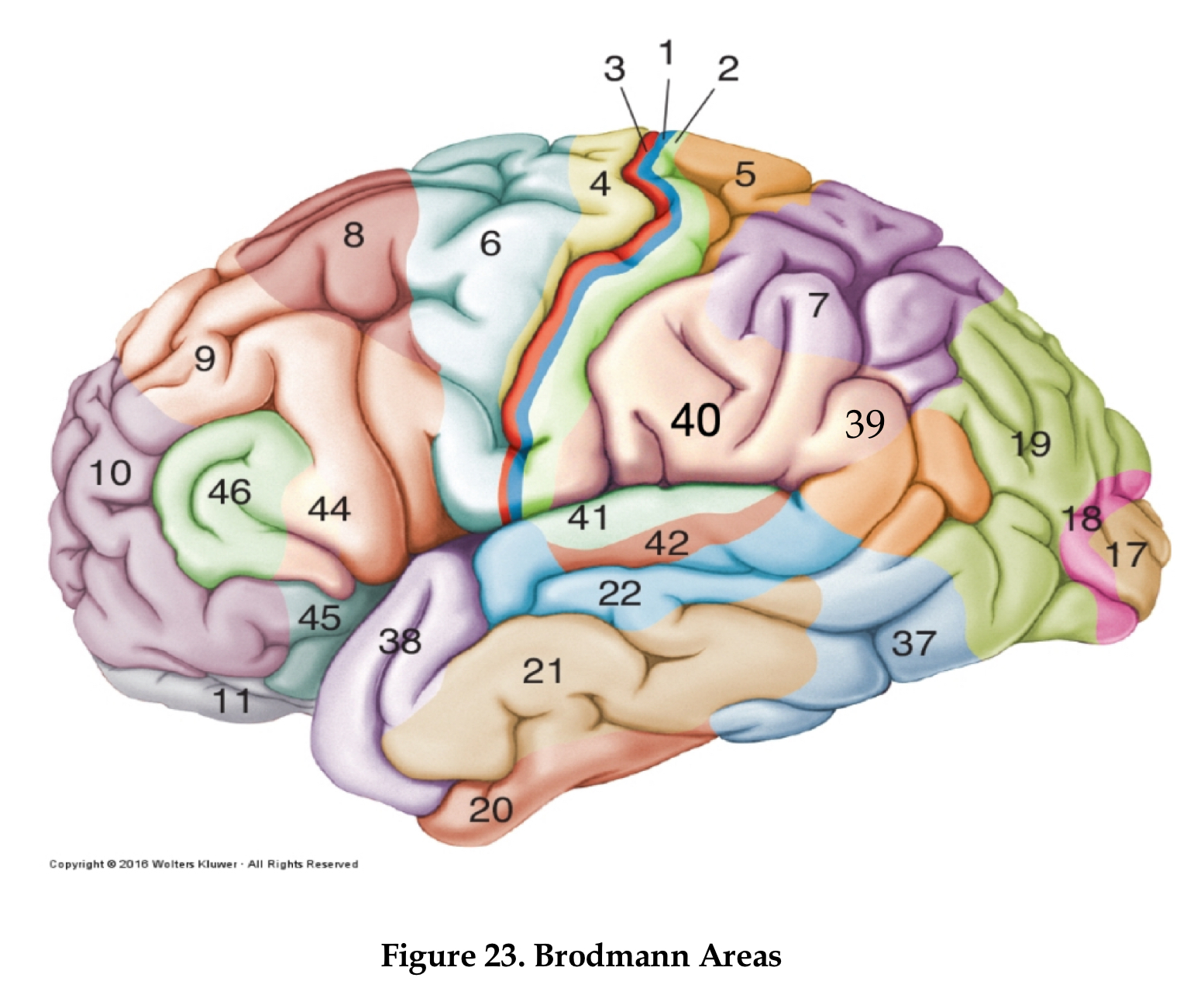
area 6
premotor cortex
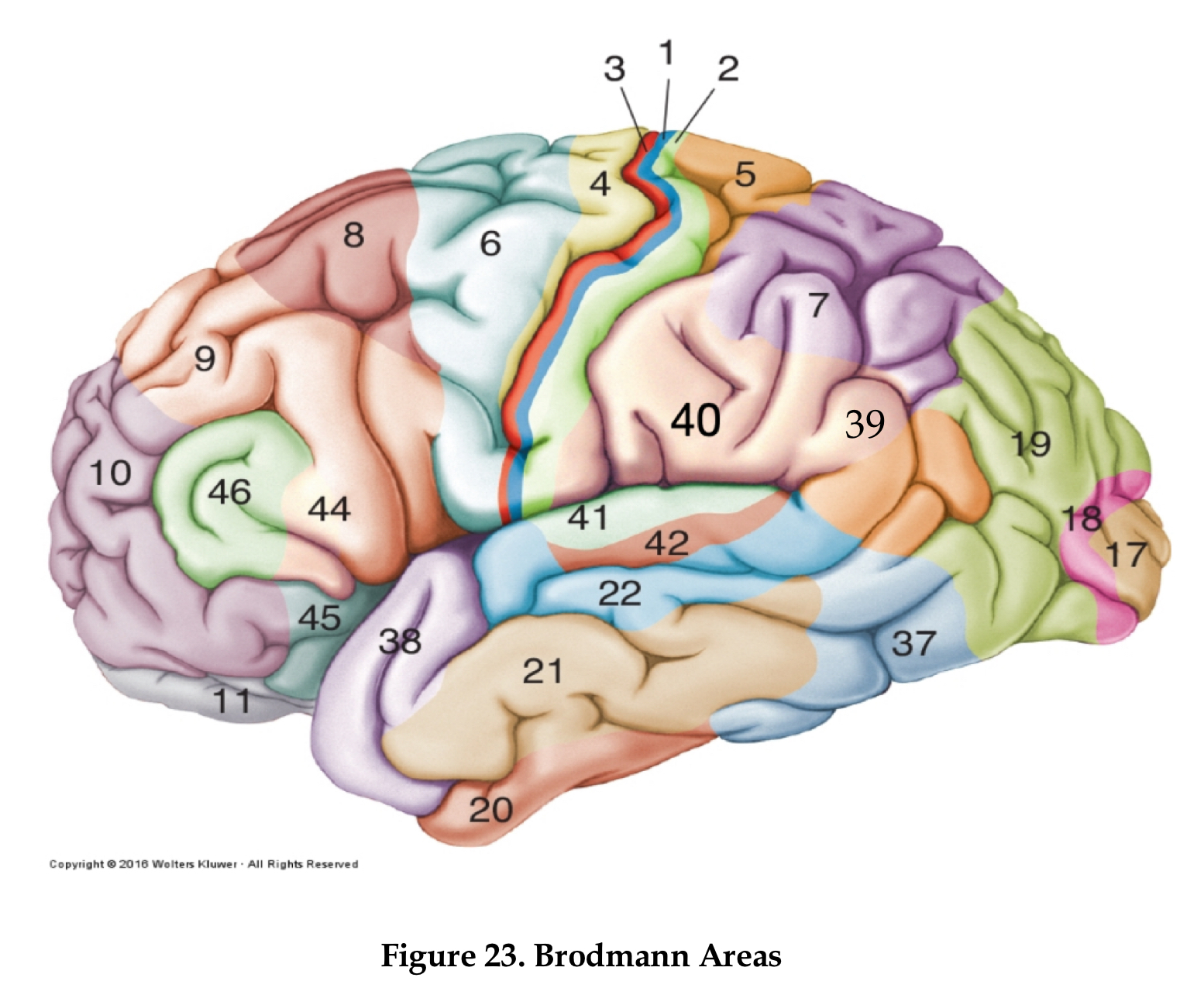
area 8
frontal eye field
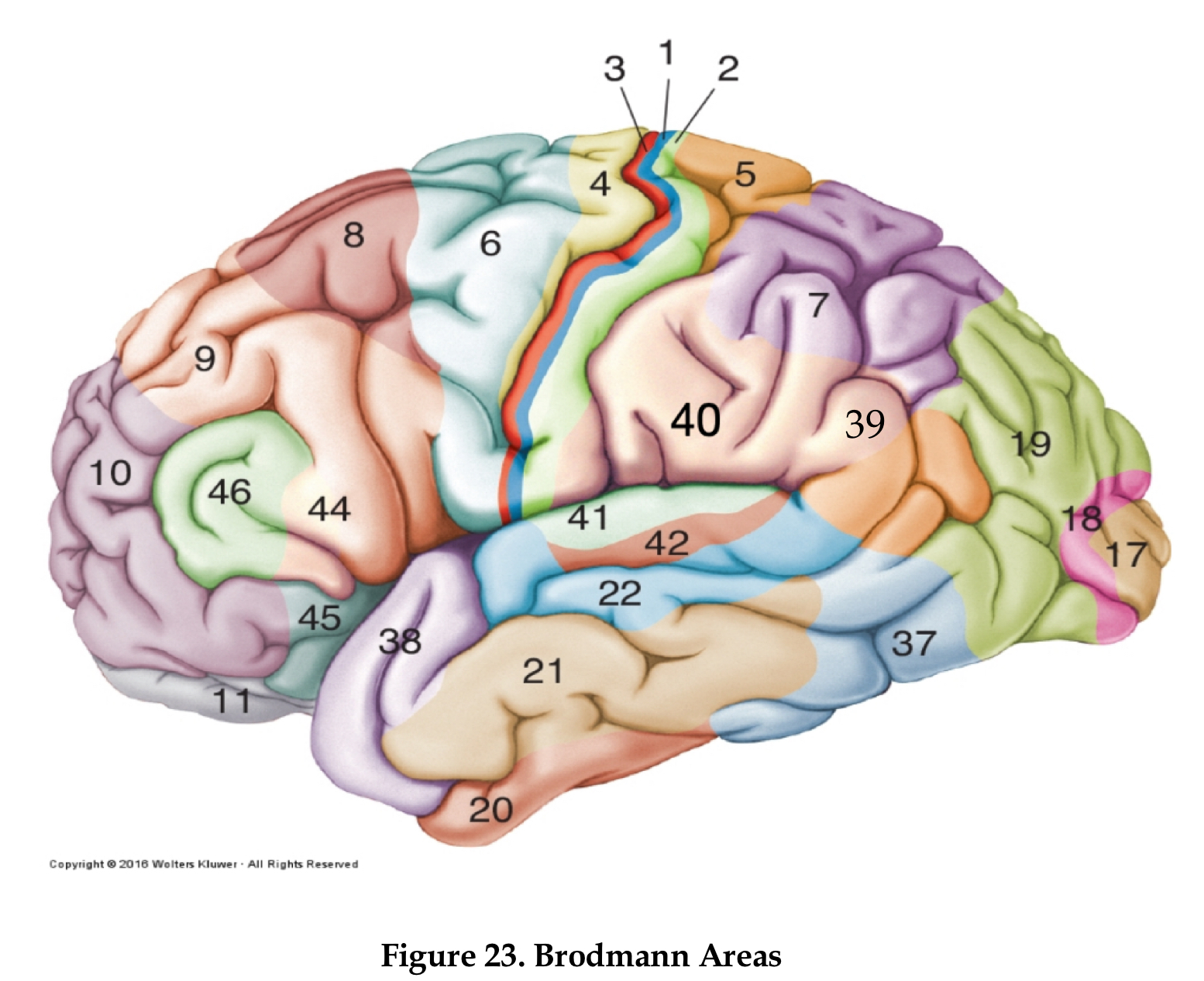
area 46
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
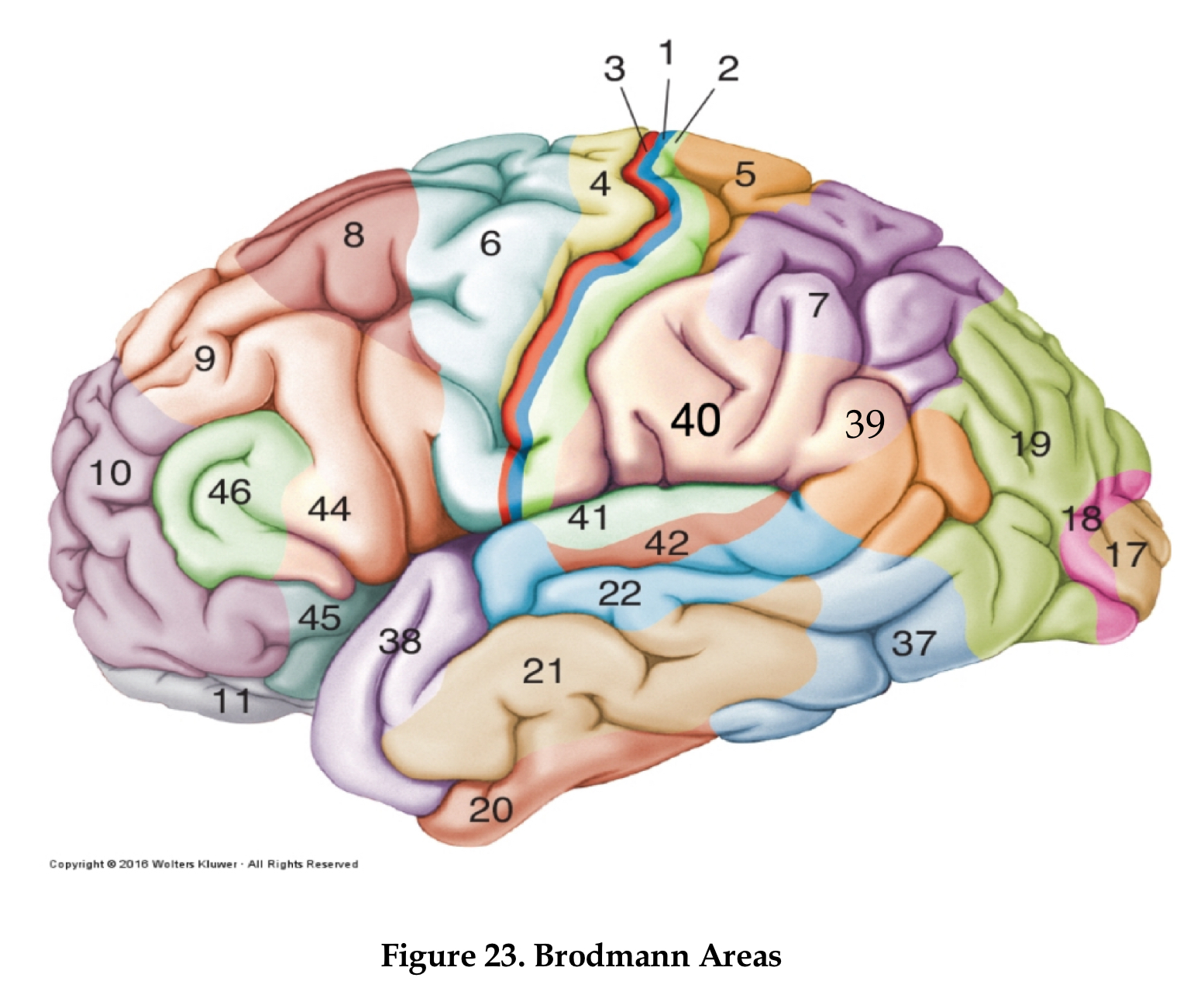
area 44
Brocha’s area
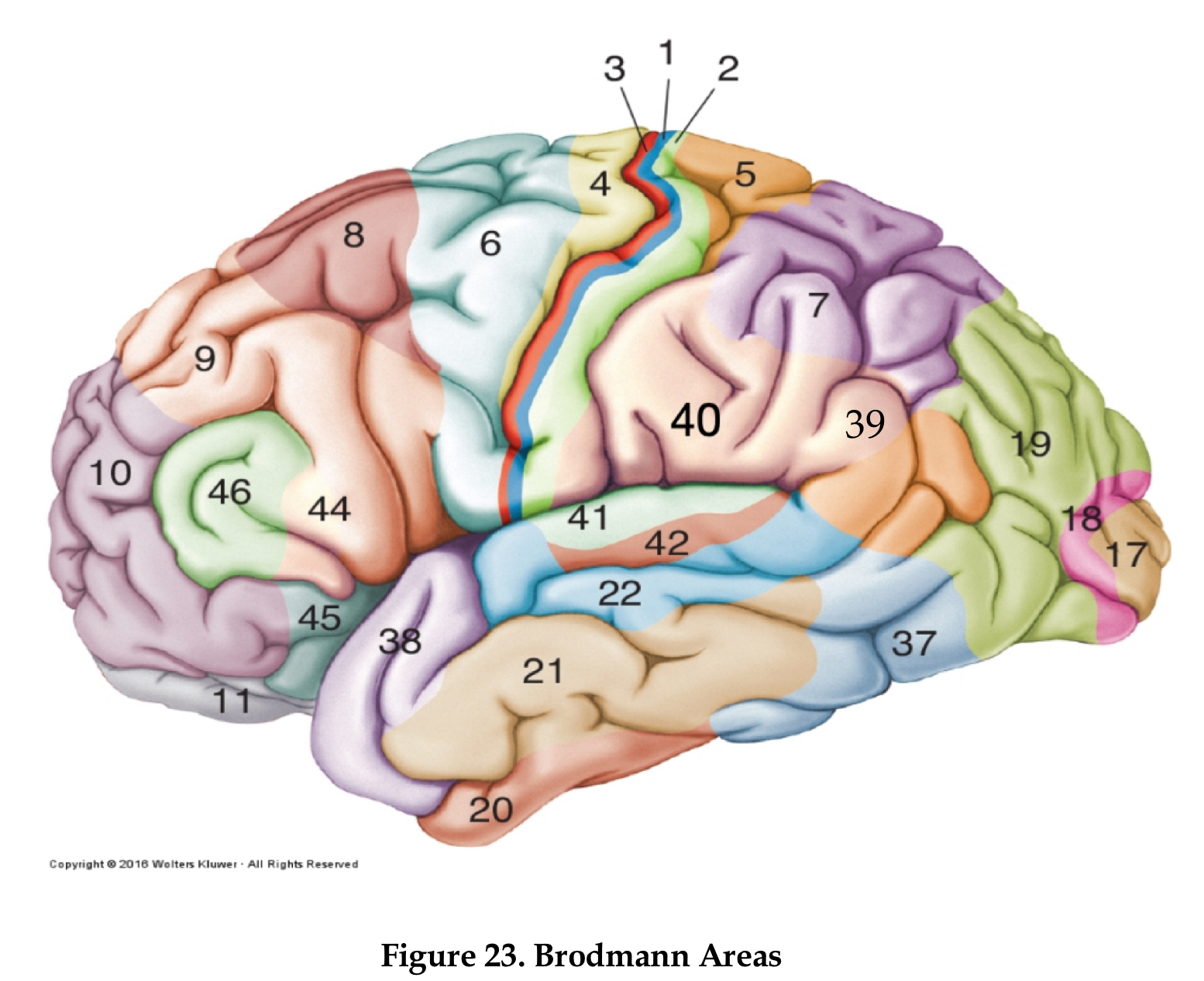
areas 1,2, and 3
primary somatosensory area