DPT 745 (Lecture 6)
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
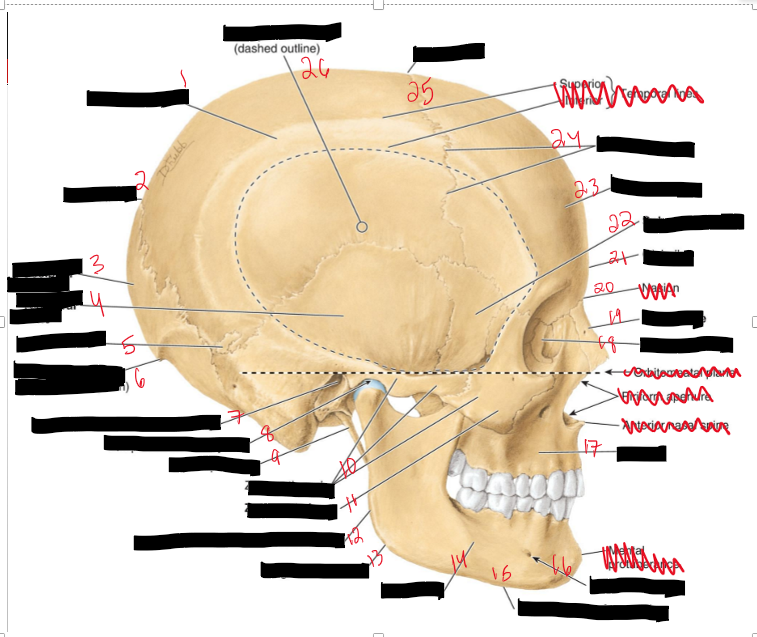
Name the structures.
Parietal Bone
Lambda
Occipital Bone
Temporal Bone
Sutural Bone
External Occipital Protuberance
External acoustic meatus opening
Temporomadibular joint
Styloid process
Zygomatic arch
Zygomatic bone
Posterior border of ramus of mandible
Angle of mandible
Mandible
Inferior border of mandible
mental foramen
Maxilla
Lacrimal Bone
Nasal Bone
Glabella
Sphenoid bone
Frontal bone
Coronal suture
Bregma
Temporal fossa
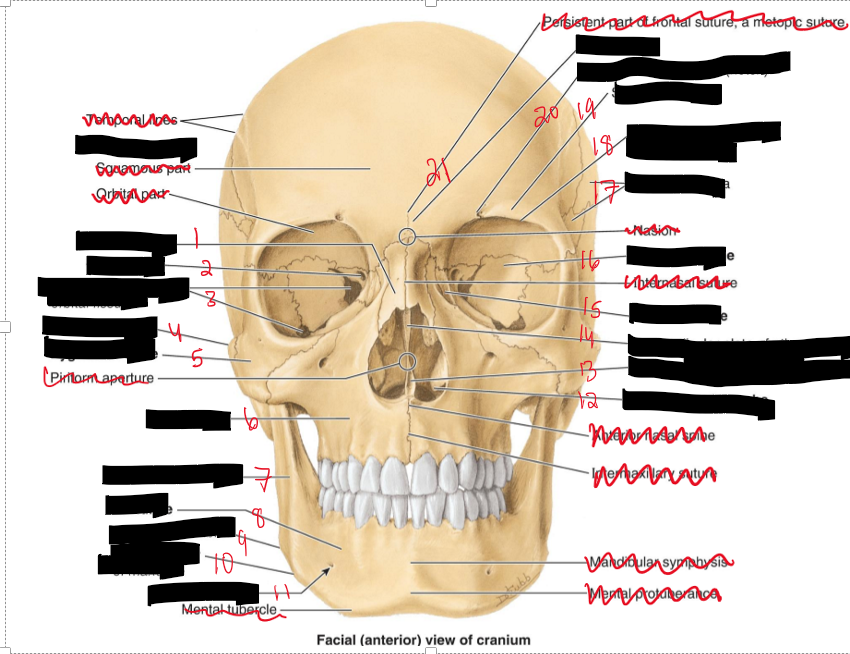
Name the structure.
Nasal Bone
Optic canal
Superior and inferior orbital fissure
Zygomatic arch
Zygomatic bone
Maxilla
Ramus of mandible
Mandible
Angle of mandible
Inferior border of mandible
Mental foramen
Inferior nasal concha
Vomer
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
Lacrimal bone
Sphenoid bone
Temporal fossa
Supra-orbital margin of frontal bone
Superciliary arch
Supra-orbital foramen
Glabella
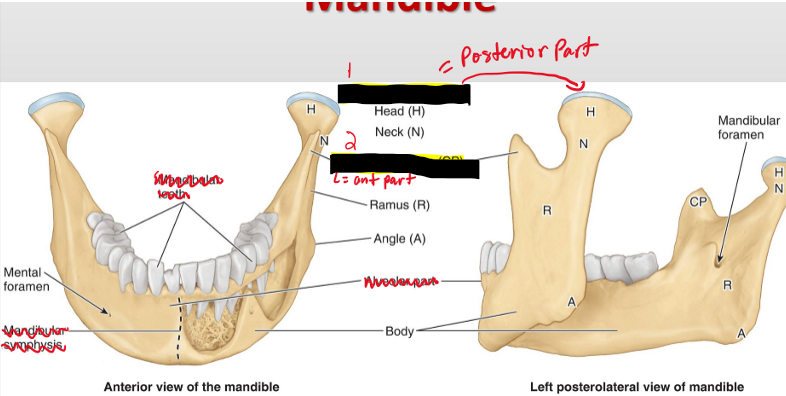
Name the structures.
Condyloid Process (Posterior part)
Coronoid Process (Anterior part)
What does the Neurocranium house and what are the bones of the neurocranium?
It houses the brain
1. Occipital 2. Sphenoid 3. Frontal 4. Parietal 5. Temporal 6. Ethmoid
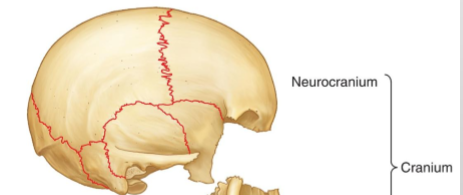
What does the Viscerocranium house and what are the bone?
It houses the faces
1. Palatine 2. Zygomatic 3. Nasal 4. Vomer 5. Maxillae 6. Mandible
Name the Bones.
Frontal Bone
Sphenoid Bone
Nasal Bone
Inferior concha bone
Ethmoid bone
Vomer bone
Zygomatic bone
Maxilla bone
Mandible bone
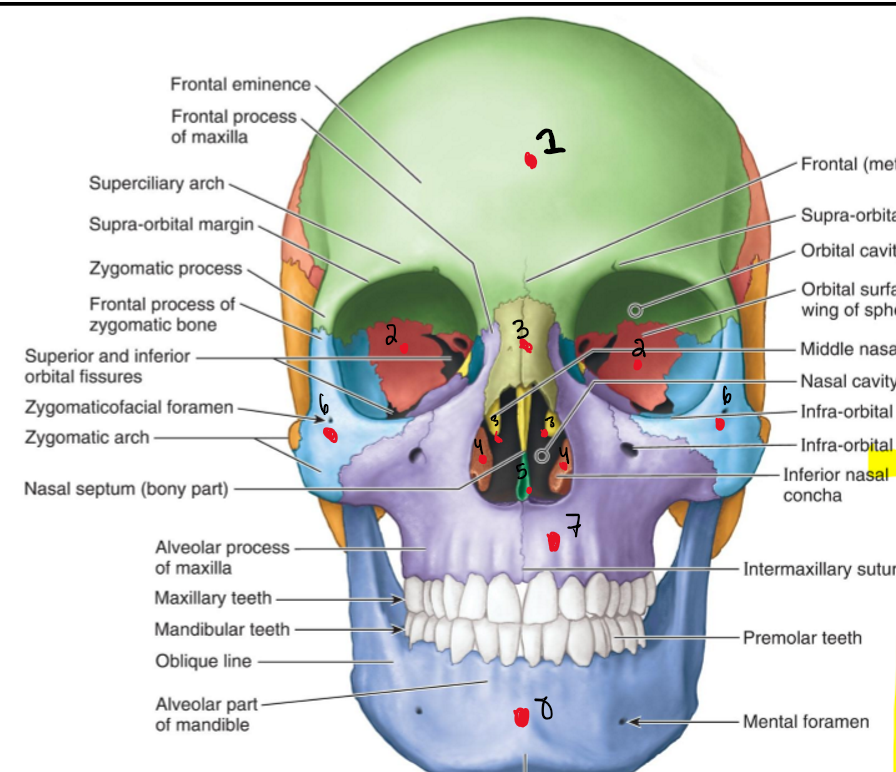
Name the Structure.
Parietal bone
Occiptial bone
Temporal bone
Sphenoid bone
Lacrimal bone
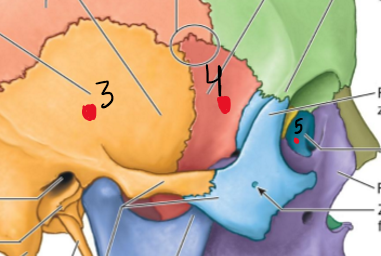
What is the Zygomatic arch consist of?
Zygomatic process of temporal bone
Temporal process of zygomatic bone
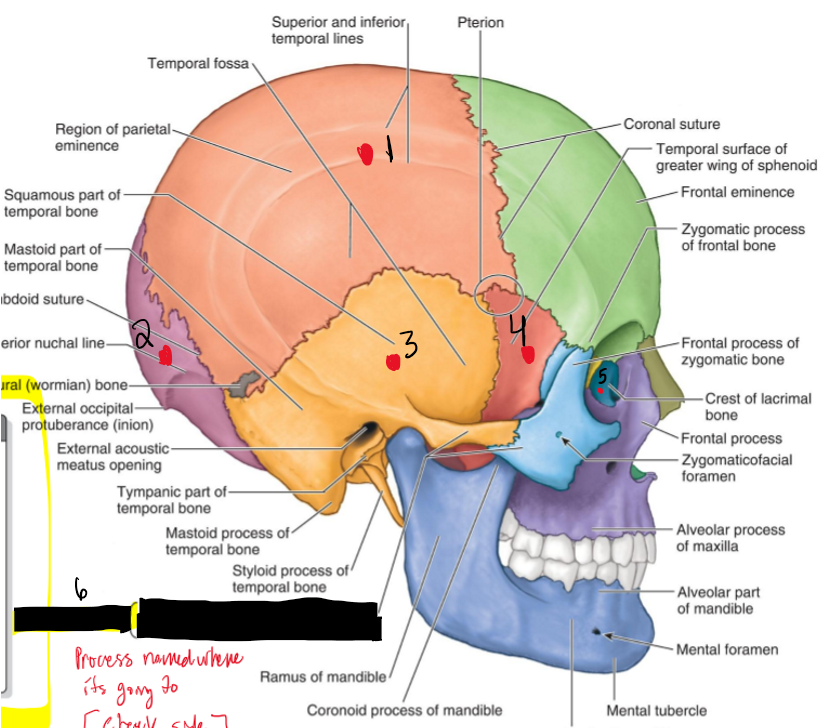
Name the structures.
Vertex (most superior aspect of head)
Sagittal fissure
Lambda
Lamboid suture
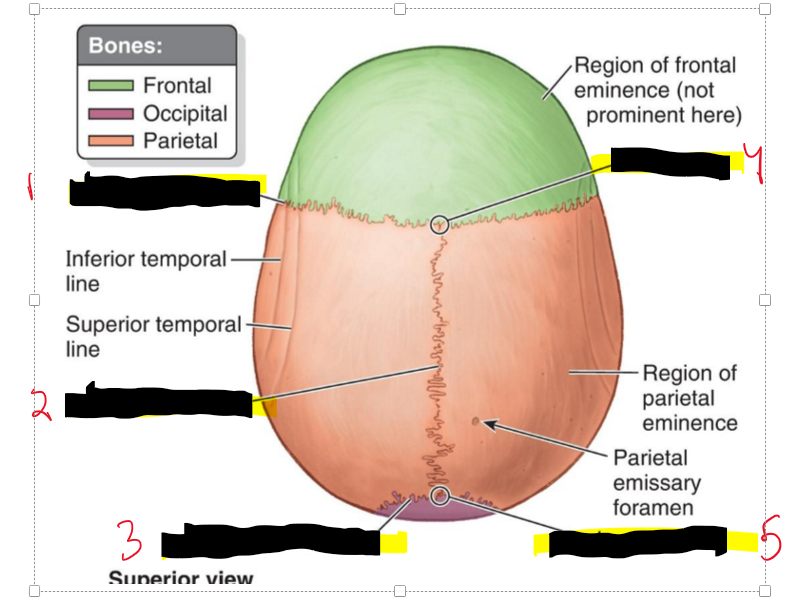
Name the structures.
Coronal Suture
Sagittal suture
Lambdoid suture
Lambda
Bregma
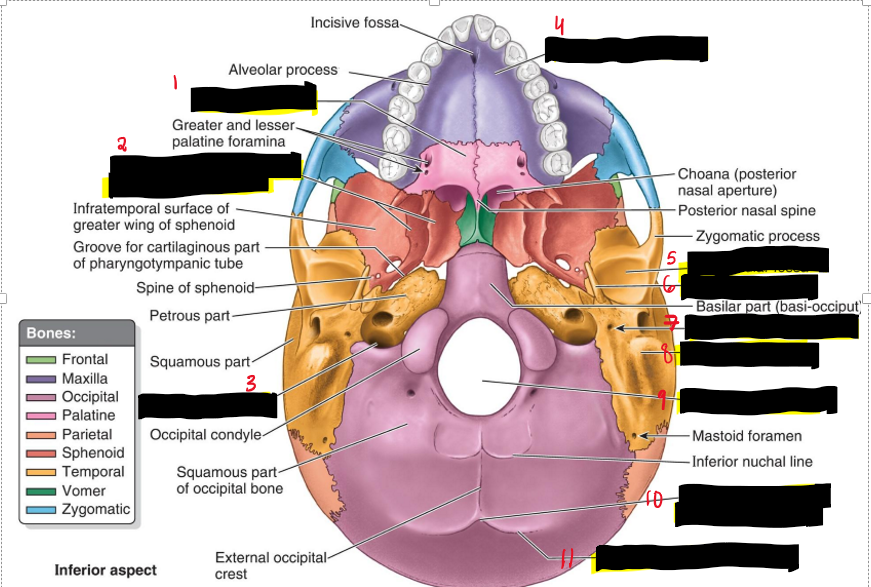
Name the structures.
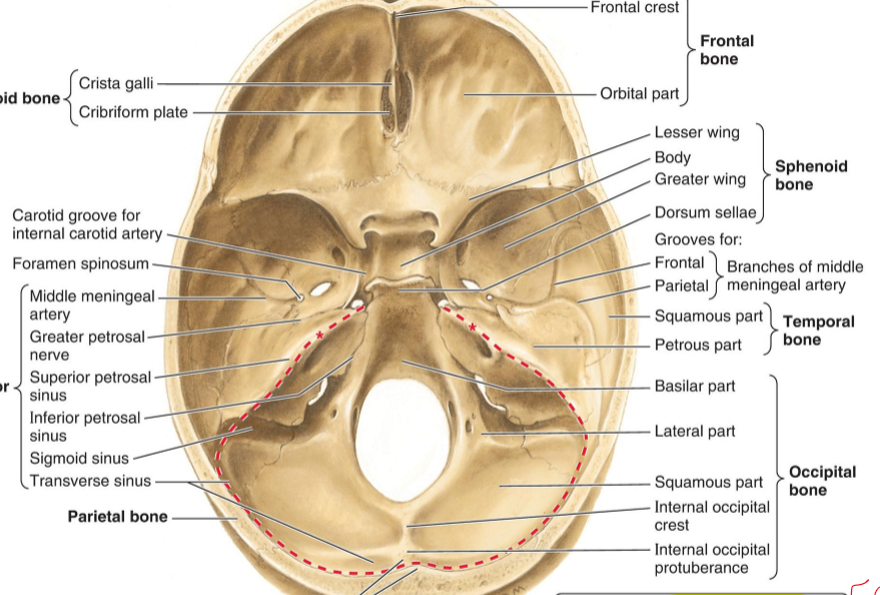
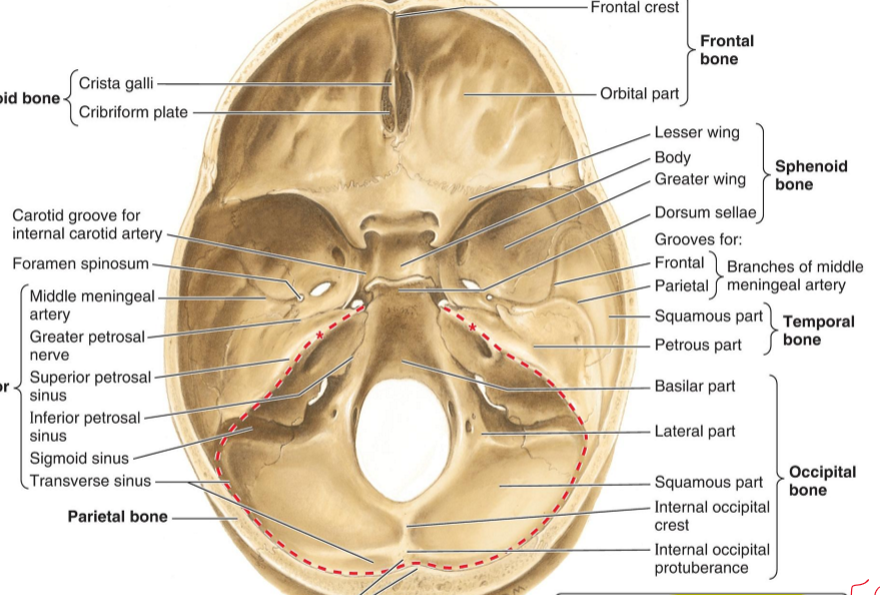
Horizontal Plate (Palatine)
Medial and lateral plates of pterygoid process (Sphenoid)
Jugular foramen (Temporal)
Palatine process (Maxilla)
Mandibular fossa (Temporal)
Styloid process (Temporal)
Stylomastoid foramen (Temporal)
Mastoid process (Temporal)
Foramen Magnum
External Occipital protuberance
Superior nuchal line
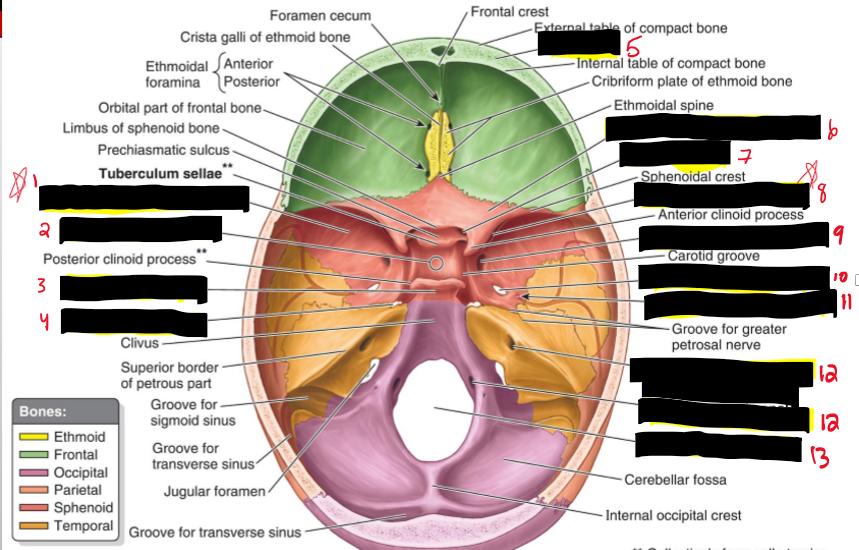
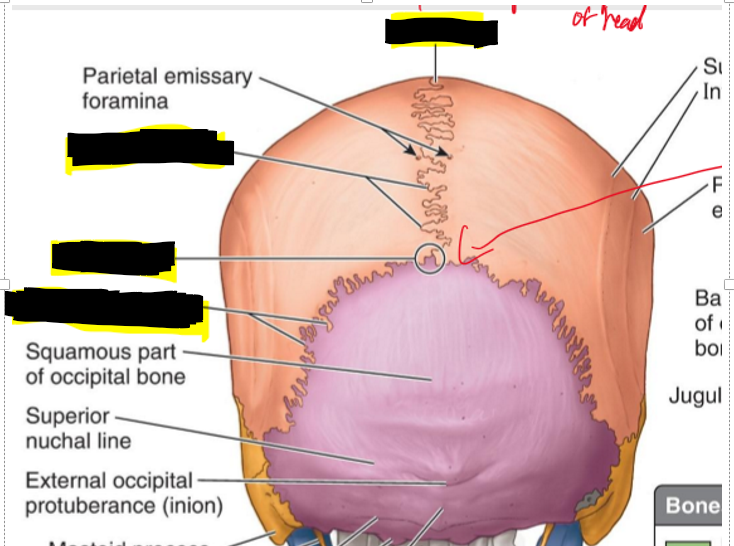
Name the structures.
Greater wing of sphenoid bone
Hypophysial fossa (sphenoid bone)
Dorsum sellae (Sphenoid bone)
Foramen lacerum
Diploe (Front bone)
Lesser wing of sphenoid bone
Optic canal (sphenoid bone)
Superior orbital fissure (sphenoid bone)
Foramen rotundum (sphenoid)
Foramen spinosum (sphenoid)
Opening of internal acoustic meatus (temporal)
Hypoglossal canal (Occiptial)
Foramen magnum
CN1
Olfactory — Smell (Olfactory mucosa of nose) — special Sensory
CN II
Optic — Vision (Retina of eye) — special Sensory
CN III
Oculomotor — Eye movement, pupil constriction (intraocular and four extra-ocular )— Motor
CN IV
Trochlear — Eye movement (superior oblique) — Motor
CN V
Trigeminal — Facial sensation, mastication (Derivatives of frontonasal process and 1st pharayngeal) — Both
CN VI
Abducens — Eye movement (lateral rectus) — Motor
CN VII
Facial — Facial expression, taste (anterior 2/3 tongue), lacrimation, salivation — Both
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear — Hearing and balance — Special Sensory - Internal ear
CN IX
Glossopharyngeal — Taste (posterior 1/3), salivation, carotid body reflexes — Both- Derivatives of 3rd pharyngeal
CN X
Vagus — Parasympathetic to thoracoabdominal viscera, voice, swallowing — Both- Derivatives of 4th pharyngeal arch
CN XI
Accessory (Spinal) — Shoulder and neck muscles (SCM, trapezius) — Motor
CN XII
Hypoglossal — Tongue movement — Motor
What is a mnemonic for the cranial nerves?
Oh- Olfactory
Oh- Optic
Oh- Oculomotor
To- Trochlear
Take- Trigeminal
A- Abducens
Family- Facial
Vacation- Vestibulocochlear
Go- Glossopharyngeal
Vegas- Vagus
After- Spinal Accessory
Hours- Hypoglossal
What is a mnemonic for Cranial nerve type of fibers?
"Some Say Marry Money, But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More"
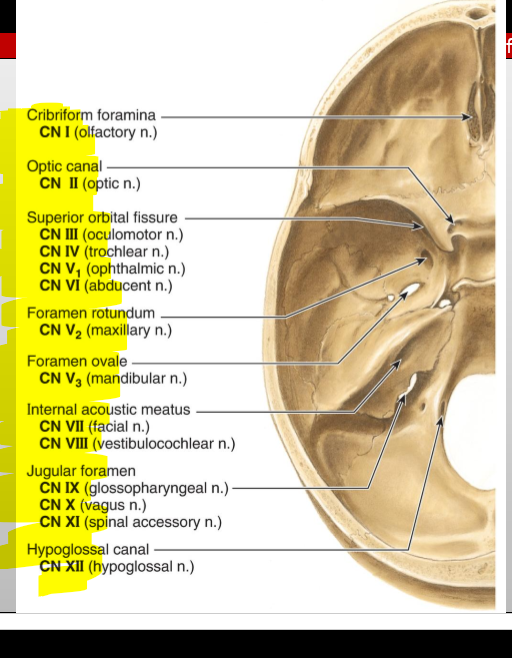
CN I (Olfactory) — where does it enter the cranial cavity?
Cribriform plate of the ethmoid (from nasal cavity)
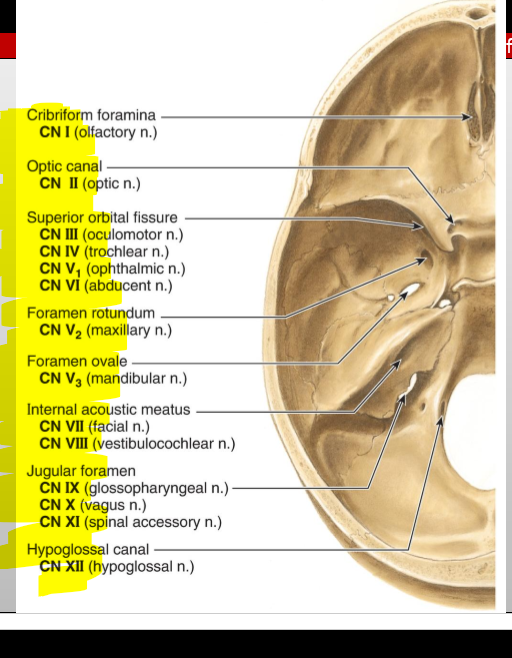
CN II (Optic) — what canal does it pass through?
Optic canal
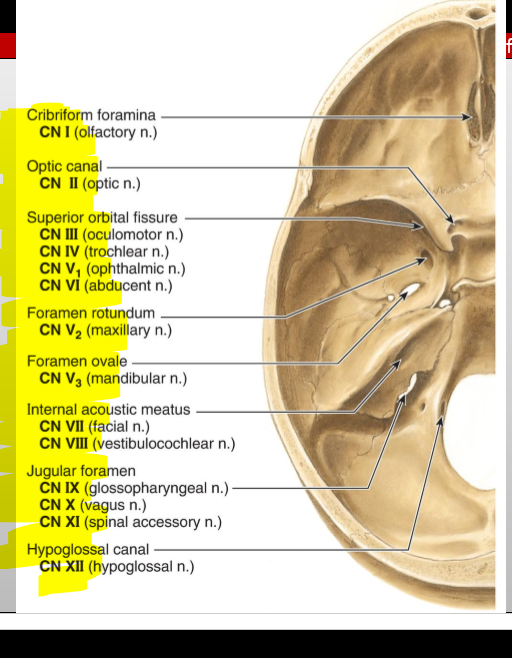
CN III (Oculomotor) — what does it exit through?
Superior orbital fissure
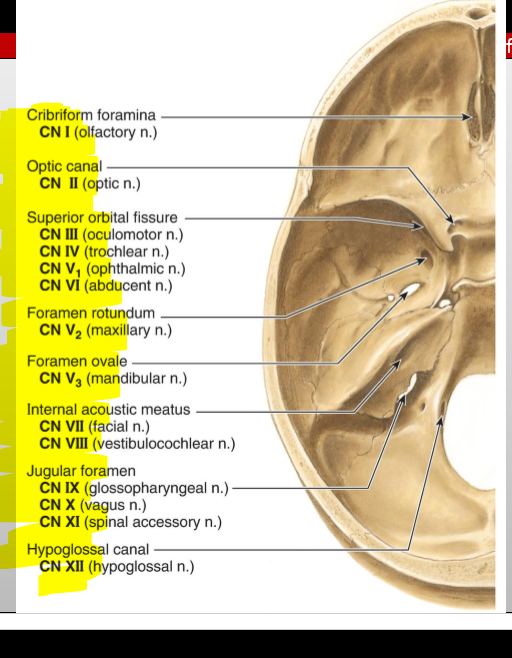
CN IV (Trochlear) — what does it exit through?
Superior orbital fissure
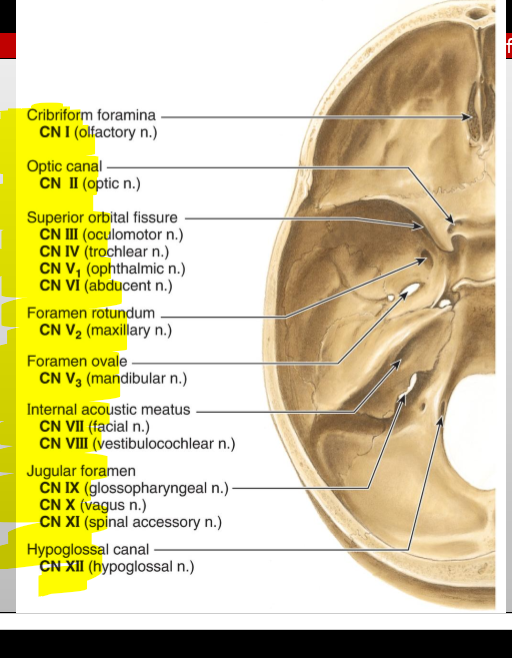
CN V₁ (Ophthalmic division of Trigeminal) — exit?
Superior orbital fissure
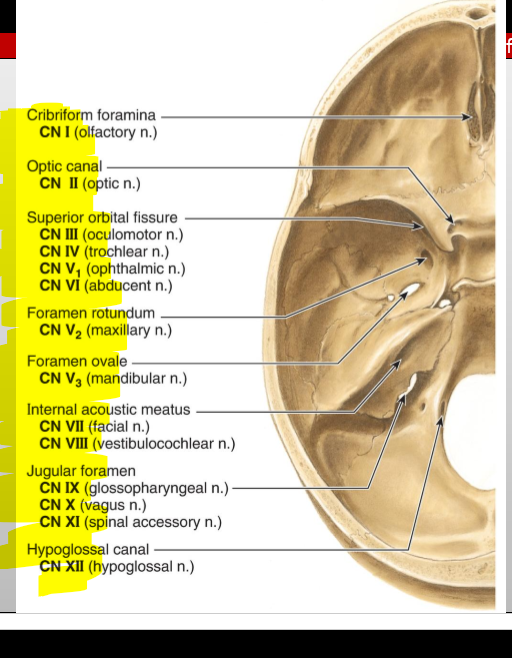
CN V₂ (Maxillary) — exit?
Foramen rotundum
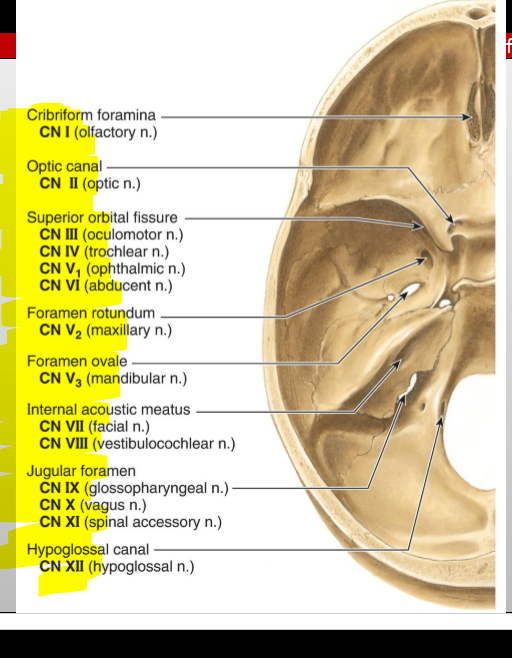
CN V₃ (Mandibular) — exit?
Foramen ovale
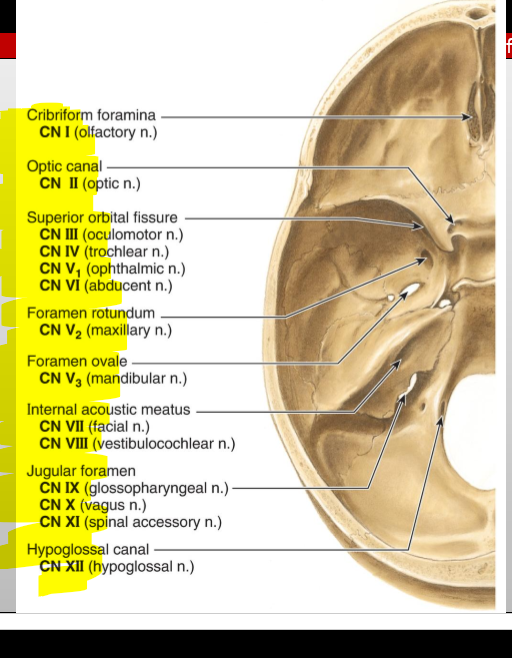
CN VI (Abducens) — exit?
Superior orbital fissure
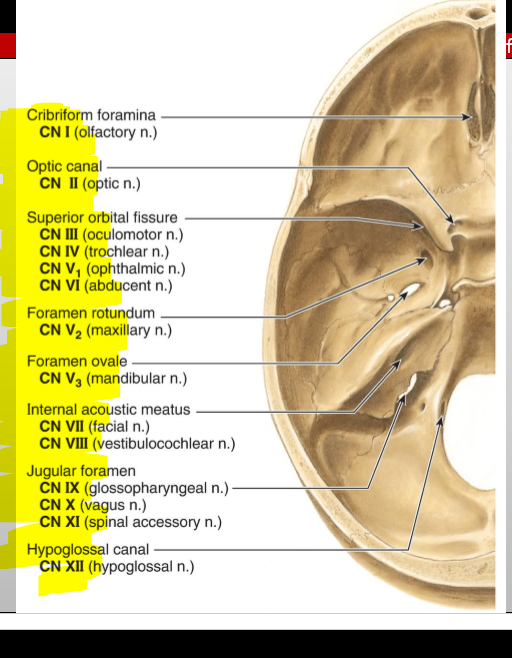
CN VII (Facial) — entry and exit pathway?
Enters internal acoustic meatus, exits skull via stylomastoid foramen
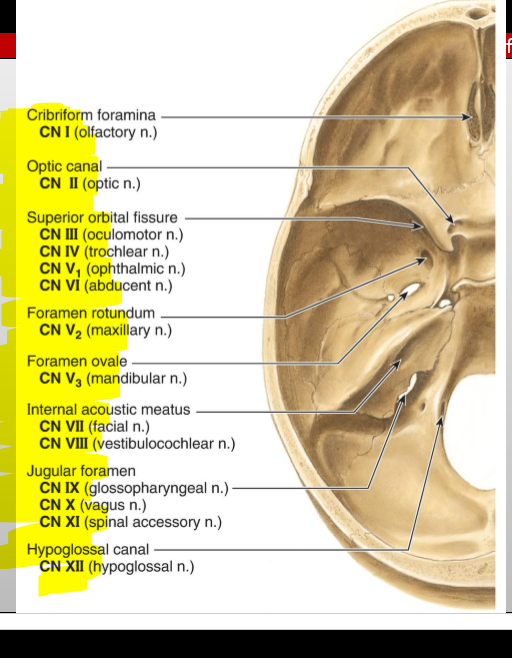
CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear) — entry?
Internal acoustic meatus
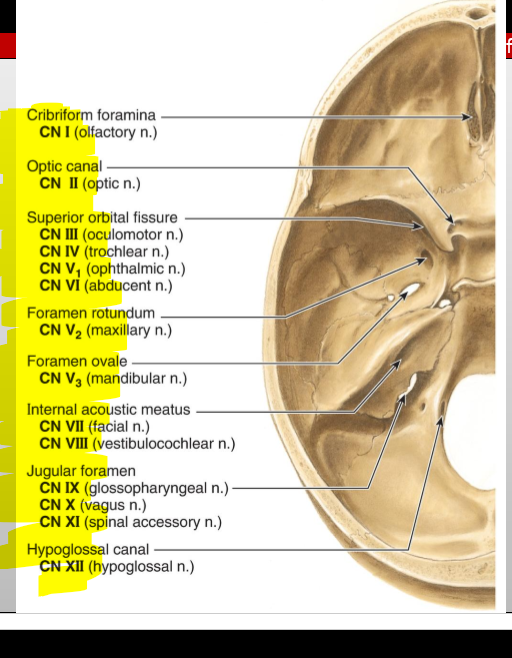
CN IX (Glossopharyngeal) — exit?
Jugular foramen
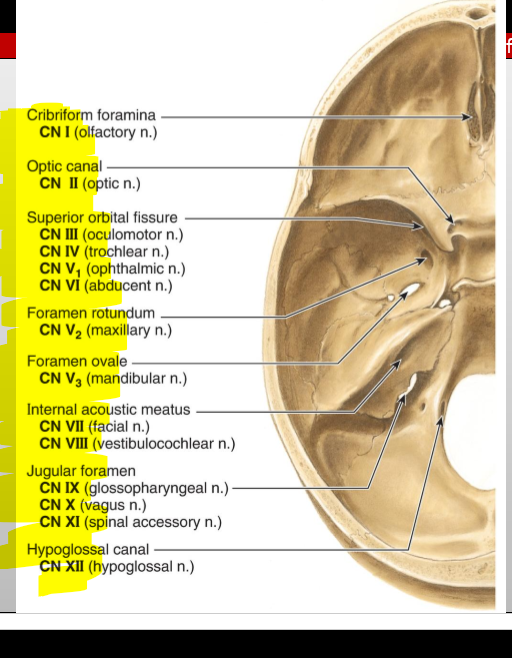
CN X (Vagus) — exit?
Jugular foramen
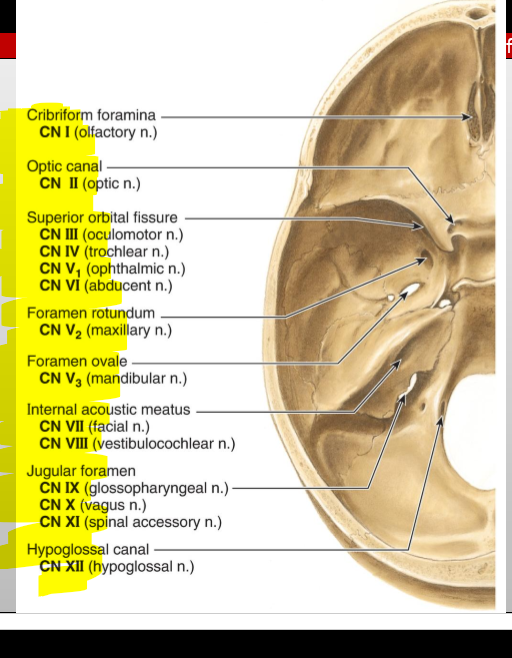
CN XI (Accessory) — pathway?
Enters via foramen magnum, exits via jugular foramen
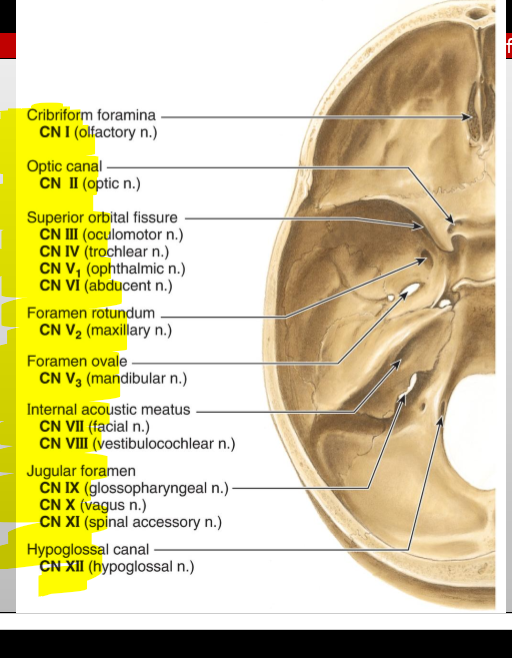
CN XII (Hypoglossal) — exit?
Hypoglossal canal
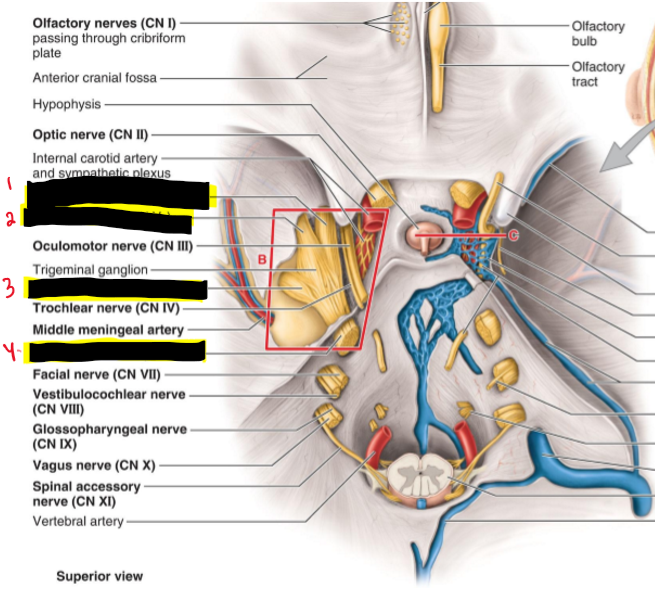
What How many nerves stem from the trigeminal n.? name the structures.
3 nerves stem from the trigeminal n.
Opthalmic n. (CNV1)
Maxillary n. (CNV2)
Mandibular n. (CNV3)
Trigeminal n. (CN V)
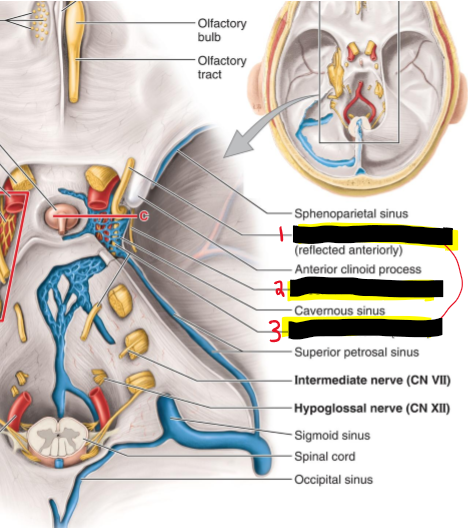
Name the structures
Oculomotor n (CN III)
Trochlear n. (CN IV)
Abducence n (CN VI)
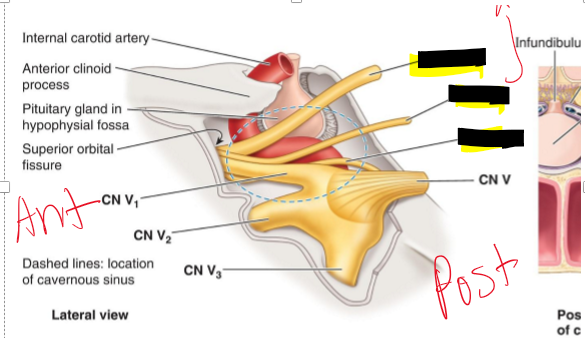
Name the structure.
CN III Oculomotor n.
CN IV Trochlear n
CN VI Abducent n.
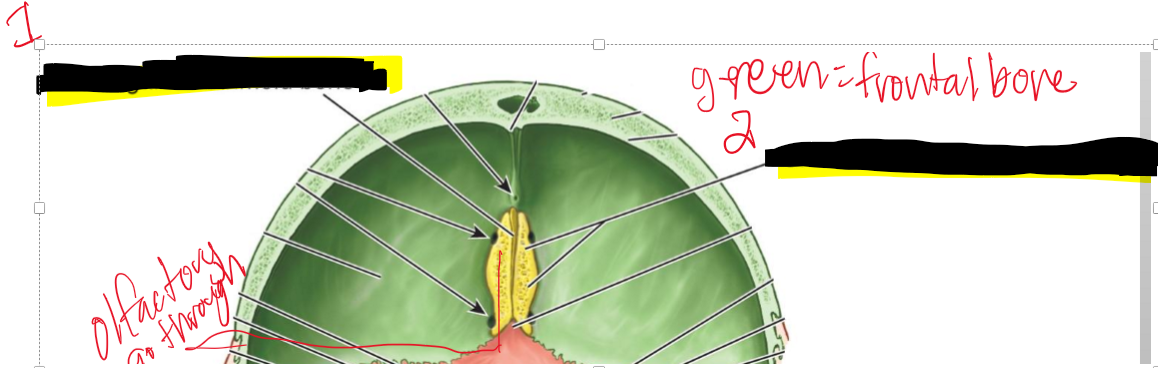
Name the structure
Crista galli of ethmoid bone
Cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
What nerve passes through the cribriform plate, and what does it connect?
CN I (Olfactory); connects nasal cavity to olfactory bulbs of the brain
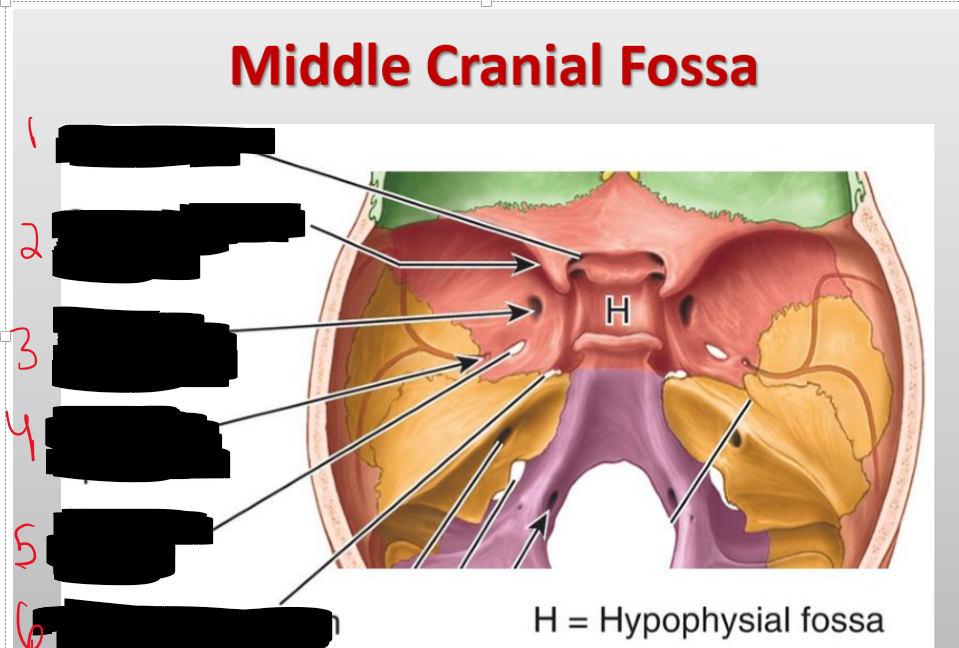
Name the structure.
Optic Canal
Superior Orbital
Foramen rotundum
Foramen spinosum
Foramen ovale
Foramen lacerum
What passes through the optic canal?
Optic nerve (CN II) and ophthalmic artery
What cranial nerve passes through the foramen rotundum?
: Maxillary nerve (CN V₂)
What structures pass through the foramen ovale?
Mandibular nerve (CN V₃) and accessory meningeal artery
What structures pass through the superior orbital fissure?
CN III, IV, V₁, VI, ophthalmic veins, ophthalmic nerve
What passes through the foramen spinosum?
Middle meningeal artery/vein and meningeal branch of CN V₃
What structures are associated with the foramen lacerum?
Internal carotid artery (with sympathetic and venous plexi)
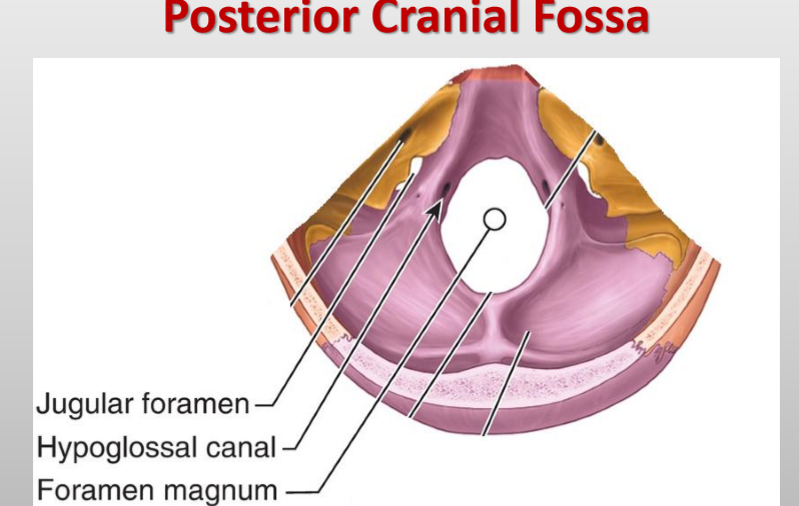
What passes through the foramen magnum? (Posterior fossa)
Medulla, meninges, vertebral arteries, CN XI (spinal root), dural veins, anterior & posterior spinal arteries
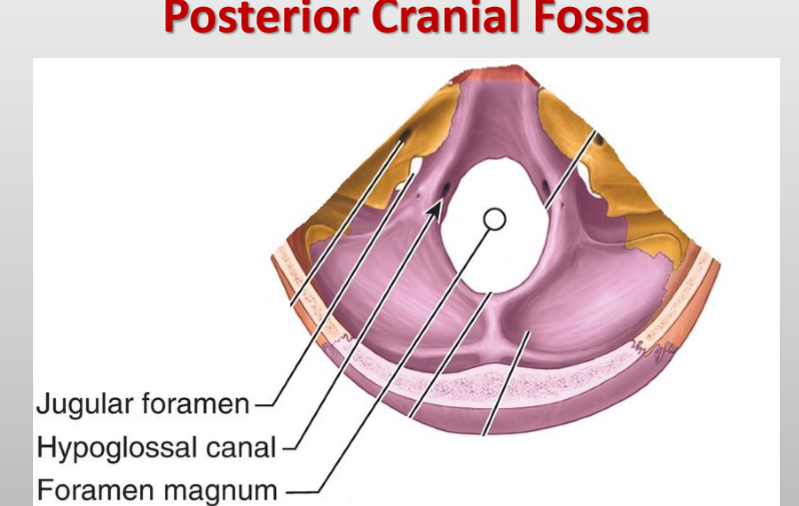
What cranial nerves pass through the jugular foramen? (posterior fossa)
CN IX (Glossopharyngeal), X (Vagus), and XI (Accessory)
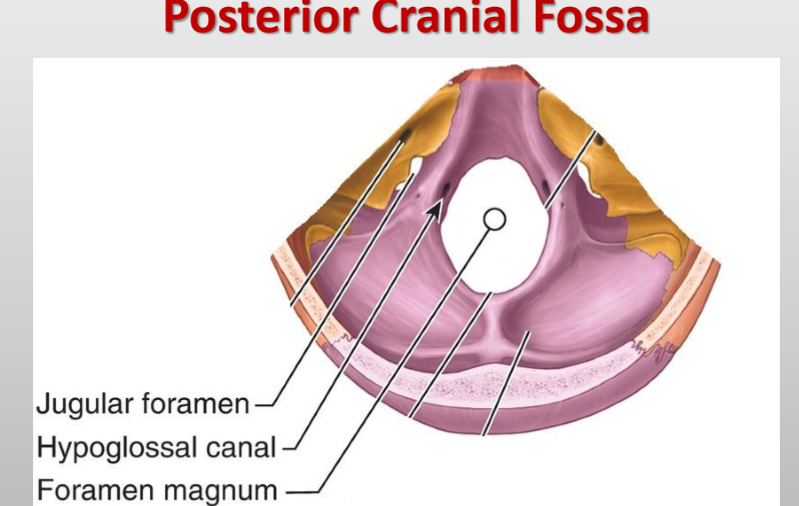
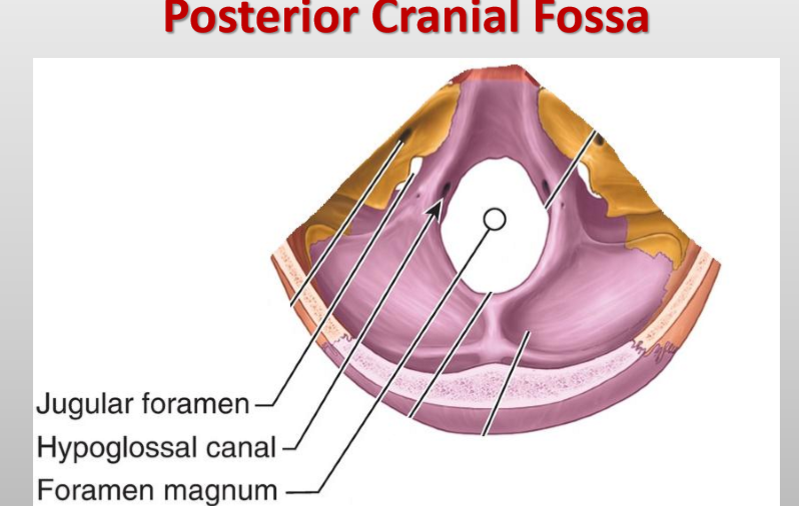
What vessels and sinuses pass through the jugular foramen? (posterior fossa)
Superior bulb of internal jugular vein, inferior petrosal sinus, sigmoid sinus
What arteries pass through the jugular foramen? (posterior fossa)
Meningeal branches of ascending pharyngeal and occipital arteries
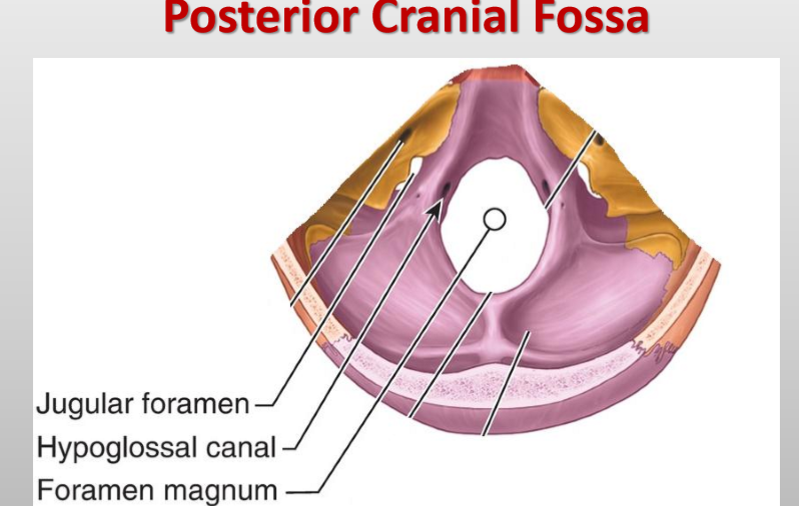
What passes through the hypoglossal canal? (posterior fossa)
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
What is diploë?
Spongy bone located between the inner and outer tables of the cranial bones
What are the cranial meninges?
Three membranes that surround the brain and continue with the meninges of the spinal cord
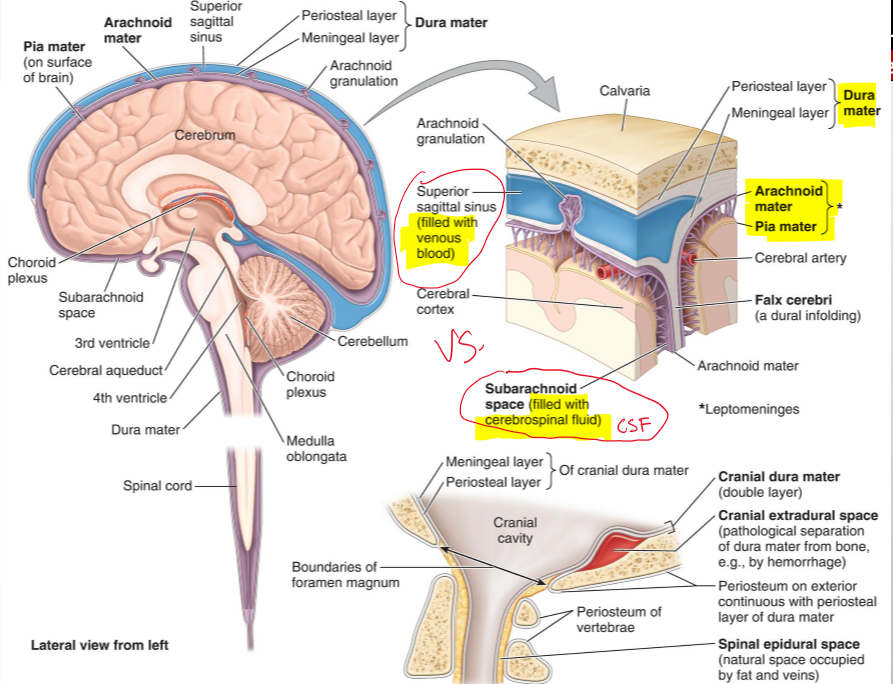
Name the three cranial meninges.
Dura mater (fused to periosteum), arachnoid mater, pia mater
What are the two parts of the dura mater in the cranial cavity?
Periosteal dura and meningeal dura
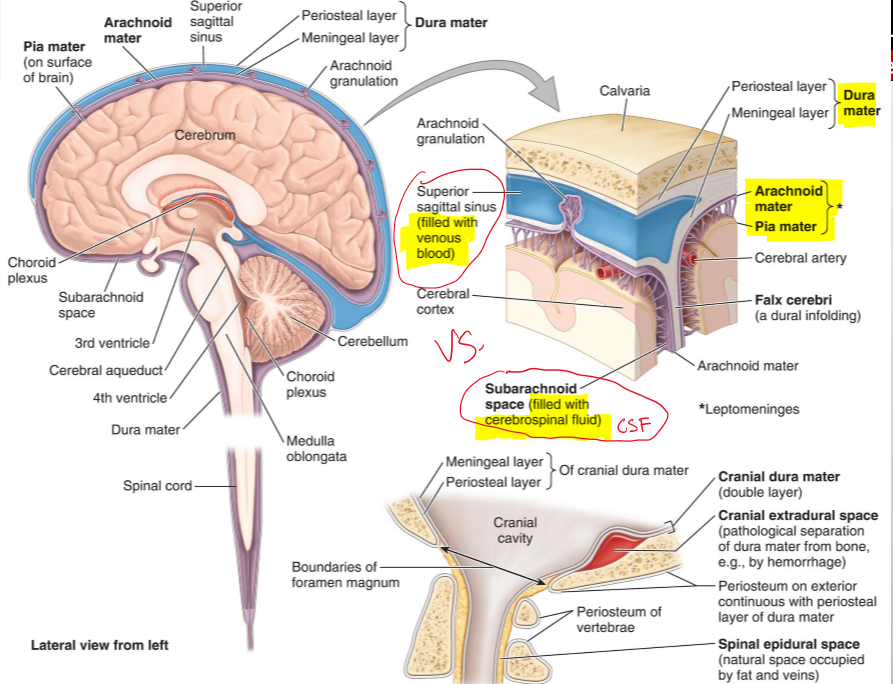
What is the periosteal dura?
The outer layer of the dura mater, continuous with the periosteum of the inner surface of the skull
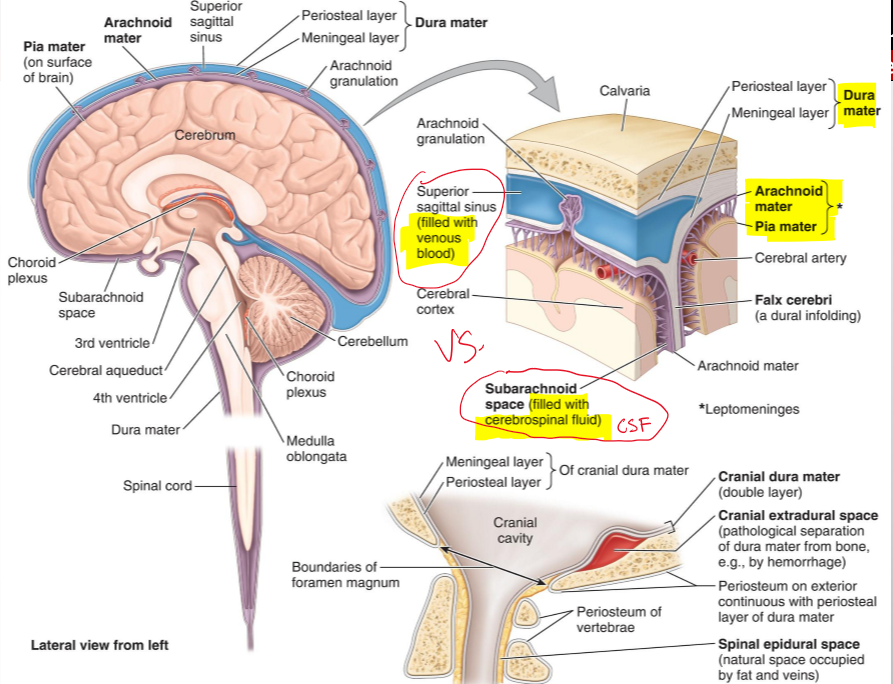
What is the meningeal dura?
The inner layer of the dura mater, continuous with the dura of the spinal cord
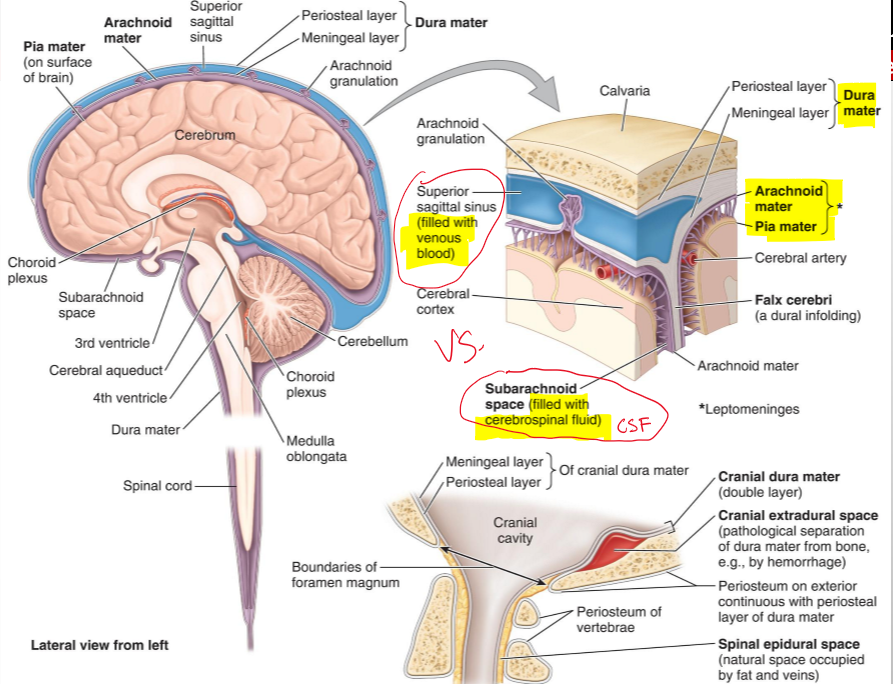
What is the arachnoid mater?
A delicate membrane that lines the inner surface of the dura mater
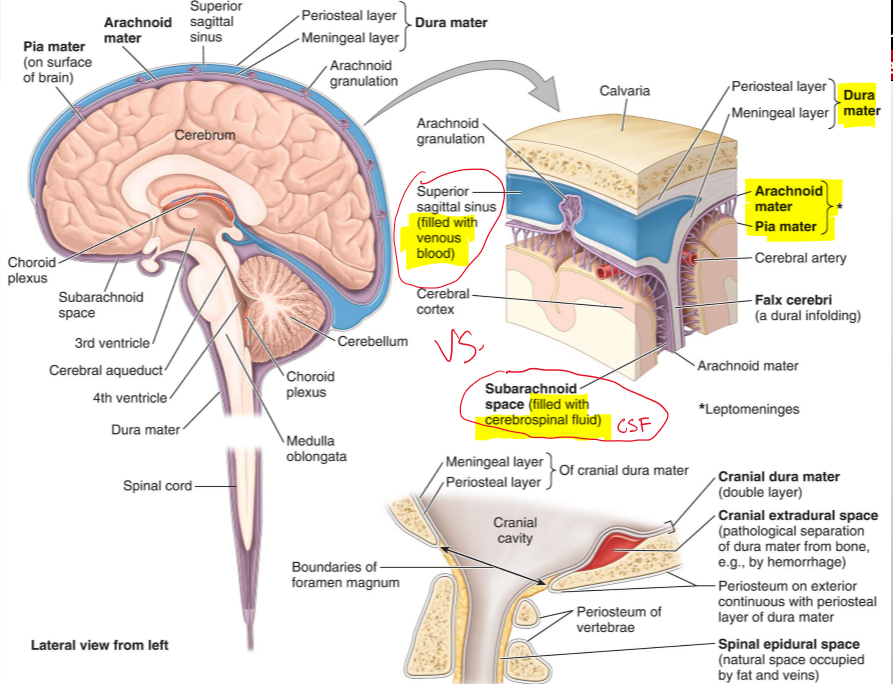
What are arachnoid trabeculae?
Fine extensions of arachnoid mater that span the subarachnoid space and attach to the pia mater
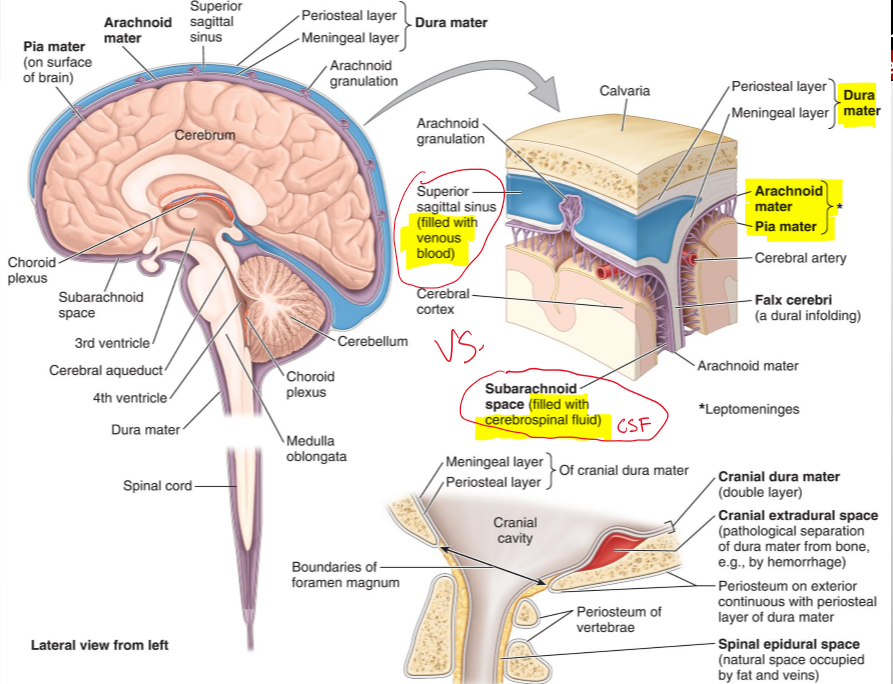
What is the subarachnoid space?
The space between the arachnoid and pia mater, filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
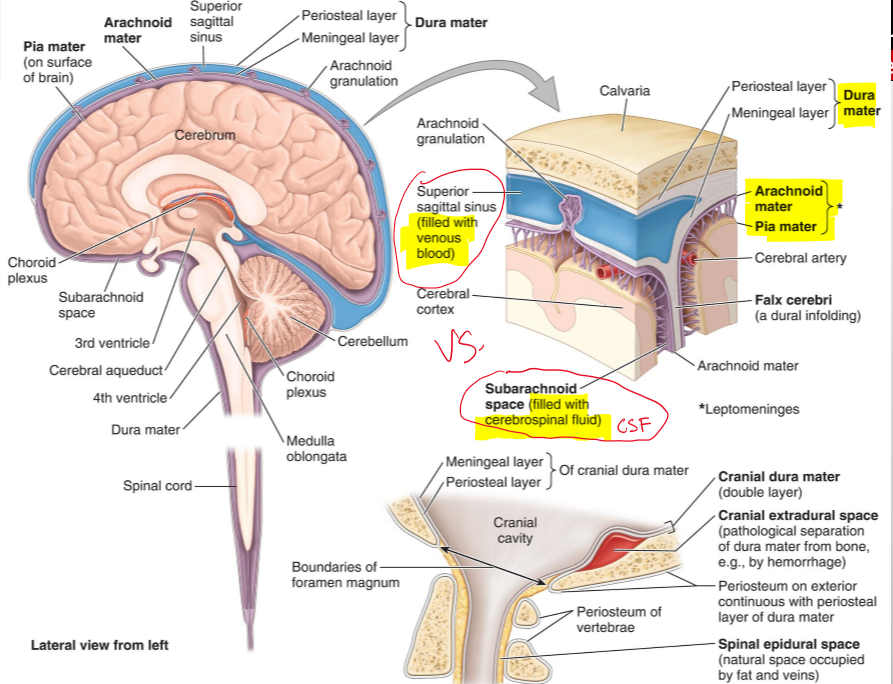
What is the pia mater?
A vascular, delicate membrane that closely adheres to the surface of the brain
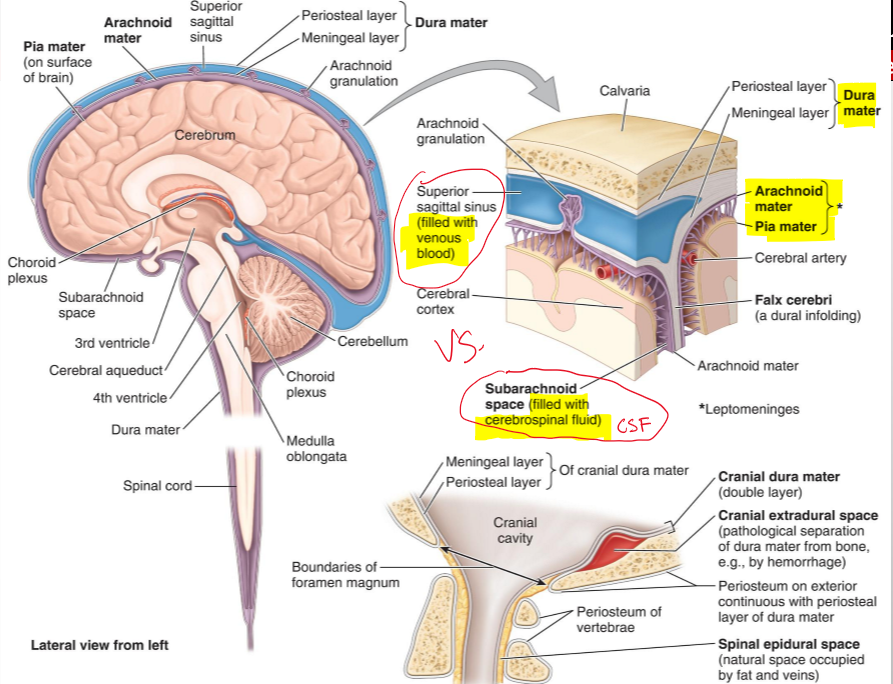
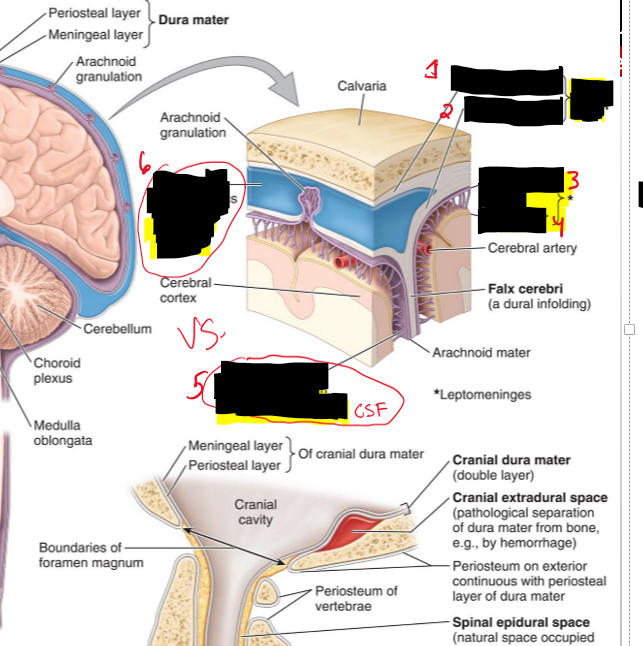
Name the structure.
Periosteal layer (dura mater)
Meningeal layer (dura mater)
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Subarachnoid space (filled CSF)
Superior sagittal sinus (filled with venous blood)
The separation of what create dural venous sinuses
The separation of meningeal dura from periosteal dura
What lines the dural venous sinuses and what are their functions?
Endothelium (same as blood vessels) and They drain venous blood from the brain and meninges
What do dural folds do?
They are infoldings of the meningeal dura that dip into fissures between parts of the brain
What are the four dural folds of the brain?
Falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, falx cerebelli, diaphragma sellae
What is Falx Cerebri?
It seperates the cerebral hemisphere [longitudinal fissure]
![<p>It seperates the cerebral hemisphere [longitudinal fissure]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c27f5fd1-f4d8-4c77-82dc-e8f5e1bad48d.png)
What dural venous sinuses are associated with the falx cerebri?
Superior sagittal sinus (superior margin) and inferior sagittal sinus (inferior margin)
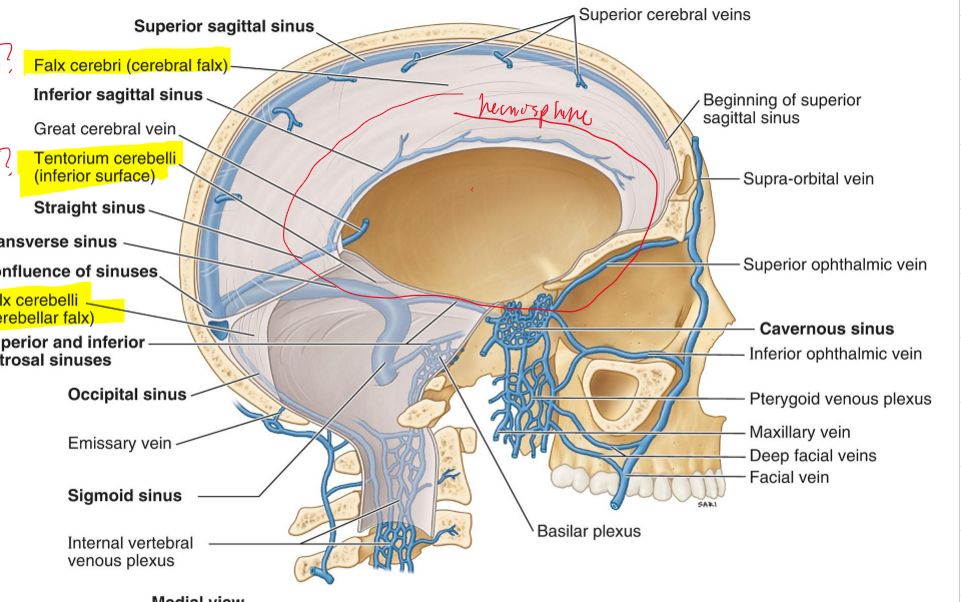
What is the falx cerebelli?
It separates the cerebellar hemisphere
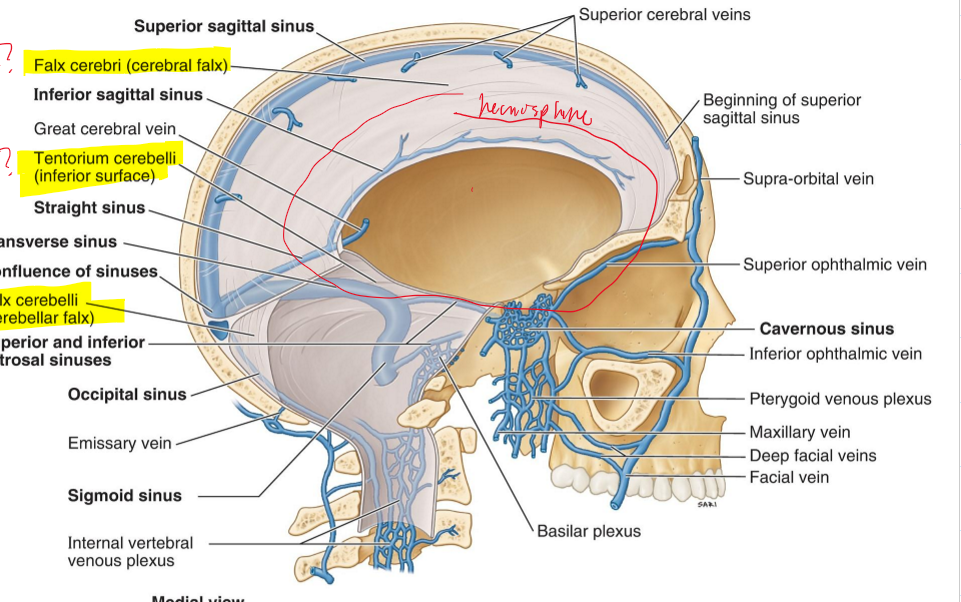
What sinus is associated with the falx cerebelli?
Occipital sinus
What is the tentorium cerebelli?
It separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum
What dural venous sinus is found along the edge of the tentorium cerebelli?
Transverse sinus
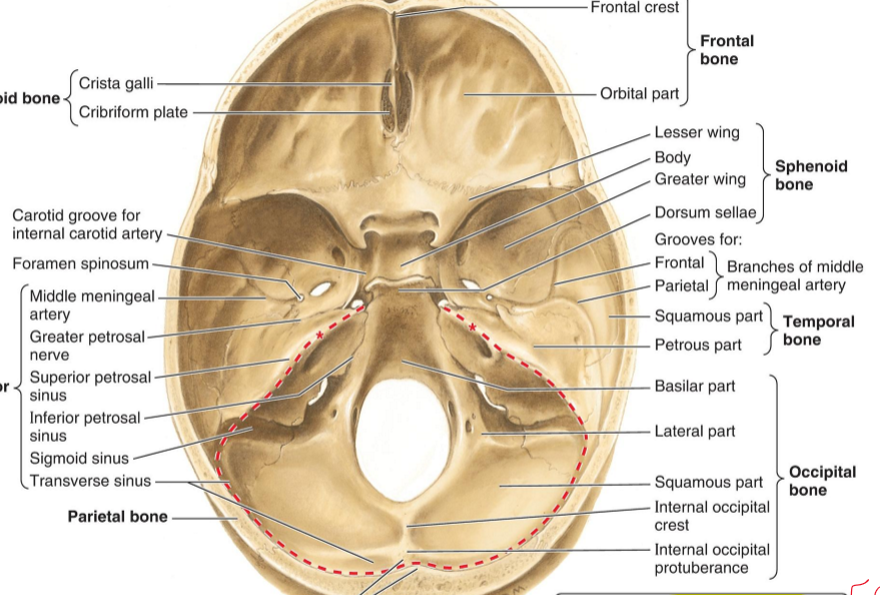
What is the diaphragma sellae?
Closes off the pituitary gland
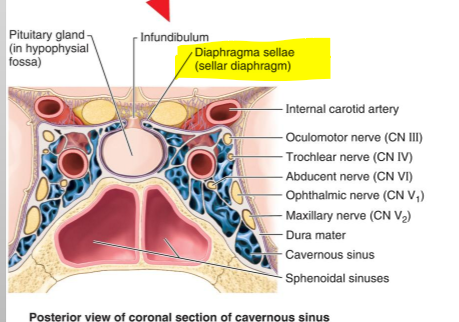
What structure passes through the diaphragma sellae?
Infundibulum (pituitary stalk) connecting the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
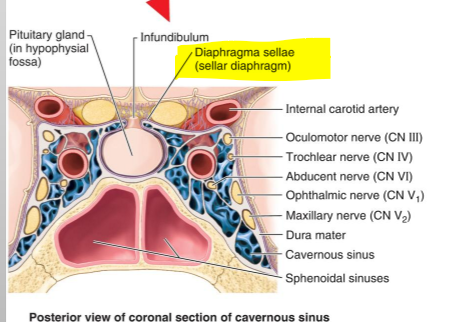
Name the structure.
Falx cerebri (cerebral falx)
Tentorium cerebelli (inferior surface)
Falx cerebelli (cerebellar falx)
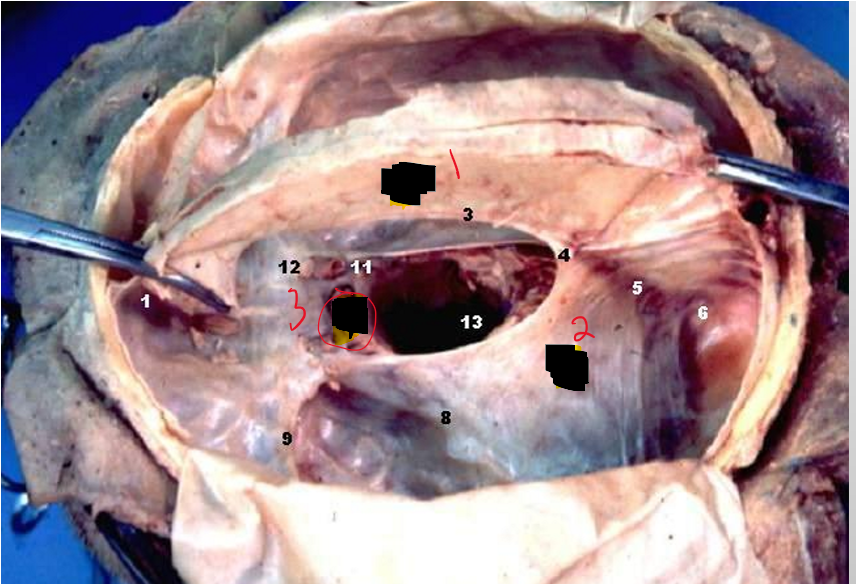
Name the Structure.
Falx cerebri
Tentorium cerebelli
Diaphragma sellae
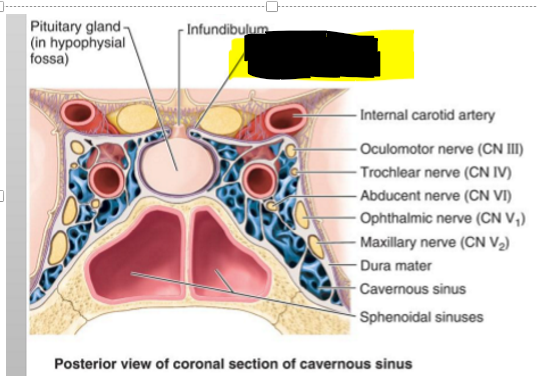
Name the structure
Diaphragma Sellae
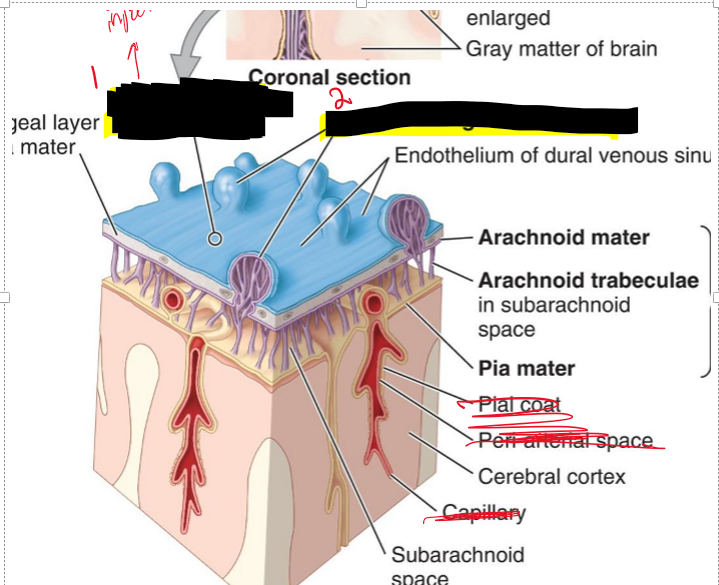
Name the structure.
Lumen of dural venous sinus
Arachnoid granulations (small protrusions of the arachnoid membrane (a thin layer of tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord) into the dural sinuses, which are large veins that drain blood from the brain. They play a crucial role in the reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
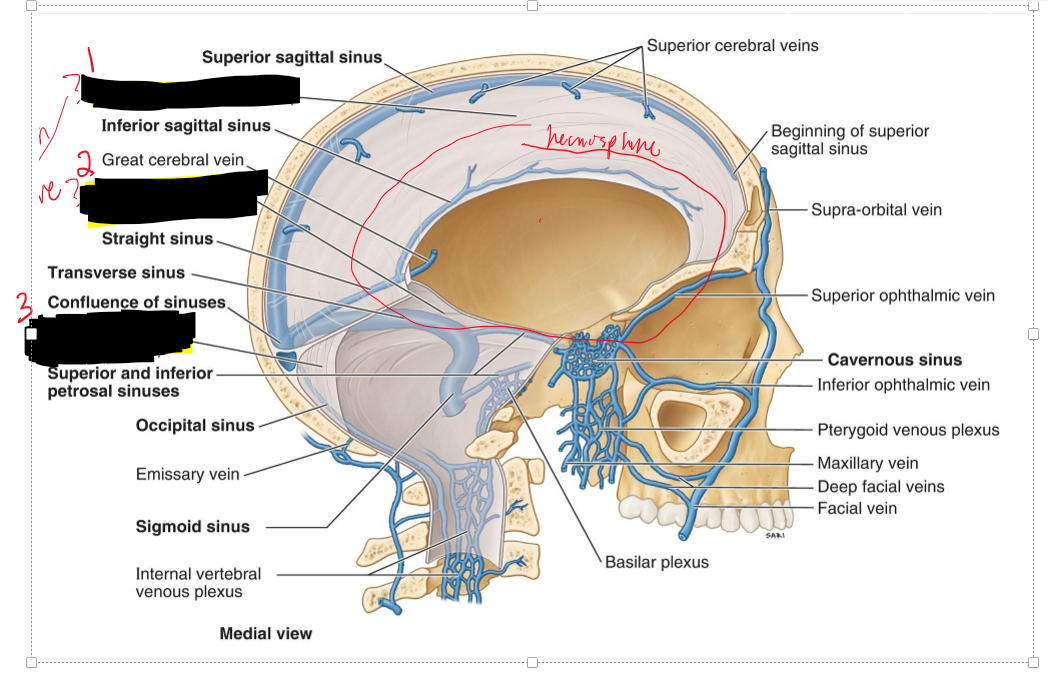
What are the 9 dural sinuses?
1. Superior sagittal sinus
2. Inferior sagittal sinus
3. Transverse sinus
4. Straight sinus
5. Occipital sinus
6. Cavernous sinuses
7. Superior petrosal sinus
8. Inferior petrosal sinus
9. Sigmoid sinus
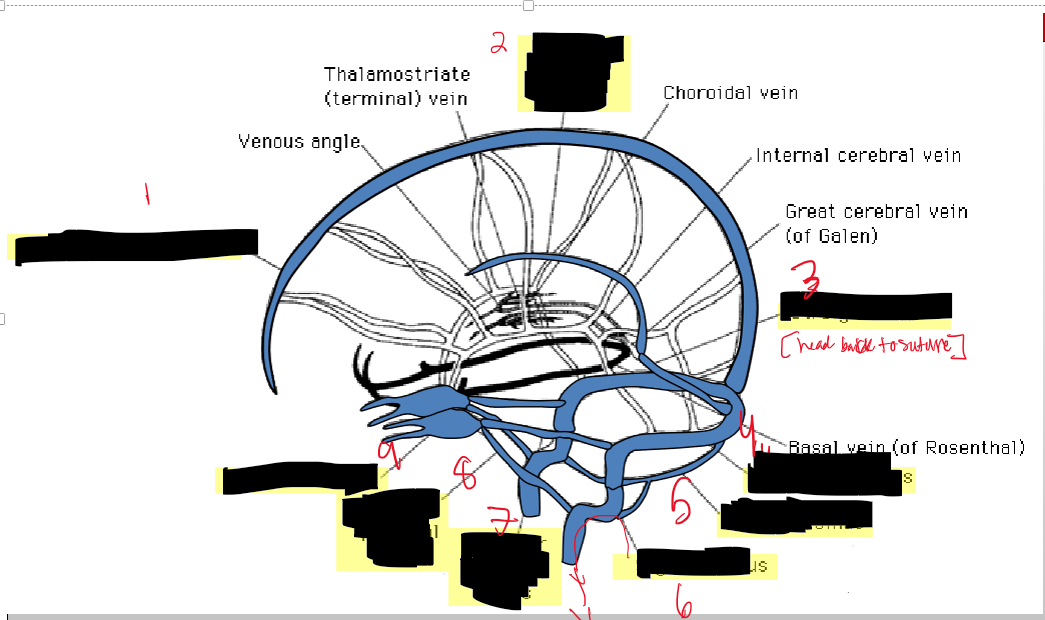
Name the structure.
Superior sagittal sinus
Inferior sagittal sinus
Straight sinus
Transverse sinus
Occipital sinus
Sigmoid sinus
Superior petrosal
Inferior petrosal
Cavernous sinus
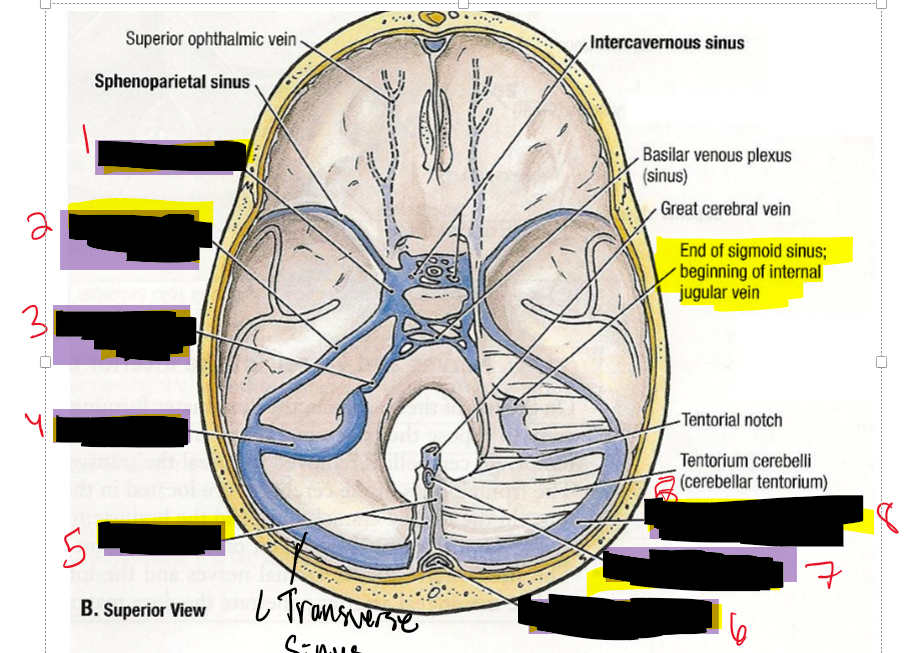
Name the structure.
Cavernous sinus
Superior petrosal sinus
Inferior petrosal sinus
Sigmoid sinus
Straight sinus
Superior sagittal sinus
Inferior sagittal sinus
Right transverse sinus
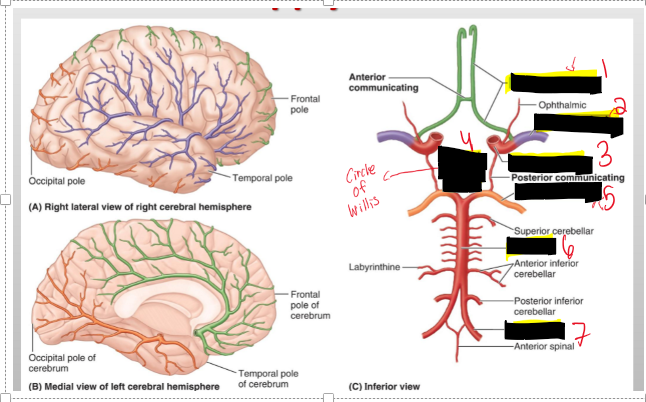
Name the structure.
Anterior cerebral
Middle cerebral
Internal carotid
Cerebral arterial circle
Basilar
Vertebral
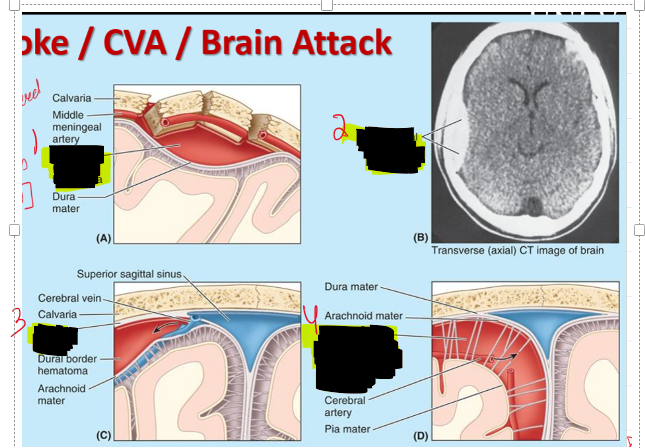
Name the structures
1 and 2. Extradural (epidural hematoma)
Dura border (subdural hematoma)
Subarachnoid hemmorrhage
If you have a stroke is it better to have a fracture related one or not and tell me why?
It is better to have a fracture related stroke because there is pressure to go out the head whereas a stroke w/ out a fracture there is no pressure to release so the pressure get pressed onto the brain.
What structures are included in the cerebrum?
The cerebral hemispheres and basal ganglia.
What separates the cerebral hemispheres?
The falx cerebri within the longitudinal cerebral fissure.
Into how many lobes is each cerebral hemisphere divided?
Four lobes.
What are the names of the four lobes of the cerebral hemispheres?
Frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes.
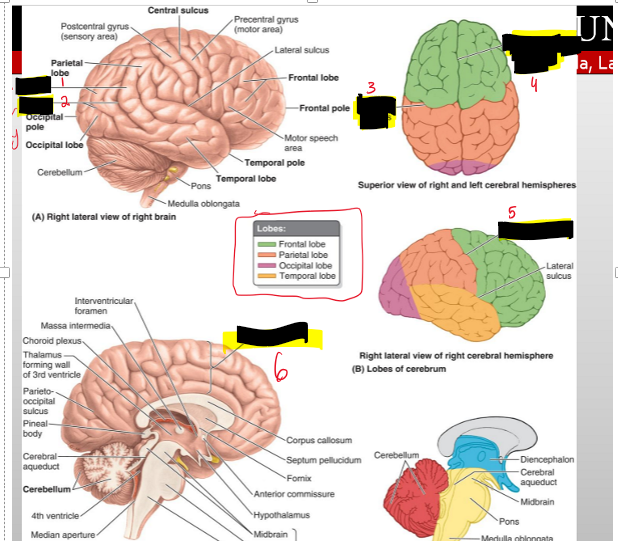
Name the structures
Gyri (Bumps)
Sulci (Valley)
Central Sulcus
Longitudinal cerebral fissure
Central sulcus
Cerebrum
From a superior view, which two landmarks divide the cerebrum into quarters?
The longitudinal cerebral fissure and the central sulcus
What sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes?
The central sulcus
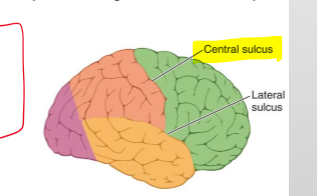
Where is the temporal lobe located in relation to the lateral sulcus?
Inferior to the lateral sulcus.
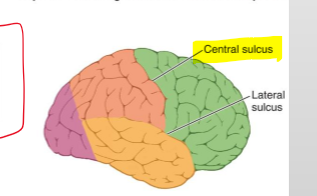
What sulcus separates the occipital lobe from the parietal and temporal lobes?
The parieto-occipital sulcus.
What are the three components of the diencephalon?
Epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus.