ANATOMY WEEK 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
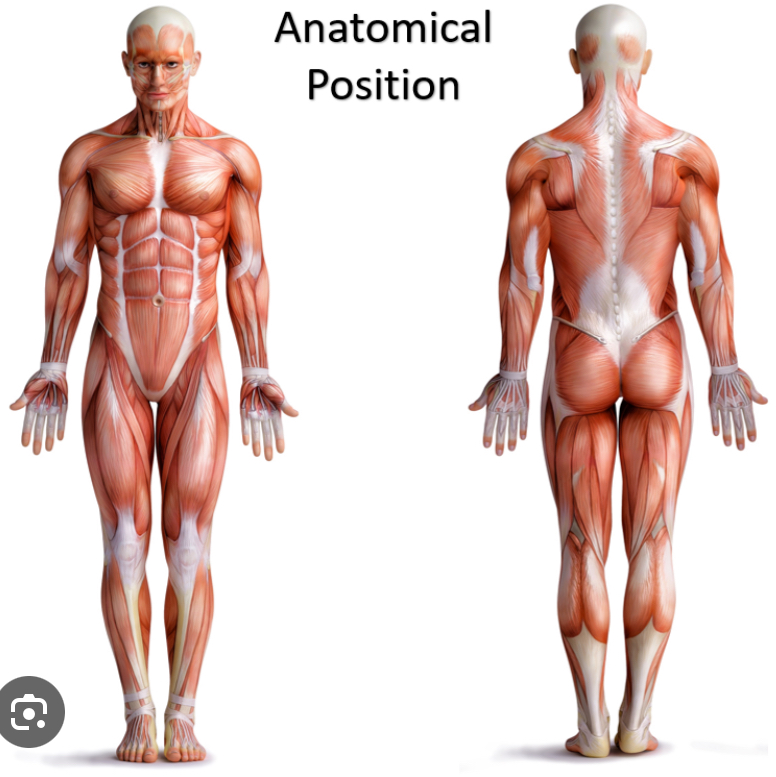
Anatomical Position
is the starting point for describing positions and directions of the human body, with the body standing upright, feet slightly apart, face and shoulders facing forward, and palms facing forward.
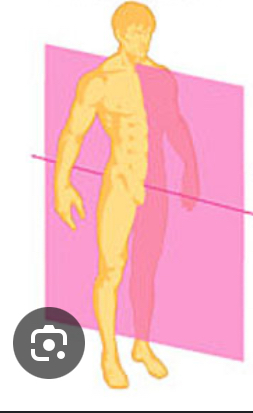
Sagittal Plane
Divides body into right and left halves
Frontal plane
Divides body into front and back halves
Transverse plane
Divides body into top and bottom halves
Anterior or ventral
Towards the front of the body
Posterior or dorsal
Towards the back of the body
Medial
Towards the midline of the body
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
Distal
Away from the trunk
Superficial
Towards the surface of the body
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
Axial body: Head and Neck
Cephalic region
Cervical region
Cranial region
Frontal region
Occipital region
Oral region
Orbital or ocular region
Axial body:Thorax
Axillary region
Deltoid region
Pectoral region
Scapular region
Sternal region
Vertebral region
Axial Body: Abdomen
Abdominal region
Gluteal region
Lumbar region
Pelvic region
Pubic region
Sacral region
Axial Body: Appendicular body, Upper extremity
Antebrachial region
Antecubital region
Brachial region
Carpal region
Cubital region
Digital region
Manual region
Palmar region
Axial Body:Appendicular body, Lower extremity
Crural region
Femoral region
Patellar region
Pedal region
Plantar region
Popliteal region
Sural region
Tarsal region
Cavities
The human body has various cavities that hold internal organs, including the: posterior or dorsal body cavity(cranial and spinal cavities), and the anterior or ventral body cavity (thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities). There are also smaller cavities like the oral, nasal, orbital, middle ear, and pleural cavities.
Atoms
Combine to form molecules
Cells
Are the smallest building blocks of living beings
Cells for 4 tissues:
epithelial, connective, muscular, and neural.
Organ
Organs are composed of different types of tissues and perform specific functions
Organ Systems
consist of two or more organs that work together
Integumentary system
skin and appendages (hair, fingernails); covering the body, protecting tissues, synthesising vitamin D, eliminating waste, regulating body temperature.
Skeletal system
bones, cartilage, ligaments; protecting and supporting organs, providing a framework for muscles, producing blood cells, storing minerals.
Muscular System
cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscle tissue; locomotion, facial expression, posture maintenance, body heat production, digestion.
Nervous System
brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors; fast-acting control system, responding to internal and external changes, activating muscles and glands.
Endocrine System
endocrine glands; secretion of hormones into the bloodstream.
Respiratory System
lungs, nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea; oxygen supply, carbon dioxide removal, gas exchange in lung air sacs.
Cardiovascular System
heart, blood vessels; pumping blood, transporting respiratory gases, nutrients, hormones, and wastes.
Lymphatic System
lymphatic vessels, nodes; collecting leaked fluid, returning it to the blood, disposing of debris, housing immune cells.
Digestive System
oesophagus, stomach, intestines, and accessory organs; breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, removing indigestible waste.
Urinary System
kidneys, bladder; eliminating nitrogen waste, regulating water, electrolyte and acid-base balance.
Male reproductive System
testes, scrotum, penis; producing sperm, delivering viable sperm to the female reproductive tract.
Female Reproductive System
ovaries, uterus, vagina; producing eggs, site for fertilization and foetal development, milk production for nourishing newborns.
Homeostasis
Homeostasis involves the coordination of organ systems to regulate factors like body temperature, blood pressure, blood sugar, water balance, and sodium levels.
Homeostasis is the state of regulated physiological balance.
Homeostatic mechanisms maintain homeostasis by the collaboration of nervous and endocrine systems.
Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and transmit information to a control centre.
The control centre analyses the information and sends commands to effectors to maintain homeostasis.
Most homeostatic mechanisms operate through negative feedback loops.
Negative feedback restores the system to its set point by counteracting changes in the opposite direction.
Examples of negative feedback include a thermostat controlling room temperature and the body's response to changes in body temperature.
Positive feedback loops can also occur, amplifying disruptive influences.
Positive feedback is involved in processes like blood clotting, nerve signal transmission, and contractions during childbirth.
Excessive positive feedback, such as a high fever, can be dangerous and requires intervention.
Homeostasis doesn't mean constant conditions, but rather routine fluctuations within a normal range.
Strenuous exercise, for example, causes temporary increases in blood pressure and body temperature.
Homeostatic mechanisms work to maintain these fluctuations within a healthy range.