Topic 1 - Quantization of Energy: Waves and Particles
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Tera (T)
1012
Giga (G)
109
Mega (M)
106
Kilo (K)
103
Deci (d)
10-1
Centi (c)
10-2
Milli (m)
10-3
Micro (μ)
10-6
Nano (n)
10-9
Classical Mechanics
Motion described as particles (Newton) or waves (Maxwell)
Quantum Mechanics
Objects like electrons or light can show both particle-like and wave-like behaviour
Classical Mechanics - Particles
Governed by Newton’s equations of motion.
Described using momentum, energy, forces, torques, etc.
Have mass - (Exception: There are massless quantum mechanical objects that can have particle-like behavior (e.g: photon — a quantised packet of light energy).
Classical Mechanics - Waves
Governed by Maxwell’s theories
Carries energy through different medias: Water waves, sound waves, vibrating strings.
Three Key Properties
Wavelength (λ) — distance between crests/troughs; unit: m.
Frequency (f or ν) — waves passing a point per second; unit: Hz (s⁻¹).
Speed (s) — waves propagate at a speed that depends on the medium; unit: m s⁻¹.
Observable Properties of Particles
Has weight (only for classical mechanics).
Momentum Transfer: When two particles collide, they can change the speed of the other by exchanging momentum.
Tip
Before using the wave equation, make sure the units are correct
Electromagnetic (EM) Waves
Includes light, X-rays, etc.
Consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles.
Travel at the speed of light
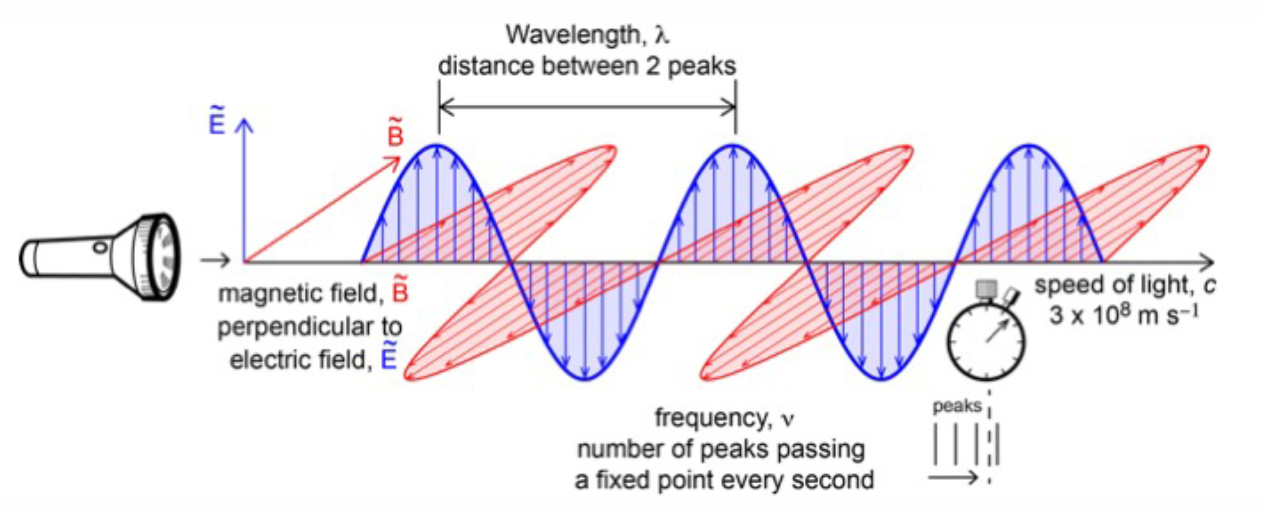
Speed of Light
c = 2.998 × 10⁸ m s⁻¹
Wave Equation
c = λν
Torque
Angular force that causes an object to rotate about an axis
Momentum
Quantity of motion that an object has
Quantization
Electrons can possess only certain, discrete energy values
Observable Properties of Waves
Allows for Direct Measurement — of wavelength or frequency (classical waves).
Observable Interference Patterns:
Waves interact (combine) to create regions of high/low intensity:
Sound: loud/soft regions.
Water waves: high/low wave regions.
Light: bright/dark regions.
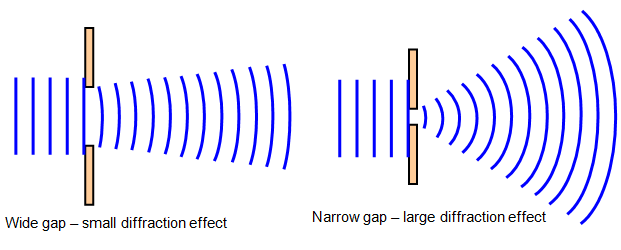
Diffraction is also a wave phenomenon.
Diffraction
Spreading/slight bending of light around obstacles (i.e: edges of an opening).
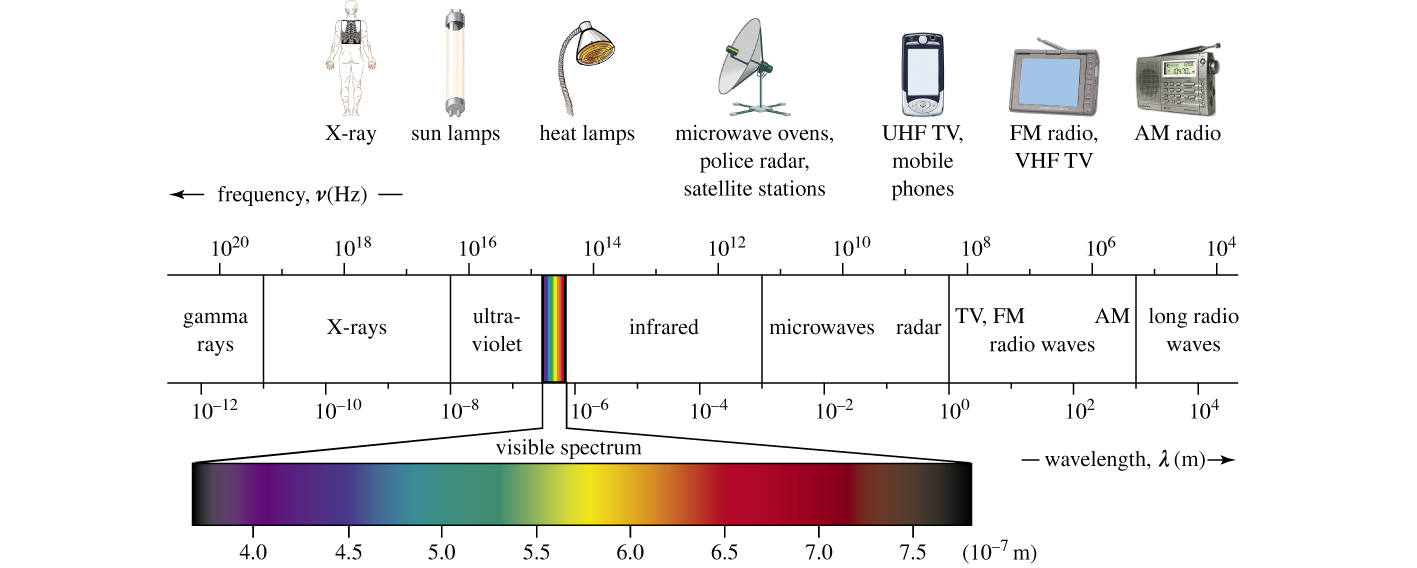
Regions of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Classified by wavelength or frequency.
Visible light: 380–780 nm.
Ultraviolet (UV): 10–380 nm.
Infrared (IR): 780 nm – 1 mm.
Unit Conversions
Between Base Unit and Prefixes Higher/Lower:
Identify the prefix and its power of 10
Write the conversion as a ratio: 1 unit of the prefix = Amount in base units (power of 10)
Multiply and cancel units: To cancel, ensure the unit to be cancelled is the denominator
Between Prefixes: Prefix A → Prefix B
Identify each prefix and their powers of 10
Apply the formula: Value x 10^(Power of A - Power of B)
Photon
Massless, chargeless particle with a discrete energy based upon its frequency