BM U3: Finance and accounts
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Capital expenditure
Investment spending on fixed assets, such as the purchase of machinery, equipment, land, and buildings
Collateral
Refers to the financial guarantee for securing external loan capital to finance investment expenditure for business growth
Revenue Expenditure
Spending on the day-to-day running of a business, such as payment of rent, wages, salaries and utility bills.
Business angels
Extremely wealthy individuals who risk their own money by investing in small to medium sized businesses that have high growth potential
Crowdfunding
The practice of raising finance for a business venture of project by getting small amounts of money from a large number of people, usually through online platforms.
External sources of finance
The funds from outside of the organisation, such as through debt (overdrafts & loan capital), share capital and business angels.
Initial public offering (IPO)
Refers to a business converting its legal status to a publicly traded company by floating (or selling) its shares on a stock exchange for the first time.
Internal sources of finance
Funds generated from within the organisation, namely through personal funds, retained profits and the sale of assets.
Leasing
A form of hiring whereby a lessee pays rental income to hire assets from the lessor, the legal owner of the assets.
Loan (or debt) capital
Refers to medium- to long-term sources of interest-bearing finance obtained from commercial lenders. E.g. mortgages, business development loans
Long-term sources of finance
Are those available for any period or more than 12 months from the accounting period, used for the purchase of fixed assets or to finance the expansion of a business.
Microfinance
A type of financial service aimed at entrepreneurs of small businesses, especially females and those on low incomes.
Overdrafts
Allows a business to spend in excess of the amount in its bank account, up to a pre-determined limit. They are the most flexible form of borrowing for most businesses in the short term.
Personal funds
Refers to the use of an entrepreneur’s own savings. Are used by (start-up) sole traders and partnerships.
Retained profits
The value of the surplus that a business keeps to use within the business after paying corporate taxes on its profits to the government and dividend payments to its shareholders.
Sale of assets
Raising finance by selling existing items of value that the business owns, such as dormant (unused) assets and obsolete (outdated) assets
Share capital
The money raised from selling shares in a limited liability company
Share issue (share placement)
An existing publicly held company raises further finance by selling more of its shares.
Short-term sources of finance
Those available for a period of less than one year, used to pay for the daily or routine operations of the business, such as overdrafts and trade credit
Sources of finance
Where or how businesses obtain their funds.
Stock exchange
A highly regulated marketplace where individuals and businesses can buy and/or sell shares in publicly traded companies
Trade credit
Allows a business to postpone payments or to ‘buy now and pay later’. The credit provider does not receive any cash from the buyer until a later date (usually between 30-60 days)
Average cost (AC)
Refers to the cost per unit of output.
= TC/Q.
Average revenue (AR)
Refers to the value of sales received from customers per unit of a good or service sold.
= TR/Q = P
Cost
Refers to the sum of money incurred by a business in the production process, such as the costs of raw material, wages and salaries, insurance, advertising, and rent.
Direct costs
Costs specifically attributed to the production or sale of a particular good or service.
Fixed costs
Are the costs that do not vary with the level of output. They exist even if there is no output.
Indirect costs (overheads)
Costs that do not directly relate to the production or sale of a specific product.
Price
Refers to the amount of money a product is sold for.
Revenue
Is the money that a business earns from the sale of goods and services.
P x Q
Revenue streams
Refers to the money coming into a business from its various business activities, such as sponsorship deals, merchandise, and receipt of royalty payments.
Running costs
The ongoing costs of running the business
Set-up costs
The items of expenditure needed to start a business
Total costs
The sum of all variable costs and all fixed costs of production
Variable costs
Costs of production that change in proportion to the level of output, such as raw materials and hourly wages of production workers.
Statement of financial position
Contains financial information about an organisation’s assets, liabilities and the capital invested by the owners, showing snapshot of the firm’s financial position.
Book value
The value of an asset as shown on a statement of financial position The market value of assets can be higher than its book value because of intangible assets.
Cost of Sales (COS)
Refers to the direct costs of producing or purchasing stock that has been sold to customers.
Creditors
Suppliers who allow a business to purchase goods and/or services on trade credit.
Current asset
Refers to cash or any other liquid asset that is likely to be turned into cash within 12 months of the balance sheet date. Cash, debtors, and stocks.
Current liabilities
Debts that must be settled within one year of the balance sheet date. E.g. bank overdrafts, trade credits, and other short-term loans.
Depreciation
The fall in the value of non-current assets over time, caused by wear and tear or obsolescence (out-dates)
Expenses
The indirect or fixed costs of production, such as administration charges, management salaries, insurance premium and rent.
Final accounts
The published annual financial statements that all limited liability companies are legally obliged to report, namely the statement of profit and loss and statement of financial position.
Goodwill
An intangible asset which exceeds when the value of a firm exceeds its book value
Gross profit
The difference between the sales revenue of a business and its direct costs incurred in making or purchasing the products that have been sold to its customers.
Historic cost
Refers to the purchase cost of a particular fixed asset. It is used in the calculation of depreciation
Intangible asset
Non-current assets that do not exist in a physical form but are of monetary value, such as goodwill, copyright, brand names, and registered trademarks.
Net assets
Shows the value of a business to its owners by calculating the value of all its assets minus its liabilities. This must match equity in the balance sheet.
Non-current (fixed) assets
Items owned by a business, not intended for sale within the next twelve months, but used repeatedly to generate revenue for the organisation, such as property, plant and equipment.
Non-current liabilities
The debts owned by a business, which are expected to take longer than year from the balance sheet date to pay
Profit
The surplus (if any) that a business earns after all expenses have been paid for from the firm’s gross profit
The statement of profit or loss
A financial record of a firm’s trading activities over the past 12 months, showing all revenues as well as costs and revenue during this time.
Residual value
An estimate of the value of the non-current asset at the end of its useful life
Retained profit
The amount of profit after interest, tax, and dividends have been paid. It is then reinvested in the business for its own use.
Share capital
Refers to the amount of money raised through the sale of shares. It shows the value raised when the shares were first sold, rather than their current market value.

Straight line method
A means of calculating depreciation that reduces the value of a fixed asset by the same value each year throughout its useful life

Units of production method
Calculating depreciation allocates an equal amount of depreciation to each unit of output rendered by a non-current asset.
Window dressing
Refers to the legal act of creative accounting by manipulating financial data to make the results appear more appealing.

Acid test ratio
A liquidity ratio that measure’s a firm’s ability to meet its short-term debts. It ignores stock because not all inventories can be easily turned into cash in a short time frame
Capital employed
Is the value of all long-term sources of finance for a business.
Non-current liabilities + equity

Current ratio
The short-term liquidity ratio that calculates the ability of a business to meet its debts within the next 12 months.

Gross profit margin (GPM)
A profitability ratio that shows the value of a firm’s gross profit expressed as a percentage of its sales revenue
Liquid assets
The possessions of a business that can be turned into cash quickly without losing their value, i.e cash, stocks and debtors
Liquidity crisis
Refers to a situation where a firm is unable to pay its short-term debts, i.e. current liabilities exceed current assets.
Liquidity ratios
Looks at the ability of a firm to pay its short-term (current) liabilities, comprised of the current ratio and acid test ratio.

Profit margin
A ratio that shows the percentage of sales revenue that turns into profit, i.e the proportion of sales revenue left after all direct and indirect costs have been paid.
Profitability ratios
Examines profit in relation to other figures, comprised of GPM, Profit margin, and ROCE ratios
Ratio analysis
A quantitative management tool that compares different financial figures to examine and judge the financial position of a business

Return on capital employed (ROCE)
A profitability ratio that measures the financial performance of a firm based on the amount of capital invested.
Bankruptcy
The legal process declared by the courts that occur when an individual or business entity is unable to repay its debts
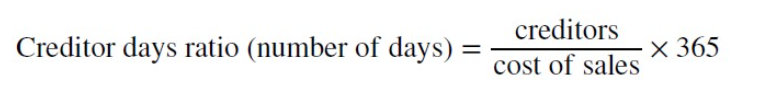
Creditor days ratio
An efficiency ratio that measures the average number of days it takes for a business to pay its creditors
Efficiency ratios
Enables a business to calculate the value of their liabilities and debts against their equity. Measure of financial stability of the business.
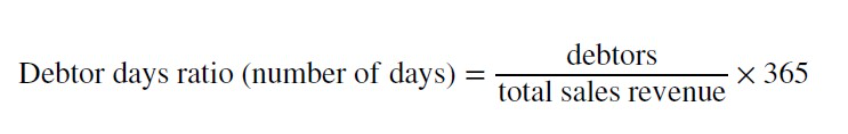
Debtor days ratio
An efficiency ratio that measures the average number of days it takes for a business to collect the money owed from debtors

Gearing ratio
Measures the percentage of an organisation’s capital employed that comes from external sources (non-current liabilities)
Insolvency
A financial state when an individual or business entity is unable to pay its debt on time
Liquidy
Refers to how easily an asset can be turned into cash. Highly liquid assets are those that can be converted into cash quickly and easily without losing their monetary value
Profit quality
Refers to the ability of a business to earn profit in the foreseeable future. A business with good profit quality is able to earn profit in the long run
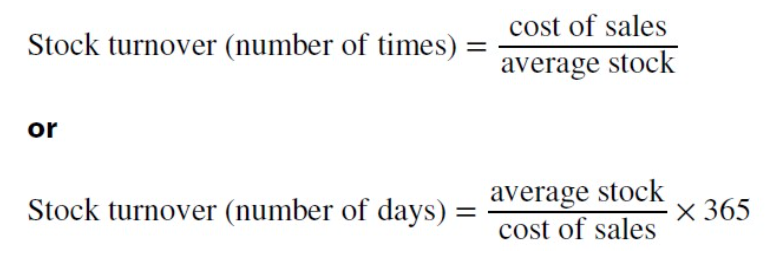
Stock turnover ratio
Measures the number of times a business sell its stocks within a year. It can also be expressed as the average number of days it takes for a business to sell all of its inventory
Bad debts
Exists when debtors are unable to pay their outstanding invoice (bills), which reduces the cash inflows of the vendors (the firm that has sold the product on credit)
Cash
A current asset and represents the actual money a business has. It can exist in the form of hash in hand or cash at bank
Cash flow
Refers to the transfer or movement of money into and out of an organisation
Cash flow forecast
A financial tool used to show the expected movement of cash into and out of a business, for a given period of time
Cash flow statement
The financial document that records the actual cash inflows and cash outflows of a business during a specified trading period, usually 12 months
Cash inflows
Refer to the cash that comes into a business during a given time period, usually from sales revenue when customers pay for the products that they have purchased
Cash outflows
Refers to cash that leaves a business during a given time period, such as when invoices or bills have to be paid.
Closing balance
Refers to the amount of cash left in a business at the end of each trading period
= Opening balance + New cash flow
Credit control
The process of monitoring and managing debtors, such as ensuring only suitable customers are permitted trade credit and that customer do not exceed the agreed credit period
Net cash flow
Refers to the difference between a firm’s cash inflows and cash outflow for a given time period usually per month
Opening balance
Refers to the value of cash in a business at the beginning of trading period, as shown it its cash flow forecast. It is the same as the closing balance in the previous month
Overtrading
Occurs when a business attempts to expand too quickly without the sufficient resources to do so, usually by accepting too many orders, thus harming its cash flow
The working capital cycle
Refers to the time between cash outflows for production costs and cash inflows from customers who pay upon receipts of their finished goods and services
Finance
Refers to the various available money that an organisation has to fund its business activities.
Cash flow forcast
A quantitative technique used by business managers to predict how cash is likely to flow into and out of the organisation for a particular period of time