IB Business Management SL - 2.4. Motivation
0.0(0)Studied by 10 people
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:19 PM on 12/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
1
New cards
Motivation
The willingness to exert high levels of effort to reach organizational goals
2
New cards
Theory of scientific management
Tasks should be based on work division and specialization, he assumed that the only motivator is money.
3
New cards
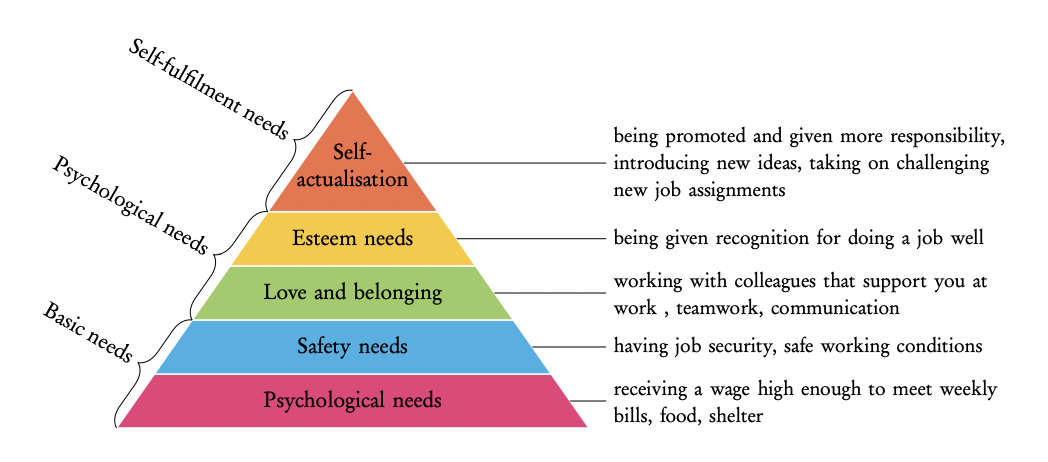
Theory of hierarchy of needs
The worker moves along a pyramid of needs to achieve motivation
4
New cards
Theory of two factors
Hygiene and satisfaction
5
New cards
Theory of equity
People will be happiest and more motivated in relationships where ‘give and take’ are about equal.
6
New cards
Theory of the third drive
Businesses need to stimulate the intrinsic motivation which occurs when someone gets satisfaction from an activity itself, without threats or rewards from the outside
7
New cards
Salary
Regular fixed payment
8
New cards
Wage
Staff is paid per hour of work
9
New cards
Commission
Staff is paid with respect to their sales results
10
New cards
Profit-related pay
The income of the employee depends on the profitability of the company
11
New cards
Empowerment
Managers give their employees more responsibility
12
New cards
Teamwork
Employees are encouraged to work collaboratively with one another in order to fulfill a task
13
New cards
Job enrichment
An attempt to give employees greater responsibility and recognition by expanding their role in the production process
14
New cards
Job rotation
An employee changing jobs and tasks from time to time in order to give them a greater sense of the whole production process.