A-Z NAVLE Study Guide part 3
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
What type of virus causes Equine Viral Arteritis (EVA), and what are its transmission routes?
Togavirus, transmitted via respiratory and venereal routes
List the clinical findings associated with EVA?
Acute severe infection of upper respiratory tract
Vasculitis causing limb and ventral edema
Abortion of partially autolyzed fetuses
Chemosis
Blepharospasm
Profuse discharge
What is the causative bacterium for Erysipelas?
Ersipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Where is Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae commonly found in the environment?
Found in water, soil, decaying material, slime on fish
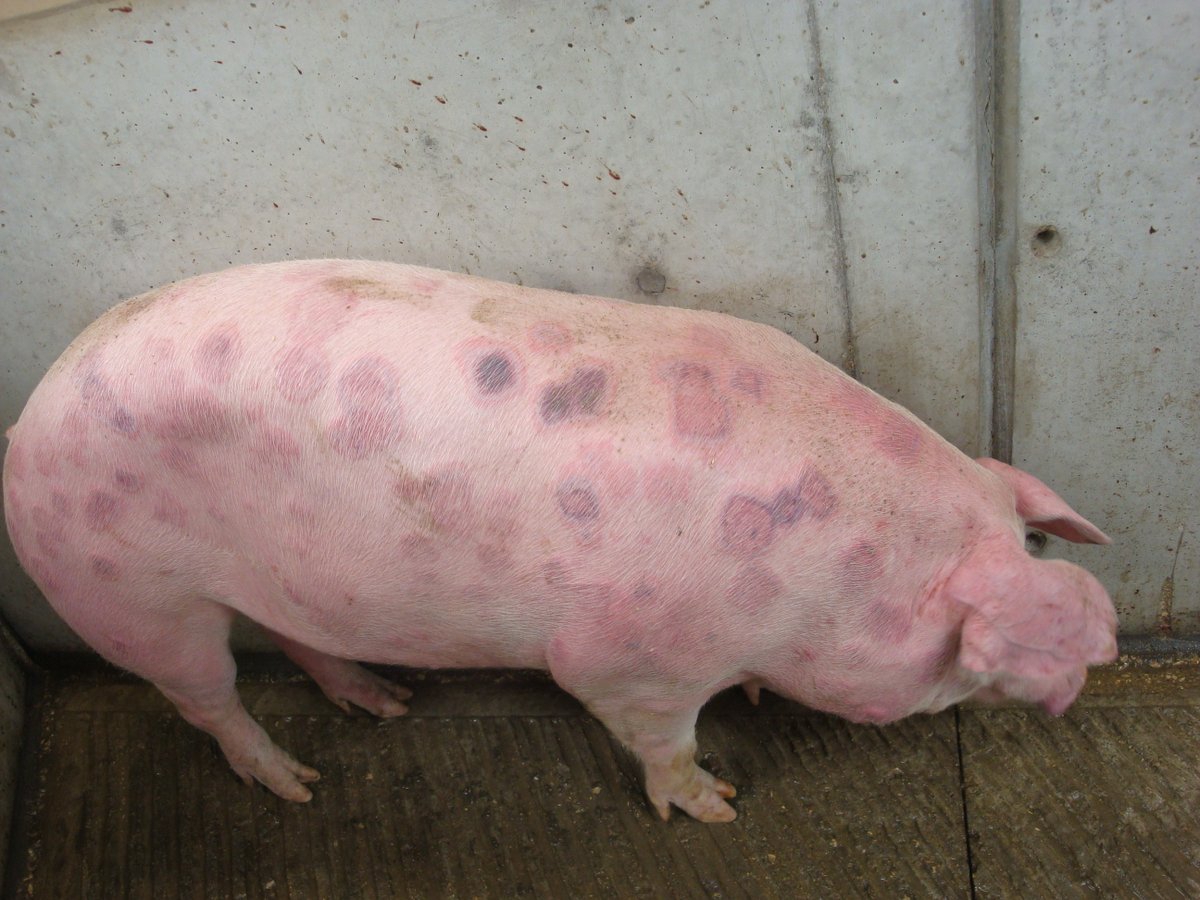
How does Erysipelas manifest in swine?
Erysipelas
How does Erysipelas manifest in sheep?
Nonsuppurative arthritis (lambs), post dipping lameness (sheep)

How does Erysipelas manifest in turkeys/ducks?
Acute septicemia
What is the specific human manifestation of Erysipelas, and how does it differ from a common Streptococcus infection in humans?
Localized termed erysipeloid
Describe CS of erysipelas in growing pigs
Acute septicemia, skin form, chronic arthritis and joint effusion
Vegetative endocarditis, death, high fever, walk on toes
Skin discoloration w/ erythema, diamond-shaped lesions
Enlarged LN, spleen, edematous and congested lungs
How is Erysipelas diagnosed?
Response to penicillin treatment w/in 24 hr, diamond shaped lesions, necropsy
What are the key strategies for prevention and treatment of Erysipelas in animals?
Immunization, antiserum, penicillin, eliminate carriers, good sanitation, regular vaccination
What is the presumed cause of Erythema Multiforme, and what is the likely underlying immune mechanism?
Unknown cause, likely immune complex
Describe characteristic appearance, progression, and location of skin lesions in erythema multiforme (EM)?
Erythematous papules on skin of abdomen that expand peripherally leading to development of annular lesions w/ normal centers
In which species does EM occur?
Pigs and other species
What is the treatment for EM?
Prednisone
How is Toxic Epidermal Necrosis related to Erythema Multiforme?
Severe whole body EM
What are the two primary manifestations of E. coli in cattle?
Young cattle → Diarrhea/dysentery
Older cattle → Mastitis
Describe the specific syndrome caused by E. coli in young calves, including age group affected
Enterotoxigenic colibacillosis in 4-7 day old
How can E. coli calf infection be prevented?
K99 antigen vaccine
What is the recommended treatment principle for esophageal strictures?
Balloon, do not cut
What diagnostic method can visualize esophageal tumors?
Rads w/ mass in chest at proper region could be esophagus
Name 3 types of esophageal tumors
Fibrosarcoma
Leiomyoma
Carcinoma
For esophageal fibrosarcoma, what specific parasite is associated w/ its development?
Spirocerca lupi
What is the typical location and prognosis for leiomyoma of the esophagus?
Location: Lower esophageal especially in beagles
Prognosis: Treatable
What are the common cause of esophagitis?
Post anesthesia due to gastroesphageal reflux
Tetracyclines
Disinfectants
What is the purpose of estrogen therapy in canines?
Mismating in canines
List the sig. side effects associated with estrogen therapy?
Bone marrow toxicity (aplastic anemia)
30% increased chance of uterine infection
Longer heat
How does timing of estrogen treatment relate to its success rate?
Directly related to time between mating and onset of treatment
What are characteristic epistaxis and presentation associated with Ethmoid Hematoma?
Not exercise induced, unilateral epistaxis, usually in middle aged horses
Describe the diagnostic approach for Ethmoid Hematoma?
Endoscopy, repaired w/ sinus flap
Outline both older and more contemporary treatment methods for Ethmoid Hematoma?
Injection w/ 10% or ND:YAG laser to burn off
What is the primary differential diagnosis for Ethmoid Hematoma?
Guttural pouch mycosis
From what specific lung region dose bleeding occur in EIPH?
Caudodorsal lung field as a consequence of exercise
Beyond epistaxis, what other CS might indicated EIPH?
Gurgling
Swallowing
Exercise intolerance
What is the definitive diagnostic method for EIPH, and what specific cellular finding on a TBAsp would support diagnosis?
Endoscopy, TBAsp→ Hemosiderin-laden macrophages
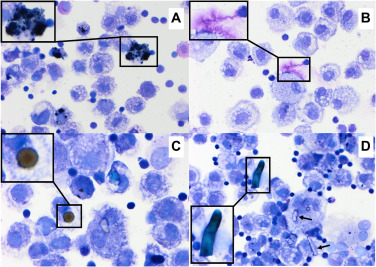
Is there is a recommended treatment for EIPH?
No treatment
What are the common names for Exertional Rhabdomyolysis Syndrome? What horses are most commonly affected?
Monday morning disease
Most common in horses affecting all breeds, >2 yo
Describe the spectrum of CS with Exertional Rhabdomyolysis
Stiffness and gait alterations
Severe cramping
Immobility, profuse sweating
Firm muscle groups
Myoglobinuria if severe

What diagnostic parameters are used to diagnose Exertional Rhabdomyolysis?
CS
Increased CPK and AST
Mild metabolic alkalosis (NOT lactic acidosis)
Decreased Cl- and calcium
Decreased fractional exertion of K+
Myoglobinuria
What is the primary treatment for acute episode of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis?
REST, supportive
What medications are used for chronic management of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis?
Phenyotoin
What medication is used for prevention of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis?
Dantrolene sodiu
What is the direct cause of Fibrotic myopathy in horses, and which muscles are typically involved?
Trauma to semimembranous or semitendinosus m.
Describe the pathological findings with fibrotic myopathy?
Thick tissue band that needs to be transected
What are the characteristic lesions for Feline Acne?
Blackheads around skin of lips and chin
When is treatment for Feline Acne generally necessary?
No treatment, unless it progresses to furunculosis
Describe the bilateral symmetrical pattern and signalment seen in Feline Endocrine Alopecia?
Bilateral symmetrical hair loss on the posterior abdomen, inner thighs, perineum of male neutered cats
What is the suspected underlying cause of Feline Endocrine alopecia?
Sex hormone deficiency suspected
What type if virus is FIV, and what is the nature of the infection it causes?
Lentivirus causes lifelong infection
What is the primary transmission for FIV?
Through cat bite
How contagious is FIV w/in a household of non-fighting casts?
Will not disseminate through a household of cats if they do not fight
Discuss the general prognosis and longevity for many FIV-positive cats
Asymptomatic and many do not die or FIV-related changes
What is the standard diagnostic test for FIV?
ELISA
What is the causative agent of FIP?
Coronavirus
What is the environmental stability and susceptibility to disinfectants of coronavirus?
Remain infectious in environment up to 6 weeks but easily killed by disinfectants
How does Coronavirus spread among cats?
Spread in secretions and excretions
List the risk factors for developing FIP
Population density
Amount of shedding
Persians and Birmans predisposed
Feline Enteric Corona virus, FeLV, and concurrent disease
What does not increase the risk for FIP?
Steroids
Explain the relationship between Feline Enteric Coronavirus (FECV) and FIP
FECV mutates to FIP
Describe the biphasic age distribution of FIP
<6-12 weeks or >13 yo
Differentiate between CS of effusive and noneffusive FIP
Effusive → Fluctuating, Antibody responsive fever, lethargy, anorexia, WL, ascites, pleural fluid, pericardial and scrotal fluid, fluid accumulate rarely
Noneffusive → Same but instead of fluid accumulation, have pyogranulomatous reaction causing local tissue necrosis and decreased organ function
What are the characteristic lab and fluid analysis findings for FIP?
Hyperproteinemia
Kidney/liver abnormal
Hyperglobinemia and thrombocytopenia
Keratic ppts in eyes
Ascites fluid in thick, straw colored
Pyogranulomatous nonseptic exudate w/ moderate cellularity and high protein levels
Eosinophilic stippied antibodies
Why are FECV serology and FIP serology considered no helpful in diagnosing FIP?
Antibody tests cross reacts w/ enteric coronavirus antibody
What is the current general approach to treatment for FIP?
Suppressing immune complex (Pred, cyclophosphamide, broad spec AB)
What is the primary method of prevention for FIP?
Environmental
Should you vaccinate FIP cat?
No
What is the specific bacterial agent agent responsible for feline leprosy?
Mycobacterium lepraemurium
Describe the typical lesions in Feline Miliary Dermatitis
A papular, crusting skin disease located predominantly on the back w/ varying degrees of pruritis
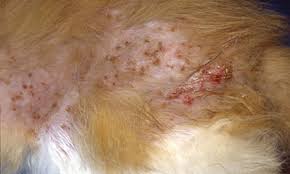
List underlying causes for Feline Miliary Dermatitis
Ectoparasites, food allergy, drug allergy, fungal or bacterial infection, feline flea allergy
What type of virus causes feline panleukopenia?
Distemper
To which canine disease is feline panleukopenia compared to?
Similar to canine parvo
What specific neurological developmental abnormality does feline panleukopenia cause?
Cerebellar hypoplasia
How is feline panleukopenia prevented?
Vaccine
What are the common CS that characterizes Feline Respiratory Disease complex?
Rhinitis, conjunctivitis, lacrimation, salivation, and oral ulceration
ID the primary viral causes of Feline Respiratory Disease complex?
Feline viral rhinotraheitis herpes (40-45%) and feline calicivirus (40-45%)
List unique CS, affected anatomical regions and characteristic microscopic findings for Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis?
Fever, sneezing, conjunctivitis, salivation
Ulcerative stomatitis, keratitis affecting conjunctiva and nasal passages
Intranuclear inclusion bodies
How are corneal ulcers associated with herpesvirus treated?
Topical acyclovir
For feline calicivirus, what are its distinguishing CS?
Ulceration of oral mucosa, serous rhinitis, conjunctivitis or oral mucosa and lower respiratory tract
For feline pneumonitis (chlamydia), what is its hallmark CS, a characteristic microscopic findings, and its primary treatment?
Intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies, chronic low grade conjunctivitis. Treat w/ tetracycline
For Feline Mycoplasma, What are its common CS and a diagnostic microscopic finding?
Conjunctivitis, rhinitis, extracellular coccoid bodies on conjunctival epithelial cells
List some common causes of feline stomatitis
Feline, herpes, calcivirus, FeLV, FIV
What type of virus is FeLV, and what are the main categories that compose the virus?
Retrovirus w/ a variety of proteins which have different biologic functions, envelope, and core proteins
What specific FeLV protein is crucial for diagnostic tests?
p27
What is the stability of FeLV in the environment?
Is very labiale and is destroyed in environment w/in minutes
Describe the most common modes of transmission for FeLV
Contact w/ body fluids is most common way
Explain the different outcomes for cats exposed to FeLV
1/3 of cats exposed become persistently infected
2/3 of cats resist development of persistent viremia
1/3 of transiently infected become latently infected
Compare and contrast IFA and ELISA test for FeLV
IFA detects cell-associated viremia
ELISA detects serum-associated viremia
What follow-up action is recommended for a cat with an initial FeLV positive ELISA result?
Should be retested 6 weeks later for seroconversion
List the four basic syndromes that encompass Feline Urologic Syndrome (FUS)
Urinary obstructions, urolithiasis, UTI, and abnormal microurita
What are the typical underlying cause of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)?
Malabsorptive syndrome due to pancreatic atrophy
What breeds is most commonly affected by EPI?
Collies and GSD
Describe the CS of EPI
Chronic SI diarrhea, ravenous appetite, WL

What common concurrent condition is often seen with EPI?
Concurrent bacterial overgrowth
What is the definitive diagnostic test for EPI?
Test with TLI (check any any dog w/ non PLE SI diarrhea
What important considerations should be made if EPI dog does not respond to enzyme replacement therapy?
Never eliminate EPI based upon failure to respond to replacement enzyme therapy
What initiates GDV, and what is considered the most probable sources of accumulating gas?
Emergency, initiated by accumulation of gas
Explain the relationship between gastric dilation and volvulus
Dilation precedes volvulus
Describe the most common direction of stomach rotation in GDV when viewed from a dorsal recumbent position
Clockwise
Detail the cascade of pathophysiological effects resulting from GDV
Displacement of pylorus from R abdominal wall → Toward ventral midline → Passing over gastric fundus and body to L abdominal wall → Compression of posterior vena cava/portal v. → sequestration of blood