Macroevolution - Lecture 10
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Taxonomy
classification and naming of organisms
What Is The Study Of Systematics
Study of evolutionary relationships between organisms (phylogenies)
Carolus ___________ is the father of taxonomy
Linnaeus
Scientists try to classify organisms by their _____________ history
Evolutionary
Taxon
One group of classification
Ex. Genus
List the taxonomy hiearchy
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Dear
King
Philip
Came
Over
For
Good
Soup
What do nodes represent
An ancestral species at the moment they split into two new species
What do the branches represent?
An evolutionary (changing) lineage through time
The tips can represent 3 things, name them
Individuals
Species
Clades (group of organisms)
What is a sister group?
2 internal branches; shares most recent common ancestor with another group
Ingroup Vs. Outgroup
Ingroup -
Most recent, closely related species
Outgroup -
Distant relative of the ingroup
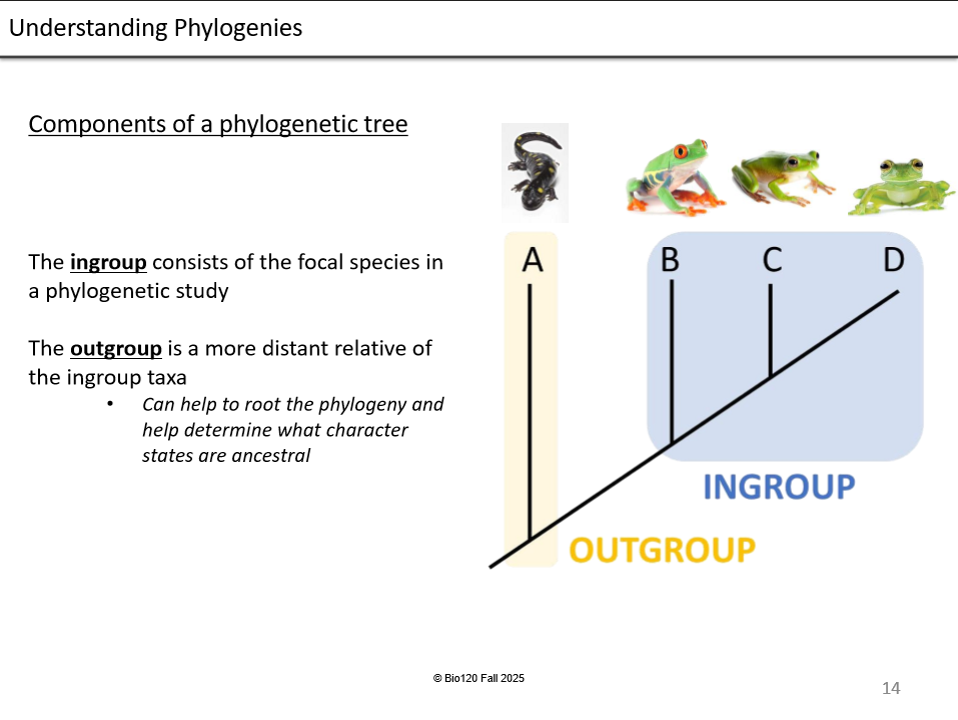
Why are outgroups helpful to scientists?
They help determine traits that are closely linked to root ancestors
What is a clade/monophyly?
Group of a phylogeny that includes a MRCA and all of it’s descendants
How to determine a clade
Sissors test
OR
Number of clades = number of nodes
(each node can be a separate clade)
Paraphyly
Group made of ancestor and some descendants
Polyphyly
A group that does not contain the MRCA of all members
Paraphyly Vs. Polyphyly Vs. Monophyly/clade
Paraphyly -
Ancestor + SOME descendants
Polyphyly -
Descendants - MRCA
Monophyly/clade -
Ancestors + ALL descendants
Derived Vs. Ancestral
Derived: not present in MRCA
Ancestral: present in MRCA
Synapomorphy
(type of homology)
Trait evolved from MRCA
Specific to a clade
Homology
Structures dervied from a common ancestor
(May look different now)
Ex. vertabrates
Homoplasy
Similar traits that don’t derive from a common ancestor
EX. human hands, gorilla hands, bear paws
Why Is Paleontology Important? (2)
Direct record of past evolutionary change
Helps understand the past & present