physio module one
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Stratified epithelial tissue
provides protection, held together by structures called intercellular junctions (junction complexes)
to close together to house blood vessels, nourished by connective tissues beneath
epithelial tissues are attached to connective tissues by a basement membrane
Nonkeratinized membranes
have living cells in all layers
reproduce and other func.
Keratinized
have cells filled with keratin: a water resistant protein: and layers of dead cells on the surface
epithelial membranes continually renew by losing surface cells and replacing with new cells
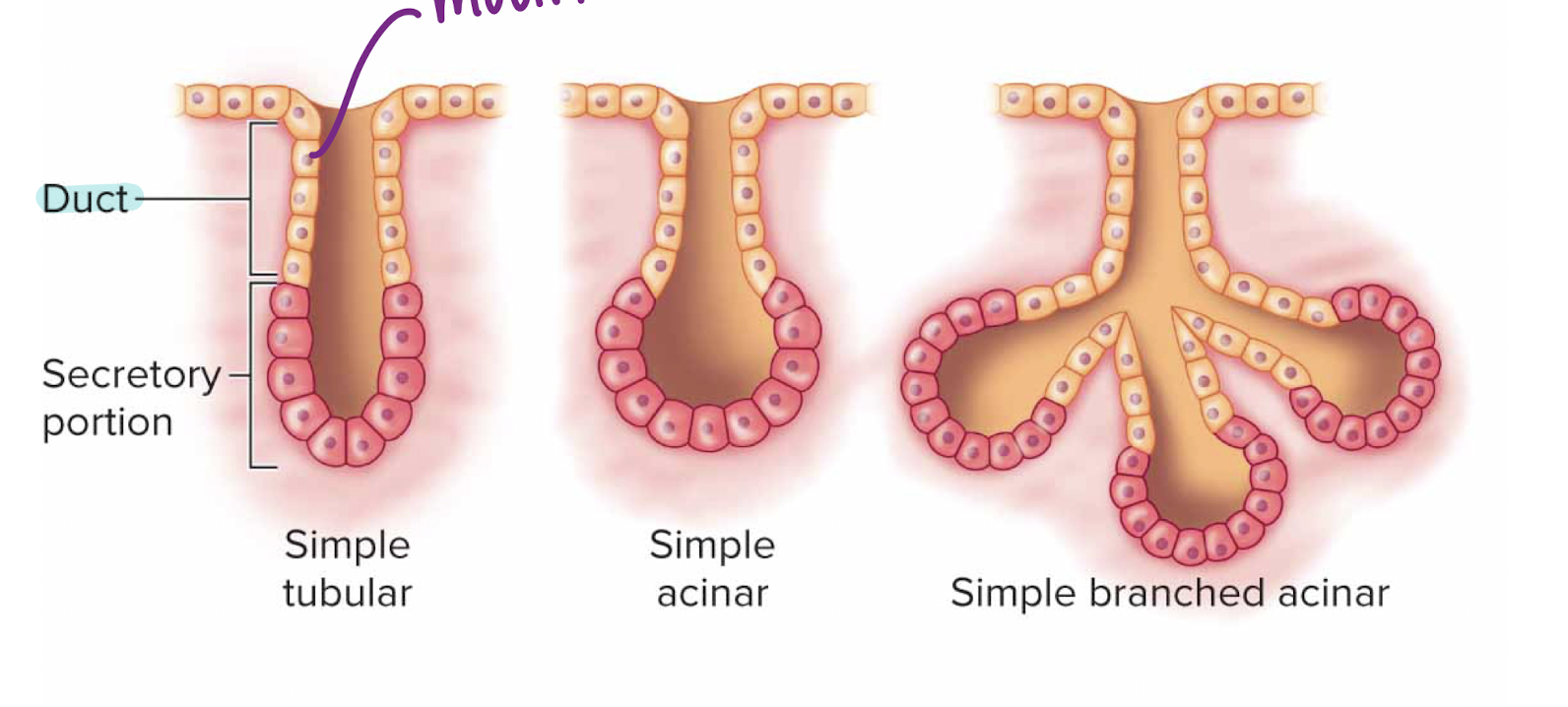
Exocrine Glands
derived from epithelial tissues
secretions are transported by ducts (main difference between exo and endo)
ex: lacrimal, sweat, sebaceous glands, digestive enzymes, and prostate
secretory portions may be tubes or acini groups
usually simple cuboidal (not always; columnar in respiratory)
Sweat Glands
Eccrine or merocrine: more numerous; secrete a salty sweat; involved in thermoregulation (simple)
Apocrine: located in axilla and pubic reg
ion; protein-rich sweat that bacteria feed on (more acinar/branched)
Endocrine Glands
derived from epithelial tissues
lack ducts and therefore secrete into capillaries within the body: taken up in the blood → move through whole body
ex. many hormone producing glands such as the thyroid gland and adrenal glands
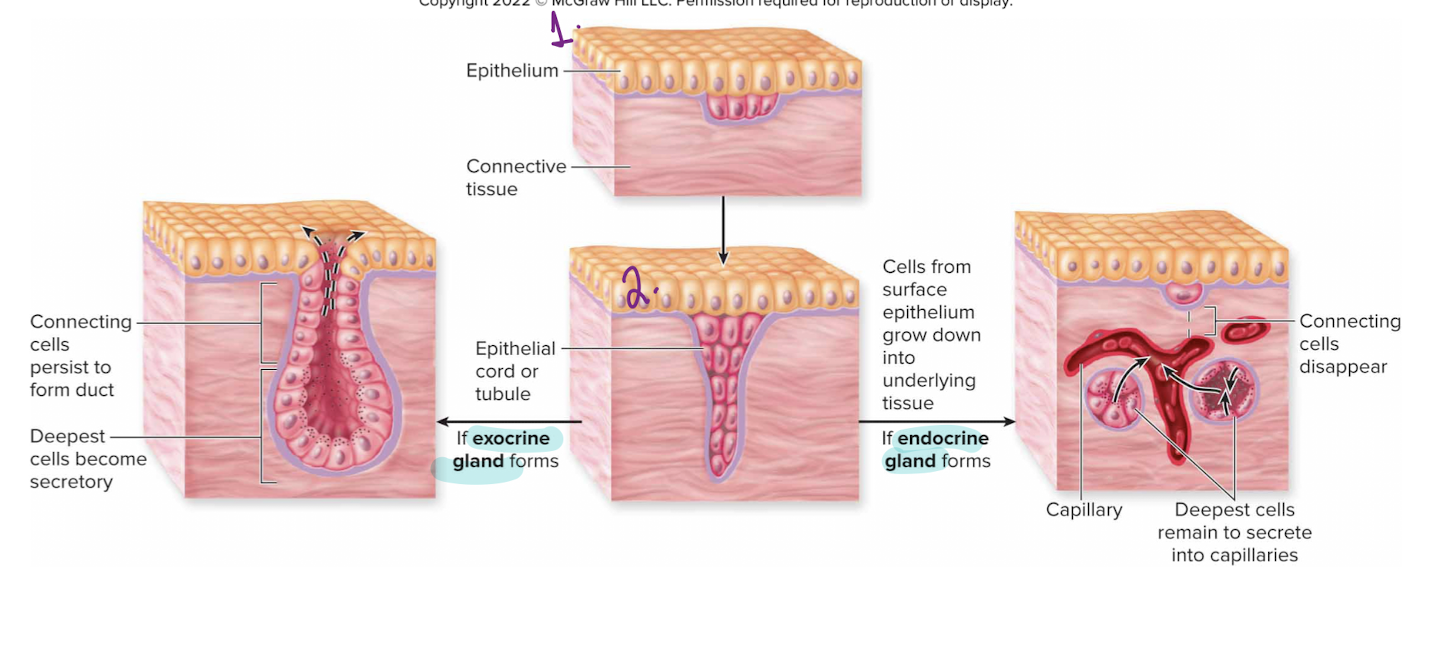
Exocrine and endocrine gland formation
epithelium and connective tissue
epithelial cord or tubule forms
it can either
exocrine gland
connecting cells persist to form duct
deepest cells become secretory
endocrine gland
cells from surface epithelium grow down into underlying tissue
deepest cells remain to secrete into capillaries
connecting cells disappear
Connective tissue
characterized by a matrix made up of protein fibers, extracellular material, and specialized cells
connective tissue proper
cartilage
bone
blood
connective tissue proper
support and flexibility
a lot of diseases arise from this
types
loose connective
dense regular connective
adipose tissue
dense irregular
loose connective
space for blood vessels and nerves (support and flexibility)
ex. dermis of skin (middle layer)
dense regular connective
not as much space, organized, very minimal ground substance
strong and resistant to stretching
organized one way → can only resist in one direction
ex. tendons and bones
Adipose tissue
stores fat
protect organs, thermoregulation
dense irregular connective tissue
composed of densely packed collagen fibers in various arrangements to resist force
strength and flex
visceral organs
Cartilage
composed of cells called chondrocytes surrounded by a semi solid ground substance
flexy and supportive but different
serves as a template skeleton during bone development
found in joint to provide a gliding surface for bones
reduce friction
ex. cushion for ears, nose, and ribcage
Bone
dynamic and STRENGTH AND SUPPORT
a. cells called osteoblasts trap mineral salts, forming concentric layers of calcified material around a canal (central) filled with blood vessels and nerves
b. once the matrix has hardened, the cells are called osteocytes and live in spaces called lacunae
trap inside mineral salts
c. the dentin of a tooth is similar to bone and is made by cells in the pulp; the outer enamel is harder than bone or dentin
Organ
composed of two or more tissues that serve different functions in the organ (overall specific function)
largest organ in the body
skin: has all four primary tissues
epidermis: keratinized stratified squamous epithelium to protect against water loss and abrasion (protective layer)
dermis: dense irregular connective tissue containing exocrine glands, hair follicles, sense receptors, and blood vessels (all 4)
hypodermis: adipose tissue for padding and insulation (subcutanious level)
errector philli: arm hair up
Types of Stem Cells
totipotent: cells can become any type of cell; true stem cells (make whole organism and supporting structures)
ex. zygotes
as cells being to differentiate, a few adult stem cells are retained to allow for cell replacement
multipotent: limited to narrow range of possibilities but can become several related cells
ex. adult stem cells
pluripotent: can form any type of unrelated cells (can make the body but not the extra-embryonic stuff)
organ systems
integumentary: protection, thermoregulation
nervous: regulation of other body systems
endocrine: secretion of regulatory molecules called hormones
skeletal: movement and support
muscular: movements of the skeleton
circulatory: movement of blood and lymph
immune: defense of the body against invading pathogens
respiratory: gas exchange
urinary: regulation of blood volume and composition
alimentary: breakdown of food into molecules that enter the body
reproductive: continuation of the human species
Body Fluid Compartments
Intracellular: area inside the cell, 65% of total body water
Extracellular: outside the cell, blood plasma and interstitial fluid
both primarily filled with water and are separated by membranes
selective movement of molecules and ions between compartments through the cell membrane
In blood, what two molecules stabalize pH?
bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) and carbonic acid (H2CO3)
if blood falls below pH 7.35, the condition is called
acidosis
If the blood rises above pH 7.45, the condition is called
alkalosis
Micelles and Water
keep lungs from collapsing
surfactants: lubricant to reduce water friction
Cholesterol
a steroid that is a per cursor for a lot of steroid hormones and other functional groups within the body
Prostaglandins
type of fatty acid with a cyclic hydrocarbon group
regulate the diameter of blood vessels
uterine contractions
Phosphatases vs. Kinases
Phosphatases: remove phosphate group
Kinases: add phosphate group
Isoenzymes
an enzyme that does the same job in two different organs has the same name, molecules may be slightly different
useful in detecting and diagnosing certain diseases
Are most metabolic pathways branched or unbranched
branched
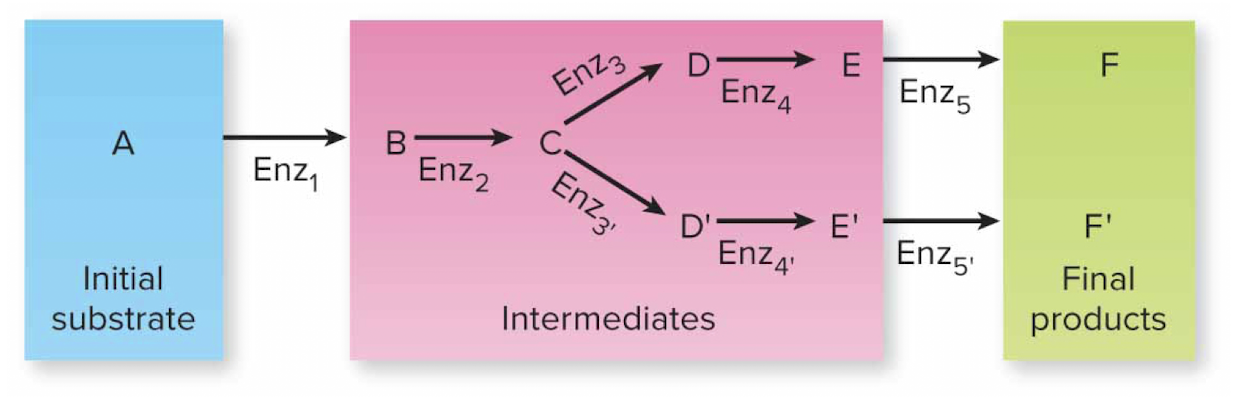
how do we mediate our bodies
through END PRODUCT INHIBITION
the effect of the production of an end product or an intermediate in between allows us to shift to a new pathway
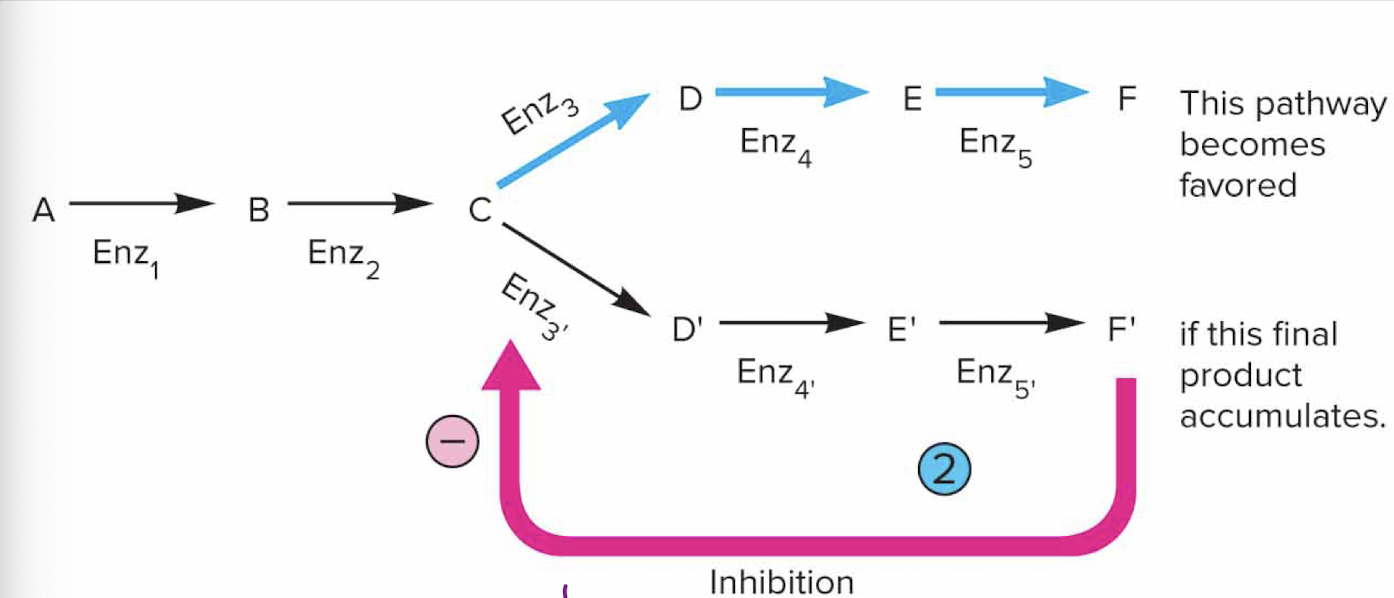
Inborn errors of metabolism
Abnormal gene makes defective enzyme (Enz3)
can no longer have access to that pathway
causes the build up of other enzymes
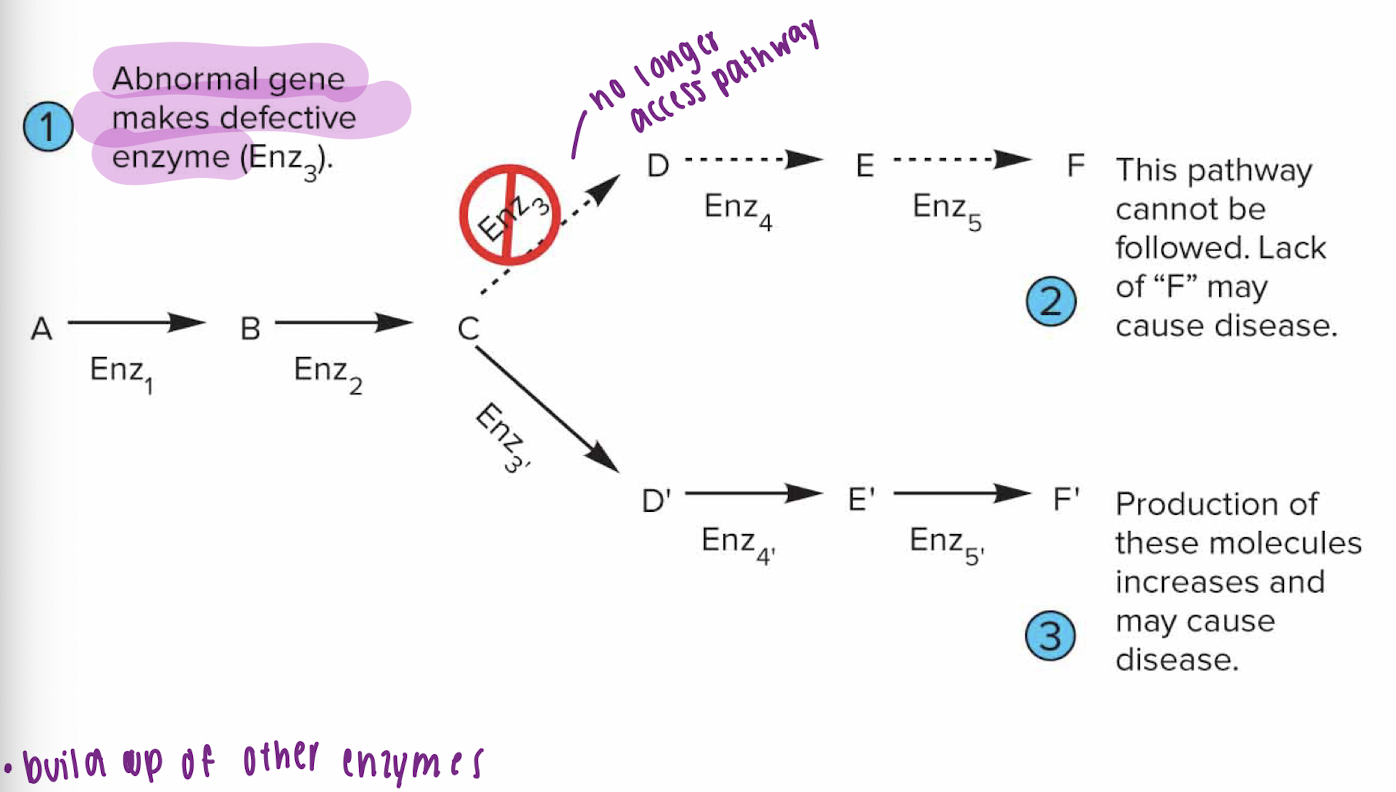
Example of Amino Acid Metabolism defect
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
increase in phenylpyruvic acid,
mental retardation, epilepsy
cant drink diet coke
Different organs rely on different molecules to supply main energy source
brain → mainly glucose
resting skeletal muscle → fatty acids
Liver → fatty acids
Heart → fatty acids
Glucose sparing
organs will restrict their use of glucose to maintain blood glucose levels for use by the brain
Extracellular Environment
includes everything located outside of the cell
cells receive nourishment from and release wastes into extracellular environment
cells (facilitate) communication with each other by secreting chemical regulators (hormones, neurotransmitters)
maintain cellular function and release waste
Extracellular environment percentages
67% of the bodies water is within the intracellular compartment of cells
the rest of the 33% which is extracellular fluid is broken down into
80% interstitial fluid (bridge between inter and blood plasma)
20% blood plasma (exchange and waste
Extracellular Matrix ECM
composed of protein fibers such as collagen and elastin: provide structural support
a gel like ground substance made of glycoproteins and proteoglycans
Integrins
a type of glycoprotein within the extracellular matrix that connects the cells cytoskeleton to the ECM
cell adhesion and mobility
relay signals between extracellular and intracellular
establish cell polarity
communication and coordination
Plasma Membrane permeability
selectively permeable
generally not permeable to proteins, nucleic acids, or other large molecules; big large polymers cannot
glucose is permeable with help from proteins, starch is not
generally permeable to wastes and nutrients
some ions are transported creating electrochemical currents in certain cells
Carrier: mediated transport
integral protein within the membrane
facilitated diffusion: no energy, just need correct protein (passive)
active transport: needs energy
Non carrier mediated transport
simple diffusion of lipid soluble molecules (steroid hormones)
simple diffusion of ions through nonspecific channels (calcium)
simple diffusion of water (osmosis) through AQUAPORIN channels
allows for movement of water through membrane
Passive Transport
molecules move from higher to lower concentration without using metabolic energy
active transport
molecules move from lower to high concentration using ATP and specific carrier pumps
Types of Passive Transport
simple diffusion of lipid soluble molecules (nonpolar) through the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane
Simple diffusion of ions (dissolved in water) through membrane channel proteins (due to their charge)
facilitated diffusion of glucose or other small organic molecules: bind to a specifc carrier protein which undergoes a conformational change to release the molecule on the other side of the membrane
how will diffusion occur?
without a physical separation or across a permeable membrane
net diffusion
due to random movement, the net direction of diffusion is from high to low solute concentration
Mean diffusion time
the average time it takes for a solute to diffuse (varies)
a. increases with the square of the distance the solute must travel (less distance, faster)
B. distance beyond 100 um, diffusion time is too long to be effective
diffusion through a dialysis membrane
wont allow large proteins out
some glucose
starch cannot move in and out
allows small diffusable molecules and ions out
Diffusion through the plasma membrane
small, nonpolar, lipid-soluble molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and steroid hormones can easily pass through the lipid bilayer → GAS EXCHANGE
oxygen diffuses into cells while carbon dioxide diffuses out, driven by concentration gradients
in the lungs, these directions will reverse (o2 out, co2 in)
water can not move freely through the membrane so it passes by through specialized channels called aquaporins → OSMOSIS
these mechanisms are essential to maintaining cellular function and homeostasis
also at the capillary beds
ions pass through membrane channels
charged ions can pass through ion channels that may be
closed/gated: closed until certain needs are met
open: free flowing
side note: large polar molecules can not pass through the membrane by simple diffusion but need special carrier proteins to passively cross if going with concentration gradient
rate of diffusion
measured by the number of diffusing particles per unit of time
depends on
magnitude of concentration difference: driving force for diffusion (great difference→ rate faster, how fast?)
permeability of the membrane to the molecules (increase permeability → rate increase)
temperature of the solution: higher temperature increases the rate
surface area of the membrane; increased by microvilli (in gastro tract)
osmosis
the movement of water molecules/ solvent through the plasma membrane
greatly facilitated by protein channels called aquaporins → allow water to move efficiently
aquaporins are abundant in tissues like the kidneys, eyes, lungs, salivary glands, and brain (precise water regulation is essential for functions)
when does osmosis occur
when there is a difference in solute concentration across a membrane that is permeable to water
the membrane must be impermeable to the solute; otherwise the solute would move eliminated the concentration gradient
solutes that cant cross the membrane but drive water movement are called osmotically active
crucial for maintaining proper fluid balance in cells and tissues
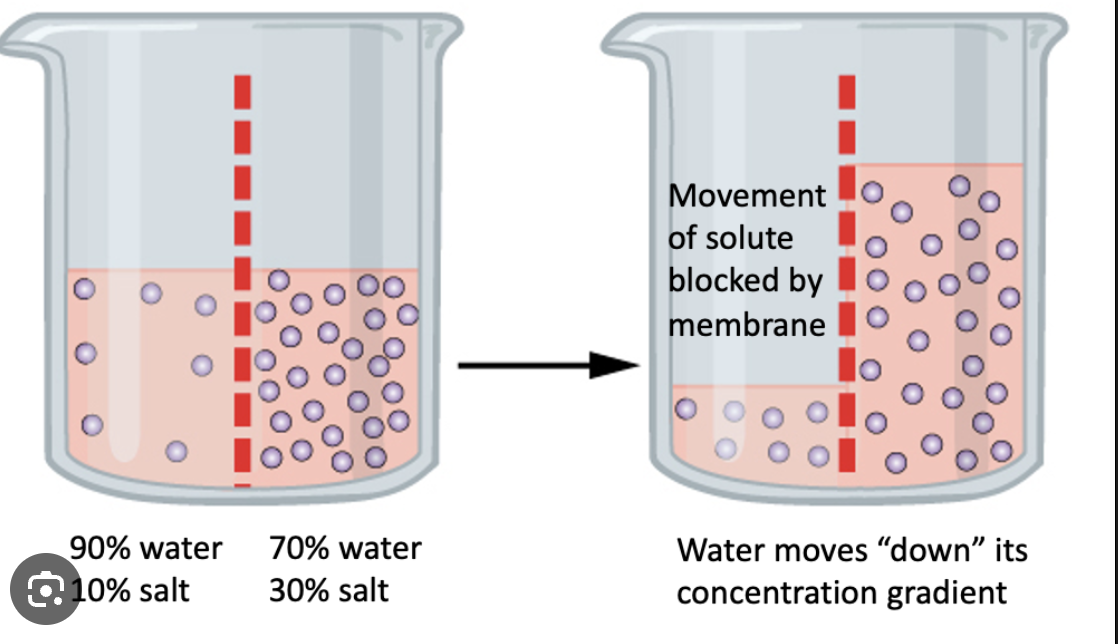
the effects of osmosis
water moves from the side with more water (a more diluted solution) to the side with less water (less diluted)
however we usually describe this in solute concentration
water moves from areas with low solute concentration to area of high solute concentration
water moves towards the side with more solutes to balance the concentration, a key process in maintaining cellular and physiological equilibrium
Osmotic pressure
the force needed to stop water movement during osmosis
reflects the “pull” a solution has on water
solutions with higher solute concentrations have higher osmotic pressure, drawing in more water
pure water has osmotic level of zero, no solute
essential for understanding how cells regulate water balance and maintain proper function in varying environements
Osmolality (not tested)
the total molality of a solution when you combine all the molecules within it
amount of solute/ amount of solvent
hyposmotic and hypotonic
solutions with lower solute concentrations; water moves into the cell; causes cells to swell and eventually burst
hemolysis in red blood cells
hyper osmotic and hypertonic
solutions with higher solute concentrations; water moves out of the cell; leads to shrinkage
crenation in red blood cells
Tonicity importance
crucial in medical setting, like administering IV fluids, to ensure cells remain in a balanced, isotonic environment
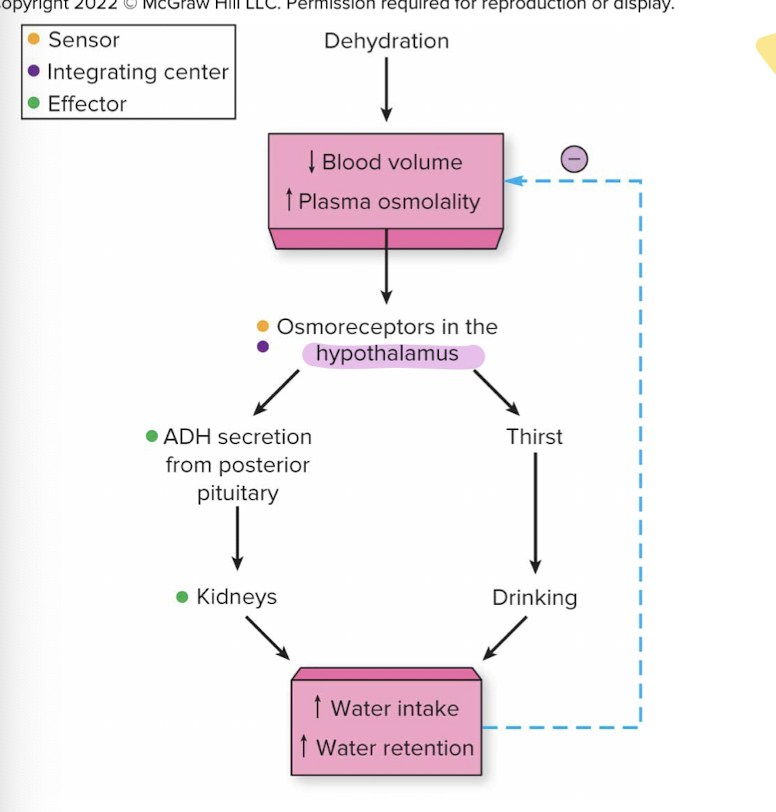
Homeostasis of Plasma Concentration
when dehydration occurs, osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect increased plasma osmolality (more solute than solvent) → triggers a negative feedback loop to restore balance
Thirst increases, prompts water intake
hypothalamus signals the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin, from the posterior pituitary. ADH reduces water excretion by the kidneys which conserves water and concentrates urine
As plasma osmolality decreases back to normal, osmorecpetors are no longer stimulated, ADH release diminishes, and the kidneys excrete more water
System ensures fluid balance and protects cellular and neural functions
Carrier Mediated Transport
movement of large, polar molecules requires membrane proteins (amino acids, glucose, and other organic compounds) due to size and charge
rely on carrier proteins embedded into the plasma membrane to facilitate their transportation
highly specific carriers to particular molecules
can be competition for similar carriers, and because the number of carriers is limited, the process can become saturated if too many molecules are trying to move at once → slows down transport
ALSO: some proteins can transport more than one molecule, but there is competition effect. Transport rates increase increased molecule concentration until saturation is met; this is the transport maximum (Tm) where all carriers are in use
Facilitated diffusion of glucose
relies on the random movement of molecules and does not require ATP
moves substances from areas of high to low concentration (follow gradient)
requires specific carrier proteins in the plasma membrane ex. those used to transport glucose into a cell
transport proteins can either 1. always be present in the membrane or 2. be inserted when needed depending on cell requirements
Glucose: carrier proteins like GLUT transporters help move glucose into cells, ensure it is available for energy production without expending cellular energy
Gluts
Glucose Transporter Proteins
maintain some at all times
14 known gluts
structural similarities are categorized together
Gluts 1, 3-5, and 8 are found in the CNS (3-5 are in the prefrontal cortex for working memory)
Glut 14 is only in the male testes
Active Transport Pump
used to move molecules from low concentration to high concentration, “moving uphill”
requires the expenditure of ATP (uses ATP/energy)
Carrier-mediated proteins that facilitate this kind of movement are known as PUMPS
Primary Active Transport
where hydrolysis of ATP directly power the transport process; the tranport protein itself acts as an ATPase enzyme, breaking down ATP to release energy; when ATP is hydrolyzed, the pump becomes activated through phosphorylation
ex. Ca2+ pump: found within the endoplasmic rectilium of striated muscle cells
pump moves calcium ions out of the cytoplasm either in the extracellular or the cisternae of the ER
This action creates a strong concentration gradient, enabling rapid movement of Ca2+ back into the cell when needed
Plays a crucial role in processes such as neurotransmitter release in neurons and muscle contractions, ensuring proper cellular function and response to stimuli
Na/ K Pump
essential for maintaining proper cellular functions; found in all body cells
it is an ATPase enzyme that actively transports sodium and potassium ions aganist their concentration gradient
pumps 3 Na out and 2 K out of the cell, crucial for several cellular functions/ maintains that intracellular negativity (3 Nathans out, 2 Katies in)
Na/ K pump functions
provides energy for coupled transport, helping other molecules move across the membrane
generates electrochemical impulses in neurons and muscle cells, allowing for nerve signaling and muscle contractions
helps maintain proper osmolality within cells, ensuring water balance
Na/ K Pump steps
three Na ions from the cytoplasm bind to the pump
the atpase enzyme activates, hydrolyzing ATP to ADP and Pi, causing both openings of the pump to be blocked
ADP is released → causes a change that allows 3 Na ions to exit the pump into the outside of the cell
Two K ions then enter the pump from the outside and the Pi is released
the pump returns to its original shape and releases the 2 K ions inside the cell
this process is critical for maintaining cell volume, membrane potential, and proper function across a wide range of tissues
transport across epithelial membrane
key role in processes like absorption and reabsorption
absorption: refers to the movement of digestive products, such as nutrients, across the intestinal epithelium into the blood stream
reabsorption: the process by which molecules are transported from the urinary filtrate back into the blood
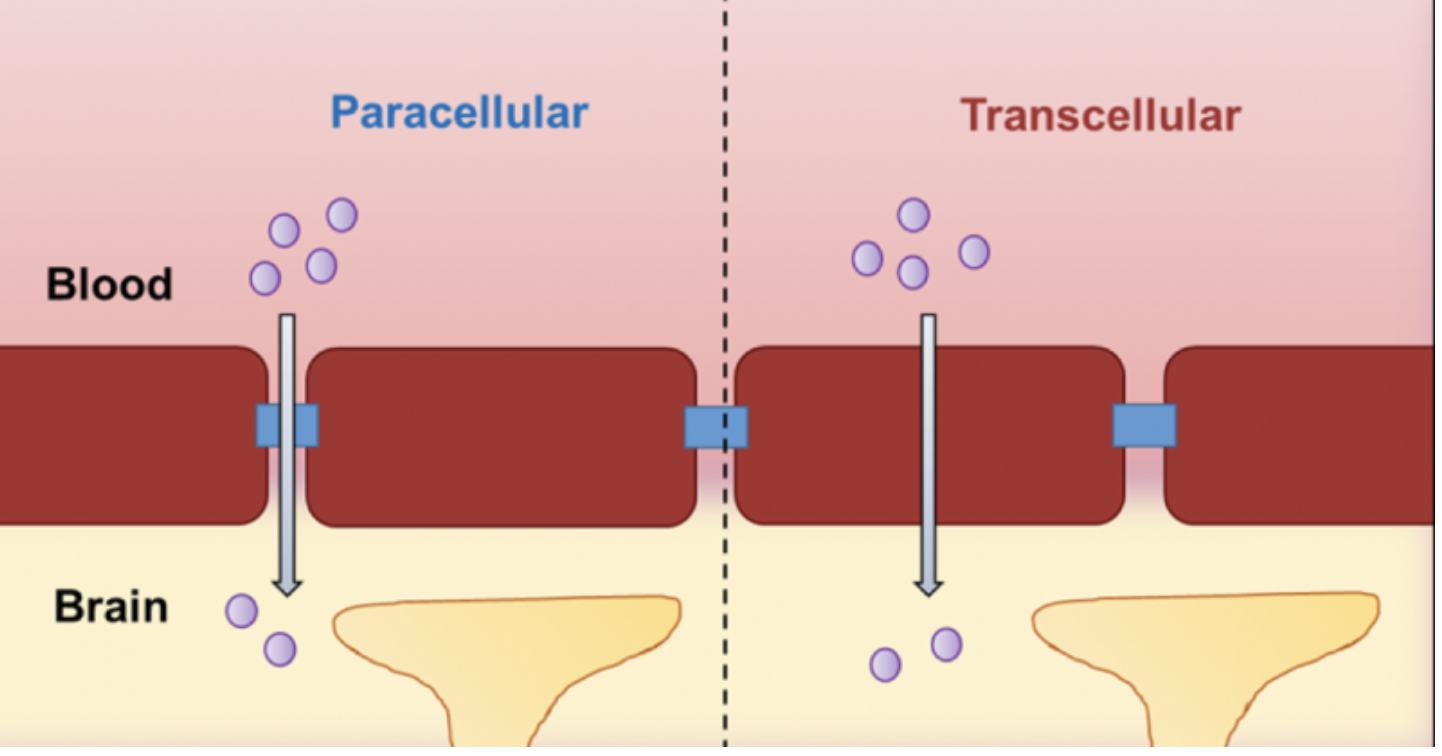
Epitheila Membrane Transport Two Pathways
Transcellular transport: molecules move through the cytoplasm of epithelial cells
Paracellular transport: molecules move through tiny gaps between epithelial cells, however this movement is limited by junctional complexes which regulate permeability
Junctional Complexes
Zonula occludens (tight junctions): these prevent easy diffusion between cells, keeps it tight ;)
Zonula adherens: help to anchor cells together and maintain tissues integrity
same for macula adherens (desmosomes)
Transport across these membranes often require specialized carrier proteins (Na/K pump or the Na/H pump) which are located at the both apical and basolateral sides of the epithelial cells
facilitate the movement of molecules in and out of the cells
ensures that esstential substances are absorbed and waste products discared and nutrients are reabsorbed effectively
Exocytosis
the process by which large molecules, like proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters are secreted by the cell
involves the fusion of a vesicle with the plasma membrane allowing the contents to be released outside the cell
this requires energy in the form of ATP to fuel the vesicles movement and fusion with the membrane
endocytosis
how large molecules, such as cholesterol, are brought into the cell
often involves receptor mediated endocytosis: specific transport proteins on the plasma membrane interact with molecules outside the cell, which triggers the formation of a vesicle that engulfs the target molecule
uses ATP
both endo and exo are crucial for maintaining cellular communication and function, enabling cells to secrete necessary substances or take in essential molecules
Chemical Signals for Cell Communication: each serves a specific purpose in regulating physiological processes
Gap junctions: allows adjacent cells to pass ions and regulatory molecules through channels between them, facilitating direct communication for coordinated cell activity (not the same as tight junctions)
Autocrine signaling: occurs when a cell releases a chemical signal that acts on itself, influencing its own function or behavior
Paracrine signaling (local): cells within the same organ releasing signaling molecules into the extracellular space, which then diffuse to nearby target cells; often referred “local” because the signals affect only nearby cells
Synaptic signaling: is unique to the nervous system; neurons release neurotransmitters across synapses to communicate with target cells, such as other neurons, muscles, or glands, enabling fast and precise control of body functions
Endocrine signaling: carried out by glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, hormones can travel long distances to target cells in various organs, allows the body to regulate broader processes, such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction
Each of these signaling methods plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and coordinating complex biological systems
How regulatory molecules affect their target cells
Recpetor proteins are crucial for cellular communication, allowing target cells to respond to specific signals
A target cell can receive a signal because it has receptor proteins either on it plasma membrane or inside of the cell, each is specific to the signal molecule
Nonpolar signal molecules
such as steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, and nitric oxide gas can easily pass through the plasma membrane due to the lipid soluble nature
once inside, they bind to intracellular receptors and initiate a response, often influencing gene expression
large polar signal molecule
like epinephrine, acetylcholine, and insulin cannot pass through the plasma membrane due to their size and charge
instead, they bind to receptors on the cell surface
these interactions trigger a cascade of intracellular signaling events through SECOND MESSENGERS
these second messengers may include ions like calcium or small molecules, carry the signal inside the cell and mediate various changes, such as altering enzyme activity or gene expression, enabling the cell to respond to the external signal
G protein cycle
Second messengers are crucial for transmitting signals inside cells, and one of the most common second messengers is cycle adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
the process begins when a signaling molecule, such as a hormone or neurotransmitter, binds to a receptor on the cells surface
the binding activates an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of ATP into cAMP
once cAMP is produced, it activates other enzymes in the cytoplasm, which triggers a variety of cellular responses and changes in cell activity, such as altering metabolism or gene expression
However, the receptor proteins that bind the signal and the enzyme proetins that produce the second messenger are rarely directly connected
they rely on G-proteins to shuttle the signal between them
G proteins are made up of three subunits; alpha, beta, and gamma
When the signaling molecule binds to the receptor, the alpha subunt dissociates from the comples and moves to the enzyme or ion channel, initiating the production of cAMP or other signaling events
this ensure that the signal is efficiently transmitted and amplified within the cell
introduction to physiology
the stud of biological functions; how the body works
normal functions of cells to organisms as a whole
mechanisms
cause and effect sequence
scientific experiments derived
Pathophysiology
a disruption of normal function
how disease or injury affects physiological processes
outlyers
why is it different
aids understanding of normal processes
Comparative physiology
studies the differences and similarities in the function of invertebrates and vertebrates
aided in the development of pharmaceutical drugs
Scientific Method
observations
hypothesize
design and conduct
analyze
results replication
present
Good Physiological Research Requires:
to ensure accuracy
quantifiable measurements
an experimental group and control group
independent and dependent variables
extraneous/ cofounding variables: miss alignment in the data we can not control
ex. biological sex, chronological age (ethically can not change)
reduction of biases
statistical analysis: qualifiers may help (ozempic); determine significance
goal: review and publication by peer reviewed journal
Developing Pharmaceuticals
a. basic research is conducted for years before a drug is ever given to a person
b. research begins by studying the effects of a chemical on cells in vitro (in a culture dish)
c. next, studies are performed on animals (usually rats and mice) to see if the same effects occur in vivo and if there are any toxic side effects
for these trials, many rats and mice are genetically modified to be susceptible to particular diseases, may take several years
d. clinal trials
Phases of Clinical trials
Phase 1: test drug on healthy human (no outlyers and normal physiology) volunteers to test for side effects, rates of passage, dosage, etc.
Phase 2: test effectiveness on people with the particular disease (ideal are otherwise healthy)
Phase 3: large number of people including both sexes, many age groups and ethnicities and people with more than one health condition (extraneous variable testing)
From here the FDA can approve
Phase IV: test other applications for the drug
ex. viagra: initially blood pressure medication, goes through phase 4 and now works for erections
It is possible to go backwards and retest certain phases
Claude Bernard
observed that the internal environment stays relatively constant although changes are occuring
Walter Cannon
coined the term homeostasis to describe the internal consistency of the body
Homeostatsis
constancy of the internal environment
main purpose of our physiological mechanisms is to maintain
deviation from homeostasis → disease (sustained deviation)
accomplished mostly by negative feedback loops (95%)
Pavlov and Crick Watson Franklin and Wilkins
Pavlov: digestion
Crick, Watson, Franklin, and Wilkins: structure of dna
Negative Feedback Loops
Pathway
Stimulus: never stops, changes within the environment
receptors, which act as sensors in the body to detect change and send information to the:
Integrating center, which assesses change around a set point, then sends instructions to:
Effector (muscle or glands) which can make the appropriate adjustments to counter the change from the set point
Mechanism of Negative Feedback Loops
a. moves in the opposite direction from the change
b. makes the change from the set point smaller
c. reverse the change in the set point
d. continuous process, always making fine adjustments to stay in homeostatsis
set point =
dynamic consistency (range of setpoints)
If effectors continuously run, what will occur
disease
antagonistic effectors
oppsoing effectors that move conditions in opposite direction
maintains conditions within a certain normal range, or dynamic consistency
when you are hot you sweat, when you are cold you shiver
ex. blood glucose levels, blood calcium levels, heart rate, and blood pH
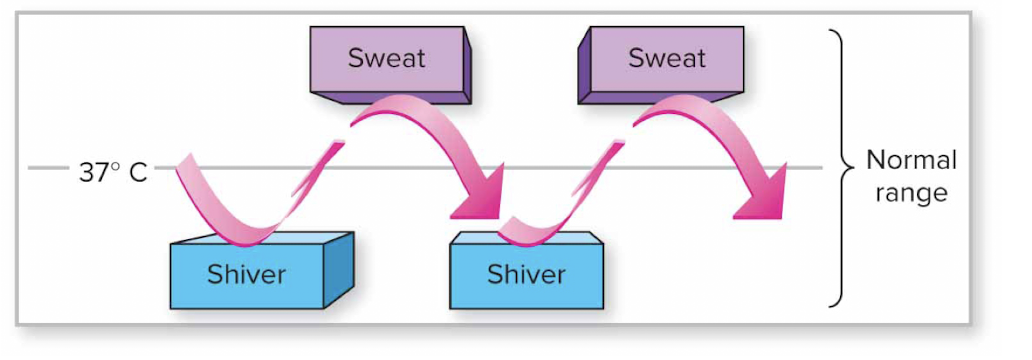
Quantitative measurements
to study physiological mechanisms, scientist must measure specific values and mathematically determine such statistics as their normal range, their averages, and their deviations from the average (set point)
knowledge of normal ranges aid in diagnoses of disease and in assessing the effects of drugs and other treatments
Normal range of
Arterial pH
Glucose
7.35 to 7.45
70 - 99 mg/100ml
Positive Feedback
the end product in a process stimulates the process
the action amplifies the changes that stimulate the effectors → completion
positive feedback can not work alone, but it does contribute to many negative feedback loops
ex. blood vessel if damaged, a process begins to form a clot (pos fed), once damage is fixed clotting ends (neg fed)
the strength of uterine contractions during childbirth is also a pos fed
Regulation of Processes within Organs
Intrinsically: cells within the organ sense a change and signal to neighboring cells to respond → changes function periodically in organ ex. clotting
Extrinsically: the brain or other organs, regulate an organ using the endocrine or nervous system
the endocrine releases hormones into the blood which transport to target organ
nervous system “innervates” organs with nerve fibers
Negative Feedback Inhibition
a closed loop control system that usually involves an antagonist to make sure homeostasis is maintained within normal levels
ex. when blood sugar is low, the hormone glucagon (antagonist) is secreted with increases blood sugar
Levels of organization
cell
tissue
organ
system
organism