6 & 7. Ligands and Nomenclature
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is nuclearity?
Related to the number of metal ions in a discrete complex unit - not necessarily the number of metal ions in the entire formula
It is the metal ion within the square bracket
What is an ambidentate ligand?
ambidentate ligands can bind through more than one type of atom in the structure - e.g. M-CN or M-NC
Which atom it will bind to depends on HSAB theory, e.g. nitrogen is harder than carbon so harder metals will bond to N and softer will bond to C
What is a chelating ligand?
chelating ligand is one that binds to one metal ion using several donor atoms
This includes polydentate ligands that form a ring - chelate ring - with the metal ion
The coordination compound formed is a chelate.
What are the reasons behind extra stability of complexes with chelate rings?
Stabilisation will arise from the bidentate being coordinated even if one coordinating atom is removed, which enables easy reformation
Stabilisation also arises from gain in entropy upon formation of the chelate
What is the bite angles? How does it impact a complex?
The bite angle is the ligand-metal-ligand angle formed with a bi or polydentate ligand coordinates to a metal centre
Given in degrees and can characterise distortion from the idealised geometry or gauge the degree of ring strain
What effect can a small bite angle have on octahedral complexes?
It can distort the octahedral into a trigonal prismatic geometry.
What is the most stable chelate ring size?
5
4 and 6 also exist but 5 is the most stable and can be formed without too much ring strain making it stable
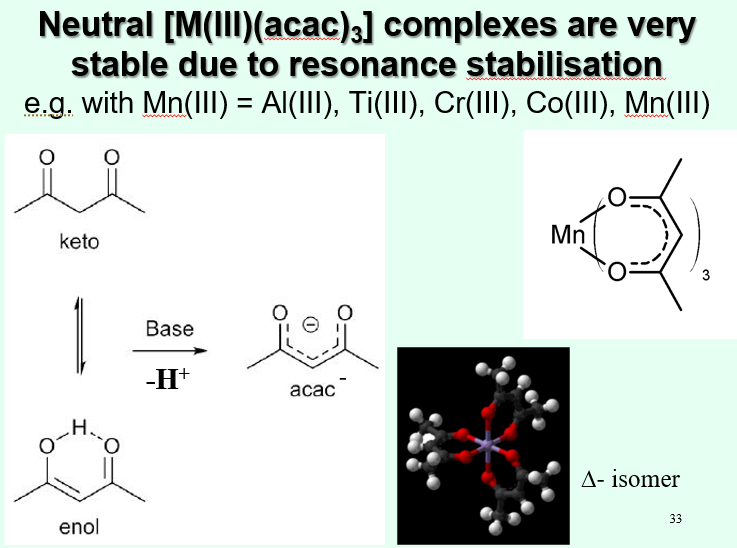
How is the chelating ring with acac stabilised?
Acac forma a 6-membered ring, so it is not as stable as the five membered ring
However, the complex can be stabilised with resonance stabilisation
How is the formulae ordered within square brackets?
Metal centre is listed first
Then anionic ligads
Then neutral ligands
E.g. [PtCl2(NH3)2]
What is the difference in bonding for the atoms listed inside or outside the square brackets?
Anything inside the square bracket is chemically bonded
Anything outside the square bracket is just a counter ion
Lattice solvent molecules may follow after a dot outside the square bracket ( e.g. .H2O)
What is the suffix for anionic ligands?
-’o-
E.g. chloro, fluoro, bromo, cyano etc
What suffix is the metal given if the complex is negatively charged overall?
‘-ate’
E.g. nickelate, aluminate etc
Some metals will use their Latin name when the ate suffix is added (just as a rule, sounds better I guess) - Ferrate, cuprate (Cu), Argentate (Ag), Plumbate (Pb
What prefixes are used for when there are multiple more complicated ligands?
bis, tris, tetrakis, pentakis, hexakis f
Followed by the ligand in parentheses
E.g. Tris(ethylenediamine)
What are the ligands Acac, bipy and en?
acac = acetylacetonato
bipy = 2,2-bipyridyl
en = ethylene diamine
What types of compounds (4) can be made with complexes?
adducts of salts: [NiCl2(DMSO)4]
[metal complex](anions): [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
(cation)[metal complex]: K2[PtCl6]
Molecular complexes: Cr(CO)6 (no square brackets)
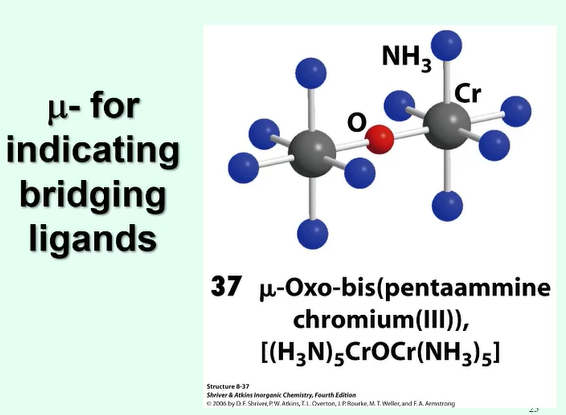
What is a bridging ligand and what is the prefix that indicates this?
μ
a bridging ligand is one which connects to two or more atoms, usually the metal ions and is the ‘bridge’ between two metal ions
How is the metal oxidation state indicated in the name of the compound?
In the brackets that follow metal centre
E.g. hexaaminecobalt (III) chloride