Health Midterm 2023
4.9(7)
Card Sorting
1/84
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
1
New cards
What does your nervous system do for you?
The nervous system is responsible for regulating your body temperature, sending signals to the brain through nerves, and controls movement. It is the master control and communication system of our body.
2
New cards
Parts of the Nervous System
Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves, Sensory Organs(5 senses)
3
New cards
Functions of the Nervous System
Sensory Input, Integration, Motor Output
4
New cards
Sensory Input
Stimuli; noticing things
5
New cards
Integration
Process of carrying out information by your CNS; translating what you notice
6
New cards
Motor Output
Muscle/Gland; Using bodily movements to control movement
7
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
\-Made up of the brain and spinal cord
\-Acts as the body’s control center and coordinates bodily activities
\-Acts as the integration and command center
\-Acts as the body’s control center and coordinates bodily activities
\-Acts as the integration and command center
8
New cards
How does the CNS act as the body’s control center?
Impulses travel through the neurons in your body to reach the brain
9
New cards
What is the primary function of CNS?
* Takes in conscious and unconscious thoughts
* Makes decision for controlling and maintaining homeostasis
* Asks as integration as a command center
* Makes decision for controlling and maintaining homeostasis
* Asks as integration as a command center
10
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
* Made up of everything else (nerves/nerve endings) that carry messages to and from the CNS
* Carries Impulses to and from CNS to glands and muscles
* Links all parts of the body by carrying impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS and from the CNS to glands or muscles
* Carries Impulses to and from CNS to glands and muscles
* Links all parts of the body by carrying impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS and from the CNS to glands or muscles
11
New cards
What are the two main parts of the PNS?
Somatic Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous System
12
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
* Relay info between the skin, skeletal muscles and CNS
* You consciously control this pathway by deciding whether or not to move muscles (except reflexes)
* You consciously control this pathway by deciding whether or not to move muscles (except reflexes)
13
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
\-Relay info from CNS to organs
14
New cards
Reflexes
automatic response to stimuli
15
New cards
Involuntary
You do not consciously control these
16
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous System
control in times of stress such as flight or fight
17
New cards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
* controls body in times of rest
18
New cards
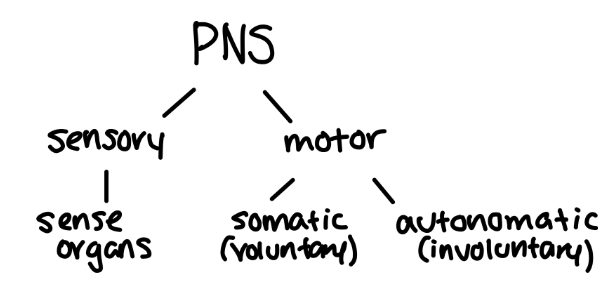
PNS DIAGRAM
look at pic
19
New cards
Sensory Division (AFFERENT)
The division of the PNS composed of nerves that carry information **TO** the CNS
20
New cards
Motor Division (EFFERENT)
The division of the PNS composed of nerves that carry information **FROM** the CNS
21
New cards
Neurons
Nerve cells
22
New cards
Dendrites
Fibers that receive and convey messages to the cell body of a neuron
23
New cards
Cell Body
Metabolic center of the cell; contains the nucleus
24
New cards
What are the two cell types?
Support Cells aka neuroglia and neurons
25
New cards
What is the job of the Supporting Cells/Neuroglia?
To insulate, support, and protect delicate neurons
26
New cards
Axon Terminal
* At their terminal end axons branch into hundreds or thousands of axon terminals
* Each contains vesicles or sacs of neurotransmitters
* When a nerve impulse reaches an axon terminal it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters
* Each contains vesicles or sacs of neurotransmitters
* When a nerve impulse reaches an axon terminal it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters
27
New cards
Synapse
The junction between neurons
28
New cards
What are synapses used for?
* Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse to continue cell to cell communication
29
New cards
Tracts
Bundles of nerve fibers in CNS
White Matter: Myelinated Axons
Grey Matter: Unmyelinated Cell Bodies
White Matter: Myelinated Axons
Grey Matter: Unmyelinated Cell Bodies
30
New cards
How are neurons classified?
* Sensory Neurons, Interneurons, Motor neurons
31
New cards
Sensory Neurons
* carry impulses from receptors such as the skin to the CNS
32
New cards
Interneurons
connect sensory and motor neurons in the CNS
33
New cards
Motor Neurons
carry impulses from the CNS to a muscle or gland
34
New cards
Proprioceptors
* Sensory receptors in the muscles and tendons
* Detect stretch or tension in skeletal muscles, tendons and joints
* Maintain balance and posture
* Detect stretch or tension in skeletal muscles, tendons and joints
* Maintain balance and posture
35
New cards
Four Types of Neuron Structure
Unipolar, Bipolar, Multipolar(most common), Pseudounipolar
36
New cards
Two major functional properties of neurons
Irritability & Conductivity
37
New cards
Irritability
Ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into a nerve impulse
38
New cards
Conductivity
Ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles, or glands
39
New cards
Things that excite a neuron
Lights, sound waves, pressure, chemicals, neurotransmitters
40
New cards
Events in a Nerve Impulse
1. Neuron at rest is polarized
2. Stimulus changes membrane permeability
3. Depolarization & generation of action potential
4. Action potential propagates along entire length of neuron
5. Repolarization-membrane returns to resting state
6. Sodium-potassium pump restores ion balance
41
New cards
Neurotransmitters
* Chemicals released at the end of an axon terminal that diffuse across the synapse and transfer the nerve impulse to another nerve, muscle, or gland
42
New cards
How do neurons communicate?
Via electrical and chemical synapses
43
New cards
4 Major Brain Regions
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brain Stem, Cerebellum
44
New cards
Cerebrum
* The largest and most superior part of the brain
* Composed of 2 cerebral hemispheres divided by longitudinal fissure
* Surface shows elevated ridges of tissues called gyri and shallow grooves called sulci
* Composed of 2 cerebral hemispheres divided by longitudinal fissure
* Surface shows elevated ridges of tissues called gyri and shallow grooves called sulci
45
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
* Outermost layer of the cerebrum
* Composed of gray matter
* Responsible for thinking and processing information from the five senses
* Composed of gray matter
* Responsible for thinking and processing information from the five senses
46
New cards
Cerebral Lobes
* Grooves or fissures divide into sections or lobes
47
New cards
Frontal Lobe
* Motor function, problem solving, memory, language, judgment, socially acceptable behavior
48
New cards
Parietal Lobe
* Processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and taste
49
New cards
Temporal Lobe
* Auditory perception, Olfactory area is deep inside
50
New cards
Occipital Lobe
Visual processing center
51
New cards
Diencephalon
* Superior to the brainstem
* 3 major structures: Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus
* 3 major structures: Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus
52
New cards
Thalamus
* Relay station for sensory impulses traveling to the sensory cortex
53
New cards
Epithalamus
* Contains the pineal gland and choroid plexus which forms the cerebrospinal fluid
54
New cards
Hypothalamus
Keeps your body in homeostasis
55
New cards
Brain Stem
Made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
56
New cards
Midbrain
* Reflex center for vision and hearing, eye movements
57
New cards
Pons
Coordinates information between brain areas, involved in breathing
58
New cards
Medulla Oblongata
* Blood pressure, breathing, heart rate
59
New cards
Cerebellum
* Precise timing of skeletal muscle activity
* Balance and equilibrium
* Makes body movement smooth and coordinated
* Balance and equilibrium
* Makes body movement smooth and coordinated
60
New cards
Bones
Skull and vertebrae
61
New cards
Meninges
Connective tissue matter
62
New cards
Dura Mater
Tough outer double layer membrane
63
New cards
Arachnoid Mater
Web-like layer spans the subarachnoid space
64
New cards
Pia Mater
Innermost membrane that clings tightly to the surface of the brain and spinal cord
65
New cards
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
* Continually formed plasma by clusters of capillaries in cavities called ventricles
* Provides a watery cushion for the brain & spinal cord
* Significant changes in CSF composition may indicate problems
* Provides a watery cushion for the brain & spinal cord
* Significant changes in CSF composition may indicate problems
66
New cards
How is CSF obtained for testing?
It’s obtained through a procedure called a spinal or lumbar tap
67
New cards
Blood Brain Barrier
* The brain depends on a very stable internal environment
* Neurons are protected from blood-borne substances by the least permeable capillaries in the body
* Neurons are protected from blood-borne substances by the least permeable capillaries in the body
68
New cards
Spinal Cord
* Continuous with the brain stem; connects the brain to nerves
* Enclosed within vertebrae; provides a 2-way path to and from the brain
* Major reflex center
* Enclosed within vertebrae; provides a 2-way path to and from the brain
* Major reflex center
69
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Endoneurium, Perineurium, Epineurium
70
New cards
Endoneurium
Surrounds each neutron
71
New cards
Perineurium
Surrounds a group of neurons or fascicle
72
New cards
Epineurium
Surrounds a nerve
73
New cards
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
* 31 pairs of spinal nerves exit from the vertebral column
74
New cards
Plexus
* All other spinal nerves form complex networks each called a plexus, which serve the motor and sensory needs of limbs
75
New cards
Cranial Nerves
Nerves that originate in the brain
76
New cards
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
12 pairs that serve the head and neck
77
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
* Motor subdivision of the PNS that automatically controls bodily activities
* Maintains homeostasis
* Includes neurons that control cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
* Maintains homeostasis
* Includes neurons that control cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
78
New cards
Fight or Flight
* The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body to either fight or run from a threat
* Enables the body to cope rapidly and vigorously with situations that may disrupt homeostasis
* Enables the body to cope rapidly and vigorously with situations that may disrupt homeostasis
79
New cards
Parkinson’s Disease
* A motor system disorder that leads to trembling of the hands, arms, legs, jaws, or face and impaired balance and coordination
* Results from a loss of brain cells in area of the midbrain called the substantia nigra
* Results from a loss of brain cells in area of the midbrain called the substantia nigra
80
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis
Occurs when the Myelin Sheath around neurons is gradually destroyed and hardens into “scleroses”
Nerve impulse are interrupted
Autoimmune disease with no cure
Nerve impulse are interrupted
Autoimmune disease with no cure
81
New cards
Alzheimer’s
A type of mental illness caused by progressive brain cell death
Leads to problems with memory, thinking, and behavior
Symptoms worsen over time and there was no cure
Leads to problems with memory, thinking, and behavior
Symptoms worsen over time and there was no cure
82
New cards
Concussion
A mild traumatic brain injury
Caused by a jolt, bump, or blow to the head that causes the brain to move rapidly inside the skull
Symptoms: Dizziness, confusion, headache & nausea
Caused by a jolt, bump, or blow to the head that causes the brain to move rapidly inside the skull
Symptoms: Dizziness, confusion, headache & nausea
83
New cards
Meningitis
Acute inflammation of the meninges
Usually caused by vital or bacterial infection
Can lead to deafness, epilepsy, brain damage, or death
Symptoms: sever headaches & neck stiffness
Usually caused by vital or bacterial infection
Can lead to deafness, epilepsy, brain damage, or death
Symptoms: sever headaches & neck stiffness
84
New cards
Epilepsy
Brain disorder that causes seizures
85
New cards
Stroke
Occurs when something blocks oxygen supply to the brain and a blood vessel bursts