BPSC 104 Class 10
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Where does photosynthesis primarily occur
Primarily in leaves (but any tissue that is green)
Within the chloroplasts
Chloroplast structure and function are important for photosynthesis
Chloroplast structure (be familiar)
Found in shoot system tissues
Site of photosynthesis
Contain chlroophyll, a green pigment
Complex internal structure containing:
Thylakoids
Lumen
Grana
Stroma
Stroma thylakoids
chocolate part is the thylakoid membrane
mint is the lumen
Thylakoids (part of chloroplast internal structure)
internal membranes in which pigment molecules are embedded
Lumen (part of chloroplast internal structure)
liquid-filled cavity inside thylakoid
Grana (part of chloroplast internal structure)
stacks of thylakoids
Stroma (part of chloroplast internal structure)
fluid surrounding the thylakoids
Stroma thylakoids (part of chloroplast internal structure)
thylakoids that connect grana
Chloroplasts may also contain stored ____
starch
During:
Daytime: when a lot of glucose is being forme,d excess may be stored as starch in the chloroplast
Night: the starch will be broken down into sucrose
Sugar is delivered through the phloem to other parts of the plant
This supplies energy for metabolic processes
Light energy powers ___
photosynthesis
Visible light makes up a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum
Within the visible light spectrum
Violet has the shortest wavelength and highest energy
Red has the longest wavelength and lowest energy
Chromophore
Pigment + Proteins (combination of the two that allow for absorbtion)
Light energy must be __ to be useful for photosynthesis
Absorbed:
Pigments
Absorbtion spectrum
Pigments (related to light energy)
molecules that absorb light
black appearance = if a pigment absorbs all wavelengths of visible light
most pigments = absorb certain wavelength and reflect others
Reflected - color that we see
Absorbtion spectrum
the light absorption pattern of a pigment
linked to action spectrum
Chlorophyll (absorbs and reflects ___)
Absorbs violet and red light
Reflects green light (why chlorophyll appears green to us)
The action spectrum
The absorption spectrum
The action spectrum (of photosynthesis)
shows the rate of photosynthesis
similar to absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis (therefore linked)
Pigments involved in photosynthesis
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
Cartenoids
Chlorophyll a (pigment in photosynthesis)
Essential for photosynthesis in plants
Chlorophyll b (pigment in photosynthesis)
Accessory (antenna) pigment
not directly involved in photosynthesis
Broadens the range of usable wavelengths
Cartenoids (pigment in photosynthesis)
Accessory (antenna) pigments, broadens the range of usable wavelengths
Protects chlorophyll from damage from light
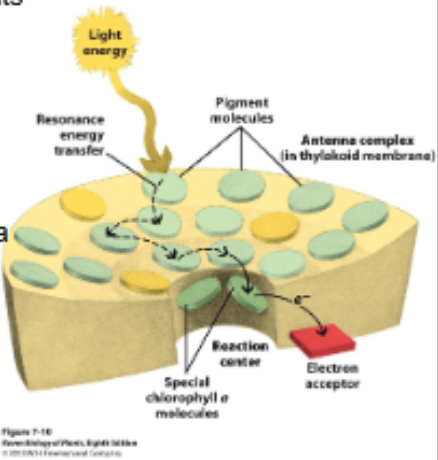
Pigments absorbing light (electrons boosted to higher energy level, excited state)
Accessory (antennae) pigments
expand wavelengths absorbed
protect leaf from excess energy
Transfer energy to reaction center - resonance energy transfer
Reaction center chlorophyl a
Unique position
Initiates photosynthesis
Loses an electron to an acceptor
think funnel
funnel photons of light down to the reaction center
change of form of the energy
Photosynthesis (2 sets of reactions)
Light reactions
Require light energy
Energy transduction reactions
Carbon fixation reactions
Carbon dioxide in converted into organic compounds
Also called the Calvin Cycle (think carbon)
(fixation means to take something inorganic and change it into CO2 and change it to sugar)
Photosynthesis reactions occur in different parts of the chloroplast
Light reactions occur in thylakoid membranes
Carbon fixation reactions occur in the stoma
photo = with light
lysis = to split
Light reactions occur in ___
Thylakoid membrane
Pigment molecules embedded in the thylakoid membranes absorb light energy
Water in lumen (interior) of the thylakoid is split into oxygen gas and hydrogen atoms (electrons and protons
Carbon fixation reactions occur in the ___
Stoma
sugar is produced
Photosynthesis (overview)
Light reactions
Requires light energy
Split H2O (PHotolysis)
Release O2
Reduce NADP+
Generate ATP from ADP
Phosphorylation
Carbon fixation reactions
Uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 to sugar
Two photosystems of light reactions
Photosystem - pigments embedded in thylakoid membrane are organized into discrete units called ___
Photosystems (in depth)
250-400 pigment molecules and two closely linked parts
Antennae Complex
Reaction center
Pigments in antennae comp:
gather light energy and funnel it to the reaction center
Proteins and chlorophyll a convert solar energy to chemical energy
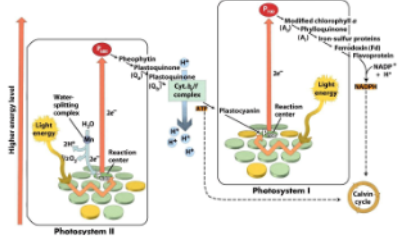
Photosystems I and II are linked together by ___
an electron transport chain
Photosystem - numbered by order of discovery, not functional order
(not going to ask intermediate electron receptors in ps1
should know:
cytochrome b f complex connects ps2 to ps1
NADP+ gets reduced to NADPH - calvin benson cycle
Process:
electrons are being energized, dumping protons in the lumen, exciting the elecgtrons from ps2, lyssi in to nadp+ and reducing?
Photosystem I reaction center is P680 (special pair)
Special pair - special pair of chlorophyll molecules in the reaction center is known as P680 (pigment 680 is the optimal absorbtion peak in nanometers)
Photosystem II reaction center is P700 (special pair)
Special pair - special pair of chlorophyll molecules in the reaction center is known as P700 (pigment 700 is the optimal absorption peak in nanometers)
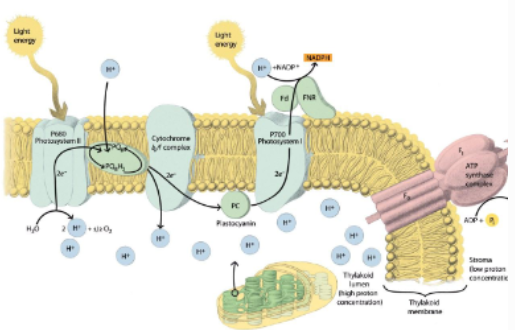
Photosystem I and II generally work ____
together simultaneously and continuously
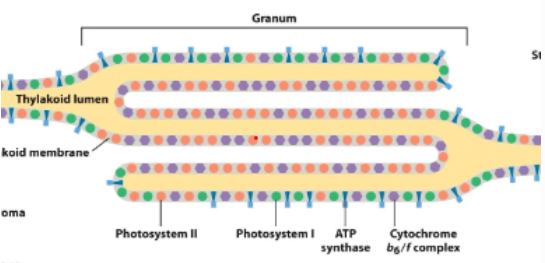
Photosystem I and II are __ separated
Spatially separated in the thylakoid membranes
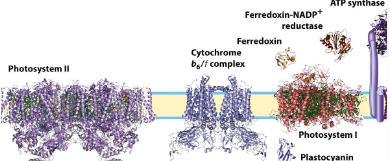
Structures of photosystems and other complexes in the photosynthetic apparatus
In photosystem II, water is ___ releasing __
oxidized; oxygen
Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll a of P680 in reaction center
Photosystem II has the unique ability to extract electrons from water - water photolysis
Energized electrons are transferred to the cytochrome b6/f complex
Protons are released into the thylakoid lumen
Proton gradient - produced by protons released from water
needed for generation of ATP-
What complex links Photosystem I and Photosystem II
Cytochrome b6/f complex
How can photosystem I work independently of photosystem II
Cyclic electron flow
Why have 2 system:
The calvin cycle requires 3 ATP for every 2 NADPH
Noncyclic electron flow produces5 ATP and 6 NADPH
Cyclic electron flow produces additional ATP
The Calvin Cycle
Present in all photosythetic plants
Occurs in 3 stages
1st reaction catalyzed by RUBP carboxylase oxygenase = Rubisco
Rubisco
most abundant protein on earth
one of largest, most complex enzymes
Balanced equation of photosynthesis
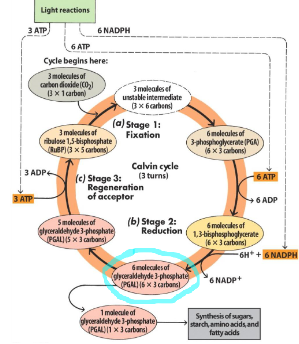
Clavin Cycle
need to know fixation step
need to know 3 PGA (1st detectable product, 3 carbon molecule)
pga gets reduced to pgal (6 carbon)
stage 3: extra 3 ATP
3 molecules of pgal is used to make the final part?
count the carbons, understand why we need cyclic reaction/light rxn to produce the additional atp needed in reaction step (good test q)
why do we need to do three times:
takes 3 molecules of co2 to make 1 pgal, which is what we use to make our sugars
why cyclic: requires more nadph than nadvadp?)