Fiscal policy
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Fiscal policy
Fiscal policy involves the use of government spending and taxation to fulfil macroeconomic objectives by influencing AD
What can Fiscal policy do and its 3 tools
Fiscal policy can be used to promote long-term economic growth and reduce unemployment
Government spending on physical capital goods
Government spending on human capital formation
Provision of incentives for firms to invest.
Fiscal policy 6 Objectives
Low unemployment
Promoting a stable economic environment for long-term growth
Low and stable inflation
Reducing business cycle fluctuations
Achieving an equitable distribution of income
Trade balance.
Direct & Indirect taxes
Direct taxes are imposed on income (rent, wages, interest, profit)
Indirect taxes are imposed on expenditure
Government revenue streams
Taxes
Operation and sale of public sector businesses. (selling a state owned business is called privatization)
Transfer payments
Transfer payments are payments made by the government without goods or services being received in return, such as welfare payments and donations.
2 types of government expenditure
Current expenditures (short-term) : stuff like wages and supplies for public sector businesses
Capital expenditures (long-term) : Stuff like infra
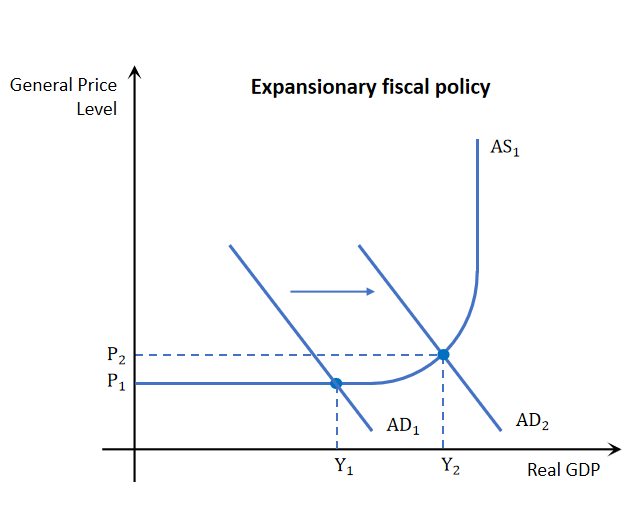
Expansionary fiscal policy affect on AD
Expansionary fiscal policy increases AD. Done using 2 ways
Increase government expenditure increasing G component in GDP
Decrease tax increasing C & I and thus GDP
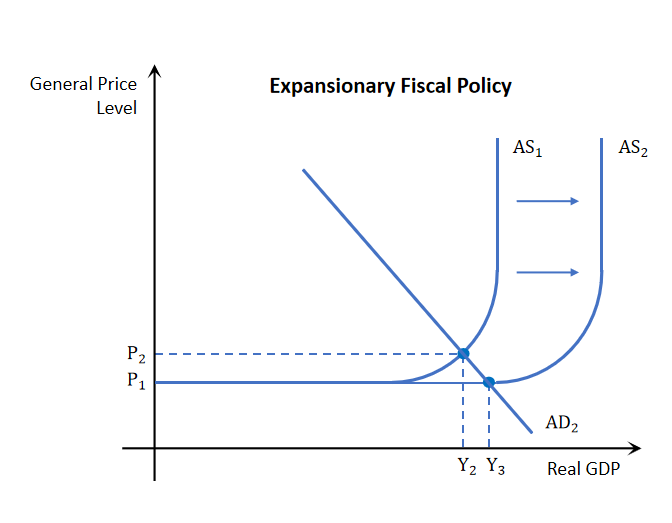
Expansionary fiscal policy affect on AS
AS is only affected on by expansionary fiscal policy, Any government spending which improves the quantity or quality of resources will improve AD and AS. So along with the shift in AD there will also be a shift in AS
this shift allows it so that in the long run national output does increase as usual but price levels will actually go down preventing inflation
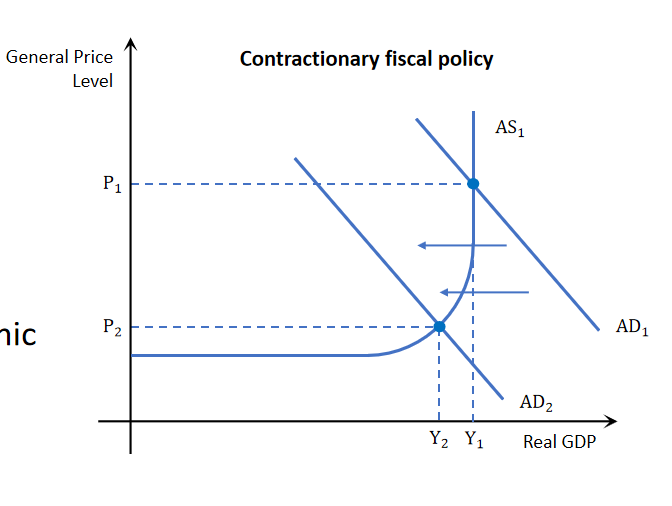
Contractionary fiscal policy
it aims to reduce AD by :
Decreasing government expenditure (↓G)
Increasing direct and indirect taxation (↓C, I)
Issues with high levels of growth
High levels of economic growth can cause:
Undesirably high levels of inflation
Shortages in the labor market.
Keynesian multiplier all Marginal factors
MPT : marginal propensity to tax
MPS : marginal propensity to save
MPC : marginal propensity to consume
MPM : marginal propensity to import
MPM + MPT + MPS + MPC = 1
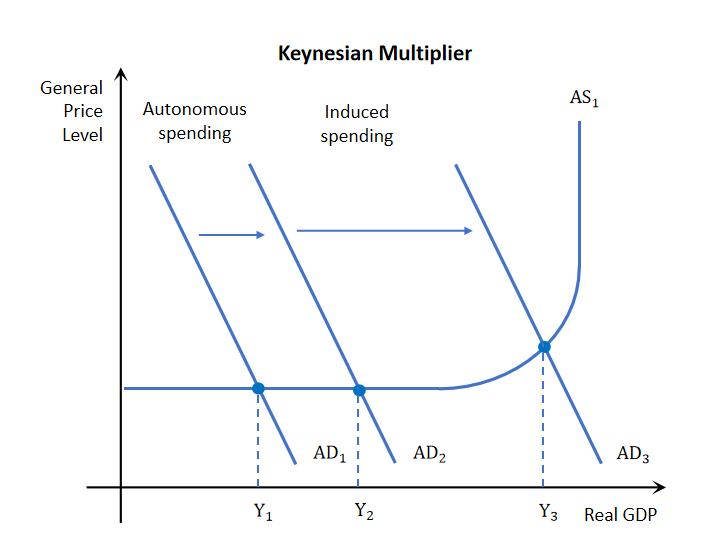
Keynesian Multiplier
This refers to the idea that the spending of one party becomes the income of another party, which then becomes further spending, with the cycle repeating infinitely.
Injection to the circular flow produces a chain reaction of further expenditures, with the effect of increasing AD and real GDP to a value greater than the initial expenditure.
Keynesian multiplier formula
Note as MPM + MPT + MPS + MPC = 1
you can replace the 1/1-MPC with 1/MPM + MPT + MPS
The idea is essentially when government invests money into the economy people spend it, so then that causes more chain reactions that increase GDP and this allows us to quantify that increase
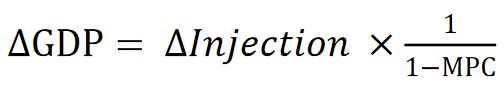
Autonomous spending and Induced spending
Initial injection to the economy is called autonomous spending. the subsequent spending is called induced spending which stimulates AD further
Pros of fiscal policy (2)
Target specific sectors : can be used to correct regional disparities in income and spending habits. like you can cut tax for low income people but increase it for the rich. government spending can be targeted to the sick or unemployed
Stimulates recovery from a deep recession : direct injection of money thanks to multiplier increases AD more then cost of injection. increases confidence which increases GDP which prevents mass unemployment
Cons of Fiscal policy
Political pressure : constraints are there so sometimes contractionary policy isn’t applied when necessary
Time lag
Sustainable Debt : can the government afford to have a budget deficit in both short and long run
3 types of time lag
Recognition lag : takes time to tell whether an economy is in need for government intervention. Sudden shocks cant be immediately dealt with
Administrative lag : Takes time for approval
Effectiveness lag : time lag between the implementation of fiscal policies to seeing the actual effects take place in the economy.
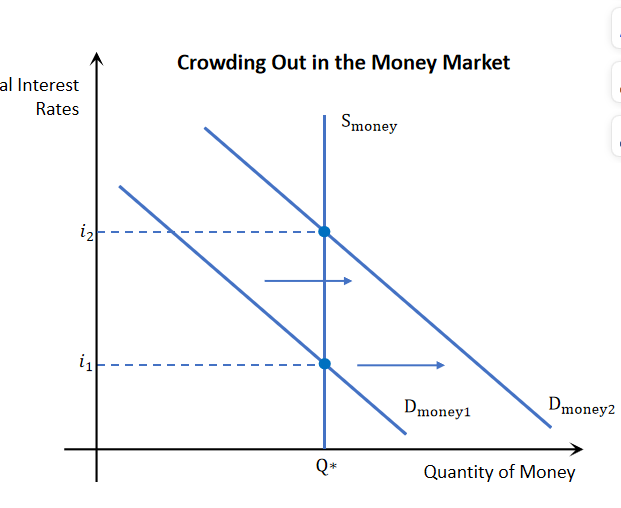
Crowding out
When a government runs a budget deficit, it needs to borrow funds. causes an increase in the demand of money → causes interest rates to increase → makes it harder for private firms to invest → as borrowing funds are more expensive → reduced investment → reduced AD
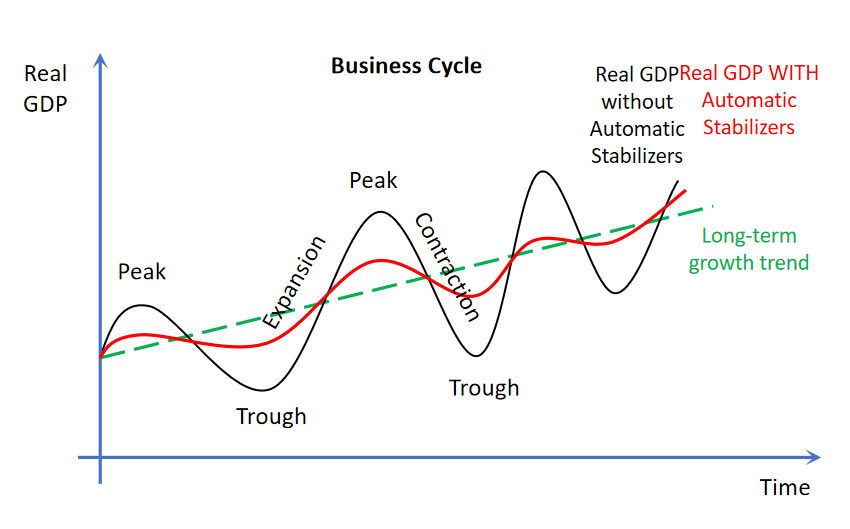
What is an automatic stabilizer
Automatic stabilizers aim to reduce the short-term fluctuations of the business cycle with lower peaks and higher troughs closer towards the long term growth trend.
Progressive tax as a Stabalizer
During expansion
Incomes rise as national output increases (GDP rise) → As incomes rise, households will be taxed a higher proportion of their income. → This prevents the economy from overheating.
During Recession
Incomes fall with national output (GDP) → As incomes fall, households will be taxed a lesser proportion of their income. → This reduces pressure on falling AD and counteracts the economic contraction.
Unemployment benefits as a Stabalizer
During expansion
Some workers may be inclined to stay unemployed to claim unemployment benefits → As a result, national output does not rise too quickly.
During Recession
The distribution of unemployment benefits rise as they are offered to more unemployed workers. → Household consumption will be somewhat maintained, lessening the downward pressure on AD.