Chapter 15 brain tings like thalamus and mamillary bodies
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
brain organization pg.~434
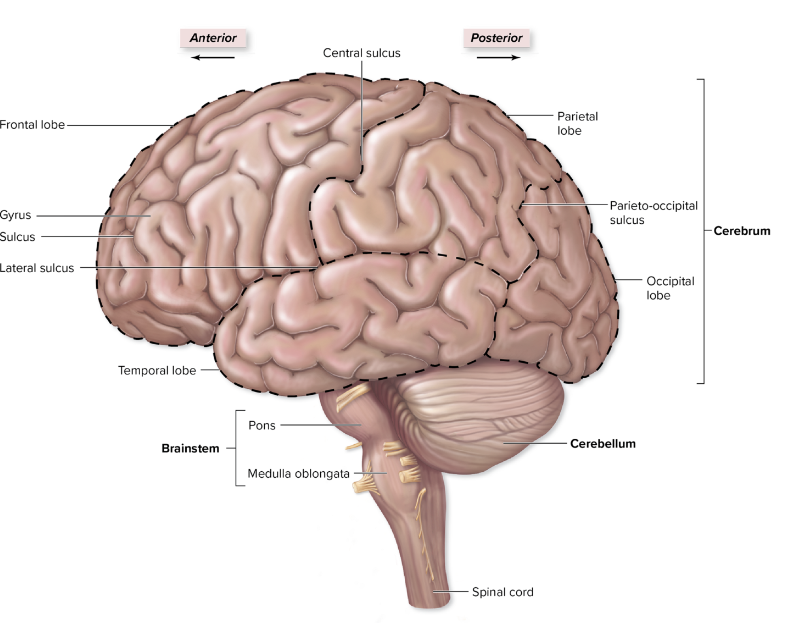
what is the largest part of the brain, and what are the main parts of it?
it is the cerebrum, which has frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes.
brain organization pg.~434
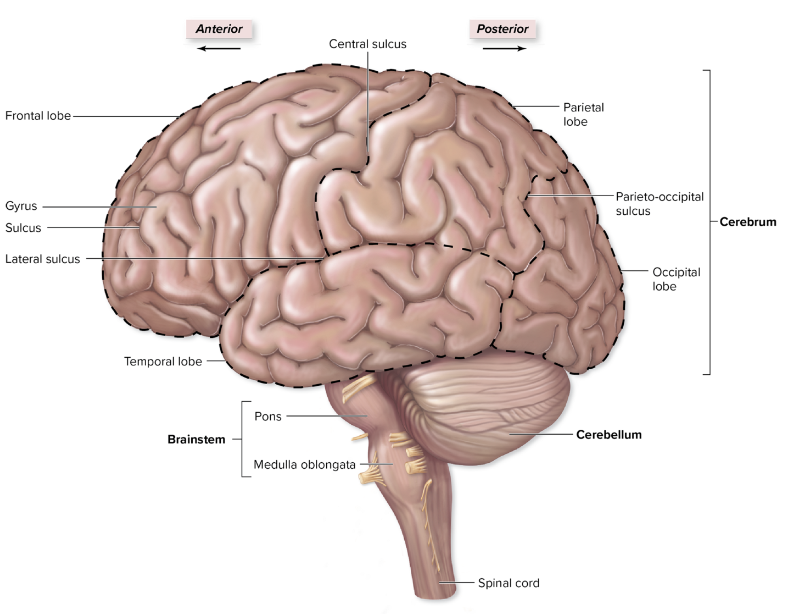
what is a gyrus?
they are the raised areas of the brain
brain organization pg.~434
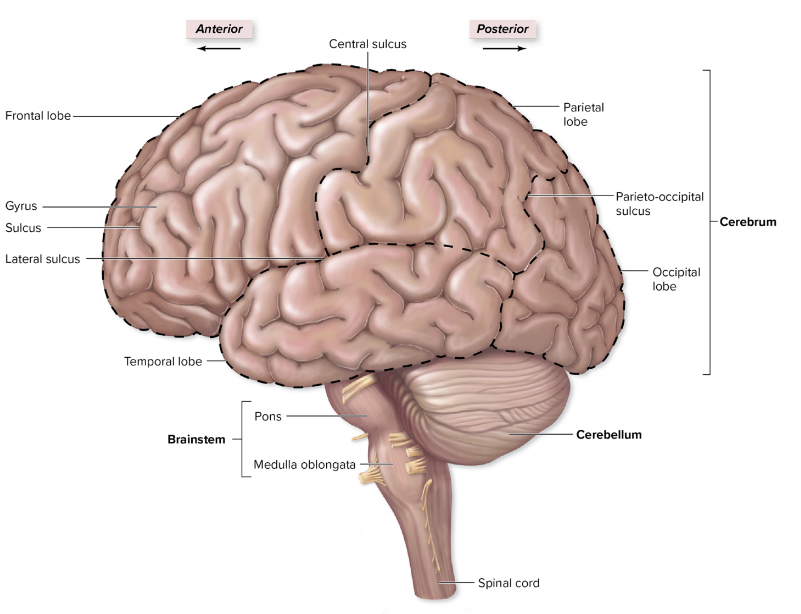
what is a sulcus?
they are the ridges of the brain
brain organization pg.~434
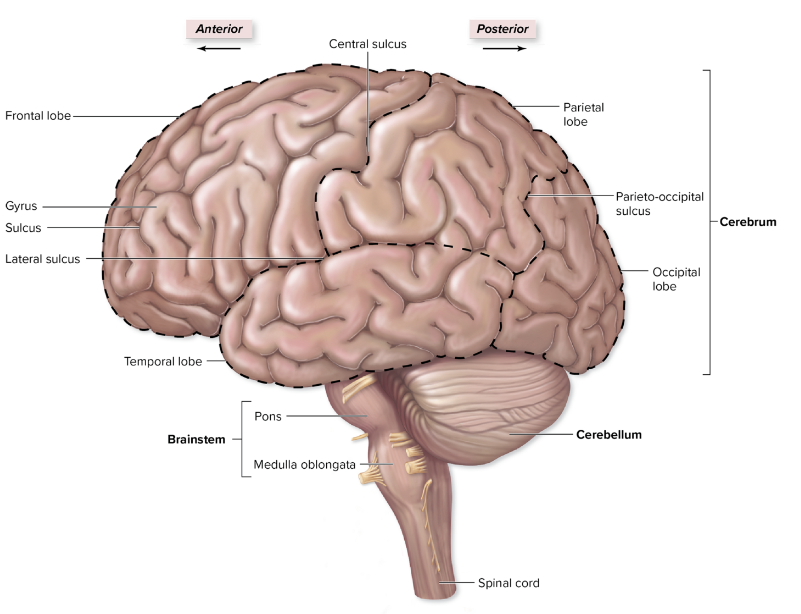
why do we have gyri and sulci?
just like basically all things we have them to increase the surface area of the brain, so we have ridges and lumps are more processing power and capabilities
brain organization pg.~434
frontal lobe
it is superior to the lateral sulcus and anterior to the central sulcus: it is basically the most anterior lobe of the lobes,
it pertains to things like emotions, cognitive abilities, and voluntary motor control
has the premotor cortex and the primary motor cortex
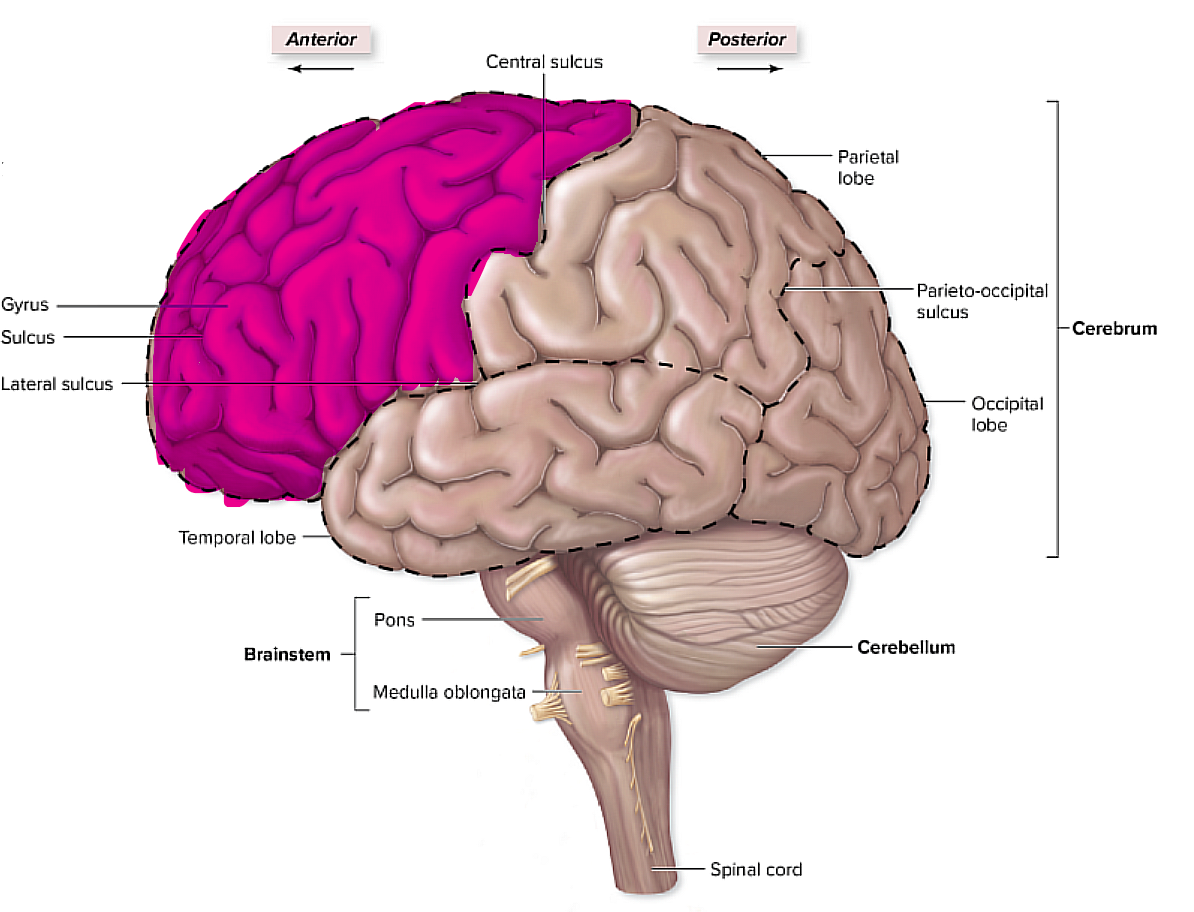
brain organization pg.~434
where is the premoror cortex and the primary motor cortex, and what do they pertain to?
they are basically in the same place of the frontal lobe
the premotor plans for the voluntary movement where the primary motor is involved more in the execution of the voluntary movements
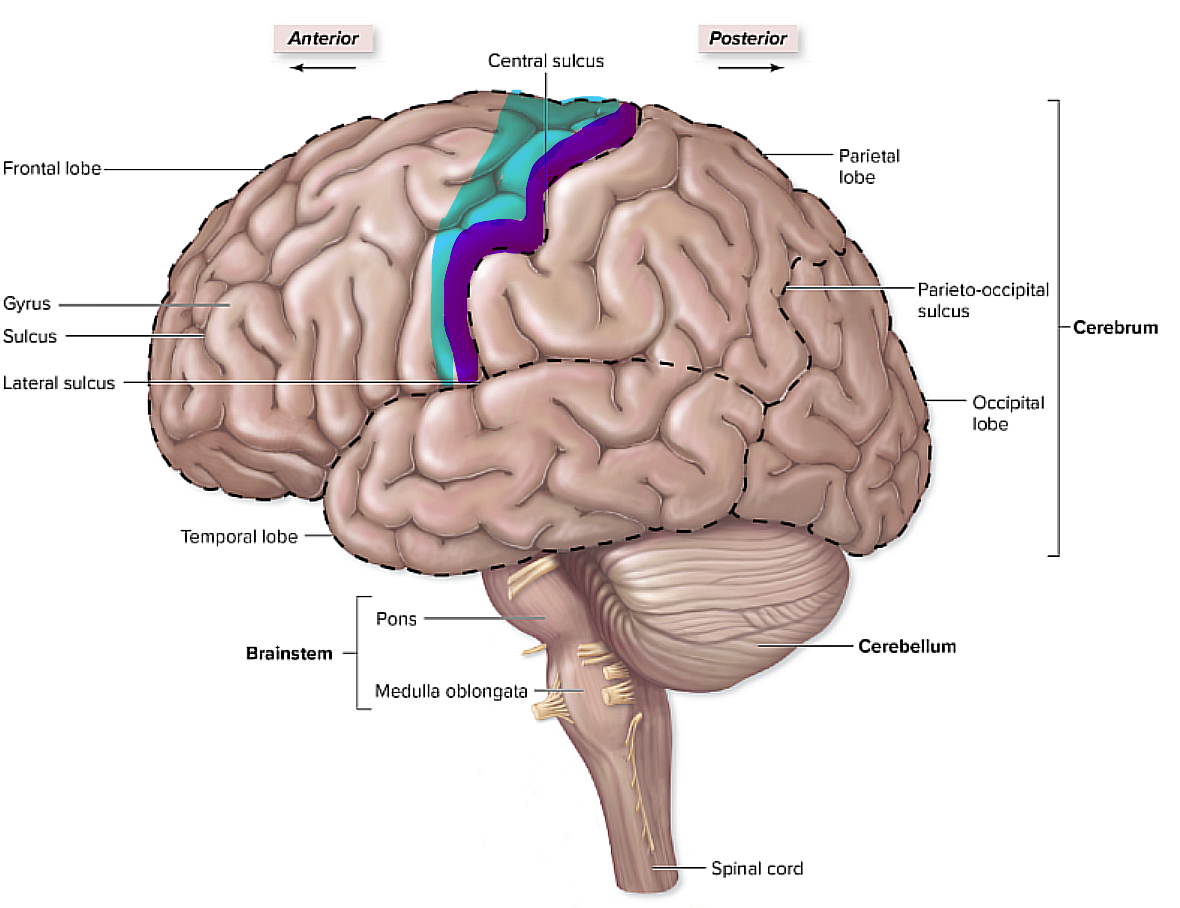
brain organization pg.~434
where is the temporal lobe, and what does it pertain to?
it is inferior to the frontal and parietal lobes,
it pertains to things like hearing
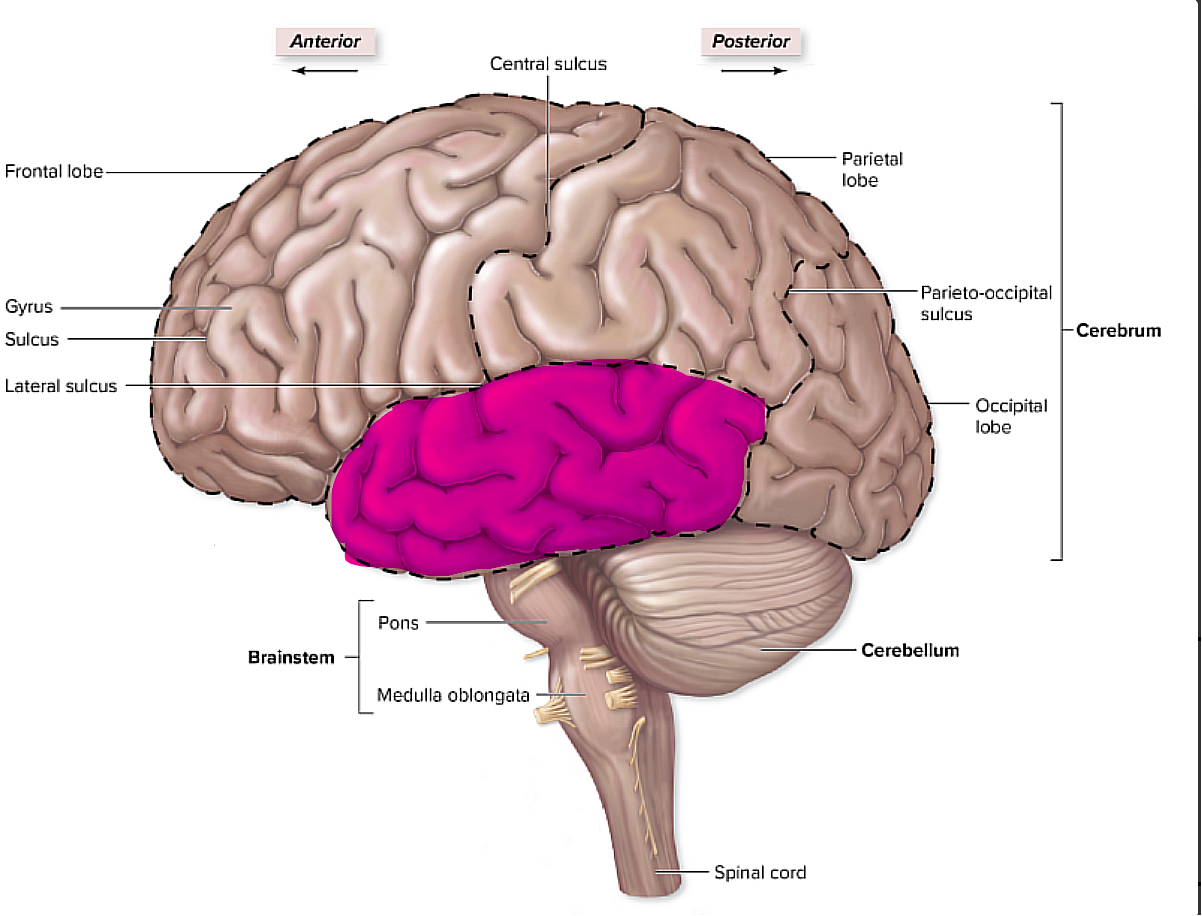
brain organization pg.~434
where is the parietal lobe, and what does it pertain to?
it is posterior to the central sulcus and the frontal lobe,
it also has the primary somatosensory cortex, right posterior to the central sulcus
pertains to things such as the somatic hot, cold, touch, pain, and is where we consciously interpret information
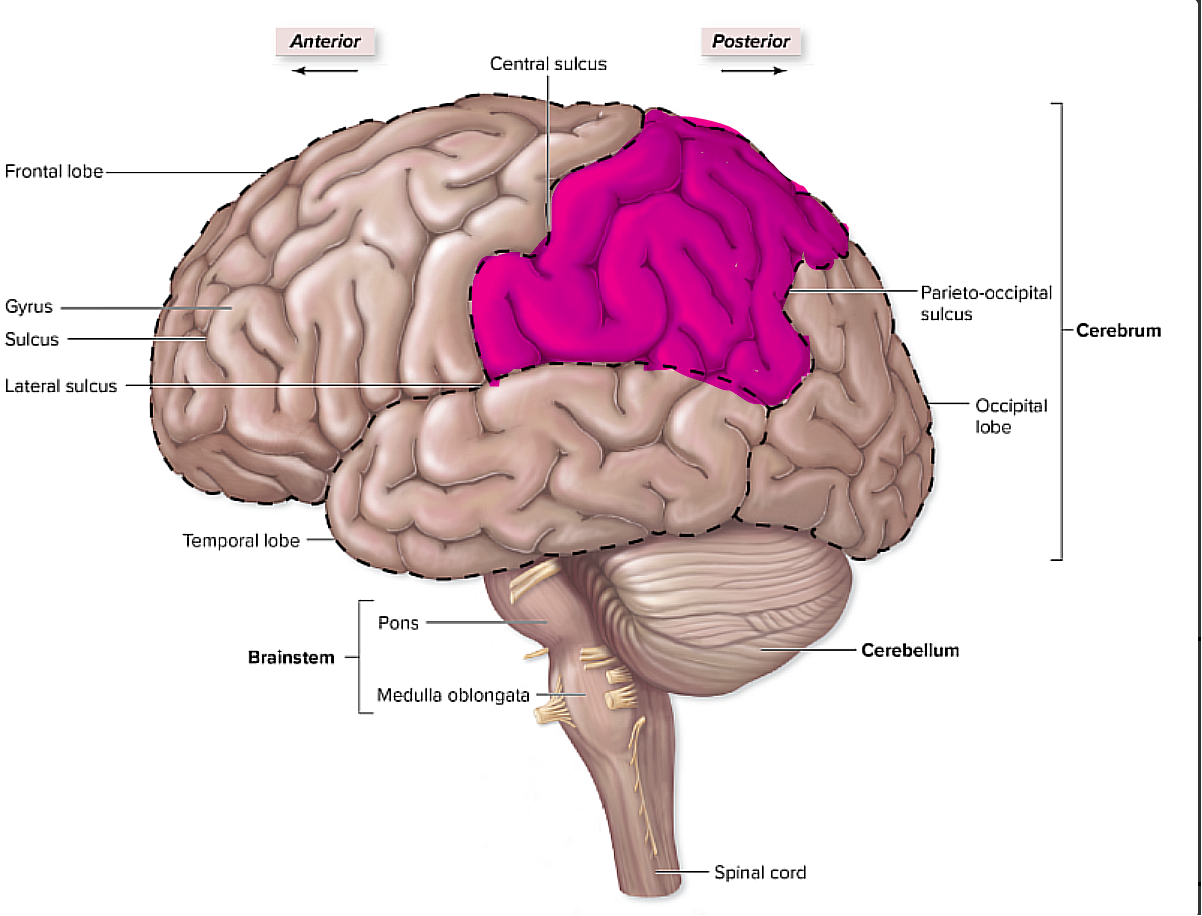
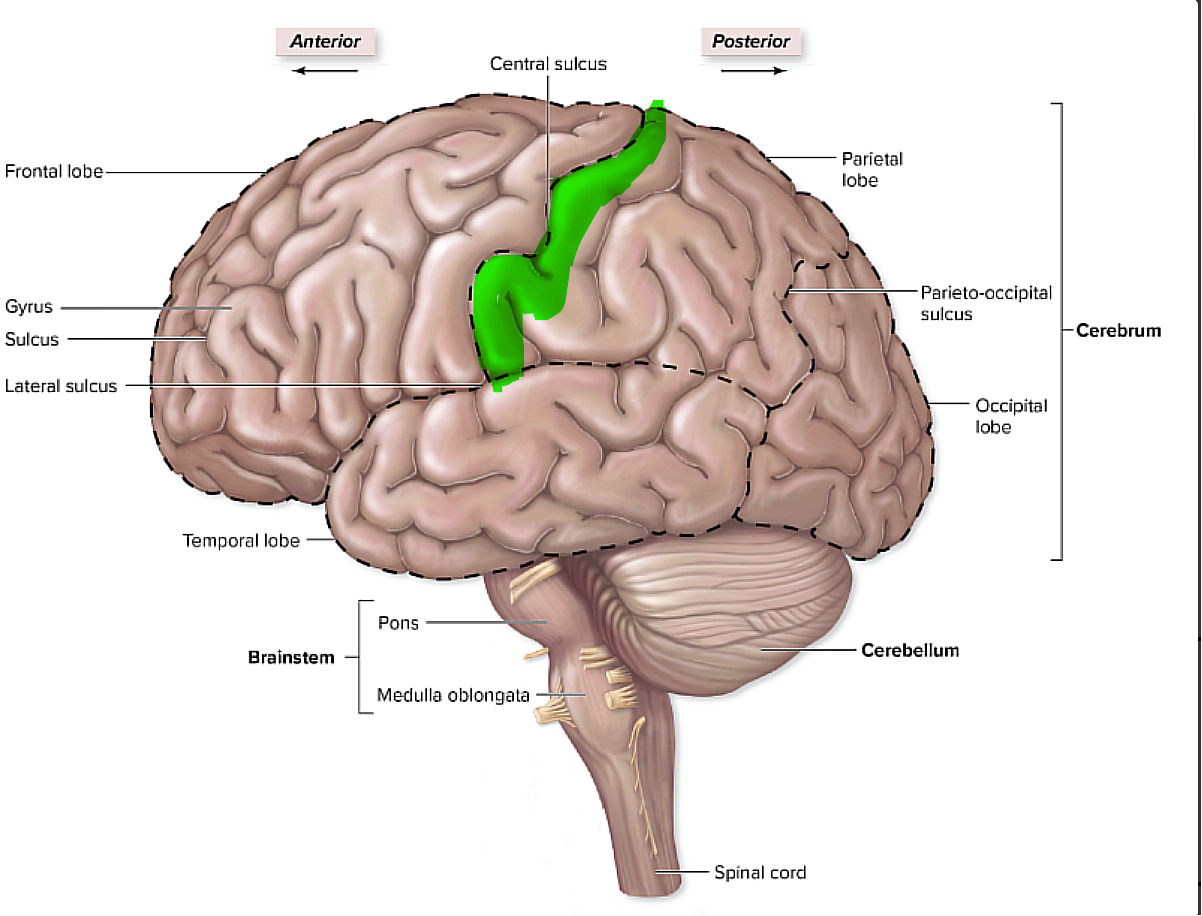
brain organization pg.~434
what is this, and what does it pertain to?
it is the primary somatosensory cortex, and is where we receive the sensory information
brain organization pg.~434
where is the occipital lobe, and what does it pertain to?
is is the most posterior lobe,
it pertains to things like vision
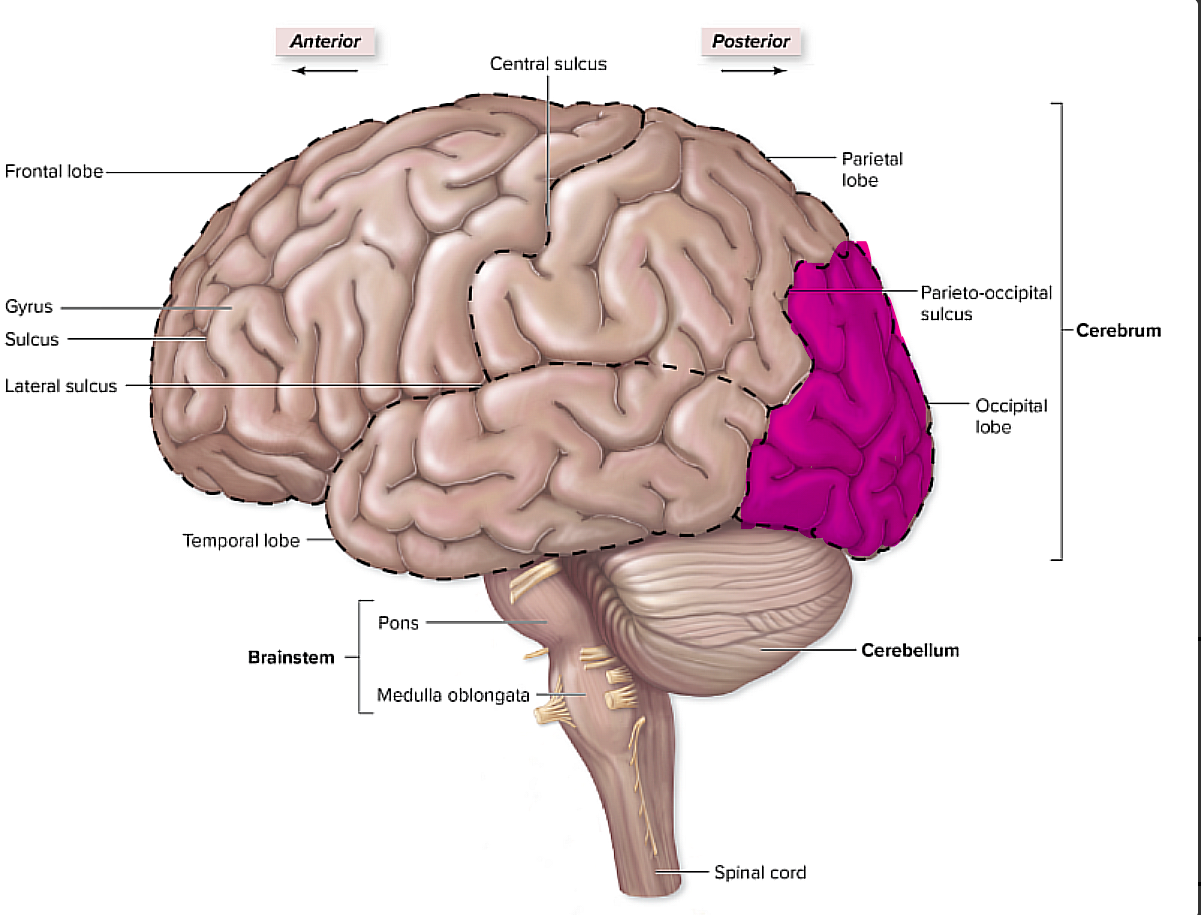
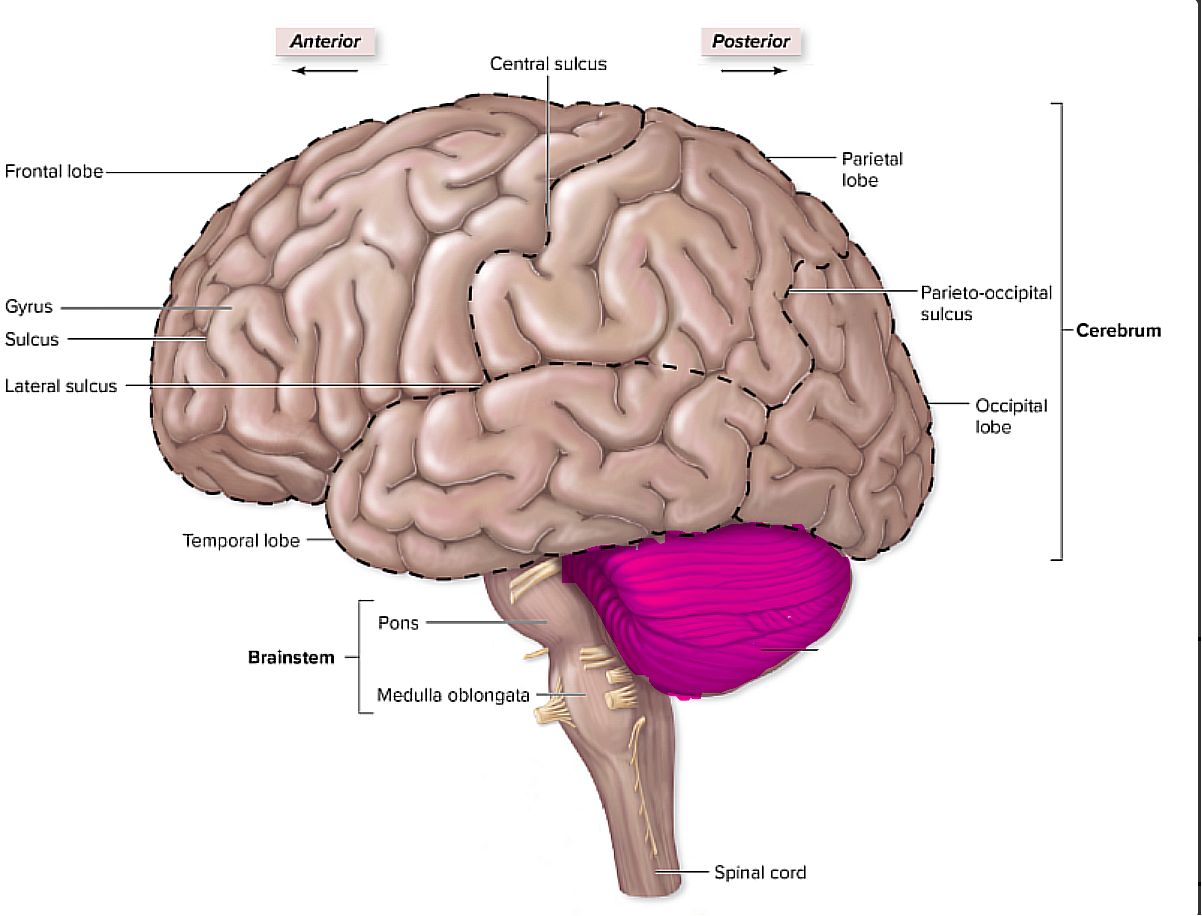
brain organization pg.~434
what is the cerebellum, and what does it pertain to?
pertains to things like balance, and skeletal muscle contractions
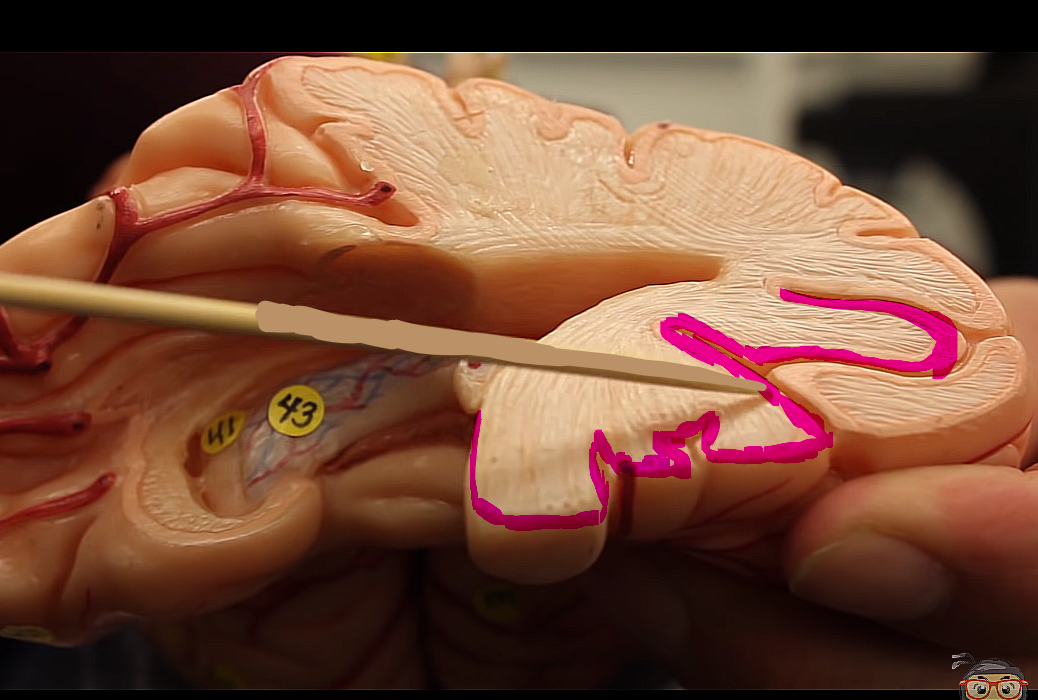
brain organization pg.~434
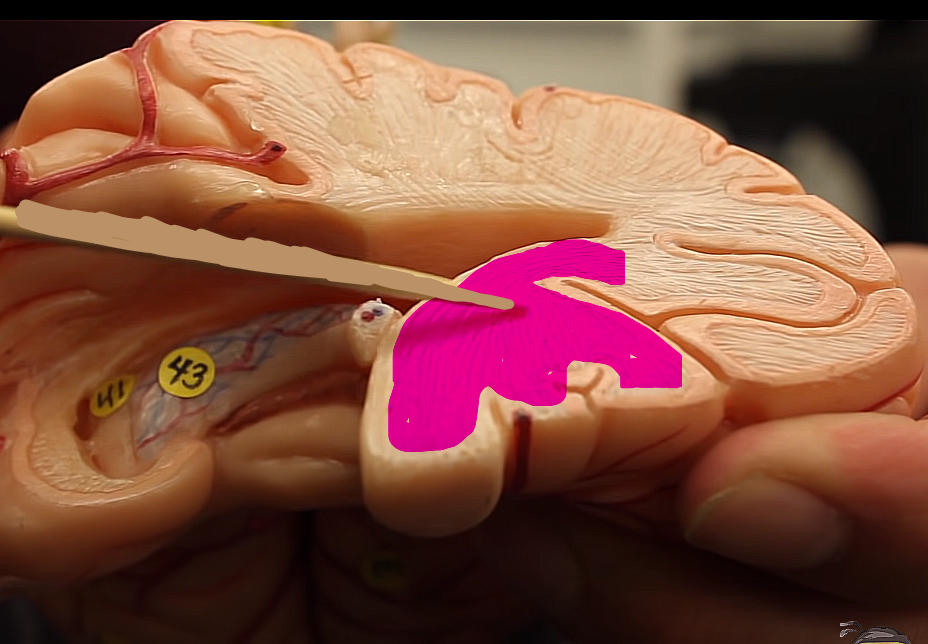
what matter is this, and what does it pertain to?
it is more superficial, so it it grey or gray matter (bish idk which gray is grey)
grey all about processing information,,,, more surface area,,,,more processing power
brain organization pg.~434
what matter is this, and what does it pertain to?
it is more deep, so it is white matter
they are the channels of communication
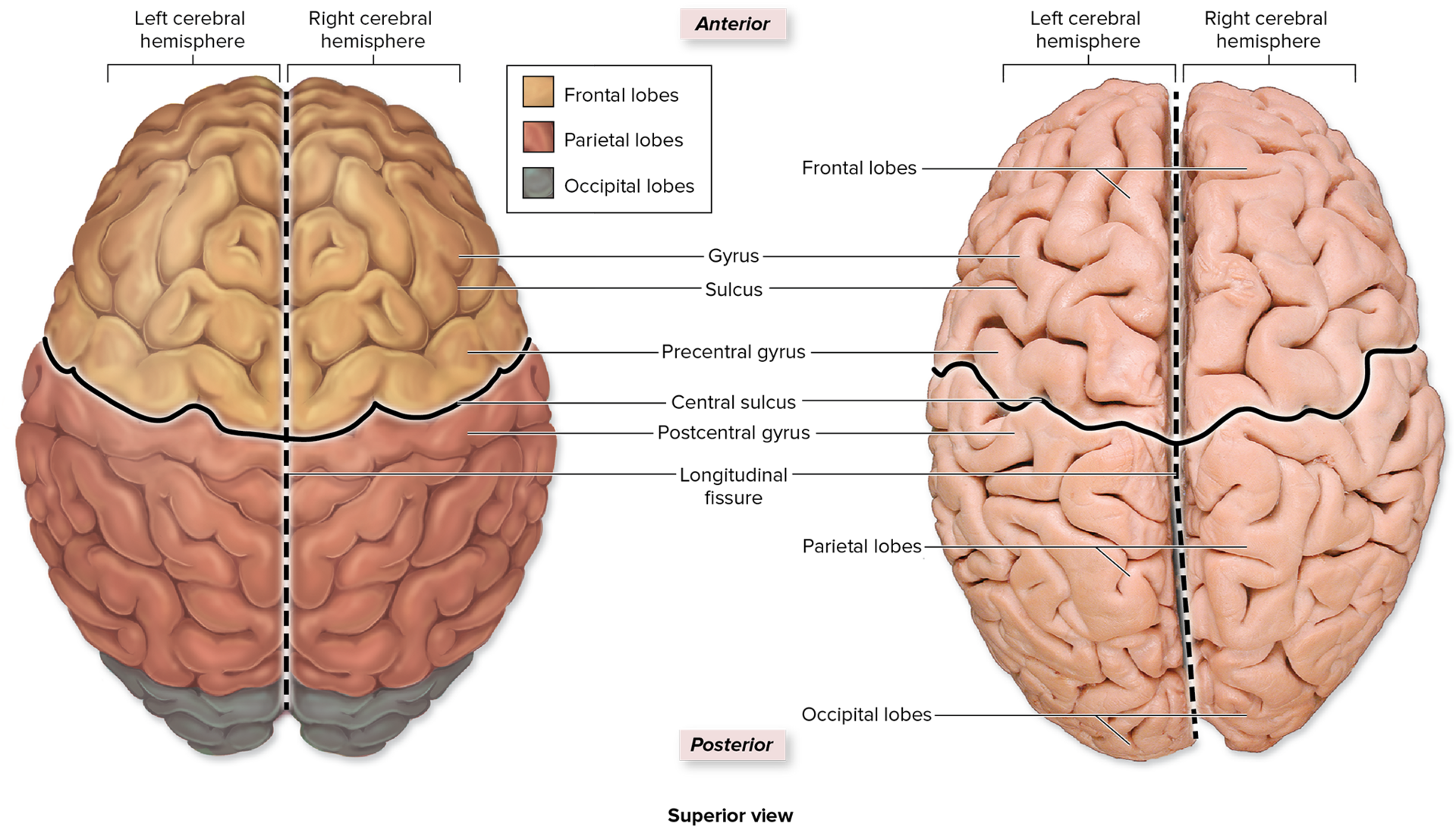
cerebral hemispheres pg.~446
what/where is the longitudinal fissure, and what is its main purpose?
it runs midsagittal, and divides the cerebrum into right and left halves.
cerebral hemispheres pg.~446
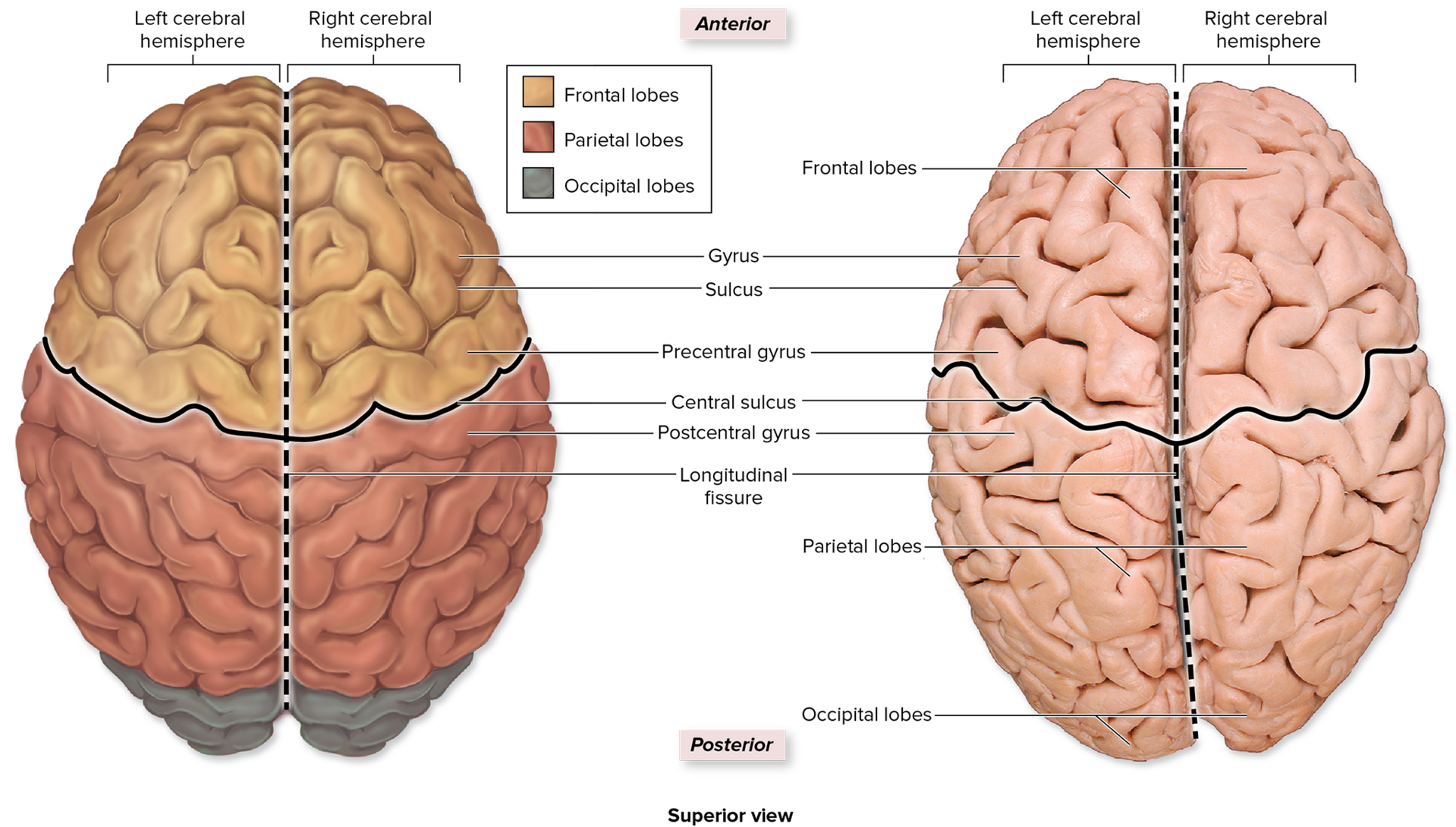
what/where is the central sulcus, and what is its main purpose?
is runs “horizontally” (in this view)
it is the only sulcus that runs from one lateral end of the brain to the other.
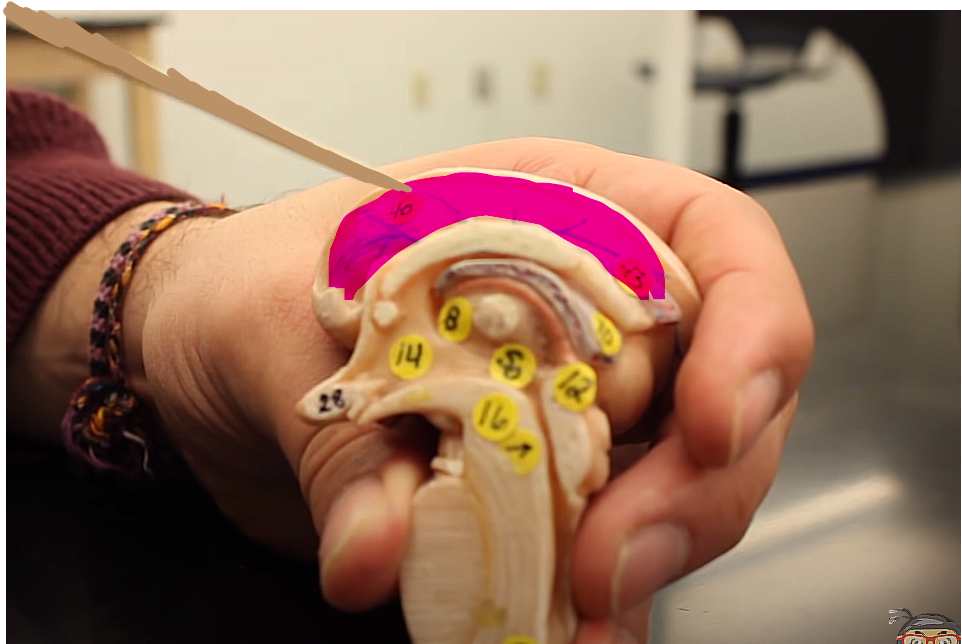
ventricles pg. ~442
what is this structure?
it is part of the lateral ventricle (the ventricle with the big two right and left parts that kinda look like little ram horns…for another reference, go to page 442)
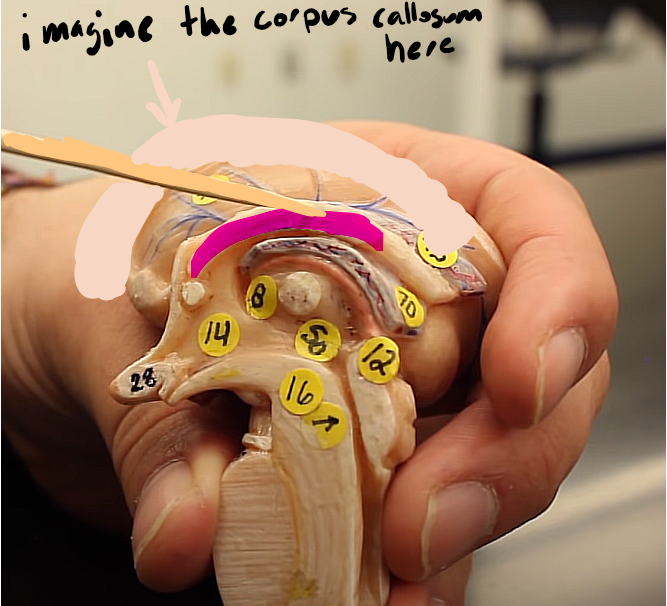
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure (it was not labeled in the book)
fornix…
a fiber tract that connect limbic nucli together (the ones associated with pleasure and pain, emotions)
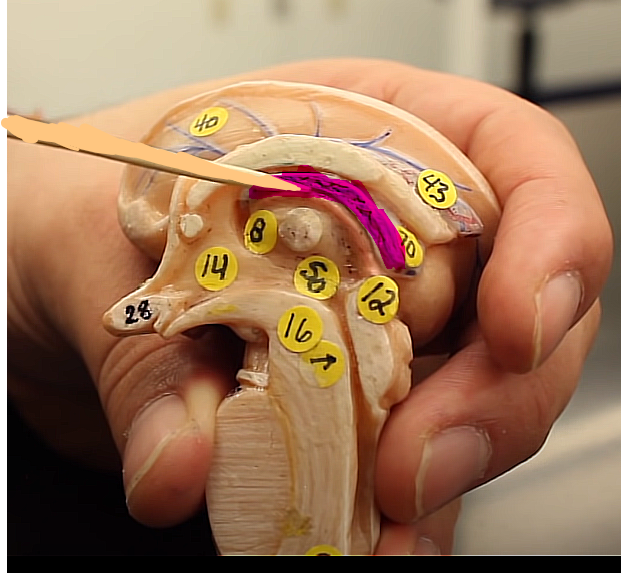
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure
this is more of a blue in the models, and is the choroid plexis of the third ventricle
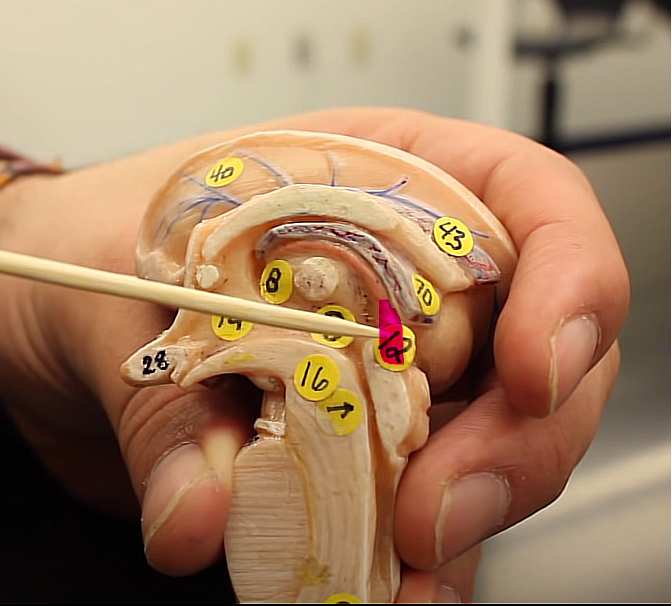
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure
pineal gland
part of the endocrine system
helps with sleep cycles
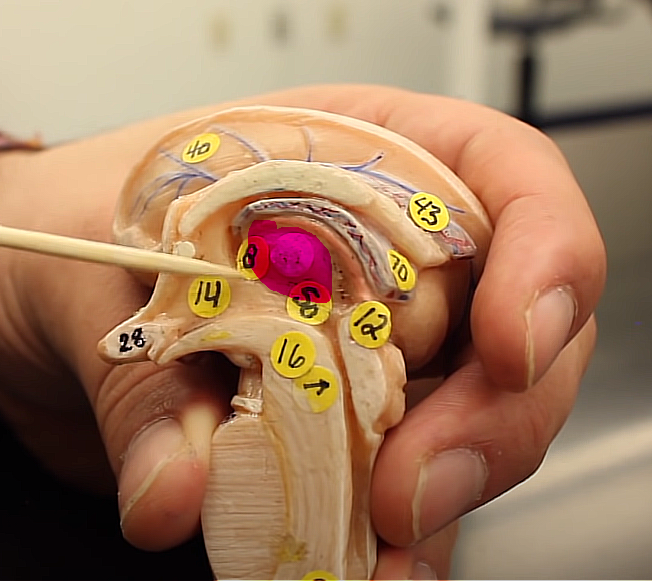
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure
the thalamus
WE HAVE TWO OF THEM,,,, SO WE HAVE THALAMI
they are basically the routing stations for almost all sensory information
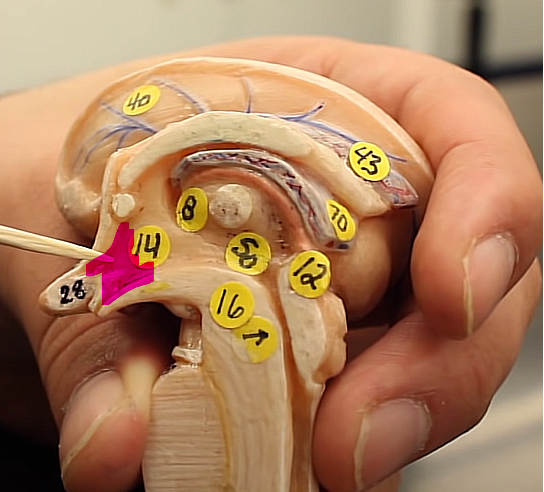
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure
the hypothalamus
it regulates things like heart rate and respiration
is also important to our biological clock, this also produces hormones
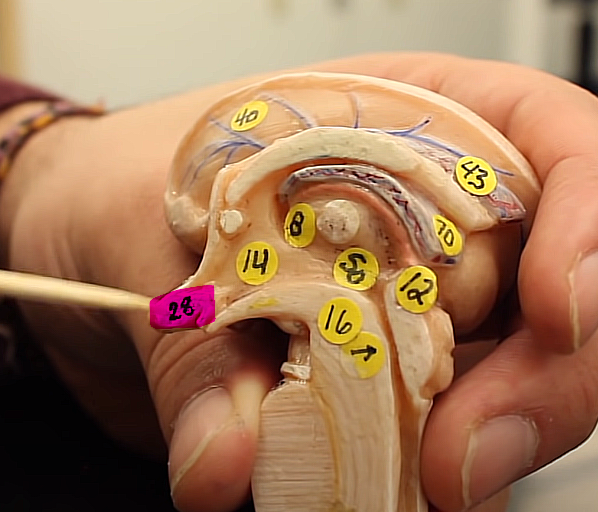
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure
the pituitary gland,,,,
it sits in the sella turkica
it regulates the endocrine structures,,, YET is regulated by the hypothalamus
this is known as the “master gland” but the hypothalamus is the “master of the master gland”
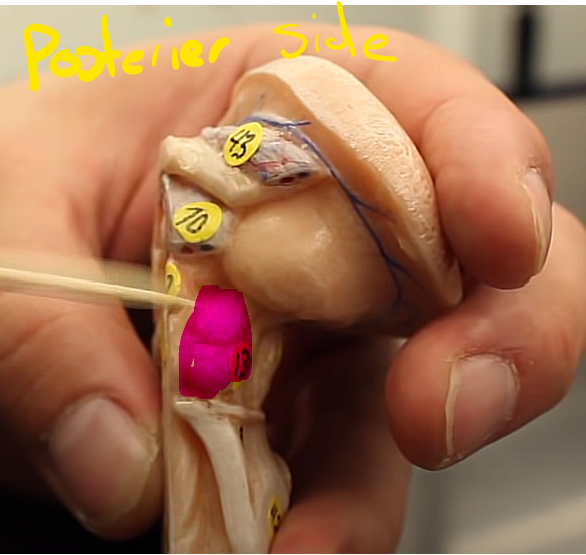
brainstem organization pg.~458
what is this structure of the midbrain
the tectal plate
have the superior and inferior colliculi
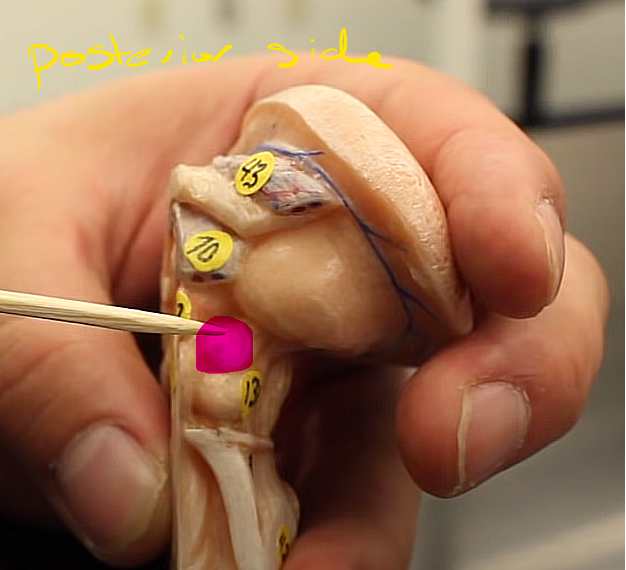
brainstem organization pg.~458
what is this structure of the midbrain
superior colliculi
controls reflectives movements of the head in response to visual stimulus
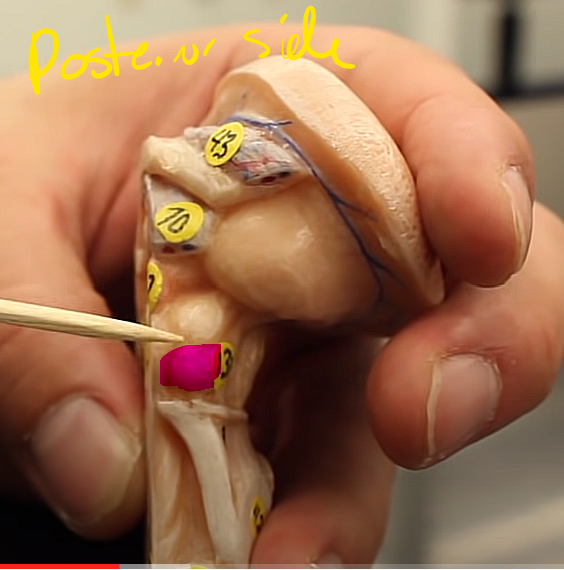
brainstem organization pg.~458
what is this structure of the midbrain
inferior colliculi
controls reflexives movements of the head in response to auditory stimulus
brainstem organization pg.~458
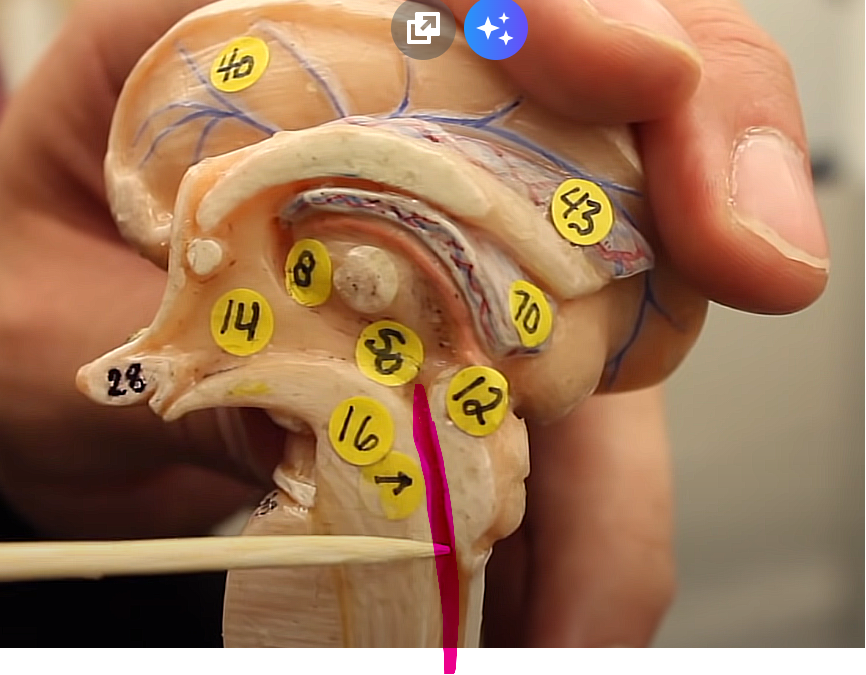
what is this structure of the midbrain
cerebral aqueduct
drains the third ventricle
ventricles pg. ~442
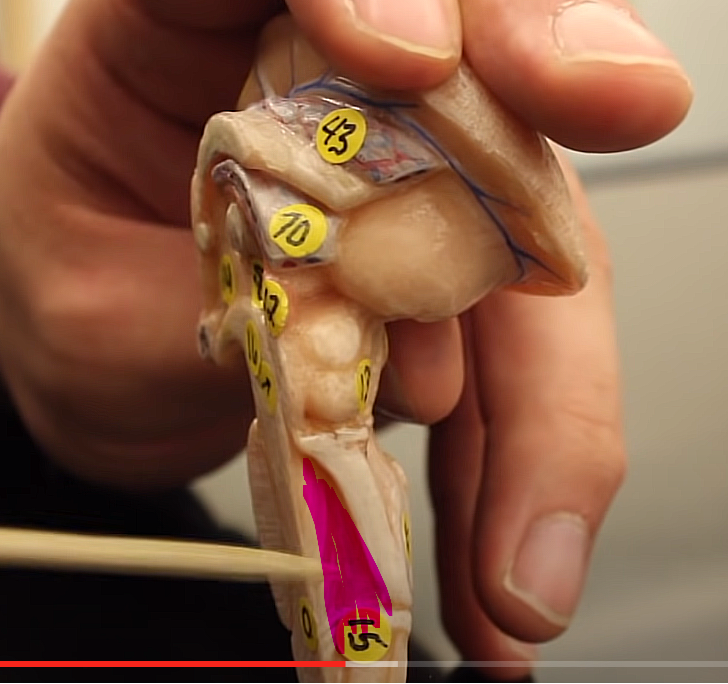
what is this structure
fourth venticle
brainstem organization pg.~458
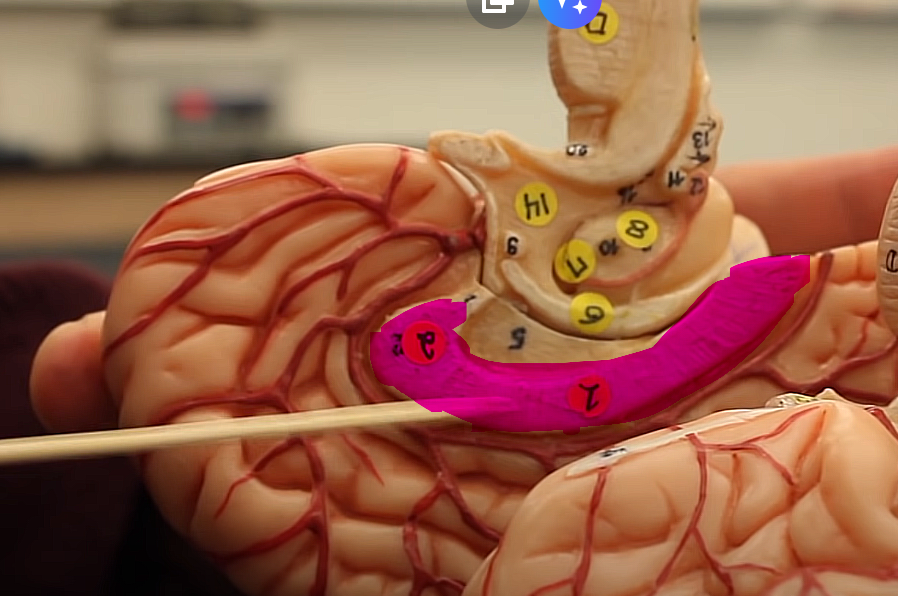
what is this structure of the midbrain
pons
regulates the breathing, respiration
brainstem organization pg.~458
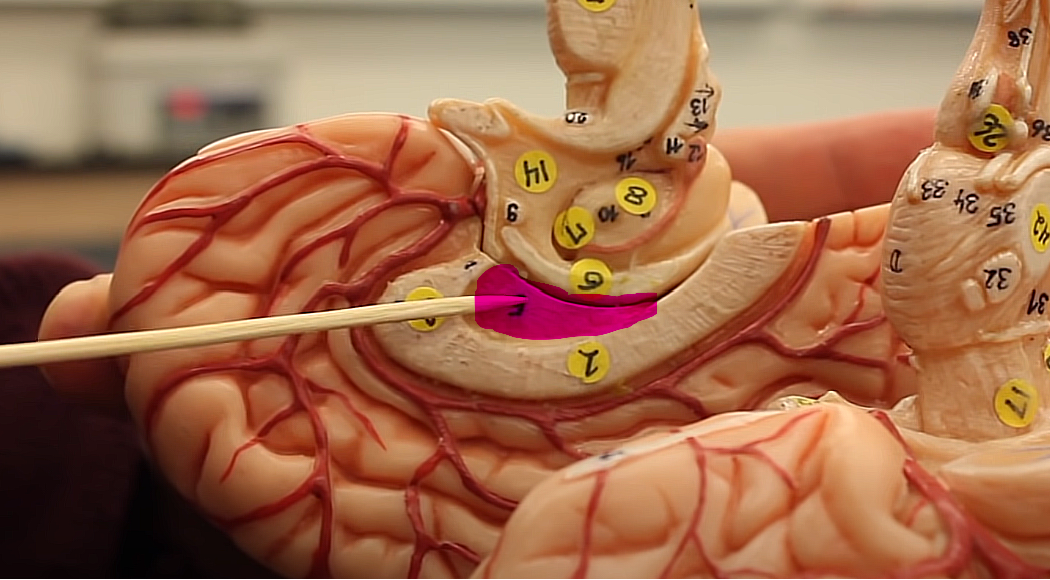
what is this structure of the midbrain
medulla oblongata
connects the spinal chord to the brain
also pertains to respiration, blood pressure, and heart rate
DECUSSATION :
where we have fibers from one side cross over to the other side
brainstem organization pg.~458
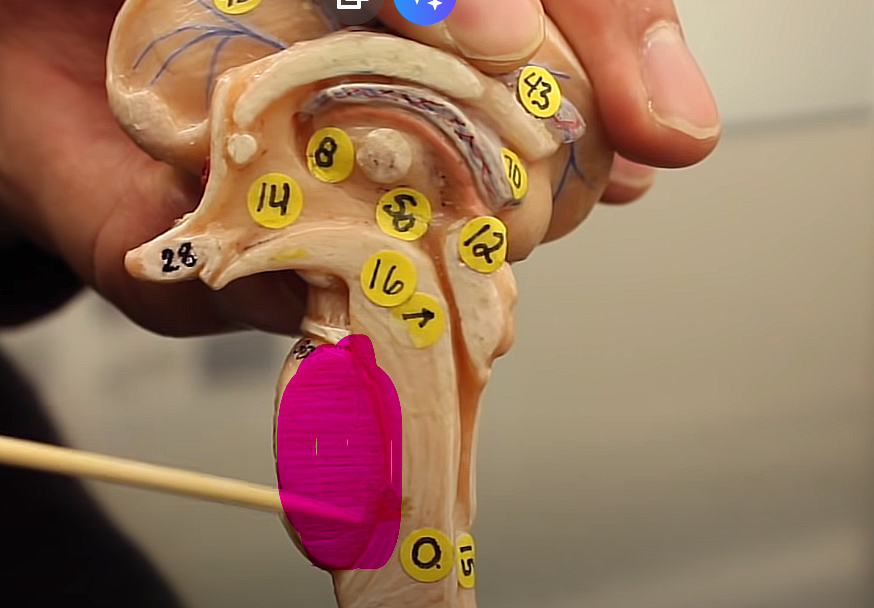
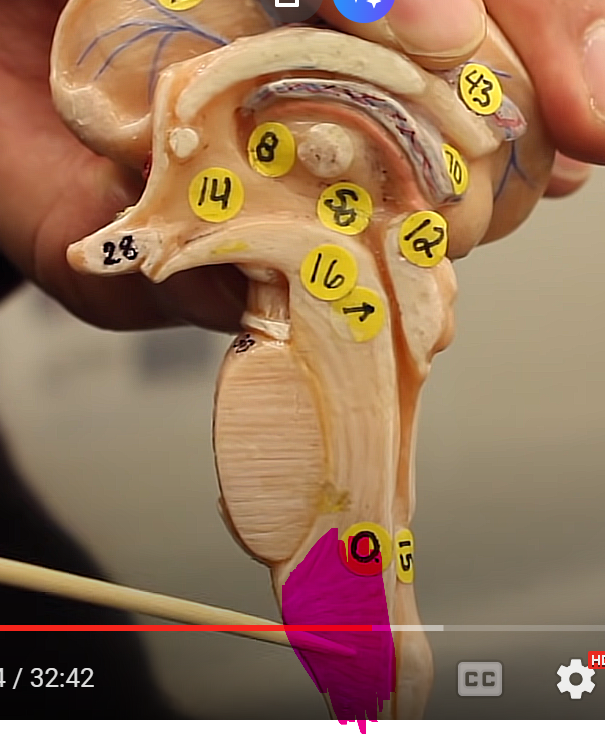
what is this structure of the midbrain
mammillary body
in the crook
reflex centers, helps with swallowing

brainstem organization pg.~458
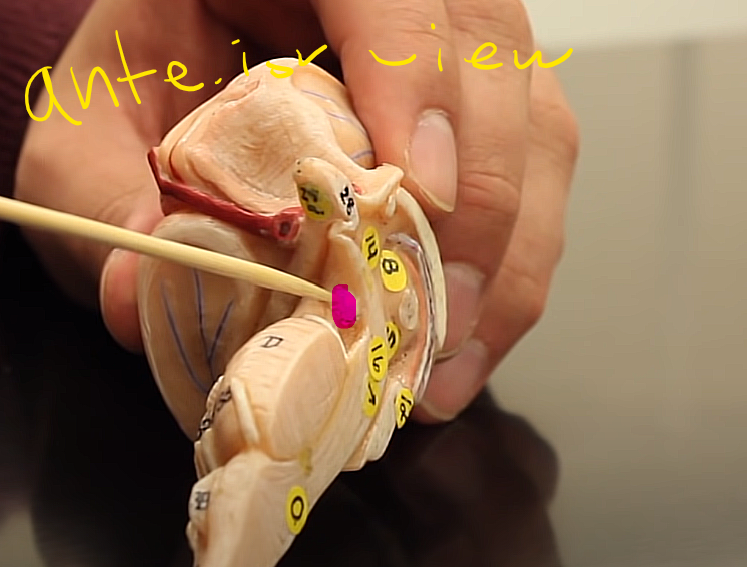
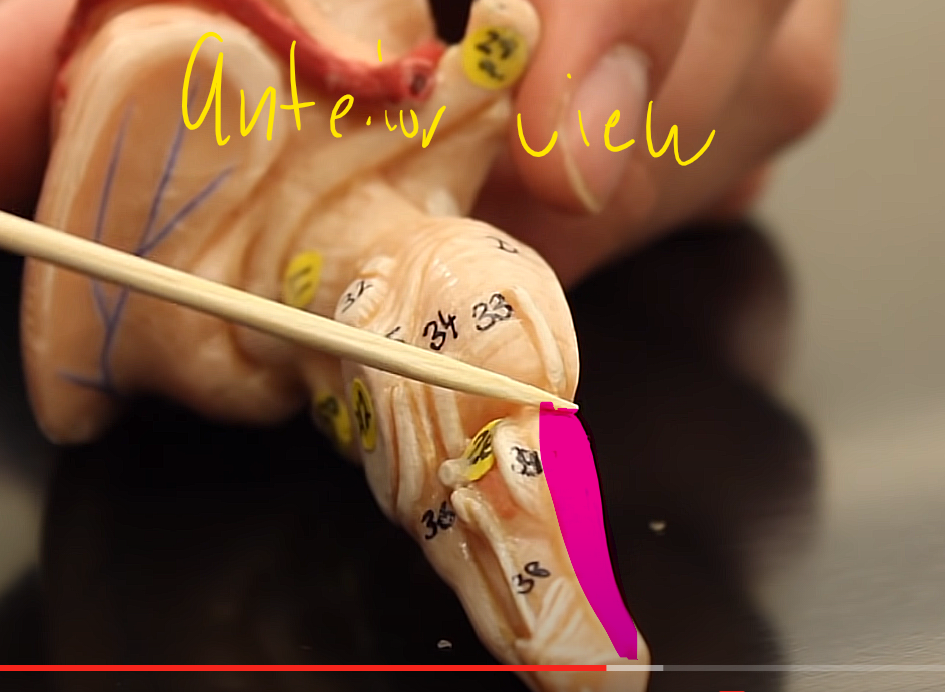
what is this structure of the midbrain
pyramids
where desiccation occurs
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure
corpus callosum
a commissural fibers, allows for connection between the R and L hemispheres
brain organization pg.~434
what is this structure
septum pellucidum
is a membrane
separates the L and R ventricles of the cerebrum