Topography of Inclined Strata
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
homoclinal ridge
slope that forms when rock layers are tilted
how do inclined strata form?
occurs when strata are subjected to stress (compression, tension, etc)
how do dip and scarp slopes form?
when erosion occurs, the more resistant rock forms a gentler slope (dip) and the less resistant rock form a steeper (scarp) slope.
characteristics of dip and scarp slopes
-dip slope is less resistant to erosion
-scarp slopes can retreat due to erosion
undercutting
erosion of rock at the base of a slope with subsequent collapse of the overhang
how does scarp recession/retreat occur? (3)
-undercutting causes the scarp slope to erode in the direction of the dip slops
-the homoclimal ridge shifts toward the dip slope but does not lower
-this is called homoclinal shifting
cuesta
a ridge with a gentle dip slope and a scarp slope
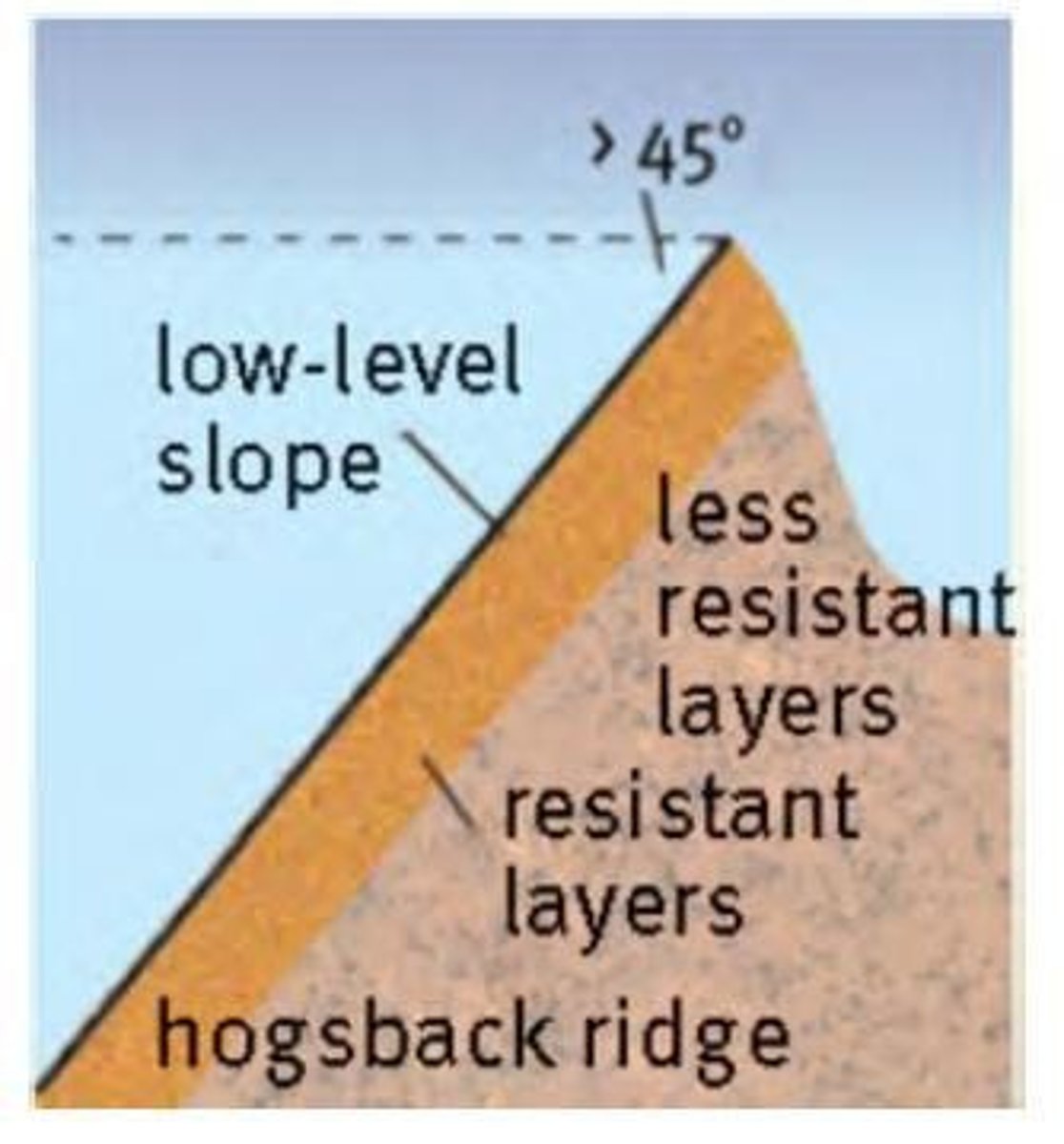
hogsback
a ridge with a steep dip slope and a scarp slope
characteristics of a cuesta (7)
1. dip and scarp slope
2. asymmetrical shape
3. gentle dip slope
4. steep scarp slope
5. alternating layers of tilted sedimentary rock
6. angle of dip = 25-45
7. formed by different rates of erosion along slope
characteristics of a hogsback (5)
1. dip and scarp slope
2. symmetrical shape
3. both sides are equally steep
4. forms a narrow, crested ridge
5. angle of dip = >45
how do Cuesta basins and domes form? (2)
-as a result of folding, strata are raised into a dome shape or bend downwards into a basin shape
-the removal of overlying material by weathering and erosion results in a Cuesta dome or basin
cuesta dome
circular/oval landform formed by an eroded anticline
cuesta basin
circular/oval landform formed by an eroded syncline
formation of a Cuesta basin (5)
1. circular depression in the crust occurs due to sedimentary rocks being intruded by lopoliths
2. the solidified magma drops downwards over time, and so does the sedimentary rock
3. this causes inclined rock strata
4. erosion results in a circular Cuesta
5. the dip slops faces in and the scarp slops faces out
formation of a Cuesta dome (5)
1. forces deep beneath the surface thrust up a portion of the earth
2. intruding batholiths and laccoliths cause the strata to tilt
3. this causes an anticline on the surface
4. weathering and erosion cause the formation of a dome
5. dip slope faces out and scarp slopes faces in
utilisation of homoclinal ridges by people (6)
-good defence when scarp faces outwards
-do not form transport barriers
-gaps between ridges are used for dam walls and roads
-infertile and coarse soil (sandstone and quartzite) is used for forestry as it is not good for farming
-less resistant rock (shale) which produces fertile soil is used for farming
-cuesta scarps are too steep for use
utilisation of Cuesta basins by people (2)
-allows for water seepage into centre = groundwater
-good for farming and settlement (London)
utilisation fo Cuesta domes by people (3)
-good for mining
-have porous sandstone and impermeable shale or salt domes
-allows for petroleum mining