Infiltration in porous media (soils)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is a representative elementary volume? and what is the use
the bridge between microscopic and macroscopic diagram. allows us to define porous media properties at this scale
How do you calculate porosity (n)?
n = porosity = (volume of voids/sample volume)
What is water content?
water content (pheta) = volume of water/ sample volume
What is the degree of saturation (s)?
saturation (s) = water content (pheta)/ porosity (n)
where s is between 0 and 1
What is hydraulic conductivity K (m/s)?
permeability
= a measure of the ease with which a fluid can move through a porous material
What does hydraulic conductivity depend on?
soil type (sand, clay or gravel)
fluid used (water, oil, industrial fluids)
degree of saturation
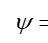
What is a capillary or matrix potential (cm) represented by phi?
a measure of the strength of attraction of water to the soil matrix
it is negative for unsaturated soils (as there is no water)
when it is positive it is known as capillary suction
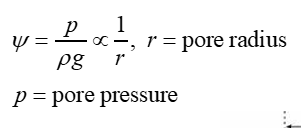
What is hydraulic head?
a measure of the total energy per unit weight of a liquid at a specific point, usually expressed as a height or length
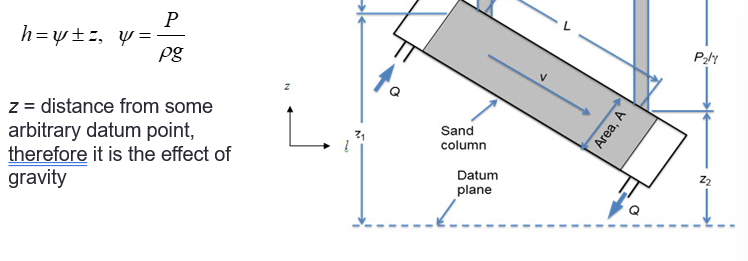
What is Darcy’s law?
the volumetric flow rate Q (m3/s) through a porous material
is proportional to the gradient in the hydraulic head h (m)
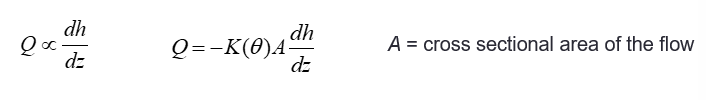
What is darcy flux (q)?
Darcy flux, specific discharge, Darcy velocity
= flow per cross-sectional area
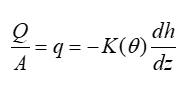
What is seepage velocity and how is it different to darcy flux?
q is not the actual water flow velocity as A includes the solid and pore space.
As the water can only flow through the pores, the seepage velocity v (m/s) is v = q/n
so seepage velocity is the actual flow of water through the pores
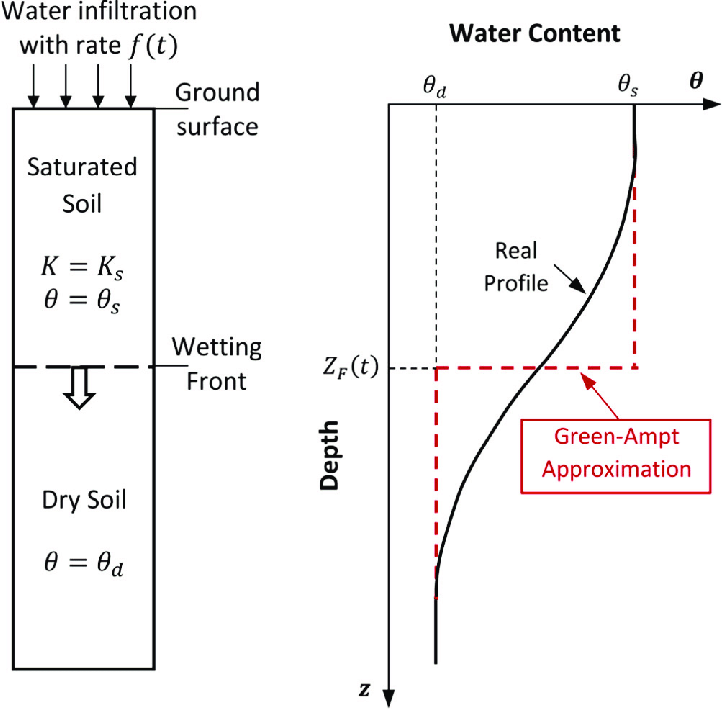
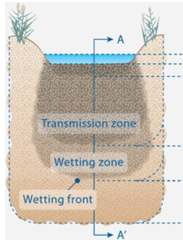
What are the different sections of the cross section of infiltrating water?
water
saturated zone
transmission zone
wetting zone
wetting front
How can we achieve sustainable stormwater management?
through the use of low impact development (LID) also known as blue-green measures where we implement natural water management into our build environment
this includes green roofs, ponds, vegetated filter strip
they minimise imperviousness and maximise the use of pervious pavement and vegetation and contaminant source reduction
What is infiltration rate?
flow rate equal to the darcy flux at the surface of the water
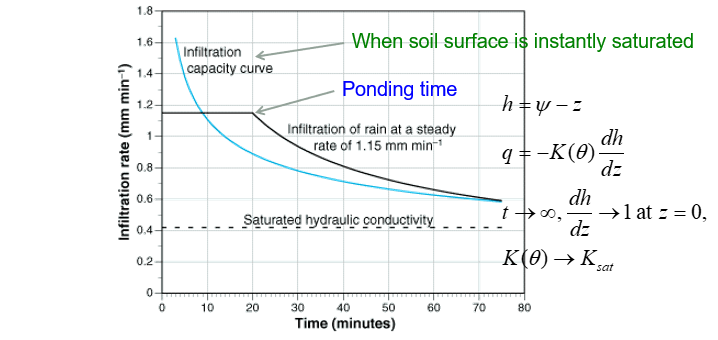
What happens when rainfall rate is greater than K_sat? (greater than the permeability)
q = rainfall rate up until ponding time
After this point, the hydraulic gradient at the surface has sufficiently
decreased so that the flow through soil can no longer match the rate
of rainfall it is receiving
what is ponding time?
the time it takes for water to begin accumulating on the soil surface, starting from the moment rainfall begins
What is Green & Ampt approximation?
an apporcimation for infiltration rate i through time
assumes rectangular flow so the cumulative infiltration (I) is the volume of water is calculated as a cuboid
when rainfall rate < K_sat