Combined
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Kaka-Problem
What to find out how many are in wellington, how do they move around but they are mostly unbanded
Kaka- Input
Pictures of head and beak, as they have distinctive beaks
Kaka-Output
Kaka- What features on beak
Beak shape: curvature, width/height ratio, length
Beak texture: gradients, spots, imperfections
kaka- Problems
How static are these features
data collection with kaka notoriously curious
Kaka-Output
Re-identification or identification, New or not
Kaka- Model
Unsupervised
Image segmentation
Feature extraction and matching
SIFT
Deep Learning
DINOv2 (a vision transformer model)
Modeling Plant Responses- Problem
• Ecosystems are changing...we don’t fully know why
• Species move or go extinct: range shift
• Can we predict where a species is likely to move?
• Can we understand the ML model to see why?
Plant-Different Models
Random forest, Logistic Regression
all have tradeoffs
using KNN to calculate noise level and remove bad data
Healthcare-Problem
Limit Staff
Underfunding
SkinC -Input
Pictures of Moles
SkinC - Output
Benign or malignant
SkinC- Model
Classifications
Healthcare Potential Issues
Data needs to be representative of whole population
Needs to be medical grade
Te Tiriti O Waitangi
Data authority, ownership, confidentiality-opt in?? be good
Oversight actually needs to be supervised
Vision of AI
magine a doctor’s practice in 2035:
We can imagine various AI-based labour-saving devices being
used by doctors. . .
Likewise for other healthcare workers. (Nurses, administrators. . . )
We can also imagine various AI devices/systems being used by
patients, before & after their appointments.
Some healthcare consultations can be carried out ‘at home’.
We can also imagine various AI systems for making hospitals run more
efficiently. For instance:
Triage & prioritisation
Surgical planning
Predicting the ‘flow’ of patients in and out of hospital beds. . .
Predictive AI systems
operate in a specific domain.
- They learn to map inputs in a given task onto outputs, using
supervised learning.
- They are relatively easy to evaluate.
E.g. you can measure accuracy on held-out training examples
Generative AI systems
They learn to generate content of a given type.
E.g. text, images.
- Their power comes from training on huge datasets of examples.
- Text generation systems (e.g. GPT) are the focus for medicine.
Ali Knott AIML131 Week 9 Lecture 2 7 / 23
Other uses of AI in healthcare
Predictive AI systems are the dominant paradigm here.
E.g. a system that identifies fractures in an X-ray image
E.g. a system identifying white blood cells in microscope images.
Weather Forecasting-Problem
Expensive,
Inaccurate in NZ - terrain, roaring40s, isolated
Computationally Expensive
Weather Forecasting-Input
t
Weather Forecasting-Output
t+1
Weather Forecasting-Outcome
cheaper, and more computationally efficient
Weather Forecasting-Issues
earths a sphere
Climate Change
If AI models are trained on past weather forecasts,
how can we be sure they will accurately predict
the future weather under a warming climate?
• Many AI models focus on only predicting the next 10
days, so if the initial state is warmer, the forecasts will
be too
• Continuously re-training (AIFS does this)
• Foundation models built on climate and weather
information
• Ensemble-based models
• Post-processing for extreme weather events
• Including climate forcings (CO2 ppm, sea surface
temperature) as a predictor
Weather Forecasting-Models
NN and Auto Regression
CNN and MLP
Transformers
Other AI applications of Ai in weather
Cyclone Tracking
Flood Forecasting
Sea Ice forecasting
Recommender systems-def
push content at users
Harmful content classifiers-def
that withhold content from users
Withholding content- things to consider
What classifies as harmful and who should
-classification done by humans but too much so Ai as well
Ranking Harmfulness→ supervise learning classifer
Remove, does nothing,borderline→ downrank
Censorship-Bias
Transparency is needed
Harms of AI in SM
keyhole, as it recommends content users they lie, pushing to radicalization,
mental health- showing perfect life
Spread of hate speech Andrew Tate
Christchurch call -> eliminating TVEC
asking companies to remove content of intimate photos. Also penalties for rumors and threats
AB tests
A/B tests: create random user groups, and give them different
versions of the system. Then measure their behaviours.
We asked companies to do A/B tests to test if they could change
the amount of TVEC users saw. They all said no
EU risk levels
Unacceptable, high and limited risk
EU unacceptable
Systems using subliminal techniques, purposeful
manipulation/deception
Systems exploiting vulnerabilities of individuals or groups
Systems identifying individuals through biometrics (e.g. faces)
- With exceptions for law enforcement
Systems for ‘social scoring’
Systems for inferring emotions, in workplaces and educational
settings.
EU high risk
safety (medical)or social issues (bias, employment, justice)
AI Act provisions about Gen AI
Publish summaries of the content
Copy with EU copyright
Write technical documentation for ‘downstream users’
The Bletchley Park AI Safety Summit
Cooperation with over 28 countries NZ joined in 2024
This event focused on large Gen AI models
recognizes risk of bio weapons, toxins, alteration of genes and cybersecurity
-transparency, evolution metric, safety testing
Recognises the risks of ‘frontier’ AI models
Commits signatories ‘to work together in an inclusive manner to
ensure human-centric, trustworthy and responsible AI that is safe,
and supports the good of all through existing international fora and
other relevant initiatives, to promote cooperation to address the
broad range of risks posed by AI’
UK legisatation
Still a year away
security institute, hand over model to be tested, copyright
US Policy
Joe biden had an order to disclose risks to national security results
develop standards for red teaming and evaluation
Donald trump removed that replaced it with how to remove ai barriers
China
No comprehensive policy’s, but big reports & committed
detailed legal requirements on AI content labelling and
watermarking are already in place
-thinking about cybersecurity, biosecurity and open source
Job impact
number of young employees declines
productivity
optimus humanoid in manufacturing, or self driving delivery vehicles
Managers - gig work
Issues in Ai in workplace gig work
monitoring
Recruiters use of Ai
In CV and Cover letter screening
Ai interviews
Ai taking notes
employee/candidate use of Ai
Using Ai for Cover letters and CV
help in practice interviews
and ai in workforce
1 Scenario of AI in NZ
The main effect of AI is to improve the productivity of workers.
No mass unemployment; instead, NZ workers are more efficient
Positive uses of Ai in recruitment
Positive uses of AI in recruitment
We can also work to build fairness into recruitment tools.
1. We can delete features that aren’t relevant from training sets.
Gender, ethnicity are often irrelevant. . .
If assessors classify applicants based on redacted application
materials, it’s harder for them to be biased.
2. We could include audit functions, that show percentages of hired
people from different demographic groups.
This way, biases will at least be visible. (Within the company and
beyond.)
Working alongside AI
Say you’re a worker making decisions. . .
- Perhaps you’re a doctor, looking at X-rays and detecting
fractures. . .
Say an AI system is working alongside you, to help you.
- Say it’s pretty reliable. . . perhaps 95%. . .
How do you stay in the loop??
- It’s hard to stay in control, if the system works well!
Also - who’s responsible, if the thing you are jointly doing goes wrong?
Ali Knott AIML131 Week 11 Lecture 2 17 / 24
Scenario 2
Replacing onshore
NZ workers are displaced by AI, into lower-value work.
The AI systems doing the displacing are NZ-owned.
(So NZ can recover some of their profits through taxation.
Replacing offshore’
NZ workers are displaced by AI, into lower-value work.
The AI systems doing the displacing are owned offshore.
-International tech tax
International Tech Tax
There is an international tech tax being organised by the OECD, for
large multinational companies. The US walked out in June.
‘Pillar 1’ sets things up so each country taxes LMCs according to
the revenue they make in that country.
‘Pillar 2’ establishes a ‘global minimum tax’ of 15%, so companies
can’t run to countries with low corporation tax.
GAN’s
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) arrived in
2014, dominated many fields until 2020
• Train two models in an adversarial fashion and they compete with each other
• Generator: E.g., a CNN model producing candidate images
• Discriminator: E.g., a CNN that judges if an image is real or
fake
• Training two NNs at a time often leads to instability
CNN for image generation
Popular in 2012
Not generative, but form backbone of GANs and autoencoders
Autoencoders
Appeared in 1990 revived in 2013.
encoder compress an image into a smaller, latent representation using a NN/CNN
Decoder learn to deconstruct the original image from latent representation
Diffusion
Gradually add noise to an image, then train a model to
learn how to remove the noise step by step, to get back
to original image
• At inference, start from noise, denoise step-by-step
• More stable than GANs and high quality images, but
slower to train and use at inference
CLIP
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training. Maps pairs. matches pairs using the cosine vector equation. encodes to the same shared space. It is a model from OpenAI trained to link text and images through a
shared encoding. Open AI in 2021
Forward / noising process:
goes from a structured image→ noise
Reverse/denoising process
trains a NN to learn how to remove the noise step by step
3 steps for image generation Diffusion
Encoder Text embedding-converts a text caption to a text encoding (a
numerical representation)
Prior predict what the image imbedding will be. eg CLIP
Decode- converts the image encoding to an image
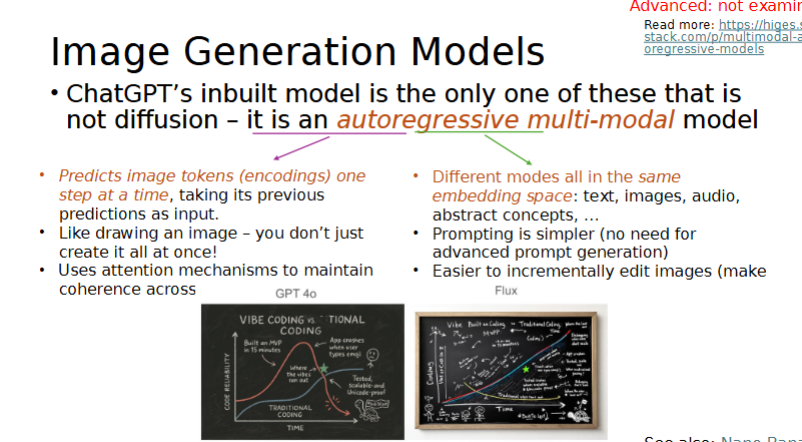
What does ChatGPT use?
Autoregressive multi-modal model. NOT DIFFUSION
Text-to-Video
Generates images from text using diffusion then uses image interpolation
Video Generation Models
Sora by OpenAI
Veo3 by Google Deepmind
Other AI image tools
Upscaling
Inpainting -Filling in missing parts of
an image, or generate
things that aren’t really
there
Outpainting- used to generate wide shot shots, extending an image beyond its original boundaries
Captioning
AI Art Ethics
Using Ai to make images - competion entry
What is art?
How do we copyright? - A comic book written entirely by midjourney - copyright was revoked as it only protects human created work, however the arranagment and story is copyrighted
Music- music not copyrighted
Harms of Generated Images
Bias - beautiful fair skined, feminine, smiling, soft emotions
Cultural appropriation
Image ownership for trainning
Benefits of Ai generated images
MRI Denoising with Diffusion Models
• Improve diagnostic tools and patient outcomes
Enlarging datasets of rare conditions, upscaling low res scans,
easier prototyping and iterating for architects -cheaper and quicker than human building digital photos
AI generated scenes of hazardous driving conditions for Ai to learn from
DeepFakes
an image or recording that has been
convincingly altered and manipulated to
misrepresent someone as doing or saying
something that was not actually done or said
History of Deepfakes
Orginally using GANs
Now can use a range of different models
diffusion
transformers
autoencoders
GANs
train the discriminator to classify which image is fake or not
train the generator to generate images from random noise- using different models such as diffusion or an autoencoder
Penalize the generator if the discriminator can tell the difference, use backpropagation to update the weights until the discriminator cannot tell the difference and just guessing randomly(50%)
Deep Fakes used for bad
Political examples
- gabonese president was absent from public due to medical situation and a deepfake was sued to show he was ok, however it was suspected of being a deepfake
-a video of Ukrainain president telling his army to surrender
-Joe bidden not to vote
Celebrity
-scams people thinking they are in a relationship
-Promoting products unaware
Pornogarphy
celebrities targeted
Women in politics
Young girls, teachers
Finace
Cybersecurity -scams, and used to bypass biometric privacy
Regulation in Politics
June 2023: The European Union’s EU Act requires AI content to be
labelled, especially in political contexts
• Jan 2024: South Korea prohibited the production of political
deepfakes for the 90 days leading up to national elections, unless
they were clearly labelled as fake
• April 2025: Singapore ban deepfakes misrepresenting political
candidates more
• American state-by-state laws:
• Texas: criminalised the creation and distribution of deepfakes intended to
influence elections within 30 days of the election
• California: bans publishing materially deceptive deepfakes of politicians
within 60 days of an election, unless labelled as fake
Good of Deepfakes and AI video
Translate in different languages, in sign language, allows people with motor disabilities to express themselves with a synthetic voice.
Social Media
X thinks good, humour, censoring
Meta- Ai info label for users to indicate, try but numerous test show that their scanning doesn’t work that effectively
Tik Tok - Asks users to self disclose, can label some content as AI generated
Detecting Deefakes
Harder and harder for humans.
Intel’s FakeCatcher claims a 96% accuracy rate (in milliseconds)
• Looks for subtle “blood flow” in video pixels!
• Our veins change colour as our heartbeats
• Social Media AI detectors require the videos/images to be digitally
watermarked by the AI deepfake models
For AI-based detection (like those used by social media platforms)
they essentially need to build a better discriminator than the one
used in the original GAN
Challenges of image generation
Realistic conditions: Lighting, shadows, and reflections
• Minute details: wrinkles, water droplets, hair, fingers!
• Image-wide coherence: everything in the image needs
to fit together, scales need to be correct
What is Māori Data Sovereignty
Māori data is data produced by Māori or about Māori
or the environments that Māori have relationships
with. Data is a living tāonga and is of value to Māori
example of Māori Data
Data from government agencies, organisations and businesses
• Data about Māori used to describe/compare Māori collectives
• Data about Te Ao Māori that emerges from research
What is Māori Algorithmic Sovereignty
Algorithms that use Māori data, or
are applied to Māori individuals, collectives, or
environments that Māori have rights or interests in,
should be subject to Māori governance structures
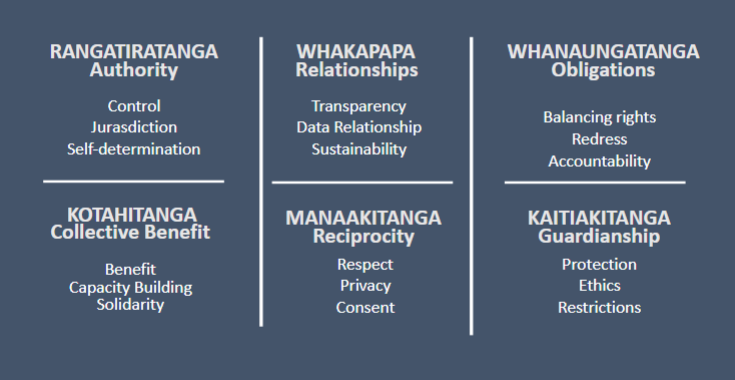
Rangatiratanga
Authority
Control
-permission, how it is collected, used and stored
Jurisdiction should be stored/deployed in a way that enhances control, within Aotearoa
Example: using a NZ cloud service (e.g. Catalyst)
where people have opted-in (informed consent) to
their health data being analysed
Whakapapa
Relationships
Transparency- whos involved, deployment, explainability
Data Relationship- how is Maori data used throughout the algorithm
Sustaianability
algorithmic outputs are used for long-
term sustainable benefit to Māori & environment
An indigenous example: the “Pima Indians” dataset was
collected from a long-term study of indigenous peoples
in the USA. Became used as an ML “benchmark
dataset” without any real permission from the Pima
Whanaungatanga
Obligations
-balancing rights and accountabijlity
Kotahitanga
Collective Benefit
-output in future helps Māori or the environment
-Builds capacity, development of a Māori workforce –
empower Māori and learn by teaching (ako)
• Solidarity: supporting connections between Māori
and other indigenous peoples to enable sharing of
ideas, strategies for fair algorithmic development
Manaakitanga
Reciprocity
respect
consent
privacy
Kaitiakitanga
Guardianship
Ethics
Restrictions- Māori should decide if input/output is tapu or noa
Overall 6 groups
—
Why XAI is important?
Insights, trust, Clever Hans, detecting bias, saftey