Physico-Chemical Properties and Drug Action
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the different places a drug can go to once it distributes within the blood?
liver (metabolism)
kidney (excretion)
site of action
CNS
ADME stands for:
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
What 2 processes does a drug have to go through when given orally?
dissolution
into aqueous environment of GIT
crossing the bio membrane
to reach the blood stream
requires lipophilic properties
What plasma protein mainly helps the lipophilic drug form a water soluble complex to allow for passage through the blood?
albumins
T/F: bio membranes are mainly lipophilic
TRUE
A drug that is very lipophilic with have (good/poor) absorption but (good/poor) dissolution.
good, poor
If polar FGs dominate in a drug, the drug will have (good/poor) absorption thru the membrane, but (good/poor) dissolution.
poor, good
What functional groups increase the polarity and dissolution of drugs?
very polar groups
hydroxyl groups
alcoholic hydroxyl (aliphatic)
phenolic hydroxyl (aromatic)
aliphatic amines
COOH, amides, imides, CN, NO2, sulfonamides
How does a hydroxyl group affect the polarity of a drug?
very polar → increases solubility of 5-6 carbons
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hydroxylfunctional-56a129e05f9b58b7d0bca5df.jpg)
How does an amino group affect the polarity of a drug?
very polar, increases solubility of 5-6 carbons
quaternary amines form ammonium salts → soluble due to charge
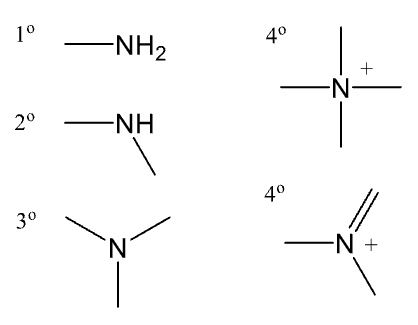
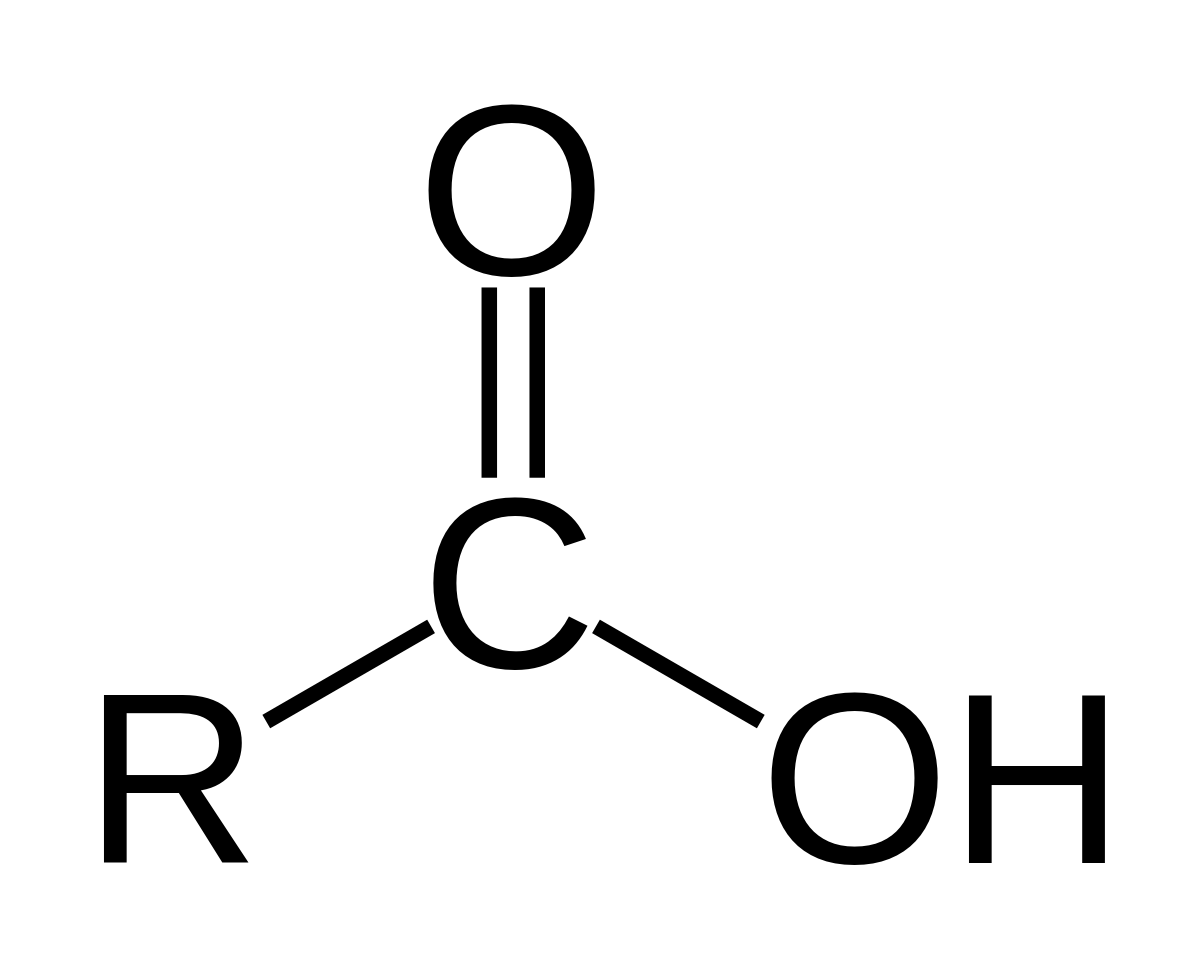
How does a carboxylic acid affect the polarity of a drug?
weakly polar → increases solubility of 2-3 carbons
acidic FG
How does a cyano group affect the polarity of a drug?
weakly polar → increases solubility of 2-3 carbons
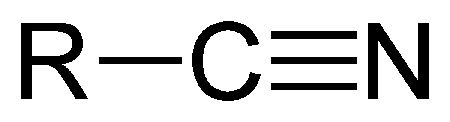
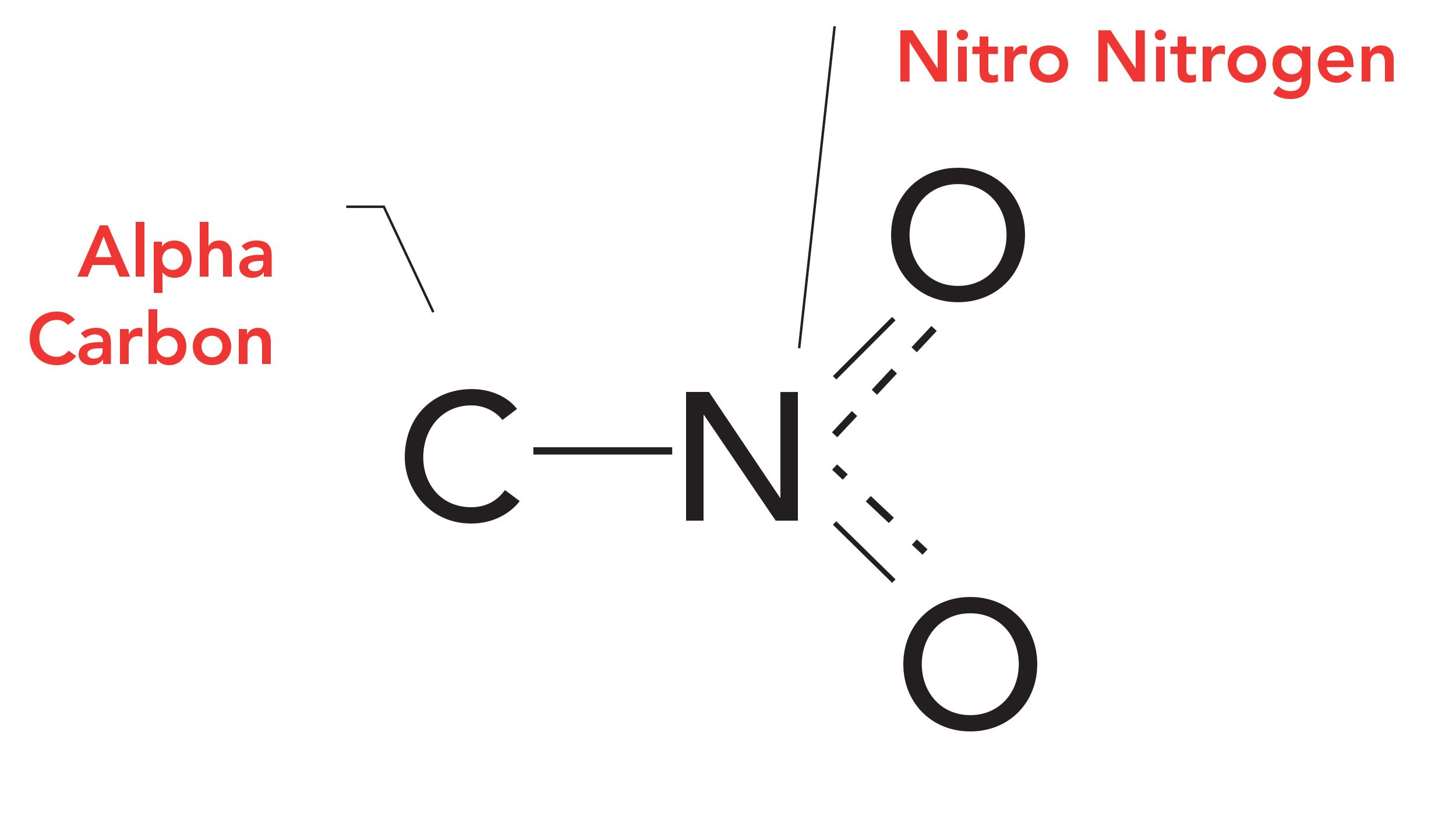
How does a nitro group affect the polarity of a drug?
weakly polar → increases solubility of 2-3 carbons
How do amides affect the polarity of a drug?
weakly polar → increases solubility of 2-3 carbons

How do imides affect the polarity of a drug?
weakly polar → increases solubility of 2-3 carbons

How do sulfonamides affect the polarity of a drug?
weakly polar → increases solubility of 2-3 carbons
What are functional groups that increase the lipophilicity of drugs?
alkyl groups
phenyl groups
halogen groups (I >Br >Cl>F)
ester: more carbons = higher lipophilicity
How does an ester group affect the lipophilicity of a drug?
more carbons makes esters more lipophilic → better absorption

How do ethers affect the lipophilicity of a drug?
very weakly polar
more lipophilic than alcohol
How do alkyl groups affect the lipophilicity of a drug?
very lipophilic → due to more carbons
better absorption

Ho
How do aromatic radicals affect the lipophilicity of a drug?
very lipophilic → highly absorbed
How do halogens affect the lipophilicity of a drug?
increases the lipophilicity of a drug
the bigger the atom → more lipophilic
I >Br >Cl>F
What is the role of albumin?
binds to lipophilic drugs to form a water soluble complex compatible with the aqueous medium of the blood
complex is reversible
What is the makeup of albumin?
water soluble protein rich in 2 types of AAs:
hydrophobic AAs
Leu
Phe
Trp
basic AAs
Arg
Lys
Drug binding to albumin occurs through what 2 types of reversible interactions?
hydrophobic interactions w/ lipophilic AAs
the major force for binding
ionic interactions with basic AAs
T/F: ibuprofen will bind strongly to albumin because it is both lipophilic and acidic.

TRUE
T/F: only a small amount of the lipophilic drug is primarily bound to albumin
FALSE
99% primarily bound to albumin
Explain the concept of drug-drug interactions by displacement.
drugs can displace one another because:
drug binding to plasma proteins is NONselective
# of binding sites with similar physicochemical characteristics can compete with
results in a change of the free drug concentration of both drugs leading to increased toxicity of the drugs
Drug A and B both have strong plasma protein binding. If the two drugs are concurrently taken and each have equal affinity to plasma proteins, what will happen?
each will displace the other by ~50%
leads to increasing the amount of free concentration of both drugs in plasma
result: excessive action and/or toxicity
If Drug A has a higher affinity than Drug B and are taken concurrently, what will happen?
drug A will take most of the binding sites on albumin
drug B will still have a higher concentration than normal